source
What are the 3 basic types of rocks?
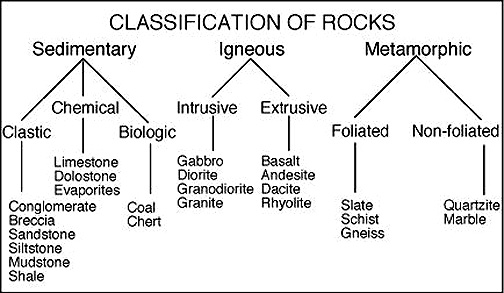
Just as any person can be put into one of two main categories of human being, all rocks can be put into one of three fundamentally different types of rocks. They are as follows:
#1. Igneous Rocks
- Igneous rocks are crystalline solids which form directly from the cooling of magma.
- This is an exothermic process (it loses heat) and involves a phase change from the liquid to the solid state.
- The earth is made of igneous rock – at least at the surface where our planet is exposed to the coldness of space.
- Igneous rocks are given names based upon two things:
- composition (what they are made of) and
- texture (how big the crystals are)

source

source
The word igneous is derived from the Latin word Ignis which means fire. The rocks formed by the solidification on the cooling of molten magma, are called igneous rocks.
Depending on where the molten magma cools, they are of the following types:
- Intrusive Rocks
- Extrusive Rocks

source
When the molten magma cools deep inside the earth’s crust, intrusive igneous rocks are formed. They:
- Cool down slowly
- Form large grains
- Granite is intrusive igneous rock. Grinding stones used to prepare paste / powder of spices and grains are made of granite.
Extrusive Igneous Rocks:
- When the molten magma (lava) comes on the earth’s surface.
- It rapidly cools down and becomes solid.
- Rocks formed in such a manner on the crust are called extrusive igneous rocks.
- They have a very fine grained structure.
- Basalt is an example of extrusive igneous rocks. The Deccan Plateau is made up of basalt rocks.
#2. Sedimentary Rocks

source
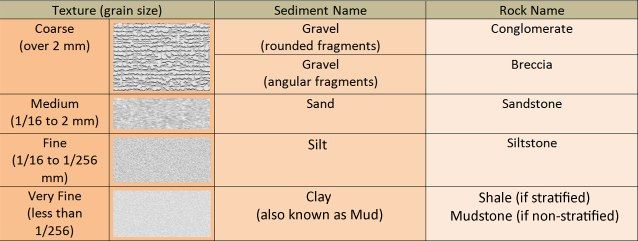
- These rocks get their name from the Latin word sedimentum which means settle down.
- These rocks are formed by the settling down of sediments.
- Sediments are the smaller particles / fragments that are formed by the breaking down of rocks when they roll down, crack and hit each other.
- These sediments are transported by wind, water etc.
- These sediments; when compressed and hardened; form sedimentary rocks.
- Sandstone is an example of sedimentary rock. It is made up of grains of sand.
- The sedimentary rocks may also contain fossils of plants, animals and other micro – organisms that once lived on them.
source

source
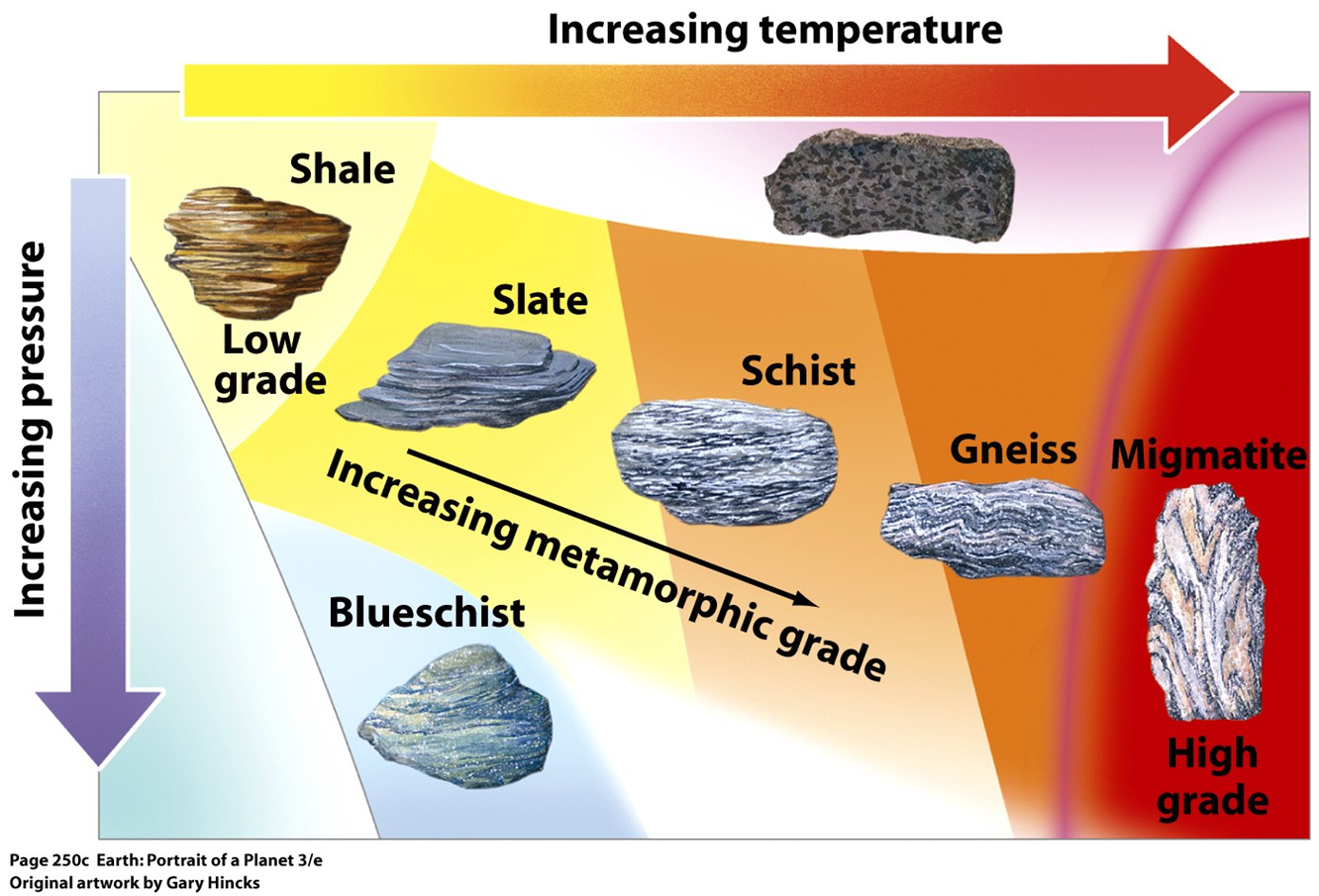
#3. Metamorphic Rocks:
The Greek word ‘metamorphose’ which means change of form, is the root of the word metamorphic. In other words, these are the rocks that are formed when the igneous and sedimentary rocks change their form under the following two circumstances:
- Great heat and
- Great pressure

source
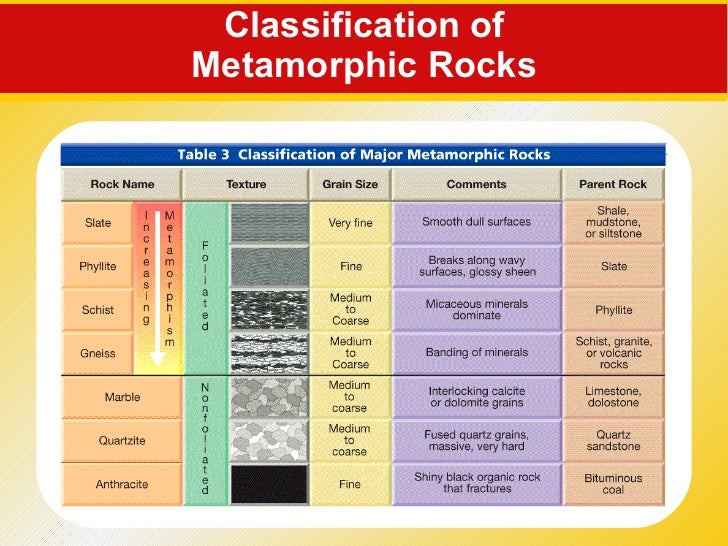
The following are the examples of metamorphic rocks:
- Slate: Clay becomes slate after metamorphosis [Texture = Foliated]
- Marble: Limestone becomes marble after metamorphosis [Texture = Non-Foliated]
source
source
#4. What is a Rock Cycle?
The Rock Cycle is a group of changes. Igneous rock can change into sedimentary rock or into metamorphic rock. Sedimentary rock can change into metamorphic rock or into igneous rock. Metamorphic rock can change into igneous or sedimentary rock.

source
NOTE: This lesson forms a part of the series on Physical Geographic Lectures – Click to read the collection
