The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is a regional political organisation comprising the energy rich Gulf monarchies – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
When and why was it founded?
- Establishment in Abu Dhabi in 1981 | HQ in Riyadh
- The founding charter focused more on issues of social and cultural cohesion, environmental and scientific coordination and economic cooperation
- Recently, Morocco and Jordan have applied for the GCC membership which is currently being studied by the GCC Expert Committee
India and GCC: Contours of cooperation
- The Gulf constitutes the “immediate” neighborhood of India separated only by the Arabian Sea
- The Gulf, as the principal source of India’s energy requirements, is central to our energy security interests: it meets 75% of our oil needs at present; as our demand increases in coming years, India’s dependence will go up to 90% by 2035.
- GCC is India’s largest trading partner as an economic grouping, with two-way trade being more than our ties with the European Union, ASEAN and North America
- Four GCC countries figure in India’s top 10 trade partners.
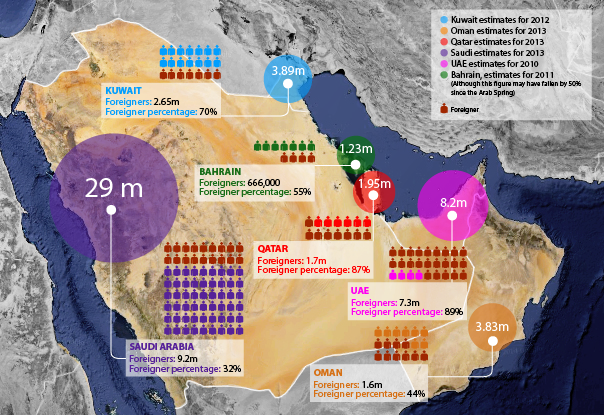
- We also have an eight-million strong community in the GCC that remits annually $35 billion to the national exchequer
- The India-GCC Free Trade Agreement which is in under negotiation could usher in a new era of trade
Although India and the GCC countries share a strong economic relationship, there is much progress to be achieved on the political front. Let’s have a close look at some of the important dimensions –
#1. Defence Diplomacy
India’s defence diplomacy with countries of the GCC is well reputed.
- India has signed a military protocol with Oman which has facilitated joint military exercises
- India has also signed a defence cooperation agreement with the UAE
- Our new naval diplomacy document increases our focus on west asian countries. Click to read more about it here.
#2. Counter Terrorism
The meteoric rise of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIS) in neighbouring countries like Iraq and Syria pose a huge threat to the peace and stability of the GCC countries.
#3. Maritime Security
Primary maritime security threats include piracy at sea, smuggling of narcotics and arms and the imminent threat of maritime terrorism.
- These threats pose major challenges to the Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs) that India depends heavily on to carry out trade by sea
- India’s international trade by sea amounts to about 90% of the foreign trade, and it takes place through 13 major ports and several minor ports
- In recent times the term “Indo Pacific era” has gained currency. You would do well to read this post on – Indian maritime challenges and its diplomatic dimensions
#4. Culture & Diaspora
- We have an eight-million strong community in the GCC that remits annually $35 billion to the national exchequer
- Minor concerns – If you remember, in 2013 Saudi Arabia issues a Nitaqat Law – The ‘Nitaqat’ law makes it mandatory for local companies to hire one Saudi national for every 10 migrant workers
- There had been widespread perception that the new policy will lead to denial of job opportunities for a large number of Indians working there.
- India had back then proactively conveyed concerns to the Saudi government
Want to read more?
- GCC Trade and Investment Flows – Economist article covering GCC’s overlaps with other nations
