Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Health Account (NHA) estimates
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central idea: The National Health Account Estimates 2019-20 report shows an increase in government spending and a decline in out-of-pocket expenditure on healthcare.
About National Health Account (NHA) estimates
- The NHA estimates for India 2019-20 is the seventh consecutive report prepared by the National Health Systems Resource Centre (NHSRC).
- NHSRC was designated as National Health Accounts Technical Secretariat (NHATS) in 2014 by the Union Health Ministry.
- The NHA estimates use an accounting framework based on the internationally accepted standard of System of Health Accounts, 2011 developed by the WHO.
- India now has a continuous series of NHA estimates from 2013-14 to 2019-20, making the estimates comparable internationally.
- The estimates enable policymakers to monitor progress in different health financing indicators of the country.
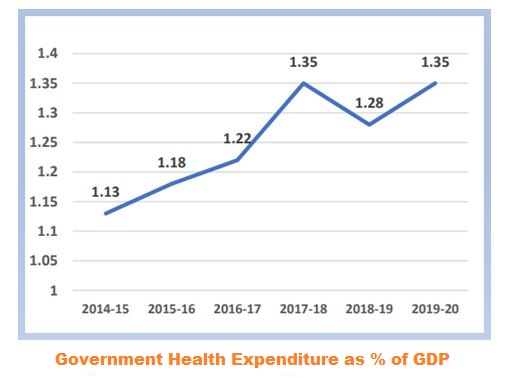
Key highlights
Description |
|
| Government spending as % of GDP |
|
| Declining out-of-pocket expenditure |
|
| Government spending on primary healthcare |
|
| Increase in social security expenditure |
|
| Increase in spending on insurance |
|
| Health spending by states |
|
Key issues
- Marginal increase: Activists are concerned about the marginal increase in government spending.
- Global laggard: This increase in government health expenditure as a percentage of GDP also takes into account capital spending, which puts India in 164th place out of 184 countries in terms of government health spending.
- No proportional increase: Total spending on health as a proportion of GDP has been going down, from 3.9% in 2015 to 3.3% in 2020, indicating a decline in consumption of healthcare services.
Conclusion
- Overall, the report shows that government spending on healthcare has been increasing, while out-of-pocket expenditure has been declining.
- There is a need to invest in public health and insurance and increase the contribution of states towards healthcare.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

