29th Apr 2021
Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) across and about 2,800 kilometres (1,700 mi) from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who was the first recorded European to encounter New Zealand and Tasmania. The British explorer Captain James Cook later extensively navigated the Tasman Sea in the 1770s as part of his first voyage of exploration.

Persian Gulf
This inland sea of some 251,000 square kilometres (96,912 sq mi) is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz; and its western end is marked by the major river delta of the Shatt al-Arab, which carries the waters of the Euphrates and the Tigris. Its length is 989 kilometres (615 miles), with Iran covering most of the northern coast and Saudi Arabia most of the southern coast. The Persian Gulf is about 56 km (35 mi) wide at its narrowest, in the Strait of Hormuz. The waters are overall very shallow, with a maximum depth of 90 metres (295 feet) and an average depth of 50 metres (164 feet).
Countries with a coastline on the Persian Gulf are (clockwise, from the north): Iran; Oman’s exclave Musandam; the United Arab Emirates; Saudi Arabia; Qatar, on a peninsula off the Saudi coast; Bahrain, on an island; Kuwait; and Iraq in the northwest. Various small islands also lie within the Persian Gulf, some of which are the subject of territorial disputes between the states of the region.

Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The sea is sometimes considered a part of the Atlantic Ocean, although it is usually identified as a separate body of water.
The countries with coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea are
- Albania
- Algeria
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Egypt
- France
- Greece
- Israel
- Italy
- Lebanon
- Libya
- Malta
- Morocco
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Syria
- Tunisia
- Tukey
In addition, the Gaza Strip (“Palestine” has been associated with the geographical area that currently covers the State of Israel, the West Bank and the Gaza Strip) and the British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Akrotiri and Dhekelia have coastlines on the sea.

Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean. It has an area of 436,400 km2 (168,500 sq mi) (not including the Sea of Azov). The roughly oval-shaped Black Sea occupies a large basin strategically situated at the southeastern extremity of Europe but connected to the distant waters of the Atlantic Ocean by the Bosporus (which emerges from the sea’s southwestern corner), the Sea of Marmara, the Dardanelles, the Aegean Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Countries bordering the Black Sea are-
- Ukraine
- Russia
- Georgia
- Turkey
- Bulgaria
- Romania

Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed inland body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world’s largest lake or a full-fledged sea. It is in an endorheic basin (a basin without outflows) located between Europe and Asia.
The Caspian Sea is bordered on the northwest by Russia, on the northeast by Kazakhstan, on the west by Azerbaijan, on the southeast by Turkmenistan, and on the south by Iran. It is classified as both a sea and a lake, and it is the largest enclosed inland body of water in the world.
- Azerbaijan
- Iran
- Kazakhstan
- Russia
- Turkmenistan

Red Sea
The Red Sea (also the Erythraean Sea) is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To the north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez (leading to the Suez Canal). The sea is underlain by the Red Sea Rift which is part of the Great Rift Valley.
The salinity of the Red Sea is greater than the world average, approximately 4 percent. This is due to several factors:
- Lack of significant rivers or streams draining into the sea.
- Limited connection with the Indian Ocean, which has lower water salinity.
- High rate of evaporation and very little precipitation.
The six countries bordering the Red Sea proper are:
Eastern shore:
- Saudi Arabia
- Yemen
- Western shore:
- Egypt
- Sudan
- Eritrea
- Djibouti

Aral Sea
The Aral Sea was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan (Aktobe and Kyzylorda Regions) in the north and Uzbekistan (Karakalpakstan autonomous region) in the south. The name roughly translates as “Sea of Islands”, referring to over 1,100 islands that once dotted its waters; in the Turkic languages aral means “island, archipelago”.

South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea that is part of the Pacific Ocean, encompassing an area from the Karimata and Malacca Straits to the Strait of Taiwan of around 3,500,000 square kilometres (1,400,000 sq mi). The area’s importance largely results from one-third of the world’s shipping sailing through its waters and that it is believed to hold huge oil and gas reserves beneath its seabed.
It is located
- south of China;
- east of Vietnam and Cambodia;
- northwest of the Philippines;
- east of the Malay peninsula and Sumatra, up to the Strait of Malacca in the western, and
- north of the Bangka–Belitung Islands and Borneo

Ross sea
The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land. It derives its name from the British explorer James Ross who visited this area in 1841. To the west of the sea lies Ross Island and to the east Roosevelt Island, while the southernmost part is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf, and is about 200 miles (320 km) from the South Pole.

Weddel sea
The Weddell Sea is part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre. Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula. The easternmost point is Cape Norvegia at Princess Martha Coast, Queen Maud Land. To the east of Cape Norvegia is the King Haakon VII Sea. Much of the southern part of the sea is covered by a permanent, massive ice shelf field, the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf .
The sea is named after the Scottish sailor James Weddell, who entered the sea in 1823 and originally named it after King George IV; it was renamed in Weddell’s honour in 1900.

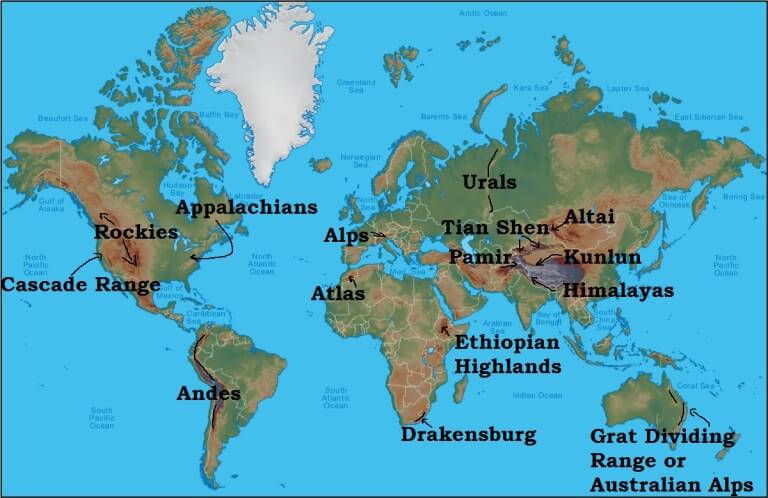
Mountain Ranges
| Sr. No. | Mountain Range | Important/Highest Peaks | Location | Description |
| 1 | Rocky Mountains | Mt. Elbert (highest peak in the Rockies) | North America | It is one of the longest fold mountains in the world and extends from Canada to Western US (New Mexico State) |
| 2 | Appalachian Mountains | Mt. Mitchell, North Carolina, US (highest peak of Appalachian Mountains) | North America | It is a fold mountain with rich in mineral resources |
| 3 | Alps | Mont Blanc (French –Italian border) | Europe | It is a folded mountain and source for rivers like Danube, Rhine, etc. |
| 4 | Sierra Nevada | Mt. Whitney | California, USA | Habitat for many Red Indian tribes |
| 5 | Alaska Range | Mt. McKinley | North America | Mt. McKinley highest peak in North America |
| 6 | Altai Mountains | Belukha mountain | Central Asia | Young folded mountain which extends from Kazakhstan to northern China. |
| 7 | Andes Mountains | Mt. Aconcagua | South America | Longest mountain chain in the world |
| 8 | Atlas Mountains | Mt. Toubkal | Northwestern Africa | Young fold mountain spreading over Morocco and Tunisia. |
| 9 | Drakensberg Mountains | Mt. Lesotho | South Africa | Young folded mountain |
| 10. | Caucasus Mountain | Mt. Elbrus | Europe | Located between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea |
| 11. | Ural Mountains | Mt. Narodnaya | Russia | This mountain range act as a boundary between Europe and Asia. |
| 12. | Hindukush Mountains | Mt. Trich Mir | Pakistan and Afghanistan | Folded mountain with rugged topography which makes it difficult for transportation. |
| 13. | Himalayas | Mt. Everest | Asia | Young fold mountains in Asia which separates Indian sub-continent from Asian plains |
| 14. | Arakan Yoma | Mt. Kennedy peak | Myanmar | It extends from north to south direction. Shifting cultivation is practised. |
| 15. | Kunlun Mountains | Mt. Muztag | North of Tibetan plateau and western China | It is one of the young folded mountains. |
| 16. | Vosges | Mt. Grand Ballon | Eastern France, Europe | Famous for the cultivation of grapes and manufacture of wines. |
| 17. | Great Dividing Range | Mt. Kosciuszko | Australia | This range is the source for the rivers Darling and Murray. |
Samanvaya: Free 1-to-1 mentorship for UPSC IAS
Fill up this form to schedule a free on-call discussion with senior mentor from Civilsdaily. Once submitted we will call you within 24 hours.

Thanks