Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Health Expenditure at 1.84% of GDP
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Health Expenditure Share of GDP
Why in the News?
The Union government has steadily increased its spending on healthcare, with the expenditure rising to 1.84% of GDP in 2021-22, up from 1.15% in 2013-14.
Overview of India’s Health Expenditure
- India has shown a consistent increase in government spending on healthcare, reflecting a growing commitment to improving the public healthcare system.
- As of 2021-22, government health expenditure (GHE) rose to 1.84% of GDP, up from 1.15% in 2013-14, and is on track to meet the National Health Policy 2017 target of 2.5% of GDP by 2025.
- The rise in health expenditure has been particularly significant post–COVID-19, with a 37% increase in government spending from 2020-21 to 2021-22.
- This has led to better healthcare accessibility, reduced financial burden on individuals, and greater focus on strengthening healthcare infrastructure.
What is Total Health Expenditure?
- Total Health Expenditure (THE) refers to the sum of all current and capital expenditures incurred by the government, private sector, and external sources for healthcare purposes in a given period.
- This includes:
- Current Health Expenditure (CHE): Ongoing spending on healthcare services, such as hospitals, doctor visits, and medical supplies.
- Capital Expenditure: Investments in healthcare infrastructure, such as building hospitals or purchasing medical equipment.
- In 2020-21, India’s THE was estimated at ₹7,39,327 crores, constituting 3.73% of GDP, with a per capita expenditure of ₹5,436.
- In 2021-22, this figure increased to ₹9,04,461 crores, representing 3.83% of GDP, reflecting a proactive government response to healthcare challenges and pandemic management.
Reasons for Reduced Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE)
The reduction in OOPE can be attributed to:
- Increased government health spending, making healthcare more affordable.
- Expansion of public health services, including vaccination and preventive care.
- Growth in government-funded health insurance and social security programs, reducing reliance on personal funds.
- Health initiatives like Ayushman Bharat have eased the financial burden.
- Improved public healthcare access and financial protection have reduced hardship for low- and middle-income families.
PYQ:[2021] “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[17th March 2025] The Hindu Op-ed: The challenges of public health education in India
PYQ Relevance:Q) “In a crucial domain like the public healthcare system, the Indian State should play a vital role to contain the adverse impact of marketisation of the system. Suggest some measures through which the State can enhance the reach of public healthcare at the grassroots level.” (2024) Reason: This question requires an understanding of the challenges within the public healthcare system, including the availability and competence of public health professionals, which is linked to the quality and accessibility of public health education. |
Mentor’s Comment: UPSC Mains have focused on the ‘Public health system’ (in 2015) and ‘role of Indian state in public healthcare system’ (2024).
The U.S. decision to leave the World Health Organization (WHO) and cut funding for the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has caused major disruptions in healthcare services in many developing countries. However, India has remained mostly unaffected because it relies very little on international aid, which makes up only 1% of its total health spending.
Today’s editorial discusses the impact of the U.S. decision to withdraw from the World Health Organization (WHO) and reduce funding for the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). This analysis is relevant for GS Paper 2, covering International Relations (IR) and Governance in the health sector.
_
Let’s learn!
Why in the News?
Recently, the U.S. decided to leave the World Health Organization (WHO) and cut funding for the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
Why has the withdrawal of U.S. funding from WHO and USAID had a limited impact on India’s public health system?
- Low Dependence on Foreign Aid – International aid accounts for only 1% of India’s total health expenditure, making the system largely self-reliant. For example, India’s Ayushman Bharat scheme is fully funded by the government, reducing dependence on external grants.
- Strong Domestic Health Programs – India has large-scale, government-funded health programs like the National Health Mission (NHM) and the Universal Immunization Programme (UIP). For instance, India’s polio eradication drive was successful primarily due to government initiatives rather than foreign aid.
- Growing Private Healthcare Sector – The private sector plays a dominant role in healthcare delivery, reducing reliance on foreign-funded public health initiatives. For example, large hospital networks like Apollo Hospitals and Narayana Health operate independently of international funding.
- Diversified Funding Sources – India receives aid from multiple global organizations, including the Gavi Vaccine Alliance and the Global Fund, ensuring that a reduction in U.S. contributions does not severely impact the overall funding pool. For example, India’s HIV/AIDS control programs receive support from UNAIDS and the Global Fund, not just USAID.
- Increased Government Health Spending – The Union Budget allocations for health have consistently increased, helping sustain key health initiatives. For instance, India’s health budget in 2023-24 was ₹89,155 crore, allowing for the continued expansion of primary health infrastructure and insurance schemes without heavy reliance on foreign aid.
What are the key challenges faced by Master of Public Health (MPH) graduates in securing employment in India?
- Limited Government Job Opportunities – Despite the increasing number of MPH graduates, government recruitment has stagnated. For example, the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) initially opened roles for non-medical public health specialists, but hiring has since slowed.
- Preference for Medical and Management Professionals – The private healthcare sector prioritizes hospital administrators and business managers over public health specialists. For instance, private hospitals often recruit MBA (Healthcare) graduates for leadership roles rather than MPH holders.
- Declining International Funding for Public Health – Many research institutions and NGOs rely on foreign grants, which are shrinking due to the U.S. withdrawal from WHO and USAID cuts. For example, NGOs working on tuberculosis control have faced funding reductions, limiting hiring capacity.
- Lack of Practical Training and Standardization – Many MPH programs lack field experience, making graduates less competitive. For example, graduates from institutions with strong internships (like PHFI) are often preferred over those from colleges with purely theoretical training.
- Absence of a Public Health Cadre – Unlike developed nations where public health professionals have dedicated government roles, India lacks a structured Public Health Management Cadre. For example, states like Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra have proposed such a cadre, but implementation remains slow.
How has the expansion of public health education in India led to concerns about the quality of MPH training?
- Lack of Standardized Curriculum – Different universities follow varied curricula, leading to inconsistencies in training quality. For example, Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS) emphasizes social determinants of health and policy, while Manipal Academy of Higher Education (MAHE) focuses more on epidemiology and biostatistics. This lack of uniformity affects the competencies of graduates.
- Insufficient Practical Training – Many MPH programs lack field-based learning, making graduates less prepared for real-world public health challenges. For instance, Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI) offers strong internship opportunities in collaboration with state governments, whereas some newer private universities, like Amity University, provide limited hands-on experience.
- Shortage of Qualified Faculty – Several institutions face a shortage of experienced public health faculty, affecting the depth of education. For example, Banaras Hindu University (BHU) has an established public health faculty, whereas some recently launched programs in private universities struggle to recruit trained professionals, leading to a reliance on general medical or social science faculty.
What are the steps taken by the Indian government?
|
Way forward:
- Establishment of a Public Health Cadre – The government should create a dedicated Public Health Management Cadre (PHMC) at the state and central levels to ensure structured employment for MPH graduates. For example, states like Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra have proposed such cadres, but national-level implementation is required.
- Standardization of MPH Curriculum – A central body like the National Medical Commission (NMC) or the University Grants Commission (UGC) should regulate MPH programs, ensuring a uniform curriculum with a balance of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. For instance, defining core competencies such as epidemiology, health policy, and program management would enhance graduate employability.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[12th March 2025] The Hindu Op-ed: Building compassion into the health-care structure
PYQ Relevance:Q) Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. (UPSC CSE 2021) |
Mentor’s Comment: UPSC mains have always focused on the moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure (2021) and Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention (2018).
On February 7, 2025, the WHO released the “Compassion and Primary Health Care” report, emphasizing compassion as a transformative force in health care. Based on my interactions with medical pioneers and global advocacy efforts, including the 74th World Health Assembly, I am encouraged to see growing recognition of compassion’s vital role in improving health care worldwide.
Today’s editorial highlights the importance of compassionate health care, offering valuable insights for GS Papers, particularly in policy-making and ethics discussions.
_
Let’s learn!
Why in the News?
Compassionate health care should guide the actions of industry leaders, hospitals, and health-care organizations.
What is the key message of the WHO report “Compassion and Primary Health Care”?
- Compassion as a Transformative Force: The report highlights compassion as a core value in improving primary health care outcomes. Example: A cancer patient’s recovery improves significantly when doctors spend an extra 40 seconds expressing support, as found in a Johns Hopkins study.
- Improved Patient Outcomes through Compassion: Compassionate care leads to faster recovery, shorter hospital stays, and reduced patient anxiety.Example: Stanford University’s CCARE research found that patients treated with compassion experience quicker healing and fewer complications.
- Benefits for Health-Care Providers: Compassion reduces stress, prevents burnout, and increases job satisfaction for medical professionals. Example: Nurses who engage in compassionate care report stronger patient relationships and improved emotional well-being.
- Distinguishing Compassion from Empathy and Sympathy: Compassion involves mindful problem-solving while maintaining emotional stability, unlike empathy, which may cause emotional fatigue. Example: A compassionate doctor can acknowledge a patient’s suffering while staying emotionally balanced to provide sustained care.
- Global Call for Compassionate Health Systems: The report urges policymakers to integrate compassion into health systems and decision-making processes. Example: The WHO calls for training programs to equip health workers with compassionate communication skills across nations.
Why is compassion considered beneficial for both patients and health-care providers?
- Faster Recovery and Better Patient Outcomes: Compassionate care leads to quicker recovery, reduced pain, and shorter hospital stays for patients. Example: A Johns Hopkins study found that when doctors express solidarity (e.g., saying, “We are in this together”), patient anxiety decreases, improving their healing process.
- Enhanced Patient Trust and Satisfaction: Patients feel heard, valued, and safe when treated with compassion, which strengthens their trust in the healthcare system. Example: Cancer patients who receive compassionate communication are more compliant with treatment and express higher satisfaction with care.
- Reduced Stress and Burnout for Health-Care Providers: Compassion reduces emotional exhaustion and prevents burnout by fostering emotional resilience. Example: Nurses trained in compassionate care report lower stress levels and improved emotional well-being.
- Stronger Patient-Provider Relationships: Compassion fosters deeper connections, improving communication and shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers. Example: Physicians who practice compassionate care build long-term patient trust, leading to better health outcomes and loyalty.
- Increased Job Satisfaction and Professional Fulfillment: Compassion enhances job satisfaction by giving healthcare providers a sense of purpose and fulfillment. Example: Doctors who engage in compassionate interactions report feeling more connected to their profession and experience greater personal reward.
How does compassion differ from sympathy, empathy, and kindness in the context of health care?
- Compassion: Compassion is the ability to recognize a patient’s suffering and actively take steps to alleviate it. It involves an emotional connection combined with a willingness to help. Example: A nurse notices that a terminally ill patient is in pain despite receiving standard treatment. She advocates for a change in medication to improve the patient’s comfort while offering emotional support to the family.
- Sympathy: Sympathy is feeling sorrow or concern for someone’s suffering but without deeply sharing their emotional experience. Example: A doctor expresses condolences to a patient’s family after delivering bad news but does not necessarily feel the pain personally.
- Empathy: Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person by mentally putting oneself in their position. Example: A physician listens to a patient with chronic pain, acknowledges the emotional toll, and adjusts treatment plans accordingly while providing reassurance.
What are the steps taken by the government?
|
Way forward:
- Integrate Compassion Training in Medical Education: Include structured programs to develop compassionate communication and patient-centered care skills for all healthcare professionals, ensuring empathy and emotional resilience.
- Strengthen Policy Frameworks for Compassionate Care: Implement guidelines that prioritize compassion in healthcare delivery, with regular assessments and incentives to encourage patient-centered, humane practices across public health systems.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Centring care in India’s economic policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Gender Budgeting;
Why in the News?
The Union Budget for 2025 allocated ₹4,49,028.68 crore to the Gender Budget (GB), which is 37.3% more than the previous year and makes up 8.86% of the total Budget.
What is the primary reason for the significant increase in the Gender Budget (GB) for 2025?
- Inclusion of PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY): This welfare scheme accounts for 24% of the total Gender Budget. Example: The free food grain distribution under PMGKAY, aimed at ensuring food security for vulnerable women-led households, significantly inflated the Gender Budget.
- Broadening the Definition of Gender-Responsive Schemes: The inclusion of non-traditional gender-related welfare programs increases the allocation. Example: Programs like Poshan Abhiyaan (nutrition for women and children) and Ujjwala Yojana (LPG subsidies) are now categorized under the Gender Budget.
- Increased Focus on Welfare Distribution Over Structural Investments: The rise is driven by consumption-based welfare rather than care infrastructure. Example: Higher allocations for schemes providing direct benefits like the Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (maternity support) rather than investment in childcare centers.
- Political Commitment to “Nari Shakti”: Emphasis on women’s empowerment as a core pillar of economic growth. Example: The Budget’s narrative aligns with promoting women-led development under the “Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam” (Women’s Reservation Bill).
- Inclusion of Large-Scale Social Security Programs: Integrating social protection schemes under the Gender Budget increases the total value. Example: Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) allocations, where a significant portion targets women beneficiaries, contribute to the budget rise.
How does it impact investments in care infrastructure?
- Limited Direct Investment in Care Services: Despite the rise in overall allocation, no substantial funding is directed toward expanding childcare, eldercare, or healthcare services. Example: There is no new budgetary provision for increasing anganwadi centers or community-based eldercare facilities.
- Invisibility of Unpaid Care Work: The focus on consumption-based schemes overlooks the need to reduce and redistribute unpaid care responsibilities. Example: While food security programs like PMGKAY provide relief, they do not alleviate the physical and time-intensive care work that women perform daily.
- Missed Opportunity for Systemic Reform: The absence of targeted funding means there is no structural change in care-related infrastructure despite policy acknowledgments. Example: The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM), which could reduce women’s water-fetching burden, faced a 4.51% budget cut, limiting its expansion.
- Inadequate Support for Working Women: Without investments in affordable care services, women’s participation in the formal workforce remains restricted. Example: Lack of childcare facilities prevents many women from rejoining the labor market after childbirth.
- Uneven Urban-Rural Access: Existing care infrastructure investments are urban-centric, leaving rural women without essential support systems. Example: The Urban Challenge Fund focuses on urban care models, while rural areas lack similar investments, exacerbating time poverty for women in low-income households.
Why do a majority of Indian women remain outside the labour force?
- Unpaid Care and Domestic Work (UCDW) Burden: Indian women perform a disproportionate share of unpaid care work, limiting their time and ability to engage in paid employment. Example: According to the ILO, 53% of Indian women remain outside the labour force due to care responsibilities, compared to just 1.1% of men.
- Lack of Care Infrastructure: Inadequate access to childcare, eldercare, and basic services increases women’s household workload, preventing workforce participation. Example: Less than half of Indian villages have functional tap water under the Jal Jeevan Mission, requiring women to spend hours fetching water.
- Gendered Social Norms and Stereotypes: Deep-rooted cultural expectations frame women as primary caregivers, discouraging their entry or return to the workforce. Example: Women in low-income households juggle 17-19 hours of unpaid and paid work, reinforcing time poverty and limiting job opportunities.
- Lack of Formal Sector Opportunities: There are limited job options offering flexible work and safe working conditions suited to women’s needs, particularly in rural areas. Example: Women’s participation in India’s formal economy remains low due to insecure jobs and a lack of family-friendly policies.
Which measures does the Economic Survey 2023-24 propose to reduce the unpaid care work burden?
|
Way forward:
- Enhance Care Infrastructure Investment: Prioritize increased funding for community-based childcare, eldercare, and healthcare services, especially in rural areas, to reduce women’s unpaid care burden and improve workforce participation.
- Implement Gender-Sensitive Policy Planning: Institutionalize time-use surveys for evidence-based policymaking and integrate care responsibilities into labor policies to promote equitable access to formal employment for women.
Mains PYQ:
Q Women empowerment in India needs gender budgeting. What are requirements and status of gender budgeting in the Indian context? (UPSC IAS/2016)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Women in South India, Delhi, Punjab have higher levels of obesity
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Issues related to health;
Why in the News?
About 25% of men and women in India were overweight or obese in 2019-21, a 4% increase from 2015-16. Obesity is more common among women in South Indian states, Delhi, and Punjab, but it is rising faster among men.
What is the definition of “overweight” and “obese” based on BMI measurements in the National Family Health Survey?
- Overweight: BMI between 25.0 and 29.9. Example: A person who is 1.65 m (5’5″) tall and weighs 70 kg would have a BMI of 25.7, categorizing them as overweight.
- Obese: BMI of 30.0 or above. Example: A person who is 1.70 m (5’7″) tall and weighs 90 kg would have a BMI of 31.1, classifying them as obese.
- Calculation Formula: BMI = Weight (kg) ÷ (Height in meters)². Example: If a person is 1.60 m tall and weighs 60 kg, their BMI would be: BMI=601.6×1.6=23.4\text{BMI} = \frac{60}{1.6 \times 1.6} = 23.4BMI=1.6×1.660=23.4 (Healthy range).
When did the share of overweight and obese individuals in India significantly increase?
- Period of Increase (2015-16 to 2019-21): The National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) recorded a significant rise in the share of overweight and obese individuals between 2015-16 (NFHS-4) and 2019-21 (NFHS-5).
- Increase in Overweight Individuals: Women: Increased from 15.5% in 2015-16 to 17.6% in 2019-21 (a rise of 2.1 percentage points). Men: Increased from 15.9% in 2015-16 to 18.9% in 2019-21 (a rise of 3 percentage points).
- Example: In Delhi, the proportion of overweight men and women was among the highest in the country during 2019-21.
- Increase in Obese Individuals: Women: Increased from 5.1% in 2015-16 to 6.4% in 2019-21. Men: Increased from 3% in 2015-16 to 4% in 2019-21. Example: Punjab recorded one of the sharpest increases in obesity among women during this period.

Which Indian states reported the highest increase in obesity levels?
- Northern States with Sharp Increases: Delhi and Punjab recorded the highest increase in obesity levels for both men and women between 2015-16 and 2019-21. Example: Delhi had the largest proportion of obese and overweight men in the country by 2019-21.
- Southern States with Persistent High Obesity Rates: Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Karnataka consistently reported high obesity levels, with a notable rise over the survey period. Example: In Kerala, a significant portion of the population—both men and women—crossed the obesity threshold by 2019-21.
- States with Accelerated Growth in Obesity: States in the South and North-West witnessed faster increases in obesity, reflecting a shift toward unhealthy dietary habits like increased consumption of fried foods and aerated drinks. Example: Punjab experienced a sharp increase in the share of obese women, making it one of the top states for rising obesity.

What are the steps taken by the Indian government?
|
Way forward:
- Strengthen Multi-Sectoral Collaboration: Enhance coordination between health, education, and food regulatory bodies to implement comprehensive obesity prevention programs. Example: Integrate nutrition education in school curricula and expand community-based health screenings.
- Promote Sustainable Food Systems: Encourage the availability of affordable, nutritious foods and regulate ultra-processed foods through taxation and clear labeling. Example: Introduce subsidies for healthy food options and enforce strict advertising regulations for unhealthy products.
Mains PYQ:
Q The increase in life expectancy in the country has led to newer health challenges in the community. What are those challenges and what steps need to be taken to meet them? (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) Campaign for Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) Elimination
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lymphatic Filariasis (LF)
Why in the News?
Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare has launched the Annual Nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) Campaign to eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (LF).
About Lymphatic Filariasis (LF):
- Lymphatic Filariasis (LF), or “Hathi Paon”, is a mosquito-borne parasitic disease caused by Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and Brugia timori.
- It affects the lymphatic system, leading to swelling of limbs (lymphoedema) and scrotal swelling (hydrocele), causing permanent disability.
- LF spreads through repeated mosquito bites, making it a major public health challenge in tropical regions, including India.
- India aims to eliminate LF by 2027, ahead of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target.
What is Mass Drug Administration (MDA)?
- MDA is a large-scale public health campaign where anti-filarial medicines are administered to all eligible individuals in endemic areas to stop LF transmission.
- Medication Regimens:
- Double Drug Therapy (DA): Diethylcarbamazine Citrate (DEC) + Albendazole
- Triple Drug Therapy (IDA): Ivermectin + DEC + Albendazole
- Key Features of MDA
- Door-to-door supervised drug administration ensures high coverage.
- Drugs are safe, free, and given twice a year in targeted districts.
- MDA is crucial for eliminating LF, as it reduces parasite transmission and protects millions from disability.
- EXCEPTIONS: Children below 2 years, pregnant women, and seriously ill individuals.
PYQ:[2017] Consider the following statements: 1. In tropical regions, Zika virus disease is transmitted by the same mosquito that transmits dengue. 2. Sexual transmission of Zika virus disease is possible. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Diagnostic sector requires Regulations
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Health Sector;
Why in the News?
India has around 3,00,000 diagnostic labs, and the number is increasing. However, the sector is largely unregulated, scattered, and concentrated in urban areas.
What is the significance of India’s Diagnostics Sector?
- Market Size and Growth: The Indian diagnostics market was valued at approximately US$13 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach US$25 billion by FY28. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 14%. Some projections estimate the market could reach US$40 billion by 2034.
- Essential Component of Healthcare: Diagnostics play a crucial role in disease prevention, early detection, and effective management, making them an essential part of modern healthcare. Doctor recommendations drive a major part of the diagnostic business, with tests being conducted for most patients before prescribing medication.
- Key Market Segments: The sector is primarily divided into pathology (60%) and radiology (40%). Pathology is further broken down into illness (acute and chronic) and wellness segments.
- Drivers of Growth: Several factors contribute to the sector’s growth, including increasing life expectancy, a growing middle class, higher penetration of government insurance schemes, rising income levels, and increasing awareness of preventive testing. An aging population and the rise in chronic diseases also fuel the demand for diagnostic services.
What are the challenges faced by the Diagnostics Sector?
- Urban-Rural Divide: A significant portion of diagnostics revenue (76%) comes from urban areas, even though 70% of India’s population resides in rural areas.
- Disparities in Infrastructure: Rural areas have fewer healthcare facilities, with only about 36.5% of the total hospital beds, leading to delayed treatments and poorer health outcomes
- Regulatory Issues: The Kerala State Clinical Establishments Act faces resistance due to stringent space (300 sq. ft. in rural areas, 500-700 sq. ft. in urban areas) and educational requirements, making compliance unviable for many small labs.
- Standardization Needs: Lack of uniform testing protocols leads to errors. Example: A government lab in Karnataka reported a platelet count of 0.47 lakh/cmm, but a private lab retest showed 2.2 lakh/cmm, highlighting the need for mandatory NABL accreditation and standard SOPs to ensure diagnostic accuracy.
- Infrastructure Gaps in Public Sector: Lack of essential upgrades in government labs (e.g., Osmania and Gandhi Hospitals in Hyderabad). Limited operational hours and unavailability of specialists in government hospitals force patients to private facilities.
What are the present Regulations implemented by the govt for this Sector?
|
Way forward:
- Expand Rural Diagnostic Infrastructure: Strengthen public-private partnerships (PPPs) to enhance diagnostic services in rural areas, improve affordability, and ensure equitable access through mobile labs and telemedicine integration.
- Enforce Uniform Regulatory Standards: Implement a nationwide mandatory NABL accreditation and standard operating procedures (SOPs) for all diagnostic centers to ensure quality, accuracy, and compliance across states.
Mains PYQ:
Q What do you understand by nanotechnology and how is it helping in health sector? (UPSC IAS/2020)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Brucellosis?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Brucellosis
Why in the News?
An 8-year-old girl in Kerala, recently succumbed to brucellosis, a bacterial infection primarily caused by the consumption of unpasteurised milk.
About Brucellosis
- Brucellosis is a bacterial infection caused by Brucella species, primarily affecting cattle, goats, sheep, swine, and dogs.
- Humans contract it through direct contact with infected animals, consuming contaminated animal products, or inhaling airborne agents.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the most common cause is the ingestion of unpasteurised milk or cheese from infected livestock.
- Symptoms and Risk Factors:
-
- Symptoms: Fever, weakness, weight loss, and general discomfort. The incubation period is 1-2 months, but most cases develop within 2-4 weeks.
- At-Risk Groups: Farmers, butchers, veterinarians, hunters, and laboratory personnel handling infected animal tissues.
- Treatment and Prevention:
-
- Treatment: Doxycycline (100 mg, twice daily for 45 days) and Streptomycin (1 g daily for 15 days) as per medical advice.
- Prevention: Vaccination of livestock, pasteurisation of milk, and public awareness campaigns to discourage the consumption of unpasteurised dairy products.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A green signal for India to assert its health leadership
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Health Sector;
Why in the News?
Recently, the Budget has acknowledged health care as a cornerstone of national growth and development.
What are India’s steps towards healthcare transformation in Budget 2025-26?
- Increased Healthcare Spending: The budget includes a substantial allocation of ₹99,859 crore to the healthcare sector, marking a 9.8% increase from the previous fiscal year.
- Expansion of Medical Education: The budget allocates resources to add 10,000 new seats in medical colleges across India in FY26, with plans to add 75,000 seats over the next five years. This expansion aims to address the rising demand for skilled healthcare professionals.
- Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure: There is an increase of ₹1,000 crore allocation under the PM Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM), which aims to strengthen health infrastructure at all levels.
- Digital Health Focus: The budget emphasizes the expansion of digital health portfolios, including telemedicine and AI-driven diagnostic solutions, to bridge care gaps and offer efficient healthcare solutions to underserved regions.
- Promoting Medical Tourism: With the launch of the ‘Heal in India’ initiative, the budget aims to position India as a top medical tourism destination by introducing on-arrival visas for international patients and streamlining visa norms.
- Healthcare Coverage for Gig Workers: The budget extends Ayushman Bharat coverage to one crore gig workers, recognizing their contribution to the new-age services economy.
- Support for AI in Healthcare: The budget announces the establishment of India’s Centre of Excellence for AI, and the expansion of the Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL) initiative, will further propel research within the Indian healthcare sector.
What would be the implications of Customs duty exemptions?
- Cost Reduction: The budget includes a full exemption of customs duty on 36 life-saving drugs used to treat cancer, rare diseases, and other severe chronic conditions. This measure will significantly reduce the cost of these essential medications, making them more accessible to patients, especially those from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Improved Access to Medications: The exemption extends to specific drugs under Patient Assistance Programs run by pharmaceutical companies, along with adding 37 new medicines and 13 new patient assistance programs by next year. This will improve access to critical medications for patients, particularly those with chronic conditions.
What are the objectives of synergy – ‘Heal in India’?
- Promote Medical Tourism: The ‘Heal in India’ initiative aims to promote medical tourism by simplifying visa procedures for international patients.
- Establish India as a Global Healthcare Destination: By enhancing hospital infrastructure and streamlining visa processes, India is poised to become the preferred medical destination for international patients.
What are the challenges in India?
|
Way forward:
- Strengthen Rural Healthcare Infrastructure – Increase investments in rural hospitals, improve transport and power infrastructure, and incentivize private sector participation to bridge accessibility gaps.
- Expand Medical Workforce & Insurance Coverage – Enhance training programs for doctors and nurses, increase medical seats, and extend affordable health insurance schemes to reduce out-of-pocket expenses for low-income groups.
Mains PYQ:
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The financial toxicity of cancer care in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Impact of Cancer;
Why in the News?
The financial strain of cancer is often ignored but can be the most harmful. It not only impacts the patient but also their family and future generations.
What is the extent of financial toxicity faced by cancer patients in India?
- High Treatment Costs: Cancer treatments, especially advanced options like immunotherapy, can be prohibitively expensive. For instance, a patient with oral cancer may face annual costs of approximately ₹10 lakh, adding to previous expenses that can total ₹25 lakh over several years. This financial strain often forces families to deplete savings or sell assets to afford care.
- Impact on Families: Financial toxicity extends beyond the patient to their families, leading to severe economic consequences. Families may resort to selling properties or skipping meals to manage treatment costs, which can entrap them in a cycle of generational poverty.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses: A significant portion of healthcare costs is borne out-of-pocket by patients. For example, outpatient expenses can account for nearly 50% of total healthcare costs, which are not covered by insurance schemes like Ayushman Bharat.
What are the contributing factors to financial toxicity in cancer care?
- Inadequate Public Health Funding: India’s public health expenditure has historically been below 2% of GDP, resulting in insufficient healthcare infrastructure and personnel in public hospitals. This leads to delays in diagnosis and treatment, particularly for advanced cancer cases that require more costly interventions.
- Limited Insurance Coverage: Existing insurance schemes primarily cover inpatient costs, leaving patients responsible for outpatient diagnostics and follow-up treatments. This gap significantly contributes to the financial burden on patients and their families.
- Economic Disparities: Patients from low and middle-income backgrounds face additional hurdles in accessing cutting-edge treatments due to their high costs and limited availability in public health systems.
What are the steps taken by the Indian Government?
|
What strategies can be implemented to mitigate financial toxicity? (Way forward)
- Strengthening Public Healthcare: Increasing government investment in public health could improve access to affordable cancer care.
- States like Delhi and Kerala have initiated schemes to support direct medical costs, but broader implementation is needed across India.
- Supportive Measures for Non-Medical Costs: Initiatives such as discounted travel fares for cancer patients can alleviate some financial burdens associated with non-medical expenses. Expanding these programs could provide significant relief.
- Role of Nonprofits and CSR: Nonprofit organizations play a crucial role in reducing out-of-pocket expenses through various support services. Increased funding from corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives could help these organisations expand their reach and impact.
- Promoting Philanthropy: Encouraging individual philanthropy among wealthier segments of society could provide critical funding for cancer care initiatives and nonprofits focused on assisting low-income patients.
- Policy Advocacy: Advocating for policies that address the gaps in insurance coverage and promote equitable access to cancer treatments is essential for reducing financial toxicity in the long term.
Mains PYQ:
Q What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Eliminating elitism in mental health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Mental Health;
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Labour and Employment’s 2024 report indicates that all States and Union Territories must complete harmonization and pre-publication of draft rules for new Labour Codes by March 31, 2025, allowing for mental health provisions.
How does social inequality impact mental health access and outcomes?
- Disparity in Access to Care: Social inequality leads to significant disparities in access to mental health care services. Individuals from lower socio-economic backgrounds, particularly blue-collar workers, often face barriers such as lack of awareness, stigma, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure, resulting in a treatment gap of 70% to 92% for mental disorders in India.
- Workplace Conditions: Blue-collar workers frequently endure demanding jobs with poor working conditions, job insecurity, and inadequate pay, which can exacerbate mental health issues. These conditions contribute to higher rates of stress and mental disorders among this demographic compared to their white-collar counterparts.
- Limited Legislative Protections: The existing labor laws primarily focus on physical safety and do not adequately address mental health concerns. This legislative gap perpetuates the marginalization of blue-collar workers in accessing mental health resources and support.
What legislative and policy changes are necessary to promote inclusivity in mental health care?
- Rights-Based Framework: Establishing a rights and duty-based legislative framework that mandates employers to ensure both physical and mental well-being is crucial. This framework should include clear definitions of occupational diseases that encompass mental health issues arising from work conditions.
- Inclusion of Mental Health in Labor Codes: The upcoming labor codes should explicitly incorporate provisions for mental health, creating a liability-based framework for employers to prioritize the mental well-being of their employees. This includes recognizing stress-related conditions as occupational hazards eligible for compensation.
- Awareness and Accessibility Initiatives: Legislative measures should mandate employers to promote awareness of available mental health resources, such as helplines and support programs like Tele Manas, ensuring that blue-collar workers are informed and encouraged to seek help without stigma.
What are the steps taken by the government?
|
How can societal attitudes towards mental health be transformed to reduce stigma? (Way forward)
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: Raising awareness through national and local campaigns can help normalize mental health discussions. For example, the “It’s Okay to Not Be Okay” campaign in India aimed at addressing mental health issues in the workplace.
- Media Representation and Positive Portrayal: The media plays a significant role in shaping public attitudes. Portraying individuals with mental health issues as strong, resilient, and capable of leading successful lives can help shift negative perceptions. For instance, Bollywood movies like “Dear Zindagi”.
- Involvement of Influential Figures: Public figures such as celebrities, politicians, and community leaders can be instrumental in reducing stigma by sharing their personal mental health stories. When Virat Kohli, an Indian cricketer, spoke openly about struggling with mental health issues, it made a powerful impact and encouraged others.
Mains PYQ:
Q ”Economic growth in the recent past has been led by increase in labour productivity.” Explain this statement. Suggest the growth pattern that will lead to creation of more jobs without compromising labour productivity. (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[28th January 2025] The Hindu Op-ed: Getting drunk, on homoeopathy
PYQ Relevance:Q.) “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. (CS Mains 2021) Q.) Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieving ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (CS Mains 2018) |
Mentor’s Comment: UPSC Mains has always focused on traditional knowledge of medicine (2019) and the health sector (2020).
A recent Supreme Court ruling in the case of Bhagwati Medical Hall vs Central Drugs Standard Control Organization & Ors. has highlighted the difficult challenge faced by state governments in controlling the public health risk caused by alcoholic tinctures sold as homoeopathic remedies in India. Despite the Union Government’s efforts to address the issue, the strong influence of the homoeopathic industry has often led to legal battles that prevent real progress.
Today’s editorial discusses the difficult challenge state governments face in managing the health risks from alcoholic tinctures sold as homoeopathic medicines in India. This information can be useful for supporting your argument in GS Paper 1 and 2 answers.
_
Let’s learn!
Why in the News?
Alcoholic tinctures sold as homoeopathic remedies in India pose a serious risk to public health.
What are the recent changes in homoeopathic tinctures?
|
What are the implications of the recent regulatory changes in homoeopathy?
- Regulatory Complexity and Taxation Issues: The regulatory architecture for homoeopathic alcoholic tinctures is highly complex, with overlapping jurisdictions between the Union and States.
- Post-GST, alcohol for medicinal purposes is taxed at 18%, significantly lower than State taxes on alcoholic beverages, making homoeopathic tinctures a cheaper alternative for consumers.
- States cannot regulate these tinctures without presidential assent, leading to a lack of quality control and public health oversight.
- Public Health Hazards: Homoeopathic tinctures containing 12% alcohol are often consumed as substitutes for alcoholic beverages, leading to alcohol-related illnesses such as alcoholic hepatitis.
- For example: States like Gujarat and Bihar, where alcohol is prohibited, have reported deaths due to the consumption of spurious homoeopathic tinctures..
- Industry Lawfare and Regulatory Delays: The homoeopathic industry has consistently challenged regulations, such as Rule 106B of the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945, through prolonged litigation.
- The Union government’s decision to pursue litigation instead of laying Rule 106B before Parliament has further delayed regulatory enforcement.
How does the public perception of homoeopathy impact healthcare choices?
- Misleading Perception of Safety: Many consumers perceive homoeopathic remedies as safe and natural, unaware of the high alcohol content in tinctures.
- This perception leads to the misuse of homoeopathic tinctures as substitutes for alcoholic beverages, especially in prohibition States like Bihar and Gujarat.
- Lack of Awareness: Poorly informed consumers may consume homoeopathic tinctures daily, believing they are curing ailments, while unknowingly risking alcohol-related diseases.
- The absence of clear labelling and warnings exacerbates the problem, as consumers are not fully aware of the health risks associated with these products.
- Impact on Healthcare Choices: The availability of cheap, alcohol-based homoeopathic tinctures influences healthcare choices, particularly among low-income groups seeking affordable alternatives to conventional medicine.
- This reliance on homoeopathy can delay or prevent access to evidence-based medical treatments, worsening health outcomes.
What role should evidence-based research play in validating homoeopathic practices? (Way forward)
- Need for Regulatory Reforms: Research should inform regulatory decisions, such as whether alcohol should be permitted in homoeopathic and ayurvedic products.
- Countries like the U.S. and U.K. are considering cancer warnings on alcoholic beverages, highlighting the need for similar scrutiny of alcohol-based medicinal products in India.
- Public Health Policy: Evidence-based research can guide public health policies, ensuring that regulations prioritize consumer safety over industry interests.
- Research should also address the misuse of homoeopathic tinctures as substitutes for alcoholic beverages, particularly in prohibition States.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
How has India revised obesity parameters?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Challenges in the Health sector;
Why in the News?
A report by the Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology Commission emphasized body fat distribution, beyond Body Mass Index (BMI), as a vital health and disease risk indicator. In this response, India has revised its obesity guidelines after 15 years.
What is the present status of Obesity?
- Rising Obesity Rates: The obesity rate in India has significantly increased, with approximately 9.8% of women and 5.4% of men classified as obese as of 2022, compared to just 1.2% for women and 0.5% for men in 1990. This translates to around eight crore individuals being classified as obese, including one crore children aged 5 to 19 years.
- Economic Impact and Healthcare Costs: It is projected that India will spend about $13 million annually on treating obesity-related illnesses by 2025 as per the World Obesity Federation. The rising prevalence of obesity is associated with various non-communicable diseases, including diabetes and cardiovascular issues.
- Changing Demographics: The prevalence of obesity is expected to continue rising, with forecasts suggesting that by 2040, around 30.5% of men and 27.4% of women will be either overweight or obese.
What are the initiatives taken by the government?
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS): This program aims to screen individuals for obesity-related risk factors and ensure early intervention to prevent complications associated with obesity. It is part of the broader National Health Mission.
- Eat Right India Movement: Launched by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), this initiative focuses on transforming the food system to promote safe, healthy, and sustainable food for all citizens. It includes awareness campaigns about nutrition and healthy eating habits.
- Ayushman Bharat Health Wellness Centres: These centres strengthen preventive healthcare by promoting wellness activities and targeted communication at the community level, addressing non-communicable diseases (NCDs) including obesity.
- Regulatory Measures: The FSSAI has set guidelines to limit trans fats in food products to no more than 2% by weight and has introduced labelling regulations that require nutritional information on food packaging, helping consumers make informed dietary choices.
What are the new guidelines?
- Terminology Update: The term “overweight” has been removed, categorizing obesity into Grade I (BMI >23 kg/m² without health issues) and Grade II (BMI >23 kg/m² with associated health limitations) to emphasize nuanced stages of obesity.
- Focus on Abdominal Obesity: Waist circumference (>90 cm for men, >80 cm for women) and waist-to-height ratio are prioritized as critical measures for assessing health risks in Asian Indians
Why has it been revised after 15 years?
- Rising Prevalence of Obesity: The prevalence of obesity in India has doubled over the past two decades, with significant increases observed in both adults and children. This alarming trend necessitated a reevaluation of existing guidelines to address the growing public health crisis effectively.
- Limitations of Previous Guidelines: The previous guidelines, established in 2009, relied solely on Body Mass Index (BMI) for diagnosing obesity.
- This approach was found inadequate as it did not consider critical factors such as abdominal fat distribution and the unique metabolic responses of Asian Indians, who tend to develop obesity-related health issues at lower BMI thresholds compared to Western populations.
- Global Framework Alignment: The revised guidelines align with global recommendations from the Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology Commission, which advocates for a broader understanding of obesity as a chronic disease rather than merely excess weight.
What are the health issues that can develop due to obesity?
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Obesity significantly increases the risk of developing heart disease and stroke. It contributes to high blood pressure and unhealthy cholesterol levels, which are critical risk factors for cardiovascular conditions.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excess body weight can disrupt the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to insulin resistance and a higher likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. This chronic condition is closely linked to obesity and can result in severe health complications if not managed properly.
- Certain Cancers: Obesity is associated with an elevated risk of various cancers, including breast, colon, endometrial, and liver cancers. The increased body fat may influence hormone levels and inflammation, contributing to cancer development.
Way forward:
- Comprehensive Public Health Strategies: Strengthen preventive measures through awareness campaigns, promote healthy lifestyles, regulate unhealthy food products, and expand screening programs under initiatives like NPCDCS and Ayushman Bharat.
- Collaborative Policy Reforms: Enhance inter-sectoral collaboration to address urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and dietary patterns while aligning with global obesity management frameworks for effective, long-term solutions.
Mains PYQ:
Q Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[24th January 2025] The Hindu Op-ed: India’s winding road to ‘#EndTB’
| PYQ Relevance:
Q) The increase in life expectancy in the country has led to newer health challenges in the community. What are those challenges and what steps need to be taken to meet them? (UPSC CSE 2022) |
Mentor’s Comment: UPSC mains have always focused on Healthcare Interventions (2018) and Emergence of Drug resistant Diseases in India (2014).
From 2015 to 2022, India experienced a 16% decline in TB incidence and an 18% reduction in TB deaths. But during 2023, India saw an unexpected rise in the cases and hence actions are necessary for strengthening diagnostic infrastructure, enhancing training for healthcare providers, integrating EP-TB into routine screening protocols, and increasing community awareness about TB symptoms.
Today’s editorial discusses the challenges and current state of tuberculosis (TB) elimination efforts in India. This content can be used for presenting the challenges in the Indian Health Care System esp with respect to TB.
_
Let’s learn!
Why in the News?
According to the World Health Organization’s Global Tuberculosis Report 2024, India has the highest TB burden globally, accounting for 26% of all cases and deaths related to TB.
- Despite ambitious national policies, there is a need to better understand the on-ground realities in India to implement effective interventions for TB elimination.
Key Highlights by WHO 2024 Report on India’s TB Burden:
|
What are the current challenges hindering TB elimination in India?
- Socio-Economic Barriers: Many patients come from marginalized communities with limited resources, which affects their ability to seek timely diagnosis and treatment. Secondly, There is still considerable stigma associated with TB, which can discourage individuals from seeking help or disclosing their condition.
- Healthcare System Challenges: The Indian healthcare system faces issues such as inadequate infrastructure, a shortage of trained healthcare professionals, and disparities in healthcare access across different regions. These challenges hinder effective case detection and management.
- Impact of COVID-19: The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted TB control programs, leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment. Vulnerable populations have been disproportionately affected.
- Need for Enhanced Engagement with Private Sector: A significant number of TB patients seek treatment from private healthcare providers, which often leads to inconsistent reporting and adherence to national guidelines. Engaging effectively with the private sector is crucial for comprehensive TB management.
National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme
|
How effective are the current strategies and initiatives under the NTEP?
- Reduction in TB Incidence and Mortality: From 2015 to 2022, India experienced a 16% decline in TB incidence and an 18% reduction in TB deaths.
- This progress indicates that the NTEP is making strides towards its goal of eliminating TB by 2025, which is five years ahead of the global target.
- The NTEP has successfully notified 24.2 lakh TB cases in 2022 (increase of over 58%), with notifications increasing to 25.5 lakh in 2023.
- Engagement with the Private Sector: There has been a sevenfold increase in TB case notifications from the private sector over the past eight years, with private notifications accounting for 30% of total cases in 2022 and rising to 33% in 2023 (proven effective in reaching more patients).
- Treatment Success Rates: The treatment success rate for TB has consistently remained above 80%, reaching 87.6% in 2023. This high success rate reflects the effectiveness of the treatment protocols implemented under the NTEP.
- Infrastructure Development: The program has expanded its diagnostic infrastructure significantly, with a 80% increase in Designated Microscopy Centers (DMCs) and the establishment of numerous molecular diagnostic laboratories. In 2023, approximately 1.89 crore sputum smear tests and 68.3 lakh nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT) were conducted.
- Addressing Drug-Resistant TB: The NTEP diagnosed 63,939 cases of multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB), highlighting its commitment to tackling drug resistance effectively through targeted treatment regimens.
| The introduction of the Nikshay Poshan Yojana, which provides financial assistance for nutrition to TB patients, has supported over 1 crore beneficiaries, disbursing approximately ₹2781 crores by 2023. This initiative addresses undernutrition, a significant risk factor for TB. |
What role do public-private partnerships play in achieving TB elimination goals?
- Increased Case Notification: Collaborations between public health programs and private healthcare providers have led to higher case notification rates which is essential for effective management and treatment.
- Enhanced Treatment Outcomes: Studies indicate that private providers participating in these collaborations often exceed the national treatment success rate target of 85% for new TB patients, demonstrating the effectiveness of these partnerships in delivering quality care.
- Comprehensive Care Models: The Patient Provider Support Agency (PPSA) model has been scaled up across numerous districts and states, enhancing the capacity of the NTEP to manage TB effectively.
- Training and Capacity Building: The NTEP provides training and supervision to private healthcare providers to align their practices with national TB guidelines.
- This capacity-building effort ensures that private practitioners are equipped to deliver high-quality TB care and adhere to standardized protocols.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Union cabinet extends National Health Mission for another 5 years
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet has approved the extension of the National Health Mission (NHM) for an additional five years(2025 to 2030).
What are the new Components of the NHM and initiatives launched?
What are the key achievements of the National Health Mission during its previous tenure?
|
What are the financial implications and commitments associated with the NHM’s extension?
- Budgetary Allocation and Funding Structure: The National Health Mission (NHM) continues based on recommendations from the Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC) and fixed spending limits. While the mission has been extended, its budget is reviewed regularly to ensure efficient use of resources.
- For funding, most states share costs with the central government in a 60:40 ratio, while northeastern and hilly states follow a 90:10 pattern. This setup ensures states have enough funds to implement health programs effectively.
- Performance-Based Funding: The NHM rewards states with additional funds for improving key health outcomes like maternal and child health. This encourages states to enhance their healthcare systems.
- Local committees, such as Rogi Kalyan Samitis (RKS), also receive untied funds, giving them the flexibility to directly address patient needs and improve services.
- Commitment to Health Targets: By 2025, the NHM aimed to achieve specific health goals, including reducing the Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) to 90, the Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) to 23, and the Under-5 Mortality Rate (U5MR) to 23. Achieving these targets will require consistent investment in health infrastructure, workforce training, and community programs.
- The government is also focused on tackling broader factors affecting health, such as nutrition and disease prevention while improving access to healthcare for disadvantaged groups.
What are the challenges?
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Many Primary Health Centres (PHCs) lack essential diagnostic tools, medical equipment, and sanitation facilities. PHCs in remote areas of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh often face electricity and water supply shortages, limiting their ability to deliver quality care.
- Shortage and Distribution of Healthcare Workforce: Despite adding 1.2 million healthcare workers, there remains a shortage of specialists such as gynaecologists, anaesthetists, and paediatricians in rural areas. Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh struggle to staff CHCs with specialized doctors.
- Financial Constraints and Inefficient Fund Utilization: Delays in fund disbursement and underutilization of allocated budgets hinder the implementation of key initiatives. Northeastern states like Nagaland and Manipur faced challenges in utilizing NHM funds due to inadequate financial planning and monitoring mechanisms.
Way forward:
- Infrastructure and Workforce Enhancement: Strengthen PHC and CHC infrastructure with essential facilities and ensure equitable distribution of healthcare specialists through targeted incentives, training, and deployment programs in underserved areas.
- Efficient Fund Utilization: Streamline fund disbursement processes, enhance financial planning, and implement robust monitoring mechanisms to ensure optimal use of allocated budgets, particularly in resource-constrained regions.
Mains PYQ:
Q “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. (UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Is the government encouraging ‘crosspathy’?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Challenges in the health sector;
Why in the News?
Recently, Maharashtra Food and Drugs Administration has allowed homeopathic doctors, who completed a course in modern medicine to prescribe allopathic medicines.
What is the difference between Homeopathy and Allopathy?
What is crosspathy?
|
Why did the Maharashtra FDA issue a directive allowing homoeopathic practitioners to prescribe allopathic medicines?
- Addressing Doctor Shortage: The directive aimed to tackle the severe shortage of doctors, particularly in rural areas, where there is a lack of healthcare professionals, especially specialists.
- Expanding Healthcare Access: By allowing certified homoeopathic practitioners to prescribe allopathic medicines, the Maharashtra FDA sought to expand healthcare services and make treatment more accessible to patients in underserved regions.
- Promoting Integrative Medicine: The directive is part of a broader initiative to promote integrative or integrated medicine, where different medical systems, such as homoeopathy and allopathy, are used to complement each other in patient care.
What is the Supreme Court’s stance on ‘crosspathy’?
|
What are the challenges faced by govt?
- Doctor Shortage: India faces a significant shortage of doctors, especially in rural areas, where the Health Dynamics of India 2022-23 report highlights an 80% deficit of specialists in community health centres. As of June 2022, there were 13.08 lakh allopathic doctors and 5.65 lakh AYUSH practitioners, indicating an insufficient number of qualified professionals to meet healthcare demands.
- Integration of AYUSH Practitioners: While AYUSH practitioners could potentially fill healthcare gaps, there is no systematic approach to integrating them effectively, which could lead to poor outcomes.
- Risk to Patients: Allowing unqualified practitioners to prescribe allopathic medicines could result in medical errors and negligence, raising concerns about patient safety.
- Opposition from Professional Bodies: Organizations like the Indian Medical Association (IMA) strongly oppose crosspathy, questioning its legality and the risks posed to patients.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clarity on who has the authority to issue such directives and manage cross-system practice leads to legal and administrative challenges.
Way forward:
- Clear Regulatory Framework: Establish clear guidelines and regulations for integrating different medical systems to ensure patient safety and effective healthcare delivery, with proper qualifications for practitioners.
- Address Doctor Shortage Strategically: Focus on training and deploying more allopathic doctors, especially in rural areas, while ensuring AYUSH practitioners are properly integrated into the healthcare system through structured programs.
Mains PYQ:
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Costly HPV vaccine needs to be part of national immunisation programme
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Challenges to the healthcare sector;
Why in the News?
The HPV vaccine works best if given before coming into contact with the virus. It is recommended for children aged 12 to 13 and for people who are more likely to get HPV.
What are the health benefits of including the HPV vaccine in the national immunization program?
- Prevention of Cervical Cancer: The HPV vaccine can prevent over 90% of cervical cancers caused by HPV, significantly reducing incidence rates and mortality associated with this disease.
- Broader Cancer Protection: Vaccination also protects against other HPV-related cancers, including those of the vagina, vulva, penis, anus, and oropharynx, promoting overall public health.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Early vaccination can lead to long-term savings in healthcare costs by reducing the need for cancer treatments and associated healthcare services.
- Equity and Accessibility: Making the HPV vaccine part of the national immunization program would enhance accessibility for all demographics, particularly in low- and middle-income regions where cervical cancer rates are disproportionately high.
What are the economic implications of integrating the HPV vaccine into the national immunization program?
- Healthcare Savings: By preventing cervical cancer, the integration of the HPV vaccine into the national immunization program can lead to substantial reductions in treatment costs and hospitalizations related to advanced cancer stages.
- Increased Productivity: Healthier populations contribute to economic productivity as fewer individuals suffer from debilitating illnesses that impede work and social engagement.
- Investment in Public Health: Allocating resources for HPV vaccination can enhance public health infrastructure and create a more robust healthcare system capable of addressing other health issues.
What are the barriers to HPV vaccination?
- High Vaccine Costs: The prohibitive cost of HPV vaccines like Gardasil and Cervarix limits their accessibility for many Indian families. Although the indigenous vaccine, CERVAVAC, offers a more affordable alternative, affordability remains a key barrier to widespread vaccination.
- Low Awareness Levels: A significant lack of awareness about HPV and its link to cervical cancer results in poor understanding of the vaccine’s benefits, contributing to low acceptance and coverage rates.
- Cultural and Social Stigma: Cultural taboos around sexual health and reproductive issues discourage parents from vaccinating children, particularly girls, due to misconceptions about the vaccine’s necessity or fears of promoting promiscuity.
- Gender Bias in Vaccination Efforts: The focus on HPV as a women-centric infection leads to insufficient promotion of vaccination among boys and young men, perpetuating gender disparities in healthcare and reducing overall campaign effectiveness.
- Policy and Budgetary Constraints: Despite recommendations for including the HPV vaccine in national immunization programs, delays caused by budgetary limitations and competing health priorities hinder its integration and accessibility.
What strategies can be employed to overcome barriers to HPV vaccination uptake? (Way forward)
- Awareness Campaigns: Implementing educational initiatives to inform communities about the benefits and safety of the HPV vaccine can help dispel myths and cultural stigmas surrounding vaccination.
- Subsidizing Costs: Reducing the financial burden through government subsidies or integrating the vaccine into public health programs can improve accessibility for lower-income populations.
- Engaging Healthcare Providers: Training healthcare professionals to communicate the importance of HPV vaccination effectively can encourage more patients to get vaccinated, particularly among hesitant parents and young adults.
Mains PYQ:
Q What is the basic principle behind vaccine development? How do vaccines work? What approaches were adopted by the Indian vaccine manufacturers to produce COVID-19 vaccines? (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
GenomeIndia project complete, PM Modi calls it historic
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Human Genomes
Why in the News?
India has created a database of 10,000 human genomes, covering 83 population groups, which is about 2% of the country’s 4,600 population groups.
What are the key achievements of the Genome India Project?
- Completion of Genome Sequencing: The project successfully sequenced 10,000 human genomes from 83 population groups, representing approximately 2% of India’s 4,600 population groups. This data is now housed at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC) in Faridabad, Haryana.
- Identification of Genetic Variants: Initial analyses revealed around 27 million genetic variants, with 7 million being low-frequency variants not found in other global databases. This highlights India’s unique genetic diversity and the potential for targeted research.
- Global Accessibility: The genome data is accessible to researchers worldwide, fostering international collaboration in genomics research and precision medicine.
What are the impact on Biotechnology and Healthcare?
- Advancement of Precision Medicine: The database is expected to facilitate advancements in precision medicine by enabling researchers to study disease risks and drug responses specific to the Indian population. This could lead to more effective treatments tailored to genetic variations.
- Potential for Drug Development: With a focus on understanding genetic predispositions to diseases, the project can support the development of new medications and therapeutic interventions, particularly for genetic and infectious diseases.
- Strengthening India’s Biotech Economy: The initiative is seen as a cornerstone for bolstering India’s biotechnology sector, enhancing its capacity for genomic research and manufacturing.
What are the challenges?
- Data Privacy and Security: India currently lacks a comprehensive Data Privacy Bill, which raises concerns about the protection of sensitive genetic information.
- The absence of robust legal frameworks increases the risk of misuse or unauthorized access to genetic data, potentially compromising individual privacy.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of genomic data for purposes such as gene editing could lead to ethical dilemmas, including issues related to “designer babies” and unintended consequences of genetic modifications.
- Public Trust and Acceptance: Gaining public trust is crucial for the success of the project. There may be apprehensions among individuals regarding how their genetic data will be used, especially if it involves sharing with commercial entities or if there are fears about potential discrimination based on genetic information.
- Integrity of Data Collection: Ensuring the integrity and accuracy of data collection, storage, and usage is essential.
- Without stringent protocols, there is a risk that the data may be misinterpreted or misused, leading to flawed conclusions about genetic predispositions and health risks.
What steps can be taken to overcome the present challenges? (Way forward)
- Expanding the Database: Experts suggest increasing the number of sequenced genomes to up to 1 million to better capture India’s vast genetic diversity. This expansion would provide deeper insights into genetic variations across different ethnic groups.
- Funding and Collaboration: Securing additional funding and forming partnerships with leading research institutions can help overcome financial limitations and enhance data enrichment efforts.
- Ethical Data Management: Ensuring robust data sharing protocols and privacy measures will be crucial for maintaining public trust and facilitating research access while protecting individual identities.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India needs to prioritise preventive care
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Issues related to health care;
Why in the News?
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and cancer are rising sharply in India which causing a heavy financial burden. In 2022, NCDs accounted for 65% of all deaths.
Why should India shift its focus from curative to preventive healthcare?
|
How can India effectively shift its focus from curative to preventive healthcare?
- Strengthening Early Intervention: Enhancing the capabilities of Ayushman Health and Wellness Centres to facilitate targeted screenings and early interventions is crucial. This can involve using data analytics to identify high-risk populations and provide tailored preventive care services.
- Encouraging Regular Screenings: Promoting regular health screenings, especially for individuals aged 40-60, can help identify conditions early. Collaborating with private health providers and insurers to offer subsidized screening programs can make preventive care more accessible.
- Policy Incentives: Revising tax deductions for preventive health checks can incentivize individuals to prioritize their health. Increasing the limit from ₹5,000 to ₹15,000 under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act can encourage more people to undergo comprehensive health assessments.
What role do technology and innovation play in enhancing preventive healthcare accessibility?
- AI and Digital Health Solutions: The integration of AI-enabled imaging modalities and telemedicine can enhance the accessibility of preventive healthcare services. These technologies can facilitate lower-cost screenings and improve diagnostic accuracy, especially in underserved areas.
- Health Data Management: The National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) can play a pivotal role in managing health data effectively, enabling better tracking of health trends and facilitating targeted interventions based on population health analytics.
- Wearable Health Devices: The use of wearable devices for monitoring vital signs and health metrics can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health, leading to earlier detection of potential health issues.
What are the expected economic and health outcomes of prioritizing preventive care?
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By prioritizing preventive care, India could significantly lower the overall financial burden on individuals and the healthcare system.
- Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent the escalation of diseases that require expensive treatments.
- Improved Health Outcomes: A focus on preventive healthcare is likely to lead to better health outcomes, including reduced morbidity and mortality rates associated with non-communicable diseases (NCDs). This shift can enhance the quality of life for many individuals.
- Economic Resilience: Investing in preventive healthcare can contribute to economic stability by reducing productivity losses associated with chronic diseases. A healthier population is more productive, which can drive economic growth and reduce the financial strain on households.
Way forward:
- Expand Preventive Care Infrastructure: Strengthen health centers with early screening capabilities, utilize data analytics to identify high-risk groups, and collaborate with private providers to offer affordable preventive services.
- Incentivize Preventive Health Practices: Revise tax benefits for health check-ups and promote the use of technology, such as wearable devices and telemedicine, to increase accessibility and awareness of preventive healthcare.
Mains PYQ:
Q The increase in life expectancy in the country has led to newer health challenges in the community. What are those challenges and what steps need to be taken to meet them? (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] National Mental Health Programme (NMHP)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Mental Health Programme
Why in the News?
The National Mental Health Programme (NMHP) is a flagship initiative by the Government of India aimed at addressing the growing mental health challenges in the country.
About National Mental Health Programme (NMHP):
| Details | Initiated in 1982 and restructured in 2003, the NMHP aims to modernize mental health facilities and upgrade psychiatric wings in medical institutions. |
| Features and Signficance | The program has 3 components: 1. Treatment of mentally ill 2. Rehabilitation 3. Prevention and promotion of positive mental health. |
| Aims and Objectives |
|
| Structural Mandate | The District Mental Health Programme (DMHP), based on the Bellary Model, focuses on community mental health services at the primary healthcare level, spanning 716 districts.
DMHP provides outpatient services, counselling, psycho-social interventions, and support for severe mental disorders.
|
Back2Basics: The Mental Healthcare Act, 2017
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Ayushman Arogya Mandirs
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Arogya Mandirs, AB-NHPM
Why in the News?
- In February 2018, the Centre had launched the initiative to establish 1,50,000 Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs), formerly known as Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs), by December 2022.
- As of 31st July 2024, 1,73,881 Ayushman Arogya Mandirs have been set up and are fully operational, exceeding the original target.
About the Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs):
| Details |
|
| Aims and Objectives |
|
| Features and Significance |
|
| Structural Mandate | Implemented via 2 Components:
|
PYQ:[2022] With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Disease X and why should the world prepare for it?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Challenges related to the Health Sector;
Why in the News?
The outbreak reported in the first week of December 2024 in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which has already claimed more than 400 lives and is yet to be classified, has sparked concerns that it might be an example of Disease X.
What is Disease X?
- Definition: Disease X is a hypothetical term coined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2018 to represent an unknown pathogen that could potentially cause a global epidemic or pandemic.
- Conceptual Origin: The term was created in the aftermath of the Ebola epidemic (2014-2016) to emphasise the need for preparedness against unpredictable infectious diseases.
- Nature of Disease X: It serves as a placeholder for both “known unknowns” (threats we are aware of but do not fully understand) and “unknown unknowns” (threats we are not yet aware of). This acknowledges the likelihood of future pandemics without specifying their characteristics.
- Potential Pathogens: Disease X could originate from a variety of sources, including viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi, helminths, or prions. Historical data indicates that about 70% of emerging infectious diseases have zoonotic origins, meaning they are transmitted from animals to humans.
- Emerging Disease Patterns: The emergence of new diseases is often linked to ecological disruptions caused by human activities such as deforestation and urbanisation, which increase contact between humans and wildlife.
Why is it Important to Prepare for Disease X?
- Global Health Security: Preparing for Disease X is essential for protecting public health globally. The emergence of new pathogens can lead to widespread illness and mortality, as demonstrated by COVID-19.
- Unpredictable Nature of Outbreaks: The unpredictable emergence of infectious diseases necessitates robust surveillance and rapid response systems. Being prepared helps mitigate the impact of unforeseen threats.
- Increasing Frequency of Outbreaks: The frequency of novel outbreaks has significantly increased since the mid-20th century due to environmental changes, urbanization, and human encroachment on wildlife habitats.
- Economic Impact: Pandemics can have devastating economic consequences, disrupting trade, travel, and healthcare systems. Preparedness can help minimize these impacts.
What should be done to prevent this? ( Way forward)
- Advances in Science and Technology: Investments in research, genomic sequencing, artificial intelligence, and public health infrastructure enhance our ability to detect and respond to emerging diseases quickly.
- International Cooperation: Global collaboration is crucial for effective outbreak response. Initiatives like the WHO’s priority pathogen list and proposed Pandemic Treaty aim to foster a unified approach to health emergencies.
- Equitable Access to Resources: Ensuring equitable access to diagnostics, treatments, and vaccines across all countries is vital for effective pandemic response, particularly in low- and middle-income nations.
Mains PYQ:
Q COVID-19 pandemic has caused unprecedented devastation worldwide. However, technological advancements are being availed readily to win over the crisis. Give an account of how technology was sought to aid the management of the pandemic. (UPSC IAS/2020)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Centre wants States to make Snakebites a Notifiable Disease
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Notifiable Diseases
Why in the News?
The Union Health Ministry has urged states to make snakebites a Notifiable Disease, meaning both private and public hospitals must report it to the government.
Snakebites Menace in India:
|
What are Notifiable Diseases?
- Notifiable diseases are those that must be reported to the government for effective public health monitoring and management. These are typically:
- Infectious diseases likely to cause outbreaks.
- Diseases that result in deaths or require quick action to prevent wider transmission.
- Legal Basis:
-
- According to WHO’s International Health Regulations, 1969, disease reporting is mandatory for global surveillance.
- The primary law governing notifiable diseases is the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897 which outlines the reporting requirements for diseases considered a public health threat.
- However, the specific list of notifiable diseases can vary across different states and is typically determined by the respective state governments under their individual public health acts.
- Common examples of notifiable diseases include tuberculosis, HIV, cholera, malaria, dengue, and hepatitis.
Why snakebite is considered a Notifiable Disease?
- Snakebites can cause severe health issues, including paralysis, fatal hemorrhages, and tissue damage, making it crucial for timely intervention.
- Victims need immediate antivenom treatment to prevent death and long-term effects.
- In 2009, the WHO added snakebite to its list of Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTD), acknowledging its widespread impact on public health.
- Making snakebites a notifiable disease will enhance surveillance, help track case numbers, and improve treatment strategies across the country.
- It will ensure the availability of adequate antivenoms in regions where snakebites are frequent.
- Medical staff will receive training to handle snakebite cases effectively, reducing mortality rates.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Jan Aushadhi Kendra’s by PACS
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras
Why in the News?
- The Government has empowered Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) to operate Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJK), aiming to provide generic medicines at affordable prices to underserved rural areas.
About Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJK) by PACS:
| Details |
|
| Aims and Objectives | To provide affordable medicines, promote healthcare equity, and reduce medical expenses for farmers, while generating local employment and ensuring PACS’ financial sustainability through the sale of medicines and allied products. |
| Structural Mandate and Implementation |
Implementation:
|
| Features and Significance |
|
PYQ:[2015] Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector could help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives would you suggest? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Indians need the right to disconnect
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Issues related to women;
Why in the News?
After an EY employee’s death allegedly linked to work pressure, a report highlights Indian women in professions like IT and auditing exceeding 55-hour workweeks, with marginalized unorganized sector workers facing varied hours.
What are the present issues arising at Workplaces in India?
- Long Working Hours: Many Indian professionals, especially women in sectors like auditing and IT, work over 55 hours per week, contributing to high levels of stress and burnout.
- Mental Health Impact: A significant percentage (49%) of Indian workers report that workplace stress negatively affects their mental health, highlighting the urgent need for better work-life balance.
- Lack of Legal Protections: Unlike several countries that have implemented laws to protect employees’ right to disconnect from work outside official hours, India lacks specific legislation addressing this issue.
- Cultural Attitudes: There is a pervasive workaholic culture where employees feel compelled to remain available outside working hours, often leading to a blurring of boundaries between personal and professional life.
What benefits and challenges would India face in enforcing a ‘right to disconnect’ law?
Benefits:
- Improved Employee Well-Being: Enforcing a right to disconnect could help mitigate stress and improve mental health among employees, leading to a healthier workforce.
- Enhanced Productivity: Research indicates that allowing employees to disconnect can lead to increased productivity during working hours as they can focus better without after-hours distractions.
- Work-Life Balance: Such legislation would promote a more balanced approach to work, allowing employees to prioritize personal time and family life.
Challenges:
- Economic Concerns: Implementing a right to disconnect may b e seen as detrimental to economic growth in a competitive landscape like India, where companies often push for extended working hours.
- Resistance from Employers: Many employers may resist such regulations, fearing it could hinder their operational flexibility and responsiveness.
- Cultural Shift Required: There would need to be a significant cultural shift within organizations to embrace the right to disconnect, moving away from the expectation of constant availability.
How does the concept align with India’s economic growth and competitive landscape?
- Boosting Productivity: Recognizing the right to disconnect could enhance overall productivity by fostering a healthier work environment. This aligns with India’s goal of becoming the third-largest economy by 2030.
- Attracting Talent: A commitment to employee well-being through such legislation could make Indian companies more attractive to skilled professionals, particularly in competitive sectors like technology.
- Global Competitiveness: As global standards for employee rights evolve, India risks falling behind if it does not adapt its labor laws. Implementing a right to disconnect could position India favorably in the global market.
Way forward:
- Legislative Framework: Introduce comprehensive laws recognizing the right to disconnect, ensuring strict enforcement mechanisms and sector-specific guidelines to accommodate diverse workplace needs while safeguarding employee well-being.
- Cultural Transformation: Promote awareness campaigns and organizational policies to shift workplace culture towards respecting personal time, emphasizing the long-term benefits of work-life balance for productivity and economic growth.
Mains PYQ:
Q What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (UPSC IAS/2019)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Frontline nutrition workers foster disability inclusion
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Issues related to disabled people;
Why in the News?
December 3, International Day of Persons with Disabilities, promotes awareness of their rights, inclusion, and needs, emphasizing support for one of the world’s most marginalized and underrepresented communities.
What are the barriers faced by individuals with disabilities in accessing nutrition services?
- Physical Accessibility: Many individuals with disabilities face challenges in accessing physical locations where nutrition services are provided, such as grocery stores or health clinics. This includes barriers like lack of ramps, inaccessible transportation, and inadequate facilities.
- Lack of Knowledge and Skills: Individuals with disabilities may have limited knowledge about nutrition and cooking skills, which can hinder their ability to prepare healthy meals. This is often compounded by the need for assistance from caregivers who may not be well-informed about nutritional needs.
- Financial Constraints: Economic factors play a significant role; many individuals with disabilities experience financial instability, limiting their ability to purchase nutritious food. This is particularly true in low-income households where resources are scarce.
- Social Isolation and Stigma: People with disabilities often face social isolation and stigma, which can affect their access to community resources and support networks that provide nutritional assistance or education.
- Complex Health Needs: Many individuals with disabilities have specific dietary requirements or face challenges related to feeding, swallowing, or digestion, making it difficult to meet their nutritional needs without tailored support.
- Inadequate Public Health Support: In many regions, public health systems fail to provide adequate nutritional support for individuals with disabilities, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where resources may be limited.
How can nutrition programs be adapted to ensure they are inclusive of individuals with disabilities?
- Tailored Nutritional Education: Nutrition programs should include educational components that cater specifically to the needs of individuals with disabilities, focusing on accessible cooking methods and meal planning that accommodate various dietary restrictions.
- Accessible Service Delivery: Programs should ensure that nutrition services are delivered in accessible locations and formats, including home visits for those unable to travel or online platforms for remote consultations.
- Community Engagement: Involving individuals with disabilities in the design and implementation of nutrition programs can help ensure that their unique needs are met. This could include feedback mechanisms to adapt services based on community input.
- Training for Caregivers: Providing training for caregivers on the specific nutritional needs of individuals with disabilities can enhance meal preparation and dietary management at home.
- Financial Assistance Programs: Implementing subsidies or financial assistance programs can help alleviate the economic burden on families caring for individuals with disabilities, enabling them to purchase healthier food options.
- Integration with Health Services: Nutrition programs should be integrated with broader health services to provide comprehensive support that addresses both nutritional needs and overall health outcomes.
What role do Anganwadi workers play in promoting disability inclusion in their communities?
- Early Identification and Referral: Anganwadi workers play a crucial role in the early identification of disabilities among children through monitoring developmental milestones and referring families to appropriate health services.
- Community Education: They engage communities through initiatives like podcasts (e.g., “Nanhe Farishtey”) to raise awareness about disabilities and promote inclusive practices within local settings.
- Nutrition Service Delivery: As frontline community nutrition providers, Anganwadi workers deliver vital nutrition services tailored to the needs of children with disabilities, ensuring they receive adequate dietary support.
- Collaboration with Other Health Workers: Anganwadi workers collaborate with Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) workers to create a network of support for families dealing with disabilities, facilitating access to medical care and government benefits.
- Capacity Building: Ongoing training on disability inclusion through protocols like the ‘Anganwadi Protocol for Divyang Children’ equips workers with the knowledge necessary to support children with disabilities effectively.
- Advocacy for Rights and Resources: They advocate for the rights of persons with disabilities within their communities, helping families navigate available resources such as disability certificates and pensions.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Inclusive Infrastructure and Services: Develop accessible infrastructure, including Anganwadi centres and transportation, while integrating nutrition programs with health services to provide tailored support for individuals with disabilities.
- Empower Community and Frontline Workers: Enhance training for Anganwadi workers and caregivers, promote community engagement to address stigma, and ensure financial support for families to improve access to nutritious food and essential services.
Mains PYQ:
Q The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 remains only a legal document without intense sensitisation of government functionaries and citizens regarding disability. Comment. (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s cities, their non-communicable disease burden
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Health Care issues in India;
Why in the News?
The recent cardiac arrest and subsequent death of a Bengaluru Metropolitan Transport Corporation (BMTC) bus driver while on duty has sparked conversations about worsening health outcomes in urban areas.
What are the primary risk factors contributing to the rising NCD burden in urban areas?
- High-Stress Work Environments: Many urban workers, including bus drivers, face high levels of stress due to long hours, erratic schedules, and demanding job conditions.
- The BMTC study indicated that over 40% of its employees aged 45-60 are at risk for cardiovascular diseases, exacerbated by factors like continuous driving and poor eating habits.
- Poor Nutrition and Lifestyle: Workers often lack access to healthy food options and exercise opportunities, leading to increased rates of obesity, hypertension, and diabetes.
- The BMTC workforce has shown alarming rates of these conditions, which are often linked to lifestyle choices made under stressful work conditions.
- Lack of Health Insurance and Support: Many informal workers do not have health insurance or access to regular health screenings. This lack of support can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment of NCDs, increasing the risk of severe health events like heart attacks.
- Socioeconomic Marginalization: A significant portion of the urban population lives in slums or informal settlements, where access to healthcare is limited. This socioeconomic status contributes to poor health outcomes and a higher prevalence of NCDs.
How can urban health systems be strengthened to effectively manage NCDs?
- Improving Access to Primary Healthcare: Urban health systems must focus on making primary healthcare services more accessible to marginalized communities. This includes expanding facilities in underserved areas and ensuring that services are affordable and culturally appropriate.
- Implementing Regular Health Screenings: Regular health evaluations for high-risk populations, such as bus drivers and other transport workers, should be mandated. These screenings can help identify risk factors early on and facilitate timely interventions.
- Integrating Health Services with Employment Policies: Employers should collaborate with health departments to create programs that promote employee wellness, including stress management workshops and nutrition education tailored for their workforce.
- Community-Based Health Promotion: Local organizations can play a crucial role in educating communities about NCD risks and promoting healthy lifestyles through workshops and outreach programs that engage residents directly.
What role do public awareness and community engagement play in combating NCDs?
- Raising Awareness About NCD Risks: Public campaigns can educate individuals about the importance of regular health screenings and lifestyle changes that reduce the risk of NCDs. Awareness initiatives can empower communities to take charge of their health.
- Encouraging Community Participation: Engaging community members in health promotion activities fosters a sense of ownership over their health outcomes. Community-led initiatives can effectively address local health issues by tailoring solutions to specific needs.
- Utilizing Technology for Monitoring Health: Digital tools can facilitate real-time monitoring of health metrics for at-risk populations, enabling proactive management of conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
- Creating Support Networks: Building networks among workers can provide emotional support and share resources for managing health issues collectively, which is particularly beneficial for those facing similar challenges in high-stress jobs.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Urban Primary Healthcare: Expand access to affordable and culturally relevant primary health services, implement regular screenings for high-risk groups, and integrate wellness programs with employment policies for vulnerable workers.
- Promote Community-Led Health Initiatives: Engage local organizations and residents to raise awareness about NCD risks, encourage healthy lifestyles, and utilize digital tools for real-time health monitoring and proactive care.
Mains PYQ:
Q “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. (UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
How should India tackle diabetes load?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Health Issues; Challenges faced by society due to NCDs;
Why in the News?
On International Diabetes Day (November 14), the Lancet shared a global study showing over 800 million adults have diabetes, and more than half aren’t receiving proper treatment.
What is the controversy over the numbers and the difference in Testing Methodology?
|
What are the issues raised in the Lancet study?
- Global Inequalities in Treatment: The study highlighted significant disparities in diabetes treatment access, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where treatment rates are stagnating despite rising diabetes cases. This raises concerns about long-term health complications for untreated individuals.
- Rising Rates of Diabetes: The findings underscore that diabetes rates have increased dramatically, especially Type 2 diabetes, which poses a growing public health challenge. This trend is alarming given that many affected individuals are younger and at risk for severe complications.
- Complications and Healthcare Burden: With a large number of individuals requiring treatment, there is a looming healthcare crisis regarding complications such as kidney failure, heart disease, and vision loss, which could overwhelm healthcare systems.
What steps need to be taken? (Way forward)
- Enhanced Awareness and Education: There is a pressing need for widespread education on diabetes prevention through nutrition and physical activity. Public health campaigns should focus on promoting healthy lifestyles to mitigate risk factors associated with diabetes.
- Policy Changes: Governments must implement policies that restrict unhealthy food options while making healthy foods more affordable. This includes subsidies for nutritious foods and initiatives to create safe spaces for physical activity.
- Targeted Interventions for Vulnerable Populations: Special attention should be directed towards vulnerable groups, particularly women who may be at higher risk post-pregnancy or during menopause. Tailored interventions can help address specific risk factors prevalent in these populations.
- Investment in Healthcare Infrastructure: To effectively manage the rising burden of diabetes, there must be significant investment in healthcare infrastructure, especially in low- and middle-income countries where resources are limited.
- Long-Term Strategic Planning: A comprehensive long-term strategy is essential to combat the growing diabetes epidemic, requiring collaboration between governments, healthcare providers, and communities to ensure sustainable health outcomes.
Mains PYQ:
Q Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is High-Altitude Sickness?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: High-Altitude Sickness
Why in the News?
The tragic death of a trekker scaling Garur Peak in Uttarakhand, underscores the dangers of high-altitude sickness in the Himalayas.
What is High-Altitude Sickness?
- Causes: High-altitude sickness, or Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS), occurs when the body struggles to acclimatise to elevations above 8,000 feet (2,400 metres) due to reduced oxygen levels.
- Symptoms: Early signs include headache, nausea, fatigue, and shortness of breath. If untreated, it may escalate to:
- High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE): Fluid in the lungs, causing breathing difficulties.
- High-Altitude Cerebral Edema (HACE): Fluid in the brain, leading to confusion, hallucinations, and coma.
Prevention and Treatment
- To prevent AMS, experts recommend a slow ascent with rest days every 3-4 days above 3,000 meters and avoiding sleeping elevation increases of more than 500 meters per day.
- Medications:
- Acetazolamide: Aids acclimatisation.
- Dexamethasone: Reduces severe inflammation.
- Nifedipine: Prevents HAPE in high-risk individuals.
Note: Medications are not foolproof and are to be taken under medical guidance.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Ayushman Vay Vandana Yojana
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Features of Ayushman Vay Vandana Yojana
Why in the News?
Within just three weeks of its launch, over 10 lakh senior citizens have enrolled for the Ayushman Vay Vandana Yojana.
| Note: Pradhan Mantri Vaya Vandana Yojana (PM-VVY) is a pension scheme and insurance policy for senior citizens in India. One must not get confused with Ayushman-VVY. |
About Ayushman Vay Vandana Yojana:
| Details | |
| Features and Provisions | • Cashless health coverage up to ₹5 lakh per year for senior citizens aged 70 and above. • Beneficiaries receive an Ayushman Vay Vandana Card, which grants them access to free treatment in empaneled hospitals across India. • Coverage includes medical consultations, treatments, pre- and post-hospitalization expenses, and complex procedures such as angioplasty. |
| Structural Mandate | • Administered under the PM-JAY framework, ensuring structured implementation and integration with India’s health insurance network. • Implemented across empaneled hospitals in both urban and rural areas, ensuring nationwide reach. • Centralized digital system tracks treatments, patient details, and expenses for transparency and accountability. • Specifically designed for senior citizens, addressing their unique healthcare needs. |
| Aims and Objectives | • Universal healthcare for senior citizens, ensuring access to essential medical treatments without financial strain. • Seeks to reduce out-of-pocket expenditure for elderly citizens and their families. • Encourages preventive care and early medical intervention to address age-related health conditions. |
| Eligibility Criteria | • Open to all Indian citizens aged 70 and above. • There are NO income/ family size restrictions, making it accessible to all senior citizens, regardless of their economic status. • Beneficiaries must be Indian citizens. • Seniors need to register under PM-JAY to receive the AVV Card and avail of the benefits. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Growing epidemic
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Biotechnology; Health sector; Diseases and it’s policies in News;
Why in the News?
Global diabetes cases surged from 200 million in 1990 to over 800 million in 2022, with adult prevalence doubling from 7% to 14%, according to The Lancet report.
What are the WHO’s targets for diabetes diagnosis and management by 2030?
- The World Health Organization (WHO) aims for 80% of people with diabetes to be diagnosed.
- The target is for 80% of diagnosed individuals to achieve good glycemic control, which is crucial for preventing complications associated with diabetes.
What is the current state of diabetes prevalence in India?
|
What strategies can India implement to achieve these targets?
- Targeted Screening and Lifestyle Interventions: India can adopt Finland’s approach of identifying high-risk individuals through targeted screening and offering lifestyle interventions, including dietary changes and exercise, to prevent diabetes.
- Enhance Public Awareness Campaigns: Community-based implementation and awareness programs align with SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) by promoting healthy lifestyles, preventing diabetes, and ensuring equitable access to healthcare for all, especially vulnerable populations.
- Improve Access to Healthcare Services: Ensure that diagnostic facilities for blood glucose testing are widely available and affordable. Strengthen primary healthcare services to facilitate easier access to diabetes care and management.
Steps taken by the government:
|
Way forward:
- Strengthen Preventive Healthcare: Focus on early detection through widespread screening, robust public awareness campaigns, and targeted interventions for high-risk groups, emphasizing healthy lifestyle promotion.
- Enhance Integrated Care Systems: Scale up access to affordable diabetes care, strengthen primary healthcare services, and integrate technology for monitoring and management to achieve WHO’s glycemic control targets by 2030.
Mains PYQ:
Q Stem cell therapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments. (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Decline in Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) in Health in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NHA estimates
Why in the News?
National Health Accounts (NHA) data for 2021-22 shows a decline in Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) on healthcare due to increased government health expenditure (GHE) and an enhanced public healthcare framework.

What are NHA estimates?
|
Key Observations from the NHA 2021-22 Data:
| Details | |
| Decline in Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) | OOPE has decreased due to increased government investment and improved public healthcare infrastructure, making healthcare more accessible and affordable. |
| Rise in Government Health Expenditure (GHE) | GHE as a percentage of GDP rose from 1.13% in 2014-15 to 1.84% in 2021-22. GHE’s share of overall government spending increased from 3.94% to 6.12%, reflecting the government’s commitment to public healthcare. |
| Increase in Per Capita Health Spending | Per capita health spending tripled from ₹1,108 in 2014-15 to ₹3,169 in 2021-22, allowing for more investment in infrastructure, workforce, and services. |
| Expansion of Social Security Expenditure (SSE) | SSE on healthcare grew from 5.7% to 8.7% of Total Health Expenditure (THE), helping protect individuals from catastrophic health expenses and reducing OOPE. |
| Growth of Government-Funded Insurance Schemes | Programs like Ayushman Bharat and state-level health insurance schemes increased healthcare access for economically vulnerable populations, reducing reliance on personal funds. |
| Foundation for Universal Health Coverage (UHC) | The decline in OOPE and increased public health spending are integral to achieving UHC, aiming for equitable healthcare access for all citizens. |
PYQ:[2021] “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. [2019] In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of: (a) Digital security infrastructure (b) Food security infrastructure (c) Health care and education infrastructure (d) Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
APOBEC (Apolipoprotein B mRNA Editing Catalytic Polypeptide)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: APOBEC
Why in the News?
Since smallpox was eradicated in 1980, research on mpox has highlighted how the virus mutates, particularly through the APOBEC family of immune system proteins.
About APOBEC
- APOBEC (Apolipoprotein B mRNA Editing Enzyme, Catalytic Polypeptide-Like) is a family of proteins involved in regulating the genetic material of viruses and cells.
- They are part of the human immune system and play a crucial role in protecting against viral infections by editing RNA and DNA.
- APOBEC consists of several enzymes, with APOBEC1, APOBEC3 family members being the most well-known.
- There are 11 identified members of the APOBEC family, primarily named APOBEC1, APOBEC2, and APOBEC3, with APOBEC3 being the most studied due to its antiviral properties.
- It has a Zinc Finger Domain, which is essential for their enzymatic activity and ability to bind to DNA or RNA.
- APOBEC proteins are found in various tissues and cells, but they are notably present in the immune cells such as T-cells, B-cells, and macrophages.
- Role in Immune Defense:
- APOBEC proteins contribute to the innate immune response by editing viral genomes, preventing the replication of viruses, and reducing the ability of viruses to establish infections.
- They are known to be cytosine deaminases, which means they modify cytosine bases in nucleic acids to uracil, leading to mutations that can prevent successful viral replication.
- APOBEC proteins target the genomes of several viruses, including retroviruses (like HIV), hepatitis B virus, and poxviruses (such as mpox and smallpox).
Functions of APOBEC Proteins:
- DNA Editing: APOBEC proteins can deaminate cytosine bases in single-stranded DNA, converting them into uracil, which can lead to mutations.
- This introduces errors in the viral genome and inhibits replication.
- RNA Editing: Some APOBEC proteins, like APOBEC1, are involved in editing mRNA. In the case of APOBEC1, it helps edit the mRNA of apolipoprotein B, which is crucial for lipid metabolism.
- Antiviral Activity: APOBEC3 proteins, particularly APOBEC3G, inhibit the replication of HIV and other retroviruses by editing viral DNA during reverse transcription.
- They also reduce the replication of poxviruses (such as mpox), making them crucial in controlling infections caused by these viruses.
- Cytosine Deamination in Viral RNA: APOBEC proteins induce mutations in viral RNA, reducing the virus’s ability to efficiently replicate and spread. This helps prevent viral evolution and adaptation.
- Inhibition of Viral Resistance: By causing mutations in viral genomes, APOBEC proteins prevent viruses from easily developing resistance to the immune system’s defenses.
- Interaction with Other Immune Mechanisms: APOBEC proteins work in concert with other immune mechanisms, like interferons, to enhance antiviral responses and limit infections.
PYQ:[2016] In the context of the developments in Bioinformatics, the term ‘transcriptome’, sometimes seen in the news, refers to: (a) a range of enzymes used in genome editing (b) the full range of mRNA molecules expressed by an organism (c) the description of the mechanism of gene expression (d) a mechanism of genetic mutations taking place in cells |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
IDF working on new guidelines to treat Type 2 Diabetes
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: International Diabetes Federation, Type 2 Diabetes
Why in the News?
- The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) is developing new Type 2 diabetes treatment guidelines in collaboration with a global expert panel.
- These guidelines aim to integrate scientific evidence and clinical practice, adapted to the healthcare environment of specific countries.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
|
About International Diabetes Federation (IDF):
| Details | |
| About |
|
| Aims and Objectives |
|
| Key Programs |
|
| Diabetes Types Covered |
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Sleep Apnea contributes to Dementia in older adults
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Why in the News?
A recent study from Michigan Medicine found that Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), a common sleep disorder, increases the risk of dementia (loss of cognitive functioning) in adults, especially in women.
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)?
|
Recent Findings on OSA and Dementia Risk
- A study from Michigan Medicine found a link between OSA and increased dementia risk, especially in older adults over 50.
- Women with known or suspected OSA were found to have a higher likelihood of developing dementia compared to men, with dementia diagnoses increasing as women age.
- Another study by NIMHANS focused on the link between stroke and OSA.
- 105 stroke patients over the age of 50 were studied using polysomnography (PSG), which tracks brain waves and sleep breathing patterns.
- Results showed that 88% of stroke patients had sleep apnea soon after their stroke, with 38% having severe OSA.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) and its spread

Why in the News?
A case of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) was confirmed in the US.
About Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)
|
Symptoms of CWD:
- Symptoms: Drastic weight loss, lack of coordination, drooling, listlessness, and excessive thirst. Infected animals may also show drooping ears and lose their fear of humans.
- Prevention: To prevent the spread of CWD, avoid handling or eating sick animals, use synthetic lures, dispose of carcass waste in landfills, and report any sick or unusual deer to local wildlife authorities.
PYQ:[2012] Vultures which used to be very common in Indian countryside some years ago are rarely seen nowadays. This is attributed to: (a) The destruction of their nesting sites by new invasive species (b) A drug used by cattle owners for treating their diseased cattle (c) Scarcity of food available to them (d) A widespread, persistent and fatal disease among them |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
World Polio Day: How India managed to eradicate polio?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: World Polio Day
Mains level: Polio Eradication
Why in the News?
October 24 is recognized as World Polio Day, a commemoration established by Rotary International to honor the birth of Jonas Salk, who spearheaded the development of the first vaccine against polio in the 1950s.
What key strategies contributed to the successful eradication of polio in India?
- Comprehensive Vaccination Campaigns: India implemented large-scale vaccination drives starting in 1972, which expanded under the Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP) in 1985.
- Community Engagement and Awareness: Targeted awareness campaigns were crucial, utilizing local health workers to administer oral polio drops, which made vaccination accessible.
- Effective Messaging: The slogan “do boond zindagi ki” (two drops of life) resonated well with the public. Utilizing celebrities like Amitabh Bachchan and integrating health messages into popular media further amplified awareness.
- Robust Surveillance System: A multilayered surveillance mechanism was developed to monitor acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) cases, enabling prompt immunisation of affected populations. This system involved local informers, including community health workers and doctors.
- Targeted Interventions for High-Risk Areas: By 2009, efforts were concentrated in specific regions, particularly in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, where most cases were reported. This targeted approach was critical in reducing transmission rates.
- Collaboration with International Agencies: The eradication campaign was supported by various international bodies such as WHO, UNICEF, and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, ensuring financial and logistical backing.
How did India address the challenges of vaccine hesitancy among specific communities?
- Engagement with Community Leaders: To address religious concerns and misinformation, influential figures such as imams and local leaders were involved. Their endorsements played a significant role in countering myths about the vaccine.
- Targeted Communication Strategies: Awareness efforts were tailored to specific communities, focusing on dispelling myths surrounding the vaccine, such as fears about impotence and cultural taboos against its ingredients.
- Culturally Sensitive Messaging: Messaging was crafted in local languages and through community-specific narratives, ensuring that it resonated with the cultural context of various groups.
What lessons can be learned from India’s polio eradication efforts for future public health campaigns?
- Importance of Community Involvement: Engaging local leaders and community members is vital for building trust and addressing vaccine hesitancy effectively.
- Flexibility in Implementation: Tailoring vaccination drives to accommodate local cultural practices, work schedules, and geographic challenges can enhance participation rates.
- Sustained Awareness Efforts: Continuous education and awareness campaigns are essential, especially in the face of evolving misinformation and cultural resistance.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The use of robust surveillance systems and data analytics to identify and target high-risk areas can help streamline public health interventions.
- Collaboration with Multiple Stakeholders: Building partnerships between government agencies, international organizations, and local communities can strengthen public health responses and resource mobilization.
Conclusion: Need to establish sustainable platforms for continuous dialogue between healthcare providers and community leaders to address health concerns, build trust, and ensure community-specific health initiatives are effectively communicated and implemented.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Issues in the treatment of ‘rare diseases’, and what the govt can do?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Definition of Rare Diseases
Mains level: Issues related to rare disease;
Why in the News?
The Delhi High Court recently issued directives to enhance the availability of “orphan drugs” to combat rare diseases.
About the Delhi High Court Verdict:
- The Delhi High Court issued directions aimed at improving the availability of “orphan drugs,” which are used to treat rare diseases.
- This intervention seeks to address challenges related to the high cost of these treatments and the barriers to access for patients with rare diseases in India.
Rare Diseases in India and Their Classification:
- Definition: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), rare diseases are debilitating, lifelong conditions that affect 1 or fewer individuals in 1,000.
- Conditions Recognized as Rare Diseases in India: Approximately 55 conditions, including Gaucher’s disease, Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSDs), and certain muscular dystrophies, are classified as rare diseases.
- National Registry: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) manages the National Registry for Rare and Other Inherited Disorders (NRROID), which has documented 14,472 patients with rare diseases.
Classification of Rare Diseases in India:
- Group 1: Diseases that can be treated with a one-time curative procedure (e.g., certain enzyme replacement therapies).
- Group 2: Conditions requiring long-term or lifelong treatment, which are relatively less expensive and have documented benefits. Regular medical check-ups are necessary for patients.
- Group 3: Diseases for which effective treatments are available, but they are highly costly and require ongoing, lifelong therapy. Selecting beneficiaries for these treatments presents a challenge due to the high costs.
Current Funding Policy in India:
- National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021: Launched to provide financial support for the treatment of rare diseases. Patients receiving treatment at designated Centres of Excellence (CoE) can get financial assistance up to Rs 50 lakh.
- Centres of Excellence: The CoEs include institutions such as AIIMS in Delhi, PGIMER in Chandigarh, and the Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research at Kolkata’s SSKM Hospital.
- Crowdfunding and Voluntary Donations Portal (2022): The Health Ministry launched a digital platform that allows donors to contribute toward the treatment of rare disease patients at CoEs. The portal provides details about patients, their conditions, estimated treatment costs, and bank account information of the CoEs.
Did you know?
|
Challenges Associated with Orphan Drugs:
- Limited Treatment Options: Therapies are available for fewer than 5% of rare diseases, resulting in less than 10% of patients receiving disease-specific treatment.
- High Treatment Costs: Many existing therapies for rare diseases are prohibitively expensive, putting a significant financial burden on patients and their families.
- Regulatory Delays: Approval processes, such as those from the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI), can be slow. For instance, delays in approving US-based Sarepta Therapeutics’ medicines in India have affected the timely availability of treatments.
- Bureaucratic Hurdles: Decision-making delays and administrative red tape further complicate access to necessary drugs, impacting patient care.
- Challenges in Beneficiary Selection: Due to high treatment costs, identifying and prioritizing beneficiaries for financial assistance is difficult, potentially leaving some patients without support.
Way forward:
- Streamline Regulatory Approvals: Expedite the approval process for orphan drugs by reducing bureaucratic hurdles and establishing a fast-track mechanism for essential treatments, ensuring timely access to life-saving medications.
- Increase Financial Support and Expand Coverage: Enhance the funding cap under the National Policy for Rare Diseases and extend financial assistance to more patients, while encouraging public-private partnerships and innovative funding mechanisms like insurance coverage for rare disease treatments.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Rise in life expectancy has slowed dramatically: New study
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Life Expectancy and related challenges,
Why in the News?
After decades of steady increases in human life expectancy due to advancements in medicine and technology, recent trends suggest that these gains are starting to slow down, according to a new study.
The Key Findings of the Study:
- Slowing of Life Expectancy Gains: After decades of rising life expectancy due to medical and technological advancements, the pace of these increases has slowed significantly. The study suggests that human life expectancy has nearly plateaued, with dramatic extensions unlikely without breakthroughs in anti-aging medicine.
- Regional Analysis: The study analyzed life expectancy data between 1990 and 2019 from regions with the longest life spans, such as Australia, Japan, and Sweden.
- Even in these regions, life expectancy increased by only 6.5 years on average over the 29-year period.
- Challenges of Radical Life Extension: Researchers found that while people live longer due to improvements in healthcare, the human body’s aging process—marked by the declining function of internal organs—limits life span. Even if diseases like cancer and heart disease are eliminated, aging itself remains a barrier.
- Low Probability of Reaching 100: The study estimates that girls born in the longest-living regions have only a 5.3% chance of reaching 100 years, while boys have a 1.8% chance. Thus, despite medical advancements, reaching 100 years remains rare without interventions to slow aging.
- Aging as the Primary Barrier: Researchers argue that extending average life expectancy dramatically will require breakthroughs that slow the aging process rather than just better treatments for common diseases.
- Some experimental drugs, like metformin, have shown potential in animal studies, but human trials are needed.
India’s Present Status:
- Lower Life Expectancy: As of 2024, India’s average life expectancy is around 70 years, In contrast, countries like Japan and Switzerland boast life expectancies exceeding 83 years.
- Healthcare Advancements: While India has made significant progress in combating infectious diseases and improving maternal and child health, chronic illnesses and lifestyle diseases (such as heart disease and diabetes) are emerging as leading causes of death.
What Needs to Be Done: (Way forward)
- Focus on Anti-Aging Research: India must invest in research on aging and regenerative medicine, exploring ways to slow down the aging process rather than just treating diseases.
- Strengthening Healthcare Systems: Expanding access to quality healthcare and preventive medicine to manage age-related diseases can enhance the quality of life in later years, even if life expectancy does not rise dramatically.
- Policy Support for Longevity Research: There is a need for policies supporting medical research into life-extension technologies, including drug trials and clinical studies focused on aging.
- Public Health Interventions: Improved public health measures targeting lifestyle diseases (obesity, diabetes) and better management of age-related conditions can enhance life span and overall well-being.
Mains PYQ:
Q The increase in life expectancy in the country has led to newer health challenges in the community. What are those challenges and what steps need to be taken to meet them? (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] WHO declares that India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem in 2024
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trachoma; Its causes and treatment
Why in the News?
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared that India has successfully eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem.
- This makes India the third country in the Southeast Asia Region to achieve this milestone.
|
What is Trachoma?
- Trachoma is a bacterial infection that affects the eyes.
- It is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia Trachomatis.
- It is contagious, spreading through contact with the eyes, eyelids, or secretions from the nose or throat of an infected person.
- If untreated, Trachoma can lead to irreversible blindness.
Trachoma in India: A Historical Perspective
- In the 1950s and 1960s, Trachoma was one of the leading causes of blindness in India.
- To tackle this, India launched the National Trachoma Control Program in 1963.
- Later, these efforts were integrated into India’s National Program for Control of Blindness (NPCB).
- In 1971, the rate of blindness due to trachoma was 5% in the country.
- Due to various interventions under the National Programme for Control of Blindness & Visual Impairment (NPCBVI), the rate has now dropped to less than 1%.
What are the key measures taken to eliminate Trachoma?
- India implemented the WHO SAFE strategy across the country. This strategy includes:
- Surgery
- Antibiotics
- Facial hygiene
- Environmental cleanliness
- Although by 2017, India was declared free from infective Trachoma, it continued surveillance of Trachoma cases from 2019 to 2024.
PYQ:[2018] Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] World Cerebral Palsy Day
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cerebral palsy
Why in the News?
- The World Cerebral Palsy Day was celebrated on October 6 with the theme ‘#UniquelyCP’.
- It celebrates the uniqueness of individuals living with cerebral palsy by emphasizing that they are not defined by their disability.
About Cerebral Palsy:
| Details | |
| Condition | A group of neurological disorders affecting movement, muscle tone, and posture. |
| Cause | Abnormal brain development, usually before birth; can also occur due to injury during birth or early childhood. |
| Types | – Spastic CP: Stiff muscles, difficulty with movement (most common, 70-80% of cases). – Dyskinetic CP: Uncontrolled movements affecting limbs. – Ataxic CP: Poor balance and coordination. – Mixed CP: Combination of symptoms from different types. |
| Symptoms | Motor skill difficulties (crawling, walking); Muscle stiffness or looseness; Poor coordination and balance; Speech or swallowing difficulties; Seizures in some cases. |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, MRI scans, developmental monitoring (usually diagnosed within first 2 years). |
| Risk Factors | Premature birth; Low birth weight; Multiple births; Maternal infections; Lack of oxygen during birth. |
| Treatment | – Physical, occupational, and speech therapies. – Medications to reduce muscle stiffness. – Surgery in severe cases. |
| Life Expectancy | Normal life expectancy in many cases, depending on severity and associated complications. |
| Prevention | Some causes are preventable with proper maternal care, but many are not. |
| Policy Support | Niramaya Health Insurance Scheme:
|
PYQ:[2020] In order to enhance the prospects of social development, sound and adequate health care policies are needed particularly in the fields of geriatric and maternal health care. Discuss. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UNAIDS and its functions
Why in the News?
According to the UNAIDS Director, without India’s significant contribution, the world is unlikely to achieve the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
What is HIV/AIDS?
India’s progress in reducing HIV Infections
|
About UNAIDS (Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS):
| Details | |
| Established | In 1996, by United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) |
| Headquarters | Geneva, Switzerland |
| Main Purpose | To coordinate global action to combat HIV/AIDS, prevent infections, and support those affected |
| Mandate | • Coordinate the global response to HIV/AIDS • Support countries in HIV/AIDS prevention and treatment strategies • Advocate for human rights and equality in access to HIV services |
| Principle | Greater Involvement of People Living with HIV (GIPA), endorsed by the UN in 2001 and 2006 |
| Global Targets | 90-90-90 targets: 90% diagnosed, 90% on treatment, 90% virally suppressed by 2020 |
| Global AIDS Strategy | 2021-2026: Aim to end inequalities driving HIV and ensure 30 million on treatment by 2025 |
| Cosponsors | 11 UN organizations, including UNICEF, WHO, UNDP, UNESCO, World Bank |
| Key Areas of Focus | Supporting countries to meet SDG 3: End AIDS by 2030.
• HIV prevention |
| Funding | Donors include governments, private foundations, and corporations |
| Key Campaigns | World AIDS Day (December 1), global awareness and advocacy efforts |
| Achievements | Significant progress toward the 90-90-90 targets, especially in countries like South Africa, Cambodia, and Eswatini |
PYQ:[2013] Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Preparing for the next pandemic: what NITI Aayog report says
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Management in Pandemic situation;
Why in the News?
Four years after the onset of Covid, an expert group formed by NITI Aayog has proposed the establishment of a comprehensive framework to handle future public health emergencies or pandemics effectively.
Lessons Learned from COVID-19:
- Gaps in Legal Frameworks: Existing laws like the Epidemic Diseases Act (1897) and National Disaster Management Act (2005) were insufficient for handling large-scale health emergencies. These laws lack clarity on definitions of epidemics and provisions for managing public health crises, drug distribution, and quarantine measures.
- Delayed Response and Coordination: The COVID-19 pandemic exposed weaknesses in coordination between central and state governments, highlighting the need for a more organized response mechanism.
- Inadequate Surveillance: Insufficient disease surveillance and early warning systems delayed the identification of threats. The role of zoonotic diseases, especially viruses linked to bat species, underscored the need for better monitoring of human-animal interactions.
What specific recommendations does the NITI Aayog report make?
- Enactment of PHEMA: Introduce the Public Health Emergency Management Act for a more robust legal framework to manage pandemics and other health emergencies.
- Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGoS): Establish a central committee to oversee pandemic preparedness, governance, R&D, surveillance, and response efforts.
- Strengthened Disease Surveillance: Create a national biosecurity and biosafety network and monitor human-animal interfaces, especially for zoonotic diseases.
- Emergency Vaccine Bank: Develop a stockpile of vaccines for rapid access during health crises, sourced domestically or internationally.
- Early Warning and Research Network: Build a forecasting and modelling network, along with Centres of Excellence (CoEs) to advance research on priority pathogens and preparedness.
How can India enhance its pandemic preparedness framework? (Way forward)
- Strengthening Legal and Institutional Frameworks: Enact a Public Health Emergency Management Act (PHEMA) and establish an Empowered Group of Secretaries for coordinated pandemic response.
- Enhancing Surveillance and Early Warning Systems: Build a robust disease surveillance network, biosecurity system, and epidemiology forecasting for early detection and response to outbreaks.
- Investing in Health Infrastructure and Vaccine Stockpiles: Develop public health cadres, boost healthcare infrastructure, and create an emergency vaccine bank for rapid deployment during health crises.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Was animal fat present in Tirupati laddus?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Adulteration issues in India;
Why in the News?
The ghee samples used by ‘Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams’ for ritual offerings and ‘Laddu Prasadam’ were found to contain foreign fats, including fish oil, beef tallow, and lard, as per the NDDB’s analysis report.
What did the ALF of the National Dairy Development Board find in the Tirupati laddus?
- The Centre for Analysis and Learning in Livestock and Food (CALF) of the National Dairy Development Board found that ghee samples supplied to the Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD) for preparing laddus were adulterated with various fats.
- Adulterants detected included:
-
- Plant-based fats: soybean, sunflower oil, rapeseed oil, linseed, wheat germ, maize germ, cotton seed, coconut, and palm kernel fat.
- Animal-based fats: fish oil, beef tallow, and lard (pig fat).
Existing Laws:
Implementation Gaps:
|
Why maintaining a good baseline data (specific to Indian conditions) is necessary?
- Biological Variation in Indian Cows: Baseline data specific to Indian cows is needed for accurate results. Indian cows may have different genetic and biochemical profiles compared to European cows, meaning the existing international standards for detecting adulteration (like the ‘s-values’) may not accurately reflect the composition of Indian cow ghee.
- Adulterants Unique to Local Conditions: The types of adulterants commonly used in India, such as certain vegetable oils or animal fats, may differ from those in other regions. Establishing baseline data for Indian adulterants would improve the precision of detecting the specific types of foreign fats used in India.
- Accurate Interpretation of Results: Without specific data on the composition of Indian cow ghee, it becomes difficult to interpret the results from methods like gas chromatography. Customized baseline data ensures that the detection methods yield accurate and meaningful conclusions in the Indian context.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Enforcement Mechanisms: Increase resources for testing facilities and train personnel to implement FSSAI standards more effectively, ensuring regular checks for sophisticated adulteration.
- Develop India-Specific Testing Protocols: Create testing standards based on baseline data specific to Indian cows and local adulterants to improve accuracy in detecting food adulteration.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)
Why in the News?
Recent research indicates that pigs may act as a transmission vehicle for a strain of the hepatitis E virus (HEV) commonly found in rats, known as Rocahepevirus ratti, or rat HEV.
Role of Pigs in Transmission
|
About Hepatitis E Virus (HEV):
- Hepatitis E is caused by the Hepatitis E Virus (HEV), which is a positive-sense, single-stranded, non-enveloped RNA virus.
- HEV is classified under the family Hepeviridae, genus Orthohepevirus.
- It was first identified during an outbreak among Soviet soldiers in Afghanistan in 1983.
- The earliest well-documented HEV epidemic occurred in New Delhi, India, in 1955, retrospectively identified as HEV.
- Transmission:
-
- The primary route of transmission is fecal-oral, especially through contaminated water and food.
- Zoonotic transmission is possible with genotypes 3 and 4, commonly spread through undercooked meat or direct animal contact.
- Symptoms:
-
- Jaundice, nausea, fatigue, and elevated liver enzymes.
- Severe cases can lead to liver failure, especially in pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals.
- Prevention and Cure:
-
- A vaccine, HEV 239, is approved for use in China, but no vaccine is widely available or approved in most countries, including the United States.
- There is no specific antiviral treatment for acute HEV.
- Prevention relies on improved sanitation, safe drinking water, and proper food handling.
PYQ:[2019] Which one of the following statements is not correct? (a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV. (b) Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine. (c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses are several times more than those infected with HIV. (d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Arogya Sanjeevani Policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Arogya Sanjeevani Policy
Why in the News?
The “Arogya Sanjeevani Policy” serves as a reference point for choosing health insurance for hospitalisation.
About Arogya Sanjeevani Policy:
| Details | |
| Launch Date | April 2020 |
| Issued by | Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) |
| Objective | To provide basic and affordable health insurance coverage to all citizens |
| Sum Insured | ₹1 lakh to ₹5 lakh per policy year |
| Coverage | Hospitalization, pre and post-hospitalization expenses, daycare procedures, AYUSH treatments, COVID-19 coverage |
| Pre-Existing Conditions | Coverage after 4 years of continuous policy renewal |
| Co-Payment | 5% co-payment on all claims |
| Premium | Varies based on age, sum insured, and insurer |
| Waiting Period | 30 days for new policies; 48 months for pre-existing diseases |
| Daycare Procedures | Covers over 50+ daycare treatments |
| Room Rent Limit | Up to 2% of the sum insured per day (maximum ₹5,000 per day) |
| ICU Room Rent | Up to 5% of the sum insured per day (maximum ₹10,000 per day) |
| AYUSH Treatments | Covers Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy treatments |
| Maternity Coverage | Not covered |
| Network Hospitals | Cashless facility in network hospitals |
| Eligibility | Individuals aged 18 to 65 years |
PYQ:[2019] Performance of welfare schemes that are implemented for vulnerable sections is not so effective due to the absence of their awareness and active involvement at all stages of the policy process – Discuss. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Amoebic Meningoencephalitis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM); Naegleria fowleri.
Why in the News?
-
- This year, Kerala faced a sudden surge in Amoebic Meningoencephalitis cases, caused by free-living amoebae (FLA) found in freshwater ponds, lakes, and rivers.
- Kerala also saw a diverse range of amoebic infections, caused by Naegleria fowleri, Vermamoeba vermiforis, and Acanthamoeba.
What is Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)?
- PAM is caused by the Naegleria fowleri, often referred to as the “brain-eating amoeba“. It destroys brain tissue, causing severe swelling and is fatal in most cases.
- An amoeba is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods.
- Higher temperatures of up to 115°F (46°C) are conducive to its growth and it can survive for short periods in warm environments.
- The amoeba enters the body through the nose, typically during activities like swimming, and travels to the brain, causing severe damage.
- PAM is also non-communicable.
- Symptoms: Headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, confusion, seizures, hallucinations, and coma.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), most people with PAM die within 1 to 18 days after symptoms begin. It usually leads to coma and death after 5 days.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Currently, there are no established effective treatments for PAM.
- Diagnosis involves PCR tests of cerebrospinal fluid, though detection can be challenging due to the rarity of PAM.
- Treatment follows CDC guidelines, including miltefosine, Azithromycin, and Amphotericin B, with miltefosine recently procured by the State Health Department from Germany.
- Medical interventions typically involve a combination of drugs, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Cabinet approves ₹5 lakh Health Cover for Senior Citizens
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AB PM-JAY and its beneficiaries
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet has approved health coverage of ₹5 lakh for all senior citizens aged 70 years and above, regardless of their income, under the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY).
About Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)
|
Eligibility Criteria:
- All senior citizens aged 70 and above are eligible for the scheme, receiving a ₹5 lakh health cover on a family basis.
- Additional Benefits:
-
- Senior citizens belonging to families already under AB PM-JAY will get an extra top-up of ₹5 lakh, exclusively for their personal healthcare.
- Those with private health insurance can also avail of the scheme.
- Senior citizens covered under other public health insurance schemes, like CGHS, ECHS, or CAPF, must choose between their current plan and AB PM-JAY.
- All eligible beneficiaries will be issued a distinct health card for easy access to the scheme’s benefits.
PYQ:[2012] With reference to National Rural Health Mission, which of the following are the jobs of Asha, a trained community health worker? 1. Accompanying women to the health facility for antenatal care checkups 2. Using pregnancy test kits for early detection of pregnancy 3. Providing information on nutrition and immunization 4. Conducting the delivery of baby Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 2 and 4 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The grave threat from AMR
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Antimicrobial resistance;
Mains level: Reason behind the AMR Increasing;
Why in the News?
Ahead of the UN General Assembly High-Level Meeting on antimicrobial resistance, WHO published its first-ever guidance on Antibiotic pollution from manufacturing.
Common Pathogens Found in IndiaThe three most common pathogens associated with antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in India, as reported by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), are:
|
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and Why is it a Cause for Concern?
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when pathogens evolve to survive despite the presence of antimicrobial drugs, rendering standard treatments ineffective. This situation arises mainly due to the misuse and overuse of antibiotics, leading to the development of resistant strains or “superbugs.”
- According to the WHO, emergence and spread of AMR could significantly undermine the effectiveness of antibiotics globally, impacting healthcare outcomes, especially for patients with multiple diseases.
Why is AMR Increasing?
Several factors contribute to the increasing rates of AMR in India:
- Self-medication: Many individuals self-prescribe antibiotics for conditions like fever without proper medical consultation, often for viral infections where antibiotics are ineffective.
- Prescribing habits: A significant percentage of antibiotics are prescribed not for treating infections but for prevention. Doctors often resort to broad-spectrum antibiotics without conducting necessary diagnostic tests, leading to inappropriate usage.
- Lack of regulation: The management of pharmaceutical waste from antibiotic manufacturing is largely unregulated, contributing to environmental pollution and the spread of resistant bacteria.
What needs to be done?
- Prevention of Infections: Implementing better hygiene practices, improving sanitation, and promoting vaccinations can help reduce the incidence of infections, thereby decreasing the reliance on antibiotics.
- Education for Healthcare Providers: Train doctors to prescribe antibiotics judiciously, reserve stronger antibiotics for hospital patients, and emphasise the importance of diagnostic testing, which can help ensure appropriate antibiotic use.
- Regulatory Improvements: Strengthening regulations around antibiotic manufacturing and waste management is crucial for controlling antibiotic pollution and preventing the emergence of resistant strains.
Mains PYQ:
Q Can overuse and free availability of antibiotics without Doctor’s prescription, be contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved. (UPSC IAS/2016)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Policy paralysis, a weakened public health sector
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Issues in the health sector
Why in the News?
Primary care remains underdeveloped, while the private sector has seen significant growth in secondary and tertiary care.
What are the major necessities in Public Health?
- Diseases of Poverty: This includes health issues predominantly affecting the poor and vulnerable populations, such as tuberculosis, malaria, undernutrition, maternal mortality, and illnesses caused by food and water-borne infections like typhoid and diarrheal diseases.
- Addressing these needs is critical not only from a health perspective but also as a matter of human rights.
- Middle-Class Health Concerns: The second category focuses on health issues related to environmental pollution, including air and water quality, waste management, and food safety.
- These issues are often exacerbated by inadequate infrastructure and poor market regulations, leading to chronic illnesses and road traffic accidents.
- Curative Care Needs: The most visible public health needs are those related to curative care, which is divided into three levels: primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
- The poor often rely on public primary health care for affordable services, while secondary care remains historically neglected.
- Tertiary care is primarily addressed through government schemes like the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) under Ayushman Bharat, aimed at providing coverage for serious health issues.
How do the private hospitals become a real beneficiary in present times?
- Limited Coverage: India’s health insurance primarily covers only hospitalisation expenses, leaving out outpatient and primary care services. This benefits private hospitals as they can monopolise high-cost medical treatments, while the larger uninsured population faces commercialised care at market rates.
- Weakening of Public Health Sector: The government’s shift in focus from strengthening public sector health care to outsourcing via insurance schemes like PMJAY indicates a failure to build adequate secondary and tertiary public health services.
Threats to Public Healthcare:
- Neglect of Secondary and Tertiary Care: The inadequate investment in strengthening secondary- and tertiary-level health care in the public sector, leads to a reliance on private hospitals.
- Transformation of Primary Health Centres (PHCs) and Sub-centres: The conversion of sub-centres and PHCs into Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) has undermined their original role in preventive and promotive health care.
- Loss of Trust in Public Healthcare: Due to overcrowding, poor infrastructure, and inadequate funding, public health institutions are losing credibility. Coupled with the commercial interests of private providers, this creates a dual crisis of access and quality in the healthcare system.
- Rebranding of Health Centres: The recent renaming of HWCs as “Ayushman Arogya Mandirs” raises concerns about cultural relevance and secularism in public health institutions, especially for non-Hindi-speaking populations, further undermining trust in the system.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Public Healthcare Infrastructure: Invest in enhancing secondary and tertiary care facilities in the public sector to reduce dependence on private hospitals.
- Integrate Health Insurance and Primary Care: Expand health insurance coverage to include outpatient and primary care services, and ensure that public health centers retain their focus on preventive and promotive care.
Mains PYQ:
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Crime, health-worker safety, and a self-examination
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Issues in the healthcare sector;
Why in the News?
- The recent brutal rape and murder case in Kolkata has sparked widespread calls for the death penalty for the accused.
- The Justice J.S. Verma Committee, formed in response to the 2012 Delhi gang rape, recommended against the death penalty for rape, even in the rarest of rare cases, arguing that it would be a regressive step.
Deeper problem in the Health Care Sector:
What does the Justice K. Hema Committee report say on the Culture of Assault?
|
Need to Rethink Violence in Healthcare:
- Understanding the Multi-faceted Nature of Violence: Violence in healthcare settings is not limited to patient assaults on healthcare workers, it also includes institutional and managerial violence. This encompasses horizontal violence among healthcare providers and the systemic issues that create a hostile work environment.
- Implementing Comprehensive Safety Measures: While immediate responses such as improving security and legal protections are necessary, they must be part of a broader strategy that includes training healthcare workers on conflict resolution, mental health support, and creating a culture of safety within healthcare institutions.
About Justice J.S. Verma Committee Recommendations
Recommendations on |
Explanation |
| Rape | • It recognized rape as a Crime of Power, not just passion. • Expand definition to include all forms of non-consensual penetration. • Remove marital rape exception; marriage should not imply automatic consent. (European Commission of Human Rights in C.R. vs U.K) |
| Sexual Assault | • Broaden definition to include all non-consensual, non-penetrative sexual acts. • Penalty: Up to 5 years of imprisonment or fines. |
| Verbal Sexual Assault | • Criminalize unwelcome sexual threats. • Punishable by up to 1 year in prison or fines. |
| Sexual Harassment at Workplace | • Include domestic workers under protections. • Replace internal complaint committees with Employment Tribunals. • Employers to compensate victims of sexual harassment. |
| Acid Attacks | • Propose a 10-year minimum punishment, separate from grievous hurt. • Establish a compensation fund for victims. |
| Women in Conflict Areas | • Review AFSPA; exclude government sanction for prosecuting sexual offenses by armed forces. • Appoint special commissioners to monitor offenses. |
| Trafficking | • Comprehensive anti-trafficking laws beyond prostitution. • Protective homes for women and juveniles overseen by High Courts. |
| Child Sexual Abuse | • Define ‘harm’ and ‘health’ in the Juvenile Justice Act to include both physical and mental aspects. |
| Death Penalty | • Opposed chemical castration and death penalty for rape. • Recommend life imprisonment. |
| Medical Examination of Rape Victims | • Ban the two-finger test; victim’s past sexual history should not influence the case. |
| Reforms in Case Management | • Set up Rape Crisis Cells, increase police accountability, allow online FIR filing. • Encourage community policing and increase police personnel. |
Need for a Comprehensive Approach:
- National Task Force: Improving hospital security and infrastructure alone may not be sufficient to address the problem. The national task force constituted by the Supreme Court should devise a comprehensive road map to prevent and arrest medical corruption, particularly in the public sector.
- Need Expertise: The task force should include experts from public health, medico-legal, and other allied fields, along with the participation of the larger governing and administrative community.
Note: Recently some states have taken steps to empower women. For example, the Himachal Pradesh Assembly passed a Bill on Tuesday to increase the minimum marriage age for women from 18 to 21 years.
Mains PYQ:
Q Appropriate local community level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (UPSC CSE 2018)
Q We are witnessing increasing instances of sexual violence against women in the country. Despite existing legal provisions against it, the number of such incidences is on the rise. Suggest some innovative measures to tackle this menace. (UPSC CSE 2014)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
WHO investigating new Polio strain in Meghalaya
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Polio and its eradication
Why in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) is investigating a suspected new strain of polio in a two-year-old child from Tikrikilla, Meghalaya.
What is Vaccine-Derived Polio?
|
About Polio:
| Details | |
| Nature of Disease | Crippling and potentially deadly viral infectious disease affecting the nervous system. |
| Types of Poliovirus | – WPV1 (Wild Poliovirus type 1) – WPV2 (Wild Poliovirus type 2, eradicated globally) – WPV3 (Wild Poliovirus type 3, eradicated globally) |
| Current Status | WPV1 remains in circulation in Afghanistan and Pakistan. |
| Transmission | Primarily through the faecal-oral route or contaminated water/food. |
| Affected Population | Largely affects children under 5 years of age. |
| Impact | Virus multiplies in the intestine, may invade the nervous system, causing paralysis. |
| Prevention | – No Cure: Preventable through immunization. – Vaccines: – OPV: Oral Polio Vaccine given at birth, with doses at 6, 10, 14 weeks, and a booster at 16-24 months. – IPV: Injectable Polio Vaccine given with the 3rd dose of DPT under UIP. |
| India’s Status |
|
PYQ:[2016] ‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to: (a) immunization of children and pregnant women (b) construction of smart cities across the country (c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space (d) New Educational Policy |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Do doctors need a Central protection Act?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Need for Central protection law for healthcare workers;
Why in the News?
Resident doctors across India are on strike, demanding safety laws after a young doctor was tragically raped and murdered at R.G. Kar Medical College in Kolkata on August 9.
Why are Healthcare Workers Protesting?
- Response to Violence: The protests were triggered by the brutal rape and murder of a young doctor at R.G. Kar Medical College and Hospital in Kolkata on August 9, 2024.
- Demand for Safety: Healthcare workers are demanding laws and measures that ensure their safety while on duty.
- Historical Context: Violence against healthcare workers is not a new issue in India. Previous incidents, such as the case of Aruna Shanbaug, a nurse who was sexually assaulted in 1973, underscore a long-standing pattern of violence in healthcare settings.
Working Conditions of Junior Doctors, Interns, and Nurses
- Poor Working Environment: Junior doctors, interns, and nurses often work in ill-lit and poorly secured hospital environments.
- Long Shifts and Exhaustion: Many healthcare workers, including the victim of the recent incident, are subjected to excessively long shifts—in this case, a 36-hour duty shift—without adequate rest or safe spaces to recuperate.
- Mental Health Concerns: The stressful working conditions, combined with the threat of violence, have raised significant concerns about the mental health and well-being of healthcare workers.
Key Demands of the Protesters
- Central Protection Act: The Indian Medical Association (IMA) is advocating for a Central protection law specifically for healthcare workers, similar to measures in other countries that classify assaults on medical staff as serious offenses.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Protesters are calling for hospital security protocols that match those of airports, including the installation of CCTV cameras, deployment of security personnel, and improved lighting in hospital corridors and wards.
- Safe Work Environment: There is a demand for immediate systemic reforms to improve working conditions, including better security arrangements and the establishment of healthcare facilities as safe zones.
- Accountability and Justice: The IMA has requested a thorough investigation into incidents of violence against healthcare workers, with a focus on timely and professional handling of cases and ensuring that perpetrators face exemplary punishment.
- Government Response: Following the protests, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare issued an order mandating that any violence against healthcare workers must be reported and acted upon swiftly, with institutional FIRs to be filed within six hours of an incident.
Sole responsible for the safety of Health workers:
|
Way forward:
- Implement a Central Protection Law for Healthcare Workers: The government should fast-track the enactment of a Central law specifically designed to protect healthcare workers from violence.
- Improve Working Conditions and Mental Health Support: Hospitals should prioritize creating safe and well-secured environments for healthcare workers, including reasonable shift hours, adequate rest periods, mental health support, and robust security protocols to prevent future incidents of violence.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Freedom from dependence, a new era in health care
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Challenges in the Indian healthcare system;
Why in the News?
India’s healthcare since globalization has improved greatly, and is globally recognized due to skilled professionals, effective policies, and strong institutions which draw patients from over 147 countries.
Economic implications of being a preferred Medical Destination:
- Foreign Exchange Savings: India saves billions in foreign exchange as fewer Indians need to travel abroad for advanced medical treatments.
- Revenue Generation: The influx of international patients generates over $9 billion annually, contributing to economic growth.
- Job Creation: The medical tourism sector creates employment opportunities in healthcare, hospitality, transportation, and pharmaceuticals.
- Cost-Effective Treatments: India’s affordable yet high-quality medical services attract patients globally, further boosting the economy.
What are the challenges?
- Shortage of Healthcare Professionals
-
-
- Current Shortage: India is estimated to be short of around 600,000 doctors, leading to a doctor-patient ratio of approximately 0.7 doctors per 1,000 people, which is significantly lower than the World Health Organization’s recommended ratio of 1 doctor per 1,000 people.
- Future Demand: By 2030, the demand for healthcare professionals in India is expected to double, driven by an ageing population and the increasing burden of non-communicable diseases.
-
- Inadequate Public Healthcare Spending
-
-
- Low Expenditure: As of 2021-22, India’s public healthcare expenditure stood at 2.1% of GDP, which is significantly lower than that of many developed countries, For instance, countries like Japan and France spend about 10% of their GDP on healthcare, while the United States spends 16.9%.
- Comparison with Neighbors: Even neighbouring countries like Bangladesh and Pakistan allocate over 3% of their GDP to public healthcare.
-
- Unequal Access to Healthcare
-
-
- Urban-Rural Disparity: There is a stark disparity in healthcare access between urban and rural areas. Rural regions often lack basic healthcare facilities, leading to limited access to quality services for a significant portion of the population.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: India’s healthcare infrastructure is inadequate to meet the growing demands of its population. For instance, India has one of the lowest per capita bed counts in the world, with only about 0.5 hospital beds per 1,000 people, compared to the OECD average of 4.7 beds per 1,000 people.
-
- High Out-of-Pocket Expenditure
-
- Financial Burden: Approximately 75% of healthcare expenditure in India is borne out-of-pocket by individuals and families.
Need for a Strong Vision (Way forward)
- “Heal in India” Initiative: The Prime Minister’s vision of “Heal in India” emphasizes positioning India as a global healthcare leader. This initiative is not merely a slogan but a strategic approach to enhance India’s reputation as a preferred medical destination.
- Youth Engagement: Inspiring the youth to pursue careers in healthcare is crucial for sustaining growth in this sector. By encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship among young Indians, the country can ensure a robust healthcare system.
- Investment in Public Healthcare: Increase public healthcare spending to improve infrastructure, especially in rural areas, and bridge the urban-rural disparity.
- Focus on Medical Device Manufacturing: Promote domestic production of medical devices under the “Make in India” initiative to reduce dependency on imports.
Mains PYQ:
Q Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
WHO declares Mpox as Public Health Emergency of International Concern
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PHEIC, Mpox
Why in the news?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared mpox as a “public health emergency of international concern” (PHEIC).
What is a PHEIC?
|
What is Mpox?
- Mpox is a disease caused by the orthopoxvirus, related to the smallpox virus.
- First detected in humans in 1970, it is endemic in central and West Africa.
- Transmission: Spread from animals to humans (zoonotic) and between humans via close contact, respiratory droplets, or contaminated materials.
- Symptoms: Fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes; can lead to severe complications or death.
- Vaccination: WHO recommends vaccines, widely used in Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) to control outbreaks.
Recent Developments:
|
PYQ:[2014] Consider the following diseases 1. Diphtheria 2. Chickenpox 3. Smallpox Which of the above diseases has/have been eradicated in India? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1, 2 and 3 (d) None |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Hidden dangers of irrational use of antibiotics on microbiome
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Antibiotics resistance;
Mains level: Concerning aspects of Antibiotic use;
Why in the news?
While vital for treating infections, antibiotics can disrupt the microbiome by indiscriminately killing both harmful pathogens and beneficial gut bacteria, especially broad-spectrum types.
Various roles played by Antibiotics (Applications):
Treatment of Infections |
Antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, significantly reducing mortality rates associated with infectious diseases |
For example, penicillin and other antibiotics, the mortality rate from strep throat dropped dramatically from 1% to less than 0.1%. |
Preventing Disease Spread |
Treating bacterial infections, antibiotics can prevent the spread of disease to other individuals |
For instance, during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic, antibiotics were used to treat secondary bacterial pneumonia, which was a major cause of death. |
Reducing Complications |
Antibiotics can reduce the risk of serious complications from bacterial infections. |
For instance, In the case of urinary tract infections (UTIs), untreated infections can lead to kidney damage or life-threatening conditions like sepsis. However, with prompt antibiotic treatment, the risk of complications is greatly reduced |
Supporting Medical Procedures |
Antibiotics are used prophylactically to prevent infections before certain medical procedures |
For example in surgery |
Concerning Aspects of Antibiotic Use
- Dysbiosis: The disruption of the microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can lead to severe health issues, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Increased Infection Risk: Antibiotics can reduce colonization resistance, which is the microbiome’s ability to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from establishing infections. This reduction increases the risk of infections by harmful bacteria, such as Clostridioides difficile.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Overuse of antibiotics contributes to the development of antimicrobial resistance, making it more challenging to treat infections. The global crisis of antibiotic resistance is exacerbated by the enrichment of antibiotic resistance genes within the gut microbiota due to antibiotic exposure.
- Long-term Health Consequences: Repeated antibiotic use can prevent full recovery of the microbiome, leading to chronic health issues. Research shows that children who receive multiple courses of antibiotics are at higher risk for developing conditions like IBD later in life.
- Impact on Other Organ Systems: Dysbiosis can affect various organ systems through gut-organ axes, influencing conditions such as mental health disorders (via the gut-brain axis), liver diseases (via the gut-liver axis), and skin conditions (via the gut-skin axis) due to altered immune responses and increased permeability.
Government initiatives:
|
Way forward:
- Antibiotic Stewardship Programs: Implement and promote antibiotic stewardship programs in healthcare settings to ensure antibiotics are prescribed only when necessary and with the appropriate dosage and duration.
- Probiotic Supplementation: Encourage the use of probiotics alongside antibiotic treatments to help maintain a healthy microbiome and mitigate the risks of dysbiosis and related health issues.
Mains PYQ:
Q Can overuse and free availability of antibiotics without Doctor’s prescription, be contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved. (2014)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Why Silica Dust could become the ‘New Asbestos’ Health Risk?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Silicosis and its health implications
Why in the News?
UK researchers suggest stricter daily silica dust exposure limits in industries could save 13,000 lives as per British Medical Journal Thorax.
What is Silicosis?
- Silicosis is a lung disease that results in the hardening of the lungs. It is caused by inhaling silica dust or crystals, commonly found in soil, sand, concrete, mortar, granite, and artificial stone.
- Silicosis is a chronic disease that develops slowly, often after 10 to 20 years of exposure.
- Silicosis can lead to other severe conditions, including lung cancer, tuberculosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
| Note: Silicosis is a recognized disease under the Mines Act (1952) and the Factories Act (1948). |
Causes of Silicosis:
- Workers in industries such as construction, mining, oil and gas extraction, kitchen engineering, dentistry, pottery, and sculpting are at high risk.
- The cutting, drilling, or breaking down of materials containing silica releases fine dust into the air.
As per National Programme on Elimination of Silicosis in India
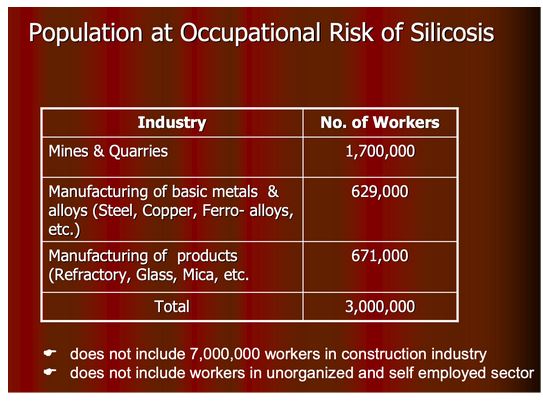
Remedies for Silicosis:
Currently, there is no cure for silicosis, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Preventive measures:
- Water Suppression Techniques: Using water or foam to suppress dust at the source.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensuring adequate airflow in work environments to reduce dust accumulation.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Providing workers with masks and respirators that filter out fine particles.
- Regular Monitoring: Implementing regular health checks for workers and monitoring air quality in workplaces.
Case study related to reducing Silica Dust Exposure
|
PYQ:[2019] Why is there a great concern about the ‘microbeads’ that are released into environment? (a) They are considered harmful to marine ecosystems. (b) They are considered to cause skin cancer in children. (c) They are small enough to be absorbed by crop plants in irrigated fields. (d) They are often found to be used as food adulterants. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Trichophyton indotineae: A drug resistant fungal infections
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trichophyton indotineae
Why in the News?
The increase in drug-resistant fungal infections, especially Trichophyton indotineae, is becoming a major health problem in India.
What Is Trichophyton Indotineae?
- Trichophyton indotineae is a dermatophyte commonly known as ringworm or jock itch.
- First identified in India, this fungus has now spread to several countries worldwide.
- It belongs to genotype VIII within the T. mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale species complex, found in regions including Australia and Oman.
Factors causing its spread
- Patients often present with persistent, treatment-resistant rashes that can be mistaken for eczema or other skin conditions.
- Misdiagnosis leads to the use of ineffective treatments, prolonging patient suffering and allowing the infection to worsen.
- Trichophyton indotineae has shown resistance to terbinafine due to genetic mutations, with growing resistance to itraconazole also a concern.
- The unregulated sale of steroid-containing combination creams further complicates treatment efforts.
Treatments available
- Alternative to terbinafine and Itraconazole are available but often come with significant side effects, requiring close monitoring by healthcare providers.
- Integrating comprehensive skin care regimens can enhance treatment efficacy, including maintaining skin hydration and using barrier creams.
PYQ:[2014] Lichens, which are capable of initiating ecological succession even on a bare rock, are actually a symbiotic association of: (a) algae and bacteria (b) algae and fungi (c) bacteria and fungi (d) fungi and mosses |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A Budget that places health on the margins
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About PMJAY
Mains level: Challenges to the Inclusivity of PMJAY
Why in the news?
- With the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic behind us (though the World Health Organization warns the virus still lingers), the Union Budget shifted focus to economic growth levers like infrastructure and employment.
- It was also hoped that recognizing population health as crucial for economic growth would lead to continued investment in strengthening health systems.
| A budget estimate refers to the initial allocation of funds designated for various programs, departments, or projects within a fiscal year. It represents the government’s expectations regarding how much money will be required to meet planned expenditures.
In contrast, revised estimates come into play later in the fiscal year. After assessing the actual expenditures and needs after the first six months, the government may adjust the initial budget estimates based on how much of the allocated funds have been utilised and what additional resources may be necessary. |
Comparisons with Previous Years
- Budgetary Estimates: The comparison of the Budget Estimates (BE) for health between 2023-24 and 2025-25, reveals minimal increases:
- Overall Health Ministry Budget: 1.98% increase
- National Health Mission (NHM): 1.16% increase
- PMJAY: 1.4% increase
- Overall Health Ministry budget: The present allocation made in the current Budget is deemed to be inadequate for expanding health coverage services and enhancing the impact of flagship health programs, particularly in light of rising non-communicable diseases and the goal of universal health coverage by 2030.
- Misleading Comparisons: When we compare the Budget estimates with the previous Revised estimates (RE) the budgetary increase of nearly 12% is misleading, as the RE reflects actual spending rather than the program’s needs.
Missed Opportunities
- Health Workforce Development: While the budget mentioned an increase in new medical colleges, it failed to address the critical need for a multi-layered, multi-skilled health workforce.
- Drug Pricing Mechanisms: Although customs duties were waived on three anti-cancer drugs. However, the budget missed the chance to implement price controls and pooled procurement strategies that could have lowered drug costs across both public and private healthcare sectors. Establishing such mechanisms could enhance the affordability and accessibility of essential medications.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: While the budget committed to climate-resilient agriculture, which is crucial for food security, it did not sufficiently link these efforts to health outcomes, such as nutrition and public health, which are critical in the context of rising health challenges.
Challenges to the Inclusivity of PMJAY
|
Way forward:
- Targeted Funding for Flagship Programs: Need to allocate a more substantial increase in the budget for the National Health Mission (NHM) and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) to the eradication of non-communicable diseases, tuberculosis elimination by 2025.
- Strengthen Primary Healthcare: Govt. should ensure adequate funding for primary healthcare services, which form the foundation for preventive and community health initiatives.
Mains PYQ:
Q The public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that the private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Why are dengue cases on the rise worldwide?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: How dengue spread?
Mains level: Are urbanisation and climate change fuelling dengue spread in the world?
Why in the news?
In recent weeks, there has been an increase in dengue cases, notably in Karnataka, with rising numbers also observed in Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
What is the global situation of dengue?
|
Are urbanisation and climate change fuelling dengue spread in the world?
Urbanization:
- Increased Population Density: Urban areas provide optimal conditions for the Aedes aegypti mosquito due to the availability of breeding sites like stagnant water in containers, tires, and other urban infrastructure.
- Expansion of Cities: Rapid urbanization leads to unplanned growth, inadequate waste management, and inadequate water supply, creating breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Human Movement: Urbanization facilitates increased human mobility, enabling the spread of the dengue virus through infected individuals travelling between urban centers.
Climate Change:
- Temperature and Rainfall Patterns: Warmer temperatures and altered rainfall patterns associated with climate change create favourable conditions for mosquito breeding and survival.
- Shifts in Geographic Distribution: Changing climate allows Aedes mosquitoes to expand their range to new regions previously unaffected by dengue, including temperate climates.
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events like hurricanes and floods provide breeding opportunities for mosquitoes and facilitate virus transmission.
Impact:
- Health Impact: India accounts for an estimated 33 million clinically apparent dengue cases each year, contributing to a third of the global dengue burden
- Economic Impact: A cost analysis study in southern India estimated the direct medical costs per hospitalized dengue patient at around ₹20,000 in 2017-18, with costs soaring to over ₹61,000 for complications requiring intensive care.
- Impact on Individuals: Dengue can cause a wide spectrum of illness, from mild flu-like symptoms to severe complications like internal bleeding, organ impairment, and potentially death if not treated promptly.
Way forward:
- Enhance Urban Infrastructure: Improve urban planning to include effective waste management, regular clearing of stagnant water sources, and sustainable water supply systems to reduce mosquito breeding grounds.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch comprehensive public awareness campaigns focusing on urban populations to promote community involvement in mosquito control measures and encourage responsible waste disposal practices.
Mains PYQ:
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Breaking the taboo around men’s reproductive health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: World Health Organization (WHO)
Mains level: Data related to infertility and What are the actual causes of infertility?
Why in the news?
Following World Population Day (July 11), amidst discussions on global population dynamics, it is essential to highlight a topic often overlooked in conversations about reproductive health: male infertility.
World Health Organization (WHO) Global Perspective on infertility:
- Prevalence: WHO estimates that 60 million to 80 million couples worldwide experience infertility.
- Male vs. Female Infertility: Globally, male infertility accounts for approximately 50% of all infertility cases.
Issues Specific to India:
- Data Deficiency: Unlike global estimates, specific prevalence data for infertility in India are outdated (from ICMR guidelines in 2005) and not comprehensive.
- Male Infertility: In India, male infertility constitutes a significant portion of all infertility cases, estimated to be around 50%, mirroring global trends.
- Contributing Factors: Unique challenges in India include environmental pollution, pesticide exposure in agriculture, lifestyle changes including late marriages and stress, which contribute to rising infertility rates.
- Access to Treatment: Disparities in access to advanced infertility treatments exist, with urban areas having better access compared to rural regions.
- Cultural and Social Stigma: Infertility remains stigmatized in Indian society, affecting mental health and social well-being of affected couples, and hindering open discussions and seeking timely medical help.
What are the actual causes of infertility?
- Male Factors: Low sperm count (oligospermia) or poor sperm motility (asthenozoospermia). Anatomical issues such as blocked sperm ducts or varicocele. Hormonal imbalances, genetic factors, and environmental influences like exposure to toxins.
- Female Factors: Ovulation disorders, including hormonal imbalances like PCOS. Structural issues like blocked fallopian tubes or uterine abnormalities. Endometriosis, is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
- Shared Factors: Age-related decline in fertility. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity. Medical conditions like cancer and its treatments, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications affecting fertility.
Treatment options
- Semen Analysis: Essential for diagnosing male infertility, conducted after a period of sexual abstinence.
- Medical Consultation: Vital to identify underlying causes, whether physical (e.g., blocked sperm flow, anatomical issues) or genetic.
- Corrective Surgeries: Address issues like blocked sperm ducts, undescended testicles, or anatomical abnormalities affecting sperm production and flow.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): Effective for cases of severe male infertility where sperm count is extremely low.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Suitable when sperm motility is good but count is low, facilitating fertilization within the uterus.
- In vitro Fertilisation (IVF): Used when both sperm count and motility are low, involving fertilization outside the body before implantation.
- Donor Sperm Insemination or Adoption: Options for couples where male infertility is irreparable, providing alternative paths to parenthood.
Way forward:
- Enhanced Data Collection and Research: Update and expand prevalence data on infertility in India through national surveys and research initiatives. This should include both urban and rural populations to understand regional disparities.
- Public Awareness and Support Programs: Launch nationwide campaigns to raise awareness about infertility as a medical condition, debunk myths, and reduce stigma.
Mains PYQ:
Q In order to enhance the prospects of social development, sound and adequate health care policies are needed particularly in the fields of geriatric and maternal health care. Discuss. (UPSC IAS/2020)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Indigenous HPV vaccine, the rhetoric and the reality
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About human papilloma virus (HPV)
Mains level: Present trends of cervical cancer prevalence in India and the Globe
Why in the news?
Recent discourse suggests HPV vaccination prevents cervical cancer, but evidence linking HPV to cancer is inconclusive and most infected individuals don’t develop cancer, raising doubts about vaccine necessity.
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the cells lining the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is usually a slow-growing cancer that may not have symptoms in its early stages.
Present trends of cervical cancer prevalence in India and the Globe
|
Recent debate – How does vaccination against HPV prevent cervical cancer and consequent death?
- Efficacy Against HPV Infection and Cervical Cancer: HPV vaccines target high-risk HPV types, notably types 16 and 18, which are responsible for a significant proportion of cervical cancer cases worldwide.
- Clinical trials and real-world data consistently demonstrate the effectiveness of HPV vaccines in reducing HPV infection rates and preventing cervical cancer.
- Public Health Impact and Benefits: Countries with high HPV vaccination coverage have observed significant declines in HPV infection rates and cervical cancer incidence among vaccinated populations.
- Vaccination programs aim to achieve herd immunity, thereby reducing overall transmission of HPV and protecting unvaccinated individuals.
- Debate and Challenges: Debate surrounds the universal versus selective vaccination strategies, with considerations on cost-effectiveness, accessibility, and cultural acceptance.
- Challenges include vaccine hesitancy, particularly in some regions, as well as affordability and logistical barriers to widespread vaccination coverage.
Challenges Prevalent in Vaccine Manufacturing
- Complex Manufacturing Processes: Vaccine manufacturing involves complex biological processes and stringent quality control measures.
- Developing and scaling up production requires specialized facilities and skilled personnel, which can be costly and time-consuming to establish.
- High Regulatory Standards: Vaccines are subject to rigorous regulatory scrutiny to ensure safety, efficacy, and consistency.
- Meeting regulatory requirements in multiple jurisdictions adds complexity and may delay the approval and market entry of new vaccines.
- Supply Chain and Distribution: Maintaining a reliable supply chain for vaccine components and ensuring cold chain storage and distribution are critical challenges.
- This becomes even more pronounced in resource-constrained settings or during global health emergencies where demand surges.
Its Impact on India
- Delayed Access to Affordable Vaccines: India’s capability to produce vaccines at scale is hindered by stringent patent laws and complex regulatory requirements.
- This delays the availability of affordable vaccines domestically, impacting public health initiatives and access for vulnerable populations.
- Economic and Health Implications: High costs associated with vaccine development and production limit affordability and accessibility, exacerbating healthcare inequalities.
- This affects India’s ability to address preventable diseases effectively, impacting public health outcomes and economic productivity.
Unavailability of Competing Vaccines and Future Scope
- Lack of Market Competition: Despite the expiration of earlier patents, there is a notable absence of competing HPV vaccines from domestic manufacturers in India.
- This limits options for consumers and healthcare providers, potentially leading to higher prices and reduced accessibility, particularly in the private market.
- Potential for Future Development: Several Indian biotech companies had announced plans to develop HPV vaccines, indicating a future scope for competition and potentially lower prices.
- However, these initiatives have not materialized into market-ready products, highlighting challenges in vaccine development and commercialization in India’s regulatory and economic environment.
Way forward:
- Promote Research and Development Incentives: Encourage and support Indian biotech companies through research grants, tax incentives, and streamlined regulatory pathways for HPV vaccine development.
- Enhance Public-Private Partnerships: Foster collaborations between government entities, academic institutions, and private-sector vaccine manufacturers to improve vaccine accessibility and affordability.
Mains PYQ:
Q What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Scientists find proof that Pain-Sensing Cells are either Male or Female
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nociceptors, Sexual dimorphism in pain perception
Why in the News?
Recent research has uncovered significant differences in how male and female nociceptors (pain receptors) are activated, paving the way for more precise, sex-specific pain management therapies.
About Pain and Differences in Perception:
- The International Association for the Study of Pain defines it as “an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage.”
- Subjectivity: Pain perception is highly personal and varies among individuals.
- Scientific Findings: Recent research by the University of Arizona Health Sciences demonstrated functional sexual dimorphism in nociceptors, the nerve cells responsible for perceiving pain
Why do we perceive Pain?
- Role of Nociceptors: Nociceptors are nerve cells with bare endings found throughout the body. They detect extreme pressure, temperature, and chemical signals, converting them into electrical signals sent to the brain via the spinal cord.
- Activation Mechanism: Nociceptors in both men and women produce similar pain perceptions but are activated differently.
- Normally, they respond to high-intensity stimuli, but their activation threshold can decrease under certain conditions, causing low-intensity stimuli to trigger pain.
Nociceptor Response Threshold
- Gender Differences: Females generally have a lower nociceptor response threshold than males.
- Peripheral Nociceptor Sensitisation: External factors can lower the pain threshold, causing nociceptors to react to stimuli they would normally ignore.
The Old Vs New Study
- Previous research showed that the hormone prolactin increases pain responses in female rodents, while the neurotransmitter orexin B sensitized male rodents to pain.
- According to the New study, the Prolactin hormone increased nociceptor activation in female mice, while orexin-B had a similar effect in male mice. These findings were consistent across monkeys and humans.
- Nociceptors in males and females can be differentially sensitized, leading to varying pain thresholds.
Significance of this Pain Research
- Sex-Specific Pain Treatment: Current pain management often overlooks the patient’s sex, despite differences in pain conditions between men and women.
- Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome, migraines, and painful bladder syndrome are more common in women, while cluster headaches and gout are more frequent in men.
| PYQ:
[2021] What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Hepatitis A vaccination will be cost-effective in Kerala: study
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About Hepatitis A, B, C ;
Mains level: Diseases and their successful case studies in Federal states;
Why in the News?
- Hepatitis A infection in Kerala is shifting from early childhood to adolescents and young adults due to better sanitation and hygiene practices.
- The inclusion of hepatitis A vaccination into the mainstream immunization program for both one-year-old children and 15-year-old individuals in Kerala shows cost-effectiveness and success.
Present State in Kerala and Overall India:
|
About Hepatitis A infection:
- The infection is usually mild or asymptomatic in children under six years but can be symptomatic and severe in older children, adolescents, and adults, occasionally leading to liver injury and fatalities.
- India has recently launched its first indigenously developed hepatitis A vaccine, called Havisure:
- Havisure was launched in January 2024 by Indian Immunologicals Limited (IIL), a subsidiary of the National Dairy Development Board.
- IIL plans to manufacture up to 1 million doses of Havisure per year initially, focusing on the domestic market first.
| Types of Hepatitis | Cause | Vaccine |
| Hepatitis A (HAV) | Spread through ingestion of contaminated food or water. | Hepatitis A vaccine (e.g., Havrix, Vaqta) |
| Hepatitis B (HBV) | Spread through contact with infectious body fluids (blood, semen, etc.) | Hepatitis B vaccine (e.g., Engerix-B, Recombivax HB) |
| Hepatitis C (HCV) | Spread primarily through blood-to-blood contact, often via injection drug use or unsafe medical procedures. | No vaccine is available currently. Treatment focuses on antiviral medications |
| Hepatitis D (HDV) | Requires HBV as a co-infection to cause illness. | No specific vaccine for HDV. Prevention relies on hepatitis B vaccination. |
| Hepatitis E (HEV) | Spread through ingestion of contaminated water, similar to HAV | A vaccine is available in some regions (e.g., Hecolin in China), but not widely used. Prevention mainly involves improving sanitation and safe drinking water |
Benefits of Hepatitis A Vaccination in Kerala:
- Lifelong Immunity: Vaccination provides lifelong immunity against the hepatitis A virus, protecting individuals from severe infections and health complications later in life.
- Less Out-of-Pocket Expenditure: Studies have shown that vaccinating children aged one year and adolescents aged 15 years in Kerala using either live attenuated or inactivated vaccines is cost-effective.
- Vaccination prevents future healthcare expenditures associated with treating hepatitis A infections.
- Increase in Household savings: Implementing vaccination for adolescents could save Kerala ₹5,872 million to ₹10,553 million over five years, depending on the type of vaccine used.
- Equal and Universal Accessibility: Due to the inclusion in the universal immunization program, these vaccines are accessible throughout all sections of society, whether rich or poor.
Government Initiatives:
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program (NVHCP): The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the NVHCP in July 2018 to prevent and control viral hepatitis in India.
- The program aims to combat hepatitis and achieve country-wide elimination of hepatitis C by 2030, reduce morbidity and mortality associated with hepatitis B and C, and reduce the risk, morbidity, and mortality due to hepatitis A and E.
- State-Level Initiatives: Some states like Punjab, Assam, Manipur, Tripura, and Haryana have started free or subsidized hepatitis C treatment programs.
- Haryana launched its own Hepatitis Control Program in 2013 at PGIMS Rohtak, which was later expanded to all district civil hospitals in the state in 2017.
What is the Prime challenge?
- Achieving high vaccination coverage among adolescents, who are not covered under the universal immunization program, remains a challenge. Strategies such as school-based vaccination campaigns are proposed to enhance this kind of coverage.
Conclusion: Implement targeted vaccination campaigns in schools and communities to ensure high coverage among adolescents aged 15 years, who are not currently included in Kerala’s universal immunization program. This can be achieved through collaboration with schools, healthcare providers, and community organizations to raise awareness and facilitate easy access to vaccinations.
Mains PYQ:
Q What is the basic principle behind vaccine development? How do vaccines work? What approaches were adopted by the Indian vaccine manufacturers to produce COVID-19 vaccines? (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Issues with ‘mandir’ tag for Ayushman Health and Wellness Centres
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Arogya Mandirs, AB-NHPM
Why in the News?
Following Mizoram and Nagaland, Meghalaya has also refused to rename its health and wellness centres as Ayushman Arogya Mandirs as per the Centre’s directive.
Context: Demographic composition of NE and its implications on policy decisions
|
About Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs)
- AB-HWCs were launched to move away from selective health care to a more comprehensive range of services spanning preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative care for all ages.
- There are 1.6 lakh such centres across India under this initiative.
- The National Health Policy of 2017 envisioned these centres as the foundation of India’s health system.
- The Union Health Ministry renamed AB-HWCs as Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAM) with the tagline ‘Arogyam Parmam Dhanam’.
- States and Union Territories were urged to complete the rebranding by the end of 2023.
Back2Basics: Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
| Details | |
| Details |
|
| Health Benefit Package |
|
| Beneficiaries |
|
| Financing |
|
| Nucleus Agency |
|
PYQ:[2022] With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
An Ageing India: The Magnitude and the Multitude
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Magnitude and Multiplication of aged population
Why in the News?
The phenomenon of ageing stands out as one of the most significant developments of this century, characterized by notable advancements in human longevity alongside historically low reproduction rates.
About the Magnitude and Multiplication of the aged population
- The magnitude of Aging Population: The 21st century is witnessing a significant demographic shift marked by a notable increase in human longevity.
- Improved healthcare and living conditions have contributed to a rise in life expectancy, leading to a larger elderly population. By mid-century, India is projected to have around 319 million elderly people, growing at a rate of approximately 3% annually.
- Multiplication of Aging Phenomenon: Despite longevity gains, there is a simultaneous decline in fertility rates, leading to an ageing population with a lower proportion of younger generations.
- This demographic shift poses challenges related to healthcare, social security, and economic sustainability. The elderly population is becoming increasingly feminized, with a higher prevalence of elderly women due to longer life expectancy and higher widowhood rates.
Aged Population as per the 2011 Census:
|
Issues and Challenges
- Vulnerabilities of the Elderly: Many elderly individuals in India face significant vulnerabilities, including limitations in activities of daily living (ADL), multi-morbidity, poverty, and lack of financial security.
- A substantial proportion of the elderly report poor health conditions, with a high prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer.
- Mental health issues, particularly depression, are also prevalent among the elderly population.
- Social and Economic Insecurities: Food insecurity affects a notable percentage of the elderly, with reports of reduced portions or skipped meals due to economic constraints.
- Lack of legal protection: Awareness and access to welfare measures and legal protections for the elderly are low, with limited knowledge about schemes like IGNOAPS, IGNWPS, and Annapurna.
- Abuse and Neglect: Elder abuse is a significant concern, especially for elderly women in rural areas who often experience neglect and mistreatment within their families and communities.
- Social exclusion and limited opportunities for productive engagement exacerbate feelings of insecurity and marginalization among the elderly.
Way Forward:
- Enhancing Social Support and Welfare Measures: Strengthening awareness and accessibility of welfare schemes and legal protections for the elderly. Implementing social security measures to ensure financial stability and improve quality of life for ageing populations.
- Healthcare and Mental Well-being: Prioritizing healthcare interventions tailored to the needs of the elderly, including preventive measures against chronic diseases and mental health support. Promoting healthy ageing through lifestyle interventions and healthcare policies that address the unique challenges of an ageing population.
- Empowerment and Social Inclusion: Fostering social inclusion through community engagement and initiatives that empower the elderly to contribute actively to society. Developing innovative institutional frameworks that value the elderly as assets and promote their participation in societal development.
Mains PYQ:
Q. Critically examine the effects of globalization on the aged population in India. (UPSC IAS/2013)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Why the Centre has extended the Digital Health Incentive Scheme?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Digital Health Incentive Scheme
Mains level: Why has the scheme been extended?
Why in the News?
The central government has granted a one-year extension to the Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS), aimed at digitizing patients’ health records and integrating them with the Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Account (ABHA ID).
About the Digital Health Incentive Scheme:
- The National Health Authority (NHA) launched the Digital Health Incentive Scheme on January 1, 2023, to implement the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) to create a digital health ecosystem in the country.
- ABDM intends to support different healthcare facilities like clinics, diagnostic centers, hospitals, laboratories and pharmacies in adopting the ABDM ecosystem to make available the benefits of digital health for all the citizens of India.
- It encourages the adoption of digital health solutions like Health Management Information Systems (HMIS) and Laboratory Management Information Systems (LMIS) by offering financial incentives for each additional record digitized beyond a specified threshold.
- Benefits of the Digital Health Incentive Scheme:
- Earn incentives for Digitization: Reimburse the expenses incurred for digitization to all the participating healthcare facilities and digital Solution Companies.
- Efficiency in Healthcare Delivery: Seamless access to patient’s longitudinal health records; Removes hassles in the healthcare process (registration, appointment, consultation, IPD admission, discharge, etc).
- Building a Robust Digital Health Ecosystem: Building a robust digital health ecosystem across different levels of healthcare facilities.
- Improved Quality of Care: Evidence-based, accessible, and good quality care. Patient’s ease of access to digitized health records and improved healthcare delivery.
Why has the scheme been extended?
- The extension aims to sustain momentum in the adoption of digital health technologies. By providing additional time, the scheme supports more healthcare providers, both public and private, in overcoming financial barriers associated with digitization and promoting a digital-first approach to healthcare delivery.
- Extending the scheme allows for incorporating feedback from stakeholders and refining its implementation based on operational insights. This iterative process ensures that the scheme remains effective in enhancing healthcare efficiency, patient care, and accessibility to medical records across the country.
How many Hospitals and Digital Health Companies have availed of the incentive?
- Registered Facilities: A total of 4,005 healthcare facilities have registered for the Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS). This includes 1,085 private healthcare facilities.
- Digital Solution Companies (DSCs): There are 41 digital solution companies (DSCs) registered under the scheme, out of which 36 are private companies.
- Availed the Scheme: Among the registered facilities and companies, 584 healthcare facilities have availed the scheme so far. This includes 83 private healthcare facilities. Additionally, 12 DSCs, including 10 private companies, have also availed the incentive.
How can it be beneficial for the patients?
- Quick Registration: Patients can benefit from quicker OPD registrations through digital systems, reducing waiting times at hospitals and clinics.
- Digital Transactions: Digital health records enable easier access to medical history and facilitate seamless sharing of information between healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care.
- Reduced Redundancy: Digital records help in avoiding duplicate tests and procedures due to lost or misplaced paper records, which is particularly beneficial for patients who move between healthcare facilities or states.
- Better Coordination: Healthcare providers can access comprehensive patient records quickly, leading to more coordinated and effective treatment plans.
- Prevention of Additional Costs: By reducing the need for repeat tests and administrative overheads associated with paper-based records, patients are less likely to incur unnecessary expenses.
- Clear Communication: Patients can securely view, access, and share their health records with healthcare providers, promoting transparency and informed decision-making about their care.
- Secure Storage: Digital health records stored under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Account (ABHA ID) ensure data security and privacy, adhering to regulatory standards.
Do you know what is ‘ABHA ID’?
|
Conclusion: The extension of the Digital Health Incentive Scheme aims to boost adoption of digital health solutions, benefiting patients with improved access and care coordination. Challenges include ensuring equitable access and addressing digital literacy barriers.
Mains PYQ:
Q Appropriate local community level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Tackling the Fatty Liver Disease Epidemic
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: International Fatty Liver Day
Mains level: India's Growing Burden of Fatty Liver Disease
Why in the news?
This year’s theme for International Fatty Liver Day, an awareness initiative observed annually in June, is ‘Act Now, Screen Today’. This theme holds more urgency now than ever before.
Liver Diseases in recent times
|
India’s Growing Burden of Fatty Liver Disease
Note: MASLD, or Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, is a reclassification of what was previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- High Prevalence Rates: The global prevalence of Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is estimated at 25-30%. In India, a 2022 meta-analysis revealed that the pooled prevalence of fatty liver among adults was 38.6%. Among obese children in India, the prevalence was around 36%.
- Progression of Disease: The continuous damage caused by fatty liver leads to more severe conditions such as steatohepatitis and cirrhosis, often requiring liver transplants.
Causes of Growing Burden of Fatty Liver Disease
- Lack of Early Detection: Fatty liver disease often goes undetected in early stages due to lack of symptoms. Diagnosis usually occurs at an advanced stage, when significant liver damage has already taken place.
- Diet and Insulin Resistance: Excessive consumption of carbohydrates, especially refined carbs and sugars, leads to metabolic problems. High carbohydrate intake results in persistently high insulin levels and insulin resistance, promoting the conversion of excess glucose into fatty acids, which are then stored in the liver.
Initiatives Taken by the Government
- Integration with NPCDCS: The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched operational guidelines for integrating NAFLD with the National Programme for Prevention & Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) in February 2021.
- Health Promotion and Prevention: The Ayushman Bharat- Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs) are being used to promote healthy living and screen for hypertension, diabetes, and other common NCDs.
Personalization is the Key
- Tailored Screening Tests: The selection of screening tests and their frequency should be based on individual risk factors, including family history, lifestyle, and pre-existing health conditions.
- Avoiding Generic Assumptions: Clinicians should not rely solely on age or physical markers; instead, they should consider a comprehensive risk profile. Non-communicable diseases are increasingly affecting diverse populations, including children.
- Integrated Health Strategies: Combining dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and effective weight management to mitigate liver disease risks.
- Frequent Screenings: Regular monitoring of liver health through non-invasive tools like vibration-controlled transient elastography. Continuous assessment of liver stiffness to detect early stages of liver fibrosis and monitor treatment responses.
- Active Health Management: Emphasis on the importance of individuals taking control of their health by being aware of their diet and lifestyle choices.Encouragement of frequent health screenings to detect and manage liver disease early.
Way Forward:
- Awareness Campaigns: Government initiatives focus on raising awareness about the importance of liver health and the risks associated with MASLD.
- Health Screenings: Programs promoting comprehensive health screenings that include physical examinations, blood tests, and abdomen ultrasounds to detect liver diseases early.
Mains PYQ
Q The public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that the private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
IRDAI’s new health insurance rules
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IRDAI and its composition
Mains level: The recent rules highlighted by IRDAI
Why in the news?
Recently, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDAI) introduced a set of reforms in the health insurance sector aimed at significantly enhancing service standards for policyholders.
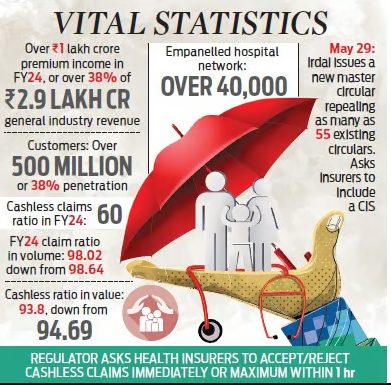
The recent rules highlighted by IRDAI (Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India) include:
- Cashless processing: Insurers are mandated to accept or reject cashless claims immediately, within one hour, and settle such claims on discharge within three hours. Any delay beyond this period would result in the insurer bearing the additional costs, if any.
- Claim settlement: Insurers cannot repudiate a claim without the approval of their claims review panel. Documents for claim settlement must be collected from hospitals or third-party administrators, not from the insured.
- Policyholders with multiple health policies: They can select the policy under which they want to make a claim, with the primary insurer coordinating the settlement of the balance amount from other insurers.
- Reward for No claims: Policyholders with no claims during the policy period may receive either an increased sum insured or discounted premium amounts.
- Renewal policies: All individual health policies are renewable and cannot be denied based on previous claims, except in cases of fraud, non-disclosures, or misrepresentation. No fresh underwriting is required for renewal policies unless there is an increase in the sum insured.
- Portability requests: Stricter timelines are imposed on portability requests via the Insurance Information Bureau of India portal.
- Customer information sheet: Insurers are required to include a customer information sheet as part of the policy document, explaining all customer-facing details such as policy type, sum assured, coverage details, exclusions, deductibles, and waiting periods.
Challenges related to health insurance in India
- Opaque Policy Details and Claim Processes: Policyholders often struggle to understand the intricacies of insurance contracts, leading to uncertainty about coverage entitlements and reimbursement procedures.
- Claim Rejections: Policyholders frequently face claim rejections due to inadequate documentation and ambiguous claims processes.
- Delays in Claim Settlement: Insurance companies often take a long time to process claims, causing inconvenience and financial stress for policyholders
IRDAI and its composition:
|
Conclusion: IRDAI’s recent health insurance reforms aim to improve service standards by mandating timely cashless claim processing, transparent claim settlement, and policyholder rewards for no claims. These changes address challenges like opaque policies and claim rejections, enhancing customer trust. IRDAI plays a vital role in ensuring a fair and efficient insurance sector.
Mains PYQ:
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] CSIR’s PI-CHeCK Project
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PI-CHeCK Project, Phenomes
Why in the News?
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) celebrated the completion of the initial phase of its groundbreaking health monitoring project, ‘Phenome India-CSIR Health Cohort Knowledgebase’ (PI-CHeCK).
What is Phenome?
|
What is the PI-CHeCK Project?
- PI-CHeCK launched on Dec 7, 2023, assesses risk factors for cardio-metabolic disorders in the Indian population.
- ‘Phenome India’ health check-up camp targets CSIR employees, pensioners, and spouses across 17 states, and 24 cities.
- Nearly 10,000 volunteers provide comprehensive health data.
Objectives:
- Developing India-Specific Algorithms: The project highlights the necessity of developing risk prediction algorithms tailored to India’s diverse genetic and lifestyle landscape, as existing algorithms may not accurately represent the Indian population.
- Advancing Precision Medicine: CSIR’s commitment to advancing precision medicine is evident through the project’s focus on Predictive, Personalized, Participatory, and Preventive healthcare.
- Catalyzing Nationwide Initiatives: By generating a comprehensive phenome database, PI-CHeCK aims to catalyze similar initiatives nationwide, ensuring more accurate risk prediction algorithms for India’s diverse population.
PYQ:[2021] “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. [2018] Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. [2011] Aspartame is an artificial sweetener sold in the market. It consists of amino acids and provides calories like other amino acids. Yet, it is used as a low-calorie sweetening agent in food items. What is the basis of this use? (a) Aspartame is as sweet as table sugar, but unlike table sugar, it is not readily oxidized in human body due to the lack of requisite enzymes. (b) When aspartame is used in food processing, the sweet taste remains, but it becomes resistant to oxidation. (c) Aspartame is as sweet as sugar, but after ingestion into the body, it is converted into metabolites that yield no calories. (d) Aspartame is several times sweeter than table sugar, hence food items made with small quantities of aspartame yield fewer calories on oxidation. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The delicate balancing of health-care costs
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Private Healthcare System in India
Why in the news?
With growing health disparities and inconsistent access to medical services, the need for fair and sustainable healthcare policies has never been more pressing.
Private Healthcare System in India
- Private hospitals in India, especially those accredited by the Joint Commission International (JCI) and National Accreditation Board for Hospitals (NABH), are hubs of specialised care and innovation.
- These institutions invest heavily in top-tier infrastructure and advanced technologies, significantly enhancing patient outcomes, particularly in complex procedures. Integration of telemedicine and remote care is common, broadening access and building patient trust.
Price Caps, Quality, and Innovation
- Affordability vs. Quality: The Supreme Court’s deliberation on standardising medical procedure rates across government and private sectors highlights the tension between affordability and quality. A study indicates a 15% increase in patient dissatisfaction in hospitals under financial pressure from price caps
- Impact on Innovation: Price caps could slow the development of new treatments and technologies, particularly in high-investment fields like cancer research and robotic surgery. Value-based pricing, where payments reflect health outcomes rather than service volume, is proposed as a potential solution.
- Economic Implications: Properly implemented rate standardisation can alleviate healthcare disparities but must avoid destabilising providers’ economic health. Dynamic pricing models, which adjust based on medical complexity and patient financial status, are recommended. Thailand’s tiered pricing system is cited as a successful example.
Legal and regulatory challenges
- No regulation on Rate Fixation: States like Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu have identified significant gaps in the provisions for rate fixation, indicating a need for more robust legal frameworks to ensure fair and standardised pricing across different regions.
- Inadequate Laws as per Local Conditions: Current laws may not adequately consider local demographic and economic conditions, necessitating reforms that allow for more customised approaches to healthcare cost management.
- Lack in uniform regulation: Moreover,” the Clinical Establishment Act of 2011″, aimed at setting standards for quality, transparency, and accountability, has been adopted by only a few states, and its implementation remains lax. This lack of uniform regulation allows for wide disparities in service costs and quality.
Role of Data in Shaping Policies
- Data-Driven Insights: Predictive analytics can foresee the long-term impacts of rate fixation on healthcare innovations, helping policymakers adjust regulations to encourage innovation and accessibility.
- Pilot Projects: Implementing pilot projects in select districts can gauge the impact of rate caps on healthcare quality and innovation.
Way Forward
- Balanced Pricing Models: Implement value-based pricing where payments are linked to health outcomes rather than the volume of services provided.
- Supporting Innovation: Allocate government subsidies and grants for research and development in private hospitals.
Mains PYQ
Q Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India and the ‘managed care’ promise
| PYQ Relevance
Q Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that the private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015) Q The increase in life expectancy in the country has led to newer health challenges in the community. What are those challenges and what steps need to be taken to meet them? (UPSC IAS/2022) |
Mentor Comment: Health insurance, now central to India’s UHC policy, is being enhanced by digital advancements, enabling reforms akin to the U.S. but with cost-effective local adaptations. A South Indian healthcare chain recently integrated insurance and care provision, forming an Indian-style MCO. This prompts reflection on MCOs’ potential to extend universal health care in India significantly.
Let’s learn_ _
Why in the news?
Universal healthcare poses a multifaceted challenge, yet managed care organizations may offer a piece of the solution that Indian healthcare requires.
What is a Managed Care Organization?
- A Managed Care Organization (MCO) is a health care company or a health plan that is focused on managed care as a model to limit costs, while keeping quality of care high.
The background of Managed Care Organizations (MCOs) in the United States and India:
Evolution of MCOs in the United States:
- MCOs have their origins in rudimentary prepaid healthcare practices in the 20th century.
- The mainstreaming of MCOs gained momentum in the 1970s due to concerns over healthcare costs.The economic slowdown post-1970s made high insurance premiums less attractive to purchasers.
- A shift occurred towards integrating insurance and healthcare provisioning functions. Focus areas included prevention, early management, and cost control, all under a fixed premium paid by enrollees.
- MCOs have evolved through multiple generations and forms, deeply penetrating the health insurance market. While evidence of their effectiveness in improving health outcomes and prioritizing preventive care is mixed, they have been effective in reducing costly hospitalizations and associated costs.
Evolution of MCOs in India:
- The first public commercial health insurance emerged in the 1980s.The focus has primarily been on indemnity insurance and covering hospitalization costs.
- There is a significant market for outpatient consultations, valued at nearly $26 billion.
- Health insurance in India has traditionally lagged behind life and general insurance. The sector faces issues such as lack of innovation and high, often unsustainable, operational costs.
- As per Thomas (2011), Health insurance has played a secondary role to other forms of insurance. The industry’s operational inefficiencies and high costs have been persistent issues.
Challenges in India:
- Lack of Natural Incentives for Cost Control: The evolutionary trajectory of Indian health insurance has not incentivized consumer-driven cost control.
- Target Demographic: Health insurance has mainly targeted a thin, urban, well-off segment, neglecting broader demographics.
- Informality in Outpatient Practices: There is widespread informality among outpatient practices, complicating efforts to standardize and regulate care.
- Lack of Clinical Protocols: The absence of widely accepted clinical protocols hampers the quality and consistency of care.
- Economic Viability: Unprofitable operations and unaffordable premiums pose significant economic challenges, preventing sustainable growth and systemic improvement.
- Limited Impact on UHC: Private initiatives, despite their potential, are unlikely to significantly contribute to Universal Health Coverage (UHC) without public support.
- Insufficient Control Over Patient Journeys: Health insurers have little control over the patient’s journey before hospitalization, limiting their ability to manage early interventions and reduce costs through comprehensive outpatient care.
Prospective Solutions and Remaining Issues:
- Potential for Big Healthcare Brands: Large healthcare brands with loyal urban patient bases and substantial resources may initiate successful managed care projects.
- Need for Public Patronage: Exploring managed care with cautious and incremental public patronage could be promising, indicating a need for government involvement to achieve broader impacts.
- Underutilization of Outpatient Insurance: Given the low share of insurance in outpatient care spending and the average of three consultations per year per person, there is significant potential to reduce healthcare costs through early interventions and comprehensive outpatient care coverage.
NITI Aayog Report:
- Outpatient care insurance scheme: In 2021, NITI Aayog released a report advocating for an outpatient care insurance scheme based on a subscription model to enhance savings through improved care integration.
- Yield significant benefits: A well-functioning managed care system can yield significant benefits, including consolidating practices, streamlining management protocols, and emphasizing preventive care in the private sector.
- Catering for the beneficiaries of PMJAY: The report highlights the potential of incentives under the Ayushman Bharat Mission to encourage the establishment of hospitals in underserved areas catering to beneficiaries of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY).
Conclusion: While Managed Care Organizations are not a perfect solution, they can play a role in addressing the complexities of achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in India by being part of a broader strategy.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Women often outlive men but in poorer health: what new Lancet study says
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lancet Report;
Mains level: Women Issues in Indian Society; Health Issues;
Why in the news?
Over 30 years, a study examining 20 diseases revealed minimal advancements in narrowing the disparity between genders as per “the Lancet Public Health Journal”.
What does the New Lancet report say?
- On Health Disparities: The study highlights that women tend to suffer more from lower back pain, depression, and headaches, while men have shorter life expectancies due to higher rates of road accidents, cardiovascular diseases, and, recently, COVID-19.
- On Health Burden: Women spend more time in poor health, while men are more likely to die prematurely from severe conditions.
- Overall Global Analysis: The analysis examines differences in the 20 leading causes of illness and death globally, considering all ages and regions.
What Causes the Differences in Diseases Between Women and Men? (Observations)
- Biological Factors:
-
-
- Hormonal Differences: Hormonal fluctuations in women, such as during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause, can influence susceptibility to certain conditions like migraines, depression, and autoimmune diseases.
- Genetic Variations: Variations in genes and genetic predispositions may contribute to differences in disease susceptibility and severity between sexes.
- Anatomical Variances: Physiological differences, such as in skeletal structure and hormonal regulation, can affect the manifestation of certain diseases like lower back pain and reproductive disorders.
-
- Societal and Gender Norms:
-
-
- Healthcare-Seeking: Societal norms and gender roles may influence healthcare-seeking behaviors, with men often less likely to seek medical attention for mental health issues due to perceived notions of masculinity.
- Occupational Hazards: Occupational differences between genders can lead to varying exposures to health risks, with certain professions associated with higher rates of injury or exposure to harmful substances.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Disparities in socioeconomic status can impact disease prevalence and outcomes differently for women and men.
-
- Healthcare System Bias:
-
-
- Diagnostic Bias: Gender biases in healthcare may result in underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis of certain conditions in women, leading to delays in treatment and poorer health outcomes.
- Treatment Disparities: Differences in treatment approaches and responses may exist between sexes, with women sometimes receiving less aggressive treatment for cardiovascular diseases or being undertreated for pain conditions.
- Research Bias: Historically, medical research has often focused on male subjects, leading to a lack of understanding of how diseases manifest and progress differently in women.
-
- No Improvement in Care for Women Over Time
-
- Stable Gender Gap: Despite overall health improvements, the disparity between male and female health conditions remains stable.
- Conditions Affecting Women: Conditions like lower back pain and depressive disorders have shown little to no decrease over time compared to male-dominated conditions.
- Reproductive Focus: Global health systems have historically focused on women’s reproductive health, neglecting other significant health issues affecting women.
What Needs to Be Done (Way Forward)
- Better Data Collection: Governments should consistently collect and categorize health data by sex and gender to better understand and address health disparities.
- Targeted Health Interventions: Specific health interventions should be developed and implemented based on detailed sex and gender data.
- Increased Funding: More financial resources should be allocated to underfunded conditions that disproportionately affect women, such as mental health.
- Addressing Healthcare Bias: Efforts should be made to eliminate biases in healthcare to ensure women receive appropriate and timely treatment for their conditions.
Mains PYQ:
Q Can the vicious cycle of gender inequality, poverty and malnutrition be broken through microfinancing of women SHGs? Explain with examples. (UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
NIMHANS bags WHO’s Nelson Mandela Award for Health Promotion for 2024
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nelson Mandela Award, NIMHANS
Why in the News?
- The National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), Bengaluru, India’s premier mental health institution, has been honoured with the “Nelson Mandela Award” for Health Promotion by the World Health Organization (WHO) for 2024.
About National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro-Sciences (NIMHANS)
| Details | |
| Location | Bangalore, India |
| Affiliation | Autonomous institute under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India |
| Ranking | Ranked 4th best medical institute in India by the “National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)” |
| History |
|
| Governance |
|
| Funding | Receives resources for academic and research activities from national and international funding organisations. |
| Outreach |
|
Back2Basics: Nelson Mandela Award for Health Promotion
|
PYQ:[2021] We can never obtain peace in the outer world until and unless we obtain peace within ourselves. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] India Hosts Digital Health Side Event at World Health Assembly
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: World Health Assembly (WHA)
Why in the News?
- India hosted a side event on Digital Health during the 77th World Health Assembly.The event saw participation from Quad countries (Australia, Japan, and the United States of America) and delegates from over 100 countries.
Key Highlights of the 7th WHA:
|
About World Health Assembly (WHA):
| Details | |
| Establishment | Established in 1948 as the decision-making body of the World Health Organization (WHO) |
| Frequency | Typically meets annually in Geneva, Switzerland |
| Membership | Includes all 194 member states of the WHO, as well as certain international organizations as observers |
| Role and Functions |
|
| Decision-Making Process | Decisions made by a simple majority vote of member states present and voting |
| Themes and Agendas | Each session focuses on specific global health priorities, addressing a wide range of health topics |
| Notable Achievements | Development and adoption of international health instruments and initiatives, including:
|
| Challenges | Resource constraints, geopolitical tensions, need for greater inclusivity and transparency in decision-making |
PYQ:[2016] ‘Doctors Without Borders (Medecins Sans Frontieres)’, often in the news, is (a) A division of World Health Organization. (b) A non-governmental international organization. (c) An inter-governmental agency sponsored by European Union. (d) A specialized agency of the United Nations. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Still no sign of the language of equity and inclusion
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Minority sections and Government Initiatives;
Mains level: Minority sections; National Programme for Prevention and Control of Deafness
Why in the news?
The ECI’s election announcement lacked sign language interpreters, highlighting the everyday exclusion of Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) citizens.
Present Issue:
- India’s societal and structural framework often neglects the needs of Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) citizens.
- This exclusion is evident in various aspects of daily life, such as the absence of sign language interpreters during major public announcements and inadequate accessibility in public services.
Sign Language versus Oralism
- The Indian education system predominantly employs “oralism,” which emphasizes teaching deaf individuals to use their voices and lip-read, rather than using sign language.
- This approach has been criticized for perpetuating social isolation and failing to remove barriers that hinder the integration of DHH individuals.
- In contrast, using sign language has been shown to aid cognitive development and prevent linguistic deprivation.
- Over 70 countries recognize their national sign languages legally, promoting accessibility and inclusion for deaf citizens.
Present Scenario:
What Does the 2011 Census Say?
|
The National Programme for Prevention and Control of Deafness
-
- The program was initiated in the year 2007 in pilot mode in 25 districts of 11 States/UTs. It has been expanded to other districts too after the 12th five-year plan.
- The Program was a 100% Centrally SponsoredScheme during the 11th Five-year plan. However, as per the 12th Five Year Plan, the Centre and the States will have to pool in resources financial norms of NHRM.
- However, it falls short of addressing the quality of life for DHH individuals. This program has been expanded to 228 districts of 27 States / U.Ts in a phased manner.
Objectives of the program:
- To prevent avoidable hearing loss on account of disease or injury.
- Early identification, diagnosis, and treatment of ear problems responsible for hearing loss and deafness.
- To medically rehabilitate persons of all age groups, suffering from deafness.
- To develop institutional capacity for ear care services by providing support for equipment and material and training personnel.
Components of the Programme:
- Manpower Training & Development to grassroots level workers.
- Service Provision Including Rehabilitation – Screening camps for early detection of hearing impairment and deafness.
- Awareness Generation for early identification of the hearing impaired.
- Monitoring and Evaluation.
What Needs to be done?
- Official Recognition of ISL: ISL should be recognized as an official language, and its use should be integrated into educational systems and public services. Teaching ISL in schools, colleges, and to the general public will promote inclusivity and fluency.
- Inclusive Health Care: Health care systems need to be updated to ensure accessible communication for DHH patients. This includes training more ISL interpreters and reducing barriers for DHH individuals pursuing healthcare professions.
- Media and Public Communication: Media channels should incorporate ISL interpretation and subtitles, especially in Hindi and regional languages. Government event announcements should have live ISL interpreters to ensure accessibility.
- Employment Opportunities: Creating more employment opportunities for DHH individuals, beyond low-skilled jobs, is essential. This includes training and employing DHH individuals as ISL instructors and ensuring accessible workplaces.
Conclusion: To ensure inclusivity for DHH citizens, India must officially recognise ISL, integrate it into education and public services, improve healthcare accessibility, and expand employment opportunities and mental health support.
Mains PYQ:
Q How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate your answer. (UPSC IAS/2020)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
How close is the World Health Organization to agreeing on pandemic response rules?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: WHO; Healthcare Initiatives;
Mains level: Health Care; Convention on Tobacco Control; Global Health Rules;
Why in the News?
Health officials of the World Health Organization (WHO) aim to finalize over two years of negotiations on new pandemic response rules when they convene in Geneva next week.
About the ‘Pandemic Treaty’
- The pandemic treaty is a new legally binding agreement being negotiated to improve the global pandemic response. The treaty aims to address the shortcomings revealed during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as inequitable vaccine distribution.
- Article 12, a critical and contentious part of the treaty, proposes reserving around 20% of tests, treatments, and vaccines for WHO distribution to poorer countries during emergencies.
- The treaty would be the second major health accord after the 2003 Framework Convention on Tobacco Control.
Convention n Tobacco Control
|
How will Global Health Rules Change?
- Updates to the existing International Health Regulations (IHR) include a new alert system for different risk assessments of outbreaks, replacing the current single-level emergency declaration.
- A new “early action alert” stage will be introduced, along with a potential “pandemic emergency” category for the most severe health threats.
- Obligations for countries: Strengthened obligations for countries to inform the WHO about public health events, changing the language from “may” to “should”.
How do the countries view this pact?
- Developed Countries
-
-
- Wealthy countries are often cautious about sharing resources such as drugs and vaccines.
- There is significant political pressure, especially from right-wing groups, fearing that the treaty could infringe on national sovereignty.
- These countries are concerned about the financial implications, debating whether to set up a new fund or use existing resources like the World Bank’s $1 billion pandemic fund.
-
- Underdeveloped Countries
-
- Poorer countries emphasize the need for equitable access to treatments and vaccines, reflecting experiences of “vaccine apartheid” during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- They advocate for stronger commitments from wealthier nations to support global health infrastructure and emergency response capabilities.
Future Scope of the New IHR Rules and the Pandemic Accord (Treaty):
- More robust framework: The IHR updates and the pandemic treaty has designed to complement each other, creating a more robust framework for global health emergencies.
- Promotes cooperation: The new rules aim to ensure faster, more transparent information sharing, and better co-operation during health crises.
- Next steps for treaty negotiations: Next week’s World Health Assembly will focus on planning the next steps for the Treaty Negotiations, with a full agreement unlikely to be reached immediately.
- Defenses against future pandemics: The successful implementation of both the IHR updates and the pandemic treaty could significantly strengthen the world’s defenses against future pandemics, addressing gaps exposed by COVID-19.
Conclusion: While there is a shared understanding of the treaty’s importance, countries’ views are shaped by their National interests, Financial concerns, and Political pressures, leading to complex and protracted negotiations.
Mains PYQ:
Q Critically examine the role of WHO in providing global health security during the Covid-19 pandemic. (UPSC IAS/2020)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Naegleria fowleri: the Brain-eating Amoeba
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Naegleria fowleri, Amoeba
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- A five-year-old girl in Kozhikode, Kerala has succumbed to primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM), caused by Naegleria fowleri.
- India has recorded 20 reported cases of PAM, with the recent case marking the seventh infection in Kerala.
What is Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)?
- PAM is a rare brain infection caused by Naegleria fowleri, a free-living amoeba found in warm freshwater and soil worldwide.
- An amoeba is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods.
- Higher temperatures of up to 115°F (46°C) are conducive to its growth and it can survive for short periods in warm environments.
- The amoeba enters the body through the nose, typically during activities like swimming, and travels to the brain, causing severe damage.
- PAM is also non-communicable.
- Symptoms: Headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, confusion, seizures, hallucinations, and coma.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), most people with PAM die within 1 to 18 days after symptoms begin. It usually leads to coma and death after 5 days.
Treatment Challenges
- Currently, there are no established effective treatments for PAM.
- Medical interventions typically involve a combination of drugs, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
IFPMA Report on Antimicrobial Resistance
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AMR, Initiatives mentioned;
Why in the news?
The International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Associations (IFPMA) released a report titled “From Resistance to Resilience: Reinforcing the Response to Antimicrobial Resistance,” emphasizing the urgent need for enhanced Antibiotic development.
Report Highlights: Current State of Antibiotic Development:
|
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
- Antimicrobials are substances designed to eliminate or suppress the growth of microorganisms.
- This category encompasses antibiotics, fungicides, antiviral drugs, and agents targeting parasites.
- AMR occurs when microbes such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi become resistant to antimicrobial treatments to which they were previously susceptible.
- Microorganisms that develop resistance to antimicrobials are sometimes referred to as “superbugs”.
Global Status of AMRA recent report from the Global Research on Anti-microbial Resistance (GRAM) project found that:
|
What are the factors that cause AMR?
- Over-prescription of Antibiotics: Frequently prescribing antibiotics for conditions that do not require them, such as viral infections, accelerates the emergence of resistance.
- Incomplete Treatment Courses: Patients not completing their antibiotic courses as prescribed can leave surviving bacteria that adapt to become resistant.
- Self-Medication: Individuals using antibiotics without a prescription, especially in regions where they are available over the counter, increases misuse and drives resistance.
- Lack of New Antibiotics: The slow pace of new antibiotic development fails to keep up with the rate of bacterial evolution, reducing effective treatment options.
- Hospital Settings: Hospitals are critical hotspots for the spread of resistant infections due to the high use of antibiotics and the concentration of vulnerable patients with open wounds, invasive devices, and weakened immune systems.
- Global Travel: International travel allows for the rapid spread of resistant mutant strains between communities and across borders.
India’s efforts to combat AMR:
| Description | |
| National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (NAP-AMR) |
|
| New Delhi Declaration on AMR |
|
| National Anti-Microbial Resistance Research and Surveillance Network |
|
| National Programme on Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance |
|
| Red Line Campaign |
|
| National One Health Program for Prevention and Control of Zoonoses |
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Niti Aayog report finds ‘huge gap’ in cancer screening at Ayushman centres
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat Scheme
Mains level: Reason behind the 'huge gap' in cancer screening at Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs)
Why in the news?
Ayushman Bharat insurance scheme reached 5.47 crore users, but cancer screening at Health and Wellness Centers (HWCs) faces significant gaps, reports NITI Aayog.
Objective of Ayushman Bharat Scheme:
- Besides providing a Rs 5-lakh insurance cover, the scheme aimed to upgrade primary health centers to HWCs, offering annual screening for Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) including oral, breast, and cervical cancers for individuals aged 30 years or older.
Coverage of Ayushman Bharat Scheme:
- Over 5.47 crore users have utilized the Ayushman Bharat insurance scheme, making it the world’s largest medical insurance scheme.
The ‘huge gap’ in cancer screening at Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- NITI Aayog Report Findings: A report from NITI Aayog, based on visits to HWCs in 13 states, highlights a significant gap in cancer screening services.
- Limited NCD Screening: Although NCD screening is underway in most HWCs, yearly screening is largely absent, with less than 10% of facilities completing a single round of NCD screening.
Reason behind the ‘huge gap’ in cancer screening at Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- Methods of Screening: Official protocol mandates distinct screening methods for oral, cervical, and breast cancers. However, implementation of these methods faces challenges.
- Lack of Awareness and Capacities: The gap in cancer screening is attributed to low awareness levels and lack of capacities among healthcare providers.
- Implementation fell short: Auxiliary Nurse and Midwife (ANMs), medical officers, and staff nurses were supposed to be trained in cancer screening methods, but implementation fell short.
- Suboptimal Screening Activities: Screening for breast cancer relies on beneficiary education for self-examination, while cervical cancer screening remains to be operationalized. Oral cancer screening is performed on a case-by-case basis.
- Infrastructure and Basic Devices: HWCs generally adhere to infrastructure standards, with basic devices and medicines available free-of-cost. However, the focus remains on improving cancer screening services to align with the government’s prevention and early detection efforts.
Way forward:
- Awareness Campaigns: Launch comprehensive awareness campaigns to educate the public about the importance of cancer screening and early detection. This can involve community outreach programs, workshops, and informational sessions.
- Utilize Technology: Integrate technology solutions such as telemedicine and mobile applications to facilitate easier access to screening services, especially in remote areas. Digital platforms can also aid in data management and monitoring of screening activities.
- Performance Monitoring: Implement robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms to track the implementation of cancer screening programs at HWCs.
Mains PYQ:
Q Appropriate local community level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Meeting Nutrition challenge: What new guidelines prescribe?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Data related to disease due to poor dietary habit
Mains level: Concerns and guidelines as per the National Institute of Nutrition (NIN)
Why in the news?
According to the National Institute of Nutrition (NIN), approximately 56.4% of India’s overall disease burden is linked to poor dietary habits.

Guidelines by the National Institute of Nutrition (NIN):The NIN, operating under the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), has issued comprehensive guidelines on nutrition for vulnerable groups, including pregnant and lactating women, children, and the elderly.
|
Key concerns as per the National Institute of Nutrition (NIN):
- Rising Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs) Among Adolescents and Children: Due to poor dietary habits led to diseases like cardiovascular disease, cancers, and diabetes are increasingly affecting adolescents and even children in India.
- Focus on Healthy Dietary Habits: The guidelines emphasize the importance of reducing salt intake and avoiding highly processed foods like packaged snacks, cookies, and sugary treats, which are linked to unhealthy diets and disease burden.
- High Prevalence of Lifestyle Conditions: The Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey 2019 highlights a concerning prevalence of lifestyle-related conditions even among children, including overweight or obesity, diabetes, pre-diabetes, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Cholesterol Levels: The survey indicates high levels of bad cholesterol (LDL and triglycerides) in children aged 5-9 and pre-teens and teens aged 10-19, along with low levels of good cholesterol in a significant portion of children and adolescents.
Other concerns related to the “Dual nutrition challenge”
- Incidence of micronutrient (zinc, iron, vitamins) deficiencies ranged from 13% to 30% of children between ages 1 and 19. But still, the prevalence of anemia is at 40.6%, 23.5%, and 28.4% in children under age 5, ages 5-9, and 10-19 respectively.
- However severe forms of undernutrition such as marasmus (a deficiency of macronutrients such as carbohydrates and proteins) and kwashiorkor (deficiency of proteins) have disappeared from the country.
Conclusion: Implementing these guidelines effectively can significantly contribute to achieving Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) targets, particularly SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
Mains PYQ:
Q How far do you agree with the view that the focus on the lack of availability of food as the main cause of hunger takes the attention away from ineffective human development policies in India? (15M) UPSC 2018
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Widal Test: Flaws of Typhoid Diagnosis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Diseases; Widal Test, Salmonella Typhi Bacteria;
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
Patients with fever in India often undergo testing and treatment for typhoid fever, primarily relying on the Widal test.
- The Widal test, though widely used, has several limitations that affect its accuracy and reliability.
Typhoid diagnosis using Widal Test

- The Widal test is used primarily to diagnose typhoid fever.
- Typhoid fever, caused by Salmonella Typhi and related bacteria, presents with symptoms like high fever, stomach pain, weakness, and gastrointestinal issues.
- It detects antibodies in the patient’s blood against the O (somatic) and H (flagellar) antigens of Salmonella Typhi.
- Procedure:
- The presence of these antibodies is detected through an agglutination reaction.
- The test involves serial dilution of the patient’s serum.
- The highest dilution at which agglutination occurs indicates the antibody titer, with higher titers suggesting an active infection.
Diagnostic Challenges:
- The gold standard for diagnosing typhoid involves isolating the bacteria from blood or bone marrow cultures, which is time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Widal test is commonly used due to its convenience and accessibility. However, the Widal test’s interpretation is complicated by factors like the need for multiple serum samples, variations in cutoff values, and potential cross-reactivity with antibodies from other infections or vaccines.
Challenges with Widal Test:
- Impractical: A single positive Widal test does not confirm typhoid.
- Complicated result interpretation: High background antibody levels and variability in test cutoff values.
- Cross-reactivity with antibodies from other infections and false negatives due to prior antibiotic therapy undermine test reliability.
Consequences of Widal Test Use:
- Erroneous results obscure the true burden of typhoid in India, leading to inappropriate treatment and financial strain on patients.
- Overuse of antibiotics based on Widal test results contributes to antimicrobial resistance, exacerbating the challenge of treating typhoid.
PYQ:[2016] Which of the following statements is/are correct? Viruses can infect 1. Bacteria 2. Fungi 3. Plants Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The unseen effects of Climate Change on Mental Health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: What is schizophrenia?
Mains level: Key concerns on health due to Extreme Heat as per the report
Why in the News?
Studies show that individuals with schizophrenia are more likely to experience fatal effects from extreme heat compared to those with kidney or heart problems as per Geo Health report.
What is schizophrenia?As per the National Institute of Mental Health, Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality, which can be distressing for them and their family and friends. |
Effects of Extreme Heat as per the Geo Health Report:
- Schizophrenia Heat-Related Deaths: GeoHealth in 2023 revealed that an extreme heat event in British Columbia in 2021 led to more fatalities among individuals with schizophrenia compared to those with kidney and heart diseases.
- Mental Health Conditions: People with mental health conditions, including schizophrenia, anxiety, and bipolar disorder, were identified as being at higher risk of succumbing to heat-related deaths during extreme heat events.
- Impact of Extreme Heat Event: British Columbia experienced an eight-day extreme heat event in 2021, with temperatures soaring as high as 40 degrees celsius, significantly above the average temperature of around 20 degrees celsius. The region recorded approximately 740 excess deaths during this heat wave.
- Researchers analyzed the data based on various medical conditions, including heart disease, schizophrenia, chronic kidney disease, dementia, depression, Parkinson’s disease, and osteoporosis.
- Higher Risk of Schizophrenia: Contrary to expectations, the study reported a 200% increase in the prevalence of schizophrenia diagnoses during the extreme heat event in 2021 compared to a summer without recorded heat waves.
Key challenges for treating Schizophrenia:
- Dysfunction of the Hypothalamus: The dysfunction of the hypothalamus, a structure deep in the brain responsible for maintaining bodily homeostasis, may contribute to increased vulnerability to heat stress among individuals with schizophrenia.
- Impact of Antipsychotic Medications: Certain antipsychotic medications prescribed for schizophrenia can interfere with the functioning of the hypothalamus, potentially raising body temperature. This side effect, when combined with high ambient temperatures, can lead to fatal outcomes.
- Psychotic Symptoms and Anosognosia (unable to be aware of the symptoms): Individuals with schizophrenia often experience psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and memory loss. The anosognosia, a condition where individuals are unaware of their illness can further complicate treatment efforts.
Way Forward:
- Enhanced Monitoring and Support Systems: Implement enhanced monitoring and support systems for individuals with schizophrenia during extreme heat events.
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: Conduct education and awareness campaigns to inform individuals with schizophrenia and their caregivers about the risks of heat-related distress and the importance of staying cool and hydrated during extreme heat events.
- Tailored Treatment Plans: Develop tailored treatment plans for individuals with schizophrenia that take into account the potential impact of antipsychotic medications on body temperature regulation.
Mains PYQ
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
With inputs from:
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2022GH000729
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] May 5: World Pulmonary Hypertension Day
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pulmonary Hypertension, 75-25 Initiative
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
Every year on May 5, pulmonary hypertension organizations and groups around the world participate in World Pulmonary Hypertension Day.
What is Pulmonary Hypertension?
- Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which are the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the lungs.
- This elevated pressure in the pulmonary arteries can lead to various symptoms and complications, affecting the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively to the lungs and the rest of the body.
Here are some key aspects of pulmonary hypertension:
Causes:
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (IPAH): In many cases, the exact cause of pulmonary hypertension is unknown, and it is referred to as idiopathic. IPAH is a subtype of PH without an identifiable cause.
- Secondary Pulmonary Hypertension: PH can also develop secondary to other underlying conditions, including:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Interstitial lung disease
- Sleep apnea
- Connective tissue diseases such as scleroderma and lupus
- Congenital heart diseases
- HIV infection
- Liver disease (cirrhosis)
- Genetic Factors: Some forms of PH may have a genetic component, with mutations in certain genes predisposing individuals to the condition.
Features:
- Symptoms: Symptoms of pulmonary hypertension may include:
-
-
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Fatigue
- Chest pain or pressure
- Dizziness or fainting spells
- Swelling in the ankles and legs (edema)
- Bluish lips or skin (cyanosis)
-
- Diagnostic Tests: Diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
-
-
- Echocardiogram (ECG)
- Right heart catheterization
- Pulmonary function tests
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan or MRI of the chest
- Blood tests
-
- Treatment: Treatment for pulmonary hypertension aims to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. Treatment options may include:
-
- Medications such as vasodilators, endothelin receptor antagonists, and prostacyclin analogs
- Oxygen therapy
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Surgery or a lung transplant in severe cases
Hypertension Control Initiatives in India:
|
PYQ:[2021] In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements : 1. Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in vitro fertilization of egg. 2. A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from mother and not from father. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A computer science conundrum that could transform healthcare
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: P versus NP Problem
Mains level: Application of Science and Technology for Healthcare;
Why in the News?
Indian Health Care system faces a new set of complex problems that seem to be harder to solve because of their inherent complexity and the constraints they threaten to impose on resources.
Quick Problems versus Complex Problems in Health Care:
- Healthcare is filled with complex problems. Consider scheduling in a hospital: assigning doctors and nurses to shifts, booking operating theatres for surgeries, and organizing patient appointments.
- It is an intricate puzzle that requires considering various factors — staff availability, urgency of medical cases, etc. — and potential changes such as emergency cases and cancellations.
- The Quick Problems vs Complex Problems in Health Care question is this: there can be a shortcut to solve ‘Complex Problems’ problems as quickly as ‘Quick Problems’ problems.
- The implication is that if Quick Problems equals Complex Problems, we could quickly find the optimal solution to these scheduling problems, thus significantly improving patient care.
Implications for the Healthcare System:
- Impact on Antibiotic Resistance: Quick analysis of bacterial genomes and prediction of resistance patterns could lead to more effective antibiotic prescriptions, improving patient outcomes and combating antibiotic resistance.
- Advancement in Cancer Treatment: Swift identification of the optimal treatment for individual cancer patients could save lives by effectively tackling the complexity of cancer mutations and treatment options.
- Optimization of Insurance Decision-Making: Insurance companies grappling with ‘NP’ problems in determining premiums and packages could benefit from a shortcut provided by solving the P versus NP problem. This could lead to fairer and more accurate premiums and conditions for customers.
- Better utilization of Government health sector funding: Efficiently solving complex problems could lead to better utilization of government spending on healthcare, minimizing leakage and contributing to achieving universal health coverage.
- Resource Constraint Reduction and Improved Health Outcomes: By solving complex healthcare problems more efficiently, there is the potential to dramatically reduce resource constraints and improve health outcomes broadly.
Way Forward: Governments can enact policies and regulations that promote the responsible use of technology in healthcare and incentivize the adoption of evidence-based practices. This includes establishing standards for data privacy and security, fostering transparency in algorithmic decision-making, and ensuring equitable access to healthcare services.
Mains PYQ
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Court’s nudge on Hospital charges, a reform opportunity
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Health; Government Initiatives;
Mains level: Challenges in benchmark for pricing
Why in the news?
The SC while hearing a PIL in February’24, directed the Central Government to find ways to regulate the rates of Hospital Procedures in the Private sector.
- The SC also warned against applying Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) rates for treatment services at private healthcare facilities until standardized rates are set.
About Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) Rates:CGHS is a health care scheme provided by the Indian Government for its central government employees and pensioners.
|
Benchmark for Pricing:
- Standard Treatment Guidelines (STGs): These can establish relevant clinical needs, the nature and extent of care, and the costs of total inputs required.
- They address confounders and ensure clinical autonomy while enabling the valuation of healthcare resources consumed for precise cost determination.
- Pooled payments by government: Formulating and adopting STGs require providers’ revenues to be tied to fewer payers.
- This necessitates reimbursements from pooled payments with low Out-Of-Pocket (OOP) payment levels, supported by the government.
- Coordination between payers and providers: Governments can support the agreement on pricing that provides a reasonable and sustainable surplus over input costs.
- However, the ability of providers to access markets with OOP payments could hinder this effort.
Challenges faced during benchmarking of the price:
- Private sector issues
-
-
- Private sector dominance: In India, over half of the total health expenditure is OOP, with the private sector predominantly composed of small-scale providers. Standardizing rates faces implementation uncertainties, and enforcement mechanisms for adherence remain unclear.
- Resistance from providers: Concerns arise about the feasibility of regulatory measures if providers do not adhere to prescribed procedure rates, as seen in various health schemes.
-
- Weak implementation
-
- Limitations of regulations: While price caps can influence behavior in the short term, weak enforcement mechanisms lead to temporary effects as the overall environment remains unchanged.
- Enforcement challenges: Despite suggested measures, enforcement remains weak, with only a fraction of states and union territories implementing the Clinical Establishment Act.
- Data-related issues: Although the insurance industry initiated STGs for hospitals in 2010, progress was hindered by a lack of representative and accurate costing data due to limited participation from private hospitals.
Government Initiatives:
- Developing STGs: The Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana and the Department of Health Research have made significant strides in developing STGs for common conditions and adopting a comprehensive costing framework.
- Efforts are also ongoing to create an Indian version of Diagnostics-Related Groups (DRGs)
Way Forward:
- Addressing anticipated challenges: Anticipated challenges in implementing rate standardization policies need to be identified and addressed proactively to ensure successful outcomes.
- Evidence-based policy: Conduct rigorous research and evaluation to generate evidence on the impact of regulatory measures on affordability, care quality, and provider behavior, informing future policy decisions.
- Ensuring broader stakeholder participation: It is essential to involve a wide range of stakeholders in the development and implementation of rate standardization policies to increase their effectiveness and acceptance.
Mains PYQ
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Glycemic Index of Diets: Importance beyond Diabetes Control
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Glycemic Index, Glycemic Load
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
Understanding and managing Glycemic Index (GI) in diets is crucial for promoting long-term health and mitigating the risk of chronic diseases.

What is Glycemic Index (GI)?
- Prof. David Jenkins of the University of Toronto introduced Glycemic Index (GI) in 1981.
- GI measures how quickly a food raises blood glucose levels compared to a reference food, typically glucose or white bread, which is assigned a value of 100.
GI Classification and Glycemic Load (GL):
- Multiplying GI by the amount of carbohydrate consumed gives the Glycemic Load (GL).
- Accordingly, foods are classified as:
- Low GI (below 55): Brown rice, steel-cut oats, legumes (such as lentils and chickpeas), most fruits (like apples, berries, and oranges), vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
- Medium GI (56-69): Whole wheat products, such as whole wheat bread and pasta, some types of rice (like basmati rice), and certain fruits like pineapple and mango.
- High GI (70 or above): Refined carbohydrates and sugary foods such as white rice, white bread, refined flour products, potatoes, sweetened drinks (like soda), candies, cookies, and sugary snacks.
Debate and Perspectives:
- The Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study, spanning 20 countries including India, revealed the link between high GI diets and cardiovascular events and mortality.
- Evidence supports the association between high GI diets and increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and mortality.
Relevance to India
- In South Asia, where diets are rich in high GI foods like white rice, efforts to reduce GI and GL are crucial.
- Lowering GI and GL can help prevent not only diabetes but also premature cardiovascular disease, which is prevalent in India.
PYQ:[2011] Regular intake of fresh fruits and vegetables is recommended in the diet since they are a good source of antioxidants. How do antioxidants help a person maintain health and promote longevity? (a) They activate the enzymes necessary for vitamin synthesis in the body and help prevent vitamin deficiency (b) They prevent excessive oxidation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body and help avoid unnecessary wastage of energy (c) They neutralize the free radicals produced in the body during metabolism (d) They activate certain genes in the cells of the body and help delay the ageing process |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
IRDAI removes Age Bar for purchasing Health Insurance
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IRDAI, Evolution of India’s Insurance Industry , LIC
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) abolished the age limit for purchasing health insurance policies, effective April 1.
- Individuals aged above 65 were ineligible previously for new health insurance policies.
About Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI)
- IRDAI is the apex regulatory body overseeing the insurance sector in India.
- It is an autonomous entity responsible for regulating and developing the insurance sector in India.
- It was established under the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999. It was formed on April 19, 2000.
- Headquarters: Located in Hyderabad, Telangana.
- Composition:
- IRDAI is a 10-member body including the chairman, five full-time and four part-time members appointed by the government of India.
- The authority is supported by various departments and divisions responsible for different aspects of insurance regulation, including life insurance, non-life insurance, reinsurance, and actuarial matters.
Regulatory Functions
IRDAI’s primary role is to regulate and promote the insurance industry in India through:
- Licensing and registration of insurance companies and intermediaries.
- Framing regulations and guidelines for insurance operations.
- Protecting the interests of policyholders.
- Promoting fair competition and innovation in the insurance sector.
- Monitoring the financial performance and solvency of insurance companies.
- Resolving disputes between insurers and policyholders.
- Promoting insurance awareness and education among the public.
Insurance Sector of India: A Timeline
|
PYQ:[2012] Consider the following:
The employees of which of the above can have the ‘Social Security’ coverage under Employees’ State Insurance Scheme? (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 4 only (c) 1, 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The advent of a holistic approach to ‘one health’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National One Health Mission; Lumpy Skin disease;
Mains level: Healthcare in India; National One Health Mission;
Why in the news?
In the past, we have seen that there is interdependence between humans, animals, and the environment has been made increasingly evident with the emergence of pandemics such as COVID-19.
- It is not just humans who are affected by pandemics but also livestock — an example being the outbreak of lumpy skin disease that has spread across countries.
Why an integrated idea like the ‘One Health’ Mission is needed?
One Health is an interdisciplinary approach that recognizes the interconnectedness of human health, animal health, and environmental health. It emphasizes collaboration across various sectors, including medicine, veterinary science, ecology, and public health, to address health challenges comprehensively.

Key features of National One Health Mission:
- Intersectoral Collaboration: The mission aims to coordinate, support, and integrate all existing One Health initiatives in the country, including the Ministries of Health and Family Welfare, Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Environment, and Science and Technology
- Integrated Disease Surveillance: The mission implements integrated disease surveillance within and across human, animal, and environmental sectors to address communicable diseases, including zoonotic diseases, and improve overall pandemic preparedness and integrated disease control.
- Consolidation of data: The mission creates an integrated, science-based environment where researchers from various disciplines can use laboratories as necessary and generate requisite inputs for One Health Science, including databases and models with a consolidated approach of ecologists, field biologists, epidemiologists, and other scientists.

Challenges in National One Health Mission
- Limited Database: There have been limited efforts to develop databases and models with a consolidated approach of ecologists, field biologists, epidemiologists, and other scientists to understand and respond to the drivers that threaten health and optimize the effectiveness of public health systems in achieving these goals within each sector.
- Lack of Awareness and Understanding: The lack of awareness and understanding of the One Health concept among stakeholders hinders collaborative efforts required to address complex public health issues
- Funding Constraints: Funding constraints are a significant barrier to implementing One Health interventions, especially in low- and middle-income countries that may need more resources to invest in One Health initiatives
Conclusion: To address challenges in the National One Health Mission, efforts must focus on enhancing data collection, raising awareness among the stakeholders, and securing adequate funding. These measures are essential for effective implementation and holistic health management.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Health Sector can’t ignore Telemedicine’s Green Gains, study shows
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Teleophthalmology
Mains level: Technology in News; Significance of teleophthalmology
Why in the news?
Recently a study by researchers at the L.V. Prasad Eye Institute (LVPEI), Hyderabad, has found that around 70-80% of people who visit an Eye Hospital can benefit from teleconsultations because their problems aren’t serious enough to require attention at a hospital.
Key points as report:
- Telemedicine in High-Income Countries: Studies in high-income countries have shown that telemedicine is both patient- and environment-friendly for delivering healthcare services.
- Carbon Emissions from the Healthcare Sector: According to the International Comparison of Healthcare Carbon Footprints analysis, India’s healthcare sector emitted 74 million tonnes of carbon dioxide in 2014, around 3% of India’s total emissions of the gas that year.
- Carbon Neutrality in Healthcare: The healthcare sector should aim for carbon neutrality to mitigate its environmental impact. Teleophthalmology is cited as an efficient and effective tool to help achieve this goal, as demonstrated by the lead author’s remarks.
The teleophthalmology process:

What are Telemedicine’s Green Gains?
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Teleophthalmology significantly reduces the need for patients, especially those from rural areas, to travel long distances to access healthcare services. This leads to a substantial reduction in carbon dioxide emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Economic Gains: Teleophthalmology results in significant cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems. Patients save money on travel expenses
- Easy Accessibility: Teleophthalmology improves access to eye care services, especially for individuals living in remote or rural areas where access to healthcare facilities is limited. It allows patients to receive timely consultations without the need for extensive travel.
- Targeted Care Gains: Teleophthalmology is particularly beneficial for patients with minor eye problems like mild refractive errors or regular preventive eye check-ups. It enables healthcare providers to target specific demographics and deliver personalized care more effectively.
Conclusion: The recent study highlights teleophthalmology’s potential in reducing carbon emissions and improving accessibility to eye care, emphasizing its role in achieving carbon neutrality and delivering cost-effective, targeted healthcare services, particularly for minor eye issues.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Implementing Universal Health Coverage
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Government Schemes and Policies in News; National Health Policy, 2017;
Mains level: Social Issues and Justice; Health Issues in India; Government Schemes and Policies in News;
Why in the news?
On the eve of World Health Day (7th April), many countries aim to implement UHC (Universal Health Coverage) in the same way as India introduced its National Health Policy, in 2017. However, there exist challenges in India too for implementing it.
Background:
- On December 12, 2012, the UN General Assembly unanimously endorsed a resolution urging countries to accelerate progress towards UHC.
- In India, the high-level expert group report, submitted to the Planning Commission in 2011, outlined a government intent to increase public financing for health to 2.5% of India’s GDP during the 12th Plan (2012-17).
BACK2BASICS:About National Health Policy, 2017:It aims to achieve Universal Health Coverage and deliver quality healthcare services to all at an affordable cost. It focuses on improving health status through preventive, promotive, curative, palliative, and rehabilitative services with an emphasis on quality. |
What are the challenges in the Implementation of UHC in India?
- Federal Issue: Health is a state subject in India, but UHC policy is envisaged at the national level. This can lead to challenges in coordination between the central government and state governments.
- While the Directive Principles of State Policy provide a basis for the right to health, the absence of a specific constitutional guarantee may create challenges in ensuring consistent and enforceable healthcare rights.
- Migrant Population and Urban Slums: Due to issues such as overcrowding, poor sanitation, and limited infrastructure, a significant portion of the population living in urban slums face issues with the availability and accessibility of Primary Health Services is hard to provide.
- Lack of Finance: Implementing UHC requires significant financial resources. Reducing out-of-pocket expenditure and strengthening primary healthcare services necessitate substantial investments, which may strain government budgets and require innovative financing mechanisms to ensure sustainability.
- Lack of Healthcare Infrastructure and Human Resources: India faces shortages in both infrastructure and human resources, particularly in rural and underserved areas, which hinders efforts to improve healthcare accessibility and quality.
- The vicious cycle of poverty: The vicious cycle of poverty and poor health perpetuates inequality in various spheres of life which eventually leads to the accessibility of health services.
Suggestive Measures:
- Addressing Urban Migrants’ Health Needs: Establishing mobile healthcare units or clinics that can reach migrant communities in urban and peri-urban areas, providing essential primary healthcare services.
- Reducing Out-of-Pocket Expenditure: Simplifying the reimbursement process by digitizing healthcare payment systems and integrating them with government identification or mobile banking platforms to facilitate easy reimbursement for medical expenses.
- Creating Inclusive Health Systems: Introducing multilingual and culturally sensitive health information materials and services to bridge language barriers and ensure accessibility for diverse urban populations.
- Implementing Community-Based Primary Healthcare: Establishing community health centers or clinics in urban and peri-urban areas staffed by trained community health workers who can provide basic healthcare services and referrals.
Conclusion: Building Constitutional backing, enhancing coordination, and federal with fiscal consensus with adequate infrastructure in addressing urban health needs can improve the reach of the Universal Health Program in India.
Mains PYQ
Q Public health system has limitation in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA), AB-PMJAY
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
This newscard is an excerpt from an explainer published in the PIB.
Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA)
- ABHA, an integral part of the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), serves as a link for all health records of an individual.
- It is a sub-component of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission launched in September 2021.
- It is a 14-digit id employed to uniquely identify individuals, verify their identity, and connect their health records (with their consent) across various systems and stakeholders.
Features of ABHA
- Cashless Transactions: ABHA enables cashless transactions for eligible beneficiaries, reducing the financial burden during medical emergencies.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): It integrates electronic health records, facilitating storage, and retrieval of patient information for streamlined healthcare delivery.
- Portability: ABHA accounts are portable across various healthcare providers under the Ayushman Bharat scheme, ensuring seamless access to services.
- Real-time Monitoring: Incorporating real-time monitoring mechanisms to track fund utilization, ABHA ensures efficient allocation and prevents misuse.
Various Components
- Beneficiary Identification: ABHA involves the identification and registration of eligible beneficiaries under the Ayushman Bharat scheme, assigning a unique health identification number (UHID).
- Funds Management: It manages the allocation and disbursement of funds for healthcare services, ensuring prompt and secure transfers.
- Claim Settlement: ABHA processes and settles claims submitted by healthcare providers, verifying authenticity, and disbursing payments.
- Audit and Oversight: Incorporating audit mechanisms to monitor fund utilization, ABHA ensures compliance with regulations and maintains system integrity.
Back2Basics: Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY)
| Details | |
| Umbrella Scheme |
|
| Launch Year | 2018 |
| Components |
|
| Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) |
|
| Coverage |
|
| Beneficiaries | Identified through Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data |
| Funding |
|
| Nodal Agency | National Health Authority (NHA)
State Health Agency (SHA)
|
PYQ:2021: “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse.
Practice MCQ:Consider the following statements about the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY): 1. 3 days pre-hospitalisation and 15 days post-hospitalisation. 2. Includes diagnostic care and expenses on medicines. 3. No restriction on family size, age, or gender. 4. Beneficiaries are identified from national family health survey. How many of the above discussed features is/are correct? (a) One (b) Two (c) Three (d) Four |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Two States: a comparison on access to life-saving C-sections
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Health Governance;
Why in the News?
The study released by IIT Madras highlights the concerns related to high rates of C-section deliveries among women in Tamil Nadu, particularly in private hospitals.
- This indicates the necessity for corrective measures to address the situation.
What is a Caesarean section?It is also known as C-section or cesarean delivery, which is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother’s abdomen. It is often performed because vaginal delivery would put the mother or child at risk. |
Changes in the share of births delivered by C-sections in public and private sector hospitals in India, Tamil Nadu, and Chhattisgarh between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
- High C-section Rate in Public Hospitals: In public sector hospitals in Tamil Nadu, nearly 40% of women underwent C-sections during 2019-21.
- High C-section Rate in Private Hospitals: Close to 64% of women underwent C-sections in private sector hospitals in Tamil Nadu during 2019-21, which is significantly higher than both the national average of around 50% and Chhattisgarh’s rate of 59%.
- Higher than the National Average: The rate of C-section deliveries in Tamil Nadu’s public sector hospitals is substantially higher than the national average, which is approximately 16%. Additionally, it surpasses the rate in Chhattisgarh, where it stands at 10%.
Reasons behind the increase in C-section rates despite a decrease in pregnancy complications:
- Regional Disparities: In Chhattisgarh, the likelihood of a woman undergoing a C-section in a private hospital is ten times higher than in a public hospital. This suggests potential disparities in access to high-quality healthcare services between public and private sectors, with implications for maternal health outcomes.
- Socioeconomic Factors: The study assumes that poorer households opt for public hospitals while richer households prefer private ones for deliveries. This socioeconomic divide may contribute to inequitable access to healthcare services at the national level.
- Higher Likelihood in Private Health Facilities: Women delivering in private health facilities are more likely to undergo C-sections compared to those in public facilities, with a notable disparity observed in Chhattisgarh.
- Maternal Age and Weight Status: Factors such as maternal age (35-49) and overweight status increase the likelihood of C-section delivery.
- High gap between Poor and Rich: In India, the gap in C-section prevalence between the poor and non-poor narrowed in private facilities, but Tamil Nadu exhibited a concerning trend where a higher percentage of the poor underwent C-sections compared to the non-poor.
Recommendations by the World Health Organization (WHO): Cesarean delivery rates should ideally not exceed 10-15% to achieve the lowest maternal and neonatal mortality rates. When C-section rates go beyond 10%, there is no significant decrease in maternal mortality. In 2021, global C-section rates surpassed 20%, and they are projected to increase to 30% by 2030.
Conclusion: Access to C-sections in Tamil Nadu shows disparities, with high rates in both public and private hospitals. Addressing regional, and socioeconomic factors and adhering to WHO recommendations are crucial for equitable maternal healthcare.
PYQ Mains
Q Appropriate local community level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The ART of India’s HIV/AIDS response
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HIV Drugs
Mains level: Objectives of India's National AIDS Control Programme (NACP)
Why in the news?
On April 1, 2004, the Indian government launched Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) for Persons living with HIV (PLHIV). This decision has been one of the most successful .
Emergence of HIV drugs
- First Antiretroviral Drug Approval: In March 1987, the US FDA approved the first antiretroviral drug, AZT (zidovudine), offering a glimmer of hope for treatment.
- Additional Drug Approvals: Three more antiretroviral drugs were approved shortly after in 1988, expanding treatment options for HIV/AIDS patients.
- Introduction of Protease Inhibitors: A significant milestone occurred in 1995 with the introduction of protease inhibitors, a new class of antiretroviral drugs.
The evolution to free ART
- Millennium Summit Declaration: In 2000, world leaders at the UN General Assembly’s Millennium Summit set a goal to stop and reverse the spread of HIV.
- Formation of the Global Fund: The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria was established in 2002, advocating for universal access to HIV prevention, treatment, care, and support services.
- High HIV Prevalence in India: In 2004, India had an estimated 5.1 million PLHIV, with a population prevalence of 0.4%. However, very few were receiving ART, with only 7,000 PLHIV on treatment by the end of the year.
- Free ART Initiative: The Indian government’s decision to provide free ART to all adults living with HIV in 2004 was groundbreaking. This initiative aimed to address the barriers of cost and geographical access to treatment.
- Expansion of ART Facilities: Over two decades, the number of ART centers in India expanded significantly, from less than 10 to around 700. Additionally, 1,264 Link ART centers have provided free ART drugs to approximately 1.8 million PLHIV.
- ART Eligibility Criteria Evolution: The criteria for initiating ART evolved over the years, starting from CD4 count less than 200 cells/mm3 in 2004, to less than 350 cells/mm3 in 2011, and less than 500 cells/mm3 in 2016. Finally, in 2017, the “Treat All” approach was adopted, initiating ART regardless of CD4 count.
- Rapid ART Initiation Policy: In 2021, India adopted a policy of rapid ART initiation, starting individuals on treatment within seven days of HIV diagnosis, and sometimes even on the same day. This swift initiation aimed to improve treatment outcomes and prevent transmission.
- Complementary initiatives to stop the HIV epidemic: Provision of free diagnostic facilities; attention on prevention of parent to child transmission of HIV (PPTCT) services; prevention, diagnosis and management of opportunistic infections including management of co-infections such as tuberculosis (TB).
Objectives of India’s National AIDS Control Programme (NACP) phase 5 by 2025
Ambitious 95-95-95 Targets: The NACP phase 5 sets ambitious targets known as the 95-95-95 targets, aligned with global targets agreed upon by UNAIDS. These targets aim for:
- 95% of all people living with HIV to know their HIV status.
- 95% of all people diagnosed with HIV infection to receive sustained antiretroviral therapy (ART).
- 95% of all people receiving antiretroviral therapy to achieve viral suppression.
- These targets are aligned with global targets agreed by the UNAIDS.
Challenges
- Delayed Enrolment to ART Facilities: Late presentation poses challenges to timely initiation of treatment and optimal disease management.
- Missed doses : Patients often start feeling better after initiating ART, leading to missed doses or discontinuation of treatment that lead to drug resistance
Measures
- Sustained Supply and Availability of ART: Ensuring consistent and uninterrupted access to ART drugs across all regions of the country
- Private Sector Engagement: Enhancing engagement with the private sector in the care of PLHIV .
- Training and Capacity Building: Continuous training and capacity building of healthcare staff are essential to ensure high-quality service delivery.
- Integration with Other Health Programs: Strengthening integration with other health programs, such as hepatitis, non-communicable diseases (NCDs
Conclusion
India’s ART initiative, launched in 2004, has been pivotal in combating HIV/AIDS. With evolving criteria, rapid initiation policies, and ambitious targets, challenges persist, but measures like sustained supply, private sector engagement, and training are being implemented.
Mains PYQ
Q What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? ( UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Hepatitis B: Everything you need to know
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hepatitis B
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- A recent study by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, revealed alarming deficiencies in public knowledge (transmission, effects & vaccination) about Hepatitis B in India.
- Despite the availability of a vaccine for over 30 years, HBV infection rates remain high in India, with prevalence estimates ranging from 2% to 8% and approximately 37 million carriers nationwide.
About Hepatitis
- Hepatitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the liver.
- It can be caused by various factors, including viral infections (hepatitis viruses), alcohol consumption, certain medications, toxins, autoimmune diseases, and metabolic disorders.
| Hepatitis A | Hepatitis B | Hepatitis C | |
| Causative Virus | Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) | Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) | Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) |
| Transmission | Fecal-oral route (contaminated food/water) | Blood and body fluids (unsafe sex, sharing needles) | Blood-to-blood contact (sharing needles, transfusions) |
| Vaccine Available | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Chronic Infection | No (usually acute) | Yes (can become chronic) | Yes (often becomes chronic) |
| Symptoms | Mild flu-like symptoms, jaundice | Variable, from none to severe symptoms | Often asymptomatic, but can lead to liver damage |
| Chronic Complications | None | Cirrhosis, liver cancer | Cirrhosis, liver cancer |
| Preventable by Vaccine | Yes | Yes | No |
| Treatment | Supportive care | Antiviral medications | Antiviral medications |
PYQ:
Which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019) (a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV. (b) Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine. (c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses are several times more than those infected with HIV. (d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013) 1. Chikungunya 2. Hepatitis B 3. HIV-AIDS Select the correct answer using the codes given below. (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3
Practice MCQ:
Consider the following statements regarding Hepatitis C virus: 1. It is spread mainly through contaminated water and food. 2. It primarily affects the functioning of respiratory system. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) Only 1 (b) Only 2 (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Global Spread of H5N1 Bird Flu
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: H5N1 Bird Flu
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- Since 2020, the highly pathogenic H5N1 bird flu has been spreading globally, posing a significant threat to both birds and mammals.
H5N1 Bird Flu: Details
- H5N1 originated from a virus outbreak on a goose farm in China in 1996 and has since evolved into a highly pathogenic strain.
- The virus quickly spread from Europe to Africa, Asia, North America, and South America, and most recently, it reached mainland Antarctica.
- H5N1 is a subtype of the influenza A virus that causes severe respiratory disease in birds, known as avian influenza or “bird flu”.
- Influenza A viruses are classified by subtypes based on the properties of their surface proteins, with H5N1 being one subtype.
How widespread is it?
- The virus has affected birds in over 80 countries, resulting in mass culling of poultry and wild birds.
- Furthermore, it has now begun infecting mammals, including seals, sea lions, and marine mammals.
- While humans rarely contract bird flu, those at risk are typically individuals who have extensive contact with infected birds at poultry farms.
- Bird flu first broke out in Maharashtra in 2006.
- The H5N1 virus led to the culling of millions of poultry so as to contain the virus. But it has resurfaced from time to time.
Impact on Animals
- Bird Species Affected: Numerous bird species, including Great Skuas and Barnacle Geese, have experienced significant mortality rates due to H5N1.
- Endangered Species Threatened: Endangered birds like the California condors have been severely affected, with a notable percentage of the population succumbing to the virus.
- Mammalian Casualties: H5N1 has crossed species barriers, infecting mammals such as foxes, pumas, skunks, and marine mammals like sea lions and dolphins.
- Devastating Consequences: Mass mortalities of marine mammals, particularly elephant seals, have been reported, raising concerns about the long-term ecological impact.
Factors behind Spread
- Climate Change: Some scientists attribute the large-scale spread of bird flu to climate change, which alters bird behavior and facilitates the transmission of the virus.
- Warmer Seas: Warmer sea temperatures have weakened marine mammal populations, making them more susceptible to disease outbreaks.
PYQ:
2015: H1N1 virus is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to which one of the following diseases? (a) AIDS (b) Bird flu (c) Dengue (d) Swine flu
Practice MCQ:How many of the given statements about H5N1 Virus is/are correct? 1. It is a type of influenza virus causing highly infectious, respiratory disease in birds. 2. It is highly contagious in humans. 3. Seals, sea lions, and other marine mammals are vulnerable to this Virus. Select the correct codes from below – (a) One (b) Two (c) Three (d) None |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
On the resurgence of Mumps in Kerala
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Science and Tech; Diseases
Mains level: Science and Tech; Diseases; Measures to control
Why in the news?
Mumps, an acute viral infection that historically affects children, has been spreading like wildfire in Kerala, for the past few months.
Context:
- Despite being a vaccine-preventable disease, mumps has never been a part of the Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP) because of the disease’s no-mortality profile and the perception that it has low public health significance.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), vaccination strategies targeting mumps control should be closely integrated with existing measles elimination and rubella control.
About: Mumps is an airborne viral disease primarily affecting children and adolescents. It manifests with symptoms like fever, headache, and painful swelling of the salivary glands, particularly the parotid glands on both sides of the face.
Is it a cause for concern?
- Self-Limiting Disease: Mumps is described as a self-limiting disease, meaning it typically resolves on its own with rest and symptomatic management within about two weeks.
- Underreporting: Due to approximately half of infected children developing classical symptoms and around 30% remaining asymptomatic, many cases of mumps go unreported. This suggests that reported cases are likely a significant underestimation of the actual prevalence in the community.
- Public Health Perspective: Historically, measles has been prioritized in public health efforts due to its potential for severe morbidity and mortality, overshadowing the attention given to mumps.
- Emerging Concerns: Despite being less prioritized, recent reports indicate a surge in mumps cases, including complications such as encephalitis, epilepsy, aseptic meningitis, and acute pancreatitis, particularly at Kozhikode Medical College hospital.
- Impact on Reproductive Health: Mumps can affect the gonads (reproductive glands) in both males and females. In males, it poses the rare but significant risk of infertility or reduced sperm count in the long term.
Why is the mumps vaccine not part of the national immunization schedule?
- Lack of Mortality: Mumps typically does not result in fatalities, further contributing to the belief that it may not warrant inclusion in routine vaccination schedules.
- Underestimation of Public Health Significance: Despite arguments from organizations like the Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) that mumps’ public health significance is underestimated, there has been insufficient evidence or data to prompt its inclusion in national immunization programs.
- Poor Documentation and Lack of Studies: Limited documentation of clinical cases, complications, and follow-up data, as well as a scarcity of published studies on mumps, have hindered efforts to fully understand its impact and advocate for its vaccine inclusion.
- Absence of Nationally Representative Data: The lack of nationally representative data on the incidence of mumps in India makes it challenging to assess its burden accurately and advocate for vaccine inclusion based on epidemiological evidence.
- Limited Information on Long-Term Morbidity: While mumps is known to have some impact on reproductive organs, there is very little information available on its actual long-term morbidity profile, further complicating decisions regarding vaccine inclusion.
How can the current outbreaks be controlled?
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch comprehensive public awareness campaigns to educate the community about mumps, its symptoms, transmission, and the importance of isolation. Emphasize the significance of vaccination and maintaining good hygiene practices.
- Improve Immunization Coverage: Strengthen efforts to improve general immunization coverage, especially targeting unimmunized children and adolescents. Ensure accessibility to vaccination services in all communities.
- Strict Isolation Measures: Enforce strict isolation measures for mumps patients for the full three-week duration to limit disease transmission. Provide clear guidelines to healthcare facilities and schools on managing mumps cases and preventing spread.
- School Closure: Consider temporary closure of schools during outbreaks to prevent further transmission, especially if a significant number of cases are reported among students. Use the summer break as an opportunity to break the chain of transmission.
- Enhanced Surveillance and Reporting: Implement robust surveillance systems to promptly detect and report mumps cases. Ensure healthcare providers are vigilant in diagnosing and reporting suspected cases to public health authorities for timely intervention.
- Contact Tracing and Monitoring: Conduct thorough contact tracing of individuals who have been in close contact with confirmed mumps cases. Monitor them for symptoms and enforce isolation measures if necessary to prevent secondary transmission.
- Healthcare Provider Training: Provide training to healthcare providers on mumps diagnosis, management, and reporting protocols. Ensure they are equipped to identify and manage cases effectively.
- Community Engagement: Engage with community leaders, schools, and parents to encourage cooperation with control measures. Encourage individuals to seek medical care promptly if they develop symptoms suggestive of mumps.
Way Forward:
- Assessment of Vaccine Effectiveness: Despite the lack of studies on the effectiveness of the mumps vaccine in India, global data suggests that two doses of the MMR vaccine can provide protection ranging from 70% to 95%, provided that coverage is high.
- Integration with Measles and Rubella Control: The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends integrating mumps vaccination strategies with existing efforts for measles elimination and rubella control. This ensures a comprehensive approach to vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Consideration of Regional Factors: Evaluate regional factors influencing vaccine effectiveness, disease burden, and immunization coverage. Tailor vaccination strategies accordingly to address the specific needs and challenges faced in Kerala.
- Consultation with Experts and Stakeholders: Engage with public health experts, immunization specialists, and stakeholders to review the evidence, assess the impact of different vaccination strategies, and determine the most effective approach moving forward.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: Strengthen monitoring and surveillance systems to track mumps cases, vaccine coverage, and vaccine effectiveness. This data will be crucial for evaluating the impact of vaccination strategies and making informed decisions.
- Policy Decision: Based on the evidence and expert recommendations, make a policy decision regarding the inclusion of MMR vaccine in the Universal Immunization Programme. Consider factors such as vaccine availability, cost-effectiveness, and logistics.
Conclusion: Addressing the resurgence of mumps in Kerala necessitates a comprehensive approach, including vaccination integration, public awareness, strict isolation measures, and policy review guided by expert consultation and regional considerations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Why has Karnataka banned certain coloring agents?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Colouring agent, harmful chemical
Mains level: Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
Why in the news?
- Karnataka has become the third state in South India to prohibit the use of specific coloring agents in cotton candy and gobi manchurian due to their identified harmful effects.
Context-
- While the Government plans to create awareness among manufacturers, it has also urged consumers to be aware of what they are consuming.
- The Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 stipulates a fine of not less than ₹10 lakh and a jail term of a minimum of seven years, extending to life imprisonment, against those using banned chemical substances in food products.
What did the survey results show?/Key findings from the sample testing
- Presence of Harmful Chemicals: Laboratory tests revealed the presence of harmful chemicals in many samples collected from the state.
- Cotton Candy Samples: Out of 25 cotton candy samples collected, 15 were found to be unsafe as they contained added colors, while the remaining 10 were deemed safe as they were made without added colors.
- Gobi Manchurian Samples: Among the 171 samples of gobi manchurian collected, 107 were declared unsafe due to the presence of added colors, while 64 were considered safe as they did not contain added colors.
What were the harmful chemicals?
- Harmful Chemicals: The unsafe samples of cotton candy contained traces of sunset yellow, tartrazine, and rhodamine-b, while unsafe gobi Manchurian samples had tartrazine, sunset yellow, and carmoisine. Rhodamine-b, a suspected carcinogen, is already banned.
- Restrictions on Tartrazine: Although tartrazine is an approved artificial food color, there are restrictions on its usage. It can only be used in specific packed food items, with prescribed amounts. It cannot be used in freshly prepared food items.
- Health Concerns: The Food Safety Commissioner emphasized that prolonged consumption of snacks containing artificial colors can lead to severe diseases like cancer, highlighting the importance of the ban in safeguarding public health.
What are the Penalties?
- Prohibition on Artificial Colors: Rule 16 of the Food Safety and Standards Act prohibits the use of artificial colors in the preparation of gobi manchurian.
- Approved Limits for Food Colors: While certain food colors are allowed within approved limits, non-permitted colors like rhodamine-b should not be used in the preparation of cotton candy.
- Penalties for Offenders: Violators face severe penalties, including cancellation of licenses for commercial activities, hefty fines, and imprisonment. The Food Safety and Standards Act specifies a minimum fine of ₹10 lakh and a jail term of at least seven years, which can extend to life imprisonment, for those found using banned chemical substances in food products.
Way Forward:
- Enforcement and Monitoring: Health safety officials will likely conduct random checks to ensure compliance with the ban on harmful chemicals and artificial colors.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: The government will continue its efforts to raise awareness among manufacturers and consumers regarding the risks associated with harmful chemicals and artificial colors in food products.
- Regulatory Review: There might be a review of existing regulations and standards related to food safety to further strengthen controls and ensure comprehensive coverage of potentially risky food items beyond gobi manchurian, such as kebabs, that may use coloring agents.
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: Collaboration between government authorities, food manufacturers, and other stakeholders in the food industry will be crucial to implement and enforce the ban effectively. This may include consultations, partnerships, and dialogues to address challenges and ensure compliance with regulations.
Conclusion: Karnataka banned certain coloring agents in response to findings of harmful chemicals in food samples. Strict penalties and enforcement measures are in place, alongside awareness campaigns and collaboration with stakeholders to ensure compliance and safeguard public health.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Changing cancer nomenclature can improve treatment outcomes: doctors
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Genetic causes behind Cancers
Mains level: Menace of Cancer in India and the World
Why in the news?
Physicians have expressed the necessity to categorize Cancers based on their genetic characteristics.
Context:
- An updated classification system could aid patients in comprehending the reasoning behind their treatment.
- While two individuals may share the same type of cancer, their therapies could vary due to differences in the biological mechanisms driving their tumors.
What motivates the need for change?
- Not limited to cancers of a single organ: With technological improvements, doctors are also able to find which genetic mutations are responsible for a tumor in many cases and target them with drugs.
- All cancers from the same organ don’t always share the same mutations, and these mutations aren’t limited to cancers of a single organ
- Access life-saving drugs sooner: This development in precision oncology requires cancers to be classified based on their molecular and genetic characteristics rather than the organ in which they originate, a team of researchers from France has written in a paper.
- This way, according to them, cancer patients can also access life-saving drugs sooner. Oncologists spend a lot of time testing new drugs in clinical trials in a sequential manner, leading to “delay in treatment access”.
Has sequential testing caused delays?
-
- A 2012 clinical trial conducted in the U.S. explored the efficacy of the drug nivolumab across various cancer types, including melanoma and kidney cancer. Nivolumab targets a specific protein receptor found in certain tumors, and it showed promising results by alleviating symptoms in individuals with tumors expressing this protein
- Challenges Due to Traditional Organ-Based Classification-
-
- Hindered by the traditional classification-Despite promising outcomes, the next logical step of testing nivolumab in individuals with tumors expressing the protein, regardless of cancer origin, was hindered by the traditional classification of cancers based on their organ of origin (e.g., breast, kidney, lung).
- Multiple trials needed: As a consequence, researchers were compelled to conduct separate trials for each type of cancer, leading to significant delays in drug accessibility for patients with tumors expressing the targeted protein.
- Time taking trails: Each trial requires substantial time and resources, from recruitment to data analysis, prolonging the process of drug approval and availability for specific cancer subtypes.
Significance of categorizing cancers based on their genetic characteristics-
- Faster drug development and availability: By targeting specific genetic mutations rather than specific cancer types, clinical trials for drugs can encompass all cancer types with those mutations. This approach potentially expedites the trial process, leading to faster drug development and availability.
- Reduces confusion among the patient: The revamped classification system not only accelerates clinical trial timelines but also enhances patient understanding of treatment rationale. Patients often receive different therapies for the same cancer due to diverse underlying biological mechanisms. Aligning cancer names with biological mechanisms reduces confusion and helps patients comprehend the reasoning behind their treatment plans.
- Personalized treatment: Physicians, including Dr. Jobanputra, emphasize the importance of educating patients about the molecular characteristics of their cancers. As the approach to cancer treatment becomes more personalized, understanding these molecular aspects becomes crucial as they directly impact prognosis and treatment costs.
- Reducing the timing in trial-naming cancers based on their biological characteristics rather than their anatomical origin can significantly reduce the time required to conduct clinical trials. This shift eliminates the need for separate trials for each cancer type defined by organ of origin, streamlining the research process
Challenges in Implementing the Proposed Cancer Classification Change:
- Limited Access to Genetic Testing: The accessibility and affordability of genetic testing are major hurdles, particularly in regions like India where many patients cannot afford these tests.
- Without widespread access to such tests, implementing a classification system based on molecular alterations becomes impractical.
- Financial Barriers to Genetic Testing: The cost of genetic testing in Indian labs and abroad is prohibitively high for many patients, further exacerbating the issue of limited access.
- Addressing these financial barriers is crucial for ensuring equitable access to precision oncology.
- Lack of Patients in Clinical Trials: Clinical trials based on molecular signatures require a significant number of patients with each type of cancer to produce meaningful results.
- Without adequate representation across cancer types, there is a risk of generalizing results, limiting the effectiveness of precision oncology approaches.
- Time-taking Process: Transitioning to a new diagnostic nomenclature based on molecular alterations will likely occur gradually and require careful implementation.
- While the proposed change has the potential to improve drug accessibility, its full realization will take time and concerted effort to overcome various challenges.
Conclusion: Categorizing cancers based on genetic characteristics can streamline treatment, improve drug accessibility, and enhance patient understanding. However, challenges like limited access to genetic testing and lack of patient representation in trials must be addressed.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Understanding dialysis outcome patterns in India through a nationwide study
Why in the News?
Recently, there are some findings from a nationwide private haemodialysis network’, the Lancet Regional Health-Southeast Asia, on the survival of patients receiving haemodialysis in India
Context:
- India has amongst the highest number of patients receiving chronic dialysis, globally estimated at around 1,75,000 people in 2018. Daily, the number of patients on dialysis has been increasing.
- The launch of the National Dialysis Service in 2016 to improve access, and ongoing efforts to develop affordable dialysis systems, are all underlined by the rising incidence of end-stage renal disease in the country.
What is Hemodialysis?A machine filters wastes, salts and fluid from your blood when your kidneys are no longer healthy enough to do this work adequately. |
Key Highlights as per study:
- Survival with Centre- and Patient-Level: The study found that both centre- and patient-level characteristics are associated with survival rates among patients undergoing haemodialysis.
- Unexplained Variation Between Centres: Despite considering various centre-based characteristics, there remained unexplained variations in survival rates between dialysis centres across India. This suggests that factors beyond those accounted for in the study may influence patient outcomes.
- Large Sample Size: The study included a substantial sample size of over 23,600 patients undergoing haemodialysis at any centre in the NephroPlus network between April 2014 and June 2019. This large sample size enhances the robustness of the study’s findings.
- Primary Outcome: The primary outcome of the study was all-cause mortality, measured from 90 days after patients joined a center. This outcome measure provides valuable insights into patient survival rates over time following the initiation of haemodialysis treatment.
- Consideration of Individual-Level Variables: The study accounted for various individual-level variables such as sex, smoking status, medical history (e.g., diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, hepatitis B, hepatitis C), education level, monthly household income, dialysis frequency, and vascular access. These variables offer comprehensive insights into patient characteristics and their impact on survival rates.
- Evaluation of Centre-Level Variables: Centre-level variables, including the frequency of nephrologist visits, number of beds, number of staff, and number of patients, were also considered. These variables help assess the influence of center resources and practices on patient outcomes.
What were the measuring differences?
- Limited Data: The only significant study conducted previously in Andhra Pradesh used claims data from a publicly-funded insurance scheme between 2008 and 2012. It included 13,118 beneficiaries and reported a 10.2% mortality rate within six months of starting hemodialysis.
- Absence of Centre-Level Effects: The previous study did not consider center-level effects on survival, limiting the understanding of differences in survival rates between dialysis centers, as observed in other countries.
- Gaps in Understanding: Major gaps existed in understanding dialysis outcome patterns in India due to the absence of comprehensive studies, hindering efforts to improve patient care.
- Lack of National Benchmark: There was no established national benchmark for survival rates among patients undergoing dialysis in India at the time of the study.
- Need for Further Research: The study highlighted the importance of conducting more extensive research to fill the gaps in knowledge and establish benchmarks for dialysis outcomes in India.
What is the recent issue related to the Mortality rate?
-
- Administrative challenges associated with Mortality:
- Impact of Centre-Level Factors: Including center-level factors such as staffing, care processes, and patient volume in the analysis reduced the variability in survival rates across dialysis centers by 31%. This suggests that center-level characteristics play a significant role in influencing patient outcomes and survival rates.
- Survival Range: After adjusting for multi-level factors, the estimated 180-day survival among patients undergoing hemodialysis ranged between 83% and 97%. This variability indicates differences in survival outcomes across dialysis centers in India.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Patients attending rural dialysis centers experienced a 32% higher mortality rate compared to those at urban centers. This disparity underscores the unique challenges faced by rural healthcare facilities in providing hemodialysis services.
- Administrative challenges associated with Mortality:
- Patient Characteristics Associated with Mortality:
-
- Catheter-Based Vascular Access: Patients using catheter-based vascular access had a higher mortality rate compared to those using arteriovenous fistula or graft access.
- Financial Support: Patients receiving financial support for dialysis treatment through government panel schemes or private insurance had a lower mortality rate compared to those paying out-of-pocket.
- Dialysis Vintage: There was an inverse relationship between mortality rate and dialysis vintage, with patients receiving dialysis for at least a year before joining a center experiencing a 17% lower mortality rate than those starting dialysis less than 30 days before joining.
- Presence of Diabetes: The presence of diabetes was associated with a higher mortality rate among hemodialysis patients.
Way Forward:
- Establishment of National Benchmark: The study proposes the first national benchmark for survival among dialysis patients in India. This benchmark will serve as a reference point for evaluating the quality of care and outcomes across dialysis centres in the country.
- Ongoing Quality Improvement Programs: As dialysis access continues to expand in India, ongoing quality improvement programs are crucial for ensuring that patients receive the best possible care and experience optimal outcomes at the point of care.
- Collaborative Quality Improvement System: The authors emphasize the need for a collaborative quality improvement system across the country to address the increasing demand for dialysis services. This system should involve stakeholders at various levels of healthcare delivery to enhance standards of care and patient outcomes.
- Understanding Multilevel Effects: It is essential to understand the multilevel effects of both centre- and patient-level characteristics on dialysis outcomes. Establishing national standards for dialysis outcomes in India requires comprehensive insights into these factors to drive improvements in care delivery.
- Comparison and Monitoring: Establishing national benchmarks enables comparison and monitoring of dialysis centres’ performances over time. This approach facilitates the identification of variations in practice patterns and outcomes, paving the way for targeted interventions and improvements in healthcare delivery.
Conclusion: The nationwide study on haemodialysis outcomes in India highlights disparities and the need for standardized care. Establishing national benchmarks, ongoing quality improvement, and collaborative efforts are essential for enhancing dialysis care and patient outcomes.
Mains PYQ-
Q- Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is the HbA1C Test for Diabetes?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HbA1C Test, Diabetes (Type-1 and 2)
Mains level: NA

Why in the news-
- India faces a significant burden of diabetes, with an estimated 10.13 crore people affected and an additional 13.6 crore individuals classified as pre-diabetic.
- One of the most commonly-used tests to diagnose pre-diabetes and diabetes (both type 1 and type 2) and to help manage diabetes, is the haemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) test.
What is the HbA1C Test?
- The HbA1C test, or glycated haemoglobin test, serves as a vital tool for diagnosing pre-diabetes and diabetes, offering insights into long-term blood glucose control.
- It measures the percentage of red blood cells coated with sugar.
- It provides a comprehensive view of average blood glucose levels over the preceding two to three months.
- It is recommended for individuals over 30 years and those with specific risk factors, with retests scheduled based on initial findings and individual health profiles.
Evolution and Acceptance
- Initially inconsistent, the test gained recognition for its correlation with blood glucose values and its role in monitoring glycemia, leading to improved standardization and accuracy.
- It is endorsed by medical bodies like World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Diabetes Association and.
- This underscores the test’s diagnostic utility, subject to stringent quality assurance measures.
Interpretation of Results
- Results are typically presented as percentages.
- Normal: Values below 5.7% are considered
- Pre-diabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
- Alternatively, results may be expressed in mmol/mol, providing a comparable metric for assessment.
Limitations of the Test
- While informative, the HbA1C test may be supplemented by other tests, particularly in populations with conditions affecting assay accuracy.
- In India, factors like thalassemia prevalence and iron-deficiency anemia may impact test reliability, necessitating caution and additional indices for glycemic assessment.
PYQ:
‘Aerial metagenomics’ best refers to which one of the following situations?
- Collecting DNA samples from air in a habitat at one go
- Understanding the genetic makeup of avian species of a habitat
- Using air-borne devices to collect blood samples from moving animals
- Sending drones to inaccessible areas to collect plant and animal samples from land surfaces and water bodies
Practice MCQ:
Consider the following statements about the HbA1C test:
- It is used in the diagnosis of Sickle Cell Disease.
- It measures the percentage of red blood cells coated with sugar.
- It is recommended for individuals over 30 years.
How many of the given statements is/are correct?
- One
- Two
- Three
- None
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Lyme Disease reported in Ernakulam
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lyme Disease and its causative borrelia bacteria
Mains level: NA

In the news
- A suspected case of Lyme disease caused by the bite of a tick carrying borrelia bacteria has been reported from Koovapady in Ernakulam district.
What is Lyme Disease?
- According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Lyme is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks.
- Typical symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash called erythema migrans.
- If left untreated, infection can spread to joints, the heart, and the nervous system.
Symptoms of Lyme DiseaseSymptoms of Lyme disease depend on the stage of the condition. (1) Stage 1
(2) Stage 2
(3) Stage 3
|
Try this PYQ from CSE Prelims 2016:
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Viruses can infect
- bacteria
- fungi
- plants
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
11 African countries sign ‘Yaounde Declaration’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Yaounde Declaration, Malaria
Mains level: NA
In the news
- Health ministers from 11 African nations grappling with the heaviest malaria burdens have recently signed the Yaounde Declaration.
What is Yaounde Declaration?
| Details | |
| Signed at | Yaoundé conference, hosted by WHO and the Government of Cameroon in Yaoundé, Cameroon (capital). |
| Participants | Ministers of Health, global malaria partners, funding agencies, scientists, civil society organizations, and other malaria stakeholders. |
| Signatory countries |
|
| Pledges |
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Children’s Vulnerability to Skincare Products
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Health hazards of Skincare Products

In the news
- With the increasing trend of children’s interest in skincare products, concerns have been raised regarding their safety and long-term impact on children’s health.
- Influenced by social media and marketing, parents are seeking skincare routines for their children, often overlooking potential risks.
In this article, we explore the implications of early skincare practices on children and the necessity for regulatory measures to ensure their well-being.
Risks Associated with Children’s Skincare Products
- Vulnerability to Harm: Children’s skin is thinner, more delicate, and less developed than adults, making them more susceptible to adverse reactions from skincare products.
- Exposure to Toxicants: Behavioral patterns like hand-to-mouth activity increase the risk of ingesting harmful chemicals present in skincare products, posing health hazards.
- Biological Susceptibility: Rapid growth rate, developing tissues, and immature immune systems make children biologically more vulnerable to the toxicants present in skincare products.
Insights from Research
- Usage Patterns: Research indicates that up to 70% of children in the U.S. have used children’s makeup and body products, highlighting the widespread exposure to skincare products among children.
- Health Risks: Studies suggest that children’s prolonged exposure to makeup and body products may lead to adverse health effects due to their developing physiology and behavioural tendencies.
Toxins in skincare products can pose risks to health due to their potential adverse effects. Some common toxic ingredients found in cosmetics include:
|
Regulatory Imperatives
- Medical Concerns: Dermatologists express concern over the unsupervised use of cosmeceuticals by children, emphasizing the potential harm caused by substances like steroids and hydroquinone present in skincare products.
- Need for Regulation: Regulatory measures are deemed essential to restrict the sale of skincare products containing harmful ingredients and protect children from inappropriate products.
Psychological Impact
- Unrealistic Standards: The promotion of flawless complexion as an ideal standard perpetuates unrealistic beauty standards among children, impacting their self-esteem and body image.
- Ethical Considerations: The ethical implications of targeting young consumers with skincare products, without adequate consideration of their long-term effects, warrant scrutiny and regulation.
Way Forward
- Prioritizing Safety: Parents are advised to prioritize safety, simplicity, and skin health when selecting skincare products for their children.
- Return to Basics: Dermatologists advocate for a return to basic skincare practices, including a healthy diet, proper cleansing, and moisturizing, to maintain children’s skin health.
- Functional Necessity: For child performers and those exposed to heavy makeup, gentle cleansing and hydration are recommended to counteract the effects of makeup and protect the skin’s integrity.
Conclusion
- As the children’s cosmetics market continues to grow, it is imperative to address the risks associated with early skincare practices and implement regulatory measures to safeguard children’s health and well-being.
- By prioritizing safety, simplicity, and skin health, parents can navigate the skincare maze for their children and foster a healthy relationship with skincare that values function over appearance.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Have India’s health centres really ‘collapsed’?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Primary Health Centres (PHCs)
Mains level: Read the attached story

In the news
- Public health centres in India have long been shrouded in infamy, perceived as symbols of systemic failure.
- The effectiveness of primary healthcare in India has always been a topic of discussion, with calls for strengthening these services through government commitment to accessibility, affordability, and quality care.
PYQ from CSE Mains 2021:
Q. “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. |
Health Centres in India
- Primary Health Centres (PHCs) also known as Public HCs play a crucial role in providing comprehensive healthcare services to the population.
- The first PHC in India was established following the proposal of the PHC concept in a paper submitted to the Executive Board of the World Health Organization (WHO) in January 1975.
- The establishment of PHCs gained further momentum with the International Conference on PHC held in Alma Ata, Kazakhstan in 1978.
- They are a fundamental component of the healthcare system, with Medical Officers at these centers required to hold an MBBS degree.
- India boasts a vast public health infrastructure with 23,391 PHCs and 145,894 sub-centers, serving a substantial percentage of the population.
- PHCs cover a significant portion of outpatient care, including services for non-communicable diseases, maternal health, and child health.
Importance of Health Centres
- Foundational Role: Health centres form the backbone of India’s public health system, providing primary care to millions.
- Access and Affordability: With nearly two lakh centres across the country, they aim to offer accessible and affordable healthcare, particularly in rural areas.
- Impact on Equity: Effective health centres can mitigate social and health inequities, reducing reliance on costly private healthcare and preventing households from falling into poverty due to healthcare expenses.
Unveiling the Reality
- Evidence of Progress: Surveys conducted across five states reveal a pattern of improving quality and utilization of health services over time, albeit at a slow pace.
-
- In Himachal Pradesh, functional health centres serve 83% of the population.
- Chhattisgarh has shown a radical expansion in the public provision of healthcare, with increased facilities, medicines, and staff presence.
- Bihar lags behind, with dismal quality of health centres and some sub-centres being dormant or non-existent.
- Policy Interventions: Increased health expenditure, initiatives like the National Rural Health Mission, and state-specific schemes have contributed to incremental improvements.
- The share of health expenditure in the Union Budget increased drastically.
- The National Health Mission’s share shrank from 69% to 44%, while allocations for the Ayushmann Bharat program and new AIIMS hospitals surged.
- COVID-19 led to a sustained increase in patient utilization of public health facilities, indicating growing trust in the system.
Challenges and Gaps
- Underutilization: Despite improvements, health centres still face challenges such as high staff absenteeism, limited services, and poor infrastructure.
- Lacunas: Health workers report irregular flow of funds, lack of facilities like toilets and transport, and inadequate supply of drugs and testing equipment.
- Social Discrimination: Caste and gender dynamics influence access to and quality of healthcare, perpetuating inequalities. Upper-caste doctors display disparaging attitudes towards marginalized communities, while upper-caste families disrespect Dalit ANMs.
- Gender Disparities: Women, particularly frontline health workers, play a crucial role in rural health settings but often face neglect and discrimination.
Way forward
- Holistic Investment: While progress has been made, it remains patchy, with allocations often prioritizing tertiary healthcare over primary care.
- Designated allocations: The composition of the healthcare budget has remained stagnant, with minimal increases in the share allocated to primary healthcare.
- Policy Reform: The paper advocates for substantial support from the central government to enable poorer states to replicate successful initiatives and enhance the role of health centres in public healthcare delivery.
Conclusion
- India’s health centres, though fraught with challenges, embody resilience and potential.
- By addressing systemic gaps and prioritizing primary healthcare, the nation can harness the transformative power of these centres to achieve equitable and accessible healthcare for all.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A vaccine that prevents six cancers
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pap smears, Human Papillomavirus
Mains level: proactive measures to prevent cervical cancer
Pyq mains
UPSC IAS/2017
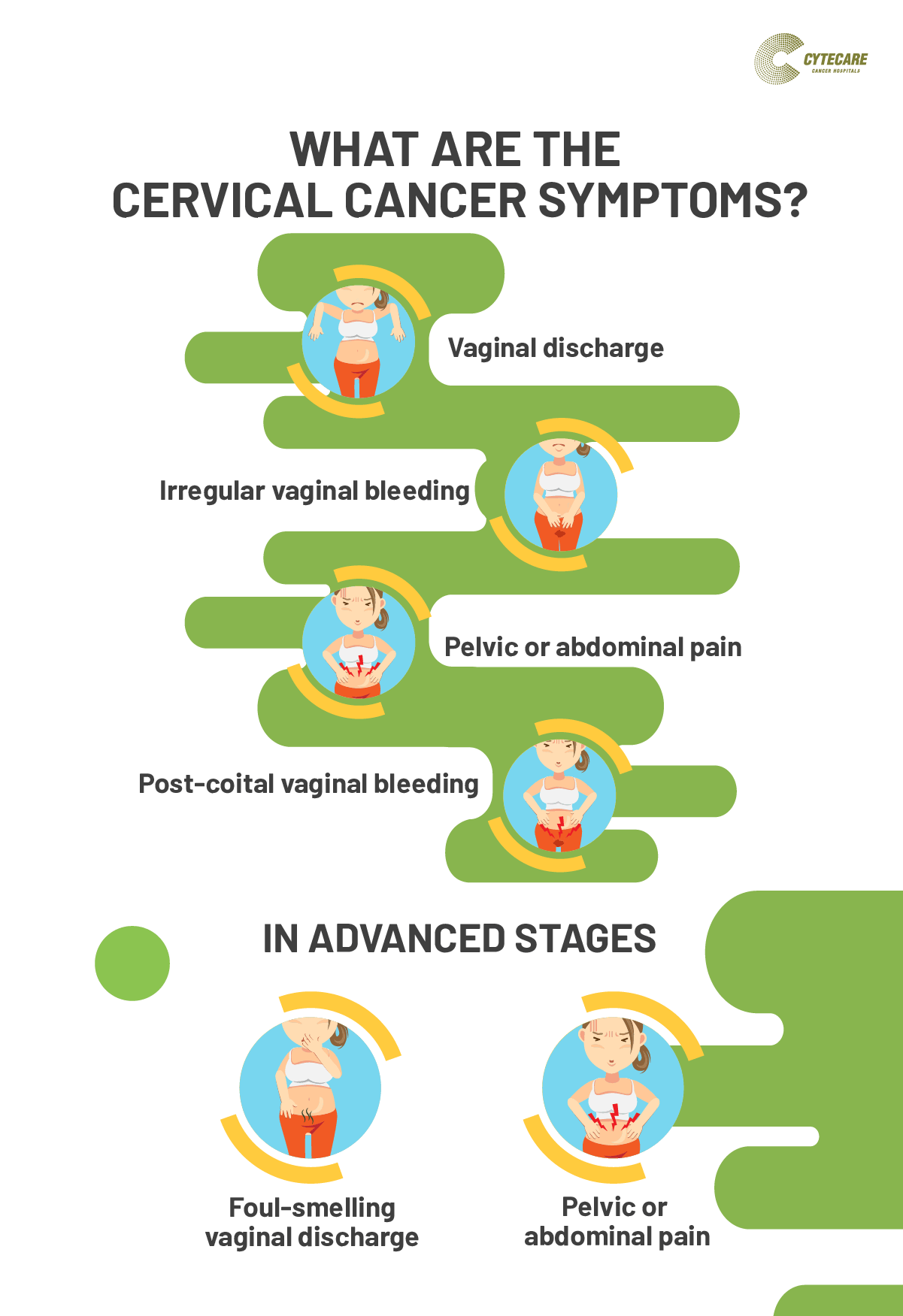
Why is it in the News?
- Cervical cancer prevention, particularly through HPV vaccination, has gained attention recently due to several factors. January was observed as Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, drawing focus to the importance of combating this disease. Additionally, March 4 marked International HPV Awareness Day, further highlighting the significance of addressing HPV-related health issues.
What is Cervical Cancer?
- Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that affects the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. It is primarily caused by certain types of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), which is transmitted through intimate contact.
- If left untreated, cervical cancer can be life-threatening. It is a significant health concern worldwide, with a particularly high burden in lower- and middle-income countries. In India, cervical cancer is the second most common cancer among women, posing a substantial threat to public health.
What is Human Papillomavirus (HPV)?
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of viruses that infect the skin and mucous membranes. It’s the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) worldwide. HPV can cause various health issues, including genital warts and certain types of cancers.
What Facts are explained in the article?
- Prevalence and Impact: Cervical cancer claims the lives of over 300,000 women annually worldwide, with a disproportionate burden in lower-income countries.
- Risk in India: With over 500 million women at risk, cervical cancer is a significant public health concern in India, second only to breast cancer.
- Role of HPV Vaccination: HPV vaccination is identified as a crucial strategy for preventing cervical cancer. It targets the underlying cause of the disease by protecting against HPV infection.
Strategies for Prevention of Cervical cancer
- HPV Vaccination: Implementing widespread HPV vaccination programs, particularly targeting adolescent girls, can significantly reduce the incidence of cervical cancer. Vaccination should ideally occur before the onset of sexual activity to maximize effectiveness.
- Screening for Precancerous Lesions: Regular screening for precancerous lesions, such as Pap smears or HPV DNA tests, can detect abnormalities early and allow for timely intervention. This is crucial for reducing the incidence of advanced-stage cervical cancer.
- Education and Awareness: Increasing education and awareness about cervical cancer, HPV infection, and the importance of vaccination and screening are essential. This includes targeting healthcare professionals, policymakers, parents, and adolescents to dispel myths and misconceptions and encourage uptake of preventive measures.
What are the Challenges?
- Limited Access: HPV vaccination may not be widely accessible, particularly in lower-resourced communities, and is often available at a significant out-of-pocket cost.
- Misconceptions Among Physicians: Some physicians underestimate the incidence and risk of cervical cancer, as well as the safety and effectiveness of HPV vaccines. This can lead to hesitancy in recommending vaccination to eligible individuals.
- Parental Hesitancy: Misinformation and concerns about vaccine safety and efficacy among parents can contribute to hesitancy in vaccinating adolescents against HPV.
| Pap Smears |
|---|
| Description: A screening procedure for cervical cancer involving collecting cells from the cervix to examine for abnormalities. |
| Purpose: To detect precancerous or cancerous changes in cervical cells early for timely intervention and prevention. |
| Procedure: Use of a speculum to visualize the cervix and collection of cells with a brush or spatula. |
| Timing: Typically performed during routine gynecological exams, starting at age 21 or within 3 years of becoming sexually active. |
Facts about HPV Vaccination:
- The HPV vaccine is safe and effective in preventing six HPV-related cancers, including cervical, vulvar, anal, vaginal, throat, and cervical cancers.
- Vaccination is recommended for adolescents starting at age 9 years to maximize its effectiveness.
- HPV vaccination is an essential component of the immunization schedule recommended by the Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP).
Best Practices for HPV Vaccination and Cervical Cancer Prevention:
- Effective Communication:
- Provide clear and accurate information to parents about HPV vaccination.
- Address concerns and misconceptions to ensure informed decision-making.
- Timely Vaccination:
- Recommend HPV vaccination for adolescents starting at age 9.
- Encourage vaccination before sexual activity begins for maximum effectiveness.
- Integration into Immunization Programs:
- Advocate for inclusion in national immunization programs for widespread access.
- Collaborate with policymakers to ensure equitable vaccine coverage.
- Promotion of Regular Screening:
- Emphasize the importance of cervical cancer screening for women over 30.
- Encourage routine Pap smears or HPV DNA tests for early detection.
- Physician Education:
- Provide comprehensive training on HPV vaccination and cervical cancer prevention.
- Equip healthcare professionals with updated guidelines and communication skills.
In conclusion, the article emphasizes the importance of proactive measures to prevent cervical cancer, particularly through HPV vaccination and screening. It underscores the role of healthcare professionals, policymakers, and community stakeholders in addressing the challenges and ensuring equitable access to preventive interventions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Rare Diseases Care in India: Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rare Diseases Definition
Mains level: Burden of Rare Diseases and Policy Interventions

In the news
- World Rare Diseases Day (February 29) was recently celebrated.
What are Rare Diseases?
- Global Perspective: Rare diseases are defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as often debilitating lifelong diseases or disorders with a prevalence of 1 or less, per 1,000 population.
- National Context: While India lacks a standardized definition, the Organisation of Rare Diseases – India suggests defining a disease as rare if it affects 1 in 5,000 people or less.
Rare Diseases: Key Facts and Figures
|
National Policy on Rare Diseases, 2021: Highlights
- Comprehensive Approach: This Policy offers a holistic framework encompassing prevention, management, and treatment strategies tailored to the unique needs of patients.
- Financial Support: Recognizing the financial burden on patients, the policy aims to lower the exorbitant costs of treatment through targeted interventions and support mechanisms.
- Research Focus: Emphasizing indigenous research, the policy lays the foundation for bolstering research initiatives in the field of rare diseases, fostering innovation and discovery.
Other Initiatives in India
- National Hospital-Based Registry: A pivotal component of the policy, the establishment of a national registry of rare diseases promises to provide invaluable epidemiological data, informing targeted interventions and resource allocation.
- Early Screening and Prevention: The creation of Nidan Kendras aims to enhance early detection and prevention efforts, crucial for improving patient outcomes and reducing disease burden.
- Capacity Building: Strengthening secondary and tertiary health facilities at Centres of Excellence underscores the commitment to enhancing healthcare infrastructure and service delivery.
Challenges and Imperatives
- Defining Rare Diseases: Despite significant progress, India lacks a standardized definition of rare diseases, necessitating clarity to guide policy and resource allocation effectively.
- Funding Utilization: Concerns arise over the underutilization of allocated funds, highlighting the urgency to streamline resource allocation and enhance accountability mechanisms.
- Patient Advocacy: Rare diseases patient advocacy groups play a pivotal role in advocating for timely access to treatment and sustainable funding support, urging policymakers and healthcare providers to prioritize patient-centric initiatives.
Way Forward
- Sustainable Funding: Ensuring sustainable funding support for rare diseases treatment is paramount to safeguarding patient well-being and fostering equitable access to care.
- National Registry Implementation: Accelerating the establishment of a hospital-based national registry is imperative to harness the power of data-driven decision-making and advance rare diseases research.
- Multidisciplinary Care: The creation of comprehensive care centers, coupled with initiatives to support caregivers, represents a crucial step towards enhancing patient outcomes and fostering a supportive healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion
- As India commemorates World Rare Diseases Day, it stands at a pivotal juncture in its journey towards rare diseases care and advocacy.
- By embracing a collaborative and patient-centric approach, India can surmount existing challenges, paving the way for a future where every individual affected by a rare disease receives the care and support they deserve.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2014:
Consider the following diseases
- Diphtheria
- Chickenpox
- Smallpox
Which of the above diseases has/have been eradicated in India?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Story of ASHAs: Navigating Challenges in Public Health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASHA
Mains level: NA
Introduction
- ASHAs, or Accredited Social Health Activists, have emerged as pivotal figures in India’s public health landscape, embodying the promise of compassionate care and community advocacy.
Who are the ASHA workers?
- Inception: Established in 2002 in Chhattisgarh, ASHAs were envisioned as community health workers, modeled after the ‘Mitanins’, to bridge the gap between the health system and local populations. Initiated in 2005-06 as part of the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM); Expanded to urban settings since 2013 via the National Urban Health Mission.
- Number: Around 10.4 lakhs employed across India. The highest numbers are in populous states like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- Geographical Distribution: One ASHA per 1,000 people in rural areas, adjusted to one per habitation in tribal, hilly, and desert regions.
- Global Recognition: Awarded by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2013.
- Functions and Responsibilities: Register newborns, pregnant women, and deaths; accompany patients to health centers; distribute medicines; conduct immunization drives; and report health statistics.
Criteria for selection of ASHA worker:
- For Rural:
- The prospective candidate must be a married, widowed or divorced female resident of the village she’s applying to work at.
- Must be aged between 25 and 45 years.
- Candidates must be literate. Preference is given to those with a 10th pass certificate. There are several interviews at the Anganwadi, block and district levels. The health committees maintain a thorough selection process.
- For Urban:
- The prospective candidates must be female residents of vulnerable clusters or slums within an urban setup.
- This slum or cluster must be identified by the City or District Health Society as priority zones for ASHA healthcare workers. The candidate should preferably be married, widowed, separated or divorced.
- Must be aged between 25 and 45 years.
- Candidates must be literate and must have fluency in the native language of the community.
Challenges Faced by ASHAs
[1] Work Challenges
- Overwork and Underpayment: ASHAs endure a “triple shift,” balancing household responsibilities, community outreach, and health center duties, often without adequate compensation or rest.
- Systemic Inequities: ASHAs experience power imbalances along gender and caste lines, compounded by their status as “volunteers,” leading to economic, physical, and psychological vulnerabilities.
- Social Stigma: Despite their crucial role in improving health outcomes, ASHAs often face social stigma and discrimination within their communities, hindering their effectiveness and well-being.
[2] Occupational Hazards
- Physical Strain: Irregular meals, inadequate sleep, and exposure to extreme weather conditions contribute to health issues like malnutrition, anaemia, and non-communicable diseases among ASHAs.
- Mental Health Challenges: The demanding nature of their work and limited social support expose ASHAs to high levels of stress, anxiety, and burnout, affecting their overall well-being and job satisfaction.
- Safety Concerns: ASHAs, particularly those working in remote or conflict-affected areas, face risks of harassment, violence, and assault while performing their duties, highlighting the need for enhanced security measures and support systems.
[3] Social and Economic Implications
- Economic Precarity: ASHAs’ honorariums serve as primary family income, yet delays in payment and out-of-pocket expenses exacerbate financial strain, perpetuating cycles of poverty and dependence.
- Gendered Burden: ASHAs, predominantly women, often bear the brunt of caregiving responsibilities within their households, leading to gender disparities in workload distribution and access to resources.
- Empowerment and Agency: Despite facing numerous challenges, ASHAs demonstrate resilience and agency in advocating for their rights, mobilizing communities, and demanding policy reforms to improve their working conditions and livelihoods.
Advocacy and Policy Recommendations
- Recognition and Fair Compensation: Advocate for institutional recognition, fair wages, and improved working conditions for ASHAs, aiming for them to become government employees with access to social security benefits and maternity support.
- Capacity Building: Support initiatives aimed at enhancing ASHA skills, knowledge, and confidence through targeted training and skill development programs.
- Community Engagement: Encourage local communities to recognize and appreciate the contributions of ASHAs, fostering stronger support, trust, and collaboration.
- Safety Measures: Enhance safety protocols and support systems for ASHAs, especially those working in remote or conflict-affected areas, to minimize risks of harassment, violence, and assault.
- Address Systemic Barriers: Tackle gender and caste-based inequalities experienced by ASHAs, promoting equal opportunities and access to resources.
- Financial Security: Ensure timely payments and reduce out-of-pocket expenses for ASHAs, mitigating financial strain and perpetual cycles of poverty.
Conclusion
- The plight of ASHAs reflects broader structural injustices within India’s healthcare sector, underscoring the urgent need for policy reforms and systemic support.
- As frontline warriors in public health, ASHAs deserve equitable treatment, recognition, and protection, essential for advancing both individual well-being and community health outcomes.
- Through collective advocacy, empowerment, and solidarity, ASHAs can continue to drive positive change and make lasting contributions to public health in India.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2012:
With reference to the National Rural Health Mission, which of the following are the jobs of ASHA, a trained community health worker?
- Accompanying women to the health facility for antenatal care checkups
- Using pregnancy test kits for early detection of pregnancy
- Providing information on nutrition and immunization
- Conducting the delivery of the baby
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Eradication of Guinea Worm Disease
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Guinea Worm Disease
Mains level: NA

Why in the News?
The imminent eradication of Guinea worm disease marks a major win for public health, showcasing the effectiveness of simple strategies in fighting diseases.
About Guinea Worm Disease
- Causes: Guinea worm disease, known since ancient times as the “fiery serpent,” is caused by the Guinea worm (Dracunculus medinensis), bringing painful blisters and severe symptoms to those affected.
- How It Spreads: People develop painful blisters, and when they come into contact with water, adult worms emerge, contaminating water sources and continuing the cycle of infection.
Symptoms and Impact
- Pain and Suffering: The disease causes intense pain, swelling, and ulcers, making it hard for people to go about their daily lives.
- Effects: Mostly affecting the legs and feet, Guinea worm disease worsens poverty and illness in areas where clean water and healthcare are scarce.
Success Story in India
- Beating the Disease: India successfully got rid of Guinea worm disease in the late 1990s by focusing on simple things like clean water and educating communities about health.
- Team Effort: India’s government, local health workers, and international partners worked together to achieve this victory.
Global Progress and Challenges
- Making Strides: Progress has been made globally, but challenges remain in places like Chad and the Central African Republic, where the disease is still a problem.
- New Hurdles: Finding Guinea worms in animals like dogs shows that the disease is tough and needs continued attention.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Electoral season and restructuring the health system
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Na
Mains level: importance of prioritizing primary healthcare

Central Idea:
The article discusses the importance of health reform in India, highlighting the necessity for political parties to prioritize it in their manifestos. It emphasizes the need to strengthen primary healthcare systems, citing successful examples from other countries like Thailand, and proposes comprehensive reforms to address India’s healthcare challenges.
Key Highlights:
- Manifestos serve as important documents reflecting political parties’ priorities and commitments.
- Both BJP and Congress manifestos in 2014 and 2019 highlighted the importance of revamping the primary healthcare system, but with differing perspectives on healthcare delivery.
- Past initiatives like the National Rural Health Mission under the UPA and policy continuity under the NDA have made incremental progress but haven’t addressed fundamental healthcare system flaws.
- Comparison with countries like Thailand and Turkey underscores India’s need for more ambitious and effective healthcare reforms.
- The focus should shift towards strengthening primary and secondary healthcare infrastructure to address the majority of health needs effectively.
- Successful reform examples emphasize deliberate planning, strong local capacity building, and a focus on community outcomes.
- Challenges include political will, overcoming preoccupation with high-end hospitals, and implementing synchronized reforms at the grassroots level.
Key Challenges:
- Political reluctance to prioritize primary healthcare over high-end hospital infrastructure.
- Resistance to reforming entrenched healthcare delivery models and governance structures.
- Capacity building and resource allocation at the district level to implement reforms effectively.
- Varying levels of capability across states necessitate tailored approaches to reform implementation.
- Addressing lifestyle factors contributing to disease incidence and out-of-pocket healthcare expenses.
- Overcoming market failures and governance challenges in healthcare service provision.
Main Terms or key terms for answer writing:
- Primary healthcare
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC)
- Health reform
- Public-private partnerships (PPP)
- Human resources for health
- Social health insurance
- Medical curriculum reform
- Decentralization
- Operational flexibilities
- Accountability framework
Important Phrases for quality answers:
- “Reforming the very architecture of the health system”
- “Building a system ‘fit for purpose'”
- “Operational flexibilities within a proactive, accountability framework”
- “Imagination to design the process of reform”
- “Infusion of new institutional and organizational capacities”
- “Reducing demand for hospitalization”
- “Out-of-pocket expenditures”
Quotes that you can use for essay writing:
- “Manifestos are useful documents… enabling people to hold the elected party accountable.”
- “India’s strategy for UHC has hinged on purchasing services from a private sector operating on the inflationary a fee for service model…”
- “Can our political parties commit themselves to such a process in their manifestos? Or, is that a big ask?”
Useful Statements:
- “Twenty years is a long time… Thailand… achieved significant outcomes within half the time span.”
- “India has a long way to go… States such as Bihar still have one doctor serving per 20,000 population.”
- “Successful examples of such reform processes show deliberate intent executed to a plan.”
Examples and References for value addition in your mains answer:
- Thailand’s Universal Health Coverage implementation in 2000.
- Turkey’s Health Transformation Program in 2003.
- India’s National Rural Health Mission and National Medical Commission establishment.
Facts and Data:
- India’s maternal mortality is three times more than the global average.
- 95% of ailments and disease reduction can be handled at the primary and secondary level.
- India’s public spending on healthcare has hovered around an average of 1.2% of GDP.
Critical Analysis:
The article provides a critical analysis of past healthcare initiatives in India, highlighting their incremental nature and failure to address fundamental system flaws. It underscores the importance of prioritizing primary healthcare and comprehensive reform to achieve equitable, effective healthcare delivery.
Way Forward:
- Prioritize strengthening primary healthcare infrastructure.
- Implement comprehensive healthcare reforms addressing governance, human resources, and service delivery.
- Tailor reform strategies to suit varying state capabilities.
- Shift focus towards community outcomes and accountability.
- Address lifestyle factors contributing to healthcare burden.
- Overcome political reluctance and vested interests to achieve meaningful reform.
Answer the following question and write your answer in comment box
How can India learn from successful healthcare reform initiatives in other countries like Thailand and Turkey to address its own healthcare challenges effectively?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Bubonic Plague is back: Should you be worried?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bubonic Plague and its causes
Mains level: Rise of zoonotic diseases

Introduction
- Recent reports from Oregon, US, confirm the reemergence of bubonic plague, marking the first case since 2005.
- Notable historical instances include the Third Pandemic in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, originating in China and spreading worldwide, reaching India by 1896.
What is Bubonic Plague?
- Cause: Bubonic plague is caused by Yersinia pestis, a zoonotic bacterium primarily found in small animals and their fleas, capable of transmission to humans.
- Transmission: The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies three primary modes of transmission:
- Through infected vector fleas,
- Contact with infectious bodily fluids or materials, and
- Inhalation of respiratory droplets from pneumonic plague patients.
Symptoms and Forms
- Bubonic Plague: Characterized by fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and weakness, typically resulting from flea bites.
- Septicemic Plague: Occurs when the bacteria enter the bloodstream, leading to severe symptoms such as abdominal pain, shock, and skin discoloration.
- Pneumonic Plague: The most perilous form, causing rapid-onset pneumonia, and posing a high risk of fatality if left untreated, with potential person-to-person transmission.
Historical Impact of the Black Death
- Deadliest Outbreak: The Black Death, spanning from 1346 to 1353, decimated up to half of Europe’s population, leaving a profound and enduring impact on survivors.
- Genetic Legacy: Genetic mutations linked to increased survival during the Black Death era have been identified, albeit with potential implications for autoimmune diseases in modern populations.
- Social and Economic Ramifications: Historians attribute Europe’s rise to global dominance partly to the aftermath of the Black Death, shaping subsequent societal, economic, and cultural trajectories.
Contemporary Outlook and Mitigation
- Limited Spread: Medical experts allay fears of a Black Death resurgence, affirming the localized nature of the recent bubonic plague case and the low likelihood of widespread transmission.
- Modern Interventions: Advancements in antibiotics and healthcare infrastructure significantly mitigate the threat posed by bubonic plague, rendering it treatable and containing its potential impact.
- Global Surveillance: Vigilant monitoring and prompt treatment protocols contribute to managing sporadic plague cases reported worldwide, underscoring the importance of continued vigilance and preparedness.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Derek O’Brien writes: How BJP government’s Data Fails Rekha, Kavita, and Mohan
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: interim budget session of Parliament
Mains level: gap between government rhetoric and ground realities, emphasizing the human impact of policy failures

Central Idea:
The article critiques the recent interim budget session of Parliament, highlighting the discrepancy between the government’s rhetoric and the lived realities of everyday Indians. Through the stories of Rekha, Kavita, and Mohan, it exposes the failure of government schemes like Ayushman Bharat, food subsidies, and employment initiatives to address the fundamental issues facing citizens.
Key Highlights:
- The government’s self-aggrandizing adjectives during the budget session are criticized for being unsubstantiated by facts.
- The article delves into the lives of ordinary Indians to reveal the truth behind government data.
- Through scenarios, it demonstrates how government schemes often fail to provide adequate healthcare, nutrition, and employment opportunities.
- The suspension of a senior professor behind a damning health report raises questions about intellectual honesty regarding data.
- The Global Hunger Index ranking and reports from international organizations highlight India’s challenges in food security.
- Unemployment rates and the plight of educated youth like Mohan illustrate the failures in job creation and protection.
Key Challenges:
- Inadequate investment in healthcare, leading to poor quality and inaccessible services for millions.
- Subsidized food options lack nutritional value, exacerbating hunger and malnutrition.
- Job scarcity and lack of protection for workers, pushing individuals to precarious employment or even dangerous situations abroad.
- Discrepancies between government claims and ground realities, highlighting issues of transparency and accountability.
Main Terms:
- Ayushman Bharat scheme
- NFHS (National Family Health Survey)
- Global Hunger Index
- Gig economy
- Unemployment rate
- Food subsidies
Important Phrases:
- “Data stored with government hospitals under the Ayushman Bharat scheme is riddled with errors.”
- “The suspension of the IIPS Director shortly after the release of the NFHS report.”
- “India ranked out of countries in the Global Hunger Index.”
- “Mohan finds himself among the percent of graduates under years of age who are unemployed.”
- “A packet of rice costs more while dal costs more than before.”
Quotes:
- “The voices of Kavita, Rekha, and Mohan did not find a place in the Prime Minister’s marathon monologue in Parliament.”
- “Every youth believes that they can cement their job position with hard work and skills.”
- “Reality gets worse for Indian women like Rekha.”
- “Three out of four Indians cannot afford a healthy diet.”
Anecdotes:
- Rekha’s struggle to access healthcare at a government hospital.
- Kavita’s dilemma between subsidized but low-nutrient food and higher quality groceries.
- Mohan’s choice between unemployment at home or precarious work abroad.
Useful Statements:
- “The numbers either misidentify the dead, incorrectly record surgery details or entirely leave out beneficiaries from the list.”
- “Half the country does not turn to government facilities in their time of need.”
- “A job in a war zone is his only option.”
- “Mohan has not found employment for months.”
Examples and References:
- Global Hunger Index ranking (India ranked out of countries).
- NFHS data highlighting issues in healthcare access.
- Mohan’s situation exemplifying unemployment among educated youth.
Facts and Data:
- India invests only percent of GDP in healthcare.
- Three out of four Indians cannot afford a healthy diet.
- percent of graduates under years of age are unemployed.
- A packet of rice costs more, while dal costs more than before.
Critical Analysis:
The article effectively exposes the gap between government rhetoric and ground realities, emphasizing the human impact of policy failures. By presenting concrete examples and data, it challenges the narrative of progress touted by the government. The suspension of the IIPS Director adds weight to concerns about data integrity and transparency. However, the article could benefit from more analysis on systemic issues contributing to these failures, such as corruption and inadequate social welfare policies.
Way Forward:
- Increase investment in healthcare to improve accessibility and quality of services.
- Reform food subsidy programs to ensure nutritious options for all citizens.
- Create more employment opportunities through targeted policies and investments in key sectors.
- Enhance transparency and accountability in data collection and reporting to address systemic issues.
- Prioritize the voices and needs of ordinary citizens in policymaking process
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Gender Disparities: Big Blindspot in India’s Health Policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Gender Gaps in Healthcare
Introduction
- Despite comprising nearly half of India’s health workforce, women face significant barriers in reaching leadership positions within the healthcare sector, highlighting deep-rooted gender disparities in health policy and decision-making.
Understanding the Gender Gap
- Data revelations: Official data reveals that while women make up almost 50% of health workers in India, only 18% occupy leadership roles across various health panels, committees, hospitals, and ministries.
- Impact of Gender Disparity: The over-representation of men at the top of the health pyramid perpetuates inequalities in decision-making and policymaking, leading to skewed health systems that fail to address the diverse needs of the population.
Insights from Research
- Diversity Gaps: Recent research highlights the prevalence of diversity gaps in India’s National Health Committees, with an “over-concentration” of men, doctors, individuals from urban areas, and bureaucrats. This centralization of power risks excluding diverse perspectives and experiences, hindering the development of inclusive health policies.
- Impact on Policy Formulation: The lack of gender diversity in health committees affects policy outcomes, as decisions are often made from a narrow lens, overlooking the nuanced needs of marginalized groups. For instance, the absence of women in decision-making bodies may lead to inadequate consideration of gender-specific health issues such as access to nutritious food for women.
Challenges Faced by Women
- Professional Barriers: Women encounter various obstacles in advancing their careers in the health sector, including limited opportunities for promotion, unequal pay, and cultural expectations regarding gender roles.
- Underrepresentation in Leadership: Women are significantly underrepresented in medical leadership positions, both within health committees and healthcare institutions, further perpetuating gender disparities in decision-making and policy formulation.
Recommendations for Change
- Policy Interventions: Affirmative policies, such as reserving seats for women and marginalized groups in health committees, can help address gender disparities and promote inclusive decision-making.
- Structural Reforms: Structural changes within healthcare institutions, such as promoting flexible working arrangements and providing dedicated resources for women leaders, are essential to breaking down barriers to gender equality in leadership.
- Community Engagement: Involving directly affected communities in policy-making processes can ensure that health policies are responsive to the needs and priorities of the population, fostering greater inclusivity and accountability.
Conclusion
- Achieving gender equality in health leadership requires concerted efforts to address systemic barriers and promote inclusive decision-making.
- By prioritizing diversity and inclusivity in health policy, India can build more responsive and equitable health systems that serve the needs of all its citizens.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
ASHA and Anganwadi Workers/Helpers in Ayushman Bharat Scheme
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat Scheme, ASHA and Anganwadi Workers
Mains level: ASHA and Anganwadi Workers

Introduction
- Following the Centre’s decision to extend health coverage under the Ayushman Bharat Scheme to Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) and Anganwadi workers and helpers, the Health Ministry has initiated the process of enrollment.
- The Health Ministry has received Aadhaar details of 23 lakh Anganwadi workers and helpers and over three lakh ASHA workers from various states.
About Ayushman Bharat Scheme
| Details | |
| Launch | 2018, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) |
| Aim | Achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) by providing promotive, preventive, curative, palliative, and rehabilitative care. |
| Funding | Centrally Sponsored Scheme (expenditure shared between Central and State governments) |
| Coverage | Targets over 10 crore families (approximately 50 crore beneficiaries) based on SECC (Socio-Economic Caste Census) |
| Implementing Agency | National Health Authority (NHA) |
| Components |
|
| Coverage Details |
|
| Portability of Benefits | Benefits are portable across the country, allowing cashless treatment at any empanelled public or private hospital in India. |
| Digital Overture | Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): Launched in 2021 to provide Unique Digital Health IDs (UHID) for all Indian citizens, facilitating electronic access to health records. |
Significance of ASHA Program
- Workforce: As of December 31, 2023, there were over 13 lakh Anganwadi workers and over 10 lakh Anganwadi helpers in the country, along with 9.83 lakh ASHAs in position.
- Program Scale: India’s ASHA program is recognized as the world’s largest community volunteer program, operating across 35 states and union territories.
- Role of ASHAs: The ASHA program serves as a vital component of community healthcare, facilitating access to care and playing a crucial role in the prevention and management of COVID-19.
- Contribution Acknowledged: ASHAs have been recognized for their substantial contribution to improving access to care for communities and are integral to various community platforms under the National Health Mission.
Ayushman Bharat Scheme Impact
- Beneficiary Coverage: Currently, 55 crore individuals corresponding to 12 crore families are covered under the Ayushman Bharat scheme, with some states/UTs expanding the beneficiary base at their own cost.
- Enrollment and Hospital Admissions: The government has issued approximately 28.45 crore Ayushman cards, authorizing over 6.11 crore hospital admissions amounting to ₹78,188 crores.
- Hospital Empanelment: A total of 26,901 hospitals, including 11,813 private hospitals, have been empanelled under AB-PMJAY to provide healthcare services to scheme beneficiaries.
- Gender Equity: The scheme ensures gender equity in access to healthcare services, with women accounting for approximately 49% of Ayushman cards created and 48% of total authorized hospital admissions.
Back2Basics:
[1] Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA)
| Details | |
| Launch Year | 2005-06 as part of the National Rural Health Mission.
Later extended to urban areas with the National Urban Health Mission in 2013. |
| Program Scope | Largest community health worker program globally, serving as health care facilitators, service providers, and health awareness generators. |
| Number of ASHAs | Over 10.52 Lakh ASHAs across all states/UTs (except Goa) as of June 2022. |
| Role | Provide maternal and child health services, family planning, and services under National Disease Control Programme. |
| Service Population | Serve populations of approximately 1,000 in rural areas and 2,000 in urban areas, with local adjustments based on workload. |
| Selection Criteria |
|
| Employment Classification | Considered honorary/volunteer positions rather than government workers. |
[2] Anganwadi Programme
| Details | |
| Initiation |
|
| Objective | To combat child hunger and malnutrition |
| Implementation | Centrally sponsored scheme implemented by States/UTs |
| Services Provided |
|
| Beneficiaries | Identified based on Aadhaar |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD): The Monkey Fever
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD) and Other Zoonotic Diseases
Mains level: NA

Introduction
- Recent fatalities due to Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), known as monkey fever, in Karnataka have sparked concerns about the spread of this viral infection.
What is Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD)?
- Origins and Identification: KFD is caused by the Kyasanur Forest disease virus (KFDV), a member of the Flaviviridae virus family. It was first identified in 1957 in Karnataka’s Kyasanur Forest.
- Incidence and Mortality: Between 400-500 human cases are reported annually, with an estimated case-fatality rate ranging from 3% to 5%.
Transmission and Spread
- Tick-Borne Transmission: Humans can contract KFD through tick bites or contact with infected animals, particularly sick or deceased monkeys.
- Limited Animal Role: While large animals like goats, cows, and sheep can become infected, they play a minor role in disease transmission. There’s no evidence of transmission through unpasteurized milk.
Signs and Symptoms
- Early Symptoms: The disease typically manifests with chills, fever, and headache after an incubation period of 3-8 days.
- Progression: Severe muscle pain, vomiting, gastrointestinal issues, and bleeding tendencies may develop within 3-4 days. Some patients experience neurological symptoms in the third week, including severe headaches and vision problems.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnostic Methods: Early diagnosis involves molecular detection through PCR or virus isolation from blood. Serologic testing using ELISA is conducted later.
- Treatment Approach: While no specific treatment exists, early hospitalization and supportive therapy, such as hydration maintenance, are crucial.
Prevention Strategies
- Vaccination: A vaccine for KFD is available and administered in endemic regions of India to prevent the disease.
- Preventive Measures: Insect repellents and protective clothing are recommended in tick-infested areas to minimize the risk of infection.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Issues in Self-Reporting of Mental Illness
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Mental Healthcare in India
Introduction
- Recent studies, including one by researchers from IIT Jodhpur, indicate alarmingly low rates of self-reporting for mental health problems in India.
Mental Health Under-Reporting in India
- NSS 2017-2018 Findings: The NSS data, based on self-reporting by over 550000 individuals, revealed mental illness self-reporting rates of less than 1%.
- Scale of Mental Illness: The 2017 NMHS conducted by NIMHANS estimated around 150 million individuals requiring treatment for mental illness in India.
- WHO Estimates: India bears a heavy burden with 2443 DALYs per 10,000 population and an age-adjusted suicide rate of 21.1 per 100,000.
- Suicide Trends: India’s contribution to global suicide deaths surged to 36% in 2016, with a concerning rise reported in 2021, especially among youth and middle-aged adults.
- National Mental Health Survey: Alarming rates of depression among teenagers and Substance Use Disorders (SUDs) prevalence of 22.4% among adults highlight the gravity of the situation.
Key Challenges
- Stigma and Awareness: Social stigma and poor awareness impede access to mental healthcare, leading to delayed treatment-seeking and social isolation.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses: The IIT Jodhpur study highlighted significant out-of-pocket expenses, particularly in the private sector, for mental health services.
- Vulnerability Factors: Individuals with lower income and education levels are more vulnerable to mental disorders, exacerbating their socioeconomic challenges.
- Socioeconomic Divide: Individuals with higher incomes were more likely to report health problems, indicating a socioeconomic disparity.
- Budget and Infrastructure: Inadequate budget allocation, lack of insurance coverage, and insufficient infrastructure pose hurdles to mental healthcare delivery.
- Shortage of Professionals: India grapples with a severe shortage of mental health professionals, with only 3 psychiatrists per million people.
Government Initiatives
- Mental Healthcare Act, 2016: Aims to safeguard the rights of individuals with mental illnesses, enhance access to mental healthcare, and decriminalize suicide attempts.
- National Mental Health Policy, 2014: Prioritizes universal access to mental healthcare and endeavors to mitigate risk factors linked to mental health issues.
Way Forward
- Combat Stigma: Launch nationwide campaigns to shift societal attitudes towards mental illness.
- Enhance Awareness: Integrate mental health education into curricula and disseminate resources in local languages.
- Improve Coordination: Strengthen collaboration between central and state governments for effective policy implementation.
- Innovative Solutions: Explore tele-mental health services, bolster support for NGOs, and foster community engagement to address resource shortages.
- Multisectoral Approach: Embrace a life-course perspective on mental health promotion and enforce legal frameworks.
- Enhance Mental Health Ecosystem: Define quality metrics, recognize mental health advocates, and ensure affordability and accessibility of care.
- Embrace Traditional Healing: Explore complementary medicines like Yoga and Ayurveda for mental health treatment.
Conclusion
- By prioritizing mental healthcare and fostering collaboration across sectors, India can build a resilient mental health ecosystem that promotes well-being and supports individuals in need.
- Embracing traditional healing practices alongside modern interventions can offer holistic solutions, paving the way for a mentally healthier nation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
An Uttar Pradesh model to tackle malnutrition
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: United Nations World Food Programme
Mains level: women's empowerment and nutrition

Central Idea:
The article highlights the success of a decentralized approach to tackling malnutrition in Uttar Pradesh by empowering women through community-based micro-enterprises. This initiative, led by self-help groups, focuses on producing fortified and nutritious foods for pregnant/breastfeeding mothers and children, distributed via the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) programme.
Key Highlights:
- Collaborative effort between the Department of Women and Child Development and the Uttar Pradesh State Rural Livelihood Mission.
- Decentralized production of take-home rations by women’s enterprises.
- Positive impact on livelihoods with over 4,000 women engaged in 204 self-help group micro-enterprises.
- Re-formulation of take-home rations to enhance nutritional value and address monotony.
- Focus on strengthening demand through diverse and nutritious products.
- Innovation through app-based solutions and QR code tracking for supply chain management.
Key Challenges:
- Ensuring consistent quality and safety standards.
- Overcoming logistical challenges in decentralized production and distribution.
- Addressing potential resistance to change from centralized to decentralized models.
- Sustaining long-term engagement and empowerment of women.
Key Terms:
- Self-help groups
- Micro-enterprises
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)
- Fortified foods
- Decentralized production
- Nutritional supplementation
- Livelihood opportunities
Key Phrases:
- Women’s empowerment for nutrition
- Decentralized model for take-home ration production
- Strengthening demand through diverse products
- Innovation and sustainability in food production
- Multi-stakeholder approach for effective solutions
Key Quotes:
- “Engaging women from the community to run the take-home ration production units is a game-changer.”
- “The State-wide expansion of micro-enterprises led by women confirms successful targeting and demonstrates how empowering women can bring about effective and sustainable processes.”
Key Examples and References:
- Collaboration between the Department of Women and Child Development and the Uttar Pradesh State Rural Livelihood Mission.
- Use of two pilot plants by the United Nations World Food Programme in Unnao and Fatehpur.
- Expansion to 202 production units across 43 districts, benefiting 12 million ICDS beneficiaries.
Key Statements:
- “This initiative presents an excellent opportunity for women to earn a livelihood and contribute to the local economy.”
- “The re-formulated take-home rations are nutritious and designed to support the health and well-being of children.”
Key Facts/Data:
- Over 4,000 women engaged in 204 self-help group micro-enterprises.
- Aim to generate an additional income of ₹8,000 a month for each woman.
- Products include sweet and savory options like aata besan halwa and daliya moong dal khichdi.
- Expansion to 202 production units across 43 districts, benefiting 12 million ICDS beneficiaries.
Critical Analysis:
- The initiative effectively addresses the intersection of women’s empowerment and nutrition, leveraging community resources for sustainable impact.
- Decentralized production and diverse product offerings enhance accessibility and acceptability.
- Challenges such as quality control and scalability need continuous monitoring and adaptation.
Way Forward:
- Continued support for women’s empowerment and capacity building.
- Strengthening of quality assurance mechanisms.
- Further research and innovation in product development and supply chain management.
- Collaboration with stakeholders for scaling up and sustainability.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Populism does not help public health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: importance of evidence-based decision-making and long-term goals in public health policies
Central Idea:
The article highlights the need for a shift in the approach to public health management in democratic setups, emphasizing the importance of prioritizing preventive measures over immediate, politically-driven responses. It advocates for a separation of health-care decision-making from short-term political goals to ensure sustainable health strategies that address both immediate and future health needs.
Key Highlights:
- Silent victories in preventing diseases often go unnoticed in the pursuit of tangible achievements.
- Immediate response-focused initiatives divert attention from critical areas like sanitation, disease surveillance, and public health education.
- The case of dengue exemplifies the prioritization of emergency relief over long-term prevention strategies.
- The article stresses the importance of evidence-based decision-making and long-term goals in public health policies.
- Gaps in public health education and the influence of the pharmaceutical industry are recognized challenges.
- Disparities in achieving health policy targets, especially in nutrition programs, reveal gaps in public health efforts.
- Socio-economic factors like poverty, sanitation, and overcrowding contribute to health disparities in diseases like tuberculosis.
Key Terms/Phrases:
- Preventive health measures
- Vector bionomics
- Public health education
- Pharmaceutical industry influence
- Socio-economic factors
- Health policy targets
- Separation of powers approach
Key Quotes:
- “In a democratic setup, leaders often chase tangible achievements and overlook vital preventive efforts.”
- “Public health decisions should be based on scientific evidence and long-term goals, not electoral cycles.”
- “Behavioural change is key to managing public health challenges.”
- “Effective public health management should encompass preventive measures, policy formulation, community health, and environmental health.”
Key Statements:
- “Health care will benefit from being separated from political processes.”
- “Investments in nutrition programs have far-reaching implications for health and productivity.”
- “Public health is not just about treating diseases but preventing them.”
Key Examples and References:
- Dengue as an example of prioritizing immediate relief over long-term prevention.
- Disparity in achieving targets in the Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme For Holistic Nourishment (POSHAN) Abhiyan Scheme.
- Disparity in TB cases between India and the United States due to socio-economic factors.
Key Facts/Data:
- 35.5% of children under five were stunted, and 32.1% were underweight in 2019-21.
- 58.6% to 67.1% increase in prevalence of anaemic children aged 6-59 months.
- India reported 21.4 lakh TB cases in 2021, an 18% increase from 2020.
Critical Analysis:
- The article effectively highlights the drawbacks of immediate, politically-driven health initiatives.
- Emphasizes the importance of evidence-based decision-making and long-term planning in public health.
- Recognizes gaps in public health education and the impact of socio-economic factors on health outcomes.
Way Forward:
- Advocate for a separation of health-care decision-making from short-term political goals.
- Strengthen public health education and adopt a multidisciplinary approach.
- Emphasize evidence-based decision-making and prioritize long-term preventive measures.
- Address socio-economic factors influencing health outcomes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Health Ministry announces new treatment regimen for Leprosy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: New Leprosy Treatment Regimen
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Central government of India has given its approval for a new treatment regimen aimed at hastening the eradication of leprosy in the country.
- The move, based on the latest global scientific research and endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO), seeks to transition from a two-drug regimen to a three-drug regimen for Pauci-Bacillary (PB) leprosy cases.
New Leprosy Treatment Regimen
- Objective: The primary goal is to halt the transmission of leprosy at the sub-national level by 2027, aligning with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals, three years ahead of schedule.
- Transition from Two to Three Drugs: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has approved a shift from the existing two-drug regimen for six months to a three-drug regimen for Pauci-Bacillary (PB) cases.
- Scientific Basis: This decision is grounded in the latest globally accepted scientific research studies and evidence-based practices.
- WHO Endorsement: The World Health Organization (WHO) has committed to supply the revised drug regimen starting April 1, 2025, signifying international recognition and support for this approach.
Key Implementation Steps
- Three-Drug Regimen: The WHO-recommended treatment regimen includes dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine, collectively referred to as MDT. MDT is highly effective in killing the pathogen and curing the patient.
- Advance Requisitions: All States and Union Territories are instructed to submit their requisitions for anti-leprosy drugs a full year in advance to ensure a smooth transition.
- Unified Implementation Date: The revised classification of leprosy and the treatment regimen for both Pauci-Bacillary (PB) and multi-bacillary (MB) cases in India will come into effect simultaneously on April 1, 2025.
Understanding Leprosy
- Leprosy Overview: Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by the Mycobacterium leprae bacteria, primarily affecting the skin and peripheral nerves.
- Transmission: It spreads through droplets from the nose and mouth during close contact with untreated cases.
- Curability: Leprosy is curable with multi-drug therapy (MDT).
Distinction between PB and MB Cases
- PB Cases: These individuals have fewer visible bacteria and show no signs of advanced disease in biopsies.
- MB Cases: They have visible bacteria and may exhibit more advanced disease in biopsies.
Significance of the New Regimen
- Eradication Target: The adoption of this new treatment regimen is expected to accelerate India’s progress towards leprosy eradication by 2027, reinforcing the country’s commitment to combat this disease.
- Previous Funding: The WHO has been providing free MDT, initially funded by the Nippon Foundation and later through an agreement with Novartis. This regimen is known as ‘Uniform MDT,’ simplifying administration and manufacturing processes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Re-evaluating the Use of Mosquitofish in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mosquitofish
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- In recent months, several regions in India, including Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Punjab, have resorted to releasing mosquitofish into local water bodies as a means to combat mosquito-borne diseases.
- While this approach aims to address a pressing public health concern, it brings to light ecological challenges associated with the introduction of mosquitofish.
Understanding Mosquitofish
- Biological Control of Mosquitoes: Mosquitofish, particularly Gambusia affinis and Gambusia holbrooki, were introduced in freshwater ecosystems in the 1960s as an eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides for mosquito control.
- Widespread Distribution: Originally native to the U.S., these fish have become global inhabitants due to their adaptability and tolerance to environmental fluctuations.
- Unintended Consequences: Despite good intentions, the proliferation of mosquitofish has led to detrimental ecological and environmental effects.
Historical Use in India
- Early Introduction: Gambusia was first introduced in India in 1928 during British rule as a measure to combat malaria.
- Government and Non-Governmental Involvement: Various governmental organizations, such as the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the National Institute of Malaria Research (NIMR), as well as local municipal corporations and health departments, were entrusted with introducing mosquitofish.
- Widespread Distribution: Gambusia species are now established in multiple habitats across India.
Ecological Impact
- Invasive Alien Species: Mosquitofish are among the hundred most detrimental invasive alien species worldwide, leading to the displacement and extinction of native fauna.
- Threat to Biodiversity: They exhibit voracious feeding habits and aggressive behavior, posing a threat to native fish, amphibians, and freshwater communities.
- Global Examples: Studies in Australia, New Zealand, and India have shown the harmful consequences of Gambusia presence, including the decline of endemic species and predation on native fish and frogs.
Sustainable Alternatives
- WHO Recommendations: The World Health Organization stopped recommending Gambusia as a mosquito control agent in 1982.
- Government Recognition: In 2018, the National Biodiversity Authority of the Government of India designated G. affinis and G. holbrooki as invasive alien species.
- Local Solutions: Collaborative efforts between mosquito biologists, entomologists, invasion ecologists, and fish taxonomists can identify native fish species capable of mosquito control.
- River Basin Approach: Authorities can compile lists of native fish species in each river basin that are effective in controlling mosquito larvae, offering an eco-friendly alternative to invasive species.
Conclusion
- The introduction of mosquitofish in India, once intended to combat mosquito-borne diseases, has led to ecological challenges and the disruption of native ecosystems.
- To mitigate the adverse effects and protect indigenous aquatic biodiversity, it is essential to discontinue the use of Gambusia and instead explore sustainable alternatives rooted in local solutions.
- By adopting a river basin approach and collaborating across disciplines, India can strike a balance between mosquito control and environmental preservation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and Cervical Cancer
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cervical Cancer
Mains level: Read the attached story
Introduction
- This article sheds light on the significance of Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, the grim reality of cervical cancer in India, and the importance of prevention through knowledge, screening, and vaccination.
Cervical Cancer: Unveiling the Facts
- Prevalence in India: Cervical cancer ranks as the second-most common cancer among Indian women, with its origin in the cervix, the entrance to the uterus from the vagina.
- HPV Connection: Persistent infection by the human papillomavirus (HPV) is the primary cause of cervical cancer. HPV is a common virus that affects nearly all sexually active individuals, often without any symptoms. While the immune system typically clears the virus, high-risk strains can lead to cancer.
- India’s Alarming Stats: India bears a heavy burden, accounting for nearly a quarter of global cervical cancer deaths. Every year, approximately 1.25 lakh women are diagnosed with cervical cancer, and tragically, around 75,000 lose their lives to this disease.
Global Efforts and India’s Progress
- WHO’s Elimination Strategy: In 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO) launched a strategy to eliminate cervical cancer as a public health concern worldwide. The strategy emphasizes three pillars: vaccination, screening, and treatment.
- Positive Trends in India: India may not meet the 2030 goals outlined by WHO, but there is a glimmer of hope. Incidence rates are declining, possibly attributed to factors like sexual hygiene, pregnancy age, contraception use, and individual immune status.
- Comprehensive Approach: Experts stress the need for a multi-pronged approach, including awareness programs, vaccination drives, regular screenings, and education to combat stigma.
Screening Methods and Challenges
- Pap Smear vs. HPV DNA Testing: Traditionally, the pap smear was the gold standard for cervical cancer screening. However, it has limitations, such as the need for cytologists and low awareness, especially in rural areas.
- Advancements in Screening: Today, HPV DNA testing is recommended as the primary screening method. It involves testing cervical cells for high-risk HPV strains. This method is more reliable and less prone to errors.
- Empowering Self-Sampling: Studies suggest that self-sampling for cervical cancer screening, where patients collect their samples, can be as effective as physician-collected samples. Offering this option can enhance screening accessibility.
Vital Role of Vaccination
- HPV Vaccine Controversy: India faced controversy in the past regarding the HPV vaccine’s safety. However, cervical cancer is preventable, and the vaccine targets HPV serotypes 16&18, responsible for 70% of cervical cancers.
- Single-Dose Effectiveness: Recent recommendations from the WHO’s Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) highlight the effectiveness of even a single dose of the HPV vaccine, crucial for countries with low population coverage.
- India’s Vaccination Efforts: Two vaccines, Merck’s Gardasil and Serum Institute of India’s Cervavac, are available in India. Expanding production and introducing the vaccine into national programs are essential steps.
Government Initiatives and Challenges
- State-Level Success: Sikkim set a positive example by introducing free HPV vaccination, achieving high coverage rates among girls aged 9 to 14.
- Slow National Rollout: The Central government’s plan for a nationwide HPV vaccination program faced delays. Despite recent reports suggesting a rollout in phases, the Union Health Ministry has yet to make a final decision.
- Global Perspective: While 100 countries have integrated the HPV vaccine into their national schedules, achieving high coverage remains a challenge, particularly in poorer nations.
Encouraging Early Action
- Optimal Age for Vaccination: Vaccination is recommended for girls aged 9 to 15, providing maximum protection. However, it can benefit adults up to the age of 45.
- Combatting Hesitation: Effective communication and education are essential to address vaccine hesitancy and dispel misconceptions.
- A Global Endeavor: The International Agency for Research on Cancer stresses the importance of scaling up screening programs, expanding HPV vaccination coverage, and increasing access to affordable treatment to meet WHO’s 2030 targets.
What You Can Do
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself and others about HPV and cervical cancer.
- Prioritize Screening: Consult your healthcare provider for cervical cancer screening, especially if you haven’t done so before.
- Consider Vaccination: Discuss the HPV vaccine with your healthcare provider and make an informed choice for yourself or your loved ones.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
ICMR to revisit current National Essential Diagnostics List (NEDL)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NEDL
Mains level: Read the attached story
Introduction
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has initiated the revision of the National Essential Diagnostics List (NEDL), acknowledging the evolving healthcare landscape since its first release in 2019.
- This move aims to optimize the availability of essential diagnostic tests across all tiers of healthcare facilities in India.
What is NEDL?
- Inception: The NEDL extends and builds upon initiatives like the Free Diagnostics Service Initiative (FDI) under which was launched in July 2015 under National Health Mission (NHM).
- Comprehensive List: The NEDL is designed to cater to all levels of healthcare, including village-level healthcare, primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care facilities.
- Scope of Tests: The NEDL focuses on diagnostic tests essential for diseases with significant burdens, such as vector-borne diseases (Malaria, Dengue, Filariasis, Chikungunya, Japanese encephalitis), as well as Leptospirosis, Brucellosis, Tuberculosis, Hepatitis (A, B, C, and E), HIV, and Syphilis. Specific tests are marked as desirable, recommended for regions or states with high disease prevalence.
- In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD): Alongside diagnostic tests, the NEDL recommends corresponding In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) products, which are tests conducted on samples like blood or tissue taken from the human body.
- Regulatory Guidance: The NEDL includes a comprehensive guidance document on the “Regulatory framework for diagnostics: National and International.”
- Human Resources: It also recommends the allocation of human resources, such as ASHA workers, lab technicians, and pathologists, tailored to the proposed list of diagnostics for different healthcare levels.
Significance of NEDL
- Quality Assurance: The availability of quality-assured diagnostics enhances the optimal utilization of the Essential Medicine List (EML).
- SDG Achievement: Implementation of the NEDL contributes to the realization of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.8, aiming for Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- Enhanced Healthcare: The NEDL facilitates evidence-based healthcare, improving patient outcomes, reducing out-of-pocket expenses, and ensuring the effective use of public health facilities. It aids in disease burden assessment, trend analysis, surveillance, outbreak identification, and addressing antimicrobial resistance.
- Standardization and R&D: The NEDL encourages the standardization of technology and diagnostic services, fostering research and development (R&D) for innovative diagnostics, ultimately leading to cost reduction.
Revisiting the List: Careful Consideration Process
- Disease Burden Analysis: The inclusion of diagnostic tests in the NEDL is based on rigorous assessments of disease burden data across India’s diverse states.
- Alignment with National Programs: Tests align with national health programs to address specific health needs.
- Adherence to Standards: The NEDL adheres to Indian public health standards and considers the necessary resources, infrastructure, and personnel required at each healthcare facility.
Factors to Consider
- Essential Test Criteria: Stakeholders are encouraged to propose tests that meet specific criteria:
-
- Priority for healthcare needs
- Alignment with disease prevalence and public health significance
- Demonstrated efficacy, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness
- Impact on Disease Management: Tests should focus on conditions with high disease burdens and substantial public health relevance. The introduction of these tests should significantly enhance disease diagnosis and management.
- Appropriate Utilization: Any proposed addition to the NEDL must align with the availability of equipment, infrastructure, and qualified personnel, by the Indian Public Health Standards of 2022.
Conclusion
- The revision of India’s National Essential Diagnostics List is a crucial step towards ensuring that essential diagnostic tests are accessible at all healthcare levels.
- By aligning with disease burden data and adhering to stringent criteria, India aims to enhance its public health infrastructure, making diagnostics an integral part of healthcare delivery.
- The involvement of stakeholders ensures a comprehensive and effective approach to meet the evolving healthcare needs of the nation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Global Surgery: Why access to essential Surgery is important?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Surgery
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Global surgery, despite its critical importance, often remains in the shadows of global health initiatives.
- This is particularly evident in South Asia, where the world’s largest population lacking access to essential surgery resides.
Why discuss this?
- Global surgery aims to address this disparity by focusing on equitable access to emergency and essential surgical care, encompassing a range of procedures.
- While 2015 marked a turning point in recognizing the significance of global surgery, this field’s history goes back several decades.
What is Global Surgery?
- Equitable Access: Global surgery prioritizes providing equitable access to emergency and essential surgical care, predominantly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), but also in under-served populations within high-income countries (HICs).
- Scope of Surgery: It encompasses essential and emergency surgeries, including surgery, obstetrics, trauma, and anaesthesia (SOTA).
Emergence of Global Surgery
- Annus Mirabilis of 2015: This year marked a pivotal moment in recognizing the global significance of surgical care.
- Influential Reports: The Disease Control Priorities Network (DCPN) report sponsored by the World Bank and The Lancet Commission on Global Surgery (LCoGS) played key roles.
- WHO Resolution 68.15: The World Health Organization Declaration on Safe Surgery highlighted the essential role of surgical systems in achieving universal health coverage.
Magnitude of the Problem
- Access Disparities: Over 70% of the global population, around five billion people, lack timely access to safe and affordable surgical care.
- Regional Disparities: Access gaps are most severe in low- and lower-middle-income countries (LLMICs), with 99% and 96% of people facing disparities, compared to 24% in HICs.
- South Asia’s Challenge: Over 1.6 billion people, over 98% of South Asia’s population, lack access to safe and affordable SOTA care.
- Disease Burden: In 2010, surgically treatable conditions caused around 17 million deaths, surpassing the combined mortality burden of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria.
- Economic Impact: The cumulative projected loss to global GDP due to insufficient surgical care could reach $20.7 trillion by 2030.
Current Efforts and Neglect
- Neglect in Policies: Surgical care often receives little attention in international and national policies.
- Limited Research Focus: Research in global surgery is underrepresented compared to global health.
- Funding Neglect: Funding for surgery is significantly lower than for other health sectors.
- Research Funding Disparity: Research funding for surgery-related projects is scarce compared to other health fields.
Way Forward
- Cost-Effectiveness: Global surgery has demonstrated that emergency and essential surgical care is cost-effective and cost-beneficial.
- Policy Commitment: Many countries have initiated National Surgical, Obstetrics, and Anaesthesia Plans (NSOAPs), demonstrating political and policy commitment.
- Positive Initiatives: Several South Asian countries have launched initiatives to expand surgical access.
- Research and Innovation: Prioritizing research, policy support, and sustainable financing are key to addressing global surgery challenges.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Kerala’s Operation AMRITH to combat Antimicrobial Resistance
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Operation AMRITH
Mains level: Not Much
Introduction
- The Kerala Drug Control Department launched Operation Amrith (Antimicrobial Resistance Intervention For Total Health), a significant initiative to curb the overuse of antibiotics in the state.
Operation AMRITH
- Objective: The initiative aims to optimize antibiotic use by preventing over-the-counter (OTC) sales and ensuring compliance with prescription requirements.
- Pharmacy Regulations: Pharmacies are required to maintain accurate records of antibiotic sales and display notices stating that antibiotics will not be sold without a doctor’s prescription.
- Public Participation: The initiative encourages public involvement by allowing individuals to report pharmacies that sell antibiotics without a prescription.
Enforcement and Compliance
- Surprise Raids: The program includes conducting surprise checks in retail medical shops to detect OTC sales of antibiotics.
- Toll-Free Complaint Number: A toll-free number (18004253182) is provided for the public to lodge complaints against medical shops violating the rules.
- Immediate Action: Complaints are swiftly transferred to relevant zonal offices for verification, followed by immediate departmental action upon confirmation of violations.
Background and Context
- Kerala’s AMR Strategy: Kerala was the first state in India to develop a state action plan on AMR, the Kerala Anti-Microbial Resistance Strategic Action Plan (KARSAP), in 2018.
- Multi-Sectoral Approach: The plan, aligned with India’s National Action Plan on AMR, addresses human, animal, and environmental aspects of AMR containment.
- Support and Collaboration: The plan was developed with contributions from the Centre for Science and Environment and involves various state departments in its implementation.
- Surveillance Networks: The Kerala Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (KARS-NET) monitors AMR in humans, while an integrated plan covers non-human sector surveillance.
- AMR Laboratory: The Kerala State Pollution Control Board (KSPCB) inaugurated an AMR laboratory for environmental surveillance in August 2023.
- PROUD Initiative: The Programme on Removal of Unused Drugs (PROUD) is a drug take-back program piloted in Thiruvananthapuram for the proper disposal of unused antibiotics.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Private: Diminishing Dietary Diversity amidst Biodiversity Emphasis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Read the attached story
Mains level: NA
Introduction
- Despite the global emphasis on biodiversity, the world’s diet has become increasingly homogenous, with staples like rice, wheat, maize, and sugar constituting over half of the global calorie intake.
- Supermarkets mirror this trend, offering a limited selection of vegetables, reflecting a decline in “dietary diversity.”
Dietary Diversity and Issues
- Nutritional Quality: A diverse diet, encompassing various food groups, enhances nutrition. However, the prevalence of monoculture (growing a single crop extensively) diminishes “agricultural biodiversity.”
- Environmental Cost: Importing diverse food groups from distant regions is expensive and environmentally taxing.
Contributors to Nutritional Variety in India
- Small-Scale Farming and Agroforestry: Smallholder farmers, shepherds, and tribal communities practicing agroforestry significantly contribute to India’s nutritional diversity.
- Regional Varieties: India boasts a wide array of local vegetables and crops, varying regionally, provided by these small-scale cultivators.
Examples of Nutrient-Rich Local Varieties
- South India: Leafy greens like Green Amaranth (Tamil, kuppi keerai; Hindi, junglee chaulayi) and Leucas (Tamil, thumbai; Sanskrit, Drona pushpi), rich in iron and calcium; starchy tubers like East Indian arrowroot (Tamil, kuva or ararut-kizhargu; Hindi, tikhur), beneficial for digestion.
- Central India: Edible flowers and oil-rich seeds from the Madhuca or Indian butter tree (Tamil, illupai; Hindi, mahua); Khejri pods (Tamil, parambai) used in local cuisine and combating desertification.
- Northeast India: Indigenous Jhum cultivation, growing diverse crops on the same land, offering dietary variety but declining in practice.
Jhum Cultivation: A Diverse Agricultural Practice
- Contrast to Modern Agriculture: Jhum cultivation, practiced in Northeast India, involves growing multiple food crops together, offering dietary diversity but losing popularity.
- Decline in Practice: Research indicates a significant reduction in Jhum cultivation areas, with a shift towards monoculture crops like areca nut, black pepper, and rubber.
Consumer Influence and Choices
- Role of Consumer Preferences: Consumer tastes significantly impact the availability and cultivation of diverse, wild food varieties.
- Encouraging Diversity: Incorporating lesser-known fruits like wood apples (velam pazham) and Jamuns (nagai) into diets can enhance nutritional quality and support small growers.
Conclusion
- Need for Awareness: Recognizing the importance of dietary diversity is crucial for nutrition, environmental sustainability, and supporting small-scale agriculture.
- Promoting Local Varieties: Embracing local, diverse food options can enrich diets and contribute to preserving agricultural biodiversity, aligning with global efforts to emphasize biodiversity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The blood management system needs a fresh infusion
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: The World Health Organization's report on global disparities in blood collection.
Mains level: public-private partnerships to improve blood collection and distribution
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Proposed Health Tax on Sugar and High-Calorie Foods in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Health Tax
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- Public health researchers recommend a health tax of 20% to 30% on sugar, sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs), and high-fat, salt, and sugar (HFSS) products, in addition to the existing GST.
- The recommendation stems from a UNICEF-funded project, aiming to influence policies to reduce sugar consumption.
Study Insights and Recommendations
- Targeting Bulk Consumers: The study suggests taxing bulk consumers like confectionery manufacturers, rather than household sugar purchases.
- Definition of Sugar: The study includes all forms of refined, unrefined sugar, and gur (brown cane sugar) used by manufacturers.
- Impact on Manufacturers: Manufacturers, who buy up to 55% of India’s annual sugar production, are expected to be more price-sensitive than households.
Tax Implications and Demand Reduction
- Niti Aayog’s Interest: Niti Aayog is exploring the impact of health taxes and warning labels on food products to promote healthy eating in India.
- Current and Proposed Tax Rates: Sugar is currently taxed at 18% GST. The proposed additional tax could raise the total tax to 38-48%.
- Price Elasticity Metric: The study uses ‘Price Elasticity’ to estimate demand reduction. A 10% price increase could lead to a 2% demand reduction for households and a 13-18% reduction for manufacturers.
- Health Tax on Beverages and HFSS Products: A 10-30% health tax on SSBs could decrease demand by 7-30%, while a similar tax on HFSS products might lead to a 5-24% decline.
Government Revenue and Public Health Impact
- Increase in Tax Revenues: Additional taxes could boost government revenues by 12-200% across different scenarios.
- Current Tax Rates on Products: Sugar attracts 18% GST, SSBs 28% GST plus 12% cess, and HFSS products 12% GST.
- Public Health Benefits: Higher taxes on unhealthy foods could reduce obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers.
India’s Sugar Consumption and Health Risks
- India’s Sugar Intake: India is the world’s largest sugar consumer, with an average consumption of 25 kg per person per year, exceeding WHO recommendations.
- Rise in Sugar-Related Health Issues: There has been a significant increase in the sale of aerated drinks and HFSS food products, contributing to obesity and diabetes.
Taxation and Reformulation
- Encouraging Product Reformulation: The proposed tax rate is linked to sugar volume, encouraging manufacturers to reduce sugar content in products.
- Taxing Sugar Replacements: The study also recommends taxing artificial sweeteners to prevent manufacturers from switching to cheaper, unhealthy alternatives.
Global Precedents and Outcomes
- Health Tax Implementation Worldwide: Over 70 countries, including Mexico, Chile, and South Africa, have implemented health taxes on sugar and related products.
- Positive Outcomes in Mexico: In Mexico, the taxation on SSBs led to decreased consumption of taxed beverages and a reduction in mean BMI among younger age groups.
Conclusion
- Potential for Health Improvement: Imposing a health tax on sugar and related products could significantly contribute to public health improvement in India.
- Consideration of Economic Factors: The success of such a policy will depend on balancing health benefits with economic impacts on consumers and manufacturers.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A call for disability inclusion that must be heeded
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: na
Mains level: neuropsychiatric disorders

Central idea
Dr. Ennapadam S. Krishnamoorthy advocates for prioritizing rehabilitation services globally, emphasizing their crucial role in treating neuropsychiatric disorders across the lifespan. He highlights the need for awareness, collaboration, and innovative solutions to address the significant burden of disabilities and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
Key Highlights:
- Dr. Ennapadam S. Krishnamoorthy emphasizes the importance of transformative solutions for persons with neuropsychiatric disorders, spanning childhood to old age.
- The focus is on enhancing activities of daily life and quality of life for individuals affected by various neuropsychiatric conditions.
- Rehabilitation services are crucial, with 2.41 billion individuals globally requiring rehabilitation according to the WHO’s Global Burden of Disease study.
Key Challenges:
- Rehabilitation is often seen as a disability-specific service, leading to under-prioritization despite its significant societal benefits.
- Lack of awareness in the community that disablement can be treated and, in some cases, reversed.
- The need for a shift in perception among medical professionals to recognize rehabilitation as an essential service.
Key Terms:
- Neuropsychiatric disorders
- Transformative solutions
- Rehabilitation
- Non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS)
- Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
- Functional Magnetic Stimulation (FMS)
- Transcranial electrical stimulation (TES)
- Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tA-VNS)
Key Phrases:
- “Rehabilitation needs are plentiful with a global burden of 2.41 billion individuals.”
- “Neurology and psychiatry are closely linked, requiring a continuum of care.”
- “Scientific advances, such as NIBS procedures, offer promising avenues for treatment.”
Key Quotes:
- “Disablement does not need to be endured; it can be treated, even reversed, in a proportion of cases.”
- “Rehabilitation services need to be multidisciplinary, multicomponent, and holistic.”
Key Statements:
- “Rehabilitation services are traditionally under-resourced despite individual and societal benefits.”
- “There is a need to build awareness that disablement can be treated.”
Key Examples and References:
- Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) as a mainstream treatment for depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- Functional Magnetic Stimulation (FMS) for pain, spasticity, and other neurological symptoms.
- Transcranial electrical stimulation (TES) showing success in improving memory, cognition, mood, and various neurological conditions.
- Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tA-VNS) being investigated for depression, migraine, and dysautonomia.
Key Facts:
- 2.41 billion individuals globally had conditions benefiting from rehabilitation in 2019.
- The number of individuals requiring rehabilitation increased by 63% from 1990 to 2019.
Key Data:
- 317 million individuals affected by neuropsychiatric disorders in childhood.
- 167 million adolescents and 970 million people affected globally by mental health conditions.
Critical Analysis:
- Lack of prioritization and resources for rehabilitation despite a significant global burden.
- The necessity for a paradigm shift in perceiving rehabilitation as essential for a broad spectrum of neurological and mental health problems.
Way Forward:
- Increase awareness about the treatability of disabilities.
- Promote collaboration between governments, public and private sectors to find innovative solutions for persons with disabilities.
- Enhance training and development opportunities for rehabilitation professionals.
- Advocate for a multidisciplinary, holistic approach to rehabilitation services.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Decriminalising Medical Negligence: Views from both sides of the bed
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Medical Negligence and its impact on the marginalized people

Central Idea
- A women recently died from septic shock after a surgery in Jamshedpur, leading her brother to allege medical negligence due to unauthorized surgeon substitution and lack of postoperative care.
- The case has ignited discussions on the legal and ethical aspects of medical negligence in India, amidst proposed changes to exempt doctors from criminal prosecution.
Understanding Medical Negligence
- Definition and Impact: Medical negligence involves a breach of duty by healthcare professionals, leading to patient harm or death.
- Legal Framework: Currently, under Section 106(1) of the Bharatiya Nyaya (Second) Sanhita (BNSS), doctors face potential imprisonment and fines if convicted of negligence, though proposed changes might alter this.
Recent Developments and Legal Provisions
- Recent Announcement: MHA proposed exempting doctors from criminal prosecution in negligence cases, sparking debate and concern among various stakeholders.
- Constitutional Rights: The proposed changes have to be balanced against constitutional protections like Article 20(3) and Article 21, which safeguard against self-incrimination and ensure the right to life and liberty.
Role of the Indian Medical Association (IMA)
- IMA’s Stance: The IMA has advocated for exempting doctors from criminal prosecution for negligence, citing the increasing harassment and detrimental impact on patient care.
- Concerns Raised: The IMA also highlighted the high number of medical negligence cases filed against doctors and the economic losses due to violence against healthcare professionals.
Ethical and Societal Implications
- Power Dynamics: Critics argue that exempting doctors from criminal prosecution might exacerbate power imbalances in the doctor-patient relationship and lead to increased medical malpractice.
- Marginalized Populations at Risk: There’s concern that such exemptions could disproportionately affect vulnerable groups, including women, queer, transgender individuals, and rural residents.
Legal and Ethical Conundrums
- Good Faith Clause: BNSS clauses provide some protection for acts done in good faith, but the distinction between negligence and accident remains unclear.
- Bioethicists’ Perspective: Experts emphasize the need for a balanced approach that considers both healthcare professionals’ challenges and patients’ rights and safety.
Way Forward
- Nationwide Dialogue: The IMA plans to engage in discussions with the government and public to advocate for their position.
- Need for Comprehensive Data: Critics like Geet suggest conducting a nationwide survey to understand the scope of medical negligence and inform policy decisions.
- Legal Recourse for Patients: Ensuring that patients have access to legal recourse and justice is crucial to maintaining trust in the healthcare system and preventing violence against doctors.
Conclusion
- Complex Decision-Making: Exempting doctors from criminal prosecution for medical negligence is a multifaceted issue requiring careful consideration of legal, ethical, and societal factors.
- Ensuring Justice and Quality Care: Any policy changes must strive to protect patients’ rights while also considering the challenges faced by medical professionals, ensuring that the healthcare system remains just, accountable, and focused on delivering high-quality care. Top of Form
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The quest for ‘happiness’ in the Viksit Bharat odyssey
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Innovation Index, Rule of Law Index, Poverty Index
Mains level: Viksit Bharat
Central idea
The article calls for a reimagining of India’s development strategy, shifting from an economic-centric model to prioritizing happiness and well-being. It critiques the current focus on GDP, highlighting the need for comprehensive social indicators in the development narrative. The central idea is to envision a “Happy India-Developed India” by 2047, where happiness becomes the central pursuit, transcending conventional economic measures.
Key Highlights:
- Viksit Bharat Launch: The launch of Viksit Bharat aims to make India a developed nation by its 100th Independence year in 2047.
- Economic Overemphasis: Critics argue that Viksit Bharat places excessive emphasis on economic development, overlooking other crucial aspects.
- Happiness as Central Pursuit: The author suggests reimagining the theme as ‘Happy India-Developed India,’ focusing on happiness as a central pursuit for meaningful development.
- Happiness Metrics: The World Happiness Report measures happiness through variables like GDP per capita, life expectancy, generosity, social support, freedom, and perception of corruption.
- Social Connections and Well-being: Countries like Finland and Denmark, ranked highest in happiness, emphasize social connections and support systems, contributing to well-being.
Key Challenges:
- Economic-Centric Development: The challenge lies in shifting the development narrative from an economic-centric model to one that prioritizes happiness and well-being.
- Social Disruption: The current economic-focused development model may lead to social disruption, imbalances, and contradictions.
- Disregard for Social Indicators: The conventional focus on GDP fails to consider crucial social indicators, neglecting human and social aspects of development.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Viksit Bharat: The development initiative launched with the goal of making India a developed nation by 2047.
- World Happiness Report: An annual report measuring happiness using multiple variables and indicators.
- Human Development Index (HDI): An index considering life expectancy, educational attainment, and income level.
- Green Index: A World Bank-developed index measuring a nation’s wealth based on produced assets, natural resources, and human resources.
- Social Development Index: Introduced by the UN Research Institute for Social Development, it includes 16 core indicators.
- Global Innovation Index, Rule of Law Index, Poverty Index, Corruption Perceptions Index, Gender Equality Index, and World Press Freedom Index: Various indices significant for comprehensive national development.
Key Quotes:
- “Without achieving happiness, development has no meaning.”
- “Happiness ought to be the central pursuit in this journey.”
- “The nations have developed, but people are not happy.”
Critical Analysis: The article critically examines the conventional economic-focused development model and advocates for a paradigm shift towards happiness-centric development. It emphasizes the inadequacy of GDP-centric measures and highlights the importance of considering social indicators for a more inclusive and balanced development approach.
Way Forward: The way forward involves reimagining the development narrative, giving importance to happiness metrics, and incorporating a broader set of indicators such as the Human Development Index, Green Index, and others. Prioritizing social connections, well-being, and happiness in development strategies will contribute to a more holistic and sustainable vision for Viksit Bharat@2047.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Loneliness in India: A Deepening Public Health Concern
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Mental Health Issues
Central Idea
- The World Health Organization (WHO) recently declared loneliness a significant global health threat, with an estimated 10% of adolescents and 25% of older people affected worldwide.
- Despite being a collectivistic society with over 140 billion people, loneliness in India remains relatively understudied and unacknowledged as a public health and social issue.
Understanding Loneliness
- Definition: Loneliness is defined as the unpleasant experience due to a deficiency in one’s network of social relations, either quantitatively or qualitatively.
- Health Impact: Comparable to smoking 15 cigarettes a day, loneliness can lead to severe mental and physical health issues, including heart disease, depression, and decreased longevity.
Data and Trends in India
- Historical Data: Studies from the early 1990s to recent years show varying rates of loneliness, with a notable increase in loneliness among the elderly and the highly educated.
- Pandemic Effect: COVID-19 and subsequent lockdowns have exacerbated loneliness, particularly among young people and those living alone.
Disparities and Challenges
- Higher Among Educated Youth: Young, highly educated individuals face disproportionately higher rates of unemployment and loneliness, indicating a structural issue in the Indian economy.
- Cultural Stigma: In India, loneliness is often dismissed as a phase or a state of mind, and discussing mental health is stigmatized, making it challenging to address the issue effectively.
Public Health Implications
- Rising Disease Burden: Loneliness contributes to an increased risk of various diseases, potentially inflaming India’s already rising communicable and non-communicable disease burden.
- Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure: India’s healthcare system struggles with inadequate staff, infrastructure, and budgetary allocation, further complicating the response to the loneliness epidemic.
The Indian Experience of Loneliness
- Cultural Differences: Unlike Western countries, India’s collectivistic culture and socioeconomic barriers present unique challenges in understanding and addressing loneliness.
- Marginalized Communities: Loneliness disproportionately affects marginalized identities, and addressing it requires understanding the intersection of social inequity and mental health.
Addressing Loneliness as a Structural Problem
- Need for Targeted Interventions: Recognizing loneliness as a distinct condition can help develop interventions tailored to India’s cultural context.
- Community-Based Solutions: Addressing loneliness may require community-focused strategies that respond to structural inequities rather than solely clinical approaches.
Conclusion
- National-Level Surveys: Conducting comprehensive surveys in local languages can help understand the true scale of loneliness in India’s diverse population.
- Holistic Approach: Combating loneliness in India requires a multifaceted approach that includes improving mental health literacy, enhancing healthcare infrastructure, and addressing social inequalities.
- Continuous Engagement: As loneliness gains recognition as a public health issue, India must continuously adapt its strategies to effectively support those affected by this silent epidemic.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Ethics and Compensation in Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS)
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- A recent paper from August 2023 discusses the ethical and financial aspects of Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS), where participants are deliberately infected with pathogens.
- The paper argues that $20,000 for a six-month hepatitis C virus challenge study in the U.S. is reasonable, based on participant experiences and responses from potential participants.
Ethical Considerations in CHIS
- Contentious Issues: One major ethical concern in CHIS is the potential for disproportionate payment, which could be seen as an inducement for participation.
- ICMR’s Bioethics Unit Stance: Emphasizes altruism in CHIS participation, suggesting compensation should cover lost wages, incidental expenses, time, and effort.
Views on Altruism and Compensation
- Jake D Eberts’ Perspective: Disagrees with the ICMR’s emphasis on altruism, arguing that monetary motivation, if accompanied by informed consent and risk understanding, isn’t inherently negative.
- Compensation in Past Studies: Eberts received $7,350 for a Shigella study and less than $5,000 for a Zika study. He advocates for higher compensation in CHIS in the U.S.
Compensation Models and Ethical Frameworks
- Dr. Anna Durbin and Dr. Wilbur H. Chen’s Approaches: Compensation based on time, specimen collection, and regional study pay standards. Dr. Chen uses a Wage-Payment model, aligning compensation with unskilled labor wages in somewhat risky jobs.
- Compensation Calculation: For the Shigella study, compensation totaled $7,350, based on various factors like visit duration, risk level, and activities completed.
Differing Opinions on CHIS Compensation
- Paul Zimmer-Harwood’s Experience: Participated in malaria and COVID-19 CHIS, with compensation based on study duration, visits, and inconvenience, not risk.
- COVID-19 CHIS Concerns: Dr. Chen questions the rationale for COVID-19 CHIS, citing the absence of effective therapies and the risk of Long COVID.
Participant Perspectives and Decisions
- Paul’s Decision-Making: Chose to participate in the COVID-19 CHIS due to low perceived risk, previous infection, and vaccination status. Compensation was higher but proportional to study demands.
- Risk Assessment: Paul viewed the risks as acceptable compared to the potential scientific contributions, emphasizing that his decision was informed and measured.
Conclusion
- Complex Ethical Landscape: CHIS presents a nuanced ethical landscape where compensation, risk, and participant motivation must be carefully balanced.
- Importance of Informed Consent: Ensuring participants are fully informed and understand the risks is crucial in maintaining ethical standards in CHIS.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA) and Its Implications
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA)
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The Odisha Government invoked its Essential Services (Maintenance) Act (ESMA) prohibiting strikes by paramedical staff, including nurses, pharmacists and technicians to ensure that medical services are not disrupted.
About Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA)
- Description: The Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA) is a significant piece of legislation enacted by the Parliament in 1968.
- Constitutional Placement: It falls under list no. 33 in the 7th schedule under the concurrent list of the Indian Constitution.
- Purpose: ESMA is primarily used by states to manage strikes by employees, especially in essential services.
- Essential Services: The Act empowers the government to designate any economic activity or service as ‘essential’, where disruption would impact the normal life of people.
Provisions and Powers under ESMA
- Police Authority: The Act grants police the authority to arrest protestors without a warrant if they violate the provisions of ESMA.
- State-Specific Provisions: Each Indian state has its unique version and provisions of the ESMA.
Right to Strike in Context
- Worker’s Basic Right: Striking is a fundamental means for workers to legitimately promote and defend their economic and social interests.
- Legal Status: While the right to protest is a fundamental right under Article 19 of the Indian Constitution, the right to strike is a legal right with certain restrictions.
- Industrial Dispute Act 1947: This act outlines the legal framework and restrictions for strikes, especially in public sectors and essential services.
- Restrictions in Specific Sectors: Strikes are particularly restricted for public sector employees, banking, oil, metropolitan transport, and education sectors under state jurisdiction.
International Labor Organization (ILO) and the Right to Strike
- ILO’s Stance: The ILO’s Committee on Freedom of Association has established principles regarding the right to strike.
- Essential Services Definition: Essential services are those whose interruption could endanger the life, safety, or health of part or all of the population.
- Examples of Essential Services: The committee identifies sectors like hospitals, electricity, water supply, telephone services, and air traffic control as essential services.
- Restriction on Strikes: Employees in these essential services are generally not permitted to strike.
Problems and Criticisms of ESMA
- Irresponsible Use: The Act has been criticized for its sometimes irresponsible and unwise implementation.
- Suppression of Democratic Rights: ESMA is seen as monopolizing power and suppressing the democratic rights of stakeholders, particularly the right to protest or strike.
- Government’s Overpowering Role: Critics argue that ESMA dangerously skews the balance in industrial relations towards the government in the public sector.
Conclusion
- Debate on ESMA’s Role: The Essential Services Maintenance Act remains a contentious topic, balancing the need for uninterrupted essential services with the rights of workers to strike.
- Need for Responsible Implementation: Responsible and democratic application of ESMA is crucial to maintain this balance.
- Ongoing Discussions: The Act continues to spark debate about the extent of government power and the protection of workers’ rights in essential sectors.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Invisible Indians – sex workers, bar dancers, trans men and women – and lessons for AIDS epidemic
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: World AIDS Day
Mains level: resilience of sex workers, bar dancers, and trans individuals

Central idea
The article on World AIDS Day sheds light on the neglected lives of Mumbai’s marginalized communities, emphasizing lessons from the HIV epidemic. It calls for grassroots engagement, holistic healthcare solutions, and dignity-centered public health strategies.
Key Highlights:
- Forgotten Narratives: Reflecting on the lives of marginalized communities in Mumbai on World AIDS Day.
- Overlooked Wisdom: Emphasizing the resilience of sex workers, bar dancers, and trans individuals.
- Lessons from the Epidemic: Drawing insights from the HIV epidemic and its impact on these communities.
Key Challenges:
- Information Gap: Sub-standard public awareness efforts leading to misinformation.
- Access Barriers: Discrimination preventing vulnerable communities from accessing healthcare.
- Top-Down Struggles: Ineffectiveness of top-down approaches in understanding diverse high-risk communities.
Key Terms:
- Grassroots Engagement: Involving local communities in decision-making and solutions.
- Holistic Solutions: Addressing issues comprehensively, considering social, economic, and cultural contexts.
- Stigma and Discrimination: Negative attitudes and actions directed towards marginalized groups.
Key Phrases:
- “Forgotten Narratives“: Bringing attention to the overlooked stories of marginalized communities.
- “Grassroots Wisdom”: Advocating for effective health interventions through community involvement.
- “Holistic Approach”: Moving beyond traditional health services for comprehensive solutions.
Key Examples and References:
- Walks in Mumbai’s Shadows: Personal anecdotes from journeys with marginalized groups.
- Voices of Resilience: Quotes sharing insights on life, disease, and discrimination.
- Epidemic Lessons: Reference to valuable knowledge gained during the HIV epidemic.

Key Facts:
- Call for Collective Action: Emphasizing the need for public trust and stakeholder involvement.
- Investment in Health: Recognizing the commitment of poor and vulnerable populations to their well-being.
- Activism’s Role: Highlighting activism as essential for equitable and accessible healthcare.
| Key Quotes, Anecdotes, Key Statements for good marks |
| “Even the best strategies falter without grassroots engagement.” |
| “The key to ending an epidemic lay in uniting diverse high-risk groups, combating stigma and discrimination.” |
| “Conversations with these communities illuminated the multidimensional aspects of human sexuality, desire, and behavior change.” |
| “Every issue had human, economic, and social dimensions.” |
| “Activism is the kernel around which change can grow. In India, even today, marginalized groups face mistreatment, and it is activism that can make care equitable and accessible.” |
| “Health must come with dignity and empowerment.” |
| “They certainly gave me life lessons in self-respect, desire, and love.” |
Critical Analysis:
- Emotional Impact: Personal anecdotes and quotes enhance the emotional connection to the narrative.
- Advocacy for Change: Effectively advocates for a shift towards inclusive, grassroots-centered health strategies.
- Learnings from Marginalized: Stresses the importance of learning from marginalized communities for effective healthcare solutions.
Way Forward:
- Dignity-Centered Strategies: Calls for strategies prioritizing dignity, equity, and grassroots engagement.
- Community Learning: Emphasizes the value of understanding and incorporating lessons from marginalized communities in public health interventions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Mosquitofish: India’s Battle against Invasive Species
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mosquitofish
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- In recent months, Indian states such as Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Punjab have introduced mosquitofish to combat mosquito infestations.
- However, the unintended ecological consequences of introducing this invasive species have raised concerns.
Backgrounder: Vector Borne Diseases
- Global Mosquito-Borne Disease Prevalence: Mosquito-borne diseases affect over 150 countries and 500 million people worldwide.
- India’s Burden: India alone reports approximately 40 million cases of mosquito-borne diseases annually.
What is Mosquitofish?
- Introduction in the 1960s: In the 1960s, biological control methods were adopted to combat mosquitoes, including the introduction of mosquitofish (Gambusia species).
- Environmental Alternatives: These methods were considered environmentally friendly alternatives to chemical pesticides, which posed health and environmental risks.
- Global Proliferation: Mosquitofish, originally from the U.S., have now become widespread globally, adapting to various environments with adverse ecological impacts.
Mosquitofish in India
- Historical Introduction: In 1928, Gambusia was introduced in India during British rule, mainly for malaria control.
- Multiple Authorities Involved: Various governmental and private organizations, including the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), National Institute of Malaria Research (NIMR), municipal corporations, and health departments, introduced mosquitofish across India.
Ecological Impact
- Invasive Alien Species: Mosquitofish are considered among the hundred most detrimental invasive alien species.
- Negative Effects: They prey on native fauna, leading to the extinction of native fish, amphibians, and freshwater communities.
- Examples from Other Countries: Australia and New Zealand have reported similar ecological harm due to introduced mosquitofish.
- WHO’s Stand: The World Health Organization stopped recommending Gambusia for mosquito control since 1982.
Current Situation and Recommendations
- Enforcement Measures: Stringent enforcement measures are essential to prevent further introduction of mosquitofish and mitigate past introductions’ consequences.
- Alternative Solutions: Collaboration between mosquito biologists, entomologists, invasion ecologists, and fish taxonomists is suggested to identify native fish species capable of controlling mosquito larvae.
- Local Solutions: Local alternatives should be favored over invasive species to preserve indigenous aquatic biodiversity and native species’ well-being.
- National Centre for Vector Borne Diseases Control (NCVBDC): The NCVBDC should remove its recommendation for the use of Gambusia and Poecilia (guppy) fishes for mosquito control.
Conclusion
- India faces a pressing ecological challenge with the unintended consequences of mosquitofish introduction.
- To safeguard the environment and native species, stringent enforcement and local solutions should replace invasive species in mosquito control efforts.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Branded, generic and the missing ingredient of quality
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: The Hathi Committee
Mains level: Nexus between pharmaceutical companies and doctors
What is the news?
Following the Indian Medical Association’s protest, the NMC has withdrawn the order on ‘generic prescribing’ since August 23, 2023
Central idea
The article highlights challenges in India’s healthcare system, emphasizing the struggle between generic and brand prescriptions. It discusses the alleged nexus between pharmaceutical companies and doctors, quality assurance concerns, and the need for comprehensive measures to ensure affordable and reliable access to medicines. The withdrawal of the generic prescribing order reflects ongoing complexities in achieving universal healthcare goals.
Key Highlights:
- Over-the-Counter Medical Sales in India: Patients often seek second opinions from non-qualified individuals in medical shops, with queries ranging from medicine strength to potential side effects.
- Generic vs. Brand Names: The National Medical Council (NMC) directed doctors to prescribe generic names over brand names, emphasizing the cost factor and the affordability of generic names. The Hathi Committee in 1975 supported the gradual phasing out of brand names.
- Alleged Nexus and Ethical Commitment: An alleged nexus between pharmaceutical companies and doctors exists, but medical associations stress their ethical commitment to improving access to affordable medicines.
- Quality Assurance Concerns: Concerns about the quality of medicines persist, with a prevalence rate of 4.5% for spurious and 3.4% for “not standard quality” medicines. The need for 100% quality-tested drugs is crucial for patient safety.
- Government’s Role: The government is urged to ensure quality through Universal Health Coverage and private healthcare networks, with calls for periodic sampling, banning batches that fail quality tests, and taking punitive actions against manufacturers.
Challenges:
- Quality Assurance Implementation: Existing mechanisms for quality assurance are not earnestly implemented, raising concerns about the reliability of the system.
- Enforcement of Generic Prescription: The moral dilemma in enforcing generic prescription without concrete evidence of standard quality poses a challenge in the healthcare system.
- Availability of Essential Medicines: The low availability rate of essential medicines, especially pediatric medicines, hampers the effective treatment of patients.
- Unscientific Combinations: The presence of unscientific combinations of medicines in the retail market adds complexity to the pharmaceutical landscape.
Analysis:
- Role of the Chemist: Concerns revolve around the chemist or less knowledgeable salesperson determining the brand, potentially based on profit motives, impacting the choice of medicines.
- Withdrawal of Generic Prescription Order: The withdrawal of the NMC order on generic prescribing, following the Indian Medical Association’s protest, reflects the ongoing challenges in healthcare policy.
| Case study to improve answer quality
The Tamil Nadu Medical Services Corporation Limited’s practice, where all supplied medicines are kept under quarantine stock till double blinded samples are cleared in quality testing by government and private sector laboratories, is worth replicating. |
Key Data:
- Prevalence of Spurious and NSQ Medicines: National drug surveys in the last 10 years indicate prevalence rates of 4.5% for spurious and 3.4% for “not standard quality” medicines, highlighting the need for stricter quality control.
- Availability of Essential Pediatric Medicines: A study in Chhattisgarh in 2010 found only a 17% availability rate of essential pediatric medicines, indicating a significant gap in accessibility.
Way Forward:
- Government Assurance and Evidence: The government should provide concrete evidence of the standard quality of medicines before enforcing generic prescriptions, ensuring patient safety.
- Comprehensive Measures: Implementing comprehensive measures, such as limiting profit margins for wholesale and retail agents, is crucial for creating a transparent and fair pharmaceutical ecosystem.
- Janaushadhi Kendras Expansion: Expanding the network of Janaushadhi kendras is essential to improve accessibility to affordable medicines and promote their widespread availability.
- Monitoring Implementation: Ensuring proper implementation and monitoring of policies for free medicines and diagnostics under Universal Health Care is vital for the success of healthcare initiatives.
- Addressing Profit Motives: Addressing profit motives influencing the choice of medicines by chemists and salespersons is essential for a patient-centric healthcare system.
Conclusion:
The withdrawal of the generic prescribing order is seen as a step back in achieving universal access to affordable generic medicines. Addressing quality concerns, ensuring availability, and monitoring implementation are crucial for a successful healthcare system.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Remission of diabetes, desirable, but not essential
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Prediabetes
Mains level: Holistic Diabetes Management
Central idea
The article highlights the importance of using precise terms like “remission” rather than “reversal” in discussing diabetes. It introduces the ABCDE criteria for potential remission, emphasizing factors like A1c, BMI, and duration. The author advocates a disciplined approach (ABCD: A1c, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, Discipline) for a healthy life, addressing India’s substantial diabetes challenges.
Key Highlights:
- Redefining ‘Reversal’: Dr. V. Mohan demystifies the trend of claiming ‘diabetes reversal,’ emphasizing the more accurate term ‘remission.’
- Remission: Temporary relief or improvement from diabetes without a permanent cure.
- ABCDE Criteria for Remission: Identification of crucial factors—A1c, BMI, C-Peptide, Duration, and Enthusiasm—that influence the likelihood of remission in type 2 diabetes.
- A1c: Glycated hemoglobin, a measure of average blood sugar levels over the past three months.
- BMI: Body Mass Index, a measure indicating body fat based on weight and height.
- C-Peptide: A marker for insulin secretion, indicating the body’s ability to produce insulin.
- Duration: Period of time since the onset of diabetes.
- Enthusiasm: Eagerness and commitment towards achieving remission.
- Legacy Effect: Recognizing the enduring benefits of achieving even short-term remission in diabetes and its role in preventing complications.
- Legacy Effect: Long-lasting positive impact resulting from past actions or conditions.
- Lifestyle Discipline: Advocating a disciplined lifestyle, with A1c below 7%, controlled blood pressure, and cholesterol as key components for a healthy life with diabetes.
Challenges:
- Deceptive Claims: Cautioning against misleading claims by commercial entities promoting diabetes reversal.
- Individual Variations: Highlighting the diverse likelihoods of achieving remission among individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Post-Remission Severity: Noting the common occurrence of increased diabetes severity upon its recurrence post-remission.
- Post-Remission Severity: Worsening of diabetes conditions after a period of temporary relief.
- Long-term Remission Challenges: Acknowledging the difficulty for a majority in achieving and sustaining long-term remission.
Key Phrases:
- ABCDE Benchmark: Proposing the ABCDE criteria as a pivotal benchmark for assessing the potential for remission in type 2 diabetes.
- Short-Term Remission Benefits: Underlining the lasting benefits, both physical and preventive, derived from short-term diabetes remission.
- Disciplined Lifestyle Advocacy: Advocating for a disciplined lifestyle encompassing A1c control, blood pressure regulation, and cholesterol management.
- Remission Duration Impact: Recognizing that even temporary remission contributes significantly to safeguarding against diabetes-related complications.
Analysis:
- Holistic Diabetes Management: Dr. Mohan stresses the importance of holistic diabetes management that extends beyond the pursuit of remission.
- Holistic Management: Comprehensive and integrated approach addressing various aspects of diabetes care.
- Remission Realities: Acknowledging the challenge for many individuals to achieve and sustain long-term remission in type 2 diabetes.
- Guidelines Adherence: Reinforcing the significance of adhering to ABCD guidelines for a healthy life despite diabetes.
- Balancing Expectations: Encouraging a balanced perspective on diabetes management, considering the varied responses to remission efforts.
Key Data:
- Diabetes Landscape: A snapshot of diabetes prevalence in India, with 101 million people diagnosed and 136 million in the prediabetes stage.
- Diabetes Prevalence: The proportion of the population affected by diabetes.
- Prediabetes Management: Recognizing the potential for delaying the onset of diabetes through lifestyle modifications in individuals with prediabetes.
- Prediabetes: A condition preceding diabetes, indicating higher-than-normal blood sugar levels.
Key Facts:
- Complications Risk: Highlighting the risks of sub-optimal diabetes control, contributing to severe complications.
- Expert Insight Impact: Dr. Mohan’s insights, drawn from extensive experience, underscore the potential for a healthy life despite diabetes.
- National Health Objective: Reinforcing the national health objective of achieving a ‘diabetes complications-free India.
Way Forward:
- World Diabetes Day Pledge: Urging a renewed commitment on World Diabetes Day to prevent diabetes complications and promote overall well-being.
- Dream of Complications-Free India: Aspiring toward realizing a ‘diabetes complications-free India’ by navigating existing challenges with determination and awareness.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Hypertension Care: Insights from India’s Healthcare Landscape
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hypertension
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- An analysis of recent National Family Health Survey data, as published in the journal JAMA, has revealed substantial disparities in the prevalence, diagnosis, treatment, and control of hypertension within Indian states and districts.
- These disparities underscore the need for targeted and decentralized solutions to address the complexities of hypertension care across the nation.
What is Hypertension?
- Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a medical condition in which the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high.
- Blood pressure is measured in millimetres of mercury (mm Hg) and is expressed as two numbers: systolic pressure over diastolic pressure.
- The systolic pressure represents the force when the heart contracts, while the diastolic pressure represents the force when the heart is at rest between beats.
- Normal blood pressure is typically around 120/80 mm Hg. Hypertension is diagnosed when blood pressure consistently measures at or above 130/80 mm Hg.
- However, different organizations may have slightly different guidelines for defining hypertension.
Key Findings of the Study
- National-Level Observations: The national-level data reveals a common trend – a significant proportion of individuals with hypertension remain undiagnosed, and even among those diagnosed, many do not initiate treatment. Moreover, among those who commence treatment, few achieve adequate blood pressure control.
- Inter-State Variation: The study notes that while the prevalence of hypertension is comparable in southern states, it is notably higher than the national average, with 29.9% of the population in these states affected compared to 26.8% nationally.
- District-Level Disparities: The study highlights substantial variations within states. For instance, in Meghalaya, the prevalence of hypertension differs significantly across Garo Hills, Jaintia Hills, and Khasi Hills districts, affecting the diagnosis rates. A similar scenario is observed in Karnataka’s Chikmagalur, Shimoga, Udupi, and Chitradurga districts.
Impact of Demographics and Education
- Gender and Age: Despite hypertension being more prevalent in men, the data surprisingly reveals that women are more likely to be diagnosed, receive treatment, and achieve blood pressure control.
- Socio-Economic Status: Individuals in the wealthiest quintile demonstrate higher rates of prevalence, diagnosis, treatment initiation, and control.
- Education Level: Completion of schooling correlates with better rates of diagnosis, treatment, and control compared to those with no schooling or up to Class 11.
Significance of Inter-State and Inter-District Variability
- Resource Allocation: District-level data can guide state governments in allocating resources efficiently. It helps identify districts with a high prevalence of hypertension that may require increased screening and diagnostic facilities or better accessibility to medicines.
- Continuum of Care: Managing chronic conditions like hypertension requires a distinct healthcare approach. Ensuring regular availability of medicines, digitization of records for follow-ups, and the establishment of accessible treatment centers are critical components of an effective continuum of care.
Controlling Hypertension in India
- WHO’s Call to Action: The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the potential to avert nearly 4.6 million deaths in India by 2040 if half of hypertensive individuals can control their blood pressure.
- Government Initiative: India launched a comprehensive initiative in 2023 to treat 75 million people with hypertension or diabetes by 2025. This endeavor extends beyond infrastructure expansion to active screening, treatment initiation, medication accessibility, and follow-up mechanisms.
Conclusion
- India’s quest to bridge the gaps in hypertension care demands a multifaceted approach.
- The district-level insights offered by this study can guide policymakers in crafting targeted solutions, ultimately enhancing the continuum of care for hypertension and contributing to better public health outcomes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Salt Consumption and Health: Striking a Delicate Balance
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Salt and its Heath Hazards
Mains level: Rising burden of NCDs in India
Central Idea
- Salt is an essential component of our diet, adding flavor to our food and serving vital bodily functions.
- However, excessive salt intake can lead to health issues, including high blood pressure.
Salt Intake in India
- In India, a recent national survey revealed that men consume 8.9 grams, while women intake 7.1 grams of salt daily (Prashant Mathur et al., Scientific Reports, 2023).
- While the World Health Organization recommends a daily salt intake of 5 grams, the global average is much higher at 10.8 grams.
Salt and Health Implications
- Diverse Health Effects: Extensive research in animals and human surveys consistently link high salt consumption to kidney, brain, vascular, and immune system diseases. Conditions such as kidney stones and osteoporosis are associated with excessive sodium intake.
- Global Impact: Excessive salt intake contributes to approximately five million deaths worldwide annually, underscoring the global health impact of salt-related health issues.
The Yanomami Example
- The Yanomami people, living in the Amazon rainforest, follow a foraging lifestyle and consume a diet primarily composed of Cassava, plantains, fruit, fish, and occasionally tapir.
- Interestingly, they use peppers for flavor but do not use salt.
- Their daily salt intake is less than one gram, yet they maintain excellent health and fitness.
Salt and Obesity Connection
- Balancing Act: While our bodies require salt for essential functions, excessive salt consumption can lead to health problems, including obesity.
- Metabolic Impact: High salt intake impairs metabolism and increases the size of adipocytes, the cells that store fat, contributing to obesity.
- Dietary Preferences: There is a connection between a preference for high-fat and salty foods. Experiments with mice showed that those exposed to high-fat diets during gestation preferred salty water.
Reducing Salt Intake and Blood Pressure
- Population Studies: Reducing salt intake by five to eight grams daily can lead to a 4 mmHg drop in systolic blood pressure and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, as demonstrated in population studies.
- Clinical Trials: Antihypertensive drugs, which lower blood pressure, show similar results, with an average reduction of 5 mmHg.
- Salt Alternatives: Replacing normal salt with a mixture of 75% sodium chloride and 25% potassium chloride reduced systolic blood pressure by 3.3 mmHg in a Chinese population study.
- Caution for Elderly: Reducing salt intake may pose risks for elderly adults, particularly if they are taking blood pressure medication, as it could lead to hypotension and falls.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
How do some Cancer Cells survive Chemotherapy?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lamin B Receptor (LBR), Chemotherapy
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Researchers at the Netherlands Cancer Institute have conducted a recent study to investigate drug resistance in cancer cells, focusing on resistance to a drug known as Taxol.
- It studied Chemotherapy and cancer relapse, particularly when a small number of cancer cells resist treatment and remain dormant, potentially leading to a resurgence of the disease.
Chemotherapy and its limitations
- Cancer cells are characterized by uncontrolled and rapid division.
- Chemotherapeutic drugs aim to halt this proliferation, often triggering programmed cell death, known as apoptosis, in response to halted cell division.
- However, this approach also damages healthy dividing cells, leading to adverse side effects.
Fine-Tuning Cancer Treatment
- Oncologists face the challenge of finding an effective drug dose that eliminates cancer cells while minimizing unbearable side effects for patients.
- One approach has been the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) that target specific proteins found mainly on cancer cells, sparing non-cancerous cells.
Unraveling Drug Resistance
- P-gp Protein: Some cancer cells escape drug treatments by overexpressing a protein called P-gp (permeability glycoprotein), which acts as a pump, expelling toxic compounds, including chemotherapeutic agents.
- ABCB1 Gene: The production of P-gp is controlled by the ABCB1 gene, and cells that produce excessive P-gp can flush out chemotherapy drugs, preventing them from accumulating at levels needed to trigger apoptosis.
Role of Cellular Location
- Recent Findings: The study examined the sensitivity of cells to Taxol and identified that the location of the ABCB1 gene within the cell’s nucleus plays a crucial role.
- Nuclear Envelope: In sensitive cells, the ABCB1 gene is located close to the nuclear envelope. In resistant cells, the gene has detached from the envelope and moved further inside the nucleus, resulting in a 100-fold increase in ABCB1 gene-related RNA.
Key Protein: Lamin B Receptor (LBR)
- LBR’s Influence: Researchers discovered that the presence or absence of a protein called Lamin B Receptor (LBR) affects the location of the ABCB1 gene.
- Depletion of LBR: When LBR is depleted, cells can activate the ABCB1 gene when exposed to Taxol. However, the absence of the LBR gene itself does not immediately increase ABCB1 expression, indicating the involvement of additional factors.
- Diverse Responses: Different cancer types exhibit varying responses to LBR depletion, highlighting the complex mechanisms governing gene expression and silencing.
- Analogy: A simple analogy illustrates the diversity: Different bathrooms offer various options for drying clothes, and cancer cell types rely on different mechanisms to tether genes to the nuclear envelope.
Significance
- These findings emphasize the need for further research into the diverse ways cancer cells express or suppress genes.
- Understanding drug resistance mechanisms opens avenues for developing strategies to maintain the potency of anti-cancer drugs while minimizing side effects, ultimately benefiting patients on their path to recovery.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Egypt attains WHO ‘Gold Tier’ status in Hepatitis C Elimination
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hepatitis
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- Egypt has become the first country to achieve the World Health Organization’s “gold tier” status on the path to elimination of Hepatitis C.
About Hepatitis
| Hepatitis A | Hepatitis B | Hepatitis C | |
| Causative Virus | Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) | Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) | Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) |
| Transmission | Fecal-oral route (contaminated food/water) | Blood and body fluids (unsafe sex, sharing needles) | Blood-to-blood contact (sharing needles, transfusions) |
| Vaccine Available | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Chronic Infection | No (usually acute) | Yes (can become chronic) | Yes (often becomes chronic) |
| Symptoms | Mild flu-like symptoms, jaundice | Variable, from none to severe symptoms | Often asymptomatic, but can lead to liver damage |
| Chronic Complications | None | Cirrhosis, liver cancer | Cirrhosis, liver cancer |
| Preventable by Vaccine | Yes | Yes | No |
| Treatment | Supportive care | Antiviral medications | Antiviral medications |
Egypt’s “Gold Tier” Status
- Stringent Criteria: To reach the “gold tier,” Egypt fulfilled specific criteria, including ensuring 100% blood and injection safety, providing a minimum of 150 needles/syringes annually for people who inject drugs, diagnosing over 80% of individuals with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV), treating over 70% of diagnosed HCV patients, and establishing a surveillance program for hepatitis sequelae, including liver cancer.
- Exemplary Results: Egypt has diagnosed 87% of its hepatitis C patients and provided curative treatment to 93% of those diagnosed, surpassing the WHO’s gold tier targets.
How did Egypt achieve this?
- “100 Million Healthy Lives” Initiative: Egypt’s ambitious initiative led to a substantial reduction in hepatitis C prevalence, from 10% in 2016 to 5% in 2018 and an estimated less than 1% in 2019, as reported by the Africa CDC.
- Leadership Role: Egypt extends support to other African countries, aiming to replicate its success in hepatitis C elimination, including enhancing access to affordable treatment.
Try this PYQ:
Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
(b) Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
(c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses are several times more than those infected with HIV.
(d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Post your answers here.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India seeks inclusion of Traditional Medicine on WHO’s ICD List
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- The Centre seeks to include traditional Indian medicines in the 11th revision of the World Health Organisation’s International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
- The traditional Indian medicine system is categorized into Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani and Yoga, Naturopathy, and Homoeopathy
About International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
| Purpose | Standardized system for classifying and coding diseases, health conditions, and related information. |
| Established | 1893, by International Statistical Institute (WHO’s predecessor) |
| Authority | Developed and maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO). |
| Scope | Covers a wide range of diseases, health conditions, injuries, and health-related factors. |
| Coding System | Assigns unique alphanumeric codes to each health condition for consistent recording and reporting. |
| Global Applicability | Internationally recognized and used for health data collection, analysis, and reporting. |
| Updates | Periodically updated to reflect advances in medical knowledge and changing health trends. |
| Latest Version | ICD-11 became effective in January 2022. |
| Uses | Clinical diagnosis, health record documentation, research, health policy, and resource allocation. |
India’s quest to update ICD-11
- Universal Language: The ICD provides a universal language that enables healthcare professionals worldwide to share standardized information.
- Traditional Medicine Module: The 11th revision includes a module dedicated to traditional medicine conditions, offering a standardized way to collect and report data on these conditions internationally.
- Formal Recognition: Ayurveda and related Indian traditional healthcare systems are formally recognized and widely practised in India, making a strong case for their inclusion.
- Chinese Medicine Inclusion: After a decade of consultations, ICD-11 included Module-1, covering traditional medicine conditions originating in ancient China.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Threat posed by cardiovascular diseases (CVD)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: World Heart Day
Mains level: World Heart Day, Rising burden of Cardio vascular diseases, efforts and challenges
What’s the news?
- World Heart Day, observed globally on September 29, serves as a crucial reminder of the escalating threat posed by cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and the need to promote heart-healthy lifestyles.
Central idea
- World Heart Day, an annual event, initiated by the World Heart Federation in collaboration with the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2000, seeks to heighten awareness, engage communities, and advocate for universal access to CVD prevention, detection, and treatment. Tackling the silent epidemic of cardiovascular diseases in India demands a multi-pronged approach.
Public Awareness Efforts on CVD
- On World Heart Day, several English-language national dailies published full-page advertorials, which are advertisements designed to resemble written articles. These advertorials aimed to raise awareness about cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and promote heart-healthy lifestyles.
- The content of these advertorials seemed to provide information about CVD rather than directly promoting a product.
- Notably, there was limited involvement or a meaningful campaign by public health agencies like the Union Ministry of Health in raising awareness about CVD on this occasion.
- These advertorials were sponsored by the diagnostics, devices, and pharmaceutical industries, indicating a partnership between these industries and media outlets for public awareness efforts.
- Additionally, clinicians from high-end corporate tertiary care hospitals contributed by providing lifestyle modification advisories as part of the public awareness campaign
Alarming Data on Hypertension
- Data from the National Family Health Survey-5 (2019–2021) and the 2017-18 National NCD Monitoring Survey (NNMS) in India reveals concerning statistics about hypertension.
- The NFHS-5 data shows that 18.3 percent of the country’s population has hypertension, while the NNMS reports a higher rate of 28.5 percent among individuals aged 18-69.
- These percentages translate to significant numbers, given India’s large population.
- Both surveys highlight low levels of awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension.
Treatment Gaps and Disparities
- The NNMS data indicates that only 28 percent of those with hypertension were aware of it.
- Among those aware, 52 percent were receiving treatment, and a smaller percentage had their blood pressure under control.
- Disparities exist based on factors such as education, income, and geographic location, with better access to healthcare services in south India.
- Vulnerable groups, including males, illiterates, those with lower income, rural residents, smokers, and alcohol users, were less likely to be part of the treatment cascades.
Efforts in India
- India launched the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS) in 2010, expanding its implementation.
- The program primarily focuses on screening and treatment.
- India is committed to the principles of primary healthcare and Universal Health Coverage (UHC), as outlined in the 2018 Astana Declaration.
Challenges
- Challenges include inadequate awareness, limited healthcare access in various regions, and disparities in healthcare access and outcomes. More resources are needed for primary healthcare.
- Contemporary approaches to managing CVD heavily emphasize risk factors, particularly lifestyle-related ones like diet, physical activity, smoking, and obesity.
- Epigenetic modifications may emerge as a consequence of a lifetime of disadvantage, structural inequalities, and discrimination, thereby influencing future generations.
- There is a challenge in retaining rural health workers.
The Need for a Holistic Approach
- Contemporary approaches to managing cardiovascular diseases (CVD) emphasize lifestyle risk factors.
- The WHO’s Commission on Social Determinants of Health highlights that these risk factors often result from systemic compromises rather than individual choices.
- The Commission emphasizes addressing socioeconomic factors that affect health across an individual’s lifespan and calls for equity and social justice in healthcare.
Conclusion
- As the WHO rightly asserts, Reducing health inequities is… an ethical imperative. Social injustice is killing people on a grand scale. World Heart Day serves as a stark reminder that the battle against CVD must continue with renewed vigor and a holistic perspective.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Mental health and the floundering informal worker
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Key findings
Mains level: Mental health: A universal human right
What’s the news?
- World Mental Health Day, observed on October 10, underscores the theme of ‘mental health as a universal human right.’
Central idea
- While the World Mental Health Day theme highlights the importance of mental health for all, it’s crucial to address the often-overlooked mental health challenges of India’s informal workers. This necessitates proactive policies aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The Global Perspective
- According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), approximately 15% of working-age adults globally live with a mental disorder.
- Decent work can positively influence mental health, but unemployment, unstable employment, workplace discrimination, and unsafe working environments pose significant risks to mental health.
- Informal workers, particularly those in low-paid and precarious jobs, often face psychosocial risks that compromise their mental well-being.
India’s Informal Workforce
- India’s informal workforce constitutes over 90% of the total working population. These workers endure unsafe conditions, work long hours, and have limited access to social and financial protections.
- Discrimination and gender disparities are prevalent, with over 95% of working women engaged in informal, low-paying, and precarious employment.
- The mental health of informal workers is further undermined by patriarchal structures and practices in their social and familial spaces.
Challenges faced by the informal workforce in India
- Lack of Formal Protections: Informal workers often lack legal and social protections. They work without employment contracts, job security, or access to benefits like health insurance and paid leave.
- Unsafe Working Conditions: Many informal workers labor in hazardous environments, increasing their risk of occupational health and safety issues.
- Long Working Hours: Informal workers frequently work long hours, often without clear boundaries between work and personal life, affecting their physical and mental well-being.
- Limited Access to Social Protections: These workers have limited access to social safety nets, making them vulnerable to economic shocks such as illness or job loss.
- Gender Disparities: Gender disparities are pronounced in the informal sector, with many women engaged in low-paying and precarious employment. Discrimination and patriarchal structures exacerbate these challenges.
- Precarious Employment: Informal work is characterized by its precarious nature, including irregular income, job insecurity, and uncertainty about future employment.
- Income Inequality: Informal workers often earn lower wages than their formal sector counterparts, contributing to income inequality.
Youth and Unemployment
- Youth unemployment is a pressing issue in India, significantly affecting mental health.
- Many young workers are forced into precarious and informal work due to desperation, accepting lower pay and poorer working conditions.
- Unemployment rates are particularly high among educated young women, reaching 42%.
- Given India’s demographic dividend, it is crucial to prioritize employment quality and long-term social security for this population.
Aging Workforce and Vulnerability
- India is expected to become an aging society in two decades, yet there is no clear social security plan for this growing demographic group.
- The Census of India 2011 reveals that 33 million elderly individuals continue working in informal sectors post-retirement.
- This vulnerable group lacks financial and health-care security, which can severely impact their physical and mental health.
Social Security and Mental Health
- Informal workers face mental distress due to accumulating debt and rising health-care costs: Informal workers often experience financial strain due to their precarious employment, leading to the accumulation of debt and increased healthcare expenses.
- Interconnectedness of Economic and Mental Health Factors: Mental health and well-being are interconnected with factors such as food security, access to livelihoods, and financial stability. These factors play a significant role in determining the mental health of informal workers.
- Post-COVID-19 Recovery Challenges: A study conducted among informal workers in Delhi, primarily migrants, reveals that the recovery post-COVID-19 remains uneven among different cohorts of informal workers. Many still report food insecurity, skipped meals, or reduced consumption, which can have detrimental effects on their mental health.
- Impact of Government Schemes: While some social security schemes have received increased funding, others, like the MNREGS, have seen reductions in funding. Adequate funding of employment guarantee programs can positively impact the mental health outcomes of informal workers.
- High Suicide Rates Among Daily Wage Earners: The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) reported that in 2021, 26% of people who died by suicide were daily wage earners. This statistic highlights the mental health challenges faced by this group and the need for better support and social security measures.
- Types of Social Security Measures: Social security measures can take various forms, including:
- Promotional: Aimed at augmenting income.
- Preventive: Intended to forestall economic distress.
- Protective: Designed to ensure relief from external shocks.
- The Code on Social Security 2020: It is necessary to revisit the Code on Social Security 2020, highlighting that it doesn’t explicitly state the goal of universalizing social security in India, particularly for informal workers.
Way Forward: Improving Mental Health Care
- Low Budgetary Allocation for Mental Health: India’s budgetary allocation for mental health currently stands at less than 1% of the total health budget. This allocation has predominantly focused on digital mental health programs.
- Importance of Community-Based Care: The World Mental Health Report 2022 emphasizes the need to strengthen community-based care as part of a comprehensive mental health approach.
- Human Rights-Oriented Care: To address mental health effectively, it is important to provide people-centered, recovery-oriented, and human rights-oriented care.
- Urgent Need for Proactive Policies: There is a pressing need for proactive policies that not only recognize the importance of mental health but also take concrete actions to improve mental health care in India.
- Basic Human Right to Good Health: Mental health is a basic human right, and it emphasizes the need to uphold this right by providing access to quality mental health care.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being: Improving mental health care aligns with SDG 3, which aims to ensure good health and well-being for all.
- SDG 8: Decent Work for All/Economic Growth: Addressing mental health issues among informal workers is crucial for advancing SDG 8, which focuses on decent work for all and economic growth.
Conclusion
- Proactive policies and comprehensive social security measures can uplift the mental well-being of this marginalized group, promoting a society where mental health is indeed a universal human right. Achieving this goal will contribute to the realization of the Sustainable Development Goals and ensure a healthier, more equitable future for all.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Ageing World: Addressing Mental Health Challenges in the Elderly
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UNFPA report on Ageing
Mains level: Elderly woes in India

Central Idea
- The world’s elderly population is larger than ever before, with 1.1 billion people aged 60 and above in 2022, constituting 13.9% of the population (UNFPA report).
- By 2050, this number is projected to rise to 2.1 billion, accounting for 22% of the global population.
Why discuss this?
- India’s Scenario: India is no exception to this trend, with 149 million older adults (10.5%) in 2022, expected to increase to 347 million (20.8%) by 2050.
- Longevity: People are living longer lives than ever before, underscoring the need to understand healthy ageing and address mental health issues in the elderly.
Misconceptions about Ageing and Mental Health
- Ageing as a Process: Ageing is a natural physiological process encompassing physical, social, and psychological dimensions. However, misconceptions and fears about ageing, particularly mental health concerns like depression, anxiety, and dementia, persist.
- Heterogeneity: The ageing process varies among individuals, influenced by factors such as genetics, lifestyle, environment, and diseases. Not all older adults experience the same physical or mental changes.
Social Challenges Faced by the Elderly
- Social Isolation and Dependency: Many elderly individuals grapple with increased dependency, social isolation, poverty, ageism, and feelings of pessimism and nihilism.
- Abuse and Neglect: Elderly individuals are vulnerable to emotional, physical, sexual, and financial abuse, often perpetrated by family members.
- Inaccessible Infrastructure: India’s towns and cities often lack elder-friendly infrastructure, including ramps, handrails, pavements, and adequate public transport, making healthcare access a challenge.
- Lack of Purpose: Many elderly men, especially after retirement, may feel unproductive and lost. Developing diverse interests earlier in life can mitigate the sense of purposelessness in retirement, reducing the risk of depression.
Psychological Aspects of Ageing
- Psychological Growth: As individuals age, they are expected to gain wisdom and a broader understanding of life’s challenges through personal or vicarious experiences.
- Erik Erikson’s Theory: Erik Erikson proposed ‘Ego integrity versus Despair’ as the final psychosocial development stage in human life. It emphasizes viewing one’s life accomplishments positively to avoid despair.
- Indian Cultural Emphasis: Indian culture underscores the importance of accepting the limitations that come with old age and renouncing responsibilities without suffering.
Mental Health Challenges
- Prevalence: Approximately 15% of elders in India (22 million individuals) experience serious mental illnesses such as depression, anxiety, dementia, and substance use disorders.
- Treatment Gap: A significant treatment gap of 90% exists, largely due to a lack of awareness among the public and healthcare professionals.
- Stigmatization: Stigma associated with both ageing and mental illness often leads to reluctance to admit mental health issues and seek treatment.
- Poverty and Access: Many elderly individuals lack access to mental healthcare services due to poverty and limited availability of interventions, particularly in rural areas.
Case Study: SCARF Partnership
|
Preserving Cultural Traditions
- Importance of Festivals and Rituals: Cultural traditions, including festivals and rituals, encourage socialization and cognitive engagement among elders.
- Risk of Tradition Loss: Neglecting these traditions risks losing their potential protective effects on elderly mental health.
Way forward
- Individual Planning: Planning for old age with financial savings and lifestyle adjustments is crucial.
- Educational Initiatives: Introducing the concept of healthy ageing in school curricula can promote awareness.
- Community Services: Accessible mental health services for elders should be available at the community level.
- Role of Retirement Homes: Retirement homes and elder care facilities, while providing care and reducing social isolation, need to address mental health issues urgently.
- Collective Responsibility: Caring for the elderly is a collective responsibility that requires the concerted efforts of individuals, families, civic society, private organizations, NGOs, and the government.
Conclusion
- The ageing world presents both opportunities and challenges, with a growing elderly population that demands a holistic approach to mental health care, community support, and cultural preservation.
- Addressing the mental health needs of the elderly is not only a matter of compassion but also a responsibility that encompasses various stakeholders and sectors of society.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s diabetes crisis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Diabetes and related facts
Mains level: India's Diabetes stress, Factors behind, exploitative marketing, measures
What’s the news?
- In June 2023, a study conducted by the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation in collaboration with the ICMR and the Union Health Ministry revealed alarming statistics about India’s diabetes crisis.
Central idea
- According to the study, 11.4% of India’s population, approximately 10.13 crore people, are living with diabetes. According to the WHO, a major reason for this is the consumption of unhealthy, ultra-processed foods and beverages. These statistics demand immediate attention and concrete actions to address the root causes of this public health crisis.
Key findings of the study
- Living with diabetes: 4% of India’s population, or 10.13 crore people, are living with diabetes.
- Pre-diabetic: 3% of the population, or an additional 13.6 crore people, are pre-diabetic.
- Obese Population: 6% of the population would be considered obese as per the BMI measure.
The consumption of ultra-processed foods: a significant contributor
- Contents of Ultra-Processed Foods:
- Ultra-processed foods encompass a wide range of products, including carbonated drinks, instant cereals, chips, fruit-flavored drinks, instant noodles, cookies, ice cream, bakery items, energy bars, sweetened yogurts, pizzas, processed meat products, and powdered infant formulas.
- These items are often characterized by their convenience and long shelf life.
- Increased Risk of Diabetes with Scientific Evidence:
- A concerning statistic reveals that a mere 10% increase in daily consumption of ultra-processed food is associated with a 15% higher risk of type-2 diabetes among adults.
- These foods are often high in sugar, fat, and salt, all of which contribute to insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels.
- Impact on Weight Gain:
- Ultra-processed foods are engineered to be hyper-palatable. They often contain combinations of sugars, fats, and artificial additives that stimulate the appetite and lead to overconsumption.
- This excessive calorie intake can result in weight gain, a known risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Structural Alteration:
- When food undergoes extensive processing, its original structure is often destroyed. Cosmetic additives, colors, and flavors are added to enhance taste and appeal.
- This altered structure and excessive processing can disrupt the body’s natural regulation of hunger and satiety, leading individuals to eat more and gain weight.
- Association with Cardiovascular Risks:
- The negative effects of ultra-processed foods extend beyond diabetes. Obesity and diabetes are key risk factors for heart disease and premature mortality.
- Research indicates that those who consume more than four servings of ultra-processed foods per day face a significantly higher risk of cardiovascular mortality compared to those who consume fewer than two servings per day.
- A similar trend is observed for all-cause mortality.
Exploitative marketing practices
- Shifting Focus to Low- and Middle-Income Countries:
- In many high-income countries, the sale of sugar-sweetened beverages has declined over the past two decades due to growing awareness of their health impacts.
- To compensate for this loss of sales, food companies have shifted their attention to low- and middle-income countries, where there may be less stringent regulations and a growing consumer base.
- Aggressive Marketing and Advertising:
- These companies invest substantial amounts of money in marketing and advertising ultra-processed food and beverages in countries like India.
- These aggressive marketing campaigns often target vulnerable populations, including children and the emerging middle class.
- Techniques like the use of cartoon characters, incentives, gifts, and celebrity endorsements are employed to make these products more appealing.
- Blaming Individuals vs. Addressing Systemic Issues:
- The food industry tends to place blame on individuals, suggesting that personal choices are responsible for unhealthy dietary habits.
- However, the environment created by aggressive marketing and the easy accessibility of ultra-processed foods play a significant role in shaping these choices.
- Impact on Public Health:
- The consequences of these marketing strategies are severe. They contribute to a deepening public health crisis, with diabetes being a ticking time bomb.
- Sugar-sweetened beverages, in particular, are highlighted as a major source of added sugar in diets, putting people at a higher risk of type 2 diabetes and other health issues.
The need for regulatory intervention
- Industry Opposition: The food industry resists marketing restrictions, citing economic concerns and portraying themselves as stakeholders.
- False Promises: Some industry initiatives, like ‘Eat Right,’ may appear health-focused but could divert attention from unhealthy product impacts.
- Impact on Regulation: Industry partnerships can hinder strong regulatory policies aimed at reducing ultra-processed food consumption.
- Role of Regulatory Authorities: Lackluster responses and industry dominance in regulatory bodies may impede effective public health regulations.
- Complementary Efforts: While exercise is essential, it should complement regulatory policies addressing marketing and warning labels on unhealthy foods.
- Balancing Interests: Governments must prioritize citizens’ health, striking a balance between industry interests and public well-being when implementing evidence-based, transparent regulations.
Strategy to safeguard: Mandatory Provisions
- To protect the public from the manipulative strategies of the food industry, the government must establish a legal framework or even an ordinance under Article 123 of the Constitution.
- This framework should focus on reducing or halting the consumption of ultra-processed foods and could include:
- Defining ‘healthy food’
- Implementing warning labels on unhealthy food
- Imposing restrictions on the promotion and marketing tactics of unhealthy food and beverages
- Raising public awareness about the risks associated with consuming such foods
Global Examples
- Several countries, including South Africa, Norway, and Mexico, have recently taken similar actions to regulate food labeling and marketing.
- The Indian government has the opportunity to demonstrate its commitment to public health by enacting similar laws.
- Much like the Infant Milk Substitutes, Feeding Bottles, and Infant Foods Act, which successfully regulated commercial baby food, this proposed legislation could make significant strides in curbing the consumption of unhealthy foods and beverages.
Conclusion
- India stands at a critical juncture in its battle against diabetes and a food industry that prioritizes profits over public health. The time has come for the government to implement robust regulations. By taking decisive action, India can protect the well-being of its citizens and set a precedent for responsible food regulation in the global context.
Also read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Bridging Gender Gaps in Cancer Care: The Lancet Commission Report
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Gender Gaps in Cancer

Central Idea
- The Lancet Commission report ‘Women, Power and Cancer’ spotlights the gender disparities in cancer care that persist in India.
Women dying of Cancer: Alarming Statistics
- The report emphasizes that approximately 6.9 million cancer-related deaths among Indian women were preventable, and 4.03 million were treatable.
- It revealed that a staggering 63% of premature cancer-related deaths in Indian women could have been prevented through risk reduction, screening, and early diagnosis.
- 37% could have been averted through timely and optimal treatment.
Understanding the Gender Gap
- Cancer Incidence and Mortality: Despite men being at a higher risk of certain cancers affecting both genders, women continue to face a significant burden of cancer incidence and mortality. Globally, women account for 48% of new cancer cases and 44% of cancer-related deaths. This happens even though some of the cancers in women, such as breast and cervical cancers, are highly preventable and treatable.
- Root Causes: The report attributes this gender gap in cancer outcomes to several factors, including limited access to timely and appropriate care due to disparities in knowledge, decision-making power, and financial resources. Women, irrespective of their socioeconomic status, often lack the necessary information and autonomy for informed decision-making in healthcare.
- Financial Strain: Additionally, women are more likely than men to experience financial devastation due to cancer-related expenses, compounding the challenges they face.
Challenges in Cancer Care for Women
- Underrepresentation: The report underscores that women are underrepresented in leadership roles in the field of cancer care. They are also susceptible to gender-based discrimination and harassment, making it a complex environment for women to thrive.
- Unrecognized Contributions: Shockingly, women constitute the largest unpaid workforce in cancer care, with their contributions estimated to be worth approximately 3.66% of India’s national health expenditure.
Expert Insights
- Healthcare-Seeking Behavior: A healthcare expert highlights the impact of gendered healthcare-seeking behavior. Women, particularly in disadvantaged sections of society, tend to exhibit lower healthcare-seeking behavior, impacting their overall health outcomes.
- Societal Changes: Beyond medical knowledge, societal changes are crucial. Women often hesitate to consult medical professionals for conditions like breast or cervical cancer, leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Significance of Screening
- Preventable and Treatable Cancers: Breast and cervical cancers, two of the most common cancers in women, are highly preventable and treatable. Experts emphasize the importance of regular screenings.
- Early Detection: Self-examination of breasts, annual clinical examinations by a medical professional, and mammography for women over 40 can aid in early breast cancer detection. For cervical cancer, regular screenings can identify pre-cancerous growth and the presence of the human papillomavirus.
Government Interventions
- Awareness Campaigns: Experts underscore the need for government-led awareness campaigns to promote cancer prevention and early detection, similar to those for other health initiatives.
- Vaccination Programs: The government’s initiative to include vaccination programs for young girls is a positive step in reducing cancer incidence.
- Primary Health Centers: Experts highlight the potential for primary health centers to play a more significant role in cancer diagnosis and early treatment, particularly for cervical cancer.
Recommendations from the Report
- Data Collection: Regularly collecting gender and social demographic data for cancer health statistics is crucial.
- Policy Development: Developing, strengthening, and enforcing policies that reduce known cancer risks is essential.
- Equitable Access: The report calls for equitable access to cancer research resources, leadership roles, and funding opportunities for women, addressing the gender imbalance in cancer care and research.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s Kidney Crisis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Laws related to organ transplantation in India
Mains level: India's kidney crisis, challenges in procurement, transplant laws and Need for reforms
What’s the news?
- India faces a grave crisis in its healthcare landscape, particularly concerning the shortage of kidneys for transplantation.
Central idea
- India is grappling with a severe kidney crisis, marked by an alarming demand-supply gap in kidney transplantation. While kidney transplantation is the most effective treatment for end-stage renal disease (ESRD), India’s regulatory framework presents formidable obstacles to innovative kidney exchange methods.
India’s Kidney Crisis
- In 2022, over two lakh patients required kidney transplants, but only about 7,500 transplants, a mere 3.4%, were performed.
- This alarming disparity can be attributed to the high prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in India, which affects approximately 17% of the population.
- CKD often progresses to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), for which kidney transplantation is the most effective treatment in terms of quality of life, patient convenience, life expectancy, and cost-effectiveness.
- However, India lags far behind developed countries like the United States, which performs about 20% of the needed kidney transplants.
- Importantly, this gap is not solely due to a lack of medical facilities but is largely influenced by stringent regulations in India.
Current kidney procurement methods in India
- Deceased Donors:
- Obtaining kidneys from deceased donors is one of the primary methods in India.
- However, this method faces challenges due to low donation rates, specific conditions required for the nature of death, and the infrastructure needed to collect and store organs.
- Families’ willingness to donate organs after a loved one’s death remains relatively low.
- Living Relatives or Friends:
- Another method for obtaining kidneys is through living relatives or friends.
- Patients can request a kidney donation from a willing living individual who is a compatible match.
- This approach requires compatibility in terms of blood type and tissue type, which can be a significant obstacle. It also involves complex emotional and ethical considerations.
Challenges related to kidney procurement methods in India
- Regulatory Barriers: Stringent regulations in India hinder innovative kidney exchange methods, such as kidney swaps and kidney chains. These regulations limit the participation of non-near-relatives in kidney swaps, and altruistic donations for kidney chains are often illegal.
- Lack of Kidney Chains: Kidney chains, a method involving a series of altruistic donations, are nearly non-existent in India due to legal restrictions. In most Indian states, it is illegal to donate a kidney out of altruism.
- Black Market for Kidneys: The stringent regulations around kidney exchange have led to the emergence of black markets for kidneys in India. The reference to selling a kidney is a mainstream expression, indicating the prevalence of such illegal operations.
The need for regulatory reform
- Stringent Regulations: Current regulations impede innovative kidney exchange methods, hindering non-near-relatives’ participation and banning altruistic donations in many states.
- Missed Opportunities: India has missed chances to expand kidney supply through effective methods like kidney swaps and chains due to legal barriers.
- Disparity in Regulations: Inconsistent regulations between swap transplants and direct donations raise questions about fairness.
- Lack of Coordination: India lacks a national coordinating authority, making it difficult to create diverse donor-recipient pools.
- Black Market Concerns: Stringent regulations have led to a black market for kidneys, endangering those involved.
Key reforms so far
- Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act 1994: This legislation laid the foundation for organ transplantation in India by recognizing the possibility of transplants from brain-stem death.
- 2011 Amendment: In 2011, an amendment legalized swap transplants and initiated a national organ transplant program in India. This represented a significant step toward expanding transplantation options.
- Reforms in February 2023: The government introduced reforms in February 2023, offering more flexibility in age and domicile requirements for organ registration. While noteworthy, the article suggests that these reforms fall short of addressing the core issue of inadequate kidney supply.
Lessons for India to transform its own organ transplantation landscape
- Altruistic Donations: Emulate countries like the US and the Netherlands in legalizing and encouraging altruistic kidney donations to expand the donor pool.
- National Registries: Follow Spain and the UK by establishing national-level registries for kidney chains and swaps to streamline coordination.
- International Collaboration: Explore international partnerships as seen in Spain to broaden the donor and recipient network.
- Continuous Improvement: Commit to ongoing regulatory enhancements, inspired by the success of the United States in facilitating kidney swaps and chains.
- Patient-Centric Approach: Prioritize patient-centered policies, drawing from global models, to improve patient access and quality of life.
Conclusion
- Reforming India’s kidney transplant laws is not only a matter of urgency but also a humanitarian imperative. Along with the domestic reforms, learning from global best practices is the key to addressing this critical issue and ensuring a brighter future for kidney transplant recipients in India.
Also read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Challenges and Opportunities of India’s Aging Population
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India's Aging Population
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Projected Demographic Shift: By 2050, the percentage of elderly individuals in India is expected to double, reaching over 20% of the total population, as per the UN Population Fund, India (UNFPA) in its 2023 India Ageing Report.
- Rapid Expansion: India is experiencing a remarkable decadal growth rate in its elderly population, currently estimated at 41%.
- Changing Dynamics: This demographic shift raises the possibility that by 2046, the elderly population may surpass the number of children (aged 0 to 15 years) in the country.
Economic Disparities among the Elderly
- Poverty Prevalence: More than 40% of India’s elderly population belongs to the poorest wealth quintile, with nearly 18.7% of them living without any source of income.
- Quality of Life Impact: Such high levels of poverty can significantly affect their quality of life and their access to healthcare services.
Understanding the Aging Population
- Rapid Growth in the 80+ Age Group: The report predicts a staggering 279% growth rate in the population of individuals aged 80 and above between 2022 and 2050.
- Gender Disparities: There is a predominance of widowed and highly dependent elderly women in this age group, a trend observed in several nations.
- Regional Variations: Life expectancy at 60 and 80 varies across states and union territories, with women generally having higher life expectancies, raising concerns about their social and economic well-being.
- Regional Disparities: States like Rajasthan, Haryana, Gujarat, Uttarakhand, Kerala, Himachal Pradesh, and the Union Territory of J&K have women with life expectancies exceeding 20 years at age 60, highlighting the need for tailored support.
Changing Sex Ratios among the Elderly
- Steady Increase: The sex ratio (females per 1,000 males) among the elderly has been steadily rising since 1991, in contrast to the stagnation in the general population’s sex ratio.
- Regional Variations: The northeast and east show an increased sex ratio among the elderly, but it remains below 1,000, indicating a male predominance. In contrast, central India saw a remarkable shift, with women outperforming men in survival after the age of 60.
Gendered Poverty in Old Age
- Inherent Gender Bias: Poverty in old age is inherently gendered, with older women more likely to be widowed, living alone, lacking personal income, and relying on family support.
- Feminization and Ruralization: The major challenges facing India’s aging population include the feminization and ruralization of the elderly. Policies must address these specific needs.
Inter-State Variations in Elderly Population
- Diverse Demographic Transition: Significant inter-state variation exists in the levels and growth of the elderly population, reflecting differing stages and rates of demographic transition.
- Regional Differences: States in the southern and select northern regions have a higher share of the elderly population, a gap expected to widen by 2036. In contrast, states with higher fertility rates, like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, will see an increase in the elderly population share but will remain below the national average.
- Ageing Index: Central and northeastern regions are characterized by a younger demographic as indicated by the aging index.
Response to Elderly Needs during the Pandemic
- Inadequate State Aid: The report reviews the government and state authorities’ response to the needs of elderly people during the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting that while most received state aid, it was insufficient.
- Only NGOs to rescue: Accessible public healthcare facilities were lacking, with NGOs and CBOs being the primary sources of help.
- Call for Preparedness: The report recommends a special focus on older persons in disaster-preparedness plans moving forward.
Enhancing Data Collection and Support
- Data Deficiency: The report underscores the lack of credible data on various issues related to the elderly in India and calls for the inclusion of questions concerning older persons in upcoming data collection exercises.
- Policy Recommendations: Suggestions include increasing awareness about elderly schemes, regulating Old Age Homes, and promoting in-situ aging.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging the creation of elderly self-help groups and emphasizing multigenerational households as well as short-term care facilities.
Promising Roadmap and Valuable Resource
- Government Acknowledgment: Social Justice Dept. termed the report a “valuable roadmap”. It emphasized its importance as a resource for scholars, policymakers, program managers, and all stakeholders involved in elder care.
- Data Sources: The report draws from various sources, including the 2011 Census, the 2017-18 Longitudinal Ageing Survey in India (LASI), population projections, and reports from the Government of India and the World Population Projection 2022.
Way forward
The report advocates for policies that enhance the well-being of India’s aging population-
- Foster community support
- Multigenerational living, and
- In-situ aging
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Challenge of Non-Communicable Disease in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Burden of Non-communicable diseases
Mains level: India's progress in healthcare progress, NCD challenges and potential of AI
What’s the news?
- India, with its emerging leadership in global issues, faces the challenge of rising NCDs, including diabetes and heart diseases. The healthcare industry calls for collaboration to address this crisis, highlighting India’s progress in healthcare, its role as a Medical Value Travel hub, and its potential in AI-driven healthcare innovations.
Central idea
- In recent years, India has emerged as a prominent voice on the global stage, leading the way in critical areas such as climate change, electrification, manufacturing, and space exploration. India’s achievements include successfully landing a mission near the moon’s south pole and a successful G-20 presidency. However, as India aims to become a global leader, it must confront a looming health crisis of NCDs.
What are Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)?
- NCDs are also known as chronic diseases, which are not caused by infectious agents and are not transmissible from person to person.
- NCDs are long-lasting and progress slowly, typically taking years to manifest symptoms.
- Examples of NCDs include cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes.
- These diseases are often caused by modifiable risk factors such as an unhealthy diet, a lack of physical activity, tobacco and alcohol use, and environmental factors.
- NCDs are a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, accounting for around 70% of all deaths.
India’s NCD challenge
- Diabetes and Hypertension Prevalence: India is facing a high prevalence of NCDs, particularly diabetes and hypertension, which affect millions of people.
- Youth Health Issues: The burden of NCDs is increasingly affecting India’s youth, leading to heart attacks, cancer, respiratory problems, depression, and more.
- Economic Consequences: If unchecked, India’s NCD burden could lead to an economic cost of nearly $4 trillion by 2030. This poses a significant roadblock to India’s development and is compared to an age tax on the country’s demographic dividend.
India’s healthcare progress
- Improved Health Metrics: India has witnessed notable improvements in key health metrics.
- Infant Mortality: India has witnessed a remarkable improvement in infant mortality rates, which have decreased by four times from previous levels.
- Maternal Mortality: Maternal mortality rates have shown remarkable progress as well, decreasing by seven times from earlier rates.
- Average Life Expectancy: The average life expectancy of an Indian has increased by nearly 30%, rising from 55 years to over 70 years, reflecting the overall improvement in healthcare and quality of life in the country.
- World-Class Healthcare Infrastructure: India is described as having world-class healthcare infrastructure. Investments have been made in modern hospitals, clinics, and medical facilities to provide high-quality healthcare services.
- Clinical Excellence: India is noted for its pool of highly skilled clinical talent. These healthcare professionals are capable of delivering best-in-class clinical outcomes and providing healthcare services at a scale and cost that are favorable compared to the global average.
India as a Medical Value Travel (MVT) hub
- Global MVT Hub: India has emerged as a prominent global destination for MVT, attracting patients from around the world, particularly in specialized medical fields such as oncology, orthopedics, and robotic surgery.
- Advanced Medical Technology: India has invested in state-of-the-art medical technology and facilities, including the introduction of proton beam therapy for cancer treatment, positioning itself as a regional leader in cancer care.
- Highly Skilled Healthcare Professionals: India has a highly skilled and trained workforce of healthcare professionals known for their expertise in complex procedures, including joint replacements, spinal surgeries, and robotic-assisted surgeries.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Many medical procedures in India are conducted using minimally invasive techniques, attracting patients seeking precise and less invasive treatments.
- Cost-Effective Care: India offers cost-effective healthcare services, making it an attractive destination for patients seeking high-quality medical care at competitive prices.
- Growth Potential: India’s MVT sector has significant growth potential, capable of creating employment opportunities and contributing to foreign exchange earnings.
India’s potential for harnessing Artificial Intelligence (AI) to transform the healthcare sector
- AI in Healthcare Transformation: AI is rapidly reshaping healthcare worldwide, and India is poised to play a leading role in this transformation. India has a wealth of talented data scientists, engineers, and healthcare professionals capable of driving innovation in AI-driven healthcare solutions.
- Diagnostic Advancements: AI can significantly impact diagnostics by enhancing accuracy and efficiency in medical diagnoses. AI-powered tools can lead to faster treatment decisions and improved patient outcomes. Moreover, AI can aid in predicting disease outbreaks, analyzing healthcare data, optimizing treatment plans, expediting healthcare procedures, and revolutionizing drug discovery.
- India’s Progress in AI: India has already made strides in the application of AI in healthcare. However, to maintain and strengthen its leadership position, India must continue to invest in research and development, encourage collaborations between academia and industry, and create an ecosystem that fosters innovation.
- Economic Potential: The AI expenditure in the country is expected to reach $11.78 billion by 2025 and could contribute $1 trillion to India’s economy by 2035.
Way forward
- AI-Driven Healthcare Transformation: India should fully embrace the transformative potential of AI in healthcare. This involves integrating AI-powered solutions for diagnostics, treatment optimization, and healthcare procedures.
- Investment in R&D: India should continue and increase investment in research and development to drive healthcare innovation. Funding and supporting research initiatives will be crucial for advancements in healthcare technology.
- Collaboration Between Academia and Industry: Strengthening partnerships between academic institutions and the healthcare industry is essential. These collaborations can expedite the application of research findings to practical healthcare solutions.
- Nurturing an Innovation Ecosystem: India should create an ecosystem conducive to healthcare innovation. This includes supporting healthcare startups, offering incentives for innovation, and facilitating the growth of healthcare technology companies.
- Economic Potential of AI: Recognizing the economic potential of AI in healthcare, India should actively invest in AI-driven healthcare solutions. The expected growth in AI expenditure presents an opportunity to contribute significantly to the country’s economy.
- Community Health Focus: Prioritizing community health is essential. Initiatives aimed at improving public health, creating awareness about preventive measures, and addressing healthcare disparities should be emphasized.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Collaboration between the public and private sectors is critical. Joint efforts can lead to infrastructure development, the promotion of medical tourism, and the establishment of international healthcare accreditation bodies.
- Leadership in NCD Prevention: India should take a leading role in addressing non-communicable diseases (NCDs). Comprehensive strategies, including prevention, early detection, and effective management, should be at the forefront of healthcare efforts.
Conclusion
- India stands at a critical juncture in its healthcare journey. By reimagining its healthcare model, India can position itself as a global leader in medical value travel, a powerhouse in AI-driven healthcare solutions, and a trailblazer in combating NCDs. With concerted efforts and a commitment to excellence, India can forge a healthier and more prosperous future for generations to come, truly realizing its destiny as a global leader.
Also read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
President launches Ayushman Bhav Campaign
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bhav Campaign
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- The President of India, Mrs. Murmu, virtually launched the Ayushman Bhav campaign and the Ayushman Bhava portal.
Ayushman Bhav Campaign
- The Ayushman Bhav campaign aims to deliver healthcare services to the remotest corners of India, playing a pivotal role in achieving the campaign’s ambitious objectives.
- It is designed to ensure that every individual receives essential health services, aligning with the overarching goals of Ayushman Bhav.
- The campaign’s goals, include-
- Facilitating access to Ayushman cards
- Generating ABHA IDs
- Raising awareness about critical health schemes and disease conditions, such as non-communicable diseases, tuberculosis, and sickle cell disease.
Three Components of Ayushman Bhav:
- President highlighted the three integral components of Ayushman Bhav:
- Ayushman – Apke Dwar 3.0
- Ayushman Melas at Health and Wellness Centres (HWC) and Community Health Clinics (CHC)
- Ayushman Sabhas in every village and panchayat
- These components are expected to accelerate the delivery of healthcare services at grassroots levels, contributing to the creation of a healthier nation.
Back2Basics: Ayushman Bharat Scheme
| Launch Year | 2018 |
| Objective | Universal Health Coverage and Financial Protection |
| Components | 1. Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
2. Health and Wellness Centers (HWCs) |
| Target Beneficiaries | Economically disadvantaged families, rural populations, vulnerable communities |
| Coverage | Health insurance for eligible families, covering various medical expenses |
| Services Offered | Comprehensive healthcare services, including preventive, promotive, and curative care |
| Impact | Improved health indicators, reduced financial burden on beneficiaries, enhanced healthcare infrastructure |
| Vision | To make healthcare a fundamental right for all Indian citizens |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Orphan Diseases in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Orphan Diseases
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- Health discussions often revolve around common ailments, such as diabetes, which affect a significant portion of the population.
- However, amidst these well-known health issues, there are numerous rare/ orphan diseases that, though infrequent, can have devastating consequences for patients and their families.
What are Orphan Diseases?
- Rare diseases, often referred to as orphan diseases, are characterized by a low prevalence rate, typically affecting one person in a population of 10,000.
Challenges Posed
- Difficulty in Diagnosis: Rare diseases are challenging to diagnose, particularly for young medical practitioners who may have limited exposure to such cases. The rarity of these conditions means that many healthcare professionals may not have encountered them during their training.
- Lack of Research: Limited prevalence has historically resulted in insufficient research efforts. With fewer cases to study, there has been a lack of scientific understanding and effective treatments for many rare diseases.
- High Treatment Costs: While advances in medical research have led to the development of therapies for some rare diseases, the costs associated with these treatments are often exorbitant. From an Indian perspective, these costs can range from Rs. 1 million to Rs. 20 million per year, making them unaffordable for many.
Initiatives and Progress in India
- Increasing Awareness: Greater awareness of rare diseases and advancements in genomic technologies for diagnosis have begun to address these challenges. As awareness spreads, more cases are being identified and correctly diagnosed.
- Regulatory Incentives: Several countries, including India, have introduced regulatory incentives to encourage pharmaceutical companies to invest in research and development for neglected diseases. This has led to increased interest in orphan drugs.
- Patient-Driven Initiatives: Patient groups and organizations in India are actively contributing to rare disease research and treatment. One notable example is the Dystrophy Annihilation Research Trust (DART), which is conducting clinical trials for Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy.
- Government Initiatives: The government’s National Policy for Treatment of Rare Diseases is gradually making an impact. It aims to address rare diseases prevalent in India, such as cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, lysosomal storage disorders, and sickle-cell anaemia.
Lessons from Leprosy
- Incidence Reduction: Leprosy, once prevalent in India, is now considered a rare disease due to successful efforts in reducing its incidence.
- Research Benefits: Research on orphan diseases like leprosy can yield broader societal benefits. For instance, studies on synthetic antibiotics have shown a potential to curb the spread of leprosy to household relatives.
- Government Goals: Research findings may contribute to achieving the government’s objective of making India leprosy-free by 2027.
Conclusion
- Rare diseases present unique healthcare challenges that have long been neglected.
- However, recent progress in diagnosis, research, and patient-driven initiatives is gradually improving the landscape for rare disease patients in India.
- As awareness grows and regulatory support continues, there is hope for enhanced diagnosis, treatment options, and affordability, ultimately improving the lives of those affected by these conditions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Mercy Petitions in Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mercy Petitions
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) 2023 seeks to replace the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC) and introduces significant changes to the mercy petition process for death sentence cases.
- These changes impact core aspects like justiciability, time limits, and the execution process.
Background on Mercy Petitions
- The Constitution granted the President (Article 72) and Governor (Article 161) the power to grant pardons or commute sentences.
- In the Supreme Court’s ruling in Maru Ram vs. Union of India (1981), it was established that the President must act based on the Council of Ministers’ advice in mercy petitions.
New Mercy Petition Provision in BNSS
- Under BNSS Section 473(1), convicts can file mercy petitions within 30 days after specific events.
- Convicts can petition the President or Governor based on dismissal of appeals or confirmation of sentences.
- For cases with multiple convicts, they all must file petitions within 60 days.
Centre’s Role in Mercy Petitions
- The Centre seeks the state government’s comments, reviews the case, and makes recommendations to the President within 60 days.
- No time limit is specified for the President’s decision.
Exclusion of Appeals against President’s Decision
- BNSS Section 473(7) states that the President’s decisions on mercy petitions are final.
- Courts cannot question or review the grounds for President’s pardons or commutations.
- Unlike the Shatrughan Chauhan vs. Union of India (2014) ruling that mandated a 14-day gap between the rejection of mercy petitions and execution, BNSS doesn’t mention such a provision.
Delay in Mercy Petition Disposal
- The Shatrughan Chauhan case highlighted the need to avoid undue delay in mercy petition disposal.
- BNSS lacks a time limit for the President to decide mercy pleas.
Conclusion
- The proposed BNSS’s alterations to mercy petitions raise concerns about transparency, judicial review, and the protection of prisoners’ rights.
- Balancing constitutional powers with timely justice remains a challenge in these proposed changes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Patient Safety and Neonatal Care: India’s Efforts and Challenges
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Patient Safety Provisions
Central Idea
- The recent conviction of a former British nurse highlights the importance of patient safety in healthcare systems.
- While neonatal safety is not governed by exclusive rules, there are provisions to ensure the wellbeing of newborns and minimize potential risks.
Patient Safety Provisions in India
- Defining Patient Safety: Patient safety is defined as freedom from harm or potential harm associated with healthcare provision, according to the ‘National Patient Safety Implementation Framework (2018-2025).’
- Legal Protection: Patients in India are protected under various laws, including the Consumer Protection Act, Clinical Establishment Act, and mechanisms by the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority and Drugs Controller General of India to safeguard patients’ rights.
- Fragmented Laws: Patient safety is governed by a range of laws, from the Hippocratic Oath to clinical establishment regulations, reflecting a multifaceted approach to ensure safe healthcare practices.
Neonatal Safety and Care
- Proactive Measures: While no exclusive rules exist for neonatal care, provisions against issues like mix-ups and abductions are present. Deliberate harm is extremely rare and often linked to complex psychiatric illnesses.
- Comprehensive Provisions: Neonatal safety is ensured through comprehensive provisions that include staffing, equipment, infection control, parental involvement, training, and continuing medical education.
- Human Errors: In a country with a high birth rate, human errors may occur in neonatal care, but planned, deliberate harm remains an exceptional occurrence.
Neonatal Health Challenges
- Global Neonatal Deaths: Despite a decline in global neonatal deaths, newborns face the highest risk of death within the first 28 days of life. A significant proportion of under-five deaths occur during the newborn period.
- India’s Scenario: India’s infant mortality rate is gradually declining, but pre-term birth, complications during birth, infections, and birth defects remain major causes of neonatal deaths.
- Improving Neonatal Survival: Ensuring proper neonatal care and addressing the key challenges can contribute to reducing neonatal mortality rates and improving child health outcomes.
Promoting Neonatal Safety
- Midwife-Led Continuity of Care: Professional midwives providing midwife-led continuity of care (MLCC) significantly reduce the risk of neonatal and pre-term birth. This approach emphasizes the importance of skilled care during childbirth and the immediate postnatal period.
- Seeking Prompt Medical Care: Families are advised to seek prompt medical care in case of danger signs in newborns and to follow vaccination schedules for timely protection. This proactive approach helps prevent and manage potential health risks in neonates.
- Ensuring Proper Training: Proper training of healthcare providers, especially those in neonatal services, is crucial for maintaining high-quality care and adherence to safety standards.
Conclusion
- Patient safety and neonatal care form the foundation of a robust healthcare system.
- The challenges of neonatal care require ongoing attention, collaboration, and innovation to ensure the best outcomes for the youngest members of society.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Somatic Genetic Variants: A genomic revolution hiding inside our cells
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Somatic genetic variants
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The human genome, comprising 23 pairs of chromosomes, is the blueprint of our genetic makeup inherited from our parents.
- The replication of this genetic information in nearly a trillion cells during development results in a complex mosaic of cellular diversity.
- Despite remarkable DNA replication accuracy, mutations still occur.
What are Somatic Genes?
- Somatic genetic variants, also known as somatic mutations or somatic alterations, are genetic changes that occur in the cells of an organism’s body (somatic cells) during its lifetime.
- These mutations are distinct from germline mutations, which are inherited from parents and are present in every cell of an individual’s body.
- Somatic mutations are acquired after conception and are not passed on to future generations.
- Somatic mutations can occur due to various factors, such as exposure to environmental mutagens (like radiation or chemicals), errors in DNA replication, and other cellular processes.
- These mutations can affect the DNA sequence of specific genes, leading to changes in protein production or function.
DNA Replication: The Copy-Paste Mechanism
- Genetic Inheritance: Ovum and sperm carry parental genetic blueprints, which combine after fertilization.
- Cell Division: The single fertilized cell, with 23 chromosomes, multiplies to form the human body’s trillions of cells.
- DNA Replication Accuracy: Proteins proofread and correct DNA during replication, resulting in an error rate of 0.64-0.78 mutations per billion base pairs per division.
Impact of Somatic Genetic Mutations
- Dependent on Timing: Errors occurring after birth but during development are somatic genetic mutations.
- Driver Mutations: Mutations that confer a fitness advantage to cells can lead to tumor formation and are called driver mutations.
- Cellular Mosaic: Human body is a mosaic of cells with subtle genomic differences, influenced by somatic genetic variants.
- Genetic Variants: Genetic variants within functional genome regions can affect protein encoding and regulation.
Somatic Variants and Physiological Processes
- Immune Cell Diversity: Immune cells undergo extensive somatic changes to create diverse antibodies recognise pathogens.
- Recent Knowledge Explosion: Technological advancements in sequencing individual cells have led to an explosion of data and knowledge on somatic variants.
- Cancer’s Role: Somatic genetic variants play a significant role in cancer development, aiding in early detection, diagnosis, and prognosis.
Cancer Mutational Signatures
- Mutational Signatures: Specific genetic variations and patterns are characteristic of certain cancers, enabling early detection.
- Blood-Based Detection: Technologies identify tumour DNA in blood to detect cancer early.
- Disease Progress Tracking: Cancer variations can be used to monitor disease progression and therapy response.
Somatic Variants in Genetic Diseases
- Genetic Diseases Origin: Many genetic disorders arise from somatic genetic variants, not inherited from parents.
- Disease Severity and Timing: The severity and distribution of genetic diseases depend on the timing of somatic mutations during development.
- Immune Disorders: Somatic changes can cause immune disorders and even beneficially reverse some genetic diseases.
SMaHT Network: Understanding Somatic Mosaicism
- Somatic Mosaicism: US has launched the ‘Somatic Mosaicism across Human Tissues’ (SMaHT) Network.
- Aims: SMaHT aims to discover somatic variants, develop tools for study, and improve analysis for biological and clinical insights.
- Investment and Research: The U.S. government has invested $140 million to study somatic variants in post-mortem samples.
Implications and Future Prospects
- Cellular Complexity: Studying somatic variants reveals the intricate diversity of cells and reshapes evolutionary understanding.
- Disease Management: Understanding somatic genetic changes can advance disease understanding and management.
- Innovative Approaches: Analyzing genes at the single-cell level paves the way for innovative disease approaches and insights into evolution.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
One Health Approach
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: One Health
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- The global spotlight on the ‘One Health’ concept is illuminating India’s strides in integrating this paradigm to enhance its response to health challenges.
- While gaining recent recognition, the One Health approach finds its roots in history.
One Health Approach
- Holistic Vision: The One Health approach acknowledges the intricate linkages between the health of humans, animals, plants, and their shared environment.
- Historical Foundation: Early traces of One Health can be found in the teachings of Hippocrates and later articulated by 19th-century physician Rudolf Virchow, emphasizing unity in animal and human medicines.
Addressing Modern Health Challenges
- Environmental Impacts: Human growth, urbanization, and industrialization contribute to biodiversity and ecosystem disruption, fostering zoonotic diseases.
- Zoonotic Diseases: Roughly 60% of emerging diseases that affect humans are zoonotic, including Ebola, bird flu, and rabies.
- Key Concerns: The rise of antimicrobial resistance, vector-borne diseases, and food safety underscores the need for an integrated approach.
Power of One Health Strategy
- Resource Efficiency: One Health fosters coordination across governmental units, reducing resource demands and promoting cross-sectoral collaborations.
- Economic Benefits: One Health proves economically prudent, potentially saving billions when compared to pandemic management through non-One-Health strategies.
Recent One Health Endeavors in India
- COVID-19 Impact: The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of the One Health approach.
- Indian Initiatives: India established a ‘Standing Committee on Zoonoses’ in 2006 and launched the ‘National One Health Mission’ for coordinated efforts.
The Transformation Process: Four Stages
- Stage 1: Communication: Setting up mechanisms for inter-ministerial communication and stakeholder engagement.
- Stage 2: Collaboration: Exchange of knowledge and expertise, defining roles in zoonoses management.
- Stage 3: Coordination: Long-term routine activities led by a dedicated agency for seamless collaboration.
- Stage 4: Integration: Developing synergies between sectors for streamlined resource sharing and coordinated initiatives.
Facilitating Collaborative Science
- Integrated Research: Beyond office-sharing, integrated research environments are crucial, allowing access to laboratories and biological samples.
- Sample Utilization: Efficient use of expensive and ethical biological samples, such as blood and tissue, enhances collaborative research outcomes.
Conclusion
- India’s embrace of the One Health approach reflects its commitment to holistic well-being.
- By recognizing the interconnectedness of humans, animals, plants, and the environment, India is laying the groundwork for comprehensive health strategies.
- With ongoing initiatives and a vision to seamlessly integrate resources and expertise, India aims to transform its health landscape, ensuring resilience against emerging challenges through a united and holistic approach.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India launches Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GIDH
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- In a significant stride towards global healthcare innovation, the World Health Organization (WHO) and India’s G20 presidency have jointly unveiled the ‘Global Initiative on Digital Health’ (GIDH).
- The announcement was made at the Health Minister’s Meeting during the G20 Summit, hosted by the Indian Government.
What is GIDH?
- WHO and G20 Partnership: The WHO and India’s G20 presidency collaboratively introduced the ‘Global Initiative on Digital Health’ (GIDH).
- Strategy Implementation: GIDH functions as a WHO-managed platform, supporting the implementation of the ‘Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020–2025.’
- Transformation Acceleration: The WHO, as the strategy’s Secretariat, facilitates the global convergence of standards, best practices, and resources for expediting digital health system transformation.
Objectives of the GIDH Initiative
- Measurable Outcomes: GIDH aspires to unite nations and partners, aiming to achieve tangible results through concerted efforts.
- Prioritizing Investment Plans: The initiative seeks to establish focused investment plans for the transformation of digital health, driven by clear priorities.
- Enhancing Resource Transparency: GIDH works towards greater transparency in reporting digital health resources, ensuring effective resource allocation.
- Facilitating Global Collaboration: The initiative fosters the exchange of knowledge and collaboration among regions and countries to expedite progress.
- Comprehensive Governance: GIDH supports holistic government approaches to digital health governance within countries.
- Boosting Support: The initiative aims to enhance both technical and financial support for the implementation of the ‘Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020–2025’ and its forthcoming phase.
India’s Role and Vision
- Digital Health Innovation: India’s G-20 Health Minister emphasized India’s role in digital health innovation at the G-20 Health Ministers’ Meeting.
- National Digital Health Architecture: India’s efforts for a comprehensive digital health ecosystem, exemplified by the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), were highlighted.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Homeopathy and associated issues
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Integrated system of medicine, Homeopathy system of medicine etc
Mains level: India's path towards universal health care, challenges and measures
What’s the news?
- In a recent development, the ICMR and the Ministry of Ayush have agreed to enhance cooperation in health research related to integrated medicine.
Central idea
- The recent push to integrate AYUSH medicinal systems into mainstream health care to achieve universal health coverage and decolonize medicine is a commendable pluralistic approach. However, this endeavor must prioritize safety and efficacy standards for every participating system. Unfortunately, Homeopathy falls short of meeting these essential criteria.
What is an integrated system of medicine?
- An integrated system of medicine refers to an approach that combines elements from different healthcare systems or modalities, such as conventional medicine and traditional, complementary, or alternative medicine, with the goal of providing comprehensive and patient-centered care.
What Is Homeopathy?
- Homeopathy is a system of alternative medicine founded in the late 18th century by Samuel Heinemann, a German physician.
- Homeopathy is a medical system based on the belief that the body can cure itself. Those who practice it use tiny amounts of natural substances like plants and minerals. They believe these stimulate the healing process.
- This is based on the idea that a substance that causes symptoms in a healthy individual can stimulate the body’s natural healing response to overcome similar symptoms in an ill person.
Key principles of Homeopathy
- The Law of Similar: Homeopathy follows the principle that a substance that produces symptoms in a healthy person can be used to treat similar symptoms in a sick person.
- Minimum Dose: Homeopathic remedies are prepared through a process of dilution and potentization, which involves repeatedly diluting the original substance and shaking it vigorously. The belief is that this process enhances the remedy’s healing properties while minimizing any potential toxicity.
- Individualization: Homeopathy treats each person as a unique individual and tailors the treatment to address their specific symptoms and overall constitution.
- Totality of Symptoms: Rather than focusing solely on a specific disease or isolated symptoms, homeopathy takes into account the totality of a person’s physical, mental, and emotional symptoms to find an appropriate remedy.
Concerns over the efficacy and safety of Homeopathy
- Weak Evidence: The evidence supporting the efficacy of homeopathy is considered weak. The Nuremberg Salt Test (1835), a well-conducted double-blind randomized controlled trial, discredited homeopathy, attributing its claimed effects to imagination, self-deception, or potential fraud.
- Inconsistent Systematic Reviews: Multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses have consistently shown that homeopathic treatments lack clinically significant effects across various ailments, population groups, study types, and treatment regimes.
- Unregistered Trials: Researchers found that more than half of the 193 homeopathic trials conducted in the last two decades were not registered. Surprisingly, unregistered trials showed some evidence of efficacy, while registered trials did not, casting doubt on the validity and reliability of the evidence.
- Lack of confidence: The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued warnings against using homeopathy for serious conditions such as HIV, tuberculosis, malaria, and infant flu and diarrhea. This indicates a lack of confidence in its effectiveness in treating such illnesses.
- Ineffectiveness for Serious Conditions: Evidence suggests that homeopathy may not work effectively in treating cancers and may not help reduce the adverse effects of cancer treatments.
- Potential Delay in Effective Treatment: One of the safety concerns related to homeopathy is its potential to delay the application of evidence-based clinical care for serious or life-threatening conditions. This delay can have detrimental effects on patients’ health outcomes.
Arguments in favor of Homeopathy
- Historical Usage: Supporters of homeopathy often highlight its long historical usage and widespread popularity, arguing that its effectiveness is demonstrated by its continued use over the centuries.
- Individualization of Treatment: Homeopathy emphasizes individualized treatment, tailoring remedies to address a person’s unique symptoms and overall constitution. This personalized approach is believed to be beneficial for patients who may not respond well to standardized treatments.
- Minimal Side Effects: Homeopathic remedies are highly diluted, which proponents claim minimizes side effects and makes them safe for use, even in sensitive patient populations.
- Holistic Approach: Advocates assert that homeopathy takes a holistic view of health, considering not only physical symptoms but also mental and emotional aspects of a person’s well-being.
- Anecdotal Testimonials: Supporters of homeopathy often provide anecdotal testimonials from patients who claim to have experienced positive outcomes from using homeopathic remedies. Supporters of homeopathy often cite testimonials from famous figures like Gandhi and Tagore to bolster its credibility.
Way forward: Key areas that India needs to focus on regarding Homeopathy
- Evidence-Based Medicine: India needs to prioritize evidence-based medicine across all healthcare systems, including homeopathy. Rigorous research, clinical trials, and systematic reviews should be conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of homoeopathic treatments.
- Integration and Pluralism: India should adopt a balanced approach to healthcare by integrating various medicinal systems, including allopatry and AYUSH, while ensuring that only evidence-based and effective practices are incorporated into mainstream healthcare.
- Regulatory Oversight: Strengthen regulatory bodies to oversee the practice of homeopathy and ensure adherence to quality standards and ethical guidelines. This will help maintain patient safety and foster trust in the healthcare system.
- Education and Awareness: Promote education and awareness among healthcare professionals and the public about the strengths and limitations of homeopathy. Informed decision-making and patient choice should be encouraged based on scientific evidence.
- Holistic Health Approach: Emphasize a holistic approach to healthcare that considers not only physical symptoms but also mental, emotional, and social aspects of health. This approach should be integrated into all medical systems, including homeopathy.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously review and update the integration of homeopathy and other medical systems based on emerging evidence and changing healthcare needs. This iterative approach will lead to a more responsive and effective healthcare system.
Conclusion
- For India’s path towards universal health care, an evidence-based and ethics-driven medicine approach should be embraced, ensuring that only safe and effective treatments are integrated into mainstream healthcare practices.
Also read:
World Ayurveda Congress: Aligning traditional medicine with modern medicines
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Ayushman Bharat expose: How to nudge India’s public health infrastructure
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PMJAY and schemes
Mains level: Government sponsored schemes, challenges, concerns and solutions
What’s the news?
- A recent report has revealed disturbing incidents of deception against poor patients at Safdarjung Hospital (‘Bypassing Ayushman Bharat, doctor at a top government hospital duped patients and made killings on implants).
Central Idea
- Designing a government-sponsored health insurance scheme for the poor presents significant challenges, including the issue of information asymmetry between doctors and patients, which may lead to the denial of benefits for the disadvantaged.
What is Ayushman Bharat?
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY), also known as Ayushman Bharat or the National Health Protection Scheme (NHPS), is a flagship government-sponsored health insurance scheme launched by the Government of India in September 2018. The primary aim of PMJAY is to provide financial protection and access to quality healthcare to economically vulnerable sections of society.
Key features
- Health Insurance Coverage: PMJAY provides health insurance coverage to eligible beneficiaries, especially those belonging to economically weaker sections (EWS) and low-income families. It aims to cover around 10 crore (100 million) families across India.
- Cashless and Paperless Treatment: Under PMJAY, eligible beneficiaries can avail of cashless and paperless treatment in empaneled public and private hospitals across the country. The scheme ensures that beneficiaries are not required to pay for the treatment at the time of hospitalization.
- Pre-Defined Medical Packages: The scheme offers a comprehensive set of pre-defined medical packages covering various medical and surgical treatments. These packages are designed to provide essential healthcare services, including diagnostics, medicines, and other treatments.
- Coverage for Pre-Existing Conditions: PMJAY provides coverage for pre-existing illnesses and health conditions from the date of enrollment. This ensures that beneficiaries with existing health conditions can also access healthcare services under the scheme.
- No Cap on Family Size: There is no restriction on the family size covered under PMJAY. All eligible family members can avail of the benefits of the scheme.
- Portability: PMJAY is portable across the country, meaning beneficiaries can avail of treatment in any empaneled hospital in any state or Union Territory, irrespective of their place of origin
- Identification of Beneficiaries: Beneficiaries under PMJAY are identified through the Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data and are issued the Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY Golden Card, which serves as proof of eligibility.
- Online Verification: The scheme employs an online verification process to ensure seamless and efficient identification and validation of beneficiaries.
- Collaborative Effort: PMJAY is a joint collaboration between the central and state governments, and each state has the flexibility to implement the scheme based on its specific requirements.
The Incident of deceptive practices at Safdarjung Hospital
- Misleading Patients: The report reveals that certain doctors deceive patients by providing false information about delays in Ayushman Bharat Clearance. This deceptive tactic aims to divert patients towards private alternatives rather than enrolling them in the PMJAY scheme.
- Influence of Treating Doctors: The incident highlights the significant role of treating doctors in determining the medical package for patients and whether they are enrolled under the PMJAY scheme.
Concerns raised over the implementation of government-sponsored health insurance schemes
- Deceptive Practices: Misinformation about Ayushman Bharat Clearance delays is used as a tactic to divert patients towards private alternatives instead of enrolling them in the PMJAY. Such practices can deprive eligible patients of government-sponsored health insurance benefits and lead to potential financial exploitation.
- Doctor’s Influence: The treating doctors wield significant influence in determining the medical package for patients and their enrollment in the PMJAY scheme. This discretionary power can create an environment where some doctors prioritize their personal interests, such as financial gains from private channels, over the best interests of their patients.
- Lack of Active Interest: Although the time taken to settle claims was reasonable, the proportion of settled claims in public facilities was lower compared to private facilities. This points to potential issues in operational dynamics that may hinder the effective implementation of the scheme and limit its benefits for the poor.
- Inadequate Incentives: The financial incentives provided to doctors in public facilities under PMJAY may not be sufficiently attractive to encourage them to actively participate in the scheme. Some doctors may find greater financial gains through rent-seeking practices with private players, leading to a preference for private alternatives over the government-sponsored scheme.
- Limited Supporting Staff: The presence of limited supporting staff, such as Arogyamitras, responsible for registering patients under PMJAY, may impact the smooth implementation of the scheme. The Arogyamitras’ remuneration being linked to pre-authorizations rather than claim settlement may result in less emphasis on claim follow-up and documentation.
Way forward: Steps to improve operational dynamics
- Enhancing Doctor Incentives: Reviewing and revising the financial incentives provided to treating doctors could make the PMJAY scheme more attractive and encourage greater participation.
- Strengthening Arogyamitras’ Role: Linking the remuneration of Arogyamitras to the successful claim settlement and providing necessary support staff can incentivize them to be more proactive in claim documentation and follow-up.
- Streamlining the Claim Settlement Process: Simplifying and expediting the claim settlement process can encourage public facilities to actively participate in PMJAY, ensuring timely reimbursements and improving their financial viability.
- Increased Oversight: Implementing regular audits and stringent penalties for fraudulent practices can help curb deceptive activities and enhance transparency and accountability within public facilities.
Conclusion
- While the potential of PMJAY has been extensively discussed in the context of private hospitals, the operational dynamics within public facilities have received less attention. A collaborative effort involving doctors, Arogyamitras, and state governments can unleash the true potential of these schemes, contributing to improved health outcomes and greater inclusivity in healthcare services.
ALso read:
Digital Birth Certificates to streamline Official Documentation
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS) in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS)
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- India has taken its first step towards introducing Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS), a research model widely used in other countries for vaccine and treatment development.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research’s (ICMR) Bioethics Unit has prepared a consensus policy statement open for public comment, addressing the need, benefits, and ethical challenges associated with CHIS.
What is Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS)?
- CHIS also known as human challenge trials, are scientific studies conducted to deliberately expose healthy human volunteers to infectious agents under controlled conditions.
- The primary objective of these studies is to gain a better understanding of the pathogens’ behavior, human immune response, and to test potential vaccines, treatments, or preventive measures against the infection.
Key points about Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS) include:
- Informed Consent: Volunteers participating in CHIS must provide informed consent, fully understanding the potential risks and benefits associated with their participation.
- Types of Pathogens: CHIS can be used to study various infectious agents, such as viruses (e.g., influenza, dengue, Zika), bacteria (e.g., cholera, typhoid), and parasites (e.g., malaria).
- Vaccine Development: CHIS plays a crucial role in vaccine development by providing controlled environments to assess the efficacy of candidate vaccines and their ability to induce protective immune responses.
- Controversy: The use of CHIS has sparked ethical debates about balancing potential risks to participants against potential benefits to public health.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding CHIS in India
- Delicate Ethical Balance: CHIS is considered ethically sensitive due to concerns about deliberate harm to participants, fair compensation, third-party risks, and withdrawal from the study, and involving vulnerable participants.
- Streamlined Ethics Review: ICMR acknowledges the need for a specialized ethics review process with additional oversight and safeguards to protect study participants.
- Deterrents and Unique Context: Technical, clinical, ethical, and legal challenges deterred India from adopting CHIS earlier, partly influenced by the nation’s unique socio-cultural context.
Potential Benefits of CHIS in India
- High Disease Burden: India faces a significant burden of morbidity and mortality from infectious diseases, contributing about 30% of the disease burden in the country.
- Novel Insights and Efficiency: CHIS offers unique insights into disease pathogenesis and enables accelerated and cost-effective outcomes with smaller sample sizes compared to large clinical trials.
- Social Value: CHIS can contribute to public health response, healthcare decision-making, policies, economic benefits, improved pandemic preparedness, and community empowerment.
Encouraging Collaboration and Expertise
- Complex Nature of CHIS: ICMR highlights the complexity of CHIS and suggests that collaborations between researchers, institutions, organizations, and countries may be necessary to ensure the right expertise is available.
- Crucial Role in Advancing Scientific Understanding: The ICMR Bioethics Unit’s consensus policy statement aims to address ethical concerns associated with CHIS, acknowledging its potential role in advancing the scientific understanding of infectious diseases and accelerating treatment strategies.
Public Consultation and Future Directions
- Open for Public Consultation: The ICMR’s consensus policy statement on CHIS is open for public consultation until August 16 to gather input from stakeholders and experts.
- Striving for Ethical Research: ICMR emphasizes its commitment to conduct CHIS in India while ensuring ethical principles are upheld and human participants are protected.
Conclusion
- The introduction of CHIS in India is a significant step towards advancing medical research and finding cost-effective solutions for infectious diseases.
- Public consultation and expert collaborations will help shape the future direction of CHIS research in India and contribute to scientific progress and improved healthcare outcomes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Is there a Rural Bias in National Surveys?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Statistical Organisation (NSO)
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- The Centre has appointed a panel to review the methodology of the National Statistical Organisation (NSO).
- This step comes amid discussions regarding the accuracy of national surveys such as the National Sample Survey (NSS), National Family Health Survey (NFHS), and Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS).
About National Statistical Office (NSO)
Historical Background:
- The NSO was established in 1950 as the Central Statistical Office (CSO) under the Ministry of Planning.
- It was later renamed the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) in 1970 and subsequently became the NSO in 2019.
- Over the years, it has evolved to become the primary statistical agency in India.
Organizational Structure:
- The NSO consists of several divisions and units responsible for different statistical functions.
- These include the Survey Design and Research Division, Field Operations Division, Data Processing Division, National Accounts Division, Price Statistics Division, and Social Statistics Division, among others.
Key organizations under NSO: Central Statistical Office (CSO)
- The CSO is a part of the NSO and focuses on macroeconomic statistics and national income accounting.
- It is responsible for producing key economic indicators such as the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Index of Industrial Production (IIP), Consumer Price Index (CPI), and Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
Important Surveys Conducted:
- Population Census: The NSO conducts a decennial Population Census in collaboration with the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India. The census collects data on population size, composition, and other demographic characteristics.
- National Sample Survey (NSS): The NSS is a large-scale household survey conducted by the NSO to collect data on various socio-economic aspects. It provides valuable information on employment, consumer expenditure, poverty, education, health, and other important indicators.
- Economic Census: The NSO conducts the Economic Census periodically to collect data on the number of business establishments, their distribution across sectors and regions, employment, and other relevant economic variables.
- Annual Survey of Industries (ASI): The ASI is conducted by the NSO to collect data on the performance and structure of the industrial sector in India. It covers various aspects such as employment, wages, production, and financial indicators.
- Agricultural Census: The NSO conducts the Agricultural Census periodically to collect comprehensive data on agricultural holdings, cropping patterns, land use, irrigation, livestock, and other relevant agricultural variables.
- Health and Morbidity Survey: The NSO conducts surveys on health and morbidity to gather data on healthcare utilization, access to healthcare services, prevalence of diseases, and other health-related indicators.
Why under review?
- Concerns about Methodology: Experts argue that the usage of outdated survey methodology in national surveys may have systematically underestimated India’s development.
- Narrower capture of data: The dynamic nature of the Indian economy over the last 30 years might not be adequately captured.
- Different Perspectives: While some experts believe there is no systematic underestimation of development by these surveys, they acknowledge the presence of errors that should be minimized.
- Role of National Data: Accurate national-level data is crucial for research, policymaking, and development planning.
Focus on NFHS Data
- Crucial development data: The National Family Health Survey provides vital data on health and family welfare indicators.
- Claims of Bias: Some experts suggest that national surveys, including NFHS, may exhibit a “rural bias” in representation, leading to an underestimation of India’s development.
- Issue of Error and Random Bias: While errors in population estimations have occurred in some rounds, they appear to be random rather than systematic.
Minimizing Errors in Data Collection
- Improving Response Rates: Efforts to increase response rates in both rural and urban areas can lead to more accurate data.
- Importance of Sample Weights: Proper assignment of sample weights can significantly improve the accuracy of estimations and correct any underrepresentation of rural or urban populations.
Recommendations for the Review Panel:
- Addressing Concerns: The review panel should focus on ensuring that the samples are adequately representative rather than proposing a complete overhaul of survey methodologies.
- Correcting Bias Where It Exists: While addressing any perceived biases, the panel should aim to eliminate bias where it genuinely exists without introducing new biases in policymaking and planning.
Conclusion
- Accurate data serves as the bedrock of progress and development in the country.
- Reviewing the methodology of national surveys is vital to ensure accurate and representative data for India’s development.
- Striking the right balance between addressing concerns and minimizing errors will lead to more informed decision-making and policy formulation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Tele-MANAS counsels 2 Lakh distressed people
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tele-MANAS
Mains level: Mental health and telemedicine

Central Idea: The government-run national tele-mental health programme, Tele MANAS, has achieved a significant milestone by receiving over 2,00,000 calls from individuals across India since its launch in October 2022.
What is Tele-MANAS?
- Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking across States (Tele-MANAS) initiative has been launched by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare in October 2022.
- It aims to provide free tele-mental health services all over the country round the clock, particularly catering to people in remote or under-served areas.
Implementation of the scheme
- Counselling: The programme includes a network of 38 tele-mental health centres of excellence spread across 27 States and UTs working in over 20 languages.
- Helpline: A toll-free, 24/7 helpline number (14416) has been set up across the country allowing callers to select the language of choice for availing services. Service is also accessible at 1-800-91-4416.
Two-tier working
- Tele-MANAS will be organised in a two-tier system; Tier 1 comprises state Tele-MANAS cells which include trained counsellors and mental health specialists.
- Tier 2 will comprise specialists at District Mental Health Programme (DMHP)/Medical College resources for physical consultation and/or e-Sanjeevani for audio-visual consultation.
Call Demographics and Concerns
- Age Group: Two-thirds of the callers fall in the 18-45 years age group, while 12.5% belong to the 46-64 years age group, and 8% are below 18 years of age.
- Gender Distribution: Of the two lakh calls, 59.6% were made by male callers, and 40% by female callers.
- Top Concerns: The most common reasons for seeking help were general feelings of sadness (28.8%), sleep-related problems (27.6%), anxiety (20.4%), relationship issues (10%), aggression (9.2%), and low interest in activities (9.7%).
Expansion of the scheme
- The initial rollout providing basic support and counselling through a centralized Interactive Voice Response system (IVRS) is being customized for use across all States and UTs.
- It is being linked with other services like National teleconsultation, e-Sanjeevani, Ayushman Bharat, mental health professionals, health centres, and emergency psychiatric facilities for specialized care.
- This will not only help in providing immediate mental healthcare services but also facilitate a continuum of care.
- Eventually, this will include the entire spectrum of mental wellness and illness, and integrate all systems that provide mental health care.
Back2Basics: National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP)
- The Indian Government announced the National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP) in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- The National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS) in Bengaluru is the nodal centre for the programme.
- The programme sought to establish a digital mental health network that can address the mental health crisis in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The pandemic has brought forth challenges to mental health, and the NTMHP aims to provide accessible and affordable mental health services to all.
- The programme will involve the use of digital platforms such as teleconsultations, chatbots, and mobile applications to deliver mental health services.
- The NTMHP will integrate with existing mental health services to provide a comprehensive and coordinated approach to mental healthcare.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever (CCHF)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever (CCHF)
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Europe is currently experiencing a heatwave and wildfires, leading to concerns about the spread of viruses that are typically not found in colder climates.
- The WHO has issued an alert regarding the Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF), a potentially fatal infection transmitted by ticks.
What is CCHF?
- CCHF is a viral haemorrhagic fever primarily transmitted by ticks.
- It can also be contracted through contact with viraemic animal tissues during animal slaughter.
- CCHF outbreaks can lead to epidemics with a high case-fatality ratio (10-40%) and pose challenges for prevention and treatment.
Transmission and Hosts
- The virus exists in the tick family of insects.
- Animals such as cattle, goats, sheep, and hares serve as amplifying hosts for the virus.
- Humans can contract CCHF through contact with infected ticks or animal blood.
- The virus can also be transmitted between humans through contact with infectious blood or body fluids.
- Migratory birds can host ticks, allowing the virus to spread over long distances.
Symptoms and Treatment
- Common symptoms of CCHF include fever, muscle aches, dizziness, neck and back pain, headache, sore eyes, and sensitivity to light.
- Early symptoms may also include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and sore throat, followed by mood swings and confusion.
- Later stages may involve sleepiness, depression, and lassitude.
- There is no vaccine available for CCHF in humans or animals, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms.
- The antiviral drug ribavirin has been used to treat CCHF infection with some apparent benefit.
Spread of CCHF in Europe
- CCHF is endemic to Africa, the Balkan countries, the Middle East, and parts of Asia.
- In 2016, Spain reported the first fatality from CCHF in Europe.
- Scientists warn that CCHF, which can have a fatality rate between 10% and 40%, is spreading northward and westward in Europe.
- Cases of CCHF have been reported in Spain, Russia, Turkey, and the UK.
Reasons for this spread
- Disrupted temperature patterns due to climate change are creating favorable conditions for pathogens.
- CCHF ticks are moving northward through Europe due to longer and drier summers caused by climate change.
- Climate change contributes to the spread of diseases by expanding tick habitats, altering water habitats, and facilitating the movement of animals and human interactions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s diabetes epidemic is making its widespread TB problem worse
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: DM and Tb related facts
Mains level: The dual burden of India, TB and Diabetes, Interconnection, challenges and treatment measures
What is the news?
- India has long grappled with two major epidemics: type 2 diabetes (diabetes mellitus, DM) and tuberculosis (TB). With a staggering 74.2 million people living with diabetes and 2.6 million new TB cases each year, it is crucial to understand the deep interconnection between these diseases.
Central Idea
- The diabetes mellitus (DM) and tuberculosis (TB) are closely interconnected in India, with DM increasing the risk and severity of TB, and TB co-infection worsening diabetes outcomes. Among people with TB, the prevalence of DM was found to be 25.3% while 24.5% were pre-diabetic. Which highlights the need for urgent action to address this dual burden and improve care coordination for individuals affected by both diseases.
What is type 2 diabetes?
- Type 2 diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus (DM), is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels.
- It is the most common form of diabetes and typically develops over time, often in adulthood.
- In type 2 diabetes, the body either becomes resistant to the effects of insulin (a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels) or does not produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.
What is tuberculosis (TB)?
- TB is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- It primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, spine, and brain.
- TB is transmitted through the air when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or speaks, releasing tiny droplets containing the bacteria. When inhaled by others, these droplets can lead to infection
The interconnection and Impact of DM on TB
- Increased Risk of TB: People with DM have a higher risk of developing TB compared to those without DM. DM weakens the immune system and impairs the body’s ability to fight off infections, including TB.
- Increased TB Severity: When individuals with DM acquire TB infection, they tend to have a higher bacterial load, which means there are more TB bacteria in their bodies. This can result in more severe symptoms and complications associated with TB.
- Delayed Sputum Conversion:
- Sputum conversion refers to the transition from having TB bacteria detectable in the sputum (positive) to no longer having detectable bacteria (negative) after initiating treatment.
- Individuals with both TB and DM often experience delayed sputum conversion compared to those with TB alone.
- It means that it takes longer for the TB bacteria to be eliminated from their bodies, prolonging the infectious period and potentially increasing the risk of transmitting the disease to others.
- Altered Treatment Outcomes:
- TB treatment outcomes can be affected by the presence of DM. Individuals with both TB and DM may experience modified TB symptoms, radiological findings, and lung functioning compared to those with TB alone.
- Studies have shown that individuals with TB and DM have reduced lung functioning even after completing TB treatment.
- Respiratory Complications: Individuals with both TB and DM are more prone to experiencing respiratory complications related to TB. Respiratory complications can be a common cause of death in this population, highlighting the increased severity of TB when DM is present.
What measures India must take to combat the dual burden of DM and TB
- Integrated Care: Implement patient-centered care approaches that address the unique needs of individuals with both TB and DM, along with other comorbidities. This includes coordinated diagnosis and treatment, bidirectional screening, patient education, and support.
- Holistic Treatment Plans: Strengthen high-quality care for TB, DM, and associated comorbidities by developing holistic treatment plans. Prioritize individual programs for TB and DM and ensure their integration into healthcare services.
- Resilient Health Systems: Build and scale up resilient and integrated health systems by garnering increased commitment from stakeholders, formulating robust policy guidance, and mobilizing additional resources. These efforts will support the development of effective strategies to combat both diseases.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Enhance the research literature on TB and DM interactions to enable better decision-making. Access to comprehensive data and ongoing studies will provide critical insights for improving patient care and raising awareness of the impact of these interconnected diseases
Conclusion
- The coexistence of diabetes mellitus and tuberculosis in India demands immediate attention. By adopting integrated care models, improving treatment outcomes, and strengthening health systems, we can effectively address the dual burden of DM and TB. It is essential for health professionals, policymakers, and communities to prioritize research, enhance collaboration, and work together to improve the lives of those affected by these intertwined epidemics.
Also read for more details:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Don’t waste the wastewater
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: public health surveillance models
Mains level: wastewater surveillance and its benefits, public health surveillance mechanism, challenges and innovative models
What’s the news?
- A recent study published in The Lancet Global Health has reintroduced wastewater surveillance as a powerful strategy for public health surveillance.
Central idea
- In 1854, during a cholera outbreak in London, physician John Snow traced the epidemic to a contaminated water pump, highlighting the importance of disease prevention. Today, advancements in public health surveillance present new opportunities to detect outbreaks early. Wastewater surveillance, a cost-effective approach, has gained prominence in tracking diseases like poliovirus and SARS-CoV-2.
What is mean by Wastewater Surveillance?
- Wastewater surveillance refers to the monitoring and analysis of wastewater samples to gather information about the presence and spread of disease-causing agents, such as viruses or bacteria, within a community.
- It involves systematically sampling and testing wastewater from various sources, such as sewage systems or wastewater ponds. The samples are then analyzed in designated laboratories to identify specific markers or genetic fragments of pathogens.

Benefits of Wastewater Surveillance
- Early Outbreak Detection: Wastewater surveillance detects disease-causing agents before clinical cases are reported, enabling prompt response and containment measures.
- Community-Level Monitoring: Analyzing wastewater samples offers insights into overall community health, aiding in disease trend identification and targeted interventions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Wastewater surveillance eliminates the need for individual samples, reducing costs associated with collection, testing, and analysis.
- Complementary to Clinical Data: Wastewater surveillance provides additional information beyond clinical data, capturing asymptomatic cases and enhancing disease prevalence understanding.
- Early Warning System: Specific genetic markers or pathogen fragments found in wastewater samples can serve as an alert for potential disease outbreaks.
- Surveillance in Resource-Limited Areas: Wastewater surveillance helps monitor disease occurrence in areas with limited access to healthcare facilities, enabling prioritized resource allocation.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making: Integrating wastewater surveillance data with other sources informs data-driven decisions for disease control, resource allocation, and targeted interventions.
Challenges in India’s public health surveillance system
- Uneven Coverage: The public health surveillance system in India does not provide uniform coverage across the country. Rural and remote areas often lack adequate surveillance infrastructure and resources, resulting in limited data collection and monitoring capabilities in these regions.
- Fragmented and Siloed Efforts: Disease surveillance efforts in India are often fragmented and focused on specific diseases or health conditions. This siloed approach makes it difficult to detect and respond to emerging health threats comprehensively.
- Inadequate Data Sharing: In India, there are challenges in sharing data between different levels of government and across departments, hindering the seamless flow of information necessary for early detection and response.
- Limited Diagnostic and Laboratory Capacity: India’s public health laboratory infrastructure and diagnostic capacity need significant improvements. Inadequate resources, outdated equipment, and a shortage of trained personnel can hamper timely and accurate testing.
- Underreporting and Data Quality Issues: Underreporting of diseases and inconsistent data quality pose significant challenges in India’s public health surveillance system.
- Limited Use of Advanced Technologies: The adoption of advanced technologies, such as real-time data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, is limited in India’s public health surveillance system.
How India can enhance its epidemiological capabilities?
- Incorporate Wastewater Surveillance into Reporting: Efforts should be made to incorporate wastewater surveillance data into existing surveillance reporting systems.
- Integration with Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission: The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, which aims to create a seamless online platform for healthcare services, offers an opportunity for the integration of wastewater surveillance.
- Strengthen Public Health Laboratory Networks: Efforts should be made to strengthen public health laboratory networks by incorporating the testing of wastewater samples into surveillance reporting. This can be achieved by providing the necessary resources, equipment, and trained personnel to conduct wastewater testing.
- Training of Public Health Professionals: Public health professionals should receive training not only in traditional epidemiological methods but also in the management and interpretation of data derived from wastewater surveillance.
- Data Management and Analysis: Develop robust data management systems to collect, store, and analyze wastewater surveillance data. This may involve creating dedicated databases or integrating wastewater surveillance data into existing surveillance information systems.
Need for Political backing and adequate funding for the successful integration of wastewater surveillance
- India’s Commitment to Public Health Surveillance: India has already demonstrated its commitment to public health surveillance and resource mobilization. It is essential for political leaders to recognize the potential of wastewater surveillance as an effective tool for disease monitoring and response.
- Niti Aayog’s Vision: The integration of wastewater surveillance aligns with Niti Aayog’s vision. Political leaders can provide strategic guidance and policy support to ensure the inclusion of wastewater surveillance in the national public health agenda
- International Platforms and Leadership: India’s leadership at international platforms like the G20 provides an opportunity to elevate the significance of innovative approaches to disease surveillance, including wastewater surveillance. Political leaders can leverage these platforms to advocate for enhanced public health surveillance and secure international commitments and support.
- Resource Allocation: Adequate funding is essential to implement wastewater surveillance effectively. Political leaders should allocate sufficient resources to build and strengthen laboratory networks, develop wastewater sampling infrastructure, and train public health professionals in data analysis and interpretation.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Political leaders can facilitate partnerships between the public and private sectors to enhance funding for wastewater surveillance.
Conclusion
- The inclusion of wastewater surveillance in India’s public health infrastructure holds great promise for enhancing disease prevention and control. Through strategic leadership, India has the potential to set a precedent in integrated public health surveillance, creating a model that prioritizes proactive measures, timely response, and a resilient healthcare system.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Leptospirosis: A disease that surges in monsoons
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Leptospirosis
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Leptospirosis has emerged as an important infectious disease in the world today.
- It is a potentially fatal zoonotic bacterial disease that tends to have large outbreaks after heavy rainfall or flooding.
What is Leptospirosis?
- Leptospirosis is a zoonotic bacterial disease that poses a significant global health threat, particularly after heavy rainfall or flooding.
- It affects millions of people annually, with a high mortality rate, and its burden is expected to increase in the future.
- The disease is caused by the bacterium Leptospira interrogans, primarily transmitted from animals to humans.
Disease Transmission and Risk Factors
- Disease transmission: Leptospira is shed in the urine of infected animals, contaminating soil and water.
- Carriers: Both wild and domestic animals, including rodents, cattle, pigs, and dogs, can transmit the disease.
- Human exposure: Direct contact with animal urine or indirectly through contaminated soil and water poses a risk.
- Occupational hazards: Agricultural workers, animal handlers, and those in sanitary services are at an increased risk.
- Recreational activities: Engaging in water-based activities in contaminated lakes and rivers can also raise the risk.
Symptoms and Misdiagnosis
- Range of symptoms: Leptospirosis symptoms vary from mild flu-like illness to life-threatening conditions affecting multiple organs.
- Misdiagnosis challenges: Symptoms mimic other diseases like dengue, malaria, and hepatitis, leading to underreporting and limited awareness.
- Limited access to diagnostics: Lack of reliable diagnostic tools hinders accurate disease detection.
- Lack of environmental surveillance: Insufficient monitoring of the environment contributes to underestimating the disease burden.
Misconceptions and Preventive Measures
- Reservoir hosts: Rats are not the sole cause; various animals act as reservoir hosts.
- Environmental factors: Humidity and extreme weather events like floods increase the risk of exposure.
- Sanitary conditions: Poor waste management, high density of stray animals, and inadequate sanitation facilities contribute to the disease spread.
- Prevention strategies: Adopting a ‘One Health’ approach involving humans, animals, and the environment is crucial.
- Personal protective equipment: People working with animals or in flooded areas should use gloves and boots.
- Animal health and prevention: Ensuring sanitary animal-keeping conditions reduces the risk of leptospirosis transmission.
- Health education and awareness: Promoting proper hygiene practices, educating about the disease, and improving health literacy are essential preventive measures.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Aspartame: the Carcinogenic additive in Diet Cola
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aspartame
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The cancer research arm of the World Health Organization (WHO) is reportedly considering listing aspartame, a popular sugar substitute ‘Aspartame’ as “possibly carcinogenic to humans.”
- This potential listing by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has generated controversy as it contradicts previous studies that found no evidence linking aspartame to cancer.
What is Aspartame?
- Aspartame is widely used as an artificial sweetener in various food and beverage products.
- It is made from the dipeptide of two amino acids, L-aspartic acid and L-phenylalanine.
- It is approximately 200 times sweeter than table sugar and is commonly used in diet soft drinks, sugar-free gum, and other sugar-free products.
- It is favored by those seeking to reduce calorie intake or manage diabetes.
Safety Record and Regulatory Approvals
- Aspartame has undergone extensive studies over 40 years, with over 100 studies finding no evidence of harm caused by its consumption.
- The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has permitted its use in food since 1981, and it has been reviewed multiple times for safety.
- The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as national regulators in various countries, also deem aspartame safe for consumption.
- However, individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU), a rare genetic disorder, should avoid aspartame due to the presence of phenylalanine.
Controversies and Impact of WHOs Listings
- Past IARC rulings have raised concerns, led to lawsuits, and influenced manufacturers to seek alternatives due to public confusion.
- The potential listing of aspartame as “possibly carcinogenic” by the IARC contradicts previous scientific consensus on its safety.
- Critics argue that IARC assessments can be confusing to the public and may create unnecessary fear and misinformation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Centre planning new Bill on Stray Dog Issue
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Stray dog attack incidences

Centre Idea:
- The Centre will soon formulate a law on the issue of stray dogs, Union Minister Parshottam Rupala said.
Stray Dog Menace in India
- Cities have witnessed a sharp increase in the stray dog population, which as per the official 2019 livestock census stood at 1.5 crore.
- However, independent estimates peg the number to be around 6.2 crore.
- The number of dog bites has simultaneously doubled between 2012 and 2020.
- Experts agree there may be a correlation between urbanisation and solid waste production, made visible due to the mismanagement of waste disposal.
- Tepid animal birth control programmes and insufficient rescue centres, in conjunction with poor waste management, result in a proliferation of street animals in India.
Reasons behind
- Poor waste management: Inadequate waste disposal facilities and the mismanagement of solid waste often lead to the congregation of stray dogs around garbage dumps and landfills, where they scavenge for food.
- Unplanned urbanization: The population boom in Indian cities has led to a sharp increase in the stray dog population. Rapid urbanization has led to the creation of slums and unmanaged solid waste, which attract dogs.
- Lack of food and shelter: The availability of food and shelter determines the carrying capacity of a city. In the absence of these facilities, free-ranging dogs become scavengers that forage around for food, eventually gravitating towards exposed garbage dumping sites.
- Territoriality: Stray dogs often become territorial and aggressive about public spaces where they are fed, leading to increased attacks on humans.
- Improper sterilization and rescue centres: Tepid animal birth control programmes and insufficient rescue centres, in conjunction with poor waste management, result in a proliferation of street animals in India.
Food wastage in India
- A population boom in Indian cities has contributed to a staggering rise in solid waste production. Indian cities generate more than 150000 metric tonnes of urban solid waste every day.
- According to a 2021 UNEP report, an estimated 931 million tonnes of food available to consumers ended up in households, restaurants, vendors and other food service retailers’ bins in 2019.
- Indian homes on average also generated 50 kg of food waste per person.
- The presence of free-roaming dogs in urban areas is determined by the “carrying capacity” of a city, which is the availability of food and shelter.
Urban Stray Dogs and Waste Disposal
- Food and shelter: The wastage food often serves as a source of food for hunger-stricken, free-roaming dogs that move towards densely-populated areas in cities, such as urban slums which are usually located next to dumping sites.
- Sanitation assists food hunt: In the absence of proper sanitation and waste disposal facilities, stray dogs become scavengers that forage for food around exposed garbage dumping sites.
Impact of Unplanned and Unregulated Urban Development
- ABC Program: Under Animal Birth Control (ABC) program, municipal bodies trap, sterilize, and release dogs to slow down the dog population. This approach aims to control the number of strays while avoiding the inhumane practice of killing them.
- Rabies Control Measures: Another anchor of India’s response is rabies control measures, including vaccination drives. Rabies is a fatal disease that can be transmitted to humans through dog bites. Thus, preventing rabies is essential in addressing the issue of stray dogs.
- Informal Measures: These include mass killing of dogs in states like Kerala, which is a controversial practice as it is often inhumane and does not address the root causes of the issue. Other measures include imposing bans on the entry of stray dogs in colonies or feeding them in public.
Why address stray dog attacks issue?
- Adds Vulnerability to the poor: The disproportionate burden of dog bites may also fall on people in urban slums, which are usually located in close proximity to dumping sites.
- Exposes harsher realities: The rise in such attacks speak to core issues of lack of serviced affordable urban housing for all, lack of safe livelihood options and improper solid waste management”.
Empathizing the strays
- Abandoned, not strayed: Stray dogs are sentient social beings capable of feeling pain, fear, and joy. Urban living patterns have largely impacted their abandonment.
- Subjected to abuse: They are often victims of neglect, abuse, and abandonment, and are forced to survive in harsh conditions on the streets.
- Neglected community guardians: Stray dogs can serve as community guardians by alerting us to potential dangers and can also provide emotional support to humans.
Way forward
- Improve waste management: Efficient management of solid waste can help reduce the availability of food for stray dogs and limit their population growth.
- Increase vaccination and sterilization: ABC and vaccination programs should be implemented in a more organized and efficient manner to control the stray dog population and the spread of rabies.
- Encourage responsible feeding practices: Regulating feeding around bakeries and restaurants and improving waste management in public spaces can reduce the carrying capacity of the environment for stray dogs and minimize the congregation of dogs in certain areas.
- Develop national policy: There is a need for a comprehensive national policy that addresses the issue of stray dogs and their management in a more systematic and humane manner.
- Stop gruesome brutality: Stopping brutality towards dogs is a crucial step towards creating a more compassionate and just management of stray dogs menace.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Mental Health in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mental health Disorders and Associated Initiatives
Mains level: Prevalence of Mental Health Disorders in India, challenges and gaps in support system and Way forward
Central Idea
- India is grappling with a significant mental health crisis, with an estimated 6%-7% of the population affected by mental disorders. The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated the situation, leading to increased stress levels across social segments. Unfortunately, most cases of mental illness remain untreated due to ignorance and social stigma, leaving patients and their families to suffer in silence.
The Prevalence of Mental Health Issues in India
- National Mental Health Survey (2016): According to this survey conducted by the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), approximately 13.7% of India’s population (around 150 million individuals) was estimated to be in need of active mental health interventions. This survey covered a wide range of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety disorders, substance use disorders, and psychosis.
- World Health Organization (WHO) Report (2017): The WHO reported that India has one of the highest rates of major depression in the world, with over 5% of the population affected by this disorder. The report also highlighted that the prevalence of anxiety disorders in India was around 3.8%.
- Global Burden of Disease Study (2017): This study estimated that mental health disorders accounted for 9.9% of the total disease burden in India. It encompassed a broad range of mental disorders, including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and substance use disorders.
- National Health Mission (NHM) Estimates: NHM estimates suggest that 6%-7% of India’s population suffers from mental disorders. This aligns with the prevalence rates reported in other studies.
Causes for Caregiver Stress
- Physical and Emotional Caregiving: Caregivers are responsible for providing physical and emotional support to individuals with mental health disorders. The demanding nature of caregiving tasks, such as managing medications, attending to personal care needs, and addressing emotional distress, can contribute to caregiver stress.
- Social Isolation: Caregivers often experience social isolation as they may have limited time for social interactions and leisure activities. The focus on caregiving can lead to a decreased social support network and feelings of loneliness.
- Financial Difficulties: Mental health disorders can place a financial burden on families. The cost of treatment, medications, therapy sessions, and other related expenses can be significant. Caregivers may face financial strain, which adds to their stress levels.
- Troublesome Behavior of the Patient: Behavioral issues associated with mental health disorders, such as aggression, mood swings, and self-harm, can be challenging for caregivers to manage. Dealing with these behaviors on a daily basis can contribute to high levels of stress.
- Non-Adherence to Treatment: Many individuals with mental health disorders may struggle with adhering to treatment plans, such as taking medication regularly or attending therapy sessions. Non-adherence to treatment can be frustrating for caregivers, as it hampers the progress and well-being of the patient, leading to increased caregiver stress.
- Primary Caregiver Burden: In larger families, the responsibility of caregiving may be shared among family members. However, with reducing family sizes and changing social dynamics, the primary caregiver burden often falls on one individual, such as the spouse. This increased responsibility and lack of support can contribute to caregiver stress.
- Balancing Multiple Roles: Women caregivers, in particular, may face challenges in balancing caregiving responsibilities with other roles such as careers, child-rearing, and household chores. The juggling of multiple roles without sufficient support can lead to increased stress levels.
The Need for Structured Interventions
- Education and Awareness: Structured interventions can provide caregivers with comprehensive education and awareness about mental health disorders. This includes understanding the nature of the illness, its symptoms, treatment options, and available resources. Education empowers caregivers with the knowledge needed to better support their loved ones and navigate the challenges associated with mental health disorders.
- Role Clarity and Responsibilities: Structured interventions help caregivers clarify their roles and responsibilities in providing care for individuals with mental health disorders. This clarity reduces confusion and uncertainty, allowing caregivers to have a better sense of control and confidence in their caregiving abilities.
- Coping Skills and Stress Management: Caregiving can be emotionally and physically demanding, leading to high levels of stress. Structured interventions can equip caregivers with coping skills and stress management techniques to better handle the challenges they face. This may include strategies for self-care, relaxation techniques, problem-solving skills, and setting boundaries to prevent burnout.
- Peer Support and Networking: Structured interventions often incorporate peer support and networking opportunities. Caregivers can connect with others who are going through similar experiences, fostering a sense of belonging and reducing feelings of isolation. Sharing experiences, exchanging advice, and receiving support from peers can be invaluable in coping with caregiver stress.
- Access to Counseling and Helplines: Structured interventions can provide caregivers with access to professional counseling services and helplines. These services offer a safe and confidential space for caregivers to express their concerns, seek guidance, and receive emotional support. Counseling can help caregivers process their emotions, manage caregiver stress, and develop effective coping strategies.
- Psychoeducation and Skill Building: Structured interventions often include psychoeducational sessions and skill-building workshops for caregivers. These sessions cover various topics such as understanding the condition, recognizing early warning signs of relapse, learning about available therapies and their effectiveness, managing treatment-related expenses, and identifying and implementing effective coping mechanisms.
- Family Counselling and Involvement: Involving the entire family in structured interventions can foster a supportive environment for the individual with a mental health disorder. Family counselling sessions can enhance communication, understanding, and cooperation within the family, leading to better overall outcomes for the individual’s mental health.
Challenges and Gaps in Support Systems
- Lack of Trained Specialists: One of the major challenges is the shortage of trained mental health specialists, such as psychiatrists and clinical psychologists. India has a low ratio of psychiatrists and psychologists per population, making it difficult to provide adequate support and interventions for caregivers.
- Cost-Effective Intervention Implementation: Implementing cost-effective intervention models for caregiver support is hindered by the lack of trained specialists. The shortage of mental health professionals makes it challenging to scale up and deliver structured interventions that are accessible and affordable for caregivers.
- Insufficient Budget Allocation: The are concerns about insufficient budget allocation for mental health patients. Inadequate funding for mental health services further exacerbates the challenges in developing and implementing interventions specifically designed to support caregivers.
- Limited Insurance Coverage: Mental illnesses are often excluded from the list of ailments covered by leading medical insurers in India. While government schemes like Ayushman Bharat provide coverage for mental disorders, coverage by private insurers remains limited. This lack of comprehensive insurance coverage creates a gap in financial support for caregivers seeking mental health services.
- Expensive Private Mental Health Institutions: Private mental health institutions may provide services, but their costs can be prohibitively expensive for many individuals and families. This restricts access to quality mental health care and support for caregivers who may not be able to afford the high costs associated with private institutions.
- Inadequate Support for Caregivers: The current counselling services provided to caregivers upon request are not sufficient. Many caregivers may not be aware of their own emotional strain or may not proactively seek support due to various reasons, such as lack of awareness, stigma, or personal barriers.
Gaps in Insurance Coverage for Mental Health Disorders
- Exclusion from Leading Medical Insurers: The mental illnesses are excluded from the list of ailments covered by leading medical insurers in India. This means that individuals seeking treatment for mental health conditions may not receive adequate insurance coverage or reimbursement for their expenses.
- Mental Healthcare Act 2017: The Mental Healthcare Act 2017 aimed to rectify this issue by mandating that mental disorders should be treated on par with physical disorders for insurance coverage. However, it suggests that private insurers still have limited coverage for mental health disorders, indicating a gap between the mandate and its implementation.
- Government Schemes and Public Sector Insurance: While government schemes like Ayushman Bharat provide coverage for mental disorders, the article mentions that coverage by private insurers remains limited. This implies that individuals relying on private insurance may face challenges in obtaining comprehensive coverage for mental health conditions.
- Affordability and Accessibility: The private mental health institutions may provide services but at a higher cost, making them financially burdensome for many individuals and families. The lack of comprehensive insurance coverage further restricts access to affordable mental health care, exacerbating the affordability and accessibility challenges
Way Forward
- Structured Intervention Programs: Introducing structured intervention programs specifically aimed at educating and supporting caregivers are essential. These programs should provide information about mental health disorders, caregiver roles and responsibilities, coping mechanisms, and resources for assistance.
- Comprehensive Treatment Approach: There is need of a comprehensive treatment approach that involves healthcare professionals, informal caregivers, and psychosocial interventions. This collaborative approach recognizes the crucial role of caregivers and their involvement in the treatment process.
- Early Support for Caregivers: Studies in developed countries have shown that providing support to family caregivers at the onset of the psychiatric illness of their loved ones is crucial. Early intervention and support can enhance caregiver well-being and improve patient treatment participation.
- Intervention Models: Successful intervention models include cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychoeducational skill building, family counseling, and peer support. These models focus on providing caregivers with practical skills, knowledge, and emotional support to effectively manage caregiver responsibilities and cope with the challenges they face.
- Addressing Systemic Gaps: There are evident gaps in the healthcare system, including the shortage of trained specialists and insufficient budget allocation for mental health patients. Addressing these systemic gaps is crucial for developing and implementing effective caregiver support programs.
- Insurance Coverage: Expanding insurance coverage for mental disorders, as mandated by the Mental Healthcare Act 2017, is essential. Private insurers should also be encouraged to provide comprehensive coverage for mental health conditions to ensure financial support for caregivers seeking mental health services.
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and Community Movements: There is need to acknowledge the work of NGOs and community movements engaged in community support for mental illness and caregivers. Scaling up their efforts and ensuring collaboration with healthcare professionals can help bridge the existing gaps in caregiver support
Conclusion
- Recognizing and addressing the caregiver burden is imperative in India’s mental health landscape. Structured interventions that educate and support caregivers are crucial for improving their well-being and promoting patient treatment participation. Moreover, bridging the gaps in healthcare infrastructure, sufficient trained specialists, and expanding insurance coverage for mental disorders are essential steps toward providing comprehensive care for psychiatric patients and their caregivers.
Also read:
| Its high time to focus on Mental Health |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Medicines Patent Pool (MPP)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Medicines Patent Pool (MPP)
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Medicines Patent Pool (MPP) has entered into sub-licence agreements with Indian and Indonesian companies to produce generic versions of the cancer drug Nilotinib.
- Nilotinib is used in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia, a type of blood cancer.
What is Medicines Patent Pool (MPP)?
- Mission and Purpose: The MPP is a United Nations-backed organization focused on increasing access to life-saving medicines for low- and middle-income countries.
- Addressing IPR: The MPP works to overcome barriers related to intellectual property rights and patents that limit the availability and affordability of essential medicines.
- Voluntary Licensing Agreements: The MPP negotiates voluntary licensing agreements with pharmaceutical companies to allow the production of generic versions of patented medicines.
- Production of Affordable Generics: By securing licenses, the MPP enables qualified manufacturers in low- and middle-income countries to produce and distribute affordable generic medicines.
Need for MPP
- Collaborative Approach: The MPP collaborates with governments, non-profit organizations, civil society groups, and pharmaceutical companies to address global health challenges and promote access to medicines.
- Focus on Priority Diseases: The MPP’s efforts are particularly significant in diseases like HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, hepatitis C, and other priority areas where access to affordable medications is crucial.
- Sustainable Supply of Generic Medicines: Through licensing agreements, the MPP ensures a sustainable supply of quality-assured generic medicines, promoting market competition and expanding treatment options.
- Improving Health Outcomes: The MPP’s work reduces the burden of high drug costs and enhances access to life-saving treatments, ultimately improving health outcomes and saving lives.
- Benefit for Low- and Middle-Income Countries: The MPP’s initiatives directly benefit patients in low- and middle-income countries by increasing access to affordable medicines and reducing disparities in healthcare.
Recent agreements signed
- Licence Agreement with Novartis: In October 2022, the MPP signed a licence agreement with Novartis Pharma AG, the Switzerland-based pharmaceutical corporation that holds the patent for Nilotinib.
- First Sub-Licence Agreements: The recent sub-licence agreements with Indian companies Eugia, Hetero, and Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, along with the Indonesian firm BrightGene, mark the first such agreements for a cancer treatment drug by the MPP.
Benefits
- Generic Versions of Nilotinib: The licensed manufacturers can produce generic versions of Nilotinib.
- Manufacturing: The selected manufacturers have the rights to manufacture generic Nilotinib in India and seven middle-income countries.
- Supply in 44 Territories: The non-exclusive licence agreement allows for the supply of generic Nilotinib in 44 territories covered by the agreement, subject to local regulatory authorisation.
- Affordable Treatment Option: Charles Gore, the executive director of the MPP, states that the production of generic Nilotinib will provide an affordable treatment option for people diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukaemia in the covered countries.
- Increasing Access to Cancer Medication: The MPP’s initiative aims to improve access to essential cancer medications by reducing costs and increasing availability.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Private: PRET Initiative
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s Rising Burden of Diabetes: Urgent Actions Needed
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Diabetes
Mains level: Rising burden of NCDs in India

Central Idea: A recent study by ICMR has raised concerns about the emerging crisis of diabetes in India and the urgent need for effective strategies to tackle this escalating issue.
What is Diabetes? |
||
| Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes | |
| Prevalence | Generally diagnosed in children and young adults | Usually diagnosed in adults, but can occur at any age |
| Autoimmune | Autoimmune condition, immune system attacks pancreas | Not autoimmune, insulin resistance or impaired insulin production |
| Insulin Dependence | Requires insulin injections or insulin pump | May be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medication, or insulin |
| Onset | Sudden onset | Gradual onset |
| Causes | Genetic predisposition and environmental factors | Genetic and lifestyle factors, including obesity |
| Body Weight | Often normal or underweight | Often overweight or obese |
| Insulin Production | Little to no insulin production | Insulin resistance or inadequate insulin production |
| Treatment | Insulin therapy, blood sugar monitoring | Lifestyle changes, oral medication, insulin therapy if needed |
| Complications | Higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis | Higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and other complications |
| Lifestyle Factors | Cannot be prevented or reversed | Can be prevented or managed through lifestyle changes |
| Prevention | No known prevention strategies | Focus on healthy lifestyle, weight management |
Burden of Diabetes in India
- The results of the largest long-term study on metabolic factors in the Indian subcontinent, known as the ICMR-InDiab study, were recently published in The Lancet.
- This study, conducted between 2008 and 2020, aimed to estimate India’s burden of chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
Key Findings
The study revealed alarming statistics regarding diabetes in India:
- Approximately 11% of the population has diabetes.
- Another 15.3% of the population is in the pre-diabetic stage.
- This translates to an estimated 101.3 million diabetics and 136 million individuals in the pre-diabetic stage.
- Urban areas have a higher prevalence (16.4%) compared to rural areas (8.9%).
These numbers underscore the need for immediate attention to prevent the further rise of diabetes and manage its complications effectively.
Reasons for India’s Rising Burden
India’s escalating burden of diabetes can be attributed to several factors:
- Genetic Predisposition: Indians have a higher genetic susceptibility to diabetes.
- Changing Lifestyles: Urbanization, sedentary habits, and unhealthy dietary patterns contribute to increased obesity and diabetes risk.
- Obesity Epidemic: Rising obesity rates in India are a major risk factor for diabetes.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Limited access to healthcare, lack of awareness, and resource constraints hinder diabetes management.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Diabetes is no longer limited to urban areas, as rural regions also experience a growing prevalence.
- Delayed Diagnosis and Treatment: Late diagnosis and treatment initiation impede effective disease management.
Addressing India’s Rising Burden of Diabetes
To combat this crisis, key interventions include:
- Prevention and Health Promotion: Encouraging healthy lifestyles and stress reduction.
- Early Detection and Diagnosis: Promoting awareness and implementing screening programs.
- Access to Quality Healthcare: Improving healthcare infrastructure and ensuring equitable access.
- Education and Awareness: Public health campaigns to raise awareness and encourage lifestyle modifications.
- Policy Interventions: Implementing policies for healthy environments and regulating unhealthy products.
Conclusion
- India is facing a significant health crisis with the rising burden of diabetes.
- It is imperative to prioritize diabetes prevention and management to ensure a healthier future for the nation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The story behind the Ban on 14 FDC Drugs
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fixed dose combination (FDC) Drug
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea: Exploring the recent ban on 14 fixed dose combination drugs in India and its rationale.
What are FDC Drugs?
- Definition: FDC drugs are combinations of active ingredients in a fixed ratio, commonly used in a single pill or syrup.
- Benefits offered: FDCs can reduce pill burden, improve adherence to therapy, and lower costs.
- Risks associated: Certain combinations can be pharmacologically incompatible, have abuse potential, and contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Issue of Irrational FDCs
- Licensed FDCs: FDCs introduced for the first time require prior approval, while many older FDCs were licensed without proper scrutiny.
- Lack of safety: Lack of evidence on safety and efficacy led to the categorization of many licensed FDCs as irrational.
- Legal challenges: A ban on 344 FDCs in 2016 was stayed by the Delhi High Court, prompting further review and subsequent ban on 329 FDCs in 2018.
Government Action and Expert Review
- Referral to Drugs Technical Advisory Board: The Supreme Court entrusted the review of FDC drugs to the government’s expert body.
- Ban on 14 Pre-1988 FDCs: An expert committee recommended banning certain FDCs licensed before 1988.
- Balancing Prior Approvals and Inquiry: The Supreme Court excluded 15 FDCs licensed prior to 1988 from the ban but allowed for an inquiry.
Implications of the Ban
- Impact on Drug Availability: The ban affects approximately 40-50 brands used for cough, fever, pain, and common infections.
- Support from Pediatricians: Many pediatricians welcome the ban, citing harmful combinations in FDC drugs.
- Call for Additional Scrutiny: Calls to consider banning Nimesulide for single-dose use due to liver risks.
Cautions Regarding Cough Syrups
- Conflicting Effects of Ingredients: Experts highlight how ingredients in cough syrups may work against each other, reducing their efficacy.
- Limited Evidence on Cough Syrups: Weak evidence suggests cough syrups may not significantly reduce cough duration.
- Caution for Cough Suppressants: Prescription-only use is advised, particularly for individuals with underlying lung conditions.
Socioeconomic impact of the Ban
- Economic Savings and Improved Quality of Life: The ban may lead to cost savings and enhanced well-being for individuals.
- Importance of Safe Drinking Water: Access to clean drinking water is crucial for public health and overall quality of life.
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making: Ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical treatments through research and evaluation.
- Addressing Emerging Health Challenges: Continuous monitoring and research are necessary to tackle evolving health risks.
- Optimizing Healthcare Practices: Ongoing efforts to improve healthcare systems and practices for better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
- The recent ban on 14 fixed dose combination (FDC) drugs in India highlights the government’s commitment to ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in the Pandemic Treaty
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AMR, Pandemic Treaty
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Pandemic Treaty: The latest version of the draft Pandemic Instrument, also known as the “pandemic treaty,” was shared with Member States at the World Health Assembly.
- Removal of AMR Mentions: It became apparent that all mentions of addressing antimicrobial resistance in the Pandemic Instrument were at risk of removal.
What is AMR?
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the development of resistance in microorganisms to drugs that were once effective against them.
- Microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites, can become “immune” to medications used to kill or control them.
- Misuse or overuse of antibiotics can contribute to the development of AMR.
About the Pandemic Treaty
- Initiation of Work: Work on the Pandemic Instrument began in December 2021.
- Objective: The instrument aims to protect nations and communities from future pandemic emergencies under the WHO’s Constitution.
Importance of Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
- Calls for Inclusion: Civil society and experts, including the Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance, have emphasized the inclusion of AMR in the Pandemic Instrument.
- Not Limited to Viruses: Not all pandemics in the past or future are caused by viruses, with bacterial pandemics like plague and cholera being devastating examples.
- Impact of Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections cause one in eight deaths globally and contribute to the rise of drug-resistant infections.
Need for Comprehensive Pandemic Preparedness
- Wider Range of Threats: Planning and developing effective tools to respond to a broader range of pandemic threats, beyond viruses, is crucial.
- Secondary Bacterial Infections: Even in viral pandemics like COVID-19, secondary bacterial infections become a serious issue, requiring effective antibiotics.
Concerns over Potential Removal of AMR Measures
- Risk to Future Pandemics: The removal of AMR measures from the Pandemic Instrument could hinder efforts to protect people from future pandemics.
- At-Risk Measures: Measures at risk of removal include better access to safe water, infection prevention and control, integrated surveillance, and antimicrobial stewardship.
Strengthening the Pandemic Instrument to Address AMR
- Inclusion of AMR Measures: Measures to address AMR can be easily incorporated into the Pandemic Instrument.
- Recommendations for Inclusion: Recommendations include addressing bacterial pathogens, tracking viral and bacterial threats, and harmonizing AMR stewardship rules.
Efforts to Highlight AMR in the Pandemic Instrument
- Involvement of Specialized Organizations: Civil society and research organizations participated in the WHO’s Intergovernmental Negotiating Body, providing analysis on AMR in the draft.
- Publication of Special Edition: Leading academic researchers and experts published a special edition outlining the importance of addressing AMR in the Pandemic Instrument.
Current State and Next Steps
- Concerns over Removal: Insertions related to AMR are at risk of removal after closed-door negotiations by Member States.
- Importance of the Pandemic Instrument: The instrument is vital for mitigating AMR and safeguarding antimicrobials for treating secondary infections in pandemics.
- Global Political Action: Collaboration and collective efforts are needed to address AMR and support the conservation and equitable distribution of safe and effective antimicrobials.
Safeguarding Antimicrobials for Future Pandemic Response
- Undermining Goals: Missing the opportunity to address AMR in the Pandemic Instrument undermines its broader goals of protecting nations and communities.
- Core Role of Antimicrobials: Antimicrobials are essential resources for responding to pandemics and must be protected.
- Call for Strengthened Measures: Member States should strengthen measures to safeguard antimicrobials and support actions for conserving their effectiveness within the instrument.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
WHO’s advisory on Non-Sugar Sweeteners
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Non-Sugar Sweeteners
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea: The World Health Organization (WHO) issued new guidelines advising against the use of non-sugar sweeteners (NSS) as a healthy alternative to sugar.
What are Non-Sugar Sweeteners?
- NSS are low or no-calorie alternatives to sugar, including aspartame, saccharin, stevia, and others.
- They are marketed for weight loss and controlling blood glucose in individuals with diabetes.
WHO’s Finding
- The WHO analyzed 283 studies on NSS intake in adults and children.
- Higher intake of NSS was associated with a 76% increase in obesity risk and a 0.14 kg/m2 increase in BMI.
- No evidence of long-term benefits on reducing body fat was found, and long-term use of NSS may increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, chronic kidney disease, and cancer.
- WHO suggests that NSS should not be used for weight control or reducing the risk of diet-related non-communicable diseases.
Concerns and Recommendations
- India has a high obesity rate and a significant number of people with pre-diabetes.
- Lifestyle-related Type 2 diabetes is increasing among young individuals.
- WHO recommends focusing on a balanced diet and minimally processed, unsweetened foods and beverages.
What lies ahead?
- WHO’s conditional guideline requires further discussions among policymakers before adoption as national policy.
- Efforts should be made to educate youngsters about taste preferences and healthy eating habits.
- Doctors can now provide more confident guidance to patients regarding NSS consumption.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Private: 75/25 Initiative
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India nears milestone with first indigenous Dengue Vaccine
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dengue
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea: Serum Institute of India and Panacea Biotec have applied to the ICMR’s call for Expression of Interest for collaborative Phase-III clinical trials for an indigenous dengue vaccine.
What is Dengue?
| Details | |
| Transmission | Primarily transmitted through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes |
| Virus and Serotypes | Dengue virus belonging to the Flaviviridae family
Four distinct serotypes: DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4 |
| Symptoms | High fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, rash, pain behind the eyes, mild bleeding |
| Severe Dengue | Progression to severe dengue can cause plasma leakage, bleeding, organ impairment |
| Geographic Distribution | Endemic in more than 100 countries, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions |
| Incidence and Global Impact | 100-400 million dengue infections occur annually globally, affecting healthcare systems and economies |
| Vector and Breeding Sites | Aedes aegypti mosquito breeds in stagnant water containers found near human dwellings |
| Treatment | No specific antiviral treatment available; supportive care, rest, fluid intake, symptom management |
| Prevention and Control | Reduce mosquito breeding sites, proper water storage, cleaning of water containers, use of insecticides |
Dengue Virus Disease and Global Impact
- Dengue virus disease causes significant morbidity and mortality worldwide, with 2 to 2.5 lakh (200,000 to 250,000) cases reported annually in India.
- The global incidence of dengue has increased dramatically, with over half of the world’s population at risk.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified dengue as one of the top ten global health threats in 2019.
- Currently, there is no specific treatment for dengue, highlighting the urgent need for effective vaccines.
Desirable Characteristics of a Dengue Vaccine
The ICMR highlights the desirable characteristics of a dengue vaccine, including a-
- Favorable safety profile
- Protection against all four serotypes of dengue
- Reduced risk of severe disease and death
- Induction of a sustained immune response and
- Effectiveness regardless of previous sero-status and age
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s G20 Presidency: Strengthening Global Health Governance for Safer and Equitable World
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Universal Health Coverage, challenges and India's G20 presidency
Central Idea
- India’s G20 presidency is gaining momentum, with a focus on harnessing shared responsibilities and collaborative governance to enhance global safety from pandemics. It seeks to bridge the gap between the Global North and Global South, recognizing the inclusive memberships of G20 and other plurilateral arrangements that span the global community.
Importance of Health as a global public good
- Interconnectedness: In today’s interconnected world, diseases can quickly spread across borders, transcending geographical boundaries. The health of individuals and communities in one part of the world can have direct implications for others. Therefore, addressing health issues becomes a shared responsibility for all nations.
- Impact on Global Stability: Health crises, such as pandemics, can have severe social, economic, and political consequences. They can disrupt economies, strain healthcare systems, and cause social unrest. By ensuring health as a global public good, we contribute to global stability, sustainable development, and peaceful coexistence.
- Humanitarian Imperative: Health is a fundamental human right. Everyone deserves access to quality healthcare and the opportunity to lead a healthy life. Treating health as a global public good ensures equitable access to healthcare services, regardless of an individual’s nationality or socioeconomic status.
- Economic Productivity: Healthy populations are essential for economic productivity and growth. By investing in health as a global public good, we can create conditions for individuals to thrive, contribute to their communities, and participate actively in economic activities.
- Prevention and Preparedness: Addressing health as a global public good requires proactive measures to prevent and prepare for health emergencies. By investing in disease surveillance, research, and robust healthcare systems globally, we can better detect and respond to outbreaks, mitigating their impact and saving lives.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Recognizing health as a global public good encourages collaboration among nations. By sharing knowledge, best practices, and resources, countries can collectively work towards improving public health outcomes, fostering innovation, and finding solutions to complex health challenges.
- Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: Health is intricately linked to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including good health and well-being (SDG 3), poverty eradication (SDG 1), and gender equality (SDG 5). Treating health as a global public good support the achievement of these interconnected goals, leading to a more equitable and sustainable world.
India’s response to Covid-19: Whole-of-society and whole-of-government approach
- Early Measures and Nationwide Lockdown: India implemented one of the world’s largest and strictest nationwide lockdowns in March 2020 to contain the spread of the virus. This decision aimed to break the chain of transmission and provide time to strengthen healthcare infrastructure.
- Testing and Surveillance: India significantly ramped up its testing capacity, expanding the network of testing laboratories across the country. The government implemented various testing strategies, including rapid antigen tests and RT-PCR tests, to detect and track Covid-19 cases.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: To bolster healthcare infrastructure, the government initiated several measures such as establishing dedicated Covid-19 hospitals, increasing the number of ICU beds, ventilators, and oxygen supply, and mobilizing healthcare professionals to regions facing surges in cases.
- Vaccine Development and Rollout: India played a crucial role in vaccine development, with its indigenous vaccine candidates receiving regulatory approval. The country launched an ambitious vaccination drive, prioritizing healthcare workers, frontline workers, and vulnerable populations. India also contributed to global vaccine supply through the export of vaccines under the Vaccine Maitri initiative.
- Economic Relief Measures: Recognizing the socioeconomic impact of the pandemic, the government introduced economic relief measures, including financial assistance, direct benefit transfers, and welfare schemes to support vulnerable sections of society affected by lockdowns and job losses.
- Collaborations and International Aid: India engaged in international collaborations, sharing its experiences and expertise, and cooperating with other countries in areas such as research, drug repurposing, and knowledge exchange. The country also received international assistance in the form of medical supplies and equipment.
- Focus on Healthcare Infrastructure and Research: The government emphasized strengthening healthcare infrastructure, investing in research and development, and promoting indigenous manufacturing of medical equipment and supplies. Efforts were made to enhance testing capacity, develop innovative solutions, and support research on therapies and diagnostics.
- Communication and Awareness: The government and health authorities prioritized public communication and awareness campaigns to disseminate accurate information, promote preventive measures, and combat misinformation related to the virus.
What is Universal Health Coverage (UHC) by 2030?
- UHC 2030 is a global movement and partnership that aims to accelerate progress towards achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC) by the year 2030.
- UHC 2030 is a collaborative initiative led by multiple stakeholders, including governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector, with the goal of ensuring that all individuals and communities have access to essential healthcare services without suffering financial hardship.
- UHC 2030 builds upon the commitment made by United Nations member states in 2015 through the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Challenges in achieving UHC by 2030?
- Financing: Adequate and sustainable financing is crucial for UHC. Many countries struggle with limited healthcare budgets, inefficient resource allocation, and inadequate public financing. Mobilizing sufficient funds to cover the costs of expanding healthcare services and ensuring financial protection for all individuals can be a significant challenge.
- Health Workforce: The availability, distribution, and quality of healthcare professionals pose challenges to UHC. Many countries face shortages of skilled healthcare workers, particularly in rural and remote areas. Strengthening the health workforce, ensuring equitable distribution, and improving their training and retention are critical for delivering quality healthcare services.
- Health Infrastructure: Insufficient and inadequate healthcare infrastructure, including facilities, equipment, and technologies, can hinder the achievement of UHC. Many regions, especially in low-income countries, lack the necessary healthcare infrastructure to provide essential services to all populations. Investments in infrastructure development and strengthening are required to expand access and ensure quality care.
- Inequities and Vulnerable Populations: UHC aims to address health inequities and reach vulnerable and marginalized populations. However, socioeconomic disparities, gender inequalities, and discrimination can hinder equitable access to healthcare services. Special attention is needed to address these inequities and ensure that UHC benefits all individuals, irrespective of their social or economic status.
- Health Information Systems: Establishing robust health information systems is essential for effective UHC implementation. However, many countries face challenges in data collection, management, and utilization. Strengthening health information systems, including electronic health records and data analytics, is crucial for monitoring progress, making informed decisions, and improving service delivery.
- Political Will and Governance: UHC requires strong political commitment and effective governance. Political will at the national level is necessary to prioritize UHC, allocate resources, and implement necessary policy reforms. Ensuring transparency, accountability, and efficient governance mechanisms are crucial to prevent corruption, ensure equitable service delivery, and maintain public trust.
- Changing Disease Patterns: The evolving burden of diseases, including the rise of non-communicable diseases, poses challenges to UHC. Chronic conditions require long-term management and specialized care, placing additional strain on healthcare systems. Adapting healthcare delivery models and integrating prevention and control strategies for these diseases are essential components of UHC.
- Global Health Security: Public health emergencies and global health security threats, as witnessed during the Covid-19 pandemic, can disrupt healthcare systems and hinder progress towards UHC. Strengthening health emergency preparedness and response capacities is vital to mitigate the impact of outbreaks and ensure continuity of healthcare services.
How India’s G20 presidency: Significant role in achieving UHC by 2030
- Knowledge Sharing and Best Practices: As the G20 president, India can facilitate the sharing of knowledge and best practices among member countries. This includes sharing successful UHC models, innovative healthcare delivery approaches, and strategies to overcome challenges. By promoting knowledge exchange, countries can learn from each other’s experiences and accelerate progress towards UHC.
- Advocacy for UHC: India can use its platform as G20 president to advocate for UHC as a global priority. Through diplomatic channels and international forums, India can emphasize the importance of UHC in achieving sustainable development and equitable healthcare access. This advocacy can encourage other G20 member countries to prioritize UHC and align their policies and actions accordingly.
- Collaboration with Global Health Organizations: India’s G20 presidency can facilitate collaboration with global health organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), World Bank, and other relevant entities. By working closely with these organizations, India can contribute to the development and implementation of strategies and initiatives that support UHC, including capacity building, technical assistance, and funding mechanisms.
- Promoting Innovative Financing Mechanisms: India can explore and promote innovative financing mechanisms for UHC. This includes advocating for increased public investment in healthcare, exploring public-private partnerships, and encouraging the development of social health insurance schemes. By identifying and sharing successful financing models, India can provide valuable insights to other G20 countries on sustainable funding for UHC.
- Strengthening Primary Healthcare Systems: India’s G20 presidency can focus on strengthening primary healthcare systems, which are integral to UHC. This involves enhancing access to quality primary healthcare services, addressing health workforce shortages, improving infrastructure, and promoting preventive and promotive healthcare measures. Sharing India’s experiences and initiatives in primary healthcare can inspire other countries to invest in this essential aspect of UHC.
- Leveraging Digital Health Technologies: India has made significant strides in adopting digital health technologies, and its G20 presidency can highlight the potential of these technologies in advancing UHC. By sharing digital health success stories and facilitating collaborations in areas such as telemedicine, health information systems, and mobile health applications, India can accelerate the adoption of digital solutions for healthcare access and delivery.
- South-South Cooperation: India’s G20 presidency can promote South-South cooperation and collaboration among G20 member countries and other nations from the Global South. By fostering partnerships, sharing experiences, and supporting capacity-building efforts, India can facilitate collective progress towards UHC in regions that face similar challenges.
Conclusion
- India’s G20 presidency aims to leverage collaborative governance and shared responsibilities to create a safer world from pandemics. India’s engagement with Japan’s G7 presidency and the focus on resilient, equitable, and sustainable UHC and global health architecture development further demonstrate shared responsibilities and the commitment to addressing public health emergencies. Through collective efforts, we can heal our planet, foster harmony within our global family, and offer hope for a better future.
Also Read:
| Digital healthcare Services |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Govt. program for Non-Communicable Diseases renamed
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)
Mains level: Govt policies and actions against NCDs

Central Idea: The article discusses the decision by the Indian Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to rename and expand its program for the control and prevention of non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
What are Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)?
- NCDs are also known as chronic diseases, which are not caused by infectious agents and are not transmissible from person to person.
- NCDs are long-lasting and progress slowly, typically taking years to manifest symptoms.
- Examples of NCDs include cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes.
- These diseases are often caused by modifiable risk factors such as unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, tobacco and alcohol use, and environmental factors.
- NCDs are a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, accounting for around 70% of all deaths globally.
Why in news?
- The addition of many new diseases and health initiatives have prompted the Indian government to expand and rename its NCD program.
Renaming of the NCD Program and Portal
- The Ministry has renamed the NPCDCS as the “National Programme for Prevention & Control of Non-Communicable Diseases [NP-NCD].”
- The application or software named Comprehensive Primary Healthcare Non-Communicable Disease (CPHC NCD IT) will now be renamed “National NCD Portal.”
- The Ministry communicated this decision to the States on May 3, 2023, through a one-page letter and asked them to adhere to the changes.
Implementation and future action
- The NPCDCS is implemented under the National Health Mission across India.
- The letter addressed to Principal Secretaries and Health Secretaries of all States and Union Territories advised the government to use the new names for the scheme and portal in all their future references and correspondences with the Indian government.
- Under NPCDCS, 677 NCD district-level clinics, 187 District Cardiac Care Units, 266 District Day Care Centres and 5,392 NCD Community Health Centre-level clinics have been set up.
Burden of NCDs in India
- The study ‘India: Health of the Nation’s States – The India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative in 2017’ by the ICMR estimated that the proportion of deaths due to NCDs in India has increased from 37.9% in 1990 to 61.8% in 2016.
- The four major NCDs are:
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs)
- Cancers
- Chronic respiratory diseases (CRDs) and
- Diabetes
- The study shared four behavioural risk factors – unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, and the use of tobacco and alcohol.
Solutions to mitigate NCD burden
- Promote healthy lifestyle: Encourage people to adopt healthy lifestyle habits such as regular physical activity, balanced and nutritious diet, avoiding tobacco and alcohol, and getting enough sleep.
- Increase awareness and education: Increase awareness among the public about the risk factors of NCDs and educate them about ways to prevent these diseases.
- Improve healthcare infrastructure: Increase access to healthcare facilities, especially in rural and remote areas, to ensure early detection, treatment, and management of NCDs.
- Implement policies and regulations: Implement policies and regulations that promote healthy living, such as increasing taxes on tobacco and alcohol products, and regulating the marketing of unhealthy food products.
- Foster public-private partnerships: Foster partnerships between the government, private sector, and civil society organizations to work collaboratively towards preventing and managing NCDs.
- Increase research and innovation: Increase research and innovation in the prevention, early detection, and treatment of NCDs to develop new and effective interventions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s One Health Approach to Tackle Future Pandemics
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Health Security Index, PM ABHIM and related schemes and facts
Mains level: India's One health approach
Central Idea
- The Covid-19 pandemic exposed weaknesses in the world’s health systems, including countries ranked high in the Global Health Security Index. It has also provided an opportunity to build stronger health systems to prevent and respond to future pandemics. India’s One Health approach aims to address the health of people, animals, and ecosystems together in order to prevent, prepare, and respond to pandemics.
What is PM Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM ABHIM)?
- PM ABHIM is being rolled out as India’s largest scheme to scale up health infrastructure.
- It is aimed at ensuring a robust public health infrastructure in both urban and rural areas, capable of responding to public health emergencies or disease outbreaks.
- Key features:
- Health and Wellness Centres: In a bid to increase accessibility it will provide support to 17,788 rural HWC in 10 ‘high focus’ states and establish 11,024 urban HWC across the country.
- Exclusive Critical Care Hospital Blocks: It will ensure access to critical care services in all districts of the country with over five lakh population through ‘Exclusive Critical Care Hospital Blocks’.
- Integrated public health labs: It will also be set up in all districts, giving people access to “a full range of diagnostic services” through a network of laboratories across the country.
- Disease surveillance system: The mission also aims to establish an IT-enabled disease surveillance system through a network of surveillance laboratories at block, district, regional and national levels.
- Integrated Health Information Portal: All the public health labs will be connected through this Portal, which will be expanded to all states and UTs, the PMO said.
Facts for prelims
What is Global Health Security Index?
|
What is mean by One health?
- One Health is an interdisciplinary approach that recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
- It emphasizes the need for collaboration between various sectors, including public health, veterinary medicine, environmental science, and others, to achieve optimal health outcomes for all.
key components of India’s One Health approach
- Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM): The flagship program launched in October 2021 aims to prevent, prepare, and respond to pandemics. It seeks to fill the gaps in health systems at the national and state levels.
- National Institute for One Health: The foundation for the institute was laid recently in Nagpur. It will identify hotspots for endemic and emerging zoonotic diseases to contain their spread early on.
- Creation of a network of institutions for genomic surveillance: During the COVID-19 pandemic, India created a formidable network of institutions that can identify new pathogens. This can now be complemented with wider testing of wastewater and samples from incoming ships and aircraft.
- Coordination between ministries: Several ministries, including health, animal husbandry, forests, and biotechnology, have been brought under the Principal Scientific Advisor to address overlapping mandates and improve coordination.
- Expansion of research laboratories: India is expanding its network of research laboratories, which primarily focused on influenza, to cover all respiratory viruses of unknown origin.
- Partnerships between research bodies and manufacturers: Indian manufacturers produced vaccines, test kits, therapeutics, masks and other items at very competitive prices, both for India and other countries. The partnerships between research bodies and manufacturers will need to be sustained and enhanced to make India a global hub in the biopharma sector.
- Clinical trial network: The clinical trial network set up under the National Biopharma Mission is a positive step toward improving access to affordable new vaccines and drugs in India and around the world.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Mission: The mission can facilitate the bringing of private hospitals and clinics under a common platform and placing data in the public domain to augment surveillance in vulnerable areas.
- Municipal corporations mandated to provide early alerts: Municipal corporations have been mandated to identify the most vulnerable areas and provide early alerts. For this to be successful, strong partnerships with communities, dairy cooperatives, and the poultry industry will be needed to identify new infections.
What are the potential advantages of the One Health approach?
- Holistic approach: The One Health approach looks at the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. By taking a holistic approach, it enables a better understanding of the complex interconnections between human, animal, and environmental health, and can lead to more effective interventions and solutions
- Early disease detection: The One Health approach emphasizes the importance of early disease detection in animals, which can serve as an early warning system for potential human outbreaks. This approach can help prevent the spread of diseases and reduce the risk of pandemics.
- Better disease surveillance: The One Health approach facilitates better disease surveillance by enabling the sharing of information and resources between different sectors, including human health, animal health, and environmental health.
- More effective responses: The One Health approach can lead to more effective responses to outbreaks by facilitating collaboration between different sectors and stakeholders, and ensuring a coordinated response.
- Improved animal health: The One Health approach recognizes the importance of animal health and welfare, and can lead to improved animal health through better disease control and prevention measures.
- Better environmental management: The One Health approach also recognizes the importance of environmental management and conservation, and can lead to more sustainable environmental practices that benefit both human and animal health.
Conclusion
- India’s One Health approach is a positive step towards addressing the health of people, animals, and ecosystems together. The country’s efforts to tackle future pandemics are commendable, and the success of these efforts will be critical. The rise of new pathogens, zoonotic diseases, and antibiotic resistance highlights the need for a comprehensive approach to prevent future pandemics. India’s efforts to build stronger health systems, prevent pandemics, and respond to outbreaks will help protect its citizens and set an example for the world.
Mains Question
Q. What do you understand by mean One Health? Discuss the advantages of One health approach the efforts of India in this direction.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Latest National Health Account figures on India’s Healthcare Sector
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Health Account (NHA) estimates
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central idea: The National Health Account Estimates 2019-20 report shows an increase in government spending and a decline in out-of-pocket expenditure on healthcare.
About National Health Account (NHA) estimates
- The NHA estimates for India 2019-20 is the seventh consecutive report prepared by the National Health Systems Resource Centre (NHSRC).
- NHSRC was designated as National Health Accounts Technical Secretariat (NHATS) in 2014 by the Union Health Ministry.
- The NHA estimates use an accounting framework based on the internationally accepted standard of System of Health Accounts, 2011 developed by the WHO.
- India now has a continuous series of NHA estimates from 2013-14 to 2019-20, making the estimates comparable internationally.
- The estimates enable policymakers to monitor progress in different health financing indicators of the country.
Key highlights
Description |
|
| Government spending as % of GDP |
|
| Declining out-of-pocket expenditure |
|
| Government spending on primary healthcare |
|
| Increase in social security expenditure |
|
| Increase in spending on insurance |
|
| Health spending by states |
|
Key issues
- Marginal increase: Activists are concerned about the marginal increase in government spending.
- Global laggard: This increase in government health expenditure as a percentage of GDP also takes into account capital spending, which puts India in 164th place out of 184 countries in terms of government health spending.
- No proportional increase: Total spending on health as a proportion of GDP has been going down, from 3.9% in 2015 to 3.3% in 2020, indicating a decline in consumption of healthcare services.
Conclusion
- Overall, the report shows that government spending on healthcare has been increasing, while out-of-pocket expenditure has been declining.
- There is a need to invest in public health and insurance and increase the contribution of states towards healthcare.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Cabinet approves the Policy for the Medical Devices Sector
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: National Medical Devices Policy, 2023

Central idea: The Union Cabinet, chaired by Hon’ble Prime Minister, approved the National Medical Devices Policy, 2023.
National Medical Devices Policy, 2023
- The Policy, 2023 aims to facilitate an orderly growth of the medical device sector to meet the public health objectives of access, affordability, quality, and innovation.
- The policy lays down a roadmap for accelerated growth of the medical devices sector to achieve various missions.
Objectives
- The policy aims to make the industry competitive, self-reliant, resilient, and innovative.
- It focuses on meeting the healthcare needs of not only India but also the world.
- It aims to accelerate the growth of the medical devices sector.
- It takes a patient-centric approach to meet the evolving healthcare needs of patients.
- It provides support and directions to the medical devices industry to achieve these goals.
Strategies to Promote Medical Device Sector
The medical devices sector will be facilitated and guided through a set of strategies that cover six broad areas of policy interventions:
Key measures and actions |
|
| 1. Regulatory Streamlining | Enhance ease of doing research and business, balance patient safety with product innovation, create a Single Window Clearance System for licensing of medical devices, enhance the role of Indian Standards like BIS, and design a coherent pricing regulation. |
| 2. Enabling Infrastructure | Establish and strengthen large medical device parks and clusters equipped with world-class common infrastructure facilities in proximity to economic zones with requisite logistics connectivity. |
| 3. Facilitating R&D and Innovation | Promote research and development in India, establish centres of excellence in academic and research institutions, innovation hubs, and support for startups. |
| 4. Attracting Investments in the Sector | Encourage private investments, funding from venture capitalists, and public-private partnerships, in addition to existing schemes and interventions like Make in India, Ayushman Bharat program, Heal-in-India, and Start-up mission. |
| 5. Human Resources Development | Ensure a steady supply of skilled workforce across the value chain by leveraging available resources in the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, supporting dedicated multidisciplinary courses for medical devices in existing institutions, and developing partnerships with foreign academic/industry organizations to develop medical technologies. |
| 6. Brand Positioning and Awareness Creation | Create a dedicated Export Promotion Council for the sector under the Department, initiate studies and projects for learning from best global practices of manufacturing and skilling system, promote more forums to bring together various stakeholders for sharing knowledge, and build strong networks across the sector. |
Medical devices sector in India: A quick recap
- The medical devices sector in India is an essential and integral part of the Indian healthcare sector.
- The sector has contributed significantly to the domestic and global battle against the COVID-19 pandemic through the large-scale production of medical devices & diagnostic kits.
Growth potential in India
- The market size of the medical devices sector in India is estimated to be $11 billion (approximately, ₹ 90,000 Cr) in 2020, and its share in the global medical device market is estimated to be 1.5%.
- The Indian medical devices sector has enormous potential to become self-reliant and contribute towards the goal of universal health care.
Current initiatives in this sector
- The Government of India has initiated the implementation of the PLI Scheme for medical devices.
- It supports for setting up of four Medical devices Parks in the States of Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Preparedness and Resilience for Emerging Threats (PRET) Initiative
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PRET Initiaitve
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea: The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a PRET initiative to be better prepared for future outbreaks of a similar scale and devastation as the COVID-19 pandemic.
What is PRET Initiative?
- The Preparedness and Resilience for Emerging Threats (PRET) initiative is launched by the WHO to prepare for future outbreaks of a similar scale and devastation as the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It is aimed at providing guidance on integrated planning for responding to any respiratory pathogen such as influenza or coronaviruses.
- The current focus of PRET is on respiratory viruses, but work is already underway to assess what should be the next group of pathogens to be mitigated under this initiative.
- It can serve to operationalize the objectives and provisions of the Pandemic Accord, which is currently being negotiated by WHO Member States.
Three-pronged approach of PRET
- The three-pronged approach includes-
- Updating preparedness plans
- Increasing connectivity among stakeholders in pandemic preparedness planning, and
- Dedicating sustained investments, financing, and monitoring of pandemic preparedness.
- The approach has a special focus on bridging the gaps highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic and ensuring community engagement and equity are at the centre of preparedness and response efforts.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Malaria soon to be a notifiable disease across India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Malaria
Mains level: Read the attached story

Malaria is all set to become a notifiable disease across India, which will require cases to be reported to government authorities by law.
About Malaria
| Description | |
| Definition | A potentially life-threatening disease caused by parasites that are transmitted through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes |
| Causes | Four species of plasmodium parasites, namely plasmodium vivax, plasmodium falciparum, plasmodium malariae, and plasmodium ovale |
| Spread | Bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes |
| Symptoms | Fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, fatigue, nausea, vomiting |
| Diagnosis | Blood test |
| Treatment | Antimalarial drugs |
| Prevention | Insecticide-treated bed nets, indoor residual spraying, wearing protective clothing, using mosquito repellent, avoiding mosquito bites |
| Vaccine | RTS,S/AS01 (Mosquirix) |
Why in news?
- The move is part of India’s vision to become malaria-free by 2027 and to eliminate the disease by 2030.
Menace of malaria in India
- In India, 80% of malaria cases occur among 20% of its population living in the 200 high-risk districts of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, West Bengal and the seven north-eastern states.
- With only fewer than half of those infected reaching a clinic or hospital, the cases and deaths are much higher than recorded.
What is Notifiable Disease?
- A notifiable disease is a disease that is required by law to be reported to government authorities.
- In India, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare maintains a list of notifiable diseases under the National Health Mission.
- This is done to track the spread of the disease and to take necessary measures to control and prevent its spread.
- Reporting notifiable diseases is important for public health surveillance and response to outbreaks.
Malaria as a Notifiable Disease
- Malaria is currently a notifiable disease in 33 states and Union Territories in India.
- Bihar, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and Meghalaya are in the process of putting malaria in the notifiable disease category.
Other measures to curb malaria
- Malaria Elimination Programme: The government has launched the National Framework for Malaria Elimination in India 2016-2030 to eliminate malaria from the country by 2030.
- Joint Action Plan: The Health Ministry has initiated a joint action plan with the Ministry of Tribal Affairs for malaria elimination in tribal areas. This plan aims to bring down malaria cases to zero in tribal areas, which are among the most vulnerable to the disease.
- HIP-Malaria Portal: The Ministry has ensured the availability of near-real-time data monitoring through an integrated health information platform and periodic regional review meetings to keep a check on malaria growth across India.
Vaccines developed so far
- The WHO has approved the rollout of two first-generation malaria vaccines, RTS,S and R21, in high-transmission African countries.
- Bharat Biotech, an Indian company, has been licensed to manufacture the RTS,S vaccine, with adjuvant provided by GSK.
- The R21 vaccine, developed by scientists at Oxford University, has shown promising results in phase 2 clinical studies and has been approved by regulatory authorities in Ghana and Nigeria.
- Scientists at the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) in New Delhi have developed and produced two experimental blood-stage malaria vaccines, with Phase I clinical trials completed for one of them.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s population to edge ahead of China’s by mid-2023: UN
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Freedom of speech and reasonable restrictions
Mains level: Global population trends

Central idea: India is set to overtake China as the world’s most populous country by mid-2023, according to data released by the United Nations.
State of World Population Report
- The report is an annual report published by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), which provides a global overview of population trends and issues.
- The report covers a wide range of topics related to the population, such as fertility, mortality, migration, family planning, and gender equality.
- It also includes analysis and recommendations for policymakers and governments to address population challenges and promote sustainable development.
- The report is widely regarded as a key reference for researchers, policymakers, and international organizations working on population and development issues.

Highlights of the 2023 report
Facts |
Data |
| World Population (2022) | 8 billion |
| Most populous regions | Eastern and Southeastern Asia, Central and Southern Asia |
| World Population Growth Rate (since 2020) | Less than 1% |
| Fertility Rate (replacement level) | 2.1 children per woman |
| Population aged 65 years or above (2050) | 16% |
| Persons aged 65 years and above (2050) | More than double that of 5-year-olds and same as 12-year-olds |
| Regions with fertility rate at or below 2.1 | 60% |
| Top countries accounting for global population increase by 2050 | DR Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Tanzania |
Population anxieties in India
| Facts | |
| India’s population | India is now the most populous country in the world, having overtaken China in population, with 1,428.6 million people. |
| Age distribution | 68% of India’s population belongs to the 15-64 years category, and 26% in the 10-24 years group, making India one of the youngest countries in the world. |
| Fertility rate | National Family Health 5 Survey (2019-21) found that India attained a Total Fertility Rate of 2.0 for the first time, less than the replacement level of 2.1, falling from 2.2 in NFHS 4 (2015-16). |
| Life expectancy | Life expectancy for men in India is 71 years, the same as the global life expectancy, while it is marginally lower for women at 74 years. |
| Population growth | India’s population growth rate has decreased from 2.3% in 1972 to less than 1% now. |
| Demographic dividend | With 68% of its population as youth, and working population, India could have one of the largest workforces in the world, giving it a global advantage. |
Way forward
The UNFPA report strongly recommended that governments introduce policies with gender equality and rights at their heart to address changing demographics. These recommendations include:
- Parental leave programs: Introducing parental leave programs that provide paid leave to both mothers and fathers after the birth or adoption of a child. This can help promote gender equality in the workplace and support families in raising children.
- Child tax credits: Providing tax credits or financial support to families with children to help them meet the costs of raising children. This can help address child poverty and support families in providing for their children’s basic needs.
- Policies to promote gender equality at workplace: Implementing policies and practices that promote gender equality in the workplace, such as equal pay for equal work, flexible work arrangements, and anti-discrimination policies.
- Universal access to sexual and reproductive health and rights: Ensuring that all people have access to comprehensive sexual and reproductive health services, including family planning, maternal health services, etc. This can help prevent unintended pregnancies, reduce maternal mortality, and promote the health and well-being of individuals and families.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Healthcare: Need For Compassionate Leadership
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Role of compassion in healthcare
Central Idea
- India’s rapid strides in health and healthcare with the help of a digital boom and the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, and the need for compassionate leadership to ensure respectful healthcare.
India’s healthcare sector
- India’s healthcare sector has shown improvement in multiple metrics due to the push for healthcare digitization, infrastructure, coverage, and other inputs.
- However, healthcare is not just about the treatment of diseases or the availability of infrastructure but also about the overall wellness of the person.
- Respectful healthcare that is available, affordable, accessible, and compassionate is a determinant of the quality of care.
Importance of Compassionate leadership
- Respectful and compassionate healthcare is essential: Healthcare is a perpetually evolving, stressful, and high-risk industry that puts a vast burden on healthcare providers. It is essential to navigate and manage the situation compassionately to deliver respectful care.
- Compassion is a beating heart if healthcare: Compassionate leadership is required to build this type of healthcare system, as it is the quiet, beating heart of the entire healthcare system.
Curriculum for compassionate healthcare
- Compassionate curriculum is very necessary: To integrate compassion into the healthcare system at every stage, it is necessary to build a curriculum and deliver it to those responsible for administering healthcare respectfully.
- Curriculum with Dalai Lama’s vision rolled out in Bihar: An eight-stage curriculum, developed by Emory University, that furthers the Dalai Lama’s vision of educating both heart and mind for the greater good of humanity is being rolled out in Bihar.
- Impact: To date, 1,200 healthcare providers across 20 districts have been impacted by the vital components of the cognitive-based compassion training, creating compassionate leaders at every level.
Institutionalizing compassionate healthcare
- Institutionalizing will bring in real change: While the curriculum is a quantum leap towards building compassionate leadership, institutionalizing it will bring in real change.
- Adopting at each level: Every academic institution and every department mandated with the responsibility to deliver health-related learning should develop and adopt compassion-based curricula.
- Building capacity: State and regional health institutions must also be built with the capacity to deliver compassionate leadership. Partnerships with established academia and development sector organizations can enable the organizing of master coaches and master facilitators, thereby creating public goods that can be delivered by all.
Strengthening internal systems
- Making compassion intrinsic to the ethos: All healthcare providers are expected to carry out a wide range of tasks within the system, which often leads to burnout and impacts patient experience adversely. It is vital to strengthen systems internally to make respect and compassion intrinsic to the ethos.
- Building a network: Building a network of compassionate practitioners in every state, district and block hospital is crucial to fan the winds of change by starting with self-compassion first and then moving to compassion for others.
- Valuing and measuring organizational culture: Valuing and measuring organizational culture is just as critical as patient outcomes. Developing sound metrics to measure culture and employee satisfaction, self-compassion, and compassion for the team assumes greater significance to building an institution whose foundation is compassion.
Conclusion
- Respectful healthcare is already mentioned in the National Health Mission (NHM) guidelines, and such guidelines need to be the warp and weft of every policy and every guideline developed by public health authorities to improve patient experience. Compassionate leadership can truly realize India’s historically known values of compassion and bring alive the words of Hippocrates, the father of medicine, “Wherever the art of medicine is loved, there is also a love of humanity”.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Sodium Intake Target: Challenge of Cardiovascular Disease and Hypertension
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Related facts
Mains level: Sodium Intake, and burden of Hypertension and cardio vascular diseases
Central Idea
- The WHO recently published the ‘Global Report on Sodium Intake Reduction’ which sheds light on the progress of its 194 member states towards reducing population sodium intake by 30% by 2025. Regrettably, progress has been lethargic, with only a few countries making considerable headway towards the objective. Consequently, there is a proposal to extend the deadline to 2030.
The target of reducing population sodium intake
- The target of reducing population sodium intake by 30% by 2025 was set by the World Health Organization (WHO) in its Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases in 2013.
- The plan aims to reduce premature deaths from non-communicable diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, by 25% by 2025, and to achieve a 30% reduction in the mean population intake of salt/sodium.
- The target of reducing population sodium intake is aimed at reducing the burden of hypertension, which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Why reducing sodium intake is essential for India?
- Reduced sodium intake and decreased blood pressure: There is a strong correlation between reduced sodium intake and decreased blood pressure, leading to a decrease in stroke and myocardial infarction incidence. Lowering sodium intake by 1 gram per day leads to a 5 mm Hg reduction in systolic blood pressure, as per a study in The BMJ.
- Cardiovascular disease: Elevated BP is a critical risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of mortality worldwide. It contributed to 54% of strokes and 47% of coronary heart diseases globally in 2001.
- Economic impact of cardiovascular disease on LMICs: Cardiovascular disease has a staggering economic impact on LMICs, estimated at $3.7 trillion between 2011 and 2025 due to premature mortality and disability. This represents 2% of the GDP of LMICs. The Indian economy alone faces losses surpassing $2 trillion between 2012 and 2030 due to cardiovascular disease, highlighting the need for effective interventions to mitigate the economic and health consequences of the disease in LMICs.
How cardiovascular disease and hypertension pose significant challenges in India?
- Cardiovascular diseases as primary cause of mortality and morbidity:
- As per data from the Registrar General of India, WHO, and the Global Burden of Disease Study, cardiovascular diseases have emerged as the primary cause of mortality and morbidity. Data from the Registrar General of India, WHO, and the Global Burden of Disease Study
- Age-adjusted cardiovascular disease mortality rate increased by 31% in the last 25 years
- Hypertension as leading risk factor for such diseases in India
- Prevalence of hypertension in India:
- More prevalent among men aged 15 and above compared to women
- More common in southern states, particularly Kerala, while Punjab and Uttarakhand in the north also report high incidence rates
- Pre-hypertensive population in India
- Defined by systolic blood pressure levels of 120-139 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure levels of 80-89 mmHg
- 5% of women and 49.2% of men at the national level
- Significant risks of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and premature mortality for Indians with BP readings between 130 and 139/80-89 mmHg
- Many Indians classified as pre-hypertensive are now included in the newly defined stage-I hypertension by the American guidelines.
- Circulatory system diseases: The 2020 Report on Medical Certification of the Cause of Death shows that circulatory system diseases account for 32.1% of all documented deaths, with hypertension being a major risk factor.
Global Efforts to Reduce Sodium Intake
- The WHO aims to reduce population sodium intake by 30% by 2025
- Only a few countries have made considerable progress towards the objective
- India’s score of 2 on the WHO sodium score signifies the need for more rigorous efforts to address the health concern
Government Initiatives
- Voluntary programmes: The Union government has initiated several voluntary programmes aimed at encouraging Indians to decrease their sodium consumption
- Eat Right India: The FSSAI has implemented the Eat Right India movement, which strives to transform the nation’s food system to ensure secure, healthy, and sustainable nutrition for all citizens
- Aaj Se Thoda Kam: FSSAI launched a social media campaign called Aaj Se Thoda Kam.
Urgent Need for a Comprehensive National Strategy
- Despite of awareness efforts, the average Indian’s sodium intake remains alarmingly high. Evidence shows an average daily consumption of approximately 11 grams.
- India needs a comprehensive national strategy to curb salt consumption
- Collaboration between State and Union governments is essential to combat hypertension, often caused by excessive sodium intake
Conclusion
- The excessive consumption of salt can lead to severe health consequences, and India has a pressing need to reduce its sodium intake. While the government has initiated several voluntary programs, these have fallen short of the goal. India needs a comprehensive national strategy, engaging consumers, industry, and the government, to curb salt consumption. Collaboration between State and Union governments is essential to combat hypertension, often caused by excessive sodium intake.
Mains Question
Q. Reducing population sodium intake is a critical step towards preventing and controlling non- cardiovascular diseases and hypertension. Comment.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Autism Spectrum Disorders: Prevalence in India and Way Ahead
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Autism
Mains level: Autism spectrum disorders, Prevalence in India and way ahead
Central Idea
- In India, the prevalence of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) is a widely debated issue due to a lack of systematic estimates. Most estimates have been derived from studies based on school children, revealing that over one crore Indians may be on the autism spectrum. However, there are notable cultural differences in diagnosing autism between countries, which highlights the need to assess the prevalence of autism spectrum disorders specifically in the Indian context.
What is Autism?
- Spectrum disorder: Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects communication, social interaction, and behaviour. It is called a spectrum disorder because the symptoms and severity can vary widely between individuals.
- Common symptoms: Some common symptoms of autism include difficulty with social interactions, such as maintaining eye contact or understanding nonverbal cues, delayed speech and language development, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities.
- Cause: Autism is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, but the exact cause is not yet fully understood.
- Cure: There is currently no cure for autism, but early interventions and therapies can help individuals with autism lead fulfilling and independent lives.
Prevalence of Autism in India
- Lack of systematic estimates: Autism is a global issue and affects individuals of all cultures, ethnicities, and socioeconomic backgrounds. However, there is a lack of systematic estimates of autism prevalence in India.
- Methos failed: Researchers have attempted to estimate prevalence through government hospitals, but this method failed due to the absence of central medical registries.
- Conservative estimates: As a result, prevalence was estimated through school-based assessments. According to conservative estimates, well over one crore Indians are on the autism spectrum. This highlights the need for further research and attention to address the prevalence of ASD in India.
- Cultural Differences and Diagnosis of Autism:
- Notable cultural differences exist in the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. In the US and UK, the majority of children with autism spectrum diagnosis are verbal, with average or higher IQ, and attending mainstream schools.
- However, in India, a significant majority of children with a clinical diagnosis of autism also have intellectual disability and limited verbal ability. This difference is driven by sociological factors, such as access to appropriate clinical expertise, provisions for inclusion in mainstream schools, and availability of medical insurance coverage.
Challenges in Assessing Autism
- Assessment tools: Assessment of autism spectrum disorder is primarily behavioral, and most widely used autism assessment tools are not available in Indian languages.
- Indigenous autism assessment tools challenges: There has been a rise in the development of indigenous autism assessment tools. Despite the development of these tools, it can be challenging to compare across different assessment measures.
Demand and Supply in India
- Shortage of mental health professionals: Most autism assessment tools need to be administered by specialist mental health professionals. However, there is a significant shortage of mental health professionals in India, with less than 10,000 psychiatrists, a majority of whom are concentrated in big cities.
- Delay is costly: Delay in interventions can be costly for neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism.
- Demand and supply gap need to be met: This gap between demand and supply cannot be met directly by specialists alone, and parallel efforts to widen the reach of diagnostic and intervention services through involving non-specialists is required. Emerging evidence suggests the feasibility of involving non-specialists in autism identification and intervention through digital technology and training programs.
Way ahead: Need for an All-India Program
- National program on autism: The need of the hour is to develop a national program on autism in India that links researchers, clinicians, service providers to the end-users in the autism community.
- Essential components: This program needs to have three essential components that are joined up: assessment, intervention, and awareness.
- Assessment: Research is needed to develop appropriate assessments and design efficient implementation pathways.
- Intervention: Clinical and support service workforce needs to be expanded by training non-specialists such that a stepped-care model can be rolled out effectively across the nation.
- Awareness: Large-scale initiatives need to be launched to build public awareness that can reduce the stigma associated with autism and related conditions.
Conclusion
- There are challenges in diagnosing and assessing autism in India which highlights the need for a comprehensive and coordinated effort to address them. By expanding the clinical and support service workforce, training non-specialists, and developing appropriate assessments and interventions, India can improve outcomes for those on the autism spectrum and reduce the stigma associated with the condition. This national program needs to be informed by consultation with different stakeholders, with a primary focus on end-users within the Indian autism community.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Duty exemption for drugs for Rare Diseases
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rare Diseases
Mains level: Not Much

Central idea: The Centre has exempted all drugs and food for special medical purposes, imported for personal use, for the treatment of rare diseases listed under the National Policy for Rare Diseases 2021 from basic customs duty.
What are Rare Diseases?
- Rare diseases are those medical conditions that affect a small percentage of the population.
- In India, a disease is considered rare if it affects less than 1 in 2,000 people.
- These diseases are often genetic and are chronic, degenerative, and life-threatening.
- There are over 7,000 known rare diseases, and it is estimated that about 70 million people in India are affected by them.
- Many of these diseases do not have a cure, and the treatment can be expensive and difficult to access.
Need for duty exemption
- This decision has been taken to help reduce the burden of the cost of treatment for patients and families.
- The drugs and food required for the treatment of these rare diseases are often expensive and need to be imported.
- This exemption will result in substantial cost savings and provide much-needed relief to patients with rare diseases.
Key medicines under this exemption
- The central government has fully exempted Pembrolizumab (Keytruda), a drug used in the treatment of various types of cancer, from basic customs duty.
- Previously, the GST rate for Keytruda was cut to 5 per cent from 12 per cent in a meeting held in September 2021 by the GST Council.
- Life-saving drugs Zolgensma and Viltepso used in the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy were exempted from GST when imported for personal use.
How the new duty exemption works?
- The exemption has been granted by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) by substituting “Drugs, Medicines or Food for Special Medical Purposes (FSMP)” instead of “drugs or medicines”.
- To avail of this exemption, the individual importer has to produce a certificate from the central or state director health services or district medical officer/civil surgeon of the district.
How are life-saving medicines taxed?
- Drugs/medicines generally attract basic customs duty of 10 per cent, while some categories of lifesaving drugs/vaccines attract a concessional rate of 5 per cent or nil.
- In its meeting in September 2021, the GST Council had reduced tax rates for several life-saving drugs.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Healthcare: Remarkable Progress But The Gaps Needs to be Addressed
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Healthcare progress and challenges
Central Idea
- The Indian healthcare system has overcome many challenges and has made significant progress, but there are still many tough health challenges that need to be addressed. There is need to bridge the gap between the services available in metropolitan and Tier-II and Tier-III cities, provide healthcare insurance to the unorganised middle class, and use Artificial Intelligence and digital technology to improve healthcare services.
Overcoming past challenges
- The Indian healthcare system has overcome seemingly insurmountable problems, including high maternal and infant mortality rates, and low hospital delivery rates.
- The National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) results show that even in the so-called BIMARU states, hospital deliveries have soared to 89 per cent.
Current Health Challenges
- Five interrelated challenges: The current macro picture shows at least five interrelated challenges that are pervading the population, including non-communicable diseases (NCDs), obesity, and chronic respiratory diseases.
- NCDs: The proportion of deaths due to NCDs has increased from around 38 per cent in 1990 to 62 per cent in 2016.
- Obesity: Obesity has increased from 19 per cent to 23 per cent between NFHS-4 and NFHS-5. Awareness about leading healthy lives will save millions from illness and decelerate premature death.
Current state of healthcare in India
- Infrastructure:
- The state of infrastructure matters. Since 2018, governments at the Centre as well as the state have been trying to bolster primary healthcare by establishing health and wellness centres.
- But there are still huge variations between states, and some states have better arrangements than others. States must step up efforts to improve infrastructure in the healthcare sector.
- Bridging the gap in hospital services:
- In urban areas, the challenge is to bridge the gap in hospital services between large urban agglomerations and Tier-II and Tier-III cities.
- Large hospital chains provide only 4-5 per cent of the beds in the private sector.
- Standalone hospitals and nursing homes provide 95 per cent of private hospital beds but are unable to provide multi-specialty, leave alone tertiary and quaternary care.
- The gaps between services available in the metros and big cities and in districts must be bridged.
- Health Insurance Coverage:
- Low health insurance penetration and the very high personal outgo on healthcare remain a challenge.
- But over the past three years, more than four crore Indians have bought health insurance.
- From 2018, the Ayushman Bharat insurance scheme for 10 crore poor families has been undertaken to provide insurance against hospitalisation for up to Rs 5 lakh per year per family.
- Nearly 74 per cent of Indians are either covered or eligible for health insurance coverage.
- Use of Artificial Intelligence and digital technology:
- An emerging concern is the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital technology to improve healthcare services.
- Surgery assisted by robots, the use of genetic codes, clinical decision support systems, and telemedicine can help in making healthcare more accessible and efficient.
Conclusion
- India has shown how the impossible can be achieved, but the healthcare system needs to overcome various challenges to fully redeem its advantage of having the youngest population. The government needs to step up efforts in improving infrastructure, bridging the gap in hospital services, and providing health insurance coverage for the unorganized middle class. It is also essential to regulate the use of AI and digital technology in the healthcare sector to ensure accountability and prevent malpractice.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Healthcare: Public Health and The Insurance Funding
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various Insurance Schemes
Mains level: Insurance based healthcare funding, benefits and drawbacks
Central Idea
- The Tamil Nadu public health model has achieved success in improving healthcare outcomes and maintaining equity in healthcare delivery. However, the shift in healthcare funding to insurance companies has brought both benefits and drawbacks to the public healthcare system.
The key features of the Tamil Nadu public health model
- Primary Healthcare: The Tamil Nadu public health model is based on a strong emphasis on primary healthcare, which is the first point of contact for patients seeking medical attention. Primary healthcare centres provide basic healthcare services and preventive care, which are critical to reducing the burden of disease.
- Public Health Infrastructure: The state has a well-established public health infrastructure, including a network of primary healthcare centres, secondary and tertiary care hospitals, and medical colleges. The state government has also invested in health infrastructure, including sanitation facilities, water supply, and waste management.
- Health Insurance: The Tamil Nadu government has implemented a comprehensive health insurance scheme, the Chief Minister’s Comprehensive Health Insurance Scheme (CMCHIS), which provides free healthcare services to families living below the poverty line and low-income groups.
- Human Resource Development: The state government has also focused on developing human resources in healthcare. It has set up a large number of nursing and paramedical institutions to train healthcare professionals.
- Health Awareness: The Tamil Nadu government has launched various health awareness campaigns to educate people about health issues, including communicable and non-communicable diseases. The government has also launched campaigns to promote healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Partnership with NGOs: The government has partnered with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to implement various health programs. These partnerships have helped in the effective delivery of healthcare services in remote and rural areas of the state.
- Innovations: Tamil Nadu has implemented several innovative approaches in healthcare, such as telemedicine, which enables patients to receive medical consultation and treatment remotely using technology. The state has also established mobile clinics to provide healthcare services to people living in remote areas.
Benefits of Decentralization
- Improved access to healthcare: Decentralization can help to improve access to healthcare services, particularly in rural or remote areas. By empowering local communities and healthcare providers to make decisions about healthcare delivery, services can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the population.
- Better quality of care: Decentralization can lead to better quality of care by enabling healthcare providers to respond more quickly and effectively to the needs of their patients. It can also promote innovation and experimentation in healthcare delivery, leading to new and improved approaches to patient care.
- Increased accountability: Decentralization can increase accountability in healthcare delivery by empowering local communities and healthcare providers to monitor and evaluate the quality of care. This can help to identify and address problems in healthcare delivery, leading to improved outcomes for patients.
- Cost savings: Decentralization can lead to cost savings in healthcare delivery by reducing the administrative costs associated with centralized decision-making and management. It can also promote greater efficiency in healthcare delivery, leading to reduced waste and duplication of services.
Insurance Funding in healthcare
- Insurance funding in healthcare refers to the use of insurance mechanisms to finance healthcare services. This involves pooling financial resources from individuals or groups through insurance schemes, which are then used to pay for healthcare services.
- Insurance funding can help to mitigate the financial risks associated with healthcare, and ensure that individuals have access to the care they need without incurring excessive costs.
Drawbacks of Insurance Funding
- Shifted focus: The focus on indemnity and negotiations with insurance companies has shifted the focus of hospitals from patient care to claiming money.
- Compromised quality of service: The appointment of contractual employees with meager pay has created a divide between permanent high-paid staff and temporary low-salaried staff, leading to a compromise in the quality of service.
Facts for prelims
| Type of Insurance Funding | Description |
| Private health insurance | Purchased by individuals or employers to cover healthcare costs. Coverage, cost, and benefits vary widely and may be offered by commercial insurers, nonprofit organizations, or government programs |
| Public health insurance | Provided by government-run programs, typically funded through taxes or other government revenues. Coverage is provided to eligible individuals based on criteria such as age, income, or medical need. Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) is a government-funded health insurance program that provides free health coverage to economically disadvantaged families across India. |
| Social health insurance | A hybrid model that combines elements of private and public insurance. Individuals and employers contribute to a national insurance fund that is used to pay for healthcare services, typically managed by a government agency but delivered by private providers |
| Employer-sponsored insurance | Private insurance provided by employers to their employees, often mandatory in many countries. Employers are required to provide a certain level of coverage to their employees. |
Conclusion
- While insurance funding has brought benefits, it has also created challenges, including the erosion of compassion among health professionals and a diversion of funds from public to private hospitals. It is necessary to strike a balance between decentralization, insurance funding, and preserving the fundamental principles of equity, compassion, and excellence in care to maintain the success of Tamil Nadu’s public healthcare system.
Mains Question
Q. Highlight the benefits of decentralization in healthcare delivery. Analyse the benefits and drawbacks of insurance funding in India?
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
ICMR releases Ethical Guidelines for AI usage in Healthcare
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AI in healthcare
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has recently released the first-ever set of ethical guidelines for the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in biomedical research and healthcare.
Ethical Guidelines for AI usage in Healthcare
- The guidelines aim to create “an ethics framework which can assist in the development, deployment, and adoption of AI-based solutions” in specific fields.
- Through this initiative, the ICMR aims to make “AI-assisted platforms available for the benefit of the largest section of common people with safety and highest precision possible”.
- It seeks to address emerging ethical challenges when it comes to AI in biomedical research and healthcare delivery.
Key features
- Effective and safe development, deployment, and adoption of AI-based technologies: The guidelines provide an ethical framework that can assist in the development, deployment, and adoption of AI-based solutions in healthcare and biomedical research.
- Accountability in case of errors: As AI technologies are further developed and applied in clinical decision making, the guidelines call for processes that discuss accountability in case of errors for safeguarding and protection.
- Patient-centric ethical principles: The guidelines outline 10 key patient-centric ethical principles for AI application in the health sector, including accountability and liability, autonomy, data privacy, collaboration, risk minimisation and safety, accessibility and equity, optimisation of data quality, non-discrimination and fairness, validity and trustworthiness.
- Human oversight: The autonomy principle ensures human oversight of the functioning and performance of the AI system.
- Consent and informed decision making: The guidelines call for the attainment of consent of the patient who must also be informed of the physical, psychological and social risks involved before initiating any process.
- Safety and risk minimisation: The safety and risk minimisation principle is aimed at preventing “unintended or deliberate misuse”, anonymised data delinked from global technology to avoid cyber attacks, and a favourable benefit-risk assessment by an ethical committee among a host of other areas.
- Accessibility, equity and inclusiveness: The guidelines acknowledge that the deployment of AI technology assumes widespread availability of appropriate infrastructure and thus aims to bridge the digital divide.
- Relevant stakeholder involvement: The guidelines outline a brief for relevant stakeholders including researchers, clinicians/hospitals/public health system, patients, ethics committee, government regulators, and the industry.
- Standard practices: The guidelines call for each step of the development process to follow standard practices to make the AI-based solutions technically sound, ethically justified, and applicable to a large number of individuals with equity and fairness.
- Ethical review process: The ethical review process for AI in health comes under the domain of the ethics committee which assesses several factors including data source, quality, safety, anonymization, and/or data piracy, data selection biases, participant protection, payment of compensation, possibility of stigmatisation among others.
Policy moves for streamlining AI in Healthcare
- India already offers streamlining of AI technologies in various sectors, including healthcare, through the National Health Policy (2017), National Digital Health Blueprint (NDHB 2019), and Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (2018) proposed by the Health Ministry.
- These initiatives pave the way for the establishment of the National Data Health Authority and other health information exchanges.
Potential applications of AI in healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the healthcare industry by enabling various applications. These applications include:
- Diagnosis and screening: AI can be used to identify diseases from medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
- Therapeutics: AI can assist in the development of personalised medicines by analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup.
- Preventive treatments: AI can predict the risk of developing a disease, helping healthcare professionals to take preventive measures.
- Clinical decision-making: AI can analyze large amounts of data to assist healthcare professionals in making treatment decisions.
- Public health surveillance: AI can be used to monitor disease outbreaks and inform public health policies.
- Complex data analysis: AI can analyze large amounts of data from multiple sources to identify patterns and inform healthcare decision-making.
- Predicting disease outcomes: AI can predict disease outcomes based on patient data, enabling early
- Behavioural and mental healthcare: AI can help diagnose and treat mental health conditions.
- Health management systems: AI can assist in managing patient records, appointment scheduling and reminders, and medication management.
Various challenges for imbibing
- Data privacy and security: With the use of AI in healthcare, there is a significant amount of personal and sensitive data is collected. This data needs to be kept secure and protected from potential cyber-attacks.
- Regulatory and ethical issues: AI technology is still in its early stages of development and there are no clear guidelines or regulations in place for its use in healthcare. There are also ethical considerations, such as accountability, transparency, and bias that need to be addressed.
- High cost involved: The implementation of AI in healthcare requires significant investment in terms of infrastructure, software, and training. This cost can be a major challenge for healthcare organizations, especially in developing countries.
- Integration with existing systems: AI systems need to be integrated with existing healthcare systems and processes. This can be challenging, especially in cases where the existing systems are outdated or incompatible with AI technology.
- Lack of trust and acceptance: AI technology is still relatively new in healthcare and there is a lack of trust and acceptance among healthcare professionals and patients. This can be a major hurdle in the widespread adoption of AI in healthcare.
Threats posed by AI to healthcare
- Data privacy and security: The use of AI in healthcare requires the collection and analysis of vast amounts of personal health data, which could be at risk of being stolen or misused.
- Bias and discrimination: There is a risk that AI algorithms could perpetuate existing biases and inequalities in healthcare, such as racial or gender bias.
- Lack of transparency: Some AI models are complex and difficult to understand, which can make it difficult to explain the reasoning behind a particular decision.
- Medical errors: AI systems can make errors if they are trained on biased or incomplete data, or if they are used inappropriately.
- Ethical concerns: There are several ethical concerns associated with the use of AI in healthcare, including the potential for AI to replace human doctors, the impact on patient autonomy, and the implications for informed consent.
Way forward
- Develop a national AI strategy for healthcare: This strategy should include policies for data sharing, privacy, and security, as well as guidelines for the ethical and responsible use of AI.
- Invest in AI research and development: The government should invest in research and development of AI technologies that can help address the challenges in healthcare.
- Promote collaboration between stakeholders: Collaboration between stakeholders such as healthcare providers, researchers, government agencies, and industry can help accelerate the development and adoption of AI technologies in healthcare.
- Train healthcare professionals in AI: The government can work with academic institutions and the industry to create training programs and certifications for healthcare professionals.
- Address regulatory challenges: The government should work to address regulatory challenges related to the use of AI in healthcare.
- Focus on affordability and accessibility: This can be achieved by promoting innovation, encouraging competition, and ensuring that AI technologies are integrated into existing healthcare infrastructure.

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Rajasthan becomes first state to guarantee Right to Health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Right to Health
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Rajasthan Assembly passed the Right to Health (RTH), even as doctors continued their protest against the Bill, demanding its complete withdrawal.
Right to Health (RTH): A conceptual insight
- RTH is a fundamental human right that guarantees everyone the right to enjoy the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health.
- It is recognized as a crucial element of the right to an adequate standard of living and is enshrined in international human rights law.
Scope of RTH
- RTH covers various health-related issues, including-
- Access to healthcare services, clean water and sanitation, adequate nutrition, healthy living and working conditions, health education, and disease prevention.
- Accessible, affordable, and quality healthcare services,
- Eliminating barriers to healthcare access
- Informed consent to medical treatment and accessing information about their health.
What is the Rajasthan Right to Health Bill?
- Free treatment: RTH gives every resident of the state the right to avail free Out Patient Department (OPD) services and In Patient Department (IPD) services at all public health facilities and select private facilities.
- Wider scope of healthcare: Free healthcare services will include consultation, drugs, diagnostics, emergency transport, procedures, and emergency care. However, there are conditions specified in the rules that will be formulated.
- Free emergency treatment: Residents are entitled to emergency treatment and care without prepayment of fees or charges.
- No delay in treatment: Hospitals cannot delay treatment on grounds of police clearance in medico-legal cases.
- State reimbursement of charges: After emergency care and stabilisation, if patients do not pay requisite charges, healthcare providers can receive proper reimbursement from the state government.
Existing schemes in Rajasthan
- The flagship Chiranjeevi Health Insurance Scheme provides free treatment up to Rs 10 lakh, which has been increased to Rs 25 lakh in the latest budget.
- The Rajasthan Government Health Scheme covers government employees, ministers, current and former MLAs, etc.
- The Nishulk Nirogi Rajasthan scheme provides free OPD and IPD services in government hospitals and covers about 1,600 medicines, 928 surgicals, and 185 sutures.
- The Free Test scheme provides up to 90 free tests in government hospitals and has benefited 2.93 crore persons between March-December 2022.
Need for the RTH Scheme
- The state prioritizes healthcare and wants Rajasthan to be a great example of good health.
- The Health Minister has received many complaints about private hospitals asking for money from patients who have the Chiranjeevi card.
- So, they are bringing in a new law to stop this.
- The new law will make sure that future governments follow it and provide free healthcare to everyone.
Controversy with the RTH Law: Emergency Care Provisions
- Emergency care was a contentious issue in the RTH.
- The clause states that people have the right to emergency treatment and care for accidental emergency, emergency due to snake bite/animal bite and any other emergency decided by the State Health Authority under prescribed emergency circumstances.
- Emergency treatment and care can be availed without prepayment of requisite fee or charges.
- Public or private health institutions qualified to provide such care or treatment according to their level of health care can offer emergency care.
Issues raised by healthcare professionals
- Existing burden of schemes: Doctors are protesting against the RTH because they question the need for it when there are already schemes like Chiranjeevi that cover most of the population.
- Specialization concerns: They are also objecting to certain clauses, such as defining “emergency” and being compelled to treat patients outside their specialty as part of an emergency.
- Unnecessary obligations: The Bill empowers patients to choose the source of obtaining medicines or tests at all healthcare establishments, which means that hospitals cannot insist on in-house medicines or tests.
Way forward
- Given the contentious nature of the Bill, it is important for all stakeholders to come to the table and engage in constructive dialogue to resolve the issues at hand.
- It should involve liaison between government, doctors, patient advocacy groups, and other relevant stakeholders to discuss the concerns raised by all parties and identify potential solutions.
- This could be followed by a revision of the Bill, incorporating feedback and suggestions from all stakeholders, and a renewed effort to build consensus and support for the legislation.
- Additionally, greater efforts could be made to improve transparency and accountability in the healthcare system, with a focus on educating patients about their rights.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Rising Cancer Cases in India And Economic Burden
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cancer and Innovative Treatment and therapies
Mains level: Rising Cancer and economic burden
Central Idea
- Cancer cases in India are predicted to cross the 15 lakh mark by 2025, highlighting concerns about the economic burden of expensive cancer treatments and the accessibility of affordable healthcare for patients.
Cancer
- Cancer is a group of diseases that arise when cells in the body begin to grow and divide uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumors.
- Normally, cells in the body grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion, but in cancer, this process goes awry, leading to the accumulation of abnormal cells that can form a mass or tumor.
- There are many different types of cancer, which can affect any part of the body. Some cancers, such as leukemia, do not form tumors but still involve the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells.
- Symptoms of cancer can vary depending on the type and location of the cancer, but common signs include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, pain, and changes in the skin or the appearance of a lump or mass.
Economic Burden of Cancer Treatment
- Inaccessible and Increasing Costs:
- The average medical expenditure per hospitalization case for cancer treatment was ₹68,259 in urban areas, according to the NSS 2017-18 report.
- A Parliamentary Standing Committee report expressed concern about the inaccessible and increasing cost of cancer treatment.
- Regulatory Challenges:
- While anti-cancer medicine costs can be regulated, the cost of radiotherapy cannot, as it has not been declared an essential service.
- Insurance Coverage and Out-of-Pocket Expenses.
- Impact on Patients:
- Cancer often strikes around the retirement age, leading to mounting debt burdens.
- The average hospital stay for 14.1% of cancer patients is more than 30 days, further increasing bills.
Insurance Coverage and Out-of-Pocket Expenses
- Poor Insurance Penetration: More than 80% of hospital bills are paid out of pocket, as per the NSS 2017-18 report.
- Ayushman Bharat Limitations: The Committee observed that the Ayushman Bharat insurance scheme launched in 2018 does not cover entire prescriptions, latest cancer therapies, or many diagnostic tests.
- State-Specific Insurance Schemes: The Committee suggested a convergence of State and Central schemes, as some State-specific insurance schemes have been highly beneficial.
State-wise Variation in Cancer Treatment Expenditure
- State-wise average medical expenditure per hospitalization case for cancer treatment in government hospitals varies, with the lowest in Tamil Nadu and Telangana, and the highest in northern and north-eastern India.
Facts for Prelims: CAR T-cell therapy
- Unlike chemotherapy or immunotherapy, which require mass-produced injectable or oral medication, CAR T-cell therapies use a patient’s own cells.
- The treatment involves modifying a patient’s own T-cells, which are a type of immune cell, in a laboratory to target and attack cancer cells.
- CAR stands for chimeric antigen receptor, which refers to the genetically engineered receptor that is added to the patient’s T-cells.
- The patient’s T-cells are collected and genetically modified in a laboratory to express the CAR.
- The modified T-cells are then infused back into the patient’s body, where they can seek out and destroy cancer cells that express the antigen targeted by the CAR.
- The cells are even more specific than targeted agents and directly activate the patient’s immune system against cancer, making the treatment more clinically effective.
- This is why they’re called living drugs.
- CAR T-cell therapy has shown promising results in treating certain types of blood cancers, including leukemia and lymphoma.
Conclusion
- The rising number of cancer cases in India underscores the need to address the economic burden of expensive cancer treatments and improve the accessibility of affordable healthcare for patients. Converging State and Central insurance schemes, expanding insurance coverage, and exploring ways to regulate treatment costs are essential steps to ensure that patients can access life-saving treatments without facing insurmountable financial challenges.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Universal Health Coverage (UHC) Must be Affordable to All
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Primary Health care and Universal Health care
Central Idea
- The Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and its implementation in India raises the question of whether we believe in health as a basic human right, which India’s Constitution guarantees under the right to life. The UHC should encompass primary, secondary, and tertiary care for all who need it at an affordable cost without discrimination.
The Definition of Health
- The definition of health according to the World Health Organization (WHO), which includes mental and social well-being and happiness beyond physical fitness, and an absence of disease and disability.
- We cannot achieve health in its wider definition without addressing health determinants, which necessitates an intersectoral convergence beyond medical and health departments.
Difference between Primary health care (PHC) and Universal health care (UHC)
- The main difference between PHC and UHC is that PHC is a level of care within the health care system, while UHC is a broader goal of ensuring access to health care for all individuals.
- PHC is typically provided at the primary care level, while UHC includes all levels of care, from primary to secondary and tertiary care.
- PHC is focused on basic health care services and health promotion, while UHC aims to provide comprehensive health care services to all individuals.
Health for All by 2000
- The slogan Health for All by 2000 proposed by Halfdan Mahler and endorsed by the World Health Assembly in 1977. It argues that universal health care/coverage (UHC) was implied as early as 1977.
- India committed itself to the ‘Health for All’ goal by 2000 through its National Health Policy 1983.
International Conference on PHC
- The International Conference on Primary Health Care, at Alma Ata, 1978, which listed eight components of minimum care for all citizens.
- Components included: It mandated all health promotion activities and the prevention of diseases, including vaccinations and treatment of minor illnesses and accidents, to be free for all using government resources, especially for the poor.
- Components excluded: Chronic diseases, including mental illnesses, and their investigations and treatment were almost excluded from primary health care. When it came to secondary and tertiary care, it was left to the individual to seek it from a limited number of public hospitals or from the private sector by paying from their own pockets.
Concerns around The Astana Declaration
- The Astana declaration of 2018, which calls for partnership with the private sector. However the commercial private sector, which contributes to alcohol, tobacco, ultra-processed foods, and industrial and automobile pollution, is well established.
- The Astana declaration never addressed poverty, unemployment, and poor livelihood, but eulogizes quality PHC only as the cornerstone for Universal Health Coverage and ignores broader Universal Health Care.
Conclusion
- Every individual has a right to be healed and not have complications, disability, and death. That right is guaranteed only by individualism in public health, the new global approach to UHC, where nobody is left uncounted and uncared for. The Alma Ata declaration of primary health care can be left behind as a beautiful edifice of past concepts, and we should move forward with a newer concept of UHC.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is ‘e-Sanjeevani App’?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: E-Sanjeevani App
Mains level: Telemedicine

The eSanjeevani app was featured in Prime Minister’s “Mann Ki Baat” address as part of the government’s efforts to promote digital healthcare in the country.
What is the e-Sanjeevani app?
- E-Sanjeevani is a browser-based platform-independent application that allows for both ‘doctor-to-doctor’ and ‘patient-to-doctor’ teleconsultations.
- During the Covid pandemic, the union health ministry launched the e-Sanjeevani telemedicine services to ensure that health consultations reach people even in remote villages.
- At the time of its launch, the union health ministry stated that it was a doctor-to-doctor telemedicine service that would provide general and specialised health care in rural areas.
How does e-Sanjeevani work?
- The e-Sanjeevani service establishes a virtual link between the beneficiary and doctor or specialist at the hub, which will be a tertiary healthcare facility.
- This network’s spoke would be a paramedic or generalist at a health and wellness centre.
- It allows for real-time virtual consultations between doctors and specialists at the hub and the beneficiary (via paramedics) at the spoke.
- The e-prescription generated at the conclusion of the session is used to obtain medications.
What is the reach of e-Sanjeevani?
- Sanjeevani HWC is currently operational in approximately 50,000 health and wellness centres across the country.
- As PM Modi stated in ‘Mann Ki Baat’, the number of tele-consultants using the e-Sanjeevani app has now surpassed 10 crore.
- Health minister has stated that 100.11 million patients were served at 115,234 Health and Wellness Centres (as spokes) via 15,731 hubs and 1,152 online OPDs staffed by 2,29,057 telemedicine-trained medical specialists and super-specialists.
- More than 57% of e-Sanjeevani beneficiaries are women, with only about 12% being senior citizens, according to union health ministry.
Attempt UPSC 2024 Smash Scholarship Test | FLAT* 100% OFF on UPSC Foundation & Mentorship programs
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Understanding India’s Mental Healthcare Act, 2017
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mental Healthcare Act, 2017
Mains level: Not Much

Central idea: The article discusses the challenges faced in implementing India’s Mental Healthcare Act, 2017 and the need for better mental healthcare services in the country.
Mental Healthcare Act, 2017
The Mental Healthcare Act, 2017 is a comprehensive legislation that provides for the protection and promotion of the rights of people with mental illness. Some of the key features of the Act are:
- Decriminalization of suicide: The Act decriminalizes suicide and prohibits the use of inhuman and degrading treatment towards those who attempt suicide.
- Advance directives: The Act allows individuals to make advance directives, specifying the type of treatment they would like to receive in the event of a mental health issue.
- Informed consent: The Act mandates that patients have the right to give or refuse consent to treatment, and to be informed about the benefits, side effects, and alternatives of the treatment.
- Mental health review boards: The Act establishes Mental Health Review Boards at the national and state levels to oversee the implementation of the Act and protect the rights of people with mental illness.
- Prohibition of inhuman treatment: The Act prohibits the use of inhuman treatment methods, including chaining, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) without anaesthesia, and solitary confinement.
- Right to access mental healthcare: The Act guarantees the right to access mental healthcare services, and mandates the establishment of mental health services in every district.
- Protection of rights and dignity: The Act aims to protect the rights and dignity of people with mental illness, and prohibits discrimination and stigmatization on the basis of mental illness.
- Establishment of a Central Mental Health Authority: The Act establishes a Central Mental Health Authority to regulate mental health services in the country.
NHRC flags alert
- Pity over healthcare institution: The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in a report flagged the “inhuman and deplorable” condition of all 46 government-run mental healthcare institutions across the country.
- Prolonged hospitalization: The report notes that the facilities are “illegally” keeping patients long after their recovery, in what is an “infringement of the human rights of mentally ill patients”.
- Need for Assessment: These observations were made after visits to all operational government facilities, to assess the implementation of the Mental Healthcare Act, 2017 (MHA).
Major issue: Lack of implementation
- Despite the act’s provisions, mental health institutions in India have been plagued by a lack of adequate infrastructure, staff, and training.
- Patients have reported human rights violations, including abuse, neglect, and violence.
Need for effective implementation
- The Mental Healthcare Act needs effective implementation and oversight to ensure that patients receive the care and treatment they need with dignity and respect.
- This requires increased investment in mental health infrastructure, including facilities, staff, and training.
Way forward
- Ensuring proper implementation of the Act: There is a need for proper implementation of this act across the country, with a focus on ensuring the rights and dignity of patients in mental healthcare institutions.
- Increasing awareness: Awareness needs to be raised about the Act, and the rights of mental healthcare patients among the general public, healthcare professionals, and law enforcement agencies.
- Providing training and capacity building: Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and caregivers, need to be trained and equipped with the skills and knowledge to provide quality care and support to mental healthcare patients.
- Strengthening mental healthcare infrastructure: There is a need to strengthen the infrastructure and facilities in mental healthcare institutions, including better staffing, improved physical facilities, and access to quality medication.
- Encouraging community-based care: Community-based care for mental health patients can help reduce the burden on mental healthcare institutions and provide a more supportive environment for patients.
- Promoting human rights: There is a need for greater emphasis on the human rights of mental healthcare patients, including the right to dignity, privacy, and freedom from discrimination and abuse.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Its high time to focus on Mental Health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Mental health problems and solutions
Context
- Suicides rates in India are amongst the highest when compared to other countries at the same socio-economic level. According to WHO, India’s suicide rate in 2019, at 12.9/1,00,000, was higher than the regional average of 10.2 and the global average of 9.0. Suicide has become the leading cause of death among those aged 15–29 in India.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Background: Mental Health
- While every precious life lost through suicide is one too many, it represents only the tip of the mental health iceberg in the country, particularly among young adults. Women tend to suffer more.
- Across the world, the prevalence of some mental health disorders is consistently higher among women as compared to men.
Prevalence of Mental ill-health
- The pandemic has further exacerbated the problem: Globally, it might have increased the prevalence of depression by 28 per cent and anxiety by 26 per cent in just one year between 2020 and 2021, according to a study published in Lancet.
- Increased among younger age groups: Again, the large increases have been noted among younger age groups, stemming from uncertainty and fear about the virus, financial and job losses, grief, increased childcare burdens, in addition to school closures and social isolation.
- Use of social media exacerbating the stress: Increased use of certain kinds of social media is also exacerbating stress for young people. Social media detracts from face-to-face relationships, which are healthier, and reduces investment in meaningful activities. More importantly, it erodes self-esteem through unfavourable social comparison.
Socio-economic implications of Mental ill-health
- People living in poverty are at greater risks: Mental ill health is a leading cause of disability globally and is closely linked to poverty in a vicious cycle of disadvantage. People living in poverty are at greater risk of experiencing such conditions.
- People experiencing mental health problems likely to fall in poverty: On the other hand, people experiencing severe mental health conditions are more likely to fall into poverty through loss of employment and increased health expenditure.
- Stigma and discrimination: Stigma and discrimination often further undermine their social support structures. This reinforces the vicious cycle of poverty and mental ill-health.
- Higher income inequality has high prevalence of ill mental ill health: Not surprisingly, countries with greater income inequalities and social polarization have been found to have a higher prevalence.
Approach to protect, promote and care for the mental health of people?
- Killing the deep stigma surrounding mental health issues: The first step should be killing the deep stigma which prevents patients from seeking timely treatment and makes them feel shameful, isolated and weak. Stigma festers in the dark and scatters in the light. We need a mission to cut through this darkness and shine a light.
- Making Mental health an integral part of public health programme: There is need to make mental health an integral part of the public health programme to reduce stress, promote a healthy lifestyle, screen and identify high-risk groups and strengthen interventions like counselling services. Special emphasis will need to be given to schools.
- Paying attention to highly vulnerable: In addition, we should pay special attention to groups that are highly vulnerable because of the issues such as victims of domestic or sexual violence, unemployed youth, marginal farmers, armed forces personnel and personnel working under difficult conditions.
- Creating a strong infrastructure for mental health care and treatment: Lack of effective treatment and stigma feed into each other. Currently, only 20-30 per cent of people with such disorders receive adequate treatment.
- Mental health services should be made affordable for all: Improved coverage without corresponding financial protection will lead to inequitable service uptake and outcomes. All government health assurance schemes, including Ayushman Bharat, should cover the widest possible range.
Why is the wide treatment gap?
- One major reason for a wide treatment gap is the problem of inadequate resources.
- Less than two per cent of the government health budget, which itself is the lowest among all G20 countries, is devoted to mental health issues.
- There is a severe shortage of professionals, with the number of psychiatrists in the country being less than those in New York City, according to one estimate.
- Substantial investments will be needed to address the gaps in the health infrastructure and human resources.
- Currently, most private health insurance covers only a restricted number of mental health conditions. Similarly, the list of essential medicines includes only a limited number of WHO-prescribed medications.
Conclusion
- We need an urgent and well-resourced whole of society approach to protecting, promoting and caring for the mental health of our people, like we did for the Covid pandemic. Brock Chisholm, the first Director General of WHO, famously said, “there is no health without mental health”.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Norovirus Cases detected in Kerala
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Norovirus
Mains level: Not Much

The Kerala Health Department confirmed two cases of the gastrointestinal infection norovirus in class 1 students in Ernakulam district.
What is Norovirus?
- Norovirus is an important cause of acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis in children as well as adults worldwide.
- It leads to diarrhoea, vomiting, nausea, and abdominal pain. Being a diarrhoeal disease, it can lead to dehydration, so drinking plenty of fluids is recommended.
- The virus was first discovered in connection with an outbreak of acute diarrhoeal disease in Norwalk, Ohio, in 1968 and was called the Norwalk Virus.
- Later, several stomach flu viruses closely linked to the Norwalk virus were found and together, these are now called Noroviruses.
- Many stomach flu outbreaks typically in cruise ships have been traced to NoV.
How deadly is this?
- Norovirus is not new; it has been circulating among humans for over 50 years and is thought to be one of the primary causes of gastroenteritis.
- The virus is estimated to kill 200,000 persons globally every year, with most deaths occurring among those below the age of five years and those over the age of 65 years.
- The virus is capable of surviving low temperatures, and outbreaks tend to be more common during the winter and in colder countries — that is why it is sometimes referred to as “winter vomiting disease”.
What is the incidence of infection in India?
- Cases of norovirus are not as common in India as in many other places — at the same time.
- The infection has been reported in previous years as well, mainly from Southern India, and especially from Kerala.
- A 2021 study from Hyderabad reported that norovirus was detected in 10.3% samples of children who came in with acute gastroenteritis.
Can norovirus infection cause a large-scale outbreak?
- Even though more cases of norovirus are being detected, experts say that this is unlikely to lead to a large-scale outbreak.
- There is no epidemiological study to co-relate of these cases.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Mental Health Problem and effective policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Strategy for better mental health policy
Context
- The fifth Global Mental Health Summit, co-sponsored by over half a dozen organisations engaged with mental health, was held in Chennai to discuss mental health in the context of human rights, ethics and justice. Highlighting the importance of mental health, it gave a call for action against the continued neglect by society at large and the governments at central and state levels, in particular.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Findings of national mental health survey
- The National Mental Health Survey (NMHS): The latest National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) conducted by National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS) in collaboration with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and WHO, was published in 2016.
- Prevalence of mental disorder: According to the survey, the prevalence of mental disorders among adults in India is around 10.6%. The most common disorders were anxiety disorders (7.3%) and mood disorders (4.5%).
- Higher among women than men: The survey also found that the prevalence of mental disorders was higher among women than men, and that the majority of people with mental disorders did not receive any treatment.
- Prevalence of mental disorders is higher in urban areas: It also found that the prevalence of mental disorders was higher in urban areas than in rural areas, and that there was a higher prevalence of mental disorders among people with lower levels of education and income.
- Gap in treatment coverage for people with mental disorder : The survey highlighted that there is a significant gap in treatment coverage for people with mental disorders, and that the majority of people with mental disorders do not receive any treatment.
- Plan for mental health: The survey has provided an important information for Indian government and mental health professional to plan and implement mental health programs and policies in the country.
What constitutes good policy making on mental health?
- Policy should be based on research and findings: Policies should be based on sound research and evidence from scientific studies. This helps to ensure that policies are effective in addressing mental health issues and are not based on assumptions or stereotypes.
- Active engagement of stakeholders: Policy making should involve a wide range of stakeholders, including people with lived experience of mental health issues, mental health professionals, and representatives from relevant government departments and non-governmental organizations.
- A comprehensive and integrated approach: Mental health policies should be comprehensive and address a wide range of issues, including prevention, early intervention, treatment, and recovery. They should also be integrated with other policies, such as those related to education, housing, and employment.
- Ensure easy access to mental health care: policies should ensure that people have access to appropriate and affordable mental health care, including both medication and psychosocial therapies.
- Public awareness and Sensitization : policies should ensure that people with mental health issues are treated with dignity and respect, and that their human rights are protected.
Case study: How India tackled HIV/AIDS?
- Active surveillance system: The need for crafting strategic interventions based on epidemiological evidence from an active surveillance system.
- Modelling different options: The importance of modelling different options of addressing the wide array of interventions required in different geographies, among different target groups, to provide the data related to cost effectiveness as well as efficacy of the interventions required for scaling up.
- Proactive advocacy of systemic issues among all influencers: The proactive advocacy of systemic issues among all influencers the media, judiciary, politicians, police and other intersectoral departments whose programmes and activities have had a direct bearing on the key populations being worked on.
- Community engagement: The use of peer leaders and civil society that was allocated over 25 per cent of the budget. Though a central sector programme was fully funded by the central government, every intervention was formulated with active participation and dialogue among the states and constituencies of local leaders.
Strategy for better implementation of mental health policy
- Clear goals and objectives: Having clear and measurable goals and objectives can help to ensure that policies are implemented effectively and that progress can be tracked.
- Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity building for mental health professionals, as well as for other relevant stakeholders such as community leaders, can help to ensure that policies are implemented effectively.
- Community engagement: Involving communities in the planning and implementation of mental health policies can help to ensure that policies are responsive to the specific needs and priorities of local populations.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Regularly monitoring and evaluating the implementation of policies can help to identify any barriers or challenges, and make adjustments as necessary.
- Multi-sectoral approach: Adopting a multi-sectoral approach that involves collaboration between different sectors, such as health, education, social welfare, housing, and employment can help to ensure that policies are implemented in a coordinated and effective manner.
- Policy flexibility: Policies should be flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances, and be responsive to feedback and suggestions from the community and stakeholders.
latest research in mental health domain
- The growing recognition of the importance of early intervention in mental health: Research has shown that early intervention can prevent mental health issues from becoming more severe, and can help individuals to recover more quickly.
- The use of technology in mental health: There has been an increase in the use of technology, such as mobile apps, virtual reality, and teletherapy, to deliver mental health care. Studies have shown that these technologies can be effective in improving mental health outcomes.
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health: The pandemic has had a significant impact on mental health, and research has been conducted to understand the extent of the impact and to develop strategies to mitigate it.
- Advancements in brain imaging and genetics: Researchers are using brain imaging techniques and genetic studies to gain a better understanding of the underlying causes of mental disorders and to develop more effective treatments.
- The use of personalized medicine in mental health: There is growing interest in the use of personalized medicine, which involves using genetic and other information to tailor treatment to the individual patient, to improve mental health outcomes.
- The benefits of nature-based interventions for mental health: Studies have shown that spending time in nature can have a positive impact on mental health, including reducing symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression.
- The importance of social determinants of mental health: Research has highlighted the importance of social determinants such as poverty, education, and social support in mental health.
- The importance of addressing mental health in the workplace: Studies have highlighted the impact of workplace stress and burnout on mental health and the importance of workplace interventions to promote mental well-being.
Do you know Neuralink?
- Neuralink is a gadget that will be surgically inserted into the brain using robotics. In this procedure, a chipset called the link is implanted in the skull.
- Neuralink can be used to operate encephalopathy. It can also be used as a connection between the human brain and technology which means people with paralysis can easily operate their phones and computer directly with their brain.

Conclusion
- Mental health problems and not related to age of persons. From children to old age all can suffer from this menace. Government of the must formulated, implement the effective, resulted oriented mental health policy as earliest as possible
Mains Question
Q. What factors need to be taken care while drafting sound mental health policy? Suggest a strategy for better implementation of metal health policy.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Digital healthcare Services
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat, UHC, ABHA etc
Mains level: Digital public goods, Success of Ayushman Bharat and India's G20 presidency.
Context
- India leveraged information and communications technologies (ICTs) during the pandemic. Digital health solutions played a crucial role in bridging the gap in healthcare delivery as systems moved online to accommodate contactless care.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
India’s spectacular demonstration of digital public good (DPG) so far
- Aadhar and UPI are like the building blocks of DPG: India has demonstrated its digital prowess by building digital public goods the digital identity system Aadhaar, the DPGs built on top of Aadhaar and the Unified Payments Interface.
- Aadhar for PDS and UPI for payments: While Aadhaar has become central to India’s public service delivery architecture, UPI has transformed how payments are made.
- One of the largest internet users: Our digital public infrastructure has reached the last mile, enabled by 1.2 billion wireless connections and 800 million internet users.
- Some examples of DPGs developed during the pandemic: For instance, the Covid Vaccine Intelligence Network (CoWIN) and the Aarogya Setu application. CoWIN propelled India to adopt a completely digital approach to its vaccination strategy. Aarogya Setu provided real-time data on active cases and containment zones to help citizens assess risk in their areas.
- Increasing use of Telemedicine platforms: Telemedicine platforms saw a steep increase in user acquisitions, as 85 per cent of physicians used teleconsultations during the pandemic, underscoring the need to better incorporate cutting-edge digital technologies into healthcare services.
Acknowledging the current need?
- Although the impact of the pandemic on health services put the spotlight on the benefits of digital innovation and technology-enabled solutions, private entities, health technology players, and the public sector have been driving digitisation in the sector for some time now.
- It has become clear that a comprehensive digital healthcare ecosystem is necessary to bring together existing siloed efforts and move toward proactive, holistic, and citizen-centric healthcare.
Government efforts in this direction?
- Shared public goods for healthcare: Recognising this need, the government has created shared public goods for healthcare and developed a framework for a nationwide digital health system. This brought healthcare to a turning point in India.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): The PM launched the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission on September 27, 2021, under the aegis of the National Health Authority. Within a year of its launch, ABDM has established a robust framework to provide accessible, affordable, and equitable healthcare through digital highways. The ABDM has implemented vital building blocks to unite all stakeholders in the digital healthcare ecosystem.
- The Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA): ABHA creates a standard identifier for patients across healthcare providers. With the ABHA and its associated Personal Health Record (PHR) app, citizens can link, store, and share their health records to access healthcare services with autonomy and consent. With more than 300 million ABHAs and 50 million health records linked, the mission is growing at a massive rate.
- The Health Facility Registry (HFR) and the Health Professional Registries (HPR) for central digital health information: HFR and HPR accounts provide verified digital identities to large and small public and private health facilities and professionals. This enables them to connect to a central digital ecosystem while serving as a single source for verified healthcare provider-related information. HFR and HPR improve the discovery of healthcare facilities and help health professionals build an online presence and offer services more effectively. The
- Drug registry for centralised repository of approved drugs: It is a crucial building block designed to create a single, up-to-date, centralised repository of all approved drugs across all systems of medicine.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI) enables a connect between healthcare providers with end users: It aims to strengthen the health sector by enabling all healthcare service providers and end-user applications to interact with each other on its network. This will provide a seamless experience for service discovery, appointment booking, teleconsultations, ambulance access, and more. The UHI is based on open network protocols and can address the current challenge of different digital solutions being unable to communicate with each other.
What the government is planning next in this domain?
- To give UHI the necessary push, the government is repurposing Aarogya Setu and CoWIN: Aarogya Setu is being transformed into a general health and wellness application. At the same time, CoWIN will be plugged with a lite Hospital Management Information System (HMIS) for small clinics, to bring digitisation to the masses.
- Addressing well the patient registration process at the hospital counters: Another use-case of ABDM is scan and share, which uses a QR code-based token system to manage queues at hospital counters. It uses the foundational elements of ABHA and PHR to streamline the outpatient registration process in large hospitals
- Expanding healthcare digital initiative worldwide: The government is also planning to expand its digital initiatives in the healthcare sector with Heal by India, making India’s healthcare professionals’ services available worldwide.
- Platform for organ donation: Additionally, a platform is being developed to automate the allocation of deceased organ and tissue donations, making the process faster and more transparent.
Way ahead
- Digitise insurance claim settlement process: With the implementation of digital solutions, the next step is to digitise and automate the insurance claim settlement process through the Health Claim Exchange platform.
- Making claim settlement process inexpensive and transparent: There is need to make claim-related information verifiable, auditable, traceable and interoperable among various entities, enabling claim processing to become inexpensive, transparent and carried out in real time.
- Bringing together global efforts for digital health: India assumes the G20 presidency this year. The G20 Global Initiative on Digital Health calls for the creation of an institutional framework for a connected health ecosystem to bring together global efforts for digital health.
- Accelerating UHC by scaling up the technologies: It also calls for the scaling-up of technologies such as global DPGs to accelerate Universal Health Coverage.
Conclusion
- The ABDM has proven to be a valuable asset and its adoption across states has been accelerated by the National Health Authority. It aims to build the foundation for a sustainable digital public infrastructure for health, enabling India to achieve universal health coverage. The mission embodies G20’s theme of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” or “One Earth. One Family. One Future”
Mains question
Q. India has demonstrated spectacular success in digital public goods, specifically in Digital health. Discuss how the government efforts are taking shape in this direction and suggest a way ahead in short.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Naegleria fowleri: The Brain-eating Amoeba
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Naegleria fowleri
Mains level: Not Much

South Korea reported its first case of infection from Naegleria fowleri or “brain-eating amoeba”.
What is Naegleria fowleri (Amoeba)?
- Amoeba is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods.
- Naegleria is an amoeba, a single-celled organism, and only one of its species, called Naegleria fowleri, can infect humans.
- It was first discovered in Australia in 1965 and is commonly found in warm freshwater bodies, such as hot springs, rivers and lakes.
- So far, Naegleria fowleri has been found in all continents and declared as the cause of PAM in over 16 countries, including India.
How does it infect humans?
- The amoeba enters the human body through the nose and then travels up to the brain.
- This can usually happen when someone goes for a swim, or dive or even when they dip their head in a freshwater body.
- In some cases, it was found that people got infected when they cleaned their nostrils with contaminated water/ vapour/ or aerosol droplets.
- Once Naegleria fowleri goes to the brain, it destroys brain tissues and causes a dangerous infection known as primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM).
What are the symptoms of PAM?
- The CDC says the first signs of PAM start showing within one to 12 days after the infection.
- In the initial stages, they might be similar to symptoms of meningitis, which are headache, nausea and fever.
- In the later stages, one can suffer from a stiff neck, seizures, hallucinations, and even coma.
- The infection spreads rapidly and on average causes death within about five days.
How its spread is linked to climate change?
- With the rising global temperatures, the chances of getting Naegleria fowleri infection will go up as the amoeba mainly thrives in warm freshwater bodies.
- The organism best grows in high temperatures up to 46°C and sometimes can survive at even higher temperatures.
- Various recent studies have found that excess atmospheric carbon dioxide has led to an increase in the temperature of lakes and rivers.
- These conditions provide a more favourable environment for the amoeba to grow.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s G20 Presidency: Healthcare should be a central agenda
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Linking PHC with UHC, India's G20 presidency and healthcare agenda
Context
- Health needs to be a central agenda for the G20 2023. It has been one of the priority areas for G20 deliberations since 2017, when the first meet of health ministers of G20 countries was organised by the German presidency. The G20 now has health finance in its financial stream and health systems development in the Sherpa stream.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Background: Prioritizing Health
- An annual G20 meeting of health ministers and a joint health and finance task force reflects the seriousness the subject has gained.
- The Berlin Declaration 2017 of the G20 health ministers provided a composite approach focusing on pandemic preparedness, health system strengthening and tackling antimicrobial resistance.
- The Covid-19 pandemic gave added urgency to pandemic preparedness and the Indonesian presidency in 2022 made it the major focus. The Indian presidency needs to advance these agendas.
Global community engagement to strengthen Health systems
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC): The concept of UHC was born in the 2000s to prevent catastrophic medical expenditures due to secondary and tertiary level hospital services by universalizing health insurance coverage.
- UHC as a strategy to ensure healthcare for all: The UHC has been the big global approach for health systems strengthening since 2010, also adopted in 2015 as the strategy for Sustainable Development Goal-3 on ensuring healthcare for all at all ages.
- Limited impact of UHC: However, the limited impact of this narrow strategy was soon evident, with expenditures on outdoor services becoming catastrophic for poor households and preventing access to necessary healthcare and medicines, while many unnecessary/irrational medical interventions were being undertaken.
What are the new approaches developed to strengthen healthcare system?
- Highlighted the need to prioritise primary healthcare (PHC): In 2018, the Astana Conference organised by WHO and UNICEF put out a declaration stating that primary healthcare (PHC) is essential for fulfilling the UHC objectives.
- Combined UHC- PHC approach: In 2019, the UN General Assembly adopted the combined UHC-PHC approach as a political declaration.
- World bank report on benefits of PHC services during pandemic: The World Bank published a report in 2021, “Walking the Talk: Reimagining Primary Health Care After COVID-19”. The dominant hospital-centred medical system is becoming unaffordable even for the high-income countries, as apparent during the 2008 recession and subsequently.
What is PHC-with-UHC approach?
- It means strengthening primary level care linked to non-medical preventive action (food security and safety, safe water and air, healthy workspaces, and so on)
- It works through whole-of-society and whole-of-government approaches, and extending the “PHC principles” to secondary and tertiary care services.
- This could be the most cost-effective systems design the comprehensive game changer that global health care requires.
What is to be strengthened, what initiatives can be applied and how?
- Making health central to development in all sectors: Health in all policies, one health (linking animal and human health for tackling antimicrobial resistance and zoonotic diseases), planetary health, pandemic preparedness.
- Health systems strengthening: Designing PHC-with-UHC for diverse contexts. Conceptualised as a continuum of care from self-care in households to community services, to primary level para-medical services and first contact with a doctor, services provided as close to homes as possible, affordable and easily deliverable.
- Appropriate technologies to be adopted as a norm: By strengthening health technology assessment, ethics of healthcare, equitable access to pharmaceutical products and vaccines, integrative health systems using plural knowledge systems rationally.
- Health and healthcare from the perspective of the marginalised: Gendered health care needs, Health care of indigenous peoples globally, occupational health, mental health and wellbeing, healthy ageing.
- Easy access to health knowledge for all: decolonization and democratization of health knowledge, with interests and perspectives of low-middle-income countries (LMICs), prevention and patient-centred healthcare.
India’s G20 Presidency: An opportunity to contribute and make inclusive healthcare system
- India has several pioneering initiatives that can contribute to the PHC-with-UHC discussion:
- National Health mission and dedicated health facilities: Lessons from the National Health Mission for strengthening public health delivery; the HIV-control programme’s successful involvement of affected persons/communities and a complex well-managed service structure.
- Democratized health knowledge: Pluralism of health knowledge systems, each independently supported within the national health system.
- Certified Health personnel: Health personnel such as the ASHAs, mid-level health providers and wellness centres, traditional community healthcare providers with voluntary quality certification;
- R&D and widely acknowledged pharmaceutical capacity: Research designed for validation of traditional systems; pharmaceutical and vaccines production capacity;
- Digital health as an example: Developments in digital health; social insurance schemes and people’s hospital models by civil society.
Conclusion
- What is required is the drafting of PHC-with-UHC (a PHC 2.0) with a broad global consensus and commitment to a more sustainable and people-empowering health system. Pursuing such an agenda would involve much dialogue within countries, regions and globally. India should use its presidency to draft a model policy focusing on primary healthcare that commits to a universal, affordable, inclusive and just healthcare system
Mains Question
Q. What is Primary HealthCare and Universal healthcare integrated approach? What steps are necessary to further strengthen sustainable healthcare system? Discuss how India can contribute to it under its G20 presidency?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Students suicides: A mismatch between rising aspirations, shrinking opportunities
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Addressing the issues of Students pressure, suicides, reasons and way ahead
Context
- Three students committed suicide within 12 hours in Rajasthan’s Kota, which is regarded as the education and coaching hub of India. Known for producing IITians, doctors and engineers, Kota has been in the news for the last few years because of the students’ suicides and depression they suffer.
What is Suicide?
- Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one’s own death.
- Mental and physical disorders, substance abuse, anxiety and depression are risk factors.
- Some suicides are impulsive acts due to stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying.
- Despite being entirely preventable, India has been increasingly losing individuals to suicide.
The National Crime Records Bureau’s Accidental Deaths and Suicide in India report 2021.
- The report released this year shows that the number of students’ deaths by suicide rose by 4.5 per cent in 2021.
- Maharashtra bearing the highest toll with 1,834 deaths, followed by Madhya Pradesh with 1,308, and Tamil Nadu with 1,246.
- According to the report, student suicides have been rising steadily for the last five years.
- According to a 2012 Lancet report, suicide rates in India are highest in the 15-29 age group the youth population.
- According to the National Crime Record Bureau (NCRB), in 2020, a student took their own life every 42 minutes; that is, every day, more than 34 students died by suicide.
What are the reasons behind these alarming stats of student’s suicide in India?
- Education is for livelihood more than knowledge: Education in India has been viewed as a gateway to employment and livelihood rather than to knowledge.
- Pressure to get into government jobs or highly paid private sector: Many students and their families dream of the coveted ‘sarkari naukri’ (government job) to escape the precarious social, caste and class predicaments they find themselves in.
- Limited educational infrastructure: The failure of the Union government to improve the country’s educational infrastructure means that exam-oriented coaching had become the norm.
- Coaching centres as prisons for many students: Cashing in on the ‘hope for a better future,’ coaching centres emerged as one of the predominant industries in the education sector. However, these centres are now being seen as prisons for the many youngsters who join them; where their bodies, souls and dreams are tamed.
- Number of factors marginalising students who are already vulnerable: Students from marginalised sections are pushed further to the margins through a number of factors, such as the lack of English-medium education; private institutions charging high fees; poor quality education in government-run schools and institutes; ever-growing economic inequality; graduates not having the adequate skills to secure jobs; and caste discrimination.
- Social ideology of success and failure: The rise of neoliberalism as an economic and social ideology has pushed the youth to blame themselves for their failure to secure their ‘dream job’ while the government continues to shirk its basic responsibility.
- Flawed neoliberal agenda for failure and success: The neo-liberal agenda keeps propagating the belief that it is not that hard to find success if one works hard enough, normalising the notion that the youth should blame themselves for their ‘failures’.
What are various solutions have been proposed?
- The myth of the Indian family being supportive also need to be called out: Family, being the primary social unit of the society, shapes the aspirations and dreams of the youth. Family should be supportive in true sense.
- Deeper introspection is needed instead of make shift solutions: Deeper introspection on structural aspects of the education system is the need of the hour. Instead, we take pride in coming up with Jugaad (makeshift solutions) to manage affairs peripherally, without dealing with the root of problem.
- Easing pressure in the students: Others have suggested like the guidelines issued by the Board of Intermediate Education in Andhra Pradesh in 2017 to ease the pressure on students, including yoga and physical exercise classes and maintaining a healthy student-teacher ratio.
- Realising today’s realities and making changes: It is painfully evident that the failure to address the larger issue of a punishing education system that is simply not designed to support young minds or prepare them for today’s economic realities continues.
- Collective responsibility: Not only family plays a significant role in students life, even the society has a huge influence. We as a society should realise true essence of life and not confine students into success and failure tags. Instead support them empathically in realising their true potential.
Did you know this solution? What any sensitive person will think of this?
- Some suggested bordering on the ludicrous, like the Indian Institute of Science’s reported move last year to replace ceiling fans in hostel rooms with those that are wall-mounted.
Conclusion
- Scholars have long linked farmers’ suicides to India’s agrarian crisis; it is time that civil society starts looking at students’ suicides as an indicator of a grave crisis of the country’s educational structure, including the institutional structure, curriculum, and the like. The combination of a large population of young people with rising aspirations and an economy with shrinking opportunities has created a public health crisis that requires urgent attention.
Mains Question
Q. There has been a steady increase in student suicides in India over the past few years. What are the reasons and suggest what should be done?
(Click) FREE1-to-1 on-call Mentorship by IAS-IPS officers | Discuss doubts, strategy, sources, and more
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Curbing individualism in public health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Issues in public health management
Context
- A failure to examine and interpret public health problems from a population perspective is leading to ineffective and unsustainable solutions as far as complex public health problems are concerned. There is a strong tendency in public health to prioritise individual-oriented interventions over societal oriented population-based approaches, also known as individualism in public health.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
What are the problems in public health approach?
- Micronutrient supplementation at Individualistic level instead sustainable approach at public level: Problems such as undernutrition, for which individualist solutions such as micronutrient supplementation and food fortification have been proposed as solutions in lieu of sustainable approaches such as a strengthening of the Public Distribution System, supplementary nutrition programmes, and the health services.
- Diagnosis and treatment than the solutions that modify health behaviours: Similar is the case with chronic disease control, wherein early diagnosis and treatment is the most popular solution, with little scope for solutions that can modify health behaviours (through organised community action).
Recent evidences that show individualism is preferred over population-based approach
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY): A nationwide publicly-funded insurance scheme, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) falls under Ayushman Bharat. It is the largest health insurance scheme in the country covering hospitalisation expenses for a family for ₹5 lakh a year. The goal is to ensure ‘free’ curative care services for all kinds of hospitalisation services so that there is no financial burden to the beneficiary.
- Approach needed: What is not talked about in the entire scheme is the need for hospitalisation services per year for any population.
- Approach preferred: Instead, every individual is given an assurance that if there is a need for hospitalisation expenses, the scheme will cover the expenses, highlighting the risk/probability of every individual facing hospitalisation in a year.
- Individualistic response: This is an individualistic response to the problem of hospitalisation expenditure faced by populations. This becomes obvious when one examines the data on annual hospitalisation across populations.
- vaccination for COVID-19 unlike other vaccinations: It was evident that a COVID-19 vaccine cannot prevent people from getting the disease but only reduce hospitalisation and deaths in the event of contracting COVID-19.
- Approach needed: To effectively manage COVID-19, what was needed was to have primary, secondary, and tertiary health-care facilities to manage the above proportion of cases. This is what a population-based approach to epidemic would be focusing on.
- Approach preferred: Instead, by focusing on a vaccination programme for the entire population, it is again an assurance and a promise to every individual that even if you get COVID-19, you will not need hospitalisation and not die. Even after the entire crisis, not much is talked about in terms of the grossly inadequate health-care infrastructure to ensure the necessary primary, secondary and tertiary care services for COVID-19 patients, in turn leading to many casualties.
- Individualistic response: The entire focus has been on the success story that every individual is protected from hospitalisation and death achieved through vaccine coverage. Most of the deaths due to COVID-19 are a reflection of the failure to offer ventilator and ICU support services to the 1%-2% in desperate need of it. Curative care provisioning is never planned at an individual level as epidemiologically, every individual will not necessarily need curative care every time. The morbidity profile of a population across age groups is an important criterion used to plan the curative care needs of a population.
What the data on population hospitalization suggests?
- Episode of hospitalization a year: Data from the National Sample Survey Organisation (75th round) show that on an average, only 3% of the total population in India had an episode of hospitalisation in a year (from 1% for Assam to 4% for Goa and 10% for Kerala the need also a function of availability). The proportion hovers around 3%-5% across most Indian States.
- Population based healthcare planning is necessary: This is population-based health-care planning. Instead, giving an assurance to every individual without ensuring the necessary health-care services to the population is not really helping in a crisis.
Determinants of individualistic approach
- Misconception in philosophy of public health: The dominance of biomedical knowledge and philosophy in the field of public health with a misconception that what is done at an individual level, when done at a population level, becomes public health. This is despite the contrasting philosophy and approaches of clinical medicine and public health and the evidence that support the latter and must be based on population characteristics and economic resources.
- Visibility impact and mistake of judging a population’s characteristics: Health effects are more visible and appear convincing at the individual level, wherein improvements at the population level will be clear only after population-level analysis; this needs a certain level of expertise and orientation about society an important skill required for public health practitioners.
- Market’s role and the effect of consumerism in public health practice: The beneficiaries for a programme become the maximum when 100% of the population is targeted. Instead of making efforts to supply evidence of the actual prevalence of public health problems, market forces would prefer to cast a wide net and cover 100% of beneficiaries. Propagating individualism has always been a characteristic feature of a consumerist society as every individual can then be a potential ‘customer’ in the face of risk and susceptibility.
Conclusion
- The need of the hour is population-level planning, which means, population as a single unit needs to be considered. All forms of individualistic approaches in public health need to be resisted to safeguard its original principles of practice, viz. population, prevention, and social justice.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The depopulation alert
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Population and population decline trend
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Context
- Recently, when the world population touched eight billion, several headlines focused on how India was the largest contributor to the last billion and is set to surpass China as the world’s most populous nation by 2023. But missing in this conversation is the real threat of depopulation that parts of India too face, and the country’s complete lack of preparedness to deal with it.
Note: “The population and Population decline are continuously in the headlines which makes the population and associated topics important for the upcoming Mains Examinations.”
India’s Population trend
- The total population of India currently stands at 1.37 billion which is 17.5% of the world population.
- Between 1992 and 2015, India’s Total fertility rate (TFR) had fallen by 35% from 3.4 to 2.2.
- Young people (15-29 age years) form 27.2% of the population in 2021. This made India enter the Demographic dividend stage.
- The percentage of the elderly population has been increasing from 6.8% in 1991 to 9.2% in 2016.
What is depopulation?
- The depopulation decline (also sometimes called population decline, underpopulation, or population collapse) in humans is a reduction in a human population size.
- Over the long term, stretching from prehistory to the present, Earth’s total human population has continued to grow; however, current projections suggest that this long-term trend of steady population growth may be coming to an end.
The depopulation discussion and the missing links
- Falling fertility rate and discussing reversal: Demographers, policy experts and politicians in countries such as Japan, South Korea and Europe, which are experiencing falling fertility and nearing the inflection point of population declines, are beginning to talk about what the future holds and whether reversal is possible.
- The missing key elements in the conversation: Talking about equitable sharing of housework; access to subsidized childcare that allows women to have families as well as a career; and lowered barriers to immigration to enable entry to working-age people from countries which aren’t yet in population decline is missing.
Fertility in India
- Falling fertility rate: It is now well-established that fertility in India is falling along expected lines as a direct result of rising incomes and greater female access to health and education. India’s total fertility rate is now below the replacement rate of fertility.
- Many states are on the verge of population decline: Parts of India have not only achieved replacement fertility, but have been below the replacement rate for so long that they are at the cusp of real declines in population. Kerala, which achieved replacement fertility in 1998, and Tamil Nadu, which achieved this in 2000, are examples.
- Decline in working age population: In the next four years, both Tamil Nadu and Kerala will see the first absolute declines in their working-age populations in their histories. With falling mortality (barring the pandemic), the total population of these States will continue to grow for the next few decades, which means that fewer working-age people must support more elderly people than ever before.
What is Replacement Level Fertility (RLF)?
- Replacement level fertility is the level of fertility at which a population exactly replaces itself from one generation to the next.
- In simpler terms, it denotes the fertility number required to maintain the same population number of a country over a given period of time.
- In developed countries, replacement level fertility can be taken as requiring an average of 2.1 children per woman.
- In countries with high infant and child mortality rates, however, the average number of births may need to be much higher.
- RLF will lead to zero population growth only if mortality rates remain constant and migration has no effect.
A depopulating future and the challenges
- Invisible trend because infuse of migrants: Access to working-age persons notably different from the situation in other States with low fertility. For instance, Delhi and Karnataka which are both net recipients of migrants, and will not confront population decline in the near future.
- A skewed sex ratio remains a danger: As the latest round of the NFHS showed, families with at least one son are less likely to want more children than families with just one daughter.
- Difference in education: The stark differences between northern and southern States in terms of basic literacy as well as enrolment in higher education, including in technical fields, will mean that workers from the southern States are not automatically replaceable.
Conclusion
- With decades of focus on lowering fertility, the conversation in India is stuck in a rut. It is for the southern States to break away from this outmoded, data-free rhetoric and join the global conversation on depopulation. India’s cannot ignore the depopulation in the name of migration to meet its current labour needs.
Mains question
Q. What is depopulation, which has been a hot topic in recent times? Where do you see India in global population trends? Discuss.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Union Health Ministry rolls out India’s 1st Suicide Prevention Policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: National Suicide Prevention Strategy
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare announced a National Suicide Prevention Strategy, the first of its kind in the country.
What is Suicide?
- Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one’s own death.
- Mental and physical disorders, substance abuse, anxiety and depression are risk factors.
- Some suicides are impulsive acts due to stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying.
- Despite being entirely preventable, India has been increasingly losing individuals to suicide.
Why need such strategy?
Ans. Suicides in India
- The burden of deaths by suicide has increased in India — by 7.2 per cent from 2020 — with a total of 1,64,033 people dying by suicide in 2021.
- In India, more than one lakh lives are lost every year to suicide, and it is the top killer in the 15-29 years category.
- In the past three years, the suicide rate has increased from 10.2 to 11.3 per 1,00,000 population, the document records.
- The most common reasons for suicide include family problems and illnesses, which account for 34% and 18% of all suicide-related deaths.
- The report follows a 2021 Lancet study that noted “India reports the highest number of suicide deaths in the world”.
About the National Suicide Prevention Strategy
The NSPS puts a time-bound action plan and multi-sectoral collaborations to achieve reduction in suicide mortality by 10% by 2030. The strategy broadly seeks to establish-
- Effective surveillance mechanisms for suicide within the next three years,
- Establish psychiatric outpatient departments that will provide suicide prevention services through the District Mental Health Programme in all districts within the next five years, and
- Integrate a mental well-being curriculum in all educational institutions within the next eight years.
The strategy also envisages:
- Developing guidelines for responsible media reporting of suicides and
- Restricting access to means of suicide
Significance of the strategy
- The most important thing is that the government has acknowledged that suicide is a problem.
- We now have a well-conceived plan involving multi-sectoral collaborations, because the only way a strategy would work would be to involve various sectors.
- The strategy should now be passed on to the States for them to develop locally relevant action plans; and then cascade to the district, primary health and community levels.
Why suicide is such a big issue?
- More youth committing: For the youth of the country (15-29 years), among whom 1/3rd of all suicides take place.
- Performance pressure: Data suggests that one student dies by suicide every 55 minutes, and 1,129 suicides among children below 18 years of age in 2020 were due to failure in examinations.
- Farm distress: This is followed by farmer’s suicide and the gendered variance observed these days.
- Gendered variances: More women are committing suicides these days.
Way forward

- Holistic approach: Promoting national and sectoral research into the reasons for suicide mortality and its rise, and making culturally and economically appropriate suggestions to help mitigate the problem is critical.
- Counselling by mass-media: During times of distress, media must promote health-seeking behaviour, correct information and counter the possible myths related to suicide.
- Evidence-based interventions: Keep in mind the needs of the most vulnerable and marginalized populations, like women and young individuals, providing the required support systems can reduce the number of lives lost and build a healthier response system.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Is India a Diabetes capital of the world?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Basics-Diabetes, Insulin, glucose. etc
Mains level: India's Diabetes stress, Measures
Context
- India is often referred to as the ‘Diabetes Capital of the World as it accounts for 17%percent of the total number of diabetes patients in the world. There are currently close to 80 million people with diabetes in India and this number is expected to increase to 135 million by 2045. World Diabetes day is observed on 14 November.
What is Diabetes?
- Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how our body turns food into energy.
- Diabetes is a metabolic disorder in which the body has high sugar levels for prolonged periods of time.
- The lack of insulin causes a form of diabetes.
- Type-I Diabetes: It is a medical condition that is caused due to insufficient production and secretion of insulin from the pancreas. Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). This reaction stops your body from making insulin. Approximately 5-10% of the people who have diabetes have type 1
- Type-2 diabetes: With type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t use insulin well and can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels. About 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2.
Type-2 diabetes in brief
- Long term Condition: It is long-term (chronic) condition which results in too much sugar circulating in the bloodstreams and poor response of insulin. Eventually, high blood sugar levels can lead to disorders of the circulatory, nervous and immune systems. Type 2 diabetes is an impairment in the way the body regulates and uses sugar (glucose) as a fuel. It is a defective response of Insulin
- More common in adults: Type 2 is more common in older adults, but the increase in the number of children with obesity has led to more cases of type 2 diabetes in younger people.
- Slow signs and symptoms: Signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly. Symptoms include, Increased thirst, Frequent urination, Increased hunger, Unintended weight loss, Fatigue, Blurred vision, Slow-healing sores, Frequent infections etc. It develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults (but more and more in children, teens, and young adults).
- Cure for Type-2: There’s no cure for type 2 diabetes, but losing weight, eating well and exercising can help you manage the disease. If diet and exercise aren’t enough to manage your blood sugar, you may also need diabetes medications or insulin therapy.
What is insulin?
- Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas.
- Insulin regulates the movement of sugar into your cells.
- Blood glucose levels tightly controlled by insulin.
- When the blood glucose elevates (for example, after eating food), insulin is released from the pancreas to normalize the glucose level
The prevalence of diabetes in India
- People living with Diabetes in India: There are an estimated 77 million people with diabetes in India. Which means one in every 10 adults in India has diabetes. Half of those who have high blood sugar levels are unaware. Even among those who have been diagnosed with diabetes, only half of them have their blood sugar level under control.
- Rapid increase in younger population: According ICMR report, the prevalence of diabetes in India has increased by 64 percent over the quarter-century. prevalence among the younger population has also increased above 10%.
- Children impacting more: Worryingly, in India, a large number of children are also impacted by diabetes. Children are developing obesity and metabolic syndrome early because of the change in diets to more processed and fast foods.
- Projected Estimation: About 98 million Indians could have diabetes by 2030, these projections come from the International Diabetes Federation and the Global Burden of Disease project.
- Children impacting more: Worryingly, in India, a large number of children are also impacted by diabetes. Children are developing obesity and metabolic syndrome early because of the change in diets to more processed and fast foods.
Why Indians are more prone to diabetes?
- Lifestyle changes: The current exponential rise of diabetes in India is mainly attributed to lifestyle changes. The rapid change in dietary patterns, physical inactivity, and increased body weight, especially the accumulation of abdominal fat, are some of the primary reasons for increased prevalence.
- Ethnically more prone: Ethnically, Indians seem to be more prone to diabetes as compared to the Caucasians, although the precise mechanisms are not well known. we Indians have a greater degree of insulin resistance which means our cells do not respond to the hormone insulin. And when compared to Europeans, our blood insulin levels also tend to rise higher and more persistently when we eat carbohydrates.
- Greater genetic predisposition: The epidemic increase in diabetes in India along with various studies on migrant and native Indians clearly indicate that Indians have an increased predilection to diabetes which could well be due to a greater genetic predisposition to diabetes in Indians.
- Decrease in traditional diets: At the same time, the increased ‘westernization’, especially in the metros and the larger cities, has led to a drastic change in our dietary pattens. Indian diets have always been carbohydrate-heavy and now the reliance on refined sugars, processed food in the form of quick bites and fuss-free cooking and trans fatty acids are creating havoc.
- Mechanization of day-to-day work: With the increasing availability of machines to do our work, there’s also a substantial drop in day-to-day activities.
- Consumption of high calorie food and lack of physical activities: Obesity, especially central obesity and increased visceral fat due to physical inactivity, and consumption of a high-calorie/high-fat and high sugar diets, thus become major contributing factors.
- Rapid urbanization: Currently, India is undergoing a rapid epidemiological transition with increased urbanization. The current urbanization rate is 35% compared to 15% in the 1950’s and this could have major implications on the present and future disease patterns in India with particular reference to diabetes and coronary artery disease.
- Rural-urban migration: The rural migration to urban areas and associated stress plays a significant role in lifestyle change.
Ways to manage Increasing Diabetes in India
- Aggressive Screening procedures: Indians need an upstream approach or prioritizing protection of the population as a whole, beginning with women and children. This can be done with aggressive screening procedures. “Anybody above 18, with a clear-cut risk like family history, weight issues and young women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) should be tested. All Indians above 30 should be screened.
- Timely diagnosis and right management: Medical experts feel that timely detection and right management can go a long way in helping patients lead a normal life.
- Diet discipline for children: For children, Doctors recommends a serious diet discipline. “Only healthy meals are the option that remains. Tutor the tastebuds of the young and stop their access to fast foods. There can be supportive policy measures making healthy fruits and vegetables accessible in a cost-effective manner to all instead of plain carbs. The mid-day meal or tiffin needs to be looked at thoughtfully and to make it healthy.
- Promoting physical activities: “The overall decline in physical activity has had devastating impacts on our metabolism,” while agreeing with the 30-minute a day exercise and activity schedule, sounds a note of caution. The recent scientific evidence suggests even five minutes of walk after any meal provides some protection.
- Adopting healthy Lifestyle: Though a chronic medical condition, Diabetes can be curbed at the initial level by introducing lifestyle changes. Experts suggests, reduce stress; sleep on time and for minimum of seven hours, maintaining ideal body weight, regular physical activity stop smoking, stopping/ minimum alcohol intake and get early treatment for any pre-existing or co-morbid health condition such as hypertension.
- Regular check-ups: Regular visits to the doctor are important to assess sugar control and assessment/ prevention of complications related to the disease.
Conclusion
- With the country having the highest number of diabetic patients in the world, the sugar disease is posing an enormous health problem to our country today. According to a World Health Organization (WHO) fact sheet on diabetes, an estimated 3.4 million deaths are caused due to high blood sugar in the world.
Mains Question
Q. Diabetes is increasing alarmingly across all age groups in India. Discuss the reasons and suggest measures to manage epidemic of diabetes if it is not curable?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Role of Private Sector in Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Mains level: Issues with interoperability of Private Sector under Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Context
- On 27 September, 2021, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the rollout of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission with the aim of integrating the different and disparate digital health systems that exist into a National Digital Health Ecosystem.
What is Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)?
- The ABDM currently has five main components:
- Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) number: A unique health identification number,
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): A repository of healthcare professionals across both modern and traditional systems of medicine,
- Health Facility Registry (HFR): A repository of both public and private health facilities, including hospitals, clinics, diagnostic laboratories, and pharmacies,
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): An open protocol for digital health services linking patients with healthcare providers,
- ABHA Mobile App: An app allowing an individual to carry electronic health records.
Analyzing the future of India’s health care system
- Digitization push of Government: To achieve the Sustainable Development Goals and targets of universal health coverage, the Indian government has expended significant efforts to promote the digitization of the healthcare sector to make health accessible, affordable, and equitably distributed.
- Citizens and doctors can access the health registry: The two registries would ostensibly create a database of India’s healthcare institutions and professionals that citizens would be able to access.
- Digital health card: The ABHA number and the application allow citizens to securely identify themselves and carry their health records to any healthcare facility.
- Targeted health care services: And lastly, the UHI would facilitate greater access to and delivery of healthcare services.
- Huge data for research: All of this activity has and will generate a tremendous quantity of data, which will be crucial for research, innovation, and policymaking.
Importance of private sector in health sector
- Mixed health care system: India has a mixed healthcare system, which means that it has both public and private healthcare providers. Without significant participation from the private healthcare providers, the ABDM’s ability to achieve its objectives will be limited.
- 81% doctors are private: This is because private healthcare infrastructure accounts for nearly 62 per cent of all of India’s health infrastructure and the private sector also provides 81 per cent of the doctors in India.
- Preference to private healthcare: Both rural and urban population in India seem to prefer seeking treatment from the private sector. Only 33 per cent of the rural and 26 per cent of the urban population depend on the public sector for healthcare.
Why Private health care are opting out of ABDM?
- Voluntary participation in ABDM: The voluntary nature of participation in the ABDM has led to a significant portion of private healthcare providers opting to not participate in the universal programme nor integrate into the UHI.
- High cost for digital records: Small healthcare providers like charitable hospitals, clinics, diagnostic labs, pharmacies, or nursing homes are less inclined to participate because of the significant costs involved.
- Requirement of manpower for digitization: The cost to these healthcare providers, who are most likely in various stages of digitisation, is the number of man hours required to digitise their health records and other data.
- Financial cost of digitization: The actual financial cost of upgrading or altering their digital health systems to meet basic required standards to participate in the ABDM and the UHI.
Impact of non-participation by private players
- A lack of participation from the private sector will negatively impact the objectives of the ABDM in major way:
- Limited success for UHI: Considering the concentration of private healthcare providers in urban areas, a lack of their participation and integration would limit the UHI’s ability to bring previously inaccessible services to the rural population who would otherwise have to travel to access them.
- Incomplete data and ineffective policy: The data generated by the ABDM and use of the UHI would be incomplete, which in turn would significantly limit the effectiveness of policy planning and programme delivery.
Conclusion
- It is unclear whether the government intends to achieve private sector participation through incentives or mandates. Without either approach, it seems that the ABDM will see little participation from smaller private healthcare providers, though how this will play out remains to be seen.
Mains Question
Q. What is the significance of Private Players in health care system of India? Explain the crucial role of Private health care in Ayushman Bharat digital Mission.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Centre opposes petition in HC against provisions of Surrogacy Law
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021
Mains level: Not Much

The Centre has opposed before the Delhi HC a petition challenging certain provisions of the surrogacy laws, including the Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Act, 2021, and the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021.
What is the case?
- The provisions challenged includes the exclusion of a single man and a married woman having a child from the benefit of surrogacy as a reproductive choice.
- It challenged the ban on commercial surrogacy.
- In their plea, the petitioners have stated that commercial surrogacy is the only option available to them.
Invoking Article 21
- The personal decision of a single person about the birth of a baby through surrogacy, that is, the right of reproductive autonomy is a facet of the right to privacy guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Thus, the right affecting a decision to bear or beget a child through surrogacy cannot be taken away, the petition said.
What rules say?
- Under the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, a married couple can opt for surrogacy only on medical grounds.
- The law defines a couple as a married Indian “man and woman” and also prescribes an age-criteria with the woman being in the age of 23 years to 50 years and the man between 26 years to 55 years.
- The couple should not have a child of their own.
- Though the law allows single women to resort to surrogacy, she has to be a widow or a divorcee between the age of 35 and 45 years.
- The law does not allow single men to go for surrogacy.
Distinct features of the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021
- Definition of surrogacy: It defines surrogacy as a practice where a woman gives birth to a child for an intending couple with the intention to hand over the child after the birth to the intending couple.
- Regulation of surrogacy: It prohibits commercial surrogacy, but allows altruistic surrogacy which involves no monetary compensation to the surrogate mother other than the medical expenses and insurance.
- Purposes for which surrogacy is permitted: Surrogacy is permitted when it is: (i) for intending couples who suffer from proven infertility; (ii) altruistic; (iii) not for commercial purposes; (iv) not for producing children for sale, prostitution or other forms of exploitation; and (v) for any condition or disease specified through regulations.
- Eligibility criteria: The intending couple should have a ‘certificate of essentiality’ and a ‘certificate of eligibility’ issued by the appropriate authority ex. District Medical Board.
Eligibility criteria for surrogate mother:
- To obtain a certificate of eligibility from the appropriate authority, the surrogate mother has to be:
- A close relative of the intending couple;
- A married woman having a child of her own;
- 25 to 35 years old;
- A surrogate only once in her lifetime; and
- Possess a certificate of medical and psychological fitness for surrogacy.
- Further, the surrogate mother cannot provide her own gametes for surrogacy.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Recognizing “ASHA”: The real hope
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Basics of ASHA workers
Mains level: Strengthening ASHA and basic medical facilities
Context
- One of the biggest issues facing rural health services is lack of information. ASHA workers are the first respondents even when there is lack of access to medical aid are threatened with violence and abused on the number of occasions while handlining the prospected patients in COVID19 pandemic.
Evolution of “ASHA” you may want to know
- The ASHA programme was based on Chhattisgarh’s successful Mitanin programme, in which a Community Worker looks after 50 households.
- The ASHA was to be a local resident, looking after 200 households.
- The programme had a very robust thrust on the stage-wise development of capacity in selected areas of public health.
- Many states tried to incrementally develop the ASHA from a Community Worker to a Community Health Worker, and even to an Auxiliary Nurse Midwife (ANM)/ General Nurse and Midwife (GNM), or a Public Health Nurse.
Who are ASHA workers?
- ASHA workers are volunteers from within the community who are trained to provide information and aid people in accessing benefits of various healthcare schemes of the government.
- The role of these community health volunteers under the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) was first established in 2005.
- They act as a bridge connecting marginalized communities with facilities such as primary health centers, sub-centers and district hospitals.
Qualifications for ASHA Workers
- ASHAs are primarily married, widowed, or divorced women between the ages of 25 and 45 years from within the community.
- They must have good communication and leadership skills; should be literate with formal education up to Class 8, as per the programme guidelines.
What role do the ASHA Workers play?
- Involved in Awareness programs: They go door-to-door in their designated areas creating awareness about basic nutrition, hygiene practices, and the health services available. They also counsel women about contraceptives and sexually transmitted infections.
- Ensures Mother and child health: They focus primarily on ensuring that pregnant women undergo ante-natal check-up, maintain nutrition during pregnancy, deliver at a healthcare facility, and provide post-birth training on breast-feeding and complementary nutrition of children.
- Actively involved in Immunization programs: ASHA workers are also tasked with ensuring and motivating children to get immunized.
- Providing medicines and therapies: Other than mother and childcare, ASHA workers also provide medicines daily to TB patients under directly observed treatment of the national programme. They also provide basic medicines and therapies to people under their jurisdiction such as oral rehydration solution, chloroquine for malaria, iron folic acid tablets to prevent anemia etc.
- Tasked with Screening tests: They are also tasked with screening for infections like malaria during the season. They also get people tested and get their reports for non-communicable diseases. They were tasked to quarantine the covid 19 infected patients in the pandemic.
- Informing the birth and death in respective areas: The health volunteers are also tasked with informing their respective primary health center about any births or deaths in their designated areas.
What are the challenges that ASHA workers face?
- Lack of communication threating the job of ASHA Workers: One of the biggest issues facing rural health services is lack of information.
- Lack of resources burdening the ASHA works job: Another area of concern is the lack of resources. Over the years, with the closest hospital being 9 km away and ambulances taking hours to respond, ASHA workers had to take multiple women in labour to the hospital in auto rickshaws.
- Poor medical health facilities: Medical facilities are understaffed and lack adequate equipment for various basic procedures like deliveries. Simple tests, like for sickle cell anemia and HIV, cannot be conducted in no of respective areas of ASHA workers.
- Low wages according to the job they do: The initial payment used to be paid was Rs 250 a month in 2009. Since ASHA’s unionized and agitated for a living wage. Thirteen years on, they earn around Rs 4,000 a month. It is simply not enough to sustain a family of four.
- Covid 19 disruptions added to the existing problems: Low wages forcing ASHA’s to work two or more jobs. In the pandemic, no of women lost their husband or the means of earnings and had to revert to farming. Weather fluctuations disrupting the farm produce leaving no of ASHA’s the sole earner for the family. Those who don’t have land are living in miserable conditions.
- Delayed payments reduce the morale: Payments are also delayed by months, Desperation for work leaves us unable to focus on the groundwork we do.
What can be done to improve the work conditions of ASHA workers?
- Improving the communication channels: Channels of communication between the government and the rural population need to be robust. A deadly pandemic makes the value of these channels obvious but in order to get people on board, information needs to be sent out much more effectively and in a hands-on manner. ASHA workers play a crucial role in aiding this effort. ASHA’s can’t do this alone. They need new systems to ensure the dissemination of life-saving information in remote areas.
- ASHA’s should have fixed income: ASHA’s should have a fixed income, giving them the stability in a job where they spend between eight to twelve hours daily.
- Role needs to be formalized ensuring the dignity: ASHA’s are recognized as “volunteers” currently. Their role needs to be formalized. Recognizing them as workers provides dignity and protection, and helps them to be taken seriously, by the state, the gram panchayat responsible for the disbursal of funds, and patients.
- Recognizing and awarding their role will empower and motivate ASHA’s further: For people in villages, ASHA’s have become lifelines. They have led innumerable immunization drives and are everybody’s first call in a medical emergency. They have labored to build trust and serve as a bridge with the state. Examples shows recognition gives some leverage to circumvent the system and seek funds for people in my community.
Conclusion
- ASHA’s are lifelines of rural primary healthcare, they are playing critical role on no of fronts ensuring the basic health of India. A better, stronger India is possible if ASHA’s are enabled to serve people. Giving them due recognition would serve this end, along with making rural India’s needs medical or otherwise a priority.
Mains Question
Q. For the villagers, ASHA has been a lifeline in the last few years. Acknowledge the problems they face on a daily basis and suggest solutions to raise their morale for the primary health of the village community and the nation as a whole.
Click and Get your FREE copy of Current Affairs Micro notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Physical Inactivity, Neglected Burden on Economy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Physical and mental health and economy
Context
- Global status report on physical activity is WHO’s first dedicated global assessment of global progress on country implementation of policy recommendations of the Global Action Plan on Physical Activity (GAPPA) 2018-2030.
What are the findings of the report?
- Poor physical activity standards: Over 80 per cent adolescents and 27 per cent adults do not meet the physical activity standards set by the World Health Organization (WHO), according to a new report.
- developing non-communicable diseases: This will lead to 500 million additional people developing non-communicable diseases from 2020-2030 and cost the global economy $27 billion annually, it added.
How physical Inactivity impacts health and Economy?
- Changing lifestyles: Sedentary lifestyle of a large share of the global population has been linked to rising prevalence of heart diseases, obesity, diabetes or other noncommunicable diseases.
- Increasing Hypertension and depression: Of the 500 million new cases projected, nearly half will be attributed to hypertension and 43 per cent to depression, the authors of the report said.
- A strain on the health systems: The report quantified the economic burden of not being able to meet the GAPPA target. The sharp rise in non-communicable diseases will also put a strain on the health systems in every country.
- Rising cost of treatment: If the current prevalence of physical inactivity doesn’t change, the world will incur treatment costs of just over $300 billion till 2030, the report mentioned.
- 70 per cent of health-care expenditure: The largest economic cost is set to occur among high-income countries, according to the analysis. This will account for 70 per cent of health-care expenditure on treating illness resulting from physical inactivity, it showed. Around 75 per cent of the cases will occur in low- and middle-income countries, it added.
What are the government efforts to address the physical inactivity menace?
- National physical activity policy: Less than half the countries in the world have any national physical activity policy, showed the analysis of 194 countries by WHO published October 19, 2022.
- National policies are in operation: Less than 40 per cent of the existing national policies are in operation, the United Nations health agency noted in the Global status report on physical activity 2022.
- Monitor physical activity among adolescents: As many as 75 per cent of countries monitor physical activity among adolescents, and less than 30 per cent monitor physical activity in children under 5 years.
- Addressing lack of public Infrastructure: The report highlighted that data regarding progress on certain policy actions is missing. These include provision of public open space, provision of walking and cycling infrastructure, provision of sport and physical education in schools.
- National physical activity guidelines: only 30 per cent of countries have national physical activity guidelines for all age groups, according to the findings of the report.
What are the Recommendations of WHO?
- Exercise benefits mental and physical health: Light exercise and even walking has proven benefits for mental and physical health, studies have shown.
- Infrastructural changes by governments: Citizens cannot make healthier lifestyle choices without infrastructural changes by governments such as safe walking and cycling lanes. “In policy areas that could encourage active and sustainable transport, only just over 40% of countries have road design standards that make walking and cycling safer,” the WHO analysts found.
- Five ways to address the policy gaps:
- Strengthen whole-of-government ownership and political leadership
- Integrate physical activity into relevant policies and support policy implementation with practical tools and guidance
- Strengthen partnerships, engage communities and build capacity in people
- Reinforce data systems, monitoring, and knowledge translation
- Secure sustainable funding and align with national policy commitments
- Four areas of policy intervention:
- Active societies,
- active environments,
- active people and
- active systems.
Government of India’s efforts to promote physical activity
- FIT India Movement: FIT INDIA Movement was launched on 29th August 2019 by Honorable Prime Minister with a view to make fitness an integral part of our daily lives. The mission of the Movement is to bring about behavioral changes and move towards a more physically active lifestyle.
- Objectives of Fit India: Fit India proposes to undertake various initiatives and conduct events to achieve the following objectives:
- To promote fitness as easy, fun and free.
- To spread awareness on fitness and various physical activities that promote fitness through focused campaigns.
- To encourage indigenous sports.
- To make fitness reach every school, college/university, panchayat/village, etc.
- To create a platform for citizens of India to share information, drive awareness and encourage sharing of personal fitness stories.
Conclusion
- Physical inactivity is silent poison, killing the future of the citizens. Work from home, remote working has increased the physical inactivity among the working populations. Indoor games, mobile addictions, e-learning have reduced the physical activity of children. It’s a collective responsibility of parents, society and government to promote and encourage the physical activity among citizens.
Mains Question Q.
What are the ill effects of physical inactivity on health and economy? What are the policies of government India to promote healthy life style?
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Reality check on India’s Population policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Population prospectus,NFHS report
Mains level: Declining fertility,Population prospectus and development
Context
- Earlier this year, the United Nations published data to show that India would surpass China as the world’s most populous country by 2023.According to the 2018-19Economic Survey, India’s demographic dividend will peak around2041, when the share of the working age population is expected to hit 59%.
What is the Present status of India’s population?
- Declining Total fertility rate (TFR): The Total fertility rate (TFR) has declined from 2.2 (reported in 2015-16) to 2.0 at the all- India level, according to the latest National Family Health Survey of India OR NFHS- 5 (phase 2) released by Union Health Ministry.1.6 in urban areas2.1 in Rural area and 2.0 all India.
- Sex ratio: There are 1,020 women per 1,000 men in India according to the recently released Fifth Edition (NFHS-5). Such a sex ratio has not been recorded in any of the previous four editions of the NFHS.
Need for population control measures
- At present, India hosts 16% of the world’s population with only 2.45% of the global surface area and 4% of water resources.
- The ecosystem assessments also pointed out the human population’s role in driving other species into extinction and precipitating a resource crunch.
- So, the population explosion would irreversibly impact India’s environment and natural resource base and limit the next generation’s entitlement and progress. Therefore, the government should take measures to control the population.
What will be the Impact of declining fertility?
- Implications on Political economy: It’s not just the economic implications that we need to think about but also the implications of the political economy.
- Spatial difference: India’s fertility fell below 2.1 births for certain States 10 years ago. In four other States, it’s just declining. So, not only is the fertility falling, the proportion of the population that will be living in various States is also changing.
- North-south imbalance: The future of India lies in the youth living in U.P., Bihar, M.P. If we don’t support these States in ensuring that their young people are well educated, poised to enter the labour market and have sufficient skills, they will become an economic liability.
How India can take advantage of its demographic dividend?
- Investing In literacy: If China hadn’t invested in literacy and good health systems, it would not have been able to lower its fertility rates. In any case, we have much to learn from China about what not to do.
- Planning for elderly: Especially in the case of the elderly, where the estimates show that12% of India’s total population by 2025 is going to be the elderly. Every fifth Indian by 2050 will be over the age of 65. So, planning for this segment merits equal consideration.
- Focusing on gendered dimension: India certainly has the capacity to invest in its youth population. But we don’t recognise the gender dimension of some of these challenges. Fertility decline has tremendous gender implications.
- Lowering the Burdon on women: What it means is that women have lower burden on them. But it also has a flip side. Ageing is also a gender issue as two thirds of the elderly are women, because women tend to live longer than men do. Unless we recognise the gender dimension, it will be very difficult for us to tap into these changes.
- Educating the young girls: So, what do we need to do? India has done a good job of ensuring educational opportunities to girls. Next, we need to improve employment opportunities for young women and increase the female employment rate. Elderly women need economic and social support networks.
Do we really need the population policy?
- Existing policy is right: India has a very good population policy, which was designed in 2000. And States also have their population policies. We just need to tweak these and add ageing to our population policy focus. But otherwise, the national population policy is the right policy.
- Reproductive health is important: What we need is a policy that supports reproductive health for individuals. We also need to start focusing on other challenges that go along with enhancing reproductive health, which is not just the provision of family planning services.
- Avoiding the stigma: We need to change our discourse around the population policy. Although we use the term population policy, population control still remains a part of our dialogue. We need to maybe call it a policy that enhances the population as resource for India’s development, and change the mindset to focus on ensuring that the population is happy, healthy, productive
- Thinking beyond two child policy: Our arguments and discussions have not gone beyond the two-child norm. The two-child norm indicates a coercive approach to primarily one community. And there are too many myths and misconceptions around population issues, which lead to this discourse, which takes away attentions of from real issues.
Way forward
- Family welfare approach: We need to move from a family planning approach to a family welfare approach. We should be focusing on empowering men and women in being able to make informed choices about their fertility, health and wellbeing.
- Thinking about automation: As fertility drops and life spans rise globally, the world is ageing at a significant pace. Can increasing automation counteract the negative effects of an ageing population or will an ageing population inevitably end up causing a slowdown in economic growth? We need to look at all of that.
- Changing the mindset: We are where we are, so let’s plan for the wellbeing of our population instead of hiding behind the excuse that we don’t have good schooling or health because there are too many people. That mindset is counterproductive.
- Skill development and making population productive: It is not about whether the population is large or small; it is about whether it is healthy, skilled and productive. Thomas Malthus had said as the population grows, productivity will not be able to keep pace with this growth, and we will see famines, higher mortality, wars, etc. Luckily, he proved to be wrong.
- Adhering to the Cairo consensus: Cairo International Conference on Population and Development in 1994 stressed population. The Cairo Consensus called for the promotion of reproductive rights, empowering women, universal education, maternal and infant health to untangle the knotty issue of poverty and high fertility. The consensus also demands an increase in the rate of modern contraceptive prevalence, male contraception. States instead of releasing population control measures can start to adhere to implementing the Cairo consensus.
- Adopting Women-Centric Approach: Population stabilisation is not only about controlling population growth, but also entails gender parity. So, states need to incentivize later marriages and childbirth, promoting women’s labor force participation, etc.
- Seeing Population as a Resource rather than Burden:
- As the Economic Survey, 2018-19, points out that India is set to witness a sharp slowdown in population growth in the next two decades.
- Further, population estimates also predict a generational divide between India’s north and south, Fifteen years from now.
- So instead of population control policies at the state level, India needs a universal policy to utilize population in a better way.
Conclusion
- We have the capacity to tap into the potential of our youth population. There is a brief window of opportunity, which is only there for the next few decades. We need to invest in adolescent wellbeing right away, if we want to reap the benefits. Otherwise, our demographic dividend could turn easily into a demographic disaster.
Mains Question
Q.Why India’s fertility rate is declining? How India can convert its demography into opportunity by investing in gendered based population policy?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Mental health in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Mental healthcare in India
10th October, yesterday was observed as World Mental Health Day.
What is the news?
- The Lancet released a new report calling for radical action to end stigma and discrimination in mental health.
- It stated that 90% of people living with mental health conditions feel negatively impacted by stigma and discrimination.
Mental Illness in India
- Mental disorders are now among the top leading causes of health burden worldwide, with no evidence of global reduction since 1990.
- In 2017, an estimation of the burden of mental health conditions for the states across India revealed that as many as 197.3 million people required care for mental health conditions.
- This included around 45.7 million people with depressive disorders and 44.9 million people with anxiety disorders.
- The situation has been exacerbated due to the Covid-19 pandemic, making it a serious concern the world over.
Reasons for Persistence of Mental Illness
- Stigma to seek help: The staggering figures are void of millions of others directly, or indirectly impacted by the challenge and those who face deep-rooted stigma, many times rendering them unable to seek help.
- Lack of awareness: This growing challenge in dealing with mental health issues is further compounded by a lack of information and awareness, self-diagnosis, and stigma.
- Psycho-social factors: Institutions like gender, race, and ethnicity, are also responsible for mental health conditions.
- Post-Treatment gap: There is a need for proper rehabilitation of mentally ill persons post/her treatment which is currently not present.
- Rise in Severity: Mental health problems tend to increase during economic downturns, therefore special attention is needed during times of economic distress.
Need for immediate intervention
- Neglected Area: Mental health which forms the core of our personhood is often neglected which impeded the development of an individual to full potential.
- Disproportionate impact: It is the poor, dispossessed and marginalised who bear the greatest burden of mental health problems, but historically their sufferings are dismissed as a natural extension of their social and economic conditions.
- Vulnerability of the ills: Mentally ill patients are vulnerable to and usually suffer from drug abuse, wrongful confinement, even at homes and mental healthcare facilities which is a cause of concern and a gross human right violation.
- Suicidal tendencies: Suicidal behavior was found to have relation with female gender, working condition, independent decision making, premarital sex, physical abuse and sexual abuse.
- Gendered nature: Females are more predisposed to mental disorders due to rapid social change, gender discrimination, social exclusion, gender disadvantage like marrying at young age, concern about the husband’s substance misuse habits, and domestic violence.
Policy initiatives
- National Mental Health Program (NMHP): To address the huge burden of mental disorders and shortage of qualified professionals in the field of mental health, the government has been implementing the NMHP since 1982.
- Mental HealthCare Act 2017: It guarantees every affected person access to mental healthcare and treatment from services run or funded by the government.
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2017: The Act acknowledges mental illness as a disability and seeks to enhance the Rights and Entitlements of the Disabled and provide an effective mechanism for ensuring their empowerment and inclusion in the society
- Manodarpan Initiative: An initiative under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan aims to provide psycho-social support to students for their mental health and well-being.
Way Forward
- Policy boost: Mental health situation in India demands active policy interventions and resource allocation by the government.
- Public sensitization: To reduce the stigma around mental health, we need measures to train and sensitize the community/society.
- Awareness: People should be made aware of the significance of mental health, as much as that of physical health.
- Destigmatising: Sharing one’s story about mental health (through media campaigns) is the most effective strategy to reduce stigma attached with mental illness
- Community Approach: There is need to deploy community health workers who, with appropriate training and supervision, effectively deliver psychosocial interventions for the needy
- Broadening the scope: Mental health care must embrace the diversity of experiences and strategies which work, well beyond the narrow confines of traditional biomedicine with its emphasis on “doctors, diagnoses, and drugs”.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Ayushman Bharat scheme
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat
Mains level: Success of India's health policies

India has completed four years of Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri-Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), the world’s largest public health insurance programme.
What is Ayushman Bharat?
- Ayushman Bharat is National Health Protection Scheme, which will cover over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families (approximately 50 crore beneficiaries) providing coverage upto 5 lakh rupees per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- It was launched in September 2018 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme and is jointly funded by both the union government and the states.
- It has subsumed the on-going centrally sponsored schemes – Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana (RSBY) and the Senior Citizen Health Insurance Scheme (SCHIS).
Features of the scheme
- It will have a defined benefit cover of Rs. 5 lakh per family per year.
- Benefits of the scheme are portable across the country and a beneficiary covered under the scheme will be allowed to take cashless benefits from any public/private empanelled hospitals across the country.
- It will be an entitlement based scheme with entitlement decided on the basis of deprivation criteria in the SECC database.
- The beneficiaries can avail benefits in both public and empanelled private facilities.
- To control costs, the payments for treatment will be done on package rate (to be defined by the Government in advance) basis.
India’s health expenditure post Ayushman Bharat
Ans. India’s public healthcare spending is still among the lowest in the world.
- Total health expenditure declined to 3.2% of GDP in 2018-19 from 3.3% in 2017-18, while the government’s health expenditure (centre and state) as a percentage of GDP fell from 1.35% to 1.28% in the same period.
- National health estimates showed the Centre’s share decreasing to 34.3% in 2018-19 from 40.8% in the previous year, while that of states rose from 59.2% to 65.7%.
- Out-of-pocket spending as a percentage of total health expenditure declined to 48.2% in 2018-19, though it is significantly higher than the world average of 18.1% in 2019
What about health insurance penetration?
Ans. Retail health insurance covers a meagre 3.2% of the country’s population.
- With a population of 1.36 billion, India is the world’s second most populous country, and is expected to surpass China soon.
- Launched in 2018 to provide universal health coverage, AB-PMJAY, takes care of the bottom 50% of the population of approximately 700 million individuals.
- The top 20% of the population is covered through social and private health insurance.
- Therefore, about 30% of the population, or about 400 million, is “the missing middle”— they don’t have any financial protection for health emergencies.
Why is sound healthcare important for the economy?
- Covid-19 exposed the economic consequences of poor healthcare. Higher out-of-pocket healthcare spending hits savings and consumption.
- In the work space, poor health impacts physical and mental abilities, increase turnover and lead to lower productivity.
- Data shows that 7% of India’s population is pushed into poverty every year due to healthcare costs.
Way forward
- Healthcare management and disease prevention should be the focus, along with an all-encompassing healthcare system, including OPD.
- The government also needs to pay attention on healthcare cover for “the missing middle” population.
- As a pilot, states may allow the authority already implementing the AB-PMJAY scheme in the state to cover the missing middle.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Congenital Heart Disease
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Heart, and Heart Diseases
Mains level: Health
 Context
Context
- Congenital Heart Disease (CHD), which the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC), Atlanta, U.S., acknowledges to be the most common congenital disorder, is responsible for 28% of all congenital birth defects, and accounts for 6%-10 % of all the infant deaths in India. 29 September is celebrated as world heart day.
What is Congenital Heart Disease (CHD)?
- Congenital heart disease is a general term for a range of birth defects that affect the normal way the heart works. The term “congenital” means the condition is present from birth.
 What is paediatric cardiac care?
What is paediatric cardiac care?
- Paediatric cardiologists diagnose, treat, and manage heart problems in children, including. “Congenital heart disease” (heart differences children are born with), such as holes between chambers of the heart, valve problems, and abnormal blood vessels
What is the Present situation of Congenital Heart Disease In India?
- It is estimated that over 1,00,000 children keep getting added to the existing pool of children awaiting surgery.
- According to the Paediatric Cardiac Society of India (PCSI), the prevalence of congenital cardiac anomalies is one in every 100 live births; or an estimated 2,00,000 children are born with CHD every year. Only 15,000 of them receive treatment.
- At least 30% of infants who have complex defects require surgical intervention to survive their first birthday but only 2,500operations can be performed each year. A case in point is the premier All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), where infants are waitlisted till 2026 for cardiac surgery.
 What are the Reasons behind this worrisome situation?
What are the Reasons behind this worrisome situation?
- Lack of money: There has been more neglect and little improvement in child health care because creating a comprehensive paediatric cardiology care service is usually considered economically unviable — it is resource intensive and requires infrastructure investment that politicians and policy makers choose to evade.
- Infrastructure: There are 22 hospitals and less than 50 centres in India with infant and neonatal cardiac services.
- Uneven distribution: Geographically, these centres are not well distributed either. 2018 cardiology department report of AIIMS, highlighted how South India accounted for 70% of these centres; most centres are located in regions with a lower burden of CHD. For instance, Kerala has eight centres offering neonatal cardiac surgeries for an estimated 4.5 lakh annual childbirths. Populous Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, with an estimated annual childbirth of 48 and 27 lakh births per annum, respectively (Census of India, 2012), do not have a centre capable of performing neonatal cardiac surgery.
- Non-priority: A 2018 article by the Department of Cardiothoracic Cardiology, AIIMS, states, “paediatric cardiology is not a priority area in the face of competing demands for the resources
What are the problems in treating congenital Heart Disease?
- Doctor population ratio: For 600 districts with a 1.4 billion population, there are only 250 paediatric cardiologists available. The doctor to patient ratio is an abysmal one for half-a-crore population. According to the Annals of Paediatric Cardiology journal, the United States had 2,966 paediatric cardiologists in 2019, ratio of one per 29,196population.
- Poverty: Poverty is another barrier before treatment. Transporting sick neonates from States with little or no cardiac care facilities to faraway centres for accurate diagnosis and treatment burdens parents financially.
- Medical devices: In addition, there is the non-availability of crucial equipment that is essential for diagnosis of heart diseases in the unborn. Accentuating the problem is the general lack of awareness about early symptoms of CHD among parents.
 What should be approach for the treatment of Congenital Heart Disease?
What should be approach for the treatment of Congenital Heart Disease?
- Timely treatment: Paediatricians say timely medical intervention can save 75% of these children and give them normal lives.
- National policy: The lack of a national policy for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases in children keeps a huge number outside the ambit of treatment.
- Echocardiography: The Child Heart Foundation, a non-governmental organisation working in Siliguri (WestBengal), Jalandhar (Punjab) and Delhi, with underprivileged children with CHD, has been flagging the need for fatal echocardiography.
- Hridayam: There are programmes worth emulating such as Kerala’s ‘Hridayam (for little hearts)’,aimed at early detection, management and support to children with CHD or the Tamilnadu Chief Minister’s Comprehensive Health Insurance Scheme offering free specialised surgeries.
- Ayushman Bharat: The National Health Protection Scheme (Ayushman Bharat), is expected to financially assist 10 crore poor families but has still to takeoff. So far, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh have apparently got going.
Conclusion
- India’s performance in neo natal care is very regrettable. India can drastically reduce its infant mortality by investing in paediatric cardiac care. Sooner we realize this better will be the future of India.
Mains Question
Q.Infant mortality India out of congenital Heart Disease is because of negligence and non-priority. Acknowledge the problems and suggest solutions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Rising number of Rabies case
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: particulars of virus
Mains level: Human health
 Context
Context
- The death of a 12-year-old girl in Pathanamthitta has sharpened the focus on the rising number of rabies cases and the growing population of stray dogs in Kerala
What is rabies?
- The rabies virus attacks the central nervous system of the host, and in humans, it can cause a range of debilitating symptoms including states of anxiety and confusion, partial paralysis, agitation, hallucinations, and, in its final phases, a symptom called “hydrophobia,” or a fear of water.
What are rabies caused by?
- Rabies is a preventable viral disease most often transmitted through the bite of a rabid animal. The rabies virus infects the central nervous system of mammals, ultimately causing disease in the brain and death.
Can rabies person survive?
- Once clinical signs of rabies appear, the disease is nearly always fatal, and treatment is typically supportive. Less than 20 cases of human survival from clinical rabies have been documented.
How long can a human live with rabies?
- Death usually occurs 2 to 10 days after first symptoms. Survival is almost unknown once symptoms have presented, even with intensive care.
 Facts on rabies
Facts on rabies
- What animal has the most rabies?
- Bats
- Wild animals accounted for 92.7% of reported cases of rabies in 2018. Bats were the most frequently reported rabid wildlife species (33% of all animal cases during 2018), followed by raccoons (30.3%), skunks (20.3%), and foxes (7.2%).
 What is the issue?
What is the issue?
- There is a blame game over the rising rabies cases: With the rabies deaths causing panic and reports of residents killing stray dogs through poisoning and strangulation, there is a blame game over the rising canine population and rabies cases. Some legal experts blame it on conflicts in the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960 and the Animal Birth Control (Dogs) Rules, 2001; others point to the flawed implementation of birth control measures.
- Legal battle over the issue in the Supreme Court: Canine culling campaigners and advocates of animal rights are also engaged in a protracted legal battle over the issue in the Supreme Court. V.K. Biju, a lawyer of the Supreme Court, who brought the issue of the “stray dog menace” before the apex court, contends that the root cause is the enactment of the Rules, which according to him, were passed in contravention of the parent Act, the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act.
- Existence of stray dogs has adversely affected the fundamental rights of citizens: Biju says that while the Act stands for the “destruction” of stray dogs, the rules are against the “destruction” of stray dogs, including the rabies affected ones, besides providing specific protection of stray dogs. In his submission before the Supreme Court, he argues that the existence of stray dogs has adversely affected the fundamental rights of citizens, i.e. the right to life and free movement.
- The quashing of the Rules to make India free of stray dogs: In his writ petition filed before the apex court, Biju has sought orders for the strict implementation of the Act and the quashing of the Rules to make India free of stray dogs.
- Animal rights campaigners are apprehensive: In the light of this, animal rights campaigners are apprehensive over the campaign to cull dogs to check rabies.
 How can we prevent rabies in animals?
How can we prevent rabies in animals?
- First, visit your veterinarian with your pet on a regular basis and keep rabies vaccinations up-to-date for all cats, ferrets, and dogs.
- Second, maintain control of your pets by keeping cats and ferrets indoors and keeping dogs under direct supervision.
- Third, spay or neuter your pets to help reduce the number of unwanted pets that may not be properly cared for or vaccinated regularly.
- Finally, call animal control to remove all stray animals from your neighbourhood since these animals may be unvaccinated or ill.
How can we prevent rabies in humans?
- Leave all wildlife alone.
- Know the risk: contact with infected bats is the leading cause of rabies deaths in people followed by exposure to rabid dogs while traveling internationally.
- Wash animal bites or scratches immediately with soap and water.
- If you are bitten, scratched, or unsure, talk to a healthcare provider about whether you need postexposure prophylaxis. Rabies in people is 100% preventable through prompt appropriate medical care.
- Vaccinate your pets to protect them and your family.
Initiatives by Government to curb Neglected Tropical Diseases
National Rabies Control Programme: This programme is being restructured as Integrated National Rabies Control Programme under ‘One Health Approach’, with a aim to provide vaccination to stray dogs and free vaccines through Government hospitals.
Way forward
- Think globally, act locally. Study and adopt global ‘best-practices’ after customising them to local needs.
- Apply integrated approach. Follow a holistic strategy.
- Ensure efficient and effective collaboration across various government departments.
- Partner with Civil Society Organisations (especially with WASH – Water, Sanitation and Hygiene – sector) for ground-level implementation and monitoring.
Mains question
Q. What is rabies? What ethical challenges are involved in culling of stray dogs? Explain the control measures for the same.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Fighting anaemia
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: iron fortification
Mains level: women health
 Context
Context
- The recent National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) data shows anaemia rates increased from 53 per cent to 57 per cent in women and 58 per cent to 67 per cent in children in 2019-21.
Definition of anaemia
- The WHO defines anaemia as a condition where the number of red blood cells or the haemoglobin concentration within them is lower than normal. This compromises immunity and impedes cognitive development.
Why anaemia is a concern?
- Adverse effects of anaemia affect all age groups lower physical and cognitive growth and alertness among children and adolescents, and lesser capacity to learn and play, directly impacting their future potential as productive citizens.
- Anaemia among adolescent girls (59.1 per cent) advances to maternal anaemiaand is a major cause of maternal and infant mortality and general morbidity and ill health in a community.
What causes anaemia?
- Imbalanced diet: Cereal-centric diets, with relatively less consumption of iron-rich food groups like meat, fish, eggs, and dark green leafy vegetables (DGLF), can be associated with higher levels of anaemia.
- Underlying factors: High levels of anaemia are also often associated with underlying factors like poor water quality and sanitation conditions that can adversely impact iron absorption in the body.
- Iron deficiency is major cause: A diet that does not contain enough iron, folic acid, or vitamin B12 is a common cause of anaemia.
- Some other conditions: That may lead to anaemia include pregnancy, heavy periods, blood disorders or cancer, inherited disorders, and infectious diseases.
 Why is anaemia so high in the country?
Why is anaemia so high in the country?
- Low vitamin intake: Iron-deficiency and vitamin B12-deficiency anaemia are the two common types of anaemia in India.
- High population and nutrition deprivation: Among women, iron deficiency prevalence is higher than men due to menstrual iron losses and the high iron demands of a growing foetus during pregnancies.
- Overemphasis on cereals: Lack of millets in the diet due to overdependence on rice and wheat, insufficient consumption of green and leafy vegetables could be the reasons behind the high prevalence of anaemia in India.
What is Iron fortification?
- Iron fortification of food is a methodology utilized worldwide to address iron deficiency. Iron fortification programs usually involve mandatory, centralized mass fortification of staple foods, such as wheat flour.
 Why need iron fortification?
Why need iron fortification?
- Iron deficiency anaemia is due to insufficient iron.
- Without enough iron, the body can’t produce enough of a substance in red blood cells that enables them to carry oxygen (haemoglobin).
- Severe anaemia during pregnancy increases risk of premature birth, having a low birth weight baby and postpartum depression. Some studies also show an increased risk of infant death immediately before or after birth.
 Success story / value addition
Success story / value addition
- Nepal’s success story to improve maternal anaemia by national action plan .
Anaemia Mukt Bharat
- The scheme aims to reduce the prevalence of anaemia in India.
- It provides bi weekly iron Folic acid supplementation to all under five children through Asha workers.
- Also, it provides biannual Deworming for children and adolescents. The scheme also establishes institutional mechanisms for advanced research in anaemia.
- It also focuses on non-nutritional causes of anaemia.
We need to focus on the following interventions
- Prophylactic Iron and Folic Acid supplementation.
- Intensified year-round Behaviour Change Communication Campaign (Solid Body, Smart Mind).
- Appropriate infant and young child feeding practices.
- Increase in intake of iron-rich food through diet diversity/quantity/frequency and/or fortified foods with focus on harnessing locally available resources.
- Testing and treatment of anaemia, using digital methods and point of care treatment, with special focus on pregnant women and school-going adolescents
- Mandatory provision of Iron and Folic Acid fortified foods in government-funded public health programmes
Way forward
- India’s nutrition programmes must undergo a periodic review.
- The Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), which is perceived as the guardian of the nation’s nutritional well-being must reassess itself and address critical intervention gaps, both conceptually and programmatically, and produce rapid outcomes.
- The nutritional deficit which ought to be considered an indicator of great concern is generally ignored by policymakers and experts. Unless this is addressed, rapid improvement in nutritional indicators cannot happen.
Conclusion
- When a person is anaemic, the capacity of his blood cells to carry oxygen decreases. This reduces the productivity of the person which in turn affects the economy of the country. Therefore, it is highly important to cover Anaemia under National Health Mission.
Mains question
Q. “Every second adolescent girl has anaemia. Every second woman of reproductive age is anaemic”. In this context do you think Women’s empowerment will not have any meaning without tackling anaemia? Discuss.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Public health should be led by doctor alone
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Health care sector reforms
 Context
Context
- Doctor shortages are creating hurdles in health emergency response
What is the crux of the article in simple words?
- Medical qualification and expertise is necessary to deliver quality health services by medical professionals unlike by general health care workers who lack competency.
What is public health?
- Public health has been defined as “the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals”.
Why there is need of qualification?
- Lack of training: Health workers have no training in public health; they are grassroots-level service providers. Asking them to be part of public health cadre trivialises the profession of public health.
- Separate profession: It is important to understand that public health is a separate profession with a specific set of competencies.
 What are 4 pillars of public health?
What are 4 pillars of public health?
- Academics: Academics refers to a good understanding of evidence generation and synthesis by having a good grounding in epidemiology and biostatistics. These competencies are also critical for monitoring and evaluating programmes, conducting surveillance, and interpreting data and routine reporting.
- Activism: Public health is inherently linked to ‘social change’ and an element of activism is core to public health. Public health requires social mobilisation at the grassroots level by understanding community needs, community organisation, etc. This requires grounding in social and behavioural sciences.
- Administration: Administration refers to administering health systems at different levels from a primary health centre to the district, State, and national level. This includes implementing and managing health programmes, addressing human resource issues, supply and logistical issues, etc. It includes microplanning of programme delivery, team building, leadership as well as financial management to some extent.
- Advocacy: In public health, there is little that one can do at an individual level; there must be communication with key stakeholders to change the status quo at different levels of government. This requires clear enunciation of the need, analysis of alternative set of actions and the cost of implementation or non-implementation. Good communication and negotiation skills are critical to perform this function. The related subjects are health policy, health economics, health advocacy and global health.
 What are the hurdles in absorbing others as public health professionals?
What are the hurdles in absorbing others as public health professionals?
- Lack of skill: Many doctors and other health professionals work at the grassroots level and develop a good sense of public health due to their inclination. But they do not become public health professionals as they may not have the necessary skills. Nevertheless, they are valuable.
- Lack of critical expertise: Clinicians with training in epidemiology and biostatistics would not qualify to be public health professionals as they lack not only other essential and critical expertise but also an appropriate perspective.
- Compromise on quality:
Current challenges faced by public healthcare in India
- Deficiency: The doctor-patient ratio of 1:1655 in India as against WHO norm of 1:1000 clearly shows the deficit of MBBS. While the government is working towards a solution and targeting to reach the required ratio, there is a need to relook at the overall medical education.
- Post pandemic scenario: The lag in formal medical education has come up evidently post-pandemic when the nation saw the medical fraternity struggling to fill the doctor deficit.
- Limited government seats: The number of seats available for medical education in India is far less than the number of aspirants who leave school with the dream of becoming doctors.
- Lack of skills: Though the institutes are managing to hire professors and lecturers, there is a lack of technical skills. Finding faculties in clinical and non-clinical disciplines is difficult and there are very few faculty development programs for upskilling the existing lot.
- Lack of infrastructure: The gap in digital learning infrastructure is currently the biggest challenge the sector is facing. There is an urgent need to adopt technology and have resources available to facilitate e-learning.
- Lack of research and innovation: The medical research and innovation needs an added push as there haven’t been many ground-breaking research here. The education system needs to focus more on increasing the quality of research. Additionally since industry academia partnership is not available, hence innovation also takes a back-seat.
Conclusion
- By establishing new medical colleges, the government can increase student intake as well as enhance equitable access to public health as separate profession. This will attract the best and the brightest people into this discipline, which is very important for the nation’s health. This is one lesson that we should learn from the pandemic.
Mains question
Q. What do you understand by public health? Do you think it is a separate profession requiring a specific set of competencies? Examine.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Global pandemic treaty to avert future mishap
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: future preparedness for pandemics
 Context
Context
- The outline of an essential global pandemic treaty.
Purpose of the treaty
- A pandemic treaty under the umbrella of the World Health Organization would build coherence and avoid fragmentation of response.
Severity of this pandemic demands such treaty
- COVID-19 would count as being among some of the most severe pandemics the world has seen in the last 100 years. An estimated 18 million people may have died from COVID-19, according various credible estimates, a scale of loss not seen since the Second World War.
- Further, with over 120 million people pushed into extreme poverty, and a massive global recession, no single government or institution has been able to address this emergency singlehandedly.
- This has given us a larger perspective of how nobody is safe until everybody is safe.
Catchy line for value addition
Nobody is safe until everybody is safe
 There is widespread inequity in healthcare
There is widespread inequity in healthcare
- Gross inequity in distribution: Health-care systems have been stretched beyond their capacity and gross health inequity has been observed in the distribution of vaccines, diagnostics, and therapeutics across the world.
- Irreversible consequences: While high-income economies are still recovering from the aftereffects, the socioeconomic consequences of the novel coronavirus pandemic are irreversible in low and low middle-income countries.
- The monopolies: Held by pharma majors such as Pfizer, BioNTech, and Moderna created at least nine new billionaires since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic and made over $1,000 a second in profits, even as fewer of their vaccines reached people in low-income countries.
- Skewed distribution: As of March 2022, only 3% of people in low-income countries had been vaccinated with at least one dose, compared to 60.18% in high-income countries. The international target to vaccinate 70% of the world’s population against COVID-19 by mid-2022 was missed because poorer countries were at the “back of the queue” when vaccines were rolled out.
 India’s lead role
India’s lead role
- Dynamic response: India’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic and reinstating global equity by leveraging its own potential has set an example to legislators worldwide.
- Vaccine diplomacy: India produces nearly 60% of the world’s vaccines and is said to account for 60%-80% of the United Nations’ annual vaccine procurement “vaccine diplomacy” or “vaccine maitri” with a commitment against health inequity.
- We lead by example: India was unfettered in its resolve to continue the shipment of vaccines and other diagnostics even when it was experiencing a vaccine shortage for domestic use. There was only a brief period of weeks during the peak of the second wave in India when the vaccine mission was halted.
- A classic example of global cooperation: As of 2021, India shipped 594.35 lakh doses of ‘Made-in-India’ COVID-19 vaccines to 72 countries a classic example of global cooperation. Among these, 81.25 lakh doses were gifts, 339.67 lakh doses were commercially distributed and 173.43 lakh doses were delivered via the Covax programme under the aegis of Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance.
Why the treaty is needed for?
- Data sharing: A treaty should cover crucial aspects such as data sharing and genome sequencing of emerging viruses.
- Rapid response mechanism: It should formally commit governments and parliaments to implement an early warning system and a properly funded rapid response mechanism.
- Health investments: Further, it should mobilise nation states to agree on a set of common metrics that are related to health investments and a return on those investments. These investments should aim to reduce the public-private sector gap.
Conclusion
- A global pandemic treaty will not only reduce socioeconomic inequalities across nation states but also enhance a global pandemic preparedness for future health emergencies. India must take the lead in this.
Mains question
Q. Nobody is safe until everybody is safe. What do you understand by this? Why there is need of global pandemic treaty?.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Mental Health in india
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: manodarpan initiative
Mains level: mental health
 Context
Context
- How to deal with mental wellness challenges in the uniformed forces
What is stress?
- Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stress is your body’s reaction to a challenge or demand.
What is mental wellness?
- Mental wellness encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences cognition, perception, and behaviour. It also determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making.
Why is Mental Health Important?
- Mental health is more important now than ever before; it impacts every area of our lives. The importance of good mental health ripples into everything we do, think, or say.
 Reasons for Persistence of Mental Illness
Reasons for Persistence of Mental Illness
- Stigma to seek help: The staggering figures are void of millions of others directly, or indirectly impacted by the challenge and those who face deep-rooted stigma, many times rendering them unable to seek help.
- Lack of awareness: This growing challenge in dealing with mental health issues is further compounded by a lack of information and awareness, self-diagnosis, and stigma.
- Psycho-social factors: Institutions like gender, race and ethnicity, are also responsible for mental health conditions.
- Post-Treatment gap: There is a need for proper rehabilitation of the mentally ill persons post/her treatment which is currently not present.
- Rise in Severity: Mental health problems tend to increase during economic downturns, therefore special attention is needed during times of economic distress.
 Ongoing challenges in mental wellness regime
Ongoing challenges in mental wellness regime
- There is a need to expand understanding of the full scope of what uniformed Services and other mental health experts can achieve.
- Stigma regarding mental health both domestically and around the world remains strong.
- There is a lack of trained personnel and healthcare and public health systems in many areas of the world.
- Training needs are broad and reach beyond direct patient care, especially regarding cultural competence, crisis communication, and consultation.
- There is a need for expanded support for the value of multi-professional and multi-organizational integration and collaboration.
Government Policy initiatives
- National Mental Health Program (NMHP): To address the huge burden of mental disorders and shortage of qualified professionals in the field of mental health, the government has been implementing the NMHP since 1982.
- Mental HealthCare Act 2017: It guarantees every affected person access to mental healthcare and treatment from services run or funded by the government.
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2017: The Act acknowledges mental illness as a disability and seeks to enhance the Rights and Entitlements of the Disabled and provide an effective mechanism for ensuring their empowerment and inclusion in the society
- Manodarpan Initiative: An initiative under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan aims to provide psycho-social support to students for their mental health and well-being.
What needs to be done?
- Open dialogue: The practice of open dialogue, a therapeutic practice that originated in Finland, runs through many programmes in the Guidance. This approach trains the therapist in de-escalation of distress and breaks power differentials that allow for free expression.
- Increase investment: With emphasis on social care components such as work force participation, pensions and housing, increased investments in health and social care seem imperative.
- Network of services: For those homeless and who opt not to enter mental health establishments, we can provide a network of services ranging from soup kitchens at vantage points to mobile mental health and social care clinics.
Conclusion
- Persons with mental health conditions need a responsive care system that inspires hope and participation without which their lives are empty. We should endeavour to provide them with such a responsive care system.
Mains question
Q. Mental disorders are now among the top leading causes of health burden worldwide, with no evidence of global reduction since 1990. Examine.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Bhang, Ganja, and criminality in the NDPS Act
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NDPS Act
Mains level: Issues with NDPS Act

While granting bail to a man arrested on June 1 for possessing 29 kg of bhang and 400 g of ganja, Karnataka High Court recently observed that nowhere in the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act is bhang referred to as a prohibited drink or prohibited drug.
What is Bhang?
- Bhang is the edible preparation made from the leaves of the cannabis plant, often incorporated into drinks such as thandai and lassi, along with various foods.
- Bhang has been consumed in the Indian subcontinent for centuries, and is frequently consumed during the festivals of Holi and Mahashivratri.
- Its widespread use caught the attention of Europeans, with Garcia da Orta, a Portuguese physician who arrived in Goa in the 16th century, noting that, “Bhang is so generally used and by such a number of people that there is no mystery about it”.
Bhang and the law
- Enacted in 1985, the NDPS Act is the main legislation that deals with drugs and their trafficking.
- Various provisions of the Act punish production, manufacture, sale, possession, consumption, purchase, transport, and use of banned drugs, except for medical and scientific purposes.
- The NDPS Act defines cannabis (hemp) as a narcotic drug based on the parts of the plant that come under its purview. The Act lists these parts as:
- Charas: “The separated resin, in whatever form, whether crude or purified, obtained from the cannabis plant and also includes concentrated preparation and resin known as hashish oil or liquid hashish.”
- Ganja: “The flowering or fruiting tops of the cannabis plant (excluding the seeds and leaves when not accompanied by the tops), by whatever name they be known or designated.”
- “Any mixture, with or without any neutral material, of any of the above forms of cannabis or any drink prepared therefrom.”
- The Act, in its definition, excludes seeds and leaves “when not accompanied by the tops”.
- Bhang, which is made with the leaves of the plant, is not mentioned in the NDPS Act.
Cannabis and criminal liability
- Section 20 of the NDPS Act lays out the punishment for the production, manufacture, sale, purchase, import and inter-state export of cannabis, as defined in the Act.
- The prescribed punishment is based on the amount of drugs seized.
- Contravention that involves a small quantity (100 g of charas/hashish or 1 kg of ganja), will result in rigorous imprisonment for a term that may extend to one year and/or a fine which may extend to Rs 10,000.
- For a commercial quantity (1 kg charas/ hashish or 20 kg ganja), rigorous imprisonment of not less than 10 years, which may extend to 20 years, including a fine that is not less than Rs 1,00,000 but may extend to Rs 2,00,000.
- Where the contravention involves quantity less than commercial, but greater than small quantity, rigorous imprisonment up to 10 years is prescribed, along with a fine which may extend to Rs 1,00,000.
Also read:
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
National Digital Health Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Digital health id
Mains level: National digital health mission
 Context
Context
- The covid-19 pandemic has presented a watershed moment, bringing the world’s healthcare systems to a halt, forcing us to rethink existing healthcare delivery models and embrace the digital health transformation of the sector.
Definition of digital health care
- Digital health is a discipline that includes digital care programs, technologies with health, healthcare, living, and society to enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery and to make medicine more personalized and precise.
Digital Health: A Backgrounder
- The National Health Policy 2017 had envisaged creation of a digital health technology eco-system aiming at developing an integrated health information system.
- A Digital Health ID was proposed to reduce the risk of preventable medical errors and significantly increase the quality of care.
- It recognised the need to establish a specialised ecosystem, called the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM).
 The National Digital Health Mission
The National Digital Health Mission
- The NDHM is a digital health ecosystem under which every Indian citizen will now have unique health IDs, digitized health records with identifiers for doctors and health facilities.
- The mission will significantly improve the efficiency, effectiveness, and transparency of health service delivery and will be a major step towards the achievement of the UN Sustainable Development Goal 3.8 of Universal Health Coverage, including financial risk protection.
 Significance of digital health
Significance of digital health
- Prioritizing patients: Say, mortality from Covid-19 is significantly increased by comorbidities or the presence of other underlying conditions like hypertension or diabetes.With digital health records, doctors can prioritise patients based on their test results.
- Portability of health records: Portability of records fairly eases in a patient with the first hospital visit, or her/his most frequently visited hospital. If she/he wishes to change a healthcare provider for cost or quality reasons, she can access her health records without carrying pieces of paper prescriptions and test reports. People will able to access their lab reports, x-rays and prescriptions irrespective of where they were generated, and share them with doctors or family members — with consent.
- Easy facilitation: This initiative will allow patients to access healthcare facilities remotely through e-pharmacies, online appointments, teleconsultation, and other health benefits. Besides, as all the medical history of the patient is recorded in the Health ID card, it will help the doctor to understand the case better, and improved medication can be offered.
- Technology impetus in policymaking: Meanwhile, it is also not just individuals who could emerge beneficiaries of the scheme. With large swathes of data being made available, the government too can form policies based on geographical, demographical, and risk-factor based monitoring of health.
Critical point to remember
In the case of lung cancer, only 18.5 % of patients survive five or more years once diagnosed. These are threats that data-led technology will help address.
Major privacy issues involved
- Informed Consent:The citizen’s consent is vital for all access. A beneficiary’s consent is vital to ensure that information is released.
- Data leakages issue:Personalised data collected at multiple levels are a “sitting gold mine” for insurance companies, international researchers, and pharma companies.
- Digital divide:Other experts add that lack of access to technology, poverty, and lack of understanding of the language in a vast and diverse country like India are problems that need to be looked into.
- Data Migration:The data migration and inter-State transfer are still faced with multiple errors and shortcomings in addition to concerns of data security.
Other challenges
- Existing digitalization is yet incomplete:India has been unable to standardise the coverage and quality of the existing digital cards like One Nation One Ration card, PM-JAY card, Aadhaar card, etc., for accessibility of services and entitlements.
- Lack of healthcare facilities:The defence of data security by expressed informed consent doesn’t work in a country that is plagued by the acute shortage of healthcare professionals to inform the client fully.
- Lack of finance:With the minuscule spending of 1.3% of the GDP on the healthcare sector, India will be unable to ensure the quality and uniform access to healthcare that it hoped to bring about.
Conclusion
- With an enabling ecosystem, supported by effective policies for digital healthcare and increased innovation, the promise of digital solutions in healthcare is immense. It’s not long before precision healthcare becomes central to the health and well-being of every citizen.
Mains question
Q. The covid-19 pandemic has presented a watershed moment, bringing the world’s healthcare systems to a halt, forcing us to rethink existing healthcare delivery models. In this context discuss challenges and opportunities of digital health ecosystem in India.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Equitable education and health care needed for better future
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: equitable health and education
 Context
Context
- To create the foundation for the next century, we need to invest in equitable education and health care in the next 25 years not just for the elite, but for all.
What is current status of education?
- Expenditure on Education: The expenses on education as a percentage to GDP, India lags behind some developed/ developing nations.
- Infrastructure deficit: Dilapidated structures, single-room schools, lack of drinking water facilities, separate toilets and other educational infrastructure is a grave problem.
- Student-teacher ratio: Another challenge for improving the Indian education system is to improve the student teacher ratio.
What is current status of healthcare?
- Weak delivery: Current health infrastructure in India paints a dismal picture of the healthcare delivery system in the country.
- Unpreparedness: Public health experts believe that India is ill-equipped to handle emergencies.
- Technical glitches in urban areas: It is not prepared to tackle health epidemics, particularly given its urban congestion.
A systemic approach to reforming education system in the country needs
- Dynamic pedagogy: Academic interventions involve the adoption of grade competence framework instead of just syllabus completion.
- Directional efforts: Effective delivery of remedial education for weaker students like after-school coaching, audio-video based education.
- Administrative reforms: that enable and incentivize teachers to perform better through data-driven insights, training, and recognition. Example: Performance based increments in Salary.
 A systemic approach to reforming healthcare system in the country needs
A systemic approach to reforming healthcare system in the country needs
- Universal health coverage: Access to healthcare in India is not equitable—the rich and the middle class would survive the COVID-19 or any other crisis but not the poor.
- Increasing healthcare professionals in numbers: India has handled the COVID-19 pandemic exceptionally well. However, India is in dire need of more medical staff and amenities.
- Revamping medical education: If the government wants to stay successful in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic, it needs to rapidly build medical institutions and increase the number of doctors.
- Cross-subsidization of health-care: How the poor managed without, or even with, any government insurance scheme is a big question. They can make up for the loss by cross-subsidizing treatments of patients with premium insurance policies.
Recent initiatives
- PLI scheme: In view of these challenges, the government announced various policies like PLI scheme for domestic manufacturing of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- National Digital Health Mission: It also announced the National Digital Health Mission.
Way forward
- India’s healthcare system is too small for such a large population.
- There seems to be a long battle ahead. The public healthcare system cannot be improved overnight.
- The country needs all hands on deck during and after this crisis—both public and private sectors must work together and deliver universal health coverage for all citizens.
Conclusion
- Providing expanded access to high quality education and healthcare supports—particularly for those young people who today lack such access—will not only expand economic opportunity for those individuals, but will also likely do more to strengthen the overall state economy.
Mains question
Q. To create the foundation for the next century, we need to invest in education and health in the next 25 years not just for the elite, but for all. Critically examine
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Govt. to enumerate Sanitation Workers
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rashtriya Garima Abhiyan
Mains level: Plight of sanitation workers in India
The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJ&E) is now preparing to undertake a nationwide survey to enumerate all people engaged in the hazardous cleaning of sewers and septic tanks.
Why such move?
- Cleaning of sewers and septic tanks has led to at least 351 deaths since 2017.
Various initiatives for sanitation workers
- The ministry now has proper distinction between sanitation work and manual scavenging.
- The practice of manual scavenging no longer takes place in the country as all manual scavengers had been accounted for and enrolled into the rehabilitation scheme, said the ministry.
- The enumeration of sanitization workers is soon to be conducted across 500 AMRUT (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation) cities, as a part of National Action Plan for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE).
- The NAMASTE scheme aims to eradicate unsafe sewer and septic tank cleaning practices.
Manual Scavenging in India
- Manual scavenging is the practice of removing human excreta by hand from sewers or septic tanks.
- India banned the practice under the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013 (PEMSR).
- The Act bans the use of any individual for manually cleaning, carrying, disposing of or otherwise handling in any manner, human excreta till its disposal.
- In 2013, the definition of manual scavengers was also broadened to include people employed to clean septic tanks, ditches, or railway tracks.
- The Act recognizes manual scavenging as a “dehumanizing practice,” and cites a need to “correct the historical injustice and indignity suffered by the manual scavengers.”
Why is it still prevalent in India?
- Low awareness: Manual scavenging is mostly done by the marginalized section of the society and they are generally not aware about their rights.
- Enforcement issues: The lack of enforcement of the Act and exploitation of unskilled labourers are the reasons why the practice is still prevalent in India.
- High cost of automated: The Mumbai civic body charges anywhere between Rs 20,000 and Rs 30,000 to clean septic tanks.
- Cheaper availability: The unskilled labourers, meanwhile, are much cheaper to hire and contractors illegally employ them at a daily wage of Rs 300-500.
- Caste dynamics: Caste hierarchy still exists and it reinforces the caste’s relation with occupation. Almost all the manual scavengers belong to lower castes.
Various policy initiatives
- Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (Amendment) Bill, 2020: It proposes to completely mechanise sewer cleaning, introduce ways for ‘on-site’ protection and provide compensation to manual scavengers in case of sewer deaths.
- Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013: Superseding the 1993 Act, the 2013 Act goes beyond prohibitions on dry latrines, and outlaws all manual excrement cleaning of insanitary latrines, open drains, or pits.
- Rashtriya Garima Abhiyan: It started national wide march “Maila Mukti Yatra” for total eradication of manual scavenging from 30th November 2012 from Bhopal.
- Prevention of Atrocities Act: In 1989, the Prevention of Atrocities Act became an integrated guard for sanitation workers since majority of the manual scavengers belonged to the Scheduled Caste.
- Compensation: As per the Prohibition of Employment of Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (PEMSR) Act, 2013 and the Supreme Court’s decision in the Safai Karamchari Andolan vs Union of India case, a compensation of Rs 10 lakh is awarded to the victims family.
- National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK): It is currently a temporary non-statutory body that investigates the conditions of Safai Karamcharis (waste collectors) in India and makes recommendations to the Government.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Drugs shortage haunts HIV-positive community
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ART therapy
Mains level: Not Much
People living with HIV are facing an acute shortage of life-saving drugs, say protesters who have been camping outside the National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) office.
What is NACO?
- The NACO established in 1992 is a division of India’s Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It provides leadership to HIV/AIDS control programme in India through 35 HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Societies.
- It is the nodal organisation for formulation of policy and implementation of programs for prevention and control of HIV/AIDS in India.
Functions of NACO
- Along with drug control authorities and NACO provides joint surveillance of Blood Bank licensing, Blood Donation activities and Transfusion Transmitted infection testing and reporting.
- NACO also undertakes HIV estimations biennially (every 2 years) in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) – National Institute of Medical Statistics (NIMS).
- The first round of HIV estimation in India was done in 1998, while the last round was done in 2017.
Why in news?
- Activists allege rationing of medicines, arbitrary change in the drug regimen and even complete deprivation of life-saving paediatric drugs.
- They fear that treatment will be interrupted, leading to drug resistance and deaths from AIDS.
NACO stand
- The protesters noted that the NACO, in its public communication, had claimed that 95% of the recipients had not faced any shortage.
- Going by the figure, 5% of 14.5 lakh, or 72,500 people, are being affected by the current shortage and stock-out.
- The impact is severe and far-reaching.
What drugs are protestors talking about?
- Protestors are for a stock-out of ART (antiretroviral) drugs such as Dolutegravir 50 mg, Lopinavir/Ritonavir (adult and child doses), and Abacavir in several states.
What is ART?
- The medicines that treat HIV are called antiretroviral drugs.
- There are more than two dozen of them, and they fall into seven main types.
- Each drug fights the virus in your body in a slightly different way.
- Research shows that a combination, or “cocktail,” of drugs is the best way to control HIV and lower the chances that the virus will become resistant to treatment.
Back2Basics: HIV/AIDS
- HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks cells that help the body fight infection, making a person more vulnerable to other infections and diseases.
- First identified in 1981, HIV is the cause of one of humanity’s deadliest and most persistent epidemics.
- It is spread by contact with certain bodily fluids of a person with HIV, most commonly during unprotected sex, or through sharing injection drug equipment.
- If left untreated, HIV can lead to the disease AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
- The human body can’t get rid of HIV and no effective HIV cure exists.
Treating HIV
- However, by taking HIV medicine (called antiretroviral therapy or ART), people with HIV can live long and healthy lives and prevent transmitting HIV to their sexual partners.
- In addition, there are effective methods to prevent getting HIV through sex or drug use, including pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP).
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What rules govern Disposal of Seized Narcotics?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Disposal of Seized Narcotics
Mains level: Not Much

The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) has destroyed 30,000 kg of seized drugs at four locations – Kolkata, Chennai, Delhi and Guwahati — in the virtual presence of Union Home Minister.
Destruction of Seized Narcotic Drugs
- Section 52-A of the Narcotics Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985 allows probe agencies to destroy seized substances after collecting required samples.
- Officials concerned must make a detailed inventory of the substance to be destroyed.
- A five-member committee comprising the area SSP, director/superintendent or the representative of the area NCB, a local magistrate and two others linked to law enforcement and legal fraternity is constituted.
- The substance is then destroyed in an incinerator or burnt completely leaving behind not any trace of the substance.
Exact procedure that is followed
- The agency first obtains permission from a local court to dispose of the seized narcotic substances.
- These substances are then taken to the designated place of destruction under a strict vigil.
- The presiding officer tallies the inventory made at the storeroom with that material brought to the spot.
- The entire process is videographed and photographed.
- Then one by one, all the packets/gunny bags of the substance/s are put in the incinerator.
- As per rules, committee members cannot leave the place until the seized drugs have been completely destroyed.
Which agency is authorized to carry out such an exercise?
- Every law enforcement agency competent to seize drugs is authorized to destroy them after taking prior permission of the area magistrate.
- These include state police forces, the CBI and the NCB among others.
Why destroy seized drugs?
- The hazardous nature of narcotic drugs or psychotropic substances, their vulnerability to theft, substitution, and constraints of proper storage space are among the reasons that make agencies destroy them.
- There have been instances when seized narcotics were pilfered from the storeroom.
- To prevent such instances, authorities try to destroy seized drugs immediately after collecting the required samples out of the seized substances.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Monkeypox outbreak: It’s time to act, not panic
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Monkeypox
Mains level: Paper 2-Challenges of zoonotic diseases
Context
Monkeypox was previously limited to the local spread in central and west Africa, close to tropical rainforests, but has recently been seen in various urban areas and now in more than 50 countries.
About monkeypox
- A virus belonging to the poxviruses family causes a rare contagious rash illness known as monkeypox.
- This zoonotic viral disease (a disease transmitted from animals to humans) has hosts that include rodents and primates.
- It is a self-limiting disease with symptoms lasting two to four weeks and a case fatality rate of 3-6 per cent.
- Symptoms: A skin rash on any part of the body could be the only presenting symptom.
- Swollen lymph nodes are another distinguishing feature. Aside from these, other symptoms of a viral illness include fever, chills, headache, muscle or back aches, and weakness.
- Mode of transmission: Touching skin lesions, bodily fluids, or clothing or linens that have been in contact with an infected person can result in transmission.
- It’s also worth noting that monkeypox does not spread from person to person through everyday activities like walking next to or having a casual conversation with an infected person.
- Treatment: Monkeypox is mostly treated by managing symptoms and preventing complications if it is diagnosed.
- In the minor proportion who are immunocompromised, complications can occur; pulmonary failure was the most common complication with a high mortality rate.
Containment Measures
- Because symptoms usually appear 5-21 days after exposure, people with rashes, sores in the mouth, rash, eye irritation or redness, or swollen lymph nodes should be monitored.
- When symptoms appear, it is critical to isolate the infected from other people and pets, cover their lesions, and contact the nearest healthcare provider.
- It is also critical to avoid close physical contact with others until instructed to do so by our healthcare provider.
- It is preferable to use home isolation whenever possible.
- Priority should be given to educating grassroots workers about symptoms, specimen collection, disease detection, acquiring sample collection equipment, and maintaining cold storage of specimens.
- Increased surveillance and detection of monkeypox cases are critical for controlling the disease’s spread and understanding the changing epidemiology of this resurging disease.
- Preventive health measures, such as avoiding infected animal or human contact and practising good hand hygiene, are the best option.
Vaccines and drugs
- In the US, pre exposure vaccination with JYNNEOS® is available to healthcare workers and lab workers exposed to this group of poxviruses.
- The smallpox vaccine is 85 percent effective against the disease.
- Another vaccine, ACAM2000, is a live vaccinia virus vaccine that is otherwise recommended for smallpox immunisation and can also be used for high-risk individuals during monkeypox outbreaks.
- In addition, Tecovirimat, an antiviral drug used to treat smallpox, is recommended for monkeypox.
- Challenges: Smallpox vaccination programmes have been discontinued for the past 50 years, resulting in a scarcity of effective vaccines.
- There are approved drugs and vaccines, but they are not widely available to scale up controlling monkeypox.
Why WHO declared it as international concern?
- The increase in monkeypox cases in a short span of time in many countries necessitated the declaration of public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) and additional research studies.
- It is unclear whether the recent sudden outbreaks in multiple countries result from genotypic mutations that alter virus transmissibility. SARS-CoV-2 and monkeypox virus co-infection can alter infectivity patterns, severity, management, and response to vaccination against either or both diseases.
- As a result, there is a need to improve diagnostic test efficiency.
Way forward
- Plan for pandemic preparedness: This is not the last such difficulty we will face, as the world is still witnessing more such public health crises.
- Zoonotic diseases are caused by various factors, including unchecked deforestation, climate coupled with a failure to prioritise public health, poverty, and climate change.
- Instead, a robust plan for pandemic preparedness should be accelerated, guided by a single health agenda.
- The world is yet to recognise emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases as a genuine threat.
- The immediate priority is to strengthen the surveillance infrastructure, including hiring public health professionals and field workers who can participate in outbreak detection and response during many future PHEICs.
Conclusion
Without prioritising public health strengthening, the threat of new and re-emerging infectious diseases, as well as the enormous social and economic challenges that accompany them, is real and grave.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] NAMASTE scheme
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NAMASTE Scheme
Mains level: Sanitation workers and their upliftment
The Government has formulated a National Action Plan for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem- NAMASTE scheme for cleaning of sewers and septic tank.
NAMASTE Scheme
- The scheme is a joint venture of Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- It aims to achieve outcomes like:
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter
- All Sewer and Septic tank sanitation workers have access to alternative livelihoods
- The Ministry has shortlisted type of machineries and core equipments required for maintenance works, safety gear for Safai Mitras.
Why such move?
Ans. Prevalence of manual scavenging in India
What is Manual Scavenging?
- Manual scavenging is the practice of removing human excreta by hand from sewers or septic tanks.
- India banned the practice under the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013 (PEMSR).
- The Act bans the use of any individual for manually cleaning, carrying, disposing of or otherwise handling in any manner, human excreta till its disposal.
- In 2013, the definition of manual scavengers was also broadened to include people employed to clean septic tanks, ditches, or railway tracks.
- The Act recognizes manual scavenging as a “dehumanizing practice,” and cites a need to “correct the historical injustice and indignity suffered by the manual scavengers.”
Why is it still prevalent in India?
- Low awareness: Manual scavenging is mostly done by the marginalized section of the society and they are generally not aware about their rights.
- Enforcement issues: The lack of enforcement of the Act and exploitation of unskilled labourers are the reasons why the practice is still prevalent in India.
- High cost of automated: The Mumbai civic body charges anywhere between Rs 20,000 and Rs 30,000 to clean septic tanks.
- Cheaper availability: The unskilled labourers, meanwhile, are much cheaper to hire and contractors illegally employ them at a daily wage of Rs 300-500.
- Caste dynamics: Caste hierarchy still exists and it reinforces the caste’s relation with occupation. Almost all the manual scavengers belong to lower castes.
Various policy initiatives
- Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (Amendment) Bill, 2020: It proposes to completely mechanise sewer cleaning, introduce ways for ‘on-site’ protection and provide compensation to manual scavengers in case of sewer deaths.
- Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013: Superseding the 1993 Act, the 2013 Act goes beyond prohibitions on dry latrines, and outlaws all manual excrement cleaning of insanitary latrines, open drains, or pits.
- Rashtriya Garima Abhiyan: It started national wide march “Maila Mukti Yatra” for total eradication of manual scavenging from 30th November 2012 from Bhopal.
- Prevention of Atrocities Act: In 1989, the Prevention of Atrocities Act became an integrated guard for sanitation workers since majority of the manual scavengers belonged to the Scheduled Caste.
- Compensation: As per the Prohibition of Employment of Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (PEMSR) Act, 2013 and the Supreme Court’s decision in the Safai Karamchari Andolan vs Union of India case, a compensation of Rs 10 lakh is awarded to the victims family.
Way forward
- Regular surveys and social audits must be conducted against the involvement of manual scavengers by public and local authorities.
- There must be proper identification and capacity building of manual scavengers for alternate sources of livelihood.
- Creating awareness about the legal protection of manual scavengers is necessary.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Kerala reports India’s first Monkeypox Case
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Monkeypox
Mains level: Rise in zoonotic diseases

The first known lab-confirmed case of monkeypox in India has been reported in a 35-year-old man in Kerala.
What is Monkeypox?
- The monkeypox virus is an orthopoxvirus, which is a genus of viruses that also includes the variola virus, which causes smallpox, and vaccinia virus, which was used in the smallpox vaccine.
- It causes symptoms similar to smallpox, although they are less severe.
- While vaccination eradicated smallpox worldwide in 1980, monkeypox continues to occur in a swathe of countries in Central and West Africa, and has on occasion showed up elsewhere.
- According to the WHO, two distinct clade are identified: the West African clade and the Congo Basin clade, also known as the Central African clade.
Its origin
- Monkeypox is a zoonosis, that is, a disease that is transmitted from infected animals to humans.
- Monkeypox virus infection has been detected in squirrels, Gambian poached rats, dormice, and some species of monkeys.
- According to the WHO, cases occur close to tropical rainforests inhabited by animals that carry the virus.
Symptoms and treatment
- Monkeypox begins with a fever, headache, muscle aches, back ache, and exhaustion.
- It also causes the lymph nodes to swell (lymphadenopathy), which smallpox does not.
- The WHO underlines that it is important to not confuse monkeypox with chickenpox, measles, bacterial skin infections, scabies, syphilis and medication-associated allergies.
- The incubation period (time from infection to symptoms) for monkeypox is usually 7-14 days but can range from 5-21 days.
- There is no safe, proven treatment for monkeypox yet.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Typhi: A more drug-resistant Typhoid
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Salmonella Typhi
Mains level: Not Much
The bacteria causing typhoid fever is becoming increasingly resistant to some of the most important antibiotics for human health.
What is the news?
- The largest genome analysis of Salmonella Typhi (S. Typhi) also shows that resistant strains — almost all originating in South Asia — have spread to other countries nearly 200 times since 1990.
- The researchers noted that typhoid fever is a global public health concern, causing 11 million infections and more than 1,00,000 deaths per year.
- Antibiotics can be used to successfully treat typhoid fever infections, but their effectiveness is threatened by the emergence of resistant S. Typhi strains.
What is Salmonella Typhi?
- Salmonella Typhi (S. Typhi) are bacteria that infect the intestinal tract and the blood.
- It is usually spread through contaminated food or water.
- Once S. Typhi bacteria are eaten or drunk, they multiply and spread into the bloodstream.
- The disease is referred to as typhoid fever. S. Paratyphi bacteria cause a similar, but milder illness, which comes under the same title.
- Paratyphoid has a shorter duration, generally, than typhoid.
- Typhi and S. Paratyphi are common in many developing countries where sewage and water treatment systems are poor.
How does it spread?
- Salmonella Typhi lives only in humans.
- Persons with typhoid fever carry the bacteria in their bloodstream and intestinal tract.
- Symptoms include prolonged high fever, fatigue, headache, nausea, abdominal pain, and constipation or diarrhoea.
- Some patients may have a rash. Severe cases may lead to serious complications or even death.
- Typhoid fever can be confirmed through blood testing.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Managing Type 1 Diabetes
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Diabetes , its types
Mains level: Not Much

Last week, the Indian Council of Medical Research (IMCR) released guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment, and management for type-1 diabetes.
Why such move?
- India is considered the diabetes capital of the world, and the pandemic disproportionately affected those living with the disease.
- Type 1 or childhood diabetes, however, is less talked about, although it can turn fatal without proper insulin therapy.
- Type 1 diabetes is rarer than type 2. Only 2% of all hospital cases of diabetes in the country are type 1.
What is Diabetes?
- Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy.
- Most of the food you eat is broken down into sugar (also called glucose) and released into your bloodstream.
- When your blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
- Type 1 diabetes is a condition where the pancreas completely stops producing insulin.
- Insulin is the hormone responsible for controlling the level of glucose in blood by increasing or decreasing absorption to the liver, fat, and other cells of the body.
- This is unlike type 2 diabetes — which accounts for over 90% of all diabetes cases in the country — where the body’s insulin production either goes down or the cells become resistant to the insulin.
How lethal diabetes is?
- Type 1 diabetes is predominantly diagnosed in children and adolescents.
- Although the prevalence is less, it is much more severe than type 2.
- Unlike type 2 diabetes where the body produces some insulin and which can be managed using various pills, if a person with type 1 diabetes stops taking their insulin, they die within weeks.
How rare is it?
- There are over 10 lakh children and adolescents living with type 1 diabetes in the world, with India accounting for the highest number.
- Of the 2.5 lakh people living with type 1 diabetes in India, 90,000 to 1 lakh are under the age of 14 years.
- For context, the total number of people in India living with diabetes was 7.7 crore in 2019.
- Among individuals who develop diabetes under the age of 25 years, 25.3% have type 2.
Who is at risk of type 1 diabetes?
- The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but it is thought to be an auto-immune condition where the body’s immune system destroys the islets cells on the pancreas that produce insulin.
- Genetic factors play a role in determining whether a person will get type-1 diabetes.
- The risk of the disease in a child is 3% when the mother has it, 5% when the father has it, and 8% when a sibling has it.
- The presence of certain genes is also strongly associated with the disease.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
CoWIN as a repurposed digital platform
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CoWIN
Mains level: Paper 2- CoWIN platform
Context
Seeing its success, other nations have also expressed interest in availing CoWIN and using it as a bridge for erecting their digital health systems. Responding to this incoming interest, our prime minister has offered CoWIN as a digital public good, free of cost, for all nations globally to adopt.
About CoWIN
- In late 2020, even before the Covid-19 vaccines had arrived, the Government of India had commenced preparations for launching the world’s largest vaccination drive.
- This led to the beginning of the CoWIN journey in January 2021.
- Scalability, modularity, and interoperability: CoWIN, or the Covid-19 Vaccine Intelligence Network, was developed in a record time, with consideration given to scalability, modularity, and interoperability.
- The platform has been made available in English and 11 regional languages to allow citizens across multiple states to access the platform with ease.
- To circumvent the lack of digital access, the platform allows for up to six members to be registered under one mobile-number linked account.
- CoWIN has scaled every 100 million milestone faster than any other platform.
- It reached the coveted one billion registered user mark which only a handful of platforms have been able to achieve globally, and none in such a short time.
- A key feature of the platform has been its modularity and evolvability.
- The CoWIN team has been adept at keeping pace with the changing policy environment and scientific research and developments in the administration of vaccines.
- It was never that CoWIN became the bottleneck or delayed the implementation of our vaccination policies or drive.
- Time and again, CoWIN has proved itself as one of the most secure and robust platforms with minimal data input and zero risk of personal data hacks.
Major phases of CoWIN
- The journey of CoWIN was staggered across three major phases, with multiple additions subsequently.
- In phase 1, the registration process went online where healthcare workers and frontline workers were sent system-generated notifications about their vaccination schedule.
- In subsequent phases, beneficiaries were allowed both walk-in and online vaccination registration, along with the choice of location and time slot as per their convenience.
- An assisted mode was also made available through the 240,000+ Common Service Centres (CSCs) and a helpline number.
- After ensuring successful orchestration using scalability and agile features of the platform to vaccinate individuals over 45 years of age, the APIs of the platform were made available to private players at the beginning of Phase III of the vaccination drive.
- Once access to its services was opened through APIs, more than 100 applications integrated with CoWIN for providing search, booking and certification facilities to their users.
Way ahead
- The inevitable question is what will we do with CoWIN when no further Covid-19 vaccines are to be administered?
- Repurpose the platform: The decision is to repurpose the platform as a universal immunisation platform.
- The credentialing service of DIVOC, used in CoWIN, has proven to be a game-changer in the world of digital certificates.
- CoWIN service is being implemented in five other countries after India and receiving global acceptance for its veracity and sound architecture.
- There is a proposal for opening the credentialing service for more use cases in health.
Conclusion
The story of CoWIN has truly been one of national impact and importance. And while the story started during the pandemic, it won’t end with the pandemic: it will segue into a repurposed digital platform for more health use-cases.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Thailand becomes first Asian country to legalize Marijuana
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Marijuana
Mains level: Substance abuse in India
Thailand has officially legalized the growing and consumption of marijuana in food and drinks, becoming the first Asian country to do so.
Films like ‘Udta Punjab’ have graphically portrayed the crisis faced by the society and its youth with regard to the drug menace.
What is Marijuana?
- Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant used primarily for medical or recreational purposes.
- The main psychoactive component of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD).
- It is used by smoking, vaporizing, within the food, or as an extract.
Prospects of legalizing Marijuana
(1) Health benefits
- The cannabinoids found in Cannabis is a great healer and has found mention in the Ayurveda.
- It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions like multiple sclerosis, arthritis, epilepsy, insomnia, HIV/AIDS treatment, cancer.
(2) Ecological benefits
- The cannabis plant and seeds apart from being labeled a ‘super-foods’ as per studies is also a super-industrial carbon negative raw material.
- Each part of the plant can be used for some industry. Hemp currently is also being used to make bio-fuel, bio-plastics and even construction material in certain countries. The cosmetic industry has also embraced Hemp seeds.
(3) Marijuana is addiction-free
- An epidemiological study showed that only 9% of those who use marijuana end up being clinically dependent on it.
- The ‘comparable rates’ for tobacco, alcohol and cocaine stood at 32%, 15% and 16% respectively.
(4) Good source of Revenue
- By legalizing and taxing marijuana, the government will stand to earn huge amounts of revenue that will otherwise go to the Italian and Israeli drug cartels.
- In an open letter to US President George Bush, around 500 economists, led by Nobel Prize winner Milton Friedman, called for marijuana to be “legal but taxed and regulated like other goods”.
(5) A potential cash crop
- The cannabis plant is something natural to India, especially the northern hilly regions. It has the potential of becoming a cash crop for poor marginal farmers.
- If proper research is done and the cultivation of marijuana encouraged at an official level, it can gradually become a source of income for poor people with small landholdings.
(6) Prohibition was ineffective
- In India, the consumption of synthetic drugs like cocaine has increased since marijuana was banned, while it has decreased in the US since it was legalized in certain states.
- Moreover, these days, it is pretty easy to buy marijuana in India and its consumption is widespread among the youth. So it is fair to say that prohibition has failed to curb the ‘problem’.
(7) Marijuana is less harmful
- Marijuana consumption was never regarded as a socially deviant behaviour any more than drinking alcohol was. In fact, keeping it legal was considered as an ‘enlightened view’.
- It is now medically proven that marijuana is less harmful than alcohol.
Risks of Legalizing Cannabis
(1) Health risks continue to persist
- There are many misconceptions about cannabis. First, it is not accurate that cannabis is harmless.
- Its immediate effects include impairments in memory and in mental processes, including ones that are critical for driving.
- Long-term use of cannabis may lead to the development of addiction of the substance, persistent cognitive deficits, and of mental health problems like schizophrenia, depression and anxiety.
- Exposure to cannabis in adolescence can alter brain development.
(2) A new ‘tobacco’ under casualization
- A second myth is that if cannabis is legalized and regulated, its harms can be minimized.
- With legalization comes commercialization. Cannabis is often incorrectly advertised as being “natural” and “healthier than alcohol and tobacco”.
- Tobacco, too, was initially touted as a natural and harmless plant that had been “safely” used in religious ceremonies for centuries.
(3) Unconvincing Advocacy
- Advocates for legalization rarely make a convincing case. To hear some supporters tell it, the drug cures all diseases while promoting creativity, open-mindedness, moral progression.
- Too much trivialization of Cannabis use could lead to its mass cultivation and a silent economy wreaking havoc through a new culture of substance abuse in India.
Way forward
- For Cannabis/ Marijuana, it’s important to make a distinction between legalization, decriminalization and commercialization.
- We must ensure that there are enough protections for children, the young, and those with severe mental illnesses, who are most vulnerable to its effects.
- Hence, laws should be made to suit people so that they do not break the law to maintain their lifestyle.
- Laws should weave around an existing lifestyle, not obstruct it. Or else laws will be broken.
Conclusion
- The debate on the legalization of marijuana in India has been consistent on social media and other noted platforms.
- As with alcohol and tobacco products, the use of cannabis needs to be regulated, taxed and monitored.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Healthcare in India is ailing. Here is how to fix it
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Health Mission
Mains level: Paper 2- Reforms in healthcare
Context
The lesson emerging from the pandemic experience is that if India does not want a repeat of the immeasurable suffering and the social and economic loss, we need to make public health a central focus.
Need for institutional reforms in the health sector
- The importance of public health has been known for decades with every expert committee underscoring it.
- Ideas ranged from instituting a central public health management cadre like the IAS to adopting an institutionalised approach to diverse public health concerns — from healthy cities, enforcing road safety to immunising newborns, treating infectious diseases and promoting wellness.
- Covid has shifted the policy dialogue from health budgets and medical colleges towards much-needed institutional reform.
About National Health Mission (NHM)
- The National Health Mission (NHM) seeks to provide universal access to equitable, affordable and quality health care which is accountable, at the same time responsive, to the needs of the people, reduction of child and maternal deaths as well as population stabilization, gender and demographic balance.
- The Framework for Implementation of NUHM has been approved by the Cabinet on May 1, 2013.
- NHM encompasses two Sub-Missions, National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) and National Urban Health Mission (NUHM).
- The National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) was launched in 2005 with a view to bringing about dramatic improvement in the health system and the health status of the people, especially those who live in the rural areas of the country.
Learning from the failure of National Health Mission (NHM)
- The National Health Mission (NHM) has been in existence for about 15 years now and the health budget has trebled— though not as a proportion of the GDP.
- Despite this less than 10 per cent of the health facilities below the district level can attain the grossly minimal Indian public health standards.
- Clearly, the three-tier model of subcentres with paramedics, primary health centres with MBBS doctors and community health centres (CHC) with four to six specialists has failed.
- Lack of accountability framework: The model’s weakness is the absence of an accountability framework.
- The facilities are designed to be passive — treating those seeking care.
Suggestions
- 1] FHT: Instead of passive design of NHM, we need Family Health Teams (FHT) like in Brazil, accountable for the health and wellbeing of a dedicated population, say 2,000 families.
- The FHTs must consist of a doctor with a diploma in family medicine and a dozen trained personnel to reflect the skill base required for the 12 guaranteed services under the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- A baseline survey of these families will provide information about those needing attention.
- Family as a unit: The team ensures a continuum of care by taking the family as a unit and ensuring its well-being over a period.
- Nudging these families to adopt lifestyle changes, following up on referrals for medical interventions and post-operative care through home visits for nursing and physiotherapy services would be their mandate.
- 2] Health cadre: The implication of and central to the success of such a reset lies in creating appropriate cadres.
- 3] Clarity to nomenclatures: There is also a need to declutter policy dialogue and provide clarity to the nomenclatures.
- Currently, public health, family medicine and public health management are used interchangeably.
- While the family doctor cures one who is sick, the public health expert prevents one from falling sick.
- The public health management specialist holds specialisation in health economics, procurement systems, inventory control, electronic data analysis and monitoring, motivational skills and team-building capabilities, public communication and time management, besides, coordinating with the various stakeholders in the field.
- 4] Move beyond doctor-led systems: India needs to move beyond the doctor-led system and paramedicalise several functions.
- Instead of wasting gynaecologists in CHCs midwives (nurses with a BSc degree and two years of training in midwifery) can provide equally good services except surgical, and can be positioned in all CHCs and PHCs.
- This will help reduce C Sections, maternal and infant mortality and out of pocket expenses.
- 5] Counsellors and physiotherapists at PHC: Lay counsellors for mental health, physiotherapists and public health nurses are critically required for addressing the multiple needs of primary health care at the family and community levels.
- 6] Review of existing system: Bringing such a transformative health system will require a comprehensive review of the existing training institutions, standardising curricula and the qualifying criteria.
- Increase spending on training: Spending on pre-service and in-service training needs to increase from the current level of about 1 per cent.
- 7] Redefining of functions: A comprehensive redefinition of functions of all personnel is required to weed out redundancies and redeploy the rewired ones.
Conclusion
Resetting the system to current day realities requires strong political leadership to go beyond the inertia of the techno-administrative status quoist structures. We can.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
ASHA Program
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASHA program
Mains level: Paper 2- Strengthening ASHA
Context
India’s one million Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) volunteers have received World Health Organization’s Global Health Leaders Awards 2022.
Background of the ASHA program
- In 1975, a WHO monograph titled ‘Health by the people’ and then in 1978, an international conference on primary health care in Alma Ata (in the then USSR and now in Kazakhstan), gave emphasis for countries recruiting community health workers to strengthen primary health-care services that were participatory and people centric.
- Soon after, many countries launched community health worker programmes under different names.
- India launched the ASHA programme in 2005-06 as part of the National Rural Health Mission.
- The biggest inspiration for designing the ASHA programme came from the Mitanin (meaning ‘a female friend’ in Chhattisgarhi) initiative of Chhattisgarh, which had started in May 2002.
- The core of the ASHA programme has been an intention to build the capacity of community members in taking care of their own health and being partners in health services.
- Each of these women-only volunteers work with a population of nearly 1,000 people in rural and 2,000 people in urban areas, with flexibility for local adjustments.
A well thought through and deliberated program
- The ASHA programme was well thought through and deliberated with public health specialists and community-based organisations from the beginning.
- 1] Key village stakeholders selected: The ASHA selection involved key village stakeholders to ensure community ownership for the initiatives and forge a partnership.
- 2] Ensure familiarity: ASHAs coming from the same village where they worked had an aim to ensure familiarity, better community connect and acceptance.
- 3] Community’s representative: The idea of having activists in their name was to reflect that they were/are the community’s representative in the health system, and not the lowest-rung government functionary in the community.
- 4] Avoiding the slow process of government recruitment: Calling them volunteers was partly to avoid a painfully slow process for government recruitment and to allow an opportunity to implement performance-based incentives in the hope that this approach would bring about some accountability.
Contribution of ASHA
- It is important to note that even before the COVID-19 pandemic, ASHAs have made extraordinary contributions towards enabling increased access to primary health-care services; i.e. maternal and child health including immunisation and treatment for hypertension, diabetes and tuberculosis, etc., for both rural and urban populations, with special focus on difficult-to-reach habitations.
- Over the years, ASHAs have played an outstanding role in making India polio free, increasing routine immunisation coverage; reducing maternal mortality; improving new-born survival and in greater access to treatment for common illnesses.
Challenges
- Linkages with AWW and ANM: When newly-appointed ASHAs struggled to find their way and coordinate things within villages and with the health system, their linkage with two existing health and nutrition system functionaries — Anganwadi workers (AWW) and Auxiliary Nurse Midwife (ANM) as well as with panchayat representatives and influential community members at the village level — was facilitated.
- This resulted in an all-women partnership, or A-A-A: ASHA, AWW and ANM, of three frontline functionaries at the village level, that worked together to facilitate health and nutrition service delivery to the community.
- No fixed salary to ASHAs: Among the A-A-A, ASHAs are the only ones who do not have a fixed salary; they do not have opportunity for career progression.
- These issues have resulted in dissatisfaction, regular agitations and protests by ASHAs in many States of India.
Way forward
- The global recognition for ASHAs should be used as an opportunity to review the programme afresh, from a solution perspective.
- 1] Higher remuneration: Indian States need to develop mechanisms for higher remuneration for ASHAs.
- 2] Avenues for career progression: It is time that in-built institutional mechanisms are created for capacity-building and avenues for career progression for ASHAs to move to other cadres such as ANM, public health nurse and community health officers are opened.
- 3] Extend the benefits of social sector services: Extending the benefits of social sector services including health insurance (for ASHAs and their families) should be considered.
- 4] Independent and external review: While the ASHA programme has benefitted from many internal and regular reviews by the Government, an independent and external review of the programme needs to be given urgent and priority consideration.
- 5] Regularisation of temporary posts: There are arguments for the regularisation of many temporary posts in the National Health Mission and making ASHAs permanent government employees.
Conclusion
The WHO award for ASHA volunteers is a proud moment and also a recognition of every health functionary working for the poor and the underserved in India. It is a reminder and an opportunity to further strengthen the ASHA programme for a stronger and community-oriented primary health-care system.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Malnutrition in India is a worry in a modern scenario
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Malnutrition challenge
Context
The country’s response to its burden of malnutrition and growing anaemia has to be practical and innovative.
What is malnutrition?
- Malnutrition refers to deficiencies, excesses or imbalances in a person’s intake of energy and/or nutrients.
- The term malnutrition covers 2 broad groups of conditions.
- One is ‘undernutrition’—which includes stunting (low height for age), wasting (low weight for height), underweight (low weight for age) and micronutrient deficiencies or insufficiencies (a lack of important vitamins and minerals).
- The other is overweight, obesity and diet-related non-communicable diseases (such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and cancer).
What are the root causes of malnutrition in India?
The following three deficits are the root cause of malnutrition in India.
1) Dietary deficit
- There is a large dietary deficit among at least 40 per cent of our population of all age groups, shown in— the National Nutrition Monitoring Bureau’s Third Repeat Survey (2012), NFHS 4, 2015-16, the NNMB Technical Report Number 27, 2017.
- Our current interventions are not being able to bridge this protein-calorie-micronutrient deficit.
- The NHHS-4 and NFHS-5 surveys reveal an acute dietary deficit among infants below two years, and considerable stunting and wasting of infants below six months.
- Unless this maternal/infant dietary deficit is addressed, we will not see rapid improvement in our nutritional indicators.
2) Information deficit at household level
- We do not have a national IEC (information, education and communication) programme that reaches targeted households to bring about the required behavioural change regarding some basic but critical facts.
- For example, IEC tells about the importance of balanced diets in low-income household budgets, proper maternal, child and adolescent nutrition and healthcare.
3) Inequitable market conditions
- The largest deficit, which is a major cause of dietary deficiency and India’s chronic malnutrition, pertains to inequitable market conditions.
- Such market conditions deny affordable and energy-fortified food to children, adolescents and adults in lower-income families.
- The market has stacks of expensive fortified energy food and beverages for higher income groups, but nothing affordable for low-income groups.
The vicious cycle of malnutrition
- Link with mother: A child’s nutritional status is directly linked to their mother.
- Poor nutrition among pregnant women affects the nutritional status of the child and has a greater chance to affect future generations.
- Impact on studies: Undernourished children are at risk of under-performing in studies and have limited job prospects.
- Impact on development of the country: This vicious cycle restrains the development of the country, whose workforce, affected mentally and physically, has reduced work capacity.
Marginal improvement on Stunting and Wasting
- The National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) has shown marginal improvement in different nutrition indicators, indicating that the pace of progress is slow.
- This is despite declining rates of poverty, increased self-sufficiency in food production, and the implementation of a range of government programmes.
- Children in several States are more undernourished now than they were five years ago.
- Increased stunting in some states: Stunting is defined as low height-for-age.
- While there was some reduction in stunting rates (35.5% from 38.4% in NFHS-4) 13 States or Union Territories have seen an increase in stunted children since NFHS-4.
- This includes Gujarat, Maharashtra, West Bengal and Kerala.
- Wasting remains stagnant: Wasting is defined as low weight-for-height.
- Malnutrition trends across NFHS surveys show that wasting, the most visible and life-threatening form of malnutrition, has either risen or has remained stagnant over the years.
Prevalence of anaemia in India
- What is it? Anaemia is defined as the condition in which the number of red blood cells or the haemoglobin concentration within them is lower than normal.
- Consequences: Anaemia has major consequences in terms of human health and development.
- It reduces the work capacity of individuals, in turn impacting the economy and overall national growth.
- Developing countries lose up to 4.05% in GDP per annum due to iron deficiency anaemia; India loses up to 1.18% of GDP annually.
- The NFHS-5 survey indicates that more than 57% of women (15-49 years) and over 67% children (six-59 months) suffer from anaemia.
Way forward
1] Increase investment:
- There is a greater need now to increase investment in women and children’s health and nutrition to ensure their sustainable development and improved quality of life.
- Saksham Anganwadi and the Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment (POSHAN) 2.0 programme have seen only a marginal increase in budgetary allocation this year (₹20,263 crore from ₹20,105 crore in 2021-22).
- Additionally, 32% of funds released under POSHAN Abhiyaan to States and Union Territories have not been utilised.
2] Adopt outcome oriented approach on the nutrition programme
- India must adopt an outcome-oriented approach on nutrition programmes.
- It is crucial that parliamentarians begin monitoring needs and interventions in their constituencies and raise awareness on the issues, impact, and solutions to address the challenges at the local level.
- Direct engagement: There has to be direct engagement with nutritionally vulnerable groups and ensuring last-mile delivery of key nutrition services and interventions.
- This will ensure greater awareness and proper planning and implementation of programmes.
- This can then be replicated at the district and national levels.
3] Increase awareness and mother’s education
- With basic education and general awareness, every individual is informed, takes initiatives at the personal level and can become an agent of change.
- Various studies highlight a strong link between mothers’ education and improved access and compliance with nutrition interventions among children.
4] Monitoring
- There should be a process to monitor and evaluate programmes and address systemic and on the ground challenges.
- A new or existing committee or the relevant standing committees meet and deliberate over effective policy decisions, monitor the implementation of schemes, and review nutritional status across States.
Conclusion
We must ensure our young population has a competitive advantage; nutrition and health are foundational to that outcome.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Accessible India Campaign
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Accessible India Campaign
Mains level: Facilitating PWDs

With its deadline of June 2022 almost up, the status of targets under the Accessible India Campaign (AIC) is likely to be discussed during a meeting of the Central Advisory Board on Disability.
What is Accessible India Campaign?
- Accessible India Campaign or Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan is a program that is launched to serve the differently-able community of the country.
- The flagship program has been launched on 3 December 2015, the International Day of People with Disabilities.
- The program comes with an index to measure the design of disabled-friendly buildings and human resource policies.
- The initiative also in line with Article 9 of the (UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities) which India is a signatory since 2007.
- The scheme also comes under the Persons with Disabilities Act, 1995 for equal Opportunities and protection of rights which provides non-discrimination in Transport to Persons with Disabilities.
Recent developments
- The Central Public Works Department (CPWD) released the Harmonised Guidelines and Standards for Universal Accessibility in India 2021.
- Drafted by a team of the IIT-Roorkee and the National Institute of Urban Affairs of the MoHUA, the revised guidelines aim to give a holistic approach.
- Earlier, the guidelines were for creating a barrier-free environment, but now they are focusing on universal accessibility.
Key highlights
- Ramps: The guidelines provide the gradient and length of ramps — for example, for a length of six metres, the gradient should be 1:12. The minimum clear width of a ramp should be 1,200 mm.
- Beyond PwDs: While making public buildings and transport fully accessible for wheelchair users is covered in the guidelines, other users who may experience temporary problems have also been considered. For instance, a parent pushing a child’s pram while carrying groceries or other bags, and women wearing saris.
- Women friendly: Built environment needs for accessibility for women should consider diverse age groups, diverse cultural contexts and diverse life situations in which women operate. Diverse forms of clothing (saris, salwar-kameez, etc.) and footwear (heels, kolhapuri chappals, etc.) require a certain orientations.
- Accessibility symbols: The guidelines call for accessibility symbols for PwD, family-friendly facilities and transgender to be inclusively incorporated among the symbols for other user groups.
- Targeted authorities: The guidelines are meant for State governments, government departments and the private sector, as well as for reference by architecture and planning institutes.
Policy measures for PwDs
- India is a signatory to the UN Convention the Right of Persons with Disabilities, which came into force in 2007.
- The Union Minister for Social justice and Empowerment has also launched the “Sugamya Bharat App” to complain for ease accessibility for PwDs.
- India has its dedicated the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, which is the principal and comprehensive legislation concerning persons with disabilities.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is the West Nile Virus?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: West Nile Virus
Mains level: Vector borne diseases

The Kerala health department is on alert after the death occurred due to the West Nile Virus.
West Nile Virus
- The West Nile Virus is a mosquito-borne, single-stranded RNA virus.
- According to the WHO, it is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese Encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae.
How does it spread?
- Culex species of mosquitoes act as the principal vectors for transmission.
- It is transmitted by infected mosquitoes between and among humans and animals, including birds, which are the reservoir host of the virus.
- Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds, which circulate the virus in their blood for a few days.
- The virus eventually gets into the mosquito’s salivary glands.
- During later blood meals (when mosquitoes bite), the virus may be injected into humans and animals, where it can multiply and possibly cause illness.
- WNV can also spread through blood transfusion, from an infected mother to her child, or through exposure to the virus in laboratories.
- It is not known to spread by contact with infected humans or animals.
Symptoms of WNV infection
- The disease is asymptomatic in 80% of the infected people.
- The rest develop what is called the West Nile fever or severe West Nile disease.
- In these 20% cases, the symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, body aches, nausea, rash, and swollen glands.
- Severe infection can lead to encephalitis, meningitis, paralysis, and even death.
- It is estimated that approximately 1 in 150 persons infected with the West Nile Virus will develop a more severe form of the disease.
- Recovery from severe illness might take several weeks or months.
- It usually turns fatal in persons with co-morbidities and immuno-compromised persons (such as transplant patients).
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Monkeypox Virus: Origins and Outbreaks
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Monkey Pox
Mains level: Rise in zoonotic diseases

With cases being reported from across the world, monkeypox has caught everyone’s attention.
What is Monkeypox?
- Monkeypox is not a new virus.
- The virus, belonging to the poxvirus family of viruses, was first identified in monkeys way back in 1958, and therefore the name.
- The first human case was described in 1970 from the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Many sporadic outbreaks of animal to human as well as human to human transmission has occurred in Central and West Africa in the past with significant mortality.
- After the elimination of smallpox, monkeypox has become one of the dominant poxviruses in humans, with cases increasing over years along with a consequent reduction in the age-group affected.
How is it transmitted?
- Since the transmission occurs only with close contact, the outbreaks have been in many cases self-limiting.
- Since in the majority of affected people, the incubation period ranges from five to 21 days and is often mild or self-limiting, asymptomatic cases could transmit the disease unknowingly.
- The outbreaks in Central Africa are thought to have been contributed by close contact with animals in regions adjoining forests.
- While monkeys are possibly only incidental hosts, the reservoir is not known.
- It is believed that rodents and non-human primates could be potential reservoirs.
Does the virus mutate?
- Monkeypox virus is a DNA virus with a quite large genome of around 2,00,000 nucleotide bases.
- While being a DNA virus, the rate of mutations in the monkeypox virus is significantly lower (~1-2 mutations per year) compared to RNA viruses like SARS-CoV-2.
- The low rate of mutation therefore limits the wide application of genomic surveillance in providing detailed clues to the networks of transmission for monkeypox.
- A number of genome sequences in recent years from Africa and across the world suggest that there are two distinct clades of the virus — the Congo Basin/Central African clade and the West African clade.
- Each of the clades further have many lineages.
What do the genomes say?
- With over a dozen genome sequences of monkeypox, it is reassuring that the sequences are quite identical to each other suggesting that only a few introductions resulted in the present spread of cases.
- Additionally, almost all genomes have come from the West African clade, which has much lesser fatality compared to the Central African one.
- This also roughly corroborates with the epidemiological understanding that major congregations in the recent past contributed to the widespread transmission across different countries.
Does it have an effective vaccine?
- It is reassuring that we know quite a lot more about the virus and its transmission patterns.
- We also have effective ways of preventing the spread, including a vaccine.
- Smallpox/vaccinia vaccine provides protection.
- While the vaccine has been discontinued in 1980 following the eradication of smallpox, emergency stockpiles of the vaccines are maintained by many countries.
- Younger individuals are unlikely to have received the vaccine and are therefore potentially susceptible to monkeypox which could partly explain its emergence in younger individuals.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
ASHA workers earn WHO’s global plaudits
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ASHA
Mains level: Contribution of ASHAs in primary healthcare in rural areas

The country’s frontline health workers or ASHAs (accredited social health activists) were one of the six recipients of the WHO’s Global Health Leaders Award 2022 which recognises leadership, contribution to the advance of global health and commitment to regional health issues.
Who are ASHA workers?
- ASHA workers are volunteers from within the community who are trained to provide information and aid people in accessing benefits of various healthcare schemes of the government.
- The role of these community health volunteers under the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) was first established in 2005.
- They act as a bridge connecting marginalised communities with facilities such as primary health centres, sub-centres and district hospitals.
Genesis & evolution
- The ASHA programme was based on Chhattisgarh’s successful Mitanin programme, in which a Community Worker looks after 50 households.
- The ASHA was to be a local resident, looking after 200 households.
- The programme had a very robust thrust on the stage-wise development of capacity in selected areas of public health.
- Many states tried to incrementally develop the ASHA from a Community Worker to a Community Health Worker, and even to an Auxiliary Nurse Midwife (ANM)/ General Nurse and Midwife (GNM), or a Public Health Nurse.
Qualifications for ASHA Workers
- ASHAs are primarily married, widowed, or divorced women between the ages of 25 and 45 years from within the community.
- They must have good communication and leadership skills; should be literate with formal education up to Class 8, as per the programme guidelines.
How many ASHAs are there across the country?
- The aim is to have one ASHA for every 1,000 persons or per habitation in hilly, tribal or other sparsely populated areas.
- There are around 10.4 lakh ASHA workers across the country, with the largest workforces in states with high populations – Uttar Pradesh (1.63 lakh), Bihar (89,437), and Madhya Pradesh (77,531).
- Goa is the only state with no such workers, as per the latest National Health Mission data available from September 2019.
What do ASHA workers do?
- They go door-to-door in their designated areas creating awareness about basic nutrition, hygiene practices, and the health services available.
- They focus primarily on ensuring that pregnant women undergo ante-natal check-up, maintain nutrition during pregnancy, deliver at a healthcare facility, and provide post-birth training on breast-feeding and complementary nutrition of children.
- They also counsel women about contraceptives and sexually transmitted infections.
- ASHA workers are also tasked with ensuring and motivating children to get immunised.
- Other than mother and child care, ASHA workers also provide medicines daily to TB patients under directly observed treatment of the national programme.
- They are also tasked with screening for infections like malaria during the season.
- They also provide basic medicines and therapies to people under their jurisdiction such as oral rehydration solution, chloroquine for malaria, iron folic acid tablets to prevent anaemia etc.
- Now, they also get people tested and get their reports for non-communicable diseases.
- The health volunteers are also tasked with informing their respective primary health centre about any births or deaths in their designated areas.
How much are ASHA workers paid?
- Since they are considered “volunteers/activists”, governments are not obligated to pay them a salary. And, most states don’t.
- Their income depends on incentives under various schemes that are provided when they, for example, ensure an institutional delivery or when they get a child immunised.
- All this adds up to only between Rs 6,000 to Rs 8,000 a month.
- Her work is so tailored that it does not interfere with her normal livelihood.
Success of the ASHAs
- It is a programme that has done well across the country.
- In a way, it became a programme that allowed a local woman to develop into a skilled health worker.
- Overall, it created a new cadre of incrementally skilled local health workers who were paid based on performance.
- The ASHAs are widely respected as they brought basic health services to the doorstep of households.
- Since then ASHA continues to enjoy the confidence of the community.
Challenges to ASHAs
- The ASHAs faced a range of challenges: Where to stay in a hospital? How to manage mobility? How to tackle safety issues?
- There have been challenges with regard to the performance-based compensation. In many states, the payout is low, and often delayed.
- It has a problem of responsibility and accountability without fair compensation.
- There is a strong argument to grant permanence to some of these positions with a reasonable compensation as sustaining motivation.
- Ideally, an ASHA should be able to make more than the salary of a government employee, with opportunities for moving up the skill ladder in the formal primary health care system as an ANM/ GNM or a Public Health Nurse.
Way forward
- The incremental development of a local resident woman is an important factor in human resource engagement in community-linked sectors.
- It is equally important to ensure that compensation for performance is timely and adequate.
- Upgrading skill sets and providing easy access to credit and finance will ensure a sustainable opportunity to earn a respectable living while serving the community.
- Strengthening access to health insurance, credit for consumption and livelihood needs at reasonable rates, and coverage under pro-poor public welfare programmes will contribute to ASHAs emerging as even stronger agents of change.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IHCI, hypertension
Mains level: Burden of NCDs in India

The IHCI project has demonstrated that blood pressure treatment and control are feasible in primary care settings in diverse health systems across various States in India.
India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI)
- It is a multi-partner initiative involving the Indian Council of Medical Research, WHO-India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and State governments.
- It aims to improve blood pressure control for people with hypertension.
- The project initiated in 26 districts in 2018 has expanded to more than 100 districts by 2022.
- More than two million patients were started on treatment and tracked to see whether they achieved BP control.
The project was built on five scalable strategies:
- Simple treatment protocol with three drugs was selected in consultation with the experts and non-communicable disease programme managers.
- Supply chain was strengthened to ensure the availability of adequate antihypertensive drugs.
- Patient-centric approaches were followed, such as refills for at least 30 days and assigning the patients to the closest primary health centre or health wellness centre to make follow-up easier.
- The focus was on building capacity of all health staff and sharing tasks such as BP measurement, documentation, and follow-up.
- There was minimal documentation using either paper-based or digital tools to track follow-up and BP control.
Prevalence of hypertension in India
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death among adults in India.
- One of the major drivers of heart attack and stroke is untreated high blood pressure or hypertension.
- Hypertension is a silent killer as most patients do not have any symptoms.
- India has more than 200 million people with hypertension, and only 14.5% of individuals with hypertension are on treatment.
Success of IHCI
- Blood pressure treatment and control were feasibly controlled in primary care settings in diverse health systems across various States in India.
- Before IHCI, many patients travelled to higher-level facilities such as community health centres (block level) or district hospitals in the public sector for hypertension treatment.
- Over three years, all levels of health staff at the primary health centres and health wellness centres were trained to provide treatment and follow-up services for hypertension.
- Nearly half (47%) of the patients under care achieved blood pressure control.
- The BP control among people enrolled in treatment was 48% at primary health centres and 55% at the health wellness centres.
Contributing to its success: A data-driven approach
- One of the unique contributions of the project was a data-driven approach to improving care and overall programme management.
- The list of people who did not return for treatment was generated through a digital system or on paper by the nurse/health workers.
- Patients were reminded either over the phone or by home visit (if feasible).
- This strategy motivated a large number of patients to continue treatment.
- In addition, programme managers reviewed aggregate data at the district and State levels to assess the performance of facilities in terms of follow-up and BP control.
- Patients were provided generic antihypertensive drugs costing only ₹200 per year.
- In addition, E-Sanjeevani, a telemedicine initiative, facilitated teleconsultations.
Back2Basics: Hypertension
- Hypertension also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated.
- High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms.
- Long-term high blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia.
- High blood pressure is classified as primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension.
- For most adults, high blood pressure is present if the resting blood pressure is persistently at or above 130/80 or 140/90 mmHg.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Bridging the health policy to execution chasm
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Public health and management cadre
Context
In April this year, the Union government released a guidance document on the setting up of a ‘public health and management cadre’ (PHMC) as well as revised editions of the Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) — for ensuring quality health care in government facilities.
Background
- The need for a public health cadre and services in India rarely got any policy attention.
- Limited understanding: The reason was that even among policymakers, there was limited understanding on the roles and the functions of public health specialists and the relevance of such cadres, especially at the district and sub-district levels.
- However, the last decade and a half was eventful.
- The initial threat of avian flu in 2005-06, the Swine flu pandemic of 2009-10; five more public health emergencies of international concern between years 2009-19; the increasing risks and regular emergence and re-emergence of of new viruses and diseases (Zika, Ebola, Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic fever, Nipah viruses, etc.) in animals and humans, resulted in increased attention on public health.
- National Public health Act: In 2017, India’s National Health Policy 2017 proposed the formation of a public health cadre and enacting a National Public Health Act.
- The COVID-19 pandemic changed the status quo.
- In the absence of trained public health professionals at the policy and decision making levels, India’s pandemic response ended up becoming bureaucrat steered and clinician led.
Different cadres and its implications
- Lack of career progression opportunities: At present, most Indian States (with exceptions such as Tamil Nadu and Odisha) have a teaching cadre (of medical college faculty members) and a specialist cadre of doctors involved in clinical services.
- This structure does not provide similar career progression opportunities for professionals trained in public health.
- Limited interest: It is one of the reasons for limited interest by health-care professionals to opt for public health as a career choice.
- The outcome has been costly for society: a perennial shortage of trained public health workforce.
Public health cadre
- The proposed public health cadre and the health management cadre have the potential to address some of these challenges.
- With the release of guidance documents, the States have been advised to formulate an action plan, identify the cadre strengths, and fill up the vacant posts in the next six months to a year.
- A public health workforce has a role even beyond epidemics and pandemics.
- A trained public health workforce ensures that people receive holistic health care, of preventive and promotive services (largely in the domain of public health) as well as curative and diagnostic services (as part of medical care).
Revised version of IPHS and significance
- This is the second revision in the IPHS, which were first released in 2007 and then revised in 2012.
- The regular need for a revision in the IPHS is a recognition of the fact that to be meaningful, quality improvement has to be an ongoing process.
- The development of the IPHS itself was a major step.
- The revised IPHS is an important development but not an end itself.
- In the 15 years since the first release of the IPHS, only a small proportion — around 15% to 20% — of government health-care facilities meets these standards. .
- If the pace of achieving IPHS is any criteria, there is a need for more accelerated interventions.
- Opportunities such as a revision of the IPHS should also be used for an independent assessment on how the IPHS has improved the quality of health services.
Implementation challenges
- The effective part of implementation is interplay: policy formulation, financial allocation, and the availability of a trained workforce.
- In this case, policy has been formulated.
- Financial allocations: Then, though the Government’s spending on health in India is low and has increased only marginally in the last two decades; however, in the last two years, there have been a few additional — small but assured — sources of funding for public health services have become available.
- The Fifteenth Finance Commission grant for the five-year period of 2021- 26 and the Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) allocations are available for strengthening public health services and could be used as States embark upon implementing the PHMC and a revised IPHS.
- Availability of trained workforce: The third aspect of effective implementation, the availability of trained workforce, is the most critical.
- As States develop plans for setting up the PHMC, all potential challenges in securing a trained workforce should be identified and actions initiated.
Conclusion
The public health and management cadres and the revised IPHS can help India to make progress towards the NHP goal. To ensure that, State governments need to act urgently and immediately.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Back2Basics: Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS)
- IPHS are a set of uniform standards envisaged to improve the quality of health care delivery in the country.
- The IPHS documents have been revised keeping in view the changing protocols of the existing programmes and introduction of new programmes especially for Non-Communicable Diseases.
- Flexibility is allowed to suit the diverse needs of the States and regions.
- These IPHS guidelines will act as the main driver for continuous improvement in quality and serve as the bench mark for assessing the functional status of health facilities.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Ensuring a sustainable vaccination programme
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gavi
Mains level: Paper 2- Future pandemic preparedness
Context
COVID-19, which disrupted supply chains across countries and in India too, marks an inflection point in the trajectory of immunisation programmes.
UIP: Showcasing India’s strength in managing large scale vaccination
- India’s Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP), launched in 1985 to deliver routine immunisation, showcased its strengths in managing large-scale vaccine delivery.
- This programme targets close to 2.67 crore newborns and 2.9 crore pregnant women annually.
- Full immunisation: To strengthen the programme’s outcomes, in 2014, Mission Indradhanush was introduced to achieve full immunisation coverage of all children and pregnant women at a rapid pace — a commendable initiative.
- India’s UIP comprises upwards of 27,000 functional cold chain points of which 750 (3%) are located at the district level and above; the remaining 95% are located below the district level.
- The COVID-19 vaccination efforts relied on the cold chain infrastructure established under the UIP to cover 87 crore people with two doses of the vaccine and over 100 crore with at least a single dose.
Why strong service delivery network is essential?
- While we have, over the years, set up a strong service delivery network, the pandemic showed us that there were weak links in the chain, especially in the cold chain.
- Nearly half the vaccines distributed around the world go to waste, in large part due to a failure to properly control storage temperatures.
- In India, close to 20% of temperature-sensitive healthcare products arrive damaged or degraded because of broken or insufficient cold chains, including a quarter of vaccines.
- Wastage has cost implications and can delay the achievement of immunisation targets.
Measures and initiatives in strengthening vaccine supply chains
- The Health Ministry has been digitising the vaccine supply chain network in recent years through the use of cloud technology, such as with the Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN).
- Developed with support from Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, and implemented by the UN Development Programme through a smartphone-based app, the platform digitises information on vaccine stocks and temperatures across the country.
- This supports healthcare workers in the last mile in supervising and maintaining the efficiency of the vaccine cold chain.
Way forward
- Electrification: There is a need to improve electrification, especially in the last mile, for which the potential of solar-driven technology must be explored to integrate sustainable development.
- For instance, in Chhattisgarh, 72% of the functioning health centres have been solarised to tackle the issue of regular power outages.
- This has significantly reduced disruption in service provision and increased the uptake of services.
Conclusion
India has pioneered many approaches to ensure access to public health services at a scale never seen before. Robust cold chain systems are an investment in India’s future pandemic preparedness; by taking steps towards actionable policies that improve the cold chain, we have an opportunity to lead the way in building back better and stronger.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Public health engineering
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Focusing on public health engineering
Context
As we confront the public health challenges emerging out of environmental concerns, expanding the scope of public health/environmental engineering science becomes pivotal.
Why does India need a specialised cadre of public health engineers
- Achieving SDGs and growing demand for water consumption: For India to achieve its sustainable development goals of clean water and sanitation and to address the growing demands for water consumption and preservation of both surface water bodies and groundwater resources, it is essential to find and implement innovative ways of treating wastewater.
- It is in this context why the specialised cadre of public health engineers, also known as sanitation engineers or environmental engineers, is best suited to provide the growing urban and rural water supply and to manage solid waste and wastewater.
- Limited capacity: The availability of systemic information and programmes focusing on teaching, training, and capacity building for this specialty cadre is currently limited.
- Currently in India, civil engineering incorporates a course or two on environmental engineering for students to learn about wastewater management as a part of their pre-service and in-service training.
- However, the nexus between wastewater and solid waste management and public health issues is not brought out clearly.
- India aims to supply 55 litres of water per person per day by 2024 under its Jal Jeevan Mission to install functional household tap connections.
- The goal of reaching every rural household with functional tap water can be achieved in a sustainable and resilient manner only if the cadre of public health engineers is expanded and strengthened.
- Different from the international trend: In India, public health engineering is executed by the Public Works Department or by health officials. This differs from international trends.
Way forward
- Introducing public health engineering as a two-year structured master’s degree programme or through diploma programmes for professionals working in this field must be considered to meet the need of increased human resource in this field.
- Interdisciplinary field: Furthermore, public health engineering should be developed as an interdisciplinary field.
- Engineers can significantly contribute to public health in defining what is possible, identifying limitations, and shaping workable solutions with a problem-solving approach.
- Public health engineering’s combination of engineering and public health skills can also enable contextualised decision-making regarding water management in India.
Conclusion
Diseases cannot be contained unless we provide good quality and adequate quantity of water. Most of the world’s diseases can be prevented by considering this. Training our young minds towards creating sustainable water management systems would be the first step.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI)
Mains level: Non-communicable diseases burden on India
A project called the India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI) finds that nearly 23% out of 2.1 million Indians have uncontrolled blood pressure.
What is the IHCI?
- Recognizing that hypertension is a serious, and growing, health issue in India, the Health Ministry, the ICMR, State Governments, and WHO-India began a five-year initiative to monitor and treat hypertension.
- The programme was launched in November 2017.
- In the first year, IHCI covered 26 districts across five States — Punjab, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Telangana, and Maharashtra.
- By December 2020, IHCI was expanded to 52 districts across ten States — Andhra Pradesh (1), Chhattisgarh (2), Karnataka (2), Kerala (4), Madhya Pradesh (6), Maharashtra (13), Punjab (5), Tamil Nadu (1), Telangana (13) and West Bengal (5).
What is Hypertension?
- Hypertension is defined as having systolic blood pressure level greater than or equal to 140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure level greater than or equal to 90 mmHg.
- The definition also assumes taking anti-hypertensive medication to lower his/her blood pressure.
Why need IHCI?
- India has committed to a “25 by 25” goal, which aims to reduce premature mortality due to non-communicable diseases (NCDs) by 25% by 2025.
- To achieve India’s target of a 25%, approximately 4.5 crore additional people with hypertension need to get their BP under control by 2025.
What has the IHCI found so far?
- Its most important discovery so far is that nearly one-fourth of (23%) patients under the programme had uncontrolled blood pressure, and 27% did not return for a follow-up in the first quarter of 2021.
- There were an estimated 20 crore adults with hypertension in the country.
- There weren’t enough validated high-quality digital blood pressure monitors in several health facilities, which affected accuracy of hypertension diagnosis.
How prevalent is the problem of hypertension?
- About one-fourth of women and men aged 40 to 49 years have hypertension.
- Southern States have a higher prevalence of hypertension than the national average, according to the latest edition of the National Family Health Survey.
- While 21.3% of women and 24% of men aged above 15 have hypertension in the country, the prevalence is the highest in Kerala where 32.8% men and 30.9% women have been diagnosed with hypertension.
- Kerala is followed by Telangana where the prevalence is 31.4% in men and 26.1% in women.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Monkeypox?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Monkey Pox
Mains level: Zoonotic Diseases

The UK health authorities have confirmed a case of Monkeypox, which is a virus passed from infected animals such as rodents to humans, in someone with a recent travel history to Nigeria where they are believed to have caught it.
What is Monkeypox?
- The monkeypox virus is an orthopoxvirus, which is a genus of viruses that also includes the variola virus, which causes smallpox, and vaccinia virus, which was used in the smallpox vaccine.
- It causes symptoms similar to smallpox, although they are less severe.
- While vaccination eradicated smallpox worldwide in 1980, monkeypox continues to occur in a swathe of countries in Central and West Africa, and has on occasion showed up elsewhere.
- According to the WHO, two distinct clade are identified: the West African clade and the Congo Basin clade, also known as the Central African clade.
Its origin
- Monkeypox is a zoonosis, that is, a disease that is transmitted from infected animals to humans.
- Monkeypox virus infection has been detected in squirrels, Gambian poached rats, dormice, and some species of monkeys.
- According to the WHO, cases occur close to tropical rainforests inhabited by animals that carry the virus.
Symptoms and treatment
- Monkeypox begins with a fever, headache, muscle aches, back ache, and exhaustion.
- It also causes the lymph nodes to swell (lymphadenopathy), which smallpox does not.
- The WHO underlines that it is important to not confuse monkeypox with chickenpox, measles, bacterial skin infections, scabies, syphilis and medication-associated allergies.
- The incubation period (time from infection to symptoms) for monkeypox is usually 7-14 days but can range from 5-21 days.
- There is no safe, proven treatment for monkeypox yet.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Highlights of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) 5 Part: II
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NFHS and other survey mentioned
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Total Fertility Rate (TFR), the average number of children per woman, has further declined from 2.2 to 2.0 at the national level between National Family Health Survey (NFHS) 4 and 5.
What is NFHS?
- The NFHS is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted in a representative sample of households throughout India.
- The IIPS is the nodal agency, responsible for providing coordination and technical guidance for the NFHS.
- NFHS was funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) with supplementary support from United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF).
- The First National Family Health Survey (NFHS-1) was conducted in 1992-93.
Objectives of the NFHS
The survey provides state and national information for India on:
- Fertility
- Infant and child mortality
- The practice of family planning
- Maternal and child health
- Reproductive health
- Nutrition
- Anaemia
- Utilization and quality of health and family planning services
Modifications in NFHS 5
NFHS-5 includes new focal areas that will give requisite input for strengthening existing programmes and evolving new strategies for policy intervention. The areas are:
- Expanded domains of child immunization
- Components of micro-nutrients to children
- Menstrual hygiene
- Frequency of alcohol and tobacco use
- Additional components of non-communicable diseases (NCDs)
- Expanded age ranges for measuring hypertension and diabetes among all aged 15 years and above.
Highlights of the NFHS 5 Part-II
(a) Fertility Rate
- There are only five States — Bihar (2.98), Meghalaya (2.91), Uttar Pradesh (2.35), Jharkhand (2.26) Manipur (2.17) —which are above replacement level of fertility of 2.1.
(b) Institutional Births
- The institutional births increased from 79% to 89% across India and in rural areas around 87% births being delivered in institutions and the same is 94% in urban areas.
- As per results of the NFHS-5, more than three-fourths (77%) children aged between 12 and 23 months were fully immunised, compared with 62% in NFHS-4.
- The level of stunting among children under five years has marginally declined from 38% to 36% in the country since the last four years.
- Stunting is higher among children in rural areas (37%) than urban areas (30%) in 2019-21.
(c) Decision making
- The extent to which married women usually participate in three household decisions (about health care for herself; making major household purchases; visit to her family or relatives) indicates that their participation in decision-making is high, ranging from 80% in Ladakh to 99% in Nagaland and Mizoram.
- Rural (77%) and urban (81%) differences are found to be marginal.
- The prevalence of women having a bank or savings account has increased from 53% to 79% in the last four years.
(d) Rise in obesity
- Compared with NFHS-4, the prevalence of overweight or obesity has increased in most States/UTs in NFHS-5.
- At the national level, it increased from 21% to 24% among women and 19% to 23% among men.
- More than a third of women in Kerala, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, AP, Goa, Sikkim, Manipur, Delhi, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Punjab, Chandigarh and Lakshadweep (34-46 %) are overweight or obese.
Also read
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Loudspeaker Crackdown: Court orders and Govt directives
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Noise Pollution
Mains level: Crackdown on noise pollution

Illegal and unauthorized loudspeakers had been taken down across the Uttar Pradesh and their loudness had been capped, under “an existing government order of 2018, and set rules for sound decibel limits and court directions”.
What is the news?
- The UP state authorities have taken action since the loudspeaker crackdown began in our country.
- Notices were served to alleged violators by local police stations citing the order of Allahabad High Court of 2017, and centre’s the Noise Pollution Rules, 2000.
- The recent UP order asked officials to remove illegal loudspeakers after dialogue and coordination with religious leaders, and to ensure that decibel levels are kept within laid down limits.
Legal basis of loudspeaker crackdowns
(a) Orders of 2022, 2018
- The April 23 order said that two earlier orders passed by the government in 2018 were not being followed, and the situation needed to be rectified.
- Those earlier orders had been passed to ensure implementation of The Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000.
- However, it had come to knowledge that many religious institutions are violating the standard decibel norms and are using loudspeakers in large numbers.
(b) The Noise Pollution Rules, 2000
- The 2000 Rules define “Ambient Air Quality Standards in Respect of Noise”, i.e., Industrial, Commercial, Residential, and Silence Zones.
- It asked officials to demarcate these areas and to ensure that the correct norms were followed.
- Each police station has been asked to prepare a list of religious institutions using loudspeakers under their jurisdiction.
What is noise pollution?
- Noise is defined as unwanted sound. A sound might be unwanted because it is loud, distracting, or annoying.
- Noise pollution is manmade sound in the environment that may be harmful to humans or animals.
Objective of the NPR, 2000: To regulate and control noise producing and generating sources with the objective of maintaining the ambient air quality standards in respect of noise
Important compliance’s under NPR, 2000
- What are the restrictions on using loud speaker or musical system at night?
: A person cannot play a loud speaker, public address system, sound producing instrument, musical instrument or a sound amplifier at night time except in closed premises like auditorium, conference rooms, community halls or banquet halls. - What is the noise level for using loudspeakers or the public address?
: The persons using loudspeakers or public address shall maintain the noise level and restrain it from exceeding 10 dB (A) above the ambient noise standards for the area specified or 75 dB (A) whichever is lower. - What is the Noise level for a private sound system?
: The persons owning a private sound system or a sound producing instrument shall not, exceed the noise above 5 dB (A) the noise standards specified for the area in which it is used. - What are the prohibitions on violating the silence zone areas?
A person shall not do the following acts in silence zone- Playing any music or uses any sound amplifiers,
- A drum or tom-tom or blows a horn either musical or pressure, or trumpet or beats or sounds any instrument, or
- Playing any musical or other performance of a to attract crowd
- Bursting sound-emitting firecrackers
- Using a loudspeaker or a public address system.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Autism Support Network to give Specialised Care in Rural India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Autism
Mains level: Mental healthcare in India
The Centre for Autism and Other Disabilities Rehabilitation Research and Education (CADRRE), a not-for-profit organization will launch “Pay Autention — a different mind is a gifted mind”, India’s first bridgital autism support network.
Pay ‘Autention’
- The initiative shall pave the way for small towns and rural India to access specialised care and support and help create an auxiliary network of champions for the differently-abled.
- This platform shall also enable mentoring, skilling and meaningful livelihoods for people with autism.
- In the first phase, the initiative will primarily focus on supporting children with autism, and subsequently, in the second stage, it will focus on young adults, empowering them with life skills and career readiness.
- The content is designed and delivered in collaboration with specialists from CADRRE who have expertise in training children with autism.
- The project aims to create a network of grassroots champions, enable early identification, first-level care, teach social skills, ways to ease activities of daily living, hold workshops for sensory and motor development.
- It also focuses on art and craft, dance, music therapy, physical and mental fitness, communication skills and enable support for academics.
What is Autism?
- Autism, also called autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a complicated condition that includes problems with communication and behaviour.
- It can involve a wide range of symptoms and skills.
- ASD can be a minor problem or a disability that needs full-time care in a special facility.
- People with autism have trouble with communication. They have trouble understanding what other people think and feel.
- This makes it hard for them to express themselves, either with words or through gestures, facial expressions, and touch.
- People with autism might have problems with learning. Their skills might develop unevenly.
- For example, they could have trouble communicating but be unusually good at art, music, math, or memory.
What are the signs of Autism?
Symptoms of autism usually appear before a child turns 3. Some people show signs from birth. Common symptoms of autism include:
- A lack of eye contact
- A narrow range of interests or intense interest in certain topics
- Doing something over and over, like repeating words or phrases, rocking back and forth, or flipping a lever
- High sensitivity to sounds, touches, smells, or sights that seem ordinary to other people
- Not looking at or listening to other people
- Not looking at things when another person points at them
- Not wanting to be held or cuddled
- Problems understanding or using speech, gestures, facial expressions, or tone of voice
- Talking in a sing-song, flat, or robotic voice
- Trouble adapting to changes in routine
What causes Autism?
- Exactly why autism happens isn’t clear. It could stem from problems in parts of your brain that interpret sensory input and process language.
- Autism is four times more common in boys than in girls. It can happen in people of any race, ethnicity, or social background.
- Family income, lifestyle, or educational level doesn’t affect a child’s risk of autism. But there are some risk factors:
- Autism runs in families, so certain combinations of genes may increase a child’s risk.
- A child with an older parent has a higher risk of autism.
- Pregnant women who are exposed to certain drugs or chemicals, like alcohol or anti-seizure medications, are more likely to have autistic children
- Other risk factors include maternal metabolic conditions such as diabetes and obesity.
Prevalence of Autism in India
- Prevalence and incidence statistics about autism in India is 1 in 500 or 0.20% or more than 2,160,000 people.
- According to a study, an estimated three million people live with autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) on the Indian subcontinent.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Why are vaccines administered into the upper arm?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vaccination
Mains level: NA
Almost everyone vaccinated for Covid-19 over the last 16 months will remember that he or she received a quick prick in the upper arm.
Why vaccines are generally administered into muscle?
- This is because most vaccines, including those for Covid-19, are most effective when administered through the intramuscular route into the upper arm muscle, known as the deltoid.
- There are several reasons, but the most important one is that the muscles have a rich blood supply network.
- This means whenever a vaccine carrying an antigen is injected into it, the muscle releases the antigen, which gets dispersed by the muscular vasculature, or the arrangement of blood vessels in the muscle.
- The antigen then gets picked up by a type of immune cells called dendritic cells, which function by showing antigens on their surface to other cells of the immune system.
- The dendritic cells carry the antigen through the lymphatic fluid to the lymph node.
Role of T Cells
- T Cells also called T lymphocyte, type of leukocyte (white blood cell) that is an essential part of the immune system.
- T cells are one of two primary types of lymphocytes—B cells being the second type—that determine the specificity of the immune response to antigens (foreign substances) in the body.
- Through the course of research over the years, it is understood that the lymph nodes have T cells and B cells — the body’s primary protector cells.
- Once this antigen gets flagged and is given to the T cells and B cells that is how we start developing an immune response against a particular virus.
- It could be any of the new viruses like SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19, or the previous viruses which we have been running vaccination programs for.
Other options for vaccination
- Conversely, if the vaccine is administered into the subcutaneous fat tissue [between the skin and the muscle], which has a poor blood supply, absorption of the antigen vaccine is poor and therefore one may have failed immune response.
- Similarly, the additives which could be toxic, could cause a local reaction.
- The same thing could happen when the vaccine is administered intradermally (just below the outermost skin layer, the epidermis).
- Hence, the route chosen now for most vaccines is intramuscular.
- Also, compared to the skin or subcutaneous tissue, the muscles have fewer pain receptors, and so an intramuscular injection does not hurt as much as a subcutaneous or an intradermal injection.
But why the upper arm muscle in particular?
- In some vaccines, such as that for rabies, the immunogenicity — the ability of any cell or tissue to provoke an immune response — increases when it is administered in the arm.
- If administered in subcutaneous fat tissues located at the thigh or hips, these vaccines show a lower immunogenicity and thus there is a chance of vaccine failure.
Why not administer the vaccine directly into the vein?
- This is to ensure the ‘depot effect’, or release of medication slowly over time to enable longer effectiveness.
- When given intravenously, the vaccine is quickly absorbed into the circulation.
- The intramuscular method takes some time to absorb the vaccine.
- Wherever a vaccination programme is carried out, it is carried out for the masses.
- To deposit the vaccine, the easiest route would be the oral route (like the polio vaccine).
- However, for other vaccines that need to be administered intravenously or intramuscularly (enabling wider field-based administration), the intramuscular route is chosen from a public health perspective over the intravenous route.
Which vaccines are administered through other routes?
- One of the oldest vaccines that for smallpox, was given by scarification of the skin.
- However, with time, doctors realised there are better ways to vaccinate beneficiaries.
- These included the intradermal route, the subcutaneous route, the intramuscular route, oral, and nasal routes.
- There are only two exceptions that continue to be administered through the intradermal route.
- These are the vaccines for BCG (Bacillus Calmette–Guérin) and for tuberculosis because these two vaccines continue to work empirically well when administered through the intradermal route.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Noise Pollution in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Noise Pollution
Mains level: Not Much
The city of Moradabad in Uttar Pradesh is the second-most noise polluted city globally, according to a recent report title Frontier 2022 by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
What is Noise Pollution?
- Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is the propagation of noise with ranging impacts on the activity of human or animal life, most of them harmful to a degree.
- It is generally defined as regular exposure to elevated sound levels that may lead to adverse effects in humans or other living organisms.
- The source of outdoor noise worldwide is mainly caused by machines, transport, and propagation systems.
- Poor urban planning may give rise to noise disintegration or pollution, side-by-side industrial and residential buildings can result in noise pollution in the residential areas.
- Some of the main sources of noise in residential areas include loud music, transportation (traffic, rail, airplanes, etc.), maintenance, construction, electrical generators, wind turbines, explosions, and people etc.
Defining Noise Pollution
- Sounds with a frequency over 70 db are considered harmful to health.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) had recommended a 55 db standard for residential areas in the 1999 guidelines, while for traffic and business sectors, the limit was 70 db.
- The WHO set the limit of noise pollution on the road at 53 db in 2018, taking into account health safety.
Noise Pollution in India
- The report identifies 13 noise polluted cities in south Asia. Five of these, including Moradabad, are in India, which have recorded alarming levels of noise pollution:
- Kolkata (89 db)
- Asansol (89 db)
- Jaipur (84 db)
- Delhi (83 db)
- The noise pollution figures given in the report relate to daytime traffic or vehicles.
- Moradabad has recorded noise pollution of a maximum of 114 decibels (db). The Frontier 2022 report mentions a total of 61 cities.
Case in the neighborhood
- The highest noise pollution of 119 db has been recorded in Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh.
- At third place is Pakistan’s capital Islamabad, where the noise pollution level has been recorded at 105 db.
Hazards created
- High levels of noise pollution affect human health and well-being by having an effect on sleep.
- This has a bad effect on the communication of many animal species living in the area and their ability to hear.
- Regular exposure for eight hours a day to 85 decibels of sound can permanently eliminate the ability to hear.
- Not only that, exposure to relatively low noise pollution for long periods in cities can harm physical and mental health.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Need for integrated approach to power sector
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: COP26
Mains level: Paper 2- Integration of development sector and electricity
Context
Electricity and development sectors need a more integrated approach to achieve the vision set forth in instruments such as the Union Budget that guide policy implementation at other administrative levels.
Reduction in allocation
- While the health sector witnessed a 16% increase in estimated Budget allocations from last year, medical and public health spending was reduced by 45% for 2022-23.
- Budget estimates demonstrate intent, but the proof of the pudding lies in the actual expenditure which reiterates the need for greater attention to be paid to our health and education sectors.
- While the health sector was allocated ₹74,602 crore in 2021-22, the Government exceeded its spending by over ₹5,000 crore more (₹80,026 crore) on health, signalling a spike in demand, likely propelled by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
- Given this scenario, a less than ₹1,000 crore increase in the Budget Estimate (₹86,606 crore) in 2022-23 when compared with last year’s Revised Estimates (₹85,915 crore) appears incongruent with the Government’s aim of providing quality public health care at scale.
Role of reliable energy
- It is widely recognised that the availability of reliable electricity supply can improve the delivery of health and education services.
- 74% of the targets of the Sustainable Development Goals are interlinked with universal access to reliable energy.
- Its reliability in terms of the number of hours that electricity is available steadily without any voltage fluctuations also plays a significant role in delivering services.
- Sometimes, multiple policies can complement each other to achieve the larger sectoral objectives.
- For example, in Assam, the Energy Vision document that lays out the electricity and development outcomes is to be applied in tandem with the Solar Energy Policy 2017 that operationalises this vision via an action plan.
Reasons for lack of integration of electrification in the development sector
- The lack of integration of electrification requirements in development sector policy documents may be partly due to lack of information about electricity and development linkages, poor coordination mechanisms between the sectors and departments, and poor access to appropriate finance.
- Even while electricity is considered, it is to the limited extent of being a one-time civil infrastructure activity rather than a continuous feature necessary for the day-to-day operations of these services.
Way forward
- To successfully integrate electricity provisioning and maintenance, policy frameworks should include innovative coordination and financing mechanisms.
- These mechanisms, while developing clear compliance mandates, must also allow sufficient room for flexibility to respond to local contexts.
- Providing reliable electricity for health centres and schools should be the responsibility of centralised decision-making entities at the State or national level.
- As India has witnessed with other cross-sectoral and centralised statistical, planning, and implementation data governance, diverse contexts must support oversight mechanisms that ensure data credibility.
- Finance is largely unavailable to ensure reliable electricity supply to schools and health facilities.
- Some directives, such as those governing the use of untied funds, need to be more flexible in allowing these facilities to prioritise providing reliable and sustainable electricity.
Conclusion
A successful policy outcome might be dependent on several invisible aspects that do not get the attention and funding necessary to aid in successful policy delivery. Electricity is one of them.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A miracle cure against HIV
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HIV/AIDS
Mains level: Communicable diseases burden on India
There is considerable excitement in the world of medicine after scientists reported that a woman living with HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and administered an experimental treatment is likely ‘cured’.
What is HIV/AIDS?
- HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks cells that help the body fight infection, making a person more vulnerable to other infections and diseases.
- First identified in 1981, HIV is the cause of one of humanity’s deadliest and most persistent epidemics.
- It is spread by contact with certain bodily fluids of a person with HIV, most commonly during unprotected sex, or through sharing injection drug equipment.
- If left untreated, HIV can lead to the disease AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
- The human body can’t get rid of HIV and no effective HIV cure exists.
Treating HIV
- However, by taking HIV medicine (called antiretroviral therapy or ART), people with HIV can live long and healthy lives and prevent transmitting HIV to their sexual partners.
- In addition, there are effective methods to prevent getting HIV through sex or drug use, including pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP).
What is the new breakthrough?
- US researchers have described the case of a 60-year-old African American woman who was diagnosed with an HIV infection in 2013.
- She was started on the standard HIV treatment regimen of anti-retroviral treatment (ART) therapy consisting of tenofovir, emtricitabine, and raltegravir.
- She was given cord blood, or embryonic stem cells, from a donor with a rare mutation that naturally blocks the HIV virus from infecting cells.
- She was also given blood stem cells, or adult stem cells, from a relative.
What actually worked?
- The adult stem cells boosted the patient’s immunity and possibly helped the cord blood cells fully integrate with the lady’s immune system.
- Now she has no sign of HIV in her blood and also has no detectable antibodies to the virus.
- Embryonic stem cells are potentially able to grow into any kind of cell and hence their appeal as therapy, though there is no explanation for why this mode of treatment appeared to be more effective.
Is this treatment the long-sought cure for AIDS?
- Not at all. While this approach is certainly a welcome addition to the arsenal of treatments, stem cell therapy is a cumbersome exercise and barely accessible to most HIV patients in the world.
- Moreover, this requires stem cells from that rare group of individuals with the beneficial mutation.
- Anti-retroviral therapy, through the years, has now ensured that HIV/AIDS isn’t always a death sentence and many with access to proper treatment have lifespans comparable to those without HIV.
- A vaccine for HIV or a drug that eliminates the virus is still elusive and would be the long-sought ‘cure’ for HIV/AIDS.
What is the prevalence of HIV/AIDS in India?
- As per the India HIV Estimation 2019 report, the estimated adult (15 to 49 years) HIV prevalence trend has been declining in India since the epidemic’s peak in the year 2000 and has been stabilizing in recent years.
- In 2019, HIV prevalence among adult males (15–49 years) was estimated at 0.24% and among adult females at 0.20% of the population.
- There were 23.48 lakh Indians living with HIV in 2019.
- Maharashtra had the maximum at 3.96 lakh followed by Andhra Pradesh (3.14 lakh) and Karnataka.
- ART is freely available to all those who require and there are deputed centers across the country where they can be availed from.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Weighing in on a health data retention plan
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Mains level: Paper 2- Privacy centric health data retention policy
Context
The National Health Authority (NHA) — the body responsible for administering the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) — has initiated a consultation process on the retention of health data by healthcare providers in India. The consultation paper asks for feedback on what data is to be retained, and for how long.
Issues with the policy for healthcare data retention
- Risk of over-collection: A simple classification system, as suggested in the consultation paper, exposes individuals to harms arising from over-collection and retention of unnecessary data.
- At the same time, this kind of one-size-fits-all system can also lead to the under-retention of data that is genuinely required for research or public policy needs.
- Instead, we should seek to classify data based on its use.
Do we need a policy for the mandatory retention of health data?
- Currently, service providers can compete on how they handle the data of individuals or health records, in theory, each of us can choose a provider whose data policies we are comfortable with.
- Whether the state should mandate a retention period at all is an open question.
- Given the landscape of healthcare access in India, including through informal providers, many patients may not think about this factor in practice.
- Nonetheless, the decision to take the choice out of the individual’s hands should not be taken lightly.
Balancing the policy for public health data retention with the right to privacy
- Four-part test for privacy: The Supreme Court of India has clarified that privacy is a fundamental right, and any interference into the right must pass a four-part test: legality; legitimate aim; proportionality, and appropriate safeguards.
- Health data and privacy: The mandatory retention of health data is one such form of interference with the right to privacy.
- 1] Legality: In this context, the question of legality becomes a question about the legal standing and authority of the NHA.
- Since the NHA is not a sector-wide regulator, it has no legal basis for formulating guidelines for healthcare providers in general.
- 2]Legitimate aim: The aim of data retention is described in terms of benefits to the individual and the public at large.
- Benefits to the individuals: Individuals benefit through greater convenience and choice, created through portability of health records.
- The broader public benefits through research and innovation, driven by the availability of more and better data to analyse.
- Risk involved: Globally, legal systems consider health data particularly sensitive, and recognise that improper disclosure of this data can expose a person to a range of significant harms.
- Benefits must be clearly defined: As per Indian law, if an individual’s rights are to be curtailed due to anticipated benefits, such benefits cannot be potential or speculatory: they must be clearly defined and identifiable.
- 3] Proportionality: This is the difference between saying that data on patients with heart conditions will help us better understand cardiac health — a vague explanation — and being able to identify a specific study that will include data from that patient.
- It would further mean demonstrating that the study requires personally identifiable information, rather than just an anonymous record — the latter flowing from the principle of proportionality, which requires choosing the least intrusive option available.
- 4] Safeguard: Standards for anonymisation are still developing.
- We are not yet able to rule out the possibility of anonymised data still being linked back to specific individuals.
- In other words, even anonymisation may not be the least intrusive solution to safeguarding patients’ rights in all scenarios.
Way forward
- Clear and specific case for retention: The test for retaining data should be that a clear and specific case has been identified for such retention, following a rigorous process run by suitable authorities.
- Anonymise data: A second safeguard would be to anonymise data that is being retained for research purposes — again, unless a specific case is made for keeping personally identifiable information.
- If neither of these is true, the data should be deleted.
- Express and informed consent: An alternate basis for retaining data can be the express and informed consent of the individual in question.
- User-based classification process: Health-care service providers — and everyone else — will have to comply with the data protection law, once it is adopted by Parliament.
- The current Bill already requires purpose limitation for collecting, processing, sharing, or retaining data; a use-based classification process would thus bring the ABDM ecosystem actors in compliance with this law as well.
Consider the question “What are the advantages and concerns with the retention of public health data? Suggest the ways to ensure the privacy-centric public health data retention policy.”
Conclusion
A privacy-centric process is needed to determine what data to retain and for how long.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
How the Budget can push India’s health system transformation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Health Authority
Mains level: Paper 2- Health system transformation
Context
After decades of low government expenditure on health, the Covid pandemic created a societal consensus on the need to strengthen our health system.
Steps to strengthen our health system
- The Fifteenth Finance Commission recommended greater investment in rural and urban primary care, a nationwide disease surveillance system extending from the block-level to national institutes, a larger health workforce and the augmentation of critical care capacity of hospitals.
- The Union budget of 2021 reflected these priorities in a proposed Pradhan Mantri Aatmanirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana (PMASBY) to be made operational over six years, with a budget of Rs 64,180 crore.
- Broader vision of health: The Finance Minister also projected a broader vision of health beyond healthcare by merging allocations to water, sanitation, nutrition and air pollution control with the health budget.
- Under the Ayushman Bharat umbrella the Digital Health Mission was launched in September 2021.
- The Health Infrastructure Mission, launched in October 2021, was a renamed and augmented version of the PMASBY.
- These missions join the two other components of Ayushman Bharat launched in 2018.
- The Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC) component is nested in the National Health Mission (NHM) while the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) is steered by the National Health Authority (NHA).
Way forward
- While much of the following needs to be done by the states, the Centre should incentivise and support such efforts by the states.
- Link synergically: Primary healthcare services under the CPHC and linkage with water, sanitation, nutrition and pollution control programmes will strengthen the capacity of the health system for health promotion and disease prevention.
- The budget of 2022 must not only fund these missions adequately but indicate how they will link synergically while functioning under different administrative agencies.
- Allocate more funds: The NHM received only a 9.6 per cent increase in the 2021 budget.
- PMJAY did not see an increase in allocation last year, because its utilisation for non-Covid care declined sharply in the previous year.
- More importantly, limiting cost coverage to hospitalised care reduces the PMJAY’s capacity to significantly lower out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE) on health, which is driven mostly by outpatient care and expenditure on medicines.
- Focus on Digital Heath Mission: The Digital Health Mission can enhance efficiency of the health systems in a variety of ways.
- These include better data collection and analysis, improved medical and health records, efficient supply chain management, tele-health services, support for health workforce training, implementation of health insurance programmes, real time monitoring and sharper evaluation of health programme performance along with effective multi-sectoral coordination.
- Improve the skill and number of healthcare workers: We need to increase the numbers and improve the skills of all categories of healthcare providers.
- While training specialist doctors could take time, the training of frontline workers like Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) and Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (ANMs) can be done in a shorter time.
- Upgrade district hospitals: District hospitals need to be upgraded, with greater investment in infrastructure, equipment and staffing.
- In underserved regions, such district hospitals should be upgraded to become training centres for students of medical, nursing and allied health professional courses.
Conclusion
The expanded ambit of health, as defined in last year’s budget, must continue for aligning other sectors to public health objectives. The Union budget of 2022 can add further momentum to our health system transformation.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
National Commission for Safai Karamcharis gets 3-year extension
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NCSK
Mains level: Manual scavenging in India
The Union Cabinet has approved a three-year extension of the tenure of the National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK) that was set to end on March 31.
About National Commission for Safai Karamcharis
- The commission was set up in 1993 under the NCSK Act 1993 for a period of three years, which has been extended since then.
- The NCSK Act is however ceased to have effect from February 29, 2004.
- After that, the tenure of the NCSK has been extended as a non-statutory body from time to time through resolutions.
Why was NCSK set up?
- The commission helps in coming up with programmes for the welfare of sanitation workers.
- It also monitors the implementation of the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013.
- Till December 31, 2021, 58,098 manual scavengers had been identified.
Need for eliminating Manual Scavenging
- Undignified life (all the 6 Fundamental Rights are compromised, directly or indirectly).
- It directly perpetuates castism.
- Modern, Secular India has no place for such “professions”.
- It no way suits India’s rising global profile – ‘super power’ aspirations.
- Women are mostly disprivileged since most manual scavengers are dalit women.
What else needs to be done?
- Though the government has taken many steps for the upliftment of the safai karamcharis, the deprivation suffered by them in socio-economic and educational terms is still far from being eliminated.
- Although manual scavenging has been almost eradicated, sporadic instances of their deaths do occur.
Way forward
- There is a continued need to monitor the various interventions and initiatives of the government for welfare of safai Karamcharis.
- The govt must strive to achieve the goal of complete mechanization of sewer/septic tanks cleaning in the country and rehabilitation of manual scavengers.
Try this question from CSP 2016:
Q.’Rashtriya Garima Abhiyaan’ is a national campaign to:
(a) rehabilitate the homeless and destitute persons and provide them with suitable sources of livelihood
(b) release the sex workers from their practice and provide them with alternative sources of livelihood
(c) eradicate the practice of manual scavenging and rehabilitate the manual scavengers
(d) release the bonded labourers from their bondage and rehabilitate them
Post your answers here:
Also try this question from our AWE initiative:
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Extinguishing the tobacco industry’s main narrative
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Price and tax measures to reduce demand of tobacco
Context
There is no doubt that tobacco use is highly detrimental to public health. We have to find the ways and the means to reduce the demand for tobacco among existing as well as aspiring users.
Impact of tobacco
- Tobacco is a product that kills more than 13 lakh Indians every year.
- Annual burden: The annual economic burden from tobacco use is estimated to be ₹177,340 crore which is more than 1% of India’s GDP.
- About 27 crore people above the age of 15 years and 8.5% of school-going children in the age group 13-15 years use tobacco in some form in India.
Are price and tax measures effective against tobacco use?
- When tobacco products become more expensive, people either quit using them or use them less, and it incentivises many to not initiate the habit.
- Because it hurts both revenue and profits, the tobacco industry, globally, is always devising tactics and narratives that will pre-empt any kind of tax increases on tobacco products.
- The narrative of “increasing illicit trade” is something the tobacco industry has historically used to pre-empt potential tax increases on tobacco products in most countries around the world.
- The story is no different in India.
- In a recent report by the Tobacco Institute of India, it was said that the illicit cigarette volume in India has grown by 44% from 2011 to 2019 while adding that high and increasing tax rates provide a profitable opportunity for tax evasion and encourage growth in illegal trade.
- A study published in 2018 which used a survey of empty cigarette packs collected from retail outlets across different cities in India estimated that illicit cigarettes constitute 2.7% of the market.
- The second study published in 2020 used tax-gap analysis to estimate that the percentage of illicit cigarettes was 5.1% in 2009-10 and 6.6% in 2016-17.
Are taxes and prices key determinants of illicit trade?
- It is to be noted that taxes and prices are not the key determinants of illicit trade.
- There is sufficient evidence in the literature on illicit trade in cigarettes that shows tax increases only have a minimal impact, if at all, on illicit trade.
- There are several countries where tobacco taxes are quite high and yet have low levels of illicit trade, while there are also countries with high levels of illicit trade despite having relatively low tax rates.
- Several factors such as the quality of tax administration, the strength of the regulatory framework, government commitment to control illicit trade, the strength of governance, social acceptance, and the presence of informal distribution networks are known to play a larger role in determining the scale and the extent of an illicit market.
Way forward
- WHO protocol: Eliminating all forms of illicit trade in tobacco products through a package of measures is one of the major objectives of the Protocol to Eliminate Illicit Trade in Tobacco Products under the World Health Organization’s Framework Convention on Tobacco Control.
- The Protocol provides the tools and the measures to eliminate or minimise illicit trade which includes strong governance, establishing an international track and trace system, and securing supply chains.
- India has already ratified the World Health Organization Protocol and it should now show leadership in implementing these measures to effectively address even the relatively lower levels of illicit trade.
Conclusion
There is no scientific or public health rationale not to increase tax on tobacco products for unfounded fear of increasing illicit trade.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Worrying trends in nutrition indicators in NFHS-5 data
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Dealing with the nutrition gap
Context
The NFHS-5 factsheets for India and all states and Union territories are now out. At first glance, it appears to be a mixed bag — much to cheer about, but concern areas remain.
Positives from the NFHS-5 survey
- Change in demographic trends: For the first time since the NFHS 1992-93 survey, the sex ratio is slightly higher among the adult population.
- Improvement in sex ratio at birth: For the first time in 15 years that the sex ratio at birth has reached 929 (it was 919 for 1,000 males in 2015-16).
- The total fertility rate has also dropped from 2.2 per cent to a replacement rate of 2 per cent, albeit with not much change in the huge fertility divide between the high and low fertility states.
- Improvement in literacy level of women: There has been an appreciable improvement in general literacy levels and in the percentage of women and men who have completed 10 years or more of schooling, which has reached 41 per cent and 50.2 per cent respectively.
- Improvements in health indicators: The health sector deserves credit for achieving a significant improvement in the percentage of institutional births, antenatal care, and children’s immunisation rates.
- There has also been a consistent drop in neonatal, infant and child mortality rates — a decrease of around 1 per cent per year for neonatal and infant mortality and a 1.6 per cent decrease per year for under five mortality rate.
Nutrition: Area of concern
- Increase in anaemic people: India has become a country with more anaemic people since NFHS-4 (2015-16), with anaemia rates rising significantly across age groups, ranging from children below six years, adolescent girls and boys, pregnant women, and women between 15 to 49 years.
- Why anaemia is a concern? Adverse effects of anaemia affect all age groups — lower physical and cognitive growth and alertness among children and adolescents, and lesser capacity to learn and play, directly impacting their future potential as productive citizens.
- Further, anaemia among adolescent girls (59.1 per cent) advances to maternal anaemia and is a major cause of maternal and infant mortality and general morbidity and ill health in a community.
- The detailed report will explain why a dedicated programme like Anaemia Mukt Bharat which focused on IFA consumption failed to gain impetus.
- Slow pace of improvement in nutritional indicators: Between NFHS 4 and NFHS 5, the percentage of children below five years who are moderately underweight has reduced from 35.8 per cent to 32.1 per cent.
- Moderately stunted children have fallen from 38.4 per cent to 35.5 per cent, moderately wasted from 21 per cent to 19.3 per cent and severely wasted have increased slightly from 7.5 per cent to 7.7 per cent.
- Inadequate diet: The root cause for this is that the percentage of children below two years receiving an adequate diet is a mere 11.3 per cent, increasing marginally from 9.6 per cent in NFHS-4.
Way forward
- India’s nutrition programmes must undergo a periodic review.
- The Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), which is perceived as the guardian of the nation’s nutritional well-being must reassess itself and address critical intervention gaps, both conceptually and programmatically, and produce rapid outcomes.
Conclusion
The nutritional deficit which ought to be considered an indicator of great concern is generally ignored by policymakers and experts. Unless this is addressed, rapid improvement in nutritional indicators cannot happen.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Put out the data, boost the dose of transparency
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Dealing with Covid
Context
The Government must make COVID-19 data including that for vaccine regulatory approvals and policy available.
Kay decisions
- On December 25, the Prime Minister of India announced two key decisions.
- Vaccination of children: All children in the 15-17 age bracket will be eligible to receive COVID-19 vaccines from January 3, 2022.
- Third shot: All health-care workers, frontline workers and the people aged 60 years and above (with co-morbidities and on the advice of a medical doctor) can get a third shot, or ‘precaution dose’.
- The eligibility for the precaution dose will be on the completion of nine months or 39 weeks after the second dose.
- Teenage children whose birth year is 2007 or before will be eligible for COVID-19 vaccines.
- Children will receive Covaxin, the reason being (according to the note) it is the only emergency use listed (EUL) World Health Organization vaccine available for use in this age group in India.
Issues with the decision
- Lack of scientific evidence: The decision is said to be based on ‘advice of the scientific community’.
- A few members of the National Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (NTAGI) in India, have written or spoken publicly about not having enough scientific evidence to administer booster doses and vaccinate children in India.
- Successive national and State-level sero-surveys have reported that a majority of children in India had got natural infection, while staying at home and thus developed antibodies.
- The studies have shown that children rarely develop moderate to severe COVID-19 disease.
- Targeted vaccination approach not adopted: Most public health and vaccine experts favour a ‘targeted vaccination approach’ by prioritising high-risk children for COVID-19 vaccination.
- However, such an approach is likely to face an operational challenge in the identification of the eligible children.
- Consultation cost: A majority of the elderly have one or other comorbidities. Of the 14 crore elderly population in India, an estimated 7 to 10 crore people could have co-morbidities.
- If they have to seek advice from a physician, in order to get vaccinated, this essentially means that there would be up to 10 crore of medical consultations, which would come at a cost — all of which is avoidable.
Suggestions
- Do away with prescription: The conditionality of comorbidities and the need for advice/prescription by a doctor for ‘the precaution shot’ in the elderly should be done away with.
- Third dose to all immunocompromised adults: There is scientific evidence and consensus on administering the third dose for immunocompromised adults.
- The Indian government should urgently consider administering a third dose for all immunocompromised adults, irrespective of age.
- Third dose on a different vaccine platform: Studies have found that a heterologous prime-boost approach — third shot on a different vaccine platform — is a better approach.
- Identify policy questions: Various pending policy questions on COVID-19 vaccine need to be identified urgently.
- The technical expert should be given complete access to COVID-19 data for analysis and to find answers to those scientific and policy questions.
- Vaccine supply and stock management: Vaccination for teenage children, exclusively with Covaxin (which means 15 crore doses for this sub-group) has other implications.
- Covaxin will also be needed for people coming for their first shot, returning for their second shot, and then for their ‘precaution dose’ if a third shot of the same vaccine is allowed.
- Focus on primary vaccination: The precaution dose and vaccination for children should not divert attention from the task of primary vaccination, which continues to be an unfinished task in India; 46 crore doses are still needed for the first and second shots.
- Make data public: It is time the Union and State governments in India make COVID-19 data — this includes clinical outcomes, testing, genomic sequencing as well as vaccination — available in the public domain.
- This would help in formulating and updating COVID-19 policy and strategies and also assess the impact of ‘precaution dose’ as well as vaccination of children.
Conclusion
The Indian government urgently needs to make COVID-19 data available, including the one used for regulatory approvals of vaccines and for vaccine policy decisions. This will bring transparency in decision making and increase the trust of the citizen in the process.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
NITI Aayog releases fourth edition of State Health Index
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: State Health Index
Mains level: Competitive Federalism

NITI Aayog has released the fourth edition of the State Health Index for 2019–20.
State Health Index
- The State Health Index is an annual tool to assess the performance of states and UTs. It is being compiled and published since 2017.
- The index is part of a report commissioned by the NITI Aayog, the World Bank, and the Union Health and Family Welfare Ministry.
- The reports aim to nudge states/UTs towards building robust health systems and improving service delivery.
Components of the index
- It is a weighted composite index based on 24 indicators grouped under the domains of ‘Health Outcomes’, ‘Governance and Information’, and ‘Key Inputs/Processes’.
- Health outcomes: It includes parameters such as neonatal mortality rate, under-5 mortality rate, and sex ratio at birth.
- Governance: This includes institutional deliveries, average occupancy of senior officers in key posts earmarked for health.
- Key inputs: It consists of the proportion of shortfall in healthcare providers to what is recommended, functional medical facilities, birth, and death registration, and tuberculosis treatment success rate.
Performance of the states
- For the fourth year in a row, Kerala has topped a ranking of States on health indicators. Uttar Pradesh has come in at the bottom.
- Kerala is followed by Tamil Nadu and Telangana, which improved its ranking.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Issues with Health Surveys in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NFHS and other survey mentioned
Mains level: Need for national health data architecture
This article discusses the feasibility of conducting a single comprehensive survey for collecting health-related data in India.
Context
- In a country perennially thirsty for reliable health data, the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) is like an oasis.
- It has a large volume of data that is openly accessible.
- The report of the fifth round of the NFHS was recently released. Since then, we had many articles covering different aspects (malnutrition, fertility, and domestic violence to name a few).
What is NFHS?
- The NFHS is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted in a representative sample of households throughout India.
- Three rounds of the survey have been conducted since the first survey in 1992-93.
- Currently, the survey provides district-level information on fertility, child mortality, contraceptive practices, reproductive and child health (RCH), nutrition, and utilization and quality of selected health services.
- The Ministry of Health has designated the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) Mumbai, as the nodal agency, responsible for providing coordination and technical guidance for the survey.
Issues with health surveys in India
- Multiple surveys: The NFHS is not the only survey. In the last five years, there has been the National NCD Monitoring Survey (NNMS), the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) etc.
- Huge cost: Each survey funding for different rounds of NFHS costs upto ₹250 crore.
- Huge chunk of data: The size of the survey has obvious implications for data quality.
- Different estimates: Multiple surveys also raise the problem of differing estimates, as is likely, due to sampling differences in the surveys.
- Limited respondents: The respondents are largely women in the reproductive age group (15-49 years) with husbands included.
- Global obligations: Some of these surveys are done to meet the global commitments on targets (NCDs, tobacco, etc.).
- Undefined purpose The health surveys have confusing research with programme monitoring and surveillance needs. Ex. Questions on domestic violence in NFHS.
Need of the hour
- Alignment of purpose: There have been previous attempts to align these surveys but they have failed as different advocates have different “demands” and push for inclusion of their set of questions.
- Regularity of surveys: NFHS is the only major survey that India has a record of doing regularly. One does not know if and when the other surveys will be repeated.
One-stop solution
- National health data architecture: With diverse aspects of health, there is a need to plan the public health data infrastructure for the country.
- Budgetary outlay: We also need to ensure that these data are collected in an orderly and regular manner with appropriate budgetary allocation.
- Purpose definition: This requires clarity of purpose and a hard-nosed approach to the issue that randomized activities.
- National-level indicators: We have to identify a set of national-level indicators and surveys that will be done using national government funds at regular intervals.
How should surveys be done?
- There should be three national surveys done every three to five years in a staggered manner:
- NFHS focuses on Reproductive and Child Health (RCH) issues
- Behavioral Surveillance Survey (focusing on HIV, NCD, water sanitation and hygiene (WASH)-related and other behaviors) and
- Nutrition-Biological Survey (entails collection of data on blood pressure, anthropometry, blood sugar, serology, etc.)
We need to look at alternate models and choose what suits us best.
Way forward
- Important public health questions can be answered by specific studies conducted by academic institutions on a research mode based on availability of funding.
- States have to become active partners including providing financial contributions to these surveys.
- It is also very important to ensure that the data arising from these surveys are in the public domain.
Conclusion
- We are ready to establish public health data architecture for our complexity of needs.
- We have the technical capacity to do so.
- All it requires now is the political will.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Extending outpatient health care coverage
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Extending coverage to OP care
Context
Over the past two decades, initiatives announced to extend health care coverage to the indigent sections have come under criticism due to their near-exclusive focus on hospitalisation (inpatient, IP) care.
Significance of outpatient health care
- What is outpatient health care: Outpatient (OP) health care, mainly comprising doctor consultations, drugs, and tests, can be called ‘the elephant in the room’ of Indian public health care policy.
- OP expenses have the majority share in total out-of-pocket (OOP) expenditure on health.
Why do we need to extend OP care coverage?
- How IP care differs from OP care? IP care comprises high-impact and unavoidable episodes that are less prone to misuse than OP care, for which demand is considerably more sensitive to price and is thus more prone to overuse under health insurance.
- IP insurance prioritised: This logic, among other reasons, has led to IP insurance schemes being prioritised.
- [1] OP care and preventive care is neglected: While a price-sensitive demand for OP care entails that it could be misused under insurance, it also means that OP care is the first to come under the knife when there is no insurance.
- In India, where there are many public IP insurance schemes but no OP coverage, this incentive is further amplified.
- The mantra of ‘prevention is better than cure’ thus goes for a toss.
- [2] Against economic sense: It defies economic sense to prioritise IP care over OP care for public funds.
- Preventive and primary care services which often come with externalities, elicit little felt need and demand, and must therefore be the primary recipients of public investment.
- Not conducive to epidemiological profile: Greater investments in IP care today translate to even greater IP care investments in future, further reduction in primary care spending, and ultimately lesser ‘health’ for the money invested.
- None of these are conducive to the epidemiological profile that characterises this country.
Issues with using private commercial insurance to extend OP care coverage nationwide
- Some recent policy pronouncements by the Centre have conveyed an inclination to expand healthcare coverage with little fiscal implications for the government.
- Challenges:
- [1] The OP practices are under-regulated and there is a lack of standards.
- [2] The difficulty to monitor OP clinical and prescribing behaviours and the concomitant higher likelihood of malpractices.
- [3] Low public awareness of insurance products and a low ability to discern entitlements and exclusions.
- [4] Add to it the inexperience that a still under-developed private OP insurance sector brings.
- All these entail tremendous and largely wasteful costs and administrative complexity, and it would be of little help even if the government was to step in with considerable subsidies.
Suggestion
- Need for fiscal and time commitment: Significant improvements in healthcare are implausible without significant fiscal and time commitments.
- No perfect model: There is no ‘perfect’ model of expanding healthcare — the emphasis must be on finding the best fit.
- Implementing even such a best fit could involve adopting certain modalities with known drawbacks.
- Expand public spending: The focus must be on expanding public OP care facilities and services financed mainly by tax revenues.
- For India, wisdom immediately points to successful countries that are (or were, at one point) much closer to its socioeconomic fabric, such as Thailand, than countries like the U.S. which we currently look to emulate.
- Now, the sparse number and distribution of public facilities offers various modes of rationing care, and their expansion is likely to result in a considerable spike in demand.
- Contracting with private players: Contracting with private players based on objective and transparent criteria would also be called for, with just enough centralised supervision to deter corruption while preserving local autonomy.
- To deter supply-side malpractices, low-powered modes of provider payment, such as capitation, may be considered for private providers wherever possible.
Conclusion
There are several compelling reasons for extending outpatient health care coverage even though there are several challenges to overcome to achieve this.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
How lack of public data on pandemic could harm us
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Omicron variant
Mains level: Paper 2- Importance of data in dealing with pandemic
Context
Questions are being asked about India’s preparedness as the cases with the Omicron variant of the Coronavirus has been on the rise in the country.
Where does India stand?
[1] The Positives
- Addressing oxygen shortage: The extreme shortages of oxygen that we saw barely six months ago will hopefully not be a feature of a third wave.
- Vaccinated population: We have now vaccinated more than 50% of the adult population with both doses of vaccine, and approximately 85% have received one or two doses.
- Ramping up testing to deal with a spike should not require an increase in capacity.
- More vaccine doses: We have more vaccine doses than in May 2021 and the potential for oral antiviral therapy in the near future.
[2] The negatives
- Lack of data: An urgent and important one is the lack of publicly available data on the pandemic from Government sources, particularly in regard to testing, but also in terms of being able to correlate disease severity with age, prior medical conditions, locations and other variables.
- Data from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), India’s premier medical research agency, remains inaccessible.
- The National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) has not responded.
- The CoWIN data contains valuable information but it is of little value for future planning and prediction unless it can be tied to testing data and clinical information at the level of individuals.
- ICMR data not correlated to CoWIN platform data: The Indian Council of Medical Research holds data on every COVID-19 test conducted in India.
- However, these data are not correlated to the vaccine data in the CoWIN platform.
- Data with States is inaccessible: Data on hospitalisations, etc. are apparently available at the State level, but seem inaccessible.
What we can know from the data about pandemic
- Infer the probability of reinfection: If we knew that a person had tested positive on successive tests separated by, say four months or more, with a negative test in-between, that would suggest a reinfection.
- We could then infer the probability of such a reinfection.
- Probability of vaccine breakthrough infection: With information about testing and vaccination status, we could compute the probability of a vaccine breakthrough event.
- To know the efficacy of single vaccine dose: By checking to see whether the positive test happened after the first but before the second dose of vaccine, or after the second dose, the relative efficacy of such single vaccine doses at preventing disease could be derived.
- Effect of the vaccine on disease severity: By examining symptoms reported after a vaccine breakthrough event, we could understand the extent to which vaccines reduce disease severity.
- Impact of new variant: Add to this a layer of sequence information, and we could study the impact of new variants.
Role of the volunteer organisation
- The most trustworthy and granular data on cases in India have resulted from the remarkable and public-spirited work of a volunteer organisation, Covid19India.org.
- Their work has now been taken over by several other voluntary groups, all operating on the same broad principles of data accessibility: covid19bharat.org, incovid19.org and covid19tracker.in.
Way forward
- Commitment towards data accessibility: We need to stress on data availability because this is the one area where a swift realignment is possible.
- The more widely data are shared, the greater the likelihood of integration of the rapidly shifting scientific frontier with clinical practice.
- Learning from the experience of South Africa: With the advantages of a relatively high-quality surveillance system among low- and middle-income countries (LMIC) countries, bolstered by a commitment towards transparency and data accessibility, South Africa’s rapid sharing allowed the world to prepare swiftly for the appearance of the highly mutated Omicron variant.
- It is clear that pre-emptive decisions on vaccination and other measures could be made faster and better if more integrated data were available.
Consider the question “Why availability and accessibility of data is important in dealing with the Covid-19 pandemic? What are the challenges facing health data accessibility in India?”
Conclusion
Now, more than ever before is the time for us to urgently reassess our attitude towards data for public health purposes and the role of national health agencies in sharing data, generated with public funds, with scientists in India and across the world.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Amendment to the NDPS Act
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NDPS Act
Mains level: Narcotics crime in India

The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (Amendment) Bill, 2021 was passed by Lok Sabha.
Must read:
About NDPS Act
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, commonly referred to as the NDPS Act was promulgated in 1985.
- It prohibits a person from the production/manufacturing/cultivation, possession, sale, purchasing, transport, storage, and/or consumption of any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance
What is the 2021 amendment?
- The 2021 Bill amends the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 and seeks to rectify a drafting “anomaly” created by a 2014 amendment to the parent legislation.
- It contains a legislative declaration about what one section refers to.
- It says Section 2 clause viii(a) corresponds to clause viii(b) in Section 27, since 2014 when the provision was first brought in.
- Section 27A of the NDPS Act, 1985, prescribes the punishment for financing illicit traffic and harbouring offenders.
Earlier amendment in 2014
- In 2014, a substantial amendment was made to the NDPS Act to allow for better medical access to narcotic drugs.
- It defined “essential drugs”; under Section 9 and allowed the manufacture, possession, transport, import inter-State, export inter-State, sale, purchase, consumption and use of essential narcotic drugs.
- But before the 2014 amendment, a Section 2(viii)a already existed and contained a catalogue of offences for which the punishment is prescribed in Section 27A.
What is Section 21A?
- Section 27A reads: Whoever indulges in financing, directly or indirectly or harbours any person engaged in any of the aforementioned activities, shall be punishable with rigorous imprisonment.
- The term shall not be less than ten years and may extend to twenty years.
- The accused shall also be liable to fine which shall not be less than one lakh rupees but which may extend to two lakh rupees.
What was the drafting “anomaly”?
- While defining “essential drugs” in 2014, the legislation re-numbered Section 2.
- The catalogue of offences, originally listed under Section 2(viii)a, was now under Section 2(viii)b.
- In the amendment, Section 2(viii)a defined essential narcotic drugs.
- However, the drafters missed amending the enabling provision in Section 27A to change Section 2(viii)a to Section 2(viii)b.
What was the result of the drafting error?
- Section 27A punished offences mentioned under Section 2(viiia) sub-clauses i-v.
- However, Section 2 (viiia) sub-clauses i-v, which were supposed to be the catalogue of offences, does not exist after the 2014 amendment. It is now Section 2(viiib).
- This error in the text meant since 2014, Section 27A was inoperable.
When was the error noticed?
- In June this year, the Tripura High Court, while hearing a reference made by the district court, flagged the drafting error, urging the Centre to bring in an amendment and rectify it.
- In 2016, an accused had sought bail before a special judge in West Tripura in Agartala, citing this omission in drafting.
Why can’t it be applied retrospectively?
- Article 20(1) of the Constitution says that no person shall be convicted of any offence except for violation of the law in force at the time of the commission.
- The person shall not be subjected to a penalty greater than that which might have been inflicted under the law in force at the time of the commission of the offence.
- This protection means that a person cannot be prosecuted for an offence that was not a “crime” under the law when it was committed.
Does the latest amendment make it retrospective?
- In September, the government brought in an ordinance to rectify the drafting error, which Lok Sabha. “It shall be deemed to have come into force on the 1st day of May 2014,” the Bill reads.
- Retrospective application is permitted in clarificatory amendments.
- This 2021 amendment is not a substantive one, that is why the retrospective is allowed.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Tobacco Consumption in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Cancer related fatality in India
Tobacco use is known to be a major risk factor for several non-communicable diseases in India.
Tobacco abuse in India
- In India, 28.6% of adults above 15 years and 8.5% of students aged 13-15 years use tobacco in some form or the other.
- This makes the country the second-largest consumer of tobacco in the world.
Concern: No action against Tobacco
- India bears an annual economic burden of over ₹1, 77,340 crores on account of tobacco use.
- There has been no major increase in taxation of tobacco products to discourage the consumption of tobacco in the past four years since the introduction of GST.
- Only in 2020-21, the Union Budget had the effect of increasing the average price of cigarettes by about 5%.
- Yet, the excise duty on tobacco in India continues to remain extremely low.
A worrying trend
- No increase in tax: The absence of an increase in tax means more profits for the tobacco industry and more tax revenue foregone for the government.
- Revenue losses: This revenue could have easily been utilized during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Losses due to GST: There has been a 3% real decline in GST revenues from tobacco products in each of the past two financial years.
Present governance of Tobacco
- GST slab: Tobacco at present is a highly taxed commodity. It is kept in the 28% GST slab (other than for tobacco leaves which is taxed at 5%).
- Heavy cess: Tobacco and its various forms are also subject to a heavy burden of cess, given that the commodity is seen as a sin good.
- Statutory warning: The government also uses pictures of cancer patients on the packages of cigarettes to discourage its use.
Federal issues
- Excise taxes on many tobacco products used to be regularly raised in the annual Union Budgets before the GST.
- Similarly, several State governments used to regularly raise value-added tax (VAT) on tobacco products.
- During the five years before the introduction of the GST, most State governments had moved from having a low VAT regime on tobacco products to having a high VAT regime.
Implication of such policies
- Increased consumption: The lack of tax increases in post-GST years might mean that some current smokers smoke more now and some non-smokers have started smoking.
- Reverse trend in decline: This could potentially lead to a reversal of the declining trend in prevalence.
- Affordability: Tobacco products are more affordable post-GST as shown in recent literature from India.
- Missing up national target: This might jeopardise India’s commitment to achieving 30% tobacco use prevalence reduction by 2025 as envisaged in the National Health Policy of 2017.
Way forward
- Several countries in the world have high excise taxes along with GST or sales tax and they are continuously being revised.
- We must adhere to the WHO recommendation for a uniform tax burden of at least 75% for each tobacco product.
- The Union government should take a considerate view of public health and significantly increase excise taxes — either basic excise duty or NCCD — on all tobacco products.
- Taxation should achieve a significant reduction in the affordability of tobacco products to reduce tobacco use prevalence and facilitate India’s march towards sustainable development goals.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Global Health Security Index, 2021
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Health Security Index, 2021
Mains level: Health security

Countries across all income levels remain dangerously unprepared to meet future epidemic and pandemic threats, according to the new 2021 Global Health Security (GHS) Index.
About GHS Index
- The GHS Index is the first comprehensive assessment and benchmarking of health security and related capabilities across the 195 countries that make up the States Parties to the International Health Regulations.
- It is a project of the Johns Hopkins Centre for Health Security, the Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI) and the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) and was first launched in October 2019.
- It assesses countries across 6 categories, 37 indicators, and 171 questions using publicly available information.
- It benchmarks health security in the context of other factors critical to fighting outbreaks, such as political and security risks, the broader strength of the health system, and country adherence to global norms.
Parameters assessed
The report is based on a questionnaire of 140 questions, organized across 6 categories, 34 indicators, and 85 sub-indicators. The six categories are:
- Prevention: Prevention of the emergence or release of pathogens
- Detection and Reporting: Early detection and reporting for epidemics of potential international concern
- Rapid Response: Rapid response to and mitigation of the spread of an epidemic
- Health System: Sufficient and robust health system to treat the sick and protect health workers
- Compliance with International Norms: Commitments to improving national capacity, financing plans to address gaps, and adhering to global norms
- Risk Environment: Overall risk environment and country vulnerability to biological threats
Global performance
- In 2021, no country scored in the top tier of rankings and no country scored above 75.9, the report showed.
- The world’s overall performance on the GHS Index score slipped to 38.9 (out of 100) in 2021, from a score of 40.2 in the GHS Index, 2019.
- This, even as infectious diseases are expected to have the greatest impact on the global economy in the next decade.
- Some 101 countries high-, middle- and low-income countries, including India, have slipped in performance since 2019.
Indian scenario
- India, with a score of 42.8 (out of 100) too, has slipped by 0.8 points since 2019.
- Three neighboring countries — Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Maldives — have improved their score by 1-1.2 points.
Conclusion
- Health emergencies demand a robust public health infrastructure with effective governance.
- The trust in government, which has been a key factor associated with success in countries’ responses to COVID-19, is low and decreasing, the index noted.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Need for closer scrutiny of reduced out-of-pocket expenditure on health
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Scrutinising reduced out-of-pocket expenditure on health
Context
The National Health Accounts (NHA) report for 2017-18 is being celebrated widely as it shows that total public spending on health as a percentage of GDP has increased to a historic high of 1.35% of GDP.
India’s total public spending on health
- One of the lowest in the world: India’s total public spending on health as a percentage of GDP or in per capita terms has been one of the lowest in the world.
- Majority spent by the States: The Union government traditionally spends around a third of the total government spending whereas the majority is borne by the States.
- There has been a policy consensus for more than a decade now that public spending has to increase to at least 2.5% of GDP.
- However, there has not been any significant increase so far.
- Despite several pronouncements, it has continued to hover around 1%-1.2% of GDP.
Why NHA report is being celebrated?
- The National Health Accounts (NHA) report capture spending on health by various sources, and track the schemes through which these funds are channelised to various providers in a given time period for a given geography.
- The National Health Accounts (NHA) report for 2017-18 is being celebrated widely as it shows that total public spending on health as a percentage of GDP has increased to a historic high of 1.35% of GDP.
- The increase shown in NHA 2017-18 is largely due to increase in Union government expenditure.
- Increase in Centre’s share: For 2017-18, the Centre’s share in total public spending on health has jumped to 40.8%.
- However, if we study the spending pattern of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Ministry of AYUSH, we see that expenditure increased to 0.32% of GDP from 0.27% in 2016-17 — insufficient to explain the overall jump.
Issues with NHA report
- Expenditure of DMS included: Much of this increase has actually happened on account of a tripling of expenditure of the Defence Medical Services (DMS).
- Compared to an expenditure of ₹10,485 in 2016-17, it increased to ₹32,118 crore.
- Though the increasing spending for the health of defence personnel is a good thing, such spending does not benefit the general population.
- Within government expenditure, the share of current health expenditure has come down to 71.9% compared to 77.9% a year ago.
- Capital expenditure included: This essentially means, capital expenditure has increased, and specifically in defence.
- There is a problem in accounting capital expenditure within the NHA framework.
- Why capital expenditure needs to be left out: Equipment brought or a hospital that is built serves people for many years, so the expenditure incurred is used for the lifetime of the capital created and use does not get limited to that particular year in which expenditure is incurred.
- The World Health Organization proposes to leave out capital expenditure from health accounts estimates, instead focus on current health expenditure.
- Incomparable to other countries: In NHA estimates in India, in order to show higher public investment, capital expenditure is included; thus, Indian estimates become incomparable to other countries.
- The NHA estimate also shows that out-of-pocket expenditure as a share of GDP has reduced to less than half of the total health expenditure.
- NSSO 2017-18 data suggest that during this time period, utilisation of hospitalisation care has declined compared to 2014 NSSO estimates for almost all States and for various sections of society.
- Sign of distress: The decline in out-of-pocket expenditure is essentially due to a decline in utilisation of care rather than greater financial protection.
- Actually, the NSSO survey happened just after six months of demonetisation and almost at the same time when the Goods and Services Tax was introduced.
- The disastrous consequences of the dual blow of demonetisation and GST on the purchasing power of people are quite well documented.
- Another plausible explanation is linked to limitations in NSSO estimates. The NSSO fails to capture the spending pattern of the richest 5% of the population (who incur a large part of the health expenditure).
- Thus, out-of-pocket expenditure measured from the NSSO could be an under-estimate as it fails to take into account the expenditure of the richest sections.
Conclusion
The reduction of out-of-pocket expenditure is a sign of distress and a result of methodological limitations of the NSSO, rather than a sign of increased financial protection.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What the latest NFHS data says about the New Welfarism
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- What findings of NHFS-5 imply
Context
The second and final phase of NFHS-5 was released which covered 11 states (including Uttar Pradesh (UP), Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh (MP), Jharkhand, Haryana, and Chhattisgarh) and about 49 per cent of the population.
Major findings
[1] Success of New Welfarism
- Figure one plots household access to improved sanitation, cooking gas and bank accounts used by women.
- The improvements are as striking as they were based on the performance of the phase 1 states.
- In all cases, access has increased significantly, although claims of India being 100 per cent open defecation-free still remain excessive.

[2] Child-related outcomes
- India-wide, stunting has declined although the pace of improvement has slowed down post-2015 compared with the previous decade.
- For example, stunting improved by 0.7 percentage points per year between 2005 and 2015 compared to 0.3 percentage points between 2015 and 2021.
- On diarrhoea too, adding the new data reverses the earlier finding.
- However, on anaemia and acute respiratory illness, there seems to have been deterioration.
- The new child stunting results are significant but also surprising because of the sharply divergent outcomes between the phase 1 and phase 2 states.
- The interesting pattern is that nearly all the phase 2 states show large improvements, whereas most of the phase 1 states exhibited a deterioration in performance.
[3] Catch up by the laggard states
- If the new child stunting numbers are right, a different picture of India emerges.
- Apparently, Madhya Pradesh now has fewer stunted children than Gujarat; Uttar Pradesh and Jharkhand are almost at par with Gujarat; Chhattisgarh fares better than Gujarat, Karnataka, and Maharashtra; and Rajasthan and Odisha fare better than Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, West Bengal, Telangana and Himachal Pradesh!
- On child stunting, the old BIMARU states (excepting Bihar) are no longer the laggards; the laggards are Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Karnataka, and to a lesser extent, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Indeed, the decline in stunting achieved by the poorer states such as UP, MP, Chhattisgarh and Rajasthan would be all the more remarkable given the overall weakness in the economy between 2015 and 2021.
Conclusion
When commentators speak of two Indias, it is now important to ask: Which ones and on what metrics.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
National Health Accounts Estimates: 2017-18
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Health Accounts Estimates: 2017-18
Mains level: Health expenditure in India

Out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE) as a share of total health expenditure and foreign aid for health has both come down as per the findings of the National Health Accounts (NHA) estimates for India for 2017-18.
What is National Health Accounts (NHA)?
- The NHA estimates are prepared by using an accounting framework based on internationally accepted System of Health Accounts 2011, provided by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- It is released by Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- It describes health expenditures and flow of funds in the country’s health system over a financial year of India.
- It answers important policy questions such as what are the sources of healthcare expenditures, who manages these, who provides health care services, and which services are utilized.
- It is a practice to describe the health expenditure estimates according to a global standard framework, System of Health Accounts 2011 (SHA 2011), to facilitate comparison of estimates across countries.
Objective of the NHA
- To describe the Current Health Expenditures (CHE).
The details of CHE are presented according to
- Revenues of healthcare financing schemes: – entities that provide resources to spend for health goods and services in the health system;
- Healthcare financing schemes: entities receiving and managing funds from financing sources to pay for or to purchase health goods and services;
- Healthcare providers: entities receiving finances to produce/ provide health goods and services;
- Healthcare functions: It describes the use of funds across various health care services.
About NHA (2017-2018)
- The 2017-18 NHA estimates shows government expenditure on health exhibiting an increasing trend and growing trust in public health care system.
- With the present estimate of NHA 2017-18, India has a continuous Time Series on NHA estimates for both government and private sources for five years since 2013-14.
- These estimates are not only comparable internationally, but also enable the policy makers to monitor progress towards universal health coverage as envisaged in the National Health Policy, 2017.
Key Highlights
Increase in GDP share: The NHA estimates for 2017-18 clearly show that there has been an increase in the share of government health expenditure in the total GDP from 1.15% in 2013-14 to 1.35% in 2017-18.
Increase in govt share in expenditures: In 2017-18, the share of government expenditure was 40.8%, which is much higher than 28.6% in 2013-14.
Per-Capita increase in expenditure: In per capita terms, the government health expenditure has increased from Rs 1042 to Rs.1753 between 2013-14 to 2017-18.
Focus on total healthcare: The primary and secondary care accounts for more than 80% of the current Government health expenditure.
Social security expenditure: The share of social security expenditure on health, which includes the social health insurance program, Government financed health insurance schemes, and medical reimbursements made to Government employees, has increased.
Decline in foreign aid: The findings also depict that the foreign aid for health has come down to 0.5%, showcasing India’s economic self-reliance.
Decline in OOPE: The government’s efforts to improve public health care are evident with out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE) as a share of total health expenditure coming down to 48.8% in 2017-18 from 64.2% in 2013-14.
Way forward
- After 18 months of Covid-19, financial year 2017-18 appears to be from another era.
- However, learnings from that year’s NHA help us to plan for health system strengthening in the post-Covid years.
- The special financing packages for Covid emergency response, announced by the central government in 2020 and 2021, represent an extraordinary situation.
- The resolve to increase public financing for health must remain strong even after Covid.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Key Demographic Transitions captured by 5th round of NFHS
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Family Health Survey
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Union health ministry released the summary findings of the fifth round of the National Family and Health Survey (NFHS-5), conducted in two phases between 2019 and 2021.
About NFHS
- The NFHS is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted in a representative sample of households throughout India.
- The previous four rounds of the NFHS were conducted in 1992-93, 1998-99, 2005-06 and 2015-16.
- The survey provides state and national information for India on:
Fertility, infant and child mortality, the practice of family planning, maternal and child health, reproductive health, nutrition, anaemia, utilization and quality of health and family planning services etc.
Objectives of the survey
Each successive round of the NFHS has had two specific goals:
- To provide essential data on health and family welfare needed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and other agencies for policy and programme purposes
- To provide information on important emerging health and family welfare issues.
Key highlights of the NFHS-5
[1] Women outnumbering men
- NFHS-5 data shows that there were 1,020 women for 1000 men in the country in 2019-2021.
- This is the highest sex ratio for any NFHS survey as well as since the first modern synchronous census conducted in 1881.
- To be sure, in the 2005-06 NFHS, the sex ratio was 1,000 or women and men were equal in number.
[2] Fertility has decreased
- The Total Fertility Rate (TFR) has also come down below the threshold at which the population is expected to replace itself from one generation to next.
- TFR was 2 in 2019-2021, just below the replacement fertility rate of 2.1. To be sure, in rural areas, the TFR is still 2.1.
- In urban areas, TFR had gone below the replacement fertility rate in the 2015-16 NFHS itself.
[3] Population is ageing
- A decline in TFR, which implies that lower number of children are being born, also entails that India’s population would become older.
- Sure enough, the survey shows that the share of under-15 population in the country has therefore further declined from 28.6% in 2015-16 to 26.5% in 2019-21.
[4] Children’s nutrition has improved
- The share of stunted (low height for age), wasted (low weight for height), and underweight (low weight for age) children have all come down since the last NFHS conducted in 2015-16.
- However, the share of severely wasted children has not, nor has the share of overweight (high weight for height) or anaemic children.
- The share of overweight children has increased from 2.1% to 3.4%.
[5] Nutrition problem for adults
- For children and their mothers, there are at least government schemes such as Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) that seek to address the nutritional needs at the time of childbirth and infancy.
- However, there is a need to address the nutritional needs of adults too.
- The survey has shown that though India might have achieved food security, 60% of Indians cannot afford nutritious diets.
- While the share of women and men with below-normal Body Mass Index (BMI) has decreased, the share of overweight and obese (those with above-normal BMI) and the share of anaemic has increased.
[6] Basic sanitation challenges
- Availability of basic amenities such as improved sanitation facilities clean fuel for cooking, or menstrual hygiene products can improve health outcomes.
- There has been an improvement on indicators for all three since the last NFHS. However, the degree of improvement might be less than claimed by the government.
- For example, only 70% population had access to an improved sanitation facility.
- While not exactly an indicator of open defecation, it means that the remaining 30% of the population has a flush or pour-flush toilet not connected to a sewer, septic tank or pit latrine.
[7] Use of clean fuel
- The share of households that use clean cooking fuel is also just 59%.
[8] Financial inclusion
- The share of women having a bank account that they themselves use has increased from 53% to 79%.
- Households’ coverage by health insurance or financing scheme also has increased 1.4 times to 41%, a clear indication of the impact of the government’s health insurance scheme.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
HomoSEP: Robot for cleaning Septic Tanks
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HomoSEP
Mains level: Manual scavenging in India

IIT Madras has developed a robot that can, if deployed extensively, put an end to this practice of sending people into septic tanks.
HomoSEP
- HomoSEP stands for “homogenizer of septic tanks”.
- It has a shaft attached to blades that can open like an inverted umbrella when introduced into a septic tank.
- This is helpful as the openings of the septic tanks are small and the tank interiors are bigger.
- The sludge inside a septic tank contains faecal matter that has thickened like hard clay and settled at the bottom.
- This needs to be shredded and homogenized so that it can be sucked out and the septic tank cleaned. The whirring blades of the robot achieve precisely this.
Manual scavenging deaths in India
- A statement by the Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry conveyed that in the five years till December 31, 2020, there have been 340 deaths due to manual scavenging.
- Uttar Pradesh (52), Tamil Nadu (43) and Delhi (36) leads in the list. Maharashtra had 34 and Gujarat and Haryana had 31 each.
- This is despite bans and prohibitory orders.
Various policy initiatives
- Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (Amendment) Bill, 2020: It proposes to completely mechanise sewer cleaning, introduce ways for ‘on-site’ protection and provide compensation to manual scavengers in case of sewer deaths.
- Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013: Superseding the 1993 Act, the 2013 Act goes beyond prohibitions on dry latrines, and outlaws all manual excrement cleaning of insanitary latrines, open drains, or pits.
- Rashtriya Garima Abhiyan: It started national wide march “Maila Mukti Yatra” for total eradication of manual scavenging from 30th November 2012 from Bhopal.
- Prevention of Atrocities Act: In 1989, the Prevention of Atrocities Act became an integrated guard for sanitation workers since majority of the manual scavengers belonged to the Scheduled Caste.
- Judicial intervention: In 2014, a Supreme Court order made it mandatory for the government to identify all those who died in sewage work since 1993 and provide Rs. 10 lakh each as compensation to their families.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Health Care Equity in Urban India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Healthcare scenario in urban areas

The report on ‘Health Care Equity in Urban India’ exploring health vulnerabilities and inequalities in cities in India was recently released.
About the report
- The report is released recently by Azim Premji University in collaboration with 17 regional NGOs across India.
- It notes that a third of India’s people now live in urban areas, with this segment seeing rapid growth from about 18% (1960) to 28.53% (2001) to 34% (in 2019).
- The study draws insights from data collected through detailed interactions with civil society organizations in major cities and towns.
- This also included an analysis of the National Family and Health Surveys (NHFS), the Census of India, and inputs from State-level health officials on the provision of health care.
- It also looks at the availability, accessibility, and cost of healthcare facilities, and possibilities in future-proofing services in the next decade.
Key highlights of the report
- Urban poverty on rise: Close to 30% of people living in urban areas are poor.
- Declining life expectancy: Life expectancy among the poorest is lower by 9.1 years and 6.2 years among men and women, respectively, compared to the richest in urban areas.
- Chaotic health governance: The report, besides finding disproportionate disease burden on the poor, also pointed to a chaotic urban health governance.
- Multiplicity and non-coordination: The multiplicity of healthcare providers both within and outside the government without coordination challenges to urban health governance.
- Lack of political attention: Urban healthcare has received relatively less research and policy attention.
Major recommendations
The report calls for:
- Strengthening community participation and governance
- Building a comprehensive and dynamic database on the health and nutrition status, including co-morbidities of the diverse, vulnerable populations
- Strengthening healthcare provisioning through the National Urban Health Mission, especially for primary healthcare services
- Putting in place policy measures to reduce the financial burden of the poor
- A better mechanism for coordinated public healthcare services and better governed private healthcare institutions
Conclusion
- As urbanization is happening rapidly, the number of the urban poor is only expected to increase.
- A well-functioning, better coordinated, and governed health care system is crucial at this point.
- The pandemic has brought to attention the need for a robust and resourced healthcare system.
- Addressing this will benefit the most vulnerable and offer critical services to city dwellers across income groups.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
More a private sector primer than health-care pathway
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- UHC and challenges
Context
NITI Aayog recently published a road map document entitled “Health Insurance for India’s Missing Middle”.
About missing middle and provision in the NITI Aayog report
- The Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), aims to extend hospitalisation cover of up to ₹5 lakh per family per annum to a poor and vulnerable population of nearly 50 crore people.
- Left out segment: Covering the left out segment of the population, commonly termed the ‘missing middle’ sandwiched between the poor and the affluent, has been discussed by the Government recently.
- Towards this, NITI Aayog recently published a road map document entitled “Health Insurance for India’s Missing Middle”.
- Primary role for private commercial health insurer: The report proposes voluntary, contributory health insurance dispensed mainly by private commercial health insurers as the prime instrument for extending health insurance to the ‘missing middle’.
Issues with the provision in the NITI Aayog report
- Narrow coverage: Government subsidies, if any at all, will be reserved for the very poor within the ‘missing middle’ and only at a later stage of development of voluntary contributory insurance.
- This is a major swerve from the vision espoused by the high-level expert group on UHC a decade ago, which was sceptical about such a health insurance model.
- No country has ever achieved UHC by relying predominantly on private sources of financing health care.
- Contributory insurance not best way: Evidence shows that in developing countries such as India, with a gargantuan informal sector, contributory health insurance is not the best way forward and can be replete with problems.
- Issues with low premium model: For hospitalisation insurance, the report proposes a model similar to the Arogya Sanjeevani scheme, albeit with lower projected premiums of around ₹4,000-₹6,000 per family per annum.
- This model is a little different from commercial private insurance, except for somewhat lower premiums.
- Low premiums are achieved by reducing administrative costs of insurers through an array of measures, including private use of government infrastructure.
- This model is vulnerable to nearly every vice that characterises conventional private insurance.
- Insufficient measures to deal with adverse selection: The report suggests enrolment in groups as a means to counter adverse selection.
- The prevailing per capita expenditure on hospital care is used to reflect affordability of hospital insurance, and thereby, a possible willingness to pay for insurance.
- Both these notions are likely to be far-fetched in practice, and the model is likely to be characterised by widespread adverse selection notwithstanding.
- OPD insurance on a subscription basis: The report proposes an OPD insurance with an insured sum of ₹5,000 per family per annum, and again uses average per capita OPD spending to justify the ability to pay.
- However, the OPD insurance is envisaged on a subscription basis, which means that insured families would need to pay nearly the entire insured sum in advance to obtain the benefits.
- Clearly, this route is unlikely to result in any significant reduction of out-of-pocket expenditure on OPD care.
- Role of government:The NITI report defies the universally accepted logic that UHC invariably entails a strong and overarching role for the Government in health care, particularly in developing countries.
Consider the question “What are the challenges in achieving universal health coverage? What are the issues with private sources financing health care to achieve UHC?”
Conclusion
The National Health Policy 2017 envisaged increasing public health spending to 2.5% of GDP by 2025. Let us not contradict ourselves so early and at this crucial juncture of an unprecedented pandemic.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Strengthening healthcare through ABHIM
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ABHIM
Mains level: Paper 2- ABHIM
Context
The Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (ABHIM), announced recently, seeks to realise greater investment in the health system as proposed in the Budget, implement the Fifteenth Finance Commission recommendations such as strengthening of urban and rural primary care, stronger surveillance systems and laboratory capacity.
Measures of ABHIM
- It will support infrastructure development of 17,788 rural health and wellness centres (HWCs) in seven high-focus States and three north-eastern States.
- In addition, 11,044 urban HWCs will be established in close collaboration with Urban Local Bodies.
- The various measures of this scheme will extend primary healthcare services across India.
- Areas like hypertension, diabetes and mental health will be covered, in addition to existing services.
- Support for 3,382 block public health units (BPHUs) in 11 high-focus States and establishment of integrated district public health laboratories in all 730 districts will strengthen capacity for information technology-enabled disease surveillance.
- To enhance the capabilities for microbial surveillance, a National Platform for One Health will be established.
- Four Regional National Institutes of Virology will be established.
- Laboratory capacity under the National Centre for Disease Control, the Indian Council of Medical Research and national research institutions will be strengthened.
- Fifteen bio-safety level III labs will augment the capacity for infectious disease control and bio-security.
Way forward
- There is a need to train and deploy a larger and better skilled health workforce.
- We must scale up institutional capacity for training public health professionals.
- Private sector participation in service delivery may be invited by States, as per need and availability.
- ABHIM, if financed and implemented efficiently, can strengthen India’s health system by augmenting capacity in several areas and creating a framework for coordinated functioning at district, state and national levels.
- Many independently functioning programmes will have to work with a common purpose by leaping across boundaries of separate budget lines and reporting structures.
- That calls for a change of bureaucratic mindsets and a cultural shift in Centre-State relations.
Conclusion
The ABHIM can fix the weaknesses in India’s healthcare system.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Preparing for outbreaks
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ABHIM
Mains level: Paper 2- ABHIM
Context
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission, one of the largest pan-India schemes for strengthening healthcare infrastructure, in his parliamentary constituency Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh.
Aims of Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (ABHIM) and how it seeks to achieve it
- This was launched with an outlay of ₹64,180 crore over a period of five years.
- In addition to the National Health Mission, this scheme will work towards strengthening public health institutions and governance capacities for wide-ranging diagnostics and treatment, including critical care services.
- The latter goal would be met with the establishment of critical care hospital blocks in 12 central institutions such as the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, and in government medical colleges and district hospitals in 602 districts.
- Laboratories and their preparedness: The government will be establishing integrated district public health labs in 730 districts to provide comprehensive laboratory services.
- Research: ABHIM will focus on supporting research on COVID-19 and other infectious diseases, including biomedical research to generate evidence to inform short-term and medium-term responses to such pandemics.
- One health approach: The government also aims to develop a core capacity to deliver the ‘one health’ approach to prevent, detect, and respond to infectious disease outbreaks in humans and animals.
- Surveillance labs: A network of surveillance labs will be developed at the block, district, regional and national levels for detecting, investigating, preventing, and combating health emergencies and outbreaks.
- Local capacities in urban areas: A major highlight of the current pandemic has been the requirement of local capacities in urban areas.
- The services from the existing urban primary health centres will be expanded to smaller units – Ayushman Bharat Urban Health and Wellness Centres and polyclinics or specialist clinics.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (ABHIM) is another addition to the arsenal we have to prepare for such oubreaks in the future.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AB- Health Infrastructure Mission
Mains level: Not Much

PM has launched the Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (AB-HIM), one of the largest pan-India schemes for strengthening healthcare infrastructure.
AB- Health Infrastructure Mission
- AB-HIM is being rolled out as India’s largest scheme to scale up health infrastructure.
- It is aimed at ensuring a robust public health infrastructure in both urban and rural areas, capable of responding to public health emergencies or disease outbreaks.
Key features
- Health and Wellness Centres: In a bid to increase accessibility it will provide support to 17,788 rural HWC in 10 ‘high focus’ states and establish 11,024 urban HWC across the country.
- Exclusive Critical Care Hospital Blocks: It will ensure access to critical care services in all districts of the country with over five lakh population through ‘Exclusive Critical Care Hospital Blocks’.
- Integrated public health labs: will also be set up in all districts, giving people access to “a full range of diagnostic services” through a network of laboratories across the country.
- Disease surveillance system: The mission also aims to establish an IT-enabled disease surveillance system through a network of surveillance laboratories at block, district, regional and national levels.
- Integrated Health Information Portal: All the public health labs will be connected through this Portal, which will be expanded to all states and UTs, the PMO said.
Why is the scheme significant?
- India has long been in need of a ubiquitous healthcare system.
- A 2019 study has highlighted how access to public health care remained elusive to those living on the margins.
- The study found that 70 per cent of the locations have public healthcare services.
- However, availability was less in rural areas (65 per cent) compared to urban areas (87 per cent).
- In 45 per cent of the surveyed locations, people could access healthcare services by walking, whereas in 43 per cent of the locations they needed to use transport.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
On Digital Health ID, proceed with caution
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: DHID
Mains level: Issues with ABDM
Much recently, the Prime Minister had launched the Digital Health ID project (DHID), generating debate on issues related to the use of technology in a broken health system.
Good intents of the DHID
- The key objective of DHID is to improve the quality, access and affordability of health services by making the service delivery “quicker, less expensive and more robust”.
- The ambition is undoubtedly high. Given that health systems are highly complex, the DHID would hardly be able to address some of the issues plaguing it.
Why need DHID?
(a) Record maintenance
- The use of technology for record maintenance is not just inevitable but necessary. Its time has certainly come.
- A decade ago, the process to shift towards electronic medical records was initiated in the private sector.
- It met with limited success, despite the strong positives.
- With DHID, the burden of storing and carrying health records for every visit to the doctor is minimised.
(b) Better tracking of medical history
- The doctor has instant access to the patient’s case history –the treatment undertaken, where and with what outcomes — enabling more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- As the DHID enables portability across geography and healthcare providers, it also helps reduce re-testing or repeating problems every time a patient consults a new doctor.
- That’s a huge gain, impacting the quality of care and enhancing patient satisfaction and confidence.
(c) Better Diagnosis
- DHID can have a transformative impact in promoting ecosystems that function as paperless facilities.
- Paperless hospitals can promote early diagnosis before the patient reaches the doctor after spending long hours in queue.
- The doctor can already go through the patient’s record and the pharmacist can make the drugs available by the time the patient reached its counter.
(d) Promoting medical research
- Digitisation of medical records is another important positive, given the problems related to space and retrieving huge databases.
- Well organised repositories that enable easy access to records can stimulate much-needed research on medical devices and drugs.
- This storehouse of patient data can be valuable for clinical and operational research.
Given our population, would this be an idealistic expectation?
- We need to conduct pilot studies to assess the use of technology for streamlining patient flows and medical records and thereby increase efficiencies across different typologies of hospitals and facilities.
- While technology helps smoothen processes and enhance patient experience, there is a cost attached.
- Investments have to be made upfront and results should not be expected overnight.
Issues with DHID
(a) A costly affair
- In the immediate short run, DHID will increase administrative costs by about 20 per cent, due to the capital investment in data infrastructure.
- Over the long run, the additional cost to healthcare is expected to be about 2 per cent.
- Any scaling up of this reform would require extensive fiscal subsidies and more importantly providing techno-logistical support to both government and private hospitals.
(b) Privacy concerns
- Most important is the issue of privacy, the high possibility of hacking and breach of confidentiality.
- The possibility of privacy being violated increases with the centralisation of all information.
- Though it is said that the patient is the owner of the information, how many of us deny access, as a matter of routine, when we download apps or programmes that seek access to all our records?
- How far is this “consent” practical for an illiterate, vulnerable patient desperate to get well?
- So, taking refuge behind a technical statement that access is contingent on patient consent is unconvincing.
Ground situation in India
- Inherently unaffordable healthcare: The costs in the Indian context can be high and that should lead to a careful assessment of the project.
- Digital divide: Such a scenario is not inconceivable and in the case of health, may cause immense hardship to the most marginalised sections of our population.
- Infrastructure gap: A large majority of facilities do not have the required physical infrastructure — electricity, accommodation, trained personnel.
- Usual nature of technical glitches: Cards getting corrupted, servers being down, computers crashing or hanging, and power outages are common in India.
- Conformity over data synchronization: The inability to synchronise biometric data with ID cards has resulted in large-scale exclusions of the poor from welfare projects.
- Accuracy of records: Besides, the efficacy of the DHID hinges on the assumption that every visit and every drug consumed by the patient is faithfully and accurately recorded.
- Increased workload on Medical Professionals: Moreover, while electronic mapping of providers may enable patients to spot a less busy doctor near their location, it is simplistic to assume that the patient will go there.
Plugging the existing gaps
- Patient preference for a doctor is dependent upon perception and trust. Likewise, teleconsultations need a huge backend infrastructure and organisation.
- Teleconsulting has certainly helped patients access medical advice for managing minor ailments, getting prescriptions on the phone and even getting drugs delivered home.
- But in handling chronic diseases that necessitate continuity of care, teleconsultations have been problematic and cannot be substituted for actual physical examination.
- Continuity of care is central to good outcomes in inpatient management of chronic diseases.
- The one serious shortcoming of using teleconsultation for such management is the high attrition rate of doctors within the context of an overall shortage of doctors.
- Technology can be of little use in the absence of doctors and basic infrastructure.
Way forward
- What is needed is building very robust firewalls and trust.
- Seeing the frequency with which Aadhaar cards have been breached, it is not unreasonable to be concerned with this issue and the implications it has at the family and societal levels.
- For this reason, instead of a big bang approach, it is better to go slow and steady.
- That’s the only way to ensure that a good policy does not die along the way due to poor implementation.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What are the concerns of digital health mission?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Mains level: Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), was recently launched by the PM.
About Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
- The pilot project of the National Digital Health Mission was announced by PM Modi during his Independence Day speech from the Red Fort on August 15, 2020.
- The mission will enable access and exchange of longitudinal health records of citizens with their consent.
- This will ensure ease of doing business for doctors and hospitals and healthcare service providers.
The key components of the project include
- Health ID for every citizen that will also work as their health account, to which personal health records can be linked and viewed with the help of a mobile application,
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR)
- Healthcare Facilities Registries (HFR) that will act as a repository of all healthcare providers across both modern and traditional systems of medicine
How will it work?
- In order to be a part of the ABDM, citizens will have to create a unique health ID – a randomly generated 14-digit identification number.
- The ID will give the user unique identification, authentication and will be a repository of all health records of a person.
- The ID can also be made by self-registration on the portal, downloading the ABMD Health Records app on one’s mobile or at a participating health facility.
- The beneficiary will also set up a Personal Health Records (PHR) address for the issue of consent, and for future sharing of health records.
Major privacy issues involved
- Informed Consent: The citizen’s consent is vital for all access. A beneficiary’s consent is vital to ensure that information is released.
- Data leakages issue: Personalised data collected at multiple levels are a “sitting gold mine” for insurance companies, international researchers, and pharma companies.
- Digital divide: Other experts add that lack of access to technology, poverty, and lack of understanding of the language in a vast and diverse country like India are problems that need to be looked into.
- Data Migration: The data migration and inter-State transfer are still faced with multiple errors and shortcomings in addition to concerns of data security.
Other challenges
- Existing digitalization is yet incomplete: India has been unable to standardise the coverage and quality of the existing digital cards like One Nation One Ration card, PM-JAY card, Aadhaar card, etc., for accessibility of services and entitlements.
- Lack of healthcare facilities: The defence of data security by expressed informed consent doesn’t work in a country that is plagued by the acute shortage of healthcare professionals to inform the client fully.
- Lack of finance: With the minuscule spending of 1.3% of the GDP on the healthcare sector, India will be unable to ensure the quality and uniform access to healthcare that it hoped to bring about.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Antimalarial drug resistance in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Malaria and it vaccines
Mains level: Non-communicable diseases burden on India
In recent years there is increasing evidence for the failure of artemisinin-based combination therapy for falciparum malaria either alone or with partner drugs.
What is Malaria?
- Malaria is caused by the bite of the female Anopheles mosquito if the mosquito itself is infected with a malarial parasite.
- There are five kinds of malarial parasites — Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax (the commonest ones), Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium knowlesi.
- Therefore, to say that someone has contracted the Plasmodium ovale type of malaria means that the person has been infected by that particular parasite.
Burden of Malaria in India
- In 2018, the National Vector-borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) estimated that approximately 5 lakh people suffered from malaria.
- 63% of the cases were of Plasmodium falciparum.
- The recent World Malaria Report 2020 said cases in India dropped from about 20 million in 2000 to about 5.6 million in 2019.
Treatment of Malaria
- Malaria is treated with prescription drugs to kill the parasite. Chloroquine is the preferred treatment for any parasite that is sensitive to the drug.
- In most malaria-endemic countries including India, Artemisinin-based antimalarial drugs are the first-line choice for malaria treatment.
- This is especially against Plasmodium falciparum parasite which is responsible for almost all malaria-related deaths in the world.
Why in news now?
- There are reports of artemisinin resistance in East Africa and is a matter of great concern as this is the only drug that has saved several lives across the globe.
- In India, after the failure of chloroquine to treat P. falciparum malaria successfully, artemisinin-based combination therapy was initially introduced in 2008.
- Currently, several combinations of artemisinin derivatives are registered in India.
Artemisinin-based combination therapy failure in India
- In 2019, a report from Eastern India indicated the presence of two mutations in P. falciparum cases treated with artemisinin that linked to its presence of resistance.
- Again in 2021, artemisinin-based combination therapy failure was reported from Central India where the partner drug SP showed triple mutations with artemisinin wild type.
- This means the failure of artemisinin-based combination therapy may not be solely linked to artemisinin. Here it is needed to change the partner drug as has been done in NE states in 2013.
History of drug resistance
- In the 1950s chloroquine resistance came to light.
- Both chloroquine and pyrimethamine resistance originated from Southeast Asia following their migration to India and then on to Africa with disastrous consequences.
- Similarly, artemisinin resistance developed from the six Southeast Asian countries and migrated to other continents, as is reported in India and Africa.
- It would not be out of context that artemisinin is following the same path as has been seen with chloroquine.
- Now, the time has come to carry out Molecular Malaria Surveillance to find out the drug-resistant variants so that corrective measures can be undertaken in time to avert any consequences.
- Some experts even advocate using triple artemisinin-based combination therapies where the partner drug is less effective.
Try this PYQ:
Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria.
Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine?
(a) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
(b) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
(c) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
(d) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
Post your answers here.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Explained: Digital Health ID
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various facts related to digital health ID
Mains level: Features of the ABDM
The PM has recently launched the flagship Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) which involves the creation not just a unique digital health ID for every citizen.
What is the unique health ID?
- If a person wants to be part of the ABDM, she must create a health ID, which is a randomly generated 14-digit number.
- The ID will be broadly used for three purposes: unique identification, authentication, and threading of the beneficiary’s health records, only with their informed consent, across multiple systems and stakeholders.
Why is this initiative significant?
- The initiative has the potential to “increase the ease of living” along with “simplifying the procedures in hospitals”.
- At present, the use of digital health ID in hospitals is currently limited to only one hospital or to a single group, and mostly concentrated in large private chains.
- The new initiative will bring the entire ecosystem on a single platform.
- The system also makes it easier to find doctors and specialists nearest to you.
- Currently, many patients rely on recommendations from family and friends for medical consultation, but now the new platform will tell the patient who to reach out to, and who is the nearest.
- Also, labs and drug stores will be easily identified for better tests using the new platform.
How can one get it?
- One can get a health ID by self-registration on the portal or by downloading the ABMD Health Records app on one’s mobile.
- Additionally, one can also request the creation of a health ID at a participating health facility.
- Health facilities may include government or private hospitals, community health centres, and wellness centres of the government across India.
- The beneficiary will also have to set up a Personal Health Records (PHR) address for consent management, and for future sharing of health records.
What is a PHR address?
- It is a simple self-declared username, which the beneficiary is required to sign into a Health Information Exchange and Consent Manager (HIE-CM).
- Each health ID will require linkage to a consent manager to enable sharing of health records data.
- An HIE-CM is an application that enables sharing and linking of personal health records for a user.
- At present, one can use the health ID to sign up on the HIE-CM; the National Health Authority (NHA), however, says multiple consent managers are likely to be available for patients to choose from in the near future.
What does one need to register for a health ID?
- Currently, ABDM supports health ID creation via mobile or Aadhaar.
- The official website states that ABDM will soon roll out features that will support health ID creation with a PAN card or a driving licence.
- For health ID creation through mobile or Aadhaar, the beneficiary will be asked to share details on name, year of birth, gender, address, mobile number/Aadhaar.
Is Aadhaar mandatory?
Ans. No, it is voluntary.
- One can use one’s mobile number for registration, without Aadhaar.
- If the beneficiary chooses the option of using her Aadhaar number, an OTP will be sent to the mobile number linked to the Aadhaar.
- However, if she has not linked it to her mobile, the beneficiary has to visit the nearest facility and opt for biometric authentication using Aadhaar number.
- After successful authentication, she will get her health ID at the participating facility.
Are personal health records secure?
- The NHA says ABDM does not store any of the beneficiary health records.
- The records are stored with healthcare information providers as per their “retention policies”.
- They are “shared” over the ABDM network “with encryption mechanisms” only after the beneficiary express consent.
Can one delete my health ID and exit the platform?
Ans. Yes, the NHA says ABDM, supports such a feature. Two options are available: a user can permanently delete or temporarily deactivate her health ID.
- On deletion, the unique health ID will be permanently deleted, along with all demographic details.
- The beneficiary will not be able to retrieve any information tagged to that health ID in the future, and will never be able to access ABDM applications or any health records over the ABDM network with the deleted ID.
- On deactivation, the beneficiary will lose access to all ABDM applications only for the period of deactivation.
- Until she reactivates her health ID, she will not be able to share the ID at any health facility or share health records over the ABDM network.
What facilities are available to beneficiaries?
- Users can access personal digital health records right from admission through treatment and discharge.
- One can access and link his/her personal health records with your health ID to create a longitudinal health history.
What other features will be rolled out?
- Upcoming new features will enable access to verified doctors across the country.
- The beneficiary can create a health ID for her child, and digital health records right from birth.
- Third, she can add a nominee to access her health ID and view or help manage the personal health records.
- Also, there will be much inclusive access, with the health ID available to people who don’t have phones, using assisted methods.
How do private players get associated with a government digital ID?
- The NHA has launched the NDHM Sandbox: a digital architecture that allows helps private players to be part of the National Digital Health Ecosystem as health information providers or health information users.
- The private player sends a request to NHA to test its system with the Sandbox environment.
- The NHA then gives the private player a key to access the Sandbox environment and the health ID application programming interface (API).
- The private player then has to create a Sandbox health ID, integrate its software with the API; and register the software to test link records and process health data consent requests.
- Once the system is tested, the system will ask for a demo to the NHA to move forward. After a successful demo, the NHA certifies and empanels the private hospital.
Now try this PYQ:
Consider the following statements:
- Aadhaar metadata cannot be stored for more than three months.
- State cannot enter into any contract with private corporations for sharing of Aadhaar data.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for obtaining insurance products.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for getting benefits funded out of the Consolidated Fund of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3 only
Post your answers here.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Meningitis?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Meningitis
Mains level: NA
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched the first-ever global strategy to defeat meningitis, a debilitating disease that kills hundreds of thousands of people each year.
What is Meningitis?
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges, the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord.
- People of any age can get meningitis.
What Causes Meningitis?
- Most cases are caused by bacteria or viruses, but some can be due to certain medicines or illnesses.
- Meningitis is usually caused by a viral infection but can also be bacterial or fungal.
- Both kinds of meningitis spread like most other common infections do — someone who’s infected touches, kisses, or coughs or sneezes on someone who isn’t infected.
- Bacterial meningitis is rare, but is usually serious and can be life-threatening if not treated right away.
- Viral meningitis (also called aseptic meningitis) is more common than bacterial meningitis and usually less serious.
- Many of the viruses that cause meningitis are common, such as those that cause colds, diarrhea, cold sores, and the flu.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Meningitis?
- Meningitis symptoms vary, depending on the person’s age and the cause of the infection.
- The first symptoms can come on quickly or start several days after someone has had a cold, diarrhea, vomiting, or other signs of an infection.
Common symptoms include:
- fever
- lack of energy
- irritability
- headache
- sensitivity to light
- stiff neck
- skin rash
Treatment
- Several vaccines protect against meningitis, including meningococcal, Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcal vaccines.
- If dealt with quickly, meningitis can be treated successfully.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Mains level: Features of the ABDM
The PM has launched the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission to provide a digital Health ID to people which will contain their health records.
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
- The pilot project of the National Digital Health Mission was announced by PM Modi during his Independence Day speech from the Red Fort on August 15, 2020.
- The mission will enable access and exchange of longitudinal health records of citizens with their consent.
- This will ensure ease of doing business for doctors and hospitals and healthcare service providers.
The key components of the project include
- Health ID for every citizen that will also work as their health account, to which personal health records can be linked and viewed with the help of a mobile application,
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR)
- Healthcare Facilities Registries (HFR) that will act as a repository of all healthcare providers across both modern and traditional systems of medicine
What makes this special?
- The mission will create integration within the digital health ecosystem, similar to the role played by the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in revolutionising payments.
- Citizens will only be a click-away from accessing healthcare facilities.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Disease surveillance system
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Integrated disease surveillance project
Mains level: Paper 2- Disease surveillance
Context
A well-functioning system can reduce the impact of diseases and outbreaks.
Importance of disease surveillance system
- Successful tackling of cholera in 1854 in London by use of the health statistics and death registration data from the General Registrar Office (GRO) started the beginning of a new era in epidemiology.
- Importance of data: The application of principles of epidemiology is possible through systematic collection and timely analysis, and dissemination of data on the diseases.
- This is to initiate action to either prevent or stop further spread, a process termed as disease surveillance.
- Subsequently, the high-income countries invested in disease surveillance systems but low- and middle-income countries used limited resources for medical care.
- Then, in the second half of the Twentieth century, as part of the global efforts for smallpox eradication and then to tackle many emerging and re-emerging diseases, many countries recognised the importance and started to invest in and strengthen the diseases surveillance system.
- These efforts received a further boost with the emergence of Avian flu in 1997 and the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) outbreak in 2002-04.
Surveillance in India
- The Government of India launched the National Surveillance Programme for Communicable Diseases in 1997.
- However, this initiative remained rudimentary.
- In wake of the SARS outbreak, in 2004, India launched the Integrated Disease Surveillance Project (IDSP).
- The focus under the IDSP was to increase government funding for disease surveillance, strengthen laboratory capacity, train the health workforce and have at least one trained epidemiologist in every district of India.
Issues with surveillance: Interstate variation
- Variation among states: The disease surveillance system and health data recording and reporting systems are key tools in epidemiology.
- In the fourth round of serosurvey, Kerala and Maharashtra States could identify one in every six and 12 infections, respectively; while in States such as Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, only one in every 100 COVID-19 infections could be detected.
- This points towards a weak disease surveillance system.
- In a well-functioning disease surveillance system, an increase in cases of any illness would be identified very quickly.
- While Kerala is picking the maximum COVID-19 cases; it could pick the first case of the Nipah virus in early September 2021.
- On the contrary, cases of dengue, malaria, leptospirosis and scrub typhus received attention only when more than three dozen deaths were reported and health facilities in multiple districts of Uttar Pradesh, began to be overwhelmed.
Way forward
- A review of the IDSP in 2015, conducted jointly by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the Government of India and World Health Organization India had made a few concrete recommendations to strengthen disease surveillance systems.
- These included increasing financial resource allocation, ensuring an adequate number of trained human resources, strengthening laboratories, and zoonosis, influenza and vaccine-preventable diseases surveillance.
- Increase allocation: The government resources allocated to preventive and promotive health services and disease surveillance need to be increased by the Union and State governments.
- Trained workforce: The workforce in the primary healthcare system in both rural and urban areas needs to be retrained in disease surveillance and public health actions.
- The vacancies of surveillance staff at all levels need to be urgently filled in.
- Capacity increase: The laboratory capacity for COVID-19 needs to be planned and repurposed to increase the ability to conduct testing for other public health challenges and infections.
- The interconnectedness of human and animal health: The emerging outbreaks of zoonotic diseases, be it the Nipah virus in Kerala or avian flu in other States as well as scrub typhus in Uttar Pradesh, are a reminder of the interconnectedness of human and animal health.
- The ‘One Health’ approach has to be promoted beyond policy discourses and made functional on the ground.
- Strengthening registration system: There has to be a dedicated focus on strengthening the civil registration and vital statistics (CRVS) systems and medical certification of cause of death (MCCD).
- Coordination: It is also time to ensure coordinated actions between the State government and municipal corporation to develop joint action plans and assume responsibility for public health and disease surveillance.
- The allocation made by the 15th Finance Commission to corporations for health should be used to activate this process.
Consider the question “Examine the measure for disease surveillance in India? How it can help reduce the impact of the diseases?”
Conclusion
We cannot prevent every single outbreak but with a well-functioning disease surveillance system and with the application of principles of epidemiology, we can reduce their impact.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Serotype 2 Dengue?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dengue
Mains level: NA
The Union Health Ministry has flagged the emerging challenge in 11 States across India of serotype 2 dengue, which it said is associated with “more cases and more complications” than other forms of the disease.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2015:
Q. Consider the following statements:
- In tropical regions, Zika virus disease is transmitted by the same mosquito that transmits dengue.
- Sexual transmission of Zika virus disease is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Post your answers here!
What is Dengue?
- Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral infection, found in tropical and sub-tropical climates worldwide, mostly in urban and semi-urban areas.
- It is transmitted by female mosquitoes mainly of the species Aedes aegypti and, to a lesser extent, Ae. albopictus.
- These mosquitoes are also vectors of chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika viruses.
- Dengue is widespread throughout the tropics, with local variations in risk influenced by rainfall, temperature, relative humidity and unplanned rapid urbanization.
Its transmission
- The virus is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female mosquitoes, primarily the Aedes aegypti
- Other species within the Aedes genus can also act as vectors, but their contribution is secondary to Aedes aegypti.
- Mosquitoes can become infected from people who are viremic with dengue.
Various serotypes
- Dengue is caused by a virus of the Flaviviridae family and there are four distinct, but closely related, serotypes of the virus that cause dengue (DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3 and DENV-4).
- Recovery from infection is believed to provide lifelong immunity against that serotype.
- However, cross-immunity to the other serotypes after recovery is only partial and temporary.
- Subsequent infections (secondary infection) by other serotypes increase the risk of developing severe dengue.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Outpatient Opioid Assisted Treatment Centres
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Drug rehabiliation
The state government in Punjab is banking on Outpatient Opioid Assisted Treatment Centres (OOAT) to curb the drug menace in the state.
What are the OOAT Centres?
- The move to set up OOAT centres in Punjab began in October 2017.
- The centres administer de-addiction medicine, a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone, to the opioid-dependent people registering there.
- Administered in the form of a pill, the treatment is primarily for addicts of opioid drugs, including heroin, poppy husk and opium.
- There are such private and state-run centres in Punjab.
Why is the Punjab government planning?
- Punjab is planning to open OOAT linked extension centres and clinics in rural areas to broaden the outreach of this treatment.
- The idea is that patients get medicine nearer their place of residence.
- It will also reduce pressure on existing OOAT centres which cater to patients from far-off places.
Administering medicine at OOAT Centres
The patients are broadly put into three categories or phases.
- In the induction phase, the newly-registered patients are administered medicine at the OOAT centres for a week or two to manage withdrawal symptoms in the presence of the doctor and counselor.
- In the second, stabilization, phase, which extends between two to four months.
- The patient is put on watch for taking any opioid-based “super-imposed” illicit drug and accordingly maximum tolerated dose is administered to nullify the kick of the “super-imposed” drug.
- In the third, maintenance, phase, the patient is given take-home medicine and it continues for a year and a half before an assessment is done to see whether the medicine can be tapered off.
Why is Punjab banking so much on OOAT therapy?
There are two major approaches to wean away opioid-dependent persons.
- One is the abstinence approach and another alternate medication approach.
- There are more chances of relapse in an abstinence-based approach as compared to alternate medication for de-addiction.
- In the abstinence approach, it would have taken years to rehabilitate patients by admitting them to facilities and there would have been increased chances of relapse.
- On the other hand, the alternate medication approach has been acknowledged as better in various scientific studies worldwide.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Why India needs an NHS-like healthcare model
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India's expenditure on health
Mains level: Paper 2- India needs NHS like healthcare model
Context
Even after the pandemic, the Indian government continues to budget less than 1 per cent of GDP for healthcare, one of the lowest in the world.
About NHS
- Every year, Britain’s legendary health network National Health Service (NHS) cures 15 million patients with chronic ailments, at a fraction of the cost spent by the US.
- The NHS funded by direct taxes is also the fifth largest employer in the world, after McDonalds and Walmart.
- One of every 20 British workers is employed as a doctor, nurse, catering and technical personnel.
Public healthcare in India
- Even after the pandemic, the Indian government continues to budget less than 1 per cent of GDP for healthcare, one of the lowest in the world.
- In contrast, China invests around 3 per cent, Britain 7 per cent and the United States 17 per cent of GDP.
- So, 62 per cent of health expenses in India are paid for by patients themselves
- This is one of the main reasons for families falling into poverty especially during the pandemic.
- In India, hospitals are beleaguered with absentee staff.
- As per a Niti Aayog database, in the worst state of Bihar in 2017-18, positions for 60 per cent of midwives, 50 per cent of staff nurses, 34 per cent of medical officers and 60 per cent of specialist doctors were vacant.
- Those on the job, despite being handsomely paid, are chronically overworked.
Conclusion
In the 21st century, not much has improved in India’s public hospitals. Still, in India doctors are often equated with gods. What India needs in NHS like healthcare model.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Issues related to people with disabilities
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CRPD
Mains level: Paper 2- Ensuring the dignity of persons with disability
Context
Twenty years ago on August 6 in Erwadi in Tamil Nadu’s Ramanathapuram, a fire broke out in a thatched shelter, engulfing 43 chained people who had psychosocial disabilities.
Legal provision for the persons with disabilities
- India ratified the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) in 2007.
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act was enacted in 2016.
- The Mental Healthcare Act (MHCA) was enacted in 2017.
Failure of the states
- Sates have failed to uphold the human rights of people with disabilities in general and those with psychosocial and intellectual disabilities in particular.
- Only eight states/UTs — Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Maharashtra, Odisha, Kerala, and West Bengal — have framed rules for implementation of MHCA.
- Unless we implement the law in letter and spirit, the Global Mental Health Movement will remain a mere buzzword and the CRPD-reliant MHCA will remain a law only on paper.
Violations of rights in private asylums
- Private asylums survive because of their close proximity to faith-based healing centres.
- Because mental health conditions carry a high stigma, caregivers flock to these faith-based facilities in the hopes of finding a cure.
- Private players take advantage of their vulnerabilities, forcing such persons with psychosocial issues to be grouped together and chained in these shelters.
- Chaining in any way or form is outlawed under Section 95 of the MHCA.
Way forward
- Human right approach: We must work to ensure that the human rights approach to disability is integrated into mental health systems, education, law, and bureaucracy.
- We move away from pathologisation, segregation, and a charity-based approach.
Conclusion
Implementation of rights of the persons with disability needs implementation in letter and spirit and human rights based approach.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s technical education: Issues and Suggestions
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AICTE
Mains level: Paper 2- Issues of technical education in India
Context
This year, AICTE approved the closure of 63 engineering colleges across the country.
Deterioration of quality
- Tweaking with curriculum: Private entrepreneurs took the lead to meet the growing demand of the country in technical education in the mid-Eighties, but with little idea of the subject.
- Subjects like materials, applied physics and thermodynamics which forms the building blocks of engineering became dispensable.
- Because they were both tough to teach for the teachers and tough to pass for the students.
- Expansion: This softening of subjects coupled with unfettered expansion in the early and mid-2000s, resulted in real dilution of the overall standards in the country.
- Lack of adequate number of teachers, lack of quality in those available, inability of the management to make adequate investments in a dynamic environment, lack of employment opportunities, shelf life of skills coming down with every technology-related intervention and a constant experimentation with curriculum have all been the bane of quality in technical education.
Issues
- Engineering education suffers from regulatory gaps, poor infrastructure, lack of qualified faculty and the non-existent industry linkage that contributed to the abysmal employability of graduates from most of these institutes.
- No linkage with Industry: Not a single industry body, be it CII, FICCI or ASSOCHAM has managed to effectively inform the education planners on the growth in different employment sectors.
- No independent body to suggest AICTEC: The government also has not taken any tangible steps to set up an independent body to advise AICTE on this vital aspect.
- Excessive changes: A constant fiddling with the curriculum, reducing total credits, giving multiple choices in the name of flexibility, dispensing with mathematics and physics at the qualification level, teaching in local languages may all be good arguments, but one must assess their utility and their effect on technical education in the long run.
Way forward
- Proactive: Rather than being reactive, institutions must proactively define the practicing elements of education.
- Investment in teaching: The corrective measures for these shortfalls are technology intensive, are experiential, and need investments in teaching.
- Quality assurance body: The ultimate measure of performance is embedded in quality assurance.
- The need of the hour is to create a truly autonomous quality assurance body at an arms-length from the government, manned by eminent persons both from the industry as well as academia.
Conclusion
The education paradigm is staring at a large shift and technical education cannot remain immune to that change.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Organ Transplantation in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NOTP
Mains level: Organ transplantation in India
The Government of India is implementing National Organ Transplant Programme (NOTP) to promote organ donation and transplantation across all States/Union Territories (UTs).
National Organ Transplant Programme (NOTP)
- In 2019, the GoI implemented the NOTP for promoting deceased organ donation.
- Organ donation in India is regulated by the Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act, 1994.
Types of Organ Donations
- The law allows both deceased and living donors to donate their organs.
- It also identifies brain death as a form of death.
- Living donors must be over 18 years of age and are limited to donating only to their immediate blood relatives or, in some special cases, out of affection and attachment towards the recipient.
(1) Deceased donors:
- They may donate six life-saving organs: kidneys, liver, heart, lungs, pancreas, and intestine.
- Uterus transplant is also performed, but it is not regarded as a life-saving organ.
- Organs and tissues from a person declared legally dead can be donated after consent from the family has been obtained.
- Brainstem death is also recognized as a form of death in India, as in many other countries.
- After a natural cardiac death, organs that can be donated are cornea, bone, skin, and blood vessels, whereas after brainstem death about 37 different organs and tissues can be donated, including the above six life-saving organs
(2) Living donors:
They are permitted to donate the following:
- one of their kidneys
- portion of pancreas
- part of the liver
Features of the NOTP
- Under the NOTP a National Level Tissue Bank (Biomaterial Centre) for storing tissues has been established at National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO), New Delhi.
- Further, under the NOTP, a provision has also been made for providing financial support to the States for setting up of Bio- material centre.
- As of now a Regional Bio-material centre has been established at Regional Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (ROTTO), Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
More moves for facilitation: Green Corridors
- Studies have suggested that the chances of transplantation being successful are enhanced by reducing the time delay between harvest and transplant of the organ.
- Therefore, the transportation of the organ is a critical factor. For this purpose, “green corridors” have been created in many parts of India.
- A “green corridor” refers to a route that is cleared out for an ambulance carrying the harvested organs to ensure its delivery at the destination in the shortest time possible.
About NOTTO
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO) is a national level organization set up under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network
- National Biomaterial Centre (National Tissue Bank)
[I] National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network
- This has been mandated as per the Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011.
- The network will be established initially for Delhi and gradually expanded to include other States and Regions of the country.
- Thus, this division of the NOTTO is the nodal networking agency for Delhi and shall network for Procurement Allocation and Distribution of Organs and Tissues in Delhi.
- It functions as apex centre for All India activities of coordination and networking for procurement and distribution of Organs and Tissues and registry of Organs and Tissues Donation and Transplantation in the country.
[II] National Biomaterial Centre (National Tissue Bank)
- The Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011 has included the component of tissue donation and registration of tissue Banks.
- It becomes imperative under the changed circumstances to establish National level Tissue Bank to fulfill the demands of tissue transplantation including activities for procurement, storage and fulfil distribution of biomaterials.
- The main thrust & objective of establishing the centre is to fill up the gap between ‘Demand’ and ‘Supply’ as well as ‘Quality Assurance’ in the availability of various tissues.
The centre will take care of the following Tissue allografts:
- Bone and bone products
- Skin graft
- Cornea
- Heart valves and vessels
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A cardinal omission in the COVID-19 package
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Importance of medical workforce in making the healthcare system robust
Context
On July 8, 2021, the Union government announced the “India COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Package: Phase II”. But it lacks provision for the medical workforce.
Objectives of the package
- The stated purpose of the package is to boost health infrastructure and prepare for a possible third wave of COVID-19.
- There is plan to increase COVID-19 beds, improve the oxygen availability and supply, create buffer stocks of essential medicines; purchase equipment and strengthen paediatric beds.
What is lacking in the package?
- Workforce shortage: The package barely has any attention on improving the availability of health human resources.
- As reported in rural health statistics and the national health profile there are vacancies for staff in government health facilities, which range from 30% to 80% depending upon the sub-group of medical officers, specialist doctors to nurses, laboratory technicians, pharmacists and radiographers, amongst others.
- Interstate variation: In addition, there are wide inter-State variations, with States that have poor health indicators with the highest vacancies.
Way forward
- Package for filling the existing vacancies: The COVID-19 package II needs to be urgently supplemented by another plan and a similar financial package (with shared Union and State government funding) to fill the existing vacancies of health staff at all levels.
- An objective approach to assess the mid-term health human resource needs could be the Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS).
- IPHS prescribes the human resources and infrastructure needed to make various types of government health facilities functional.
- The pandemic should be used as an opportunity to prepare India’s health system for the future.
- Scrutiny of the progress on policy decision: The progress on key policy decisions, for the last few years, to strengthen India’s health system, including those in India’s national health policy of 2017, need to be objectively scrutinised.
- These two sets of policy decisions should be reviewed and progress monitored, through a meeting of the Central Council of Health and Family Welfare, of which the Health Ministers of the States are members.
Conclusion
India’s health system will not benefit from ad hoc and a patchwork of one or other small packages. It essentially needs some transformational changes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Mental health care in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Shift in mental health care system needed
Context
Recently, a High Court suggested that homeless persons with health conditions be branded with a permanent tattoo, when vaccinated against COVID-19.
Issue
- In many countries, persons with severe mental health conditions live in shackles in their homes, in overcrowded hospitals, and even in prison.
- On the other hand, many persons with mental health issues live and even die alone on the streets.
- Three losses dominate the mental health systems narrative: dignity, agency and personhood.
- Issues with the laws: Far-sighted changes in policy and laws have often not taken root and many laws fail to meet international human rights standards.
- Many also do not account for cultural, social and political contexts resulting in moral rhetoric that doesn’t change the scenario of inadequate care.
- There is also the social legacy of the asylum, and of psychiatry and mental illness itself, that guides our imagination in how care is organised.
Way forward: A responsive care system
- We must understand mental health conditions for what they are and for how they are associated with disadvantage.
- These situations are linked, but not always so, therefore, not all distress can be medicalised.
- Adopt WHO guidelines: Follow the Guidance on Community Mental Health Services recently launched by the World Health Organization.
- The Guidance, which includes three models from India, addresses the issue from ‘the same side’ as the mental health service user and focuses on the co-production of knowledge and on good practices.
- Drawn from 22 countries, these models balance care and support with rights and participation.
- Open dialogue: The practice of open dialogue, a therapeutic practice that originated in Finland, runs through many programmes in the Guidance.
- This approach trains the therapist in de-escalation of distress and breaks power differentials that allow for free expression.
- Increase investment: With emphasis on social care components such as work force participation, pensions and housing, increased investments in health and social care seem imperative.
- Network of services: For those homeless and who opt not to enter mental health establishments, we can provide a network of services ranging from soup kitchens at vantage points to mobile mental health and social care clinics.
- Small emergency care and recovery centres for those who need crisis support instead of larger hospitals, and long-term inclusive living options in an environment that values diversity and celebrates social mixing, will reframe the archaic narrative of how mental health care is to be provided.
Conclusion
Persons with mental health conditions need a responsive care system that inspires hope and participation without which their lives are empty. We should endeavour to provide them with such a responsive care system.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
NITI Aayog releases study on ‘Not-for-Profit’ hospital model
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: India's healthcare system and its limitations
NITI Aayog has released a comprehensive study on the not-for-profit hospital model in the country, in a step towards closing the information gap on such institutions and facilitating robust policymaking in this area.
‘Not-for-Profit’ hospitals
- The “Not-for-Profit” Hospital Sector has the reputation of providing affordable and accessible healthcare for many years.
- This sector provides not only curative healthcare, but also preventive healthcare, and links healthcare with social reform, community engagement, and education.
- They utilize the resources and grants provided to them by the Government to provide cost-effective healthcare to the population without being overly concerned about profits.
- However, this sector remains largely understudied, with a lack of awareness about its services in the public domain.
Significance for India
- As per the NITI Aayog’s report, the not-for-profit hospitals account for only 1.1% of treated ailments as of June 2018.
- The report further revealed that for-profit hospitals account for 55.3% of in-patients, while not-for-profit hospitals account for only 2.7% of in-patients in the country.
- The cumulative cost of care at not-for-profit hospitals is lesser than for-profit hospitals by about one-fourth in the in-patient department.
- This is reckoned by the package component of cost, which is approximately 20% lower, the doctor’s or surgeon’s charges, which are approximately 36% lower and the major aspect being the bed charges, which are approximately 44% lower than the for-profit hospitals.
NITI Aayog’s approach
- Categorization of the prominent not-for-profit hospitals based on the premise of services and their ownership
- Understanding the business model of the hospitals i.e. the financial viability, and their dependence on donations and grants
- Understanding the challenges faced by these hospitals
- Formulation of recommendations for policy interventions to promote the sector
Categories of such hospitals
Using the above-mentioned approach and secondary research, the following four categories were defined for the not-for-profit hospitals:
- Faith-based Hospitals
- Community-based Hospitals
- Cooperative Hospitals
- Private Trust Hospitals
Why need such hospitals?
- There has been relatively low investment in the expansion of the health sector in the private domain.
- The not-for-profit hospital sector provides not only curative but also preventive healthcare.
- It links healthcare with social reform, community engagement, and education.
- It uses government resources and grants to provide cost-effective healthcare to people without being concerned about profits.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Centre must make way for states in Covid fight
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Role of the States in health crisis
The States are better equipped to deal with the health emergencies and the Centre needs to augment them in their efforts. The article deals with this issue.
Role of the States in health crisis
- Covid-19 pandemic is a national crisis calling for concerted efforts by both, the Government of India (GoI) and state governments.
- Health is a state subject, and the states have been pioneering many health programmes on their own, some with support and funding from the GoI, for a very long time.
- The number of employees in the health wing of the GoI is negligible as compared to that in any state government.
- The GoI must help them, motivate them to do better and assist them in their task.
- Also, the GoI must and can play a major role is in vaccination.
Role of the Central government
- It must try to augment supplies by encouraging companies to produce more and through imports/gifts.
- However, whatever it procures must be allotted to states in proportion to their eligible population.
- State governments must be involved in this policy.
- The vaccination policy may be left to the state governments based on the allocation.
- The GoI must also augment supplies of critical medical goods through imports and donations from friendly nations in view of their acute shortage.
- It must distribute them to the needy states transparently and equitably.
Steps that need to be taken
- Lockdowns need to be lifted in a calibrated manner depending on local conditions.
- Lockdowns are not the solution, they just buy breathing time which can be used by governments to ramp up capacity.
- State governments must set up efficient and well-functioning control rooms and telemedicine centres to guide people on home treatment and timely admission to hospitals.
- The private sector can also be fully involved in these efforts.
- Bed capacity must be increased in both private and public sectors, with all necessary requirements such as oxygen, medicines, and health workers.
- It is also important to put in place a standard guidance protocol for health workers and control rooms to guide patients through the disease.
- Enforcement of masks and distancing in public places must go on till the country is fully vaccinated.
- The measures suggested above require hard work and efficient management by state governments, by a team of reputed professionals and civil servants.
- Daily briefing by a professional, not a politician, is the need of the hour at both the Centre and state level, giving some confidence and assurance to the public.
Consider the question “In dealing with the health crisis the Union Government and the State governments are better placed for certain roles. In light of this, examine the important role of the States in dealing with the Covid pandemic and how the Union government can complement it.”
Conclusion
The central government must realise that states are on the forefront in this war, and therefore, play a supporting and proactive role. It has only a minor, behind-the-scenes role in the health sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A place for disruptive technology in India’s health sector
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Use of disruptive technologies in medical sector
The adoption of technologies such as AI and blockchain has the potential to transform the medical sector.
How new technologies can play important role in medical sector
1) Blockchain technology
- Blockchain technology can help in addressing the interoperability challenges that health information and technology systems face.
- The health blockchain would contain a complete indexed history of all medical data, including formal medical records and health data from mobile applications and wearable sensors.
- This can also be stored in a secure network and authenticated, besides helping in seamless medical attention.
2) Big data analytics
- Big data analytics can help improve patient-based services tremendously such as early disease detection.
- AI and the Internet of Medical Things, or IoMT are shaping healthcare applications.
- IoMT is defined as a connected infrastructure of medical devices, software applications, and health systems and services.
3) Medical autonomous system
- Medical autonomous systems can also improve health delivery to a great extent and their applications are focused on supporting medical care delivery in dispersed and complex environments with the help of futuristic technologies.
- This system may also include autonomous critical care system, autonomous intubation, autonomous cricothyrotomy and other autonomous interventional procedures.
4) Cloud computing
- Cloud computing is another application facilitating collaboration and data exchanges between doctors, departments, and even institutions and medical providers to enable best treatment.
Challenges
- The possible constraints in this effort are standardisation of health data, organisational silos, data security and data privacy, and also high investments.
Using technology for Universal Health Coverage
- According to the World Health Organization, Universal health coverage (UHC) is a powerful social equalizer and the ultimate expression of fairness.
- Studies by WHO show that weakly coordinated steps may lead to stand-alone information and communication technology solutions.
- India needs to own its digital health strategy that works and leads towards universal health coverage and person-centred care.
- Such a strategy should emphasise the ethical appropriateness of digital technologies, cross the digital divide, and ensure inclusion across the economy.
- ‘Ayushman Bharat’ and tools such as Information and Communication Technology could be be fine-tuned with this strategy to promote ways to protect populations.
- Online consultation should be a key part of such a strategy.
Using local knowledge
- In addition to effective national policies and robust health systems, an effective national response must also draw upon local knowledge.
- Primary health centres in India could examine local/traditional knowledge and experience and then use it along with modern technology.
Way forward
- Initial efforts in this direction should involve synchronisation and integration, developing a template for sharing data, and reengineering many of the institutional and structural arrangements in the medical sector.
- Big data applications in the health sector should help hospitals provide the best facilities and at less cost, provide a level playing field for all sectors, and foster competition.
Consider the question “Examine the role technologies such as AI and data analytics could play in the medical sector. What are the challenges in the adoption of such technologies?”
Conclusion
The above-discussed aspects highlight the potential benefits of the adoption of disruptive technologies in the healthcare system. India should embrace it while addressing the concerns with such technologies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
China to allow couples for third child
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: One-Child Policy
China will for the first time allow couples to have a third child in a further relaxation of family planning rules five years after a “two-child policy” largely failed to boost birth rates.
Do you think that the One-Child Policy would be effective for population control in India?
What was the One-Child Policy?
- China embarked upon its one-child policy in 1980 when the Communist Party was concerned that the country’s growing population, which at the time was approaching one billion, would impede economic progress.
- The policy was implemented more effectively in urban areas.
- It was enforced through several means, including incentivizing families financially to have one child, making contraceptives widely available, and imposing sanctions against those who violated the policy.
How well did the policy fare?
- Chinese authorities have long hailed the policy as a success, claiming that it helped the country avert severe food and water shortages by preventing up to 40 crore people from being born.
- However, the policy was also a source of discontent, as the state used brutal tactics such as forced abortions and sterilizations.
- It also met criticism and remained controversial for violating human rights, and for being unfair to poorer Chinese since the richer ones could afford to pay economic sanctions if they violated the policy.
- Additionally, China’s rulers have been accused of enforcing reproductive limits as a tool for social control.
- The Uighur Muslim ethnic minority, for example, has been forced to have fewer children to restrict the growth of their population.
Demographic changes due to the policy
- Due to the policy, while the birth rate fell, the sex ratio became skewed towards males.
- This happened because of a traditional preference for male children in the country, due to which abortion of female fetuses rose and so did the number of girls who were placed in orphanages or abandoned.
- Experts have also blamed the policy for making China’s population age faster than other countries, impacting the country’s growth potential.
- It is also suggested that because of the long-lingering impact of the policy, China would be unable to reap the full benefits of its economic growth and will need other ways to support it.
Skeptics of the new move
- Experts say relaxing limits on reproductive rights alone cannot go a long way in averting an unwanted demographic shift.
- The main factors behind fewer children being born, they say, are rising costs of living, education, and supporting aging parents.
- The problem is made worse by the country’s pervasive culture of long working hours.
- There has also been a cultural shift during the decades in which the one-child policy remained in force, with many couples believing that one child is enough, and some expressing no interest in having children.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What are Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTD)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Neglected Tropical Diseases
Mains level: Burden of NTD in India
The ongoing World Health Assembly has declared January 30 as ‘World Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTD) Day’.
Neglected Tropical Diseases

- NTDs are a group of infections that are most common among marginalized communities in the developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- They are caused by a variety of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms.
- These diseases generally receive less funding for research and treatment than malaises like tuberculosis, HIV-AIDS and malaria.
- Some examples of NTDs include snakebite envenomation, scabies, yaws, trachoma, Leishmaniasis and Chagas disease.
Significance of global recognition
- NTDs affect more than a billion people globally, according to the WHO. They are preventable and treatable.
- However, these diseases and their intricate interrelationships with poverty and ecological systems — continue to cause devastating health, social and economic consequences.
- A major milestone in the movement to recognize the global burden of these diseases was the London Declaration on NTDs that was adopted January 30, 2012.
- The first World NTD Day was celebrated informally in 2020. This year, the new NTD road map was launched.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
WHO BioHub: Global Facility for Pathogen Storage
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: WHO BioHub and its purpose
Mains level: Not Much
The World Health Organization (WHO) and Switzerland have signed an MoU to launch a BioHub facility that will allow rapid sharing of pathogens between laboratories and partners to facilitate better analysis and preparedness against them.
WHO BioHub
- The BioHub will enable member states to share biological materials with and via the BioHub under pre-agreed conditions, including biosafety, biosecurity, and other applicable regulations.
- The facility will help in the safe reception, sequencing, storage, and preparation of biological materials for distribution to other laboratories, so as to facilitate global preparedness against these pathogens.
- It would be based in Spiez, Switzerland.
- Pathogens are presently shared bilaterally between countries: A process that can be sluggish and deny the benefits to some.
Its significance
- This will ensure timeliness and predictability in response activities.
- The move is significant in the view of the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic and the need to underline the importance of sharing pathogen information to assess risks and launch countermeasures.
- The move will help contribute to the establishment of an international exchange system for novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and other emerging pathogens.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The fault line of poor health infrastructure
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Poor public health infrastructure in India and its consequences
The poor public health infrastructure in India hits the poor hard. The article examines the factors responsible for poor public health infrastructure and suggests the measures to deal with it.
Poor state of health infrastructure
- World Bank data reveal the poor state of India’s health infrastructure.
- It reveals that India had 85.7 physicians per 1,00,000 people in 2017.
- In contrast, it is 98 in Pakistan, 58 in Bangladesh, 100 in Sri Lanka and 241 in Japan.
- India had 53 beds per 1,00,000 people.
- It is 63 in Pakistan, 79.5 in Bangladesh, 415 in Sri Lanka and 1,298 in Japan.
- India had172.7 nurses and midwives per 1,00,000 people in contrast to 220 in Sri Lanka, 40 in Bangladesh, 70 in Pakistan, and 1,220 in Japan.
What are the factors responsible for poor health infrastructure?
- Stagnant expenditure: Analysis by the Centre for Economic Data and Analysis (CEDA), Ashoka University, shows that health expenditure has been stagnant for years.
- Lack of expertise with states: Despite health being a state subject, the main bodies with technical expertise are under central control.
- The States lack corresponding expert bodies such as the National Centre for Disease Control or the Indian Council of Medical Research.
- Inter-State variation: States also differ a great deal in terms of the fiscal space to deal with the novel coronavirus pandemic because of the wide variation in per capita health expenditure.
- Kerala and Delhi have been close to top in years from 2011 to 2019-20.
- Bihar, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh, States that have been consistently towards the bottom of the ranking in the same years.
Out-of-pocket expenditure and its impact on the poor
- Due to low levels of public health provision, the World Health Organization estimates that 62% of the total health expenditure in India is OOP, among the highest in the world.
- Some of the poorest States, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand and Odisha, have a high ratio of OOP expenditures in total health expenditure.
- Impact on the poor: High ratio of OOP means that the poor in the poorest States, the most vulnerable sections, are the worst victims of a health emergency.
Way forward
1) Coordinated national plan
- The inter-State variation in health expenditure highlights the need for a coordinated national plan at the central level to fight the pandemic.
- The Centre already tightly controls major decisions, including additional resources raised specifically for pandemic relief, e.g. the PM CARES Fund.
- The need for a coordinated strategy on essential supplies of oxygen and vaccines is acute.
- The Centre can bargain for a good price from vaccine manufacturers in its capacity as a single large buyer like the European Union did for its member states.
- Centre will also benefit from the economies of scale in transportation of vaccines into the country.
- Once the vaccines arrive in India, these could be distributed across States equitably in a needs-based and transparent manner.
- Another benefit of central coordination is that distribution of constrained resources like medical supplies, financial resources can internalise the existing disparities in health infrastructure across States.
2) Form Pandemic Preparedness Unit
- There is a need for the creation of a “Pandemic Preparedness Unit” (PPU) by the central government.
- PPU would streamline disease surveillance and reporting systems; coordinate public health management and policy responses across all levels of government.
- It will also formulate policies to mitigate economic and social costs, and communicate effectively about the health crisis.
Consider the question “India has among the highest out-of-pocket expenditure in the world, which is the result of poor public health infrastructure. Examine the factors responsible for poor public health infrastructure and suggest the ways to deal with it.”
Conclusion
As and when we emerge on the other side of the pandemic, bolstering public health-care systems has to be the topmost priority for all governments: the Centre as well as States.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Medicine from the Sky Project
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Medicine from the Sky Project
Mains level: Innovation in healthcare services

The Telangana government has selected 16 primary healthcare centres (PHCs) spread around Vikarabad area hospital for pilot testing the ambitious ‘Medicine from the sky’, the first-of-its-kind project involving delivery of medicines through multiple drones.
Medicine from the Sky Project
- A consortium of seven operators headed by Blue Dart Med-Express had been selected for the project to be launched in the VLOS range of 500 metres initially and will be scaled up gradually to a 9 km range.
- The selected PHCs are both within the Visual Line of Sight (VLOS) and Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) range.
- The project would be launched in three waves starting with a pilot followed by mapping the route network for the operation of drones for delivering vaccine/medicine in the desired community health centres and PHCs.
- The project is being launched following the approval granted by the Civil Aviation Ministry to the request made by the State to grant conditional exemption from the Unmanned Aircraft System Rules 2021.
Benefits of the project
- The project is aimed at assessing alternative logistics route in providing safe, accurate and reliable pickup and delivery of health care items like medicines, vaccines, units of blood and other lifesaving equipment from the distribution centre to a specific location and back.
- The model, once successful, would enable deliveries from district medical stores and blood banks to PHCs, CHCs and further from PHCs/CHCs to central diagnostic laboratories.
Back2Basics: What is VLOS (Visual Line of Sight)?

- Visual Line of Sight (‘VLOS’) operations are a type of operation in which the remote pilot maintains continuous, unaided visual contact with the unmanned aircraft. In its simplest term, the aircraft must always be visible to the pilot.
- This allows the remote pilot to control the flight path of the unmanned aircraft in relation to other aircraft, people, and obstacles for the purpose of avoiding collisions.
- Extended Visual Line of Sight operations (‘EVLOS’) allows flight Beyond Visual Line of Sight of the Remote Pilot by using ‘trained observers’.
- Trained observers are used to comply with the separation and collision avoidance responsibilities of the operator.
- ‘Beyond Visual Line of Sight’ operations is where the flying of a drone is without a pilot maintaining a visual line of sight on the aircraft at all times.
- Instead, the pilot operates the UAV using Remote Pilot Station (RPS) / Ground Control Station (GCS) instruments.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Brain drain of India’s health worker
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- India's health worker brain drain
The article highlights the issue of shortage of healthcare workers in India even as it exports its healthcare workers to other countries.
India as an exporter of healthcare workers
- For several decades, India has been a major exporter of healthcare workers to developed nations particularly to the Gulf Cooperation Council countries, Europe and other English-speaking countries.
- As per OECD data, around 69,000 Indian trained doctors worked in the UK, US, Canada and Australia in 2017.
- In these four countries, 56,000 Indian-trained nurses were working in the same year.
- There is also large-scale migration of health workers to the GCC countries but there is a lack of credible data on the stock of such workers in these nations.
- There is no real-time data on high-skilled migration from India as in the case of low-skilled and semi-skilled migration.
Shortage of nurses and doctors
- The migration of healthcare workers is part of the reason for the shortage in nurses and doctors.
- If we look at the figures for countries where we export our healthcare workers, we see just how big the difference is between the sending and the receiving countries.
- As per government reports, India has 1.7 nurses per 1,000 population and a doctor to patient ratio of 1:1,404.
- This is well below the WHO norm of 3 nurses per 1,000 population and a doctor to patient ratio of 1:1,100.
- But, this does not convey the entire problem.
- The distribution of doctors and nurses is heavily skewed against some regions.
- Moreover, there is high concentration in some urban pockets.
Factors driving migration
- There are strong pull factors associated with the migration of healthcare workers, in terms of higher pay and better opportunities in the destination countries.
- However, there are strong push factors that often drive these workers to migrate abroad.
- The low wages in private sector outfits along with reduced opportunities in the public sector plays a big role in them seeking employment opportunities outside the country.
- The lack of government investment in healthcare and delayed appointments to public health institutions act as a catalyst for such migration.
Measures to check brain drain and issues with it
- Over the years, the government has taken measures to check the brain drain of healthcare workers with little or no success.
- In 2014, it stopped issuing No Objection to Return to India (NORI) certificates to doctors migrating to the US.
- The NORI certificate is a US government requirement for doctors who migrate to America on a J1 visa and seek to extend their stay beyond three years.
- The non-issuance of the NORI would ensure that the doctors will have to return to India at the end of the three-year period.
- The government has included nurses in the Emigration Check Required (ECR) category.
- This move was taken to bring about transparency in nursing recruitment and reduce the exploitation of nurses in the destination countries.
- The government’s policies to check brain drain are restrictive in nature and do not give us a real long-term solution to the problem.
Way forward
- We require systematic changes that could range from increased investment in health infrastructure, ensuring decent pay to workers and building an overall environment to motivate them to stay in the country.
- The government should focus on framing policies that promote circular migration and return migration — policies that incentivise healthcare workers to return home after the completion of their training or studies.
- It could also work towards framing bilateral agreements that could help shape a policy of “brain-share” between the sending and receiving countries.
- The 2020 Human Development Report shows that India has five hospital beds per 10,000 people — one of the lowest in the world.
- Increased investment in healthcare, especially in the public sector, is thus the need of the hour.
- This would, in turn, increase employment opportunities for health workers.
Consider the question “What are the factors driving the migration of healthcare workers from India? Suggest the measure to stem their migration.”
Conclusion
India needs systematic changes that could range from increased investment in health infrastructure, ensuring decent pay to health workers and building an overall environment that could prove to be beneficial for them and motivate them to stay in the country.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Risk of mucormycosis in Covid-19 patients
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mucormycosis
Mains level: Paper 2- Mucormycosis infection risk in Covid-19 patients
About mucormycosis
- Mucormycosis is a fungal infection that has a high mortality rate of 50 per cent.
- An increasing number of Covid-19 patients have been developing this infection while still at the hospital or after discharge.
- The disease often manifests in the skin and also affects the lungs and the brain.
- Some of the common symptoms include sinusitis, blackish nasal discharge, facial pain, headaches, and pain around the eyes.
Who is at risk
- Patients who have been hospitalised for Covid-19 and particularly those who require oxygen therapy during Covid-19 illness are at a much higher risk of mucormycosis.
- However, there are some cases of mucormycosis in patients with asymptomatic Covid-19 infection.
- Before the pandemic, patients with uncontrolled diabetes were at a higher risk of mucormycosis.
- The risk of mucormycosis rises for these patients for two reasons.
- First is that Covid-19 further impairs their immune system.
- Second, they are given corticosteroids for their treatment it leads to a rise in their blood sugar level thus increasing their risk of mucormycosis.
Treatment
- Today, we have a number of drugs and anti-fungal medicines that can treat mucormycosis.
- These are given by IV or taken orally.
- Surgery is needed to remove the affected dead tissues along with antifungal therapy.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Digital Technologies and Inequalities
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Growing inequality in access to health and education
Impact of pandemic
- The novel coronavirus pandemic has accelerated the use of digital technologies in India, even for essential services such as health and education, where access to them might be poor.
- Economic inequality has increased: people whose jobs and salaries are protected, face no economic fallout.
- Well-recognised channels of economic and social mobility — education and health — are getting rejigged in ways that make access more inequitable in an already unequal society.
Growing inequality in access to education
- According to National Sample Survey data from 2017, only 6% rural households and 25% urban households have a computer.
- Access to Internet facilities is not universal either: 17% in rural areas and 42% in urban areas.
- Surveys by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), the Azim Premji Foundation, ASER and Oxfam suggest that between 27% and 60% could not access online classes for a range of reasons: lack of devices, shared devices, inability to buy “data packs”, etc.
- Further, lack of stable connectivity jeopardises their evaluations.
- Besides this, many lack a learning environment at home.
- Peer learning has also suffered.
Inequality in access to health care
- India’s public spending on health is barely 1% of GDP.
- Partly as a result, the share of ‘out of pocket’ (OOP) health expenditure (of total health spending) in India was over 60% in 2018.
- Even in a highly privatised health system such as the United States, OOP was merely 10%.
- Moreover, the private health sector in India is poorly regulated in practice.
- Both put the poor at a disadvantage in accessing good health care.
- Right now, the focus is on the shortage of essentials: drugs, hospital beds, oxygen, vaccines.
- In several instances, developing an app is being seen as a solution for allocation of various health services.
- Digital “solutions” create additional bureaucracy for all sick persons in search of these services without disciplining the culprits.
- Platform- and app-based solutions can exclude the poor entirely, or squeeze their access to scarce health services further.
- In other spheres (e.g., vaccination) too, digital technologies are creating extra hurdles.
- The use of CoWIN to book a slot makes it that much harder for those without phones, computers and the Internet.
Issues with the creation of centralised database
- The digital health ID project is being pushed during the pandemic when its merits cannot be adequately debated.
- Electronic and interoperable health records are the purported benefits.
- For patients, interoperability i.e., you do not have to lug your x-rays, past medication and investigations can be achieved by decentralising digital storage say, on smart cards as France and Taiwan have done.
- Given that we lack a data privacy law in India, it is very likely that our health records will end up with private entities without our consent, even weaponised against us.
- For example, a private insurance companies may use health record to deny poor people an insurance policy or charge a higher premium.
- There are worries that the government is using the vaccination drive to populate the digital health ID database.
Way forward
- Unless health expenditure on basic health services (ward staff, nurses, doctors, laboratory technicians, medicines, beds, oxygen, ventilators) is increased, apps such as Aarogya Setu, Aadhaar and digital health IDs can improve little.
- Unless laws against medical malpractices are enforced strictly, digital solutions will obfuscate and distract us from the real problem.
- We need political, not technocratic, solutions.
Conclusion
Today, there is greater understanding that the harms from Aadhaar and its cousins fall disproportionately on the vulnerable. Hopefully, the pandemic will teach us to be more discerning about which digital technologies we embrace.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A ‘One Health’ approach that targets people, animals
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zoonotic diseases
Mains level: Paper 2- 'One Health' approach to deal with infections diseases
The article highlights the need for a holistic approach to animal and human health as more than two-thirds of existing and emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic.
Need to document the link between environment animal and human health
- Studies indicate that more than two-thirds of existing and emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic, or can be transferred between animals and humans, and vice versa.
- Another category of diseases, anthropozoonotic infections, gets transferred from humans to animals.
- The transboundary impact of viral outbreaks in recent years such as the Nipah virus, Ebola, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) has reinforced the need for us to consistently document the linkages between the environment, animals, and human health.
India’s ‘One Health’ vision
- India’s ‘One Health’ vision derives its blueprint from the agreement between the tripartite-plus alliance.
- The alliance comprises the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE), the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) — a global initiative supported by the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and the World Bank under the overarching goal of contributing to ‘One World, One Health’.
- In keeping with the long-term objectives, India established a National Standing Committee on Zoonoses as far back as the 1980s.
- This year, funds were sanctioned for setting up a ‘Centre for One Health’ at Nagpur.
- Further, the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) has launched several schemes to mitigate the prevalence of animal diseases since 2015.
- Hence, under the National Animal Disease Control Programme, ₹13,343 crore have been sanctioned for Foot and Mouth disease and Brucellosis control.
- In addition, DAHD will soon establish a ‘One Health’ unit within the Ministry.
- Additionally, the government is working to revamp programmes that focus on capacity building for veterinarians such as Assistance to States for Control of Animal Diseases (ASCAD).
- There is increased focus on vaccination against livestock diseases and backyard poultry.
- DAHD has partnered with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in the National Action Plan for Eliminating Dog Mediated Rabies.
Need for coordination
- There are more than 1.7 million viruses circulating in wildlife, and many of them are likely to be zoonotic.
- Therefore, unless there is timely detection, India risks facing many more pandemics in times to come.
- There is need to address challenges pertaining to veterinary manpower shortages, the lack of information sharing between human and animal health institutions, and inadequate coordination on food safety at slaughter.
- These issues can be remedied by consolidating existing animal health and disease surveillance systems — e.g., the Information Network for Animal Productivity and Health, and the National Animal Disease Reporting System.
Conclusion
As we battle yet another wave of a deadly zoonotic disease (COVID-19), awareness generation, and increased investments toward meeting ‘One Health’ targets is the need of the hour.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] MANAS Platform
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MANAS Platform
Mains level: Not Much
The MANAS App to promote wellbeing across age groups was recently launched.
Name, acronym and the purpose; thats all. The rest of the theory is of less importance.
MANAS Platform
- MANAS is an acronym for Mental Health and Normalcy Augmentation System.
- It is a comprehensive, scalable, and national digital wellbeing platform and an app developed to augment the mental well-being of Indian citizens.
- MANAS was initiated by the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India and jointly executed by NIMHANS Bengaluru, AFMC Pune and C-DAC Bengaluru.
- It was endorsed as a national program by the Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC).
- It integrates the health and wellness efforts of various government ministries, scientifically validated indigenous tools with gamified interfaces developed/researched by various national bodies and research institutions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
NCAHP Bill 2020
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Commission for Allied and Healthcare Professions Bill 2020
Mains level: Paper 2- NCAHP Bill 2020
The article highlights the key aspects of NCAHP Bill 2020 which recognises the allied healthcare professionals and seeks to regulate and set the standards of education.
Regulating allied health professions
- The National Commission for Allied and Healthcare Professions Bill, 2020 (NCAHP) was passed by Parliament in March.
- Global evidence demonstrates the vital role of allied professionals in the delivery of healthcare services.
- They are the first to recognise the problems of the patients and serve as safety nets.
- Their awareness of patient care accountability adds tremendous value to the healthcare team in both the public and private sectors.
- The passage of this Bill has the potential to overhaul the entire allied health workforce by establishing institutes of excellence and regulating the scope of practice by focusing on task shifting and task-re distribution.
What the Bill provides for
- This legislation provides for regulation and maintenance of standards of education and services by allied and healthcare professionals and the maintenance of a central register of such professionals.
- It recognises over 50 professions such as physiotherapists, optometrists, nutritionists, medical laboratory professionals, radiotherapy technology professionals, which had hitherto lacked a comprehensive regulatory mechanism.
- This Bill classifies allied professionals using the International System of Classification of Occupations (ISCO code).
- This facilitates global mobility and enables better opportunities for such professionals.
- The Act aims to establish a central statutory body as a National Commission for Allied and Healthcare Professions.
- The Bill has the provision for state councils to execute major functions through autonomous boards.
Shift in perception and policy in healthcare delivery
- There has been a paradigm shift in perception, policy, and programmatic interventions in healthcare delivery in India since 2017.
- In the past, curative healthcare received substantially greater attention than preventive and promotive aspects.
- Ayushman Bharat as a programmatic intervention, with its two pillars of Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY), operationalised certain critical recommendations of the National Health Policy, 2017, emphasising wellness in healthcare.
- With PMJAY, the neediest are protected from catastrophic expenditure and India took the first step towards delivering comprehensive primary healthcare with HWCs.
Conclusion
Caring for patients with mental conditions, the elderly, those in need of palliative services, and enabling professional services for lifestyle change related to physical activity and diets, all require a trained, allied health workforce. The NCAHP is not only timely but critical to this changing paradigm.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] ‘Anamaya’ Initiative
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ‘Anamaya’ Initiative
Mains level: Not Much
Anamaya, the Tribal Health Collaborative was recently launched.
Simply keep in mind, the name and purpose.
‘Anamaya’ Initiative
- The Collaborative is a multi-stakeholder initiative of the Tribal Affairs Ministry supported by Piramal Foundation and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF).
- It aims to build a sustainable, high-performing health eco-system to address the key health challenges faced by the tribal population of India.
- It will converge efforts of various Government agencies and organisations to enhance the health and nutrition status of the tribal communities of India.
- This collaborative is a unique initiative bringing together governments, philanthropists, national and international foundations, NGOs/CBOs to end all preventable deaths among the tribal communities of India.
Terms of references
- It will begin its operations with 50 tribal, Aspirational Districts (with more than 20% ST population) across 6 high tribal population states.
- Over a 10-year period, the work of the THC will be extended to 177 tribal Districts as recognised by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Integrated Health Information Platform (IHIP)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IHIP
Mains level: Digital health mission
The Union Minister of Health & Family Welfare has launched the Integrated Health Information Platform (IHIP).
About IHIP
- The new version of IHIP will house the data entry and management for India’s disease surveillance program.
- In addition to tracking 33 diseases now as compared to the earlier 18 diseases, it shall ensure near-real-time data in digital mode, having done away with the paper mode of working.
Various functions
- IHIP will provide a health information system developed for real-time, case-based information, integrated analytics, advanced visualization capability.
- It will provide analyzed reports on mobile or other electronic devices. In addition, outbreak investigation activities can be initiated and monitored electronically.
- It can easily be integrated with another ongoing surveillance program while having the feature of the addition of special surveillance modules.
Unique features
- This is the world’s biggest online disease surveillance platform.
- It is in sync with the National Digital Health Mission and fully compatible with the other digital information systems presently being used in India.
- The refined IHIP with automated -data will help in a big way in real-time data collection, aggregation & further analysis of data that will aid and enable evidence-based policymaking.
- With IHIP, the collection of authentic data will become easy as it comes directly from the village/block level; the last mile from the country.
- With its implementation, we are fast marching towards AtmaNirbhar Bharat in healthcare through the use of technology.
Also read:
[Burning Issue] Rolling-out of National Digital Health Mission
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
N K Singh bats for moving Health Sector to Concurrent List
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Concurrent List
Mains level: India's healthcare

Health should be shifted to the Concurrent list under the Constitution, and a developmental finance institution (DFI) dedicated to healthcare investments set up, Fifteenth Finance Commission Chairman N.K. Singh has said.
Other key recommendations
- Bringing health into the Concurrent list would give the Centre greater flexibility to enact regulatory changes and reinforce the obligation of all stakeholders towards providing better healthcare.
- He has urged the government spending to enhance expenditure on health to 2.5% of GDP by 2025.
- He said primary healthcare should be a fundamental commitment of all States in particular and should be allocated at least two-thirds of such spending.
The Concurrent List or List-III (of Seventh Schedule) is a list of 52 items (though the last subjects are numbered 47) given in the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution of India.
What is the Seventh Schedule?
- This Schedule of the Indian Constitution deals with the division of powers between the Union government and State governments.
- It defines and specifies the allocation of powers and functions between Union & States. It contains three lists; i.e. 1) Union List, 2) State List and 3) Concurrent List.
The Union List
- It is a list of 98 (Originally 97) numbered items as provided in the Seventh Schedule.
- The Union Government or Parliament of India has exclusive power to legislate on matters relating to these items.
The State List
- It is a list of 59 (Originally 66) items.
- The respective state governments have exclusive power to legislate on matters relating to these items.
The Concurrent List
- There are 52 (Originally 47) items currently in the list.
- This includes items which are under the joint domain of the Union as well as the respective States.
Must read
[Burning Issue] India’s Ailing Health Sector and Coronavirus
Healthcare in India
- The Indian Constitution has incorporated the responsibility of the state in ensuring basic nutrition, basic standard of living, public health, protection of workers, special provisions for disabled persons, and other health standards, which were described under Articles 39, 41, 42, and 47 in the DPSP.
- Article 21 of the Constitution of India provides for the right to life and personal liberty and is a fundamental right.
- Public Health comes under the state list.
- India’s expenditure on healthcare has shot up substantially in the past few years; it is still very low in comparison to the peer nations (at approx. 1.28% of GDP).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
ACT-Accelerator Coalition
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ACT-Accelerator
Mains level: Coronovirus outbreak
ACT-Accelerator, a global coalition formed in April 2020 to fight the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is facing a severe fund crunch to meet its goals for 2020-21.
ACT-Accelerator
- The Access to COVID-19 Tools Accelerator (ACT Accelerator) is a G20 initiative announced on 24 April 2020.
- A call to action was published simultaneously by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The ACT Accelerator is a cross-discipline support structure to enable partners to share resources and knowledge.
- It comprises four pillars, each managed by two to three collaborating partners:
- Vaccines (also called “COVAX”)
- Diagnostics
- Therapeutics
- Health Systems Connector
- India is an active donor in this alliance.
Try this PYQ based on a global coalition:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) to Reduce Short Lived Climate Pollutants is a unique initiative of G20 group of countries.
- The CCAC focuses on methane, black carbon and Hydrofluorocarbons.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What we must consider before digitising India’s healthcare
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Digital Health Mission
Mains level: Paper 2- Issues to consider in digitising health infrastructure
As India seeks to create digital health infrastructure, it must consider several issues.
Integrated digital health infrastructure
- The National Digital Health Mission aims to develop the backbone needed for the integrated digital health infrastructure of India.
- This can help not only with diagnostics and management of health episodes, but also with broader public health monitoring, socio-economic studies, epidemiology, research, prioritising resource allocation and policy interventions.
- However, before we start designing databases and APIs and drafting laws, we must be mindful of certain considerations for design choices and policies to achieve the desired social objectives.
Factors to be considered
1) Carefully developing pathway to public good
- There must be a careful examination of how exactly digitisation may facilitate better diagnosis and management, and an understanding of the data structures required for effective epidemiology.
- We must articulate how we may use digitisation and data to understand and alleviate health problems such as malnutrition and child stunting.
- We need the precise data we require to better understand crucial maternal- and childcare-related problems.
2) Balancing between public good and individual rights
- The potential tensions between public good and individual rights must be examined, as must the suitable ways to navigate them.
- Moreover, for the balancing to be sound and for determining the level of due diligence required, it is imperative to clearly define the operational standards for privacy management.
- Conflating privacy with security, as is typical in careless approaches, will invariably lead to problematic solutions.
- In fact, most attempts at building health data infrastructures worldwide — including in the UK, Sweden, Australia, the US and several other countries — have led to serious privacy-related controversies and have not yet been completely successful.
3) Managing the sector specific identities
- Even if we define and use a sector-specific identity, the question of when and how to link it with that of other sectors remains.
- For example, with banking or insurance for financial transactions, or with welfare and education for transactions and analytics.
- Indiscriminate linking may break silos and create a digital panopticon, whereas not linking at all will result in not realising the full powers of data analytics and inference.
4) Working out the operational requirement of data infrastructure
- We need to work out the operational requirements of the data infrastructure in ways that are informed by, and consonant with, the previous points.
- In other words, the design of the operationalisation elements must follow the deliberations on above points, and not run ahead of them.
- This requires identifying the diverse data sources and their complexity — which may include immunisation records, birth and death records, informal health care workers, dispensaries etc.
- It also requires an understanding of their frequency of generation, error models, access rights, interoperability, sharing and other operational requirements.
- There also are the complex issues of research and non-profit uses of data, and of data economics for private sector medical research.
5) Issue of due process
- Finally, “due process” has always been a weak point in India, particularly for technological interventions.
- Building an effective system that can engender people’s trust not only requires managing the floor of the Parliament and passing a just and proportional law, but also building a transparent process of design and refinement through openness and public consultations.
- In particular, technologists and technocrats should take care to not define “public good” as what they can conveniently deliver, and instead understand what is actually required.
- While we can understand the urge to move forward quickly, given the urgent need to improve health outcomes in the country, deliberate care is needed.
Consider the question “While seeking to develop digital health infrastructure through the National Digital Health Mission, we should be mindful of certain considerations for design choices and policies to achieve the desired social objectives. Comment.”
Conclusion
Developing a comprehensive understanding of the considerations related to health data infrastructure may also inform the general concerns of e-governance and administrative digitisation in India, which have not been all smooth sailing.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What are Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases (NAFLD)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NAFLD
Mains level: Health threats posed by Fats
The Union Govt has integrated the Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke.
Try this MCQ:
Q.A Company marketing food products advertises that its items do not contain trans-fats. What does this campaign signify to the customers?
- The food products are not made out of hydrogenated oils.
- The food products are not made out of animal fats/oils.
- The oils used are not likely to damage the cardiovascular health of the consumers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
NAFLD
- NAFLD is the abnormal accumulation of fat in the liver in the absence of secondary causes of fatty liver, such as harmful alcohol use, viral hepatitis, or medications.
- According to doctors, it is a serious health concern as it encompasses a spectrum of liver abnormalities.
- It can cause non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL, simple fatty liver disease) to more advanced ones like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis and even liver cancer.
Why such a move?
- NAFLD is emerging as an important cause of liver disease in India.
- Epidemiological studies suggest the prevalence of NAFLD is around 9% to 32% of the general population in India with a higher prevalence in those with overweight or obesity and those with diabetes or prediabetes.
- Researchers have found NAFLD in 40% to 80 % of people who have type 2 diabetes and in 30% to 90% of people who are obese.
- Studies also suggest that people with NAFLD have a greater chance of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in NAFLD.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
vaccine hesitancy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Dealing with vaccine hesitancy
Reluctance to take the vaccine has several implications. The misinformation around the vaccines needs to be fought through several measures.
Understanding vaccine hesitancy
- According to the World Health Organization, vaccine hesitancy is defined as a reluctance or refusal to vaccinate despite the availability of vaccine services.
- To date, two vaccines have been approved for inoculation in India: Pune-based Serum Institute’s Covishield and Hyderabad-based Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin.
- An adequate supply of vaccines is in place at least for the first phase, but the trickier part is to persuade the population for vaccination.
- Like Western nations, vaccine hesitancy has been a cause of concern in the past in India as well.
- Social media has seen a rising number of self-proclaimed experts who have been making unsubstantiated claims.
- The debates around hesitancy for COVID-19 vaccines include concerns over safety, efficacy, and side effects due to the record-breaking timelines of the vaccines, competition among several companies, misinformation, and religious taboos.
Need to adopt libertarian paternalism
- It is suggested that we adopt the idea of libertarian paternalism, which says it is possible and legitimate to steer people’s behaviour towards vaccination while still respecting their freedom of choice.
- Vaccine hesitancy has a different manifestation in India, unlike in the West.
- According to the World Economic Forum/Ipsos global survey, COVID-19 vaccination intent in India, at 87%, exceeds the global 15-country average of 73%.
Way forward
- Instead of anti-vaxxers, the target audience must be the swing population i.e., people who are sceptical but can be persuaded through scientific facts and proper communication.
- The second measure is to pause before you share any ‘news’ from social media.
- It becomes crucial to inculcate the habit of inquisitive temper to fact-check any news related to COVID-19 vaccines.
- The third measure is to use the celebrity effect — the ability of prominent personalities to influence others to take vaccines.
- Celebrities can add glamour and an element of credibility to mass vaccinations both on the ground and on social media.
Consider the question “What is vaccine hesitancy? Suggest the measures to deal with it”
Conclusion
The infodemic around vaccines can be tackled only by actively debunking myths, misinformation and fake news on COVID-19 vaccines.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
First steps in India’s journey to universal health care
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PM-JAY
Mains level: Paper 2- Achieving universal health coverage
The article highlights the issues with India’s approach in achieving universal health care and issues with it.
Learning from the experience of Thailand
- About 20 years ago, Thailand rolled out universal health coverage at a per capita GDP similar to today’s India.
- What made this possible was a three decade-long tradition of investing gradually but steadily in public health infrastructure and manpower.
- This meant that alongside the availability of funds, there also existed robust institutional capacity to assimilate those funds.
- This is important because enough evidence exists on weak fund-absorbing capacities particularly in the backward States in India.
Budgetary allocations for health
- The Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare budget for 2021-22, viz. ₹73,932 crore, saw a 10.2% increase over the Budget estimate (BE) of 2020-21.
- Also, a corpus of ₹64,180 crore over six years has been set aside under the PM Atma Nirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana, (PMANSBY).
- ₹13,192 crore has been allocated as a Finance Commission grant.
- These allocations could make the first steps towards sustainable universal health coverage through incremental strengthening of grass-root-level institutions and processes.
Two important and prominent arms of universal health coverage in India merit discussion here
1) Insurance route for achieving universal health coverage and issues with it
- The Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) has stagnated at ₹6,400 crores for the current and a preceding couple of years.
- Large expenditure projections and time constraints involved in the input-based strengthening of public health care have inspired the shift to the insurance route.
- However, insurance does not provide a magic formula for expanding health care with low levels of public spending.
- Beyond low allocations, poor budget reliability merits attention.
- Another related issue is the persistent and large discrepancies between official coverage figures and survey figures (for e.g. the National Sample Surveys, or NSS, and National Family Health Survey) across Indian States.
- Such discrepancies indicate that official public health insurance coverage fails to translate into actual coverage on the ground.
- Robust research into the implementational issues responsible for such discrepancies and addressing them is warranted.
- Without the same, the PM-JAY’s quest for universal health coverage is likely to be precarious.
- Finally, even high actual coverage should not be equated with effective financial protection.
- For example, Andhra Pradesh has among the highest public health insurance coverage scores (71.36%, NSS 75), but still has an out-of-pocket spending share much above the national average.
2) Comprehensive primary care
- Health and Wellness Centres — 1,50,202 of them — offering a comprehensive range of primary health-care services are to be operationalised until December 2022.
- Of these, 1,19,628 would be upgraded sub health centres and the remaining would be primary health centres and urban primary health centres.
- Initially, most States prioritised primary health centres/urban primary health centres for upgradation over sub health centres, since the former required fewer additional investments.
- Till February 2, 58,155 health and wellness centres were operational, of which 34,733 were sub health centres and 23,422 were primary health centres/urban primary health centres.
- This means that of the remaining 92,047 health and wellness centres to be operationalised by December 2022, 84,895 will be sub health centres.
- This offers huge cost projections.
- The current allocation of ₹1,900 crore, an increase of ₹300 crore from previous year, is a paltry sum in comparison.
- Since 2018-19, when the health and wellness centre initiative began, allocations have not kept pace with the rising targets each year.
- Additional funding under the PMANSBY and Finance Commission grants is reassuring, but a greater focus on rural health and wellness centres would be warranted.
- Two untoward implications could result from under-investing and spreading funds too thinly.
- Continuing the expansion of health and wellness centres without enough funding would mean that the full range of promised services will not be available, thus rendering the mission to be more of a re-branding exercise.
- Second, under-funding would waste an opportunity for the health and wellness centre initiative to at least partially redress the traditional rural-urban dichotomy by bolstering curative primary care in rural areas.
Consider the question “What are the challenges in adopting the insurance model in achieving the universal health coverage in India?”
Conclusion
COVID-19 has prodded us to make a somewhat stout beginning in terms of investing in health. The key, and the most difficult part, would be to keep the momentum going unswervingly.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
The unmet health challenge
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PMANSY
Mains level: Paper 2- Allocation in Budget for health
The article analyses the allocation for the health sector in the Budget and highlights the need for more allocations.
Need to increase spending on health
- The Economic Survey argues for the need to increase public spending on healthcare to 2.5-3 per cent of the GDP — it’s about 1.5 per cent currently.
- The Survey points out that there is not much difference in terms of outcomes and quality between healthcare services in the private sector and such services in public centres.
- The Economic Survey, therefore, calls for strengthening the National Health Mission (NHM) along with Ayushman Bharat.
- NHM was initiated in 2005-06 to strengthen public health services.
- The Ayushman Bharat provide social insurance, thereby financing private sector services with public funds.
- The Economic Survey makes a strong pitch for greater regulation of health services in the private sector.
Break-up of allocation in Budget on health (and well being)
- The finance minister described “health and well-being” as one of the pillars of the budget in her budget speech and announcing a 137 per cent increase in allocations for it.
- She placed healthcare, water and sanitation and nutrition as the key components of this pillar.
- However, the figures in the budget documents reveal a different story.
- There is an absolute increase of 9.6 per cent in allocations for the Department of Health and Family Welfare that includes NHM and Ayushman Bharat.
- A 26.8 per cent increase for the Department of Health Research and 40 per cent increase for the AYUSH Ministry do not add up to much since each of them are only 3-4 per cent of the total health budget.
- A Finance Commission grant of Rs 13,000-crore and Rs 35,000-crore for COVID-19 vaccination are one-time allocations and, therefore, do not strengthen the overall system.
- The core health service and research ministries (H&FW and AYUSH) have together received only an 11 per cent increase.
- Even in COVID times, the health services get only 2.21 per cent of the total central budget — down from 2.27 per cent in the 2020-21 budget.
- Computing for inflation, the increase in allocation for health services alone disappears and actually becomes negative.
- Water and sanitation received a 179 per cent increase from Rs 21,518 crore to Rs 60,030 crore already earmarked for the flagship schemes, Swachh Bharat and Jal Jeevan Mission.
- But allocation for nutrition decreased by 27 per cent, with the “new” Poshan 2.0 merely combining the poorly performing Supplementary Nutrition Programme and Poshan project.
- Added together, health, water and sanitation and nutrition make up the claimed 137 per cent increase in allocation to “health” services — with a real decline in healthcare and nutrition.

Pradhan Mantri Atma Nirbhar Swasthya Yojana (PMANSY)
- Finance Minister also announced a new scheme, the Pradhan Mantri Atma Nirbhar Swasthya Yojana, to support the almost 29,000 health and wellness centres in the country.
- The scheme also envisages the creation of public health laboratories and critical care hospital blocks and virology institutes.
Concerns with PMANSY
- PMANSY has an announced allocation of Rs 64,180 crore over six years, but it does not find a place in the present budget documents.
- But these additional activities could have been slotted in the NHM.
- Since 2014, the allocation for NHM has been on the wane.
- Therefore, even the marginal 1.33 per cent increase (from Rs 27,039 crore to Rs 30,100 crore) is a demonstration of the government’s realisation that public services do matter.
- The allocations of about Rs 10,000-Rs 11,000 crore each year for the PMANSY is not enough for making the public services capable of “universal health coverage”.
- The High-Level Expert Group on Universal Health Coverage had estimated that by 2020, we need a 114 per cent increase in sub-centres and primary health centres, 179 per cent increase in community health centres and a 230 per cent increase in sub-district and district hospitals.
- Getting anywhere close to this requires doubling of real allocations every year over a five-year period to reach something like 10 per cent of the budget.
- In the present budget, it declines to a mere 2.21 per cent.
Way forward
- If such public provisioning for universal health coverage can’t be done, then effective low-cost rationalised service system options have to be designed.
- Insurance schemes only create the mirage of affordability of health services while adding to peoples’ expenses.
- Community and public services are indisputably the most cost-effective for any society.
Consider the question “Examine the benefits of the idea of health and well being under which health, water and sanitation and nutrition are clubbed together.”
Conclusion
Water and sanitation are meaningful for health, but not if it only inflates the allocation to “Health and Wellbeing”. What we need is the real increase in spending on health.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Building a robust healthcare system
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Maternal Mortality Rate, Infant Morality Rate
Mains level: Paper 2- Disparity among states in health parameters
The article focuses on the wide variation across the state in terms of the important health parameters and suggests prioritising health.
Variation across the states
- The efficacy of the public health system varies widely across the country since it is a State subject.
- Public health system can be judged just by looking at certain health parameters such as Infant Mortality Rate, Maternal Mortality Ratio and Total Fertility Rate.
- In Madhya Pradesh, the number of infant deaths for every 1,000 live births is as high as 48 compared to seven in Kerala. In U.P. the Maternal Mortality Ratio is 197 compared to Kerala’s 42 and Tamil Nadu’s 63.
- The northern States are performing very poorly in these vital health parameters.
- The percentage of deliveries by untrained personnel is very high in Bihar, 190 times that of Kerala.
- Since health is a State subject, the primary onus lies with the State governments.
- Each State government must focus on public health and aim to improve the health indicators mentioned above.
- Unless all the States perform well, there will be no dramatic improvement in the health system.
Steps needed to be taken
- The governments — both at the Centre and the Empowered Action Group States — should realise that public health and preventive care is a priority and take steps to bring these States on a par with the southern States.
- The Government of India has a vital role to play.
- Public and preventive health should be his focus by holding the Empowered Action Group States accountable to the SDGs.
- They must be asked to reach the levels of the southern States within three to five years.
- An important measure that can make a difference is a public health set-up in these States that addresses primary and preventive health.
Conclusion
Unless we invest in human capital, FDI will not help. Investing in health and education is the primary responsibility of any government. It is time the governments — both at the Centre and States — gave health its due importance.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Ayushman Bharat for CAPFs
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat
Mains level: Universal health coverage

Union Home Minister has rolled out the ‘Ayushman CAPF’ scheme, extending the benefit of the central health insurance programme to the personnel of all Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) in the country.
Who are the CAPFs?
- The CAPFs refers to uniform nomenclature of five security forces in India under the authority of the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Their role is to defend the national interest mainly against the internal threats.
- They are the Border Security Force (BSF), Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), Central Industrial Security Force (CISF), Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB)
Ayushman CAPF
- Under this scheme, around 28 lakh personnel of CAPF, Assam Rifles and National Security Guard (NSG) and their families will be covered by ‘Ayushman Bharat: PM Jan Arogya Yojana’ (AB PM-JAY).
- For the CAPF, the existing health coverage was not comprehensive as compared to other military forces.
Do you know?
The goal of universal health coverage (UHC) as stated in the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs no. 3) is one of the most significant commitments to equitable quality healthcare for all.
About Ayushman Bharat
- PM-JAY aims to provide free access to healthcare for 40% of people in the country.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme and is jointly funded by both the union government and the states.
- It was launched in September 2018 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The ministry has later established the National Health Authority as an organization to administer the program.
Key features:
- Providing health coverage for 10 crores households or 50 crores Indians.
- It provides a cover of 5 lakh per family per year for medical treatment in empanelled hospitals, both public and private.
- Offering cashless payment and paperless recordkeeping through the hospital or doctor’s office.
- Using criteria from the Socio-Economic and Caste Census 2011 to determine eligibility for benefits.
- There is no restriction on family size, age or gender.
- All previous medical conditions are covered under the scheme.
- It covers 3 days of pre-hospitalization and 15 days of post-hospitalization, including diagnostic care and expenses on medicines.
- The scheme is portable and a beneficiary can avail medical treatment at any PM-JAY empanelled hospital outside their state and anywhere in the country.
Note these features. They cannot be memorized all of sudden but can be recognized if a tricky MCQ comes in the prelims.
Must read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India’s burden of heart diseases
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Report
Mains level: Not Much

According to the Global Burden of Disease, nearly a quarter (24.8 per cent) of all deaths in India is due to cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).
The fastest-growing economy has some perils. In this newscard, you will get to see how CVDs are a legacy of economic growth.
Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Report
- The GBD is a comprehensive regional and global research program of disease burden that assesses mortality and disability from major diseases, injuries, and risk factors.
- GBD is a collaboration of over 3600 researchers from 145 countries.
- It is based out of the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington and funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Indian burden of CVDs
- About a third of the senior citizens have been diagnosed with hypertension, 5.2% with chronic heart disease and 2.7% with stroke
- Even an analysis of the medical certification of cause of death (MCCD) reports points to an increase in the proportion of deaths due to CVD. It went from 20.4 per cent in 1990 to 27.1 per cent in 2004.
- According to MCCD report, 2018, CVDs accounted for more than half (57%) of the total deaths in the age group of 25–69 years.
- Case fatality due to CVD in low-income countries, including India, appears to be much higher than in middle and high-income countries.
- In India, for example, the mean age at which people get the first myocardial infarction is 53 years, which is about 10 years earlier than their counterparts in developed countries.
- About a third (32 per cent) of the senior citizens have been diagnosed with hypertension, 5.2 per cent were diagnosed with chronic heart disease and 2.7 per cent with stroke.
Women are more vulnerable
- Numerous studies have also pointed out that CVD remains the number-one threat to women’s health as more women than men die annually due to these diseases.
- A Harvard study shows low high-density lipoproteins and high triglycerides appear are the main factors that increase the chances of death from cardiovascular disease in women over age 65.
- As per the LASI report, gender differences were evident in cross-state variations.
- CVD among men was higher in Kerala (45 per cent), Goa (44 per cent), Andaman and Nicobar (41 per cent) and lower in Chhattisgarh (15 per cent), Meghalaya (16 per cent), Nagaland (17 per cent).
Why CVDs are prevalent in India?
- Epidemiological evidence suggests that CVD is associated with behavioural factors such as smoking, alcohol use, low physical activity, and insufficient vegetable and fruit intake.
- In the Indian context, poverty, maternal malnutrition, and early life changes enhance an individual’s risk of CVDs.
- Rural to urban migration that happens in distress leads to over-crowded and unclean environments in urban slums.
- Problems of inadequate housing, indoor pollution, infectious diseases, inappropriate diet, stress and smoking crop up as a result.
Need of the hour
- CVD-risk prevention is one of the important priorities among India’s sustainable development goals.
- In an earlier estimate, WHO had said with India’s present CVD burden, the country would lose $237 billion from the loss of productivity and spending on healthcare over 10 years (2005–2015).
- This is because the diseases affect the country’s working population.
Way ahead
- The government should devise an approach that can improve the efficiency of care and health system preparedness to curb the CVD epidemic currently sweeping India.
- Attempts in direction to preserve the traditional lifestyle are also necessary.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Longitudinal Ageing Study of India (LASI)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Longitudinal Ageing Study of India (LASI)
Mains level: India's age-old population

The Union Minister for Health & Family Welfare has released INDIA REPORT on Longitudinal Ageing Study of India (LASI) Wave-1.
Discuss various issues pertaining to old-age care in India.
Longitudinal Ageing Study of India (LASI)
- LASI is a full–scale national survey of scientific investigation of the health, economic, and social determinants and consequences of population ageing in India.
- The LASI, Wave 1 covered a baseline sample of 72,250 individuals aged 45 and above till the oldest-old persons aged 75 and above from all States and UTs of India (excluding Sikkim).
- It is India’s first and the world’s largest ever survey that provides a longitudinal database for designing policies and programmes for the older population in the broad domains of social, health, and economic well-being.
- The evidence from LASI will be used to further strengthen and broaden the scope of National Programme for Health Care of the Elderly.
- It would also help in establishing a range of preventive and health care programmes for older population and most vulnerable among them.
Why need such survey?
- In 2011 census, the 60+ population accounted for 8.6% of India’s population, accounting for 103 million elderly people.
- Growing at around 3% annually, the number of elderly age population will rise to 319 million in 2050.
- 75% of the elderly people suffer from one or the other chronic disease.
- 40% of the elderly people have one or the other disability and 20% have issues related to mental health.
- This report will provide base for national and state level programmes and policies for elderly population.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Bird Flu Outbreak
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bird Flu
Mains level: Not Much
An outbreak of bird flu was confirmed in Kerala, Rajasthan and Himachal.
Try this question from our AWE initiative:
What is Bird Flu?
- Bird flu is an infection caused by avian influenza viruses, which are of different types A, B and C.
- Type A avian influenza viruses are the most frequently associated with avian influenza epidemics and pandemics.
- There are 16 hemagglutinin (H1 to H16) and 9 neuraminidase types (N1 to N9) identified till date.
- There are various modes of transmission of human influenza including inhalation, direct or indirect contact etc. can have manifestations ranging from mild to severe or fatal disease.
- Avian influenza A (H5N1) results in a high death rate amongst infants and young children.
- The first outbreak of human infection by avian influenza viruses (H5N1) was observed in 1997 in Hong Kong. Since then a large number of outbreaks have been reported in different parts of the world.
The H5N8 strain
- The presence of the H5N8 subtype of the Influenza A virus was reported in ducks in parts of Kerala.
- While it can prove lethal for birds, the H5N8 strain of avian influenza has a lower likelihood of spreading to humans compared to H5N1.
- While the source of infection is yet to be pinpointed, the role of migratory birds in passing on the virus is suspected.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (GAVI)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GAVI
Mains level: Global collaboration against COVID

Union Health Minister has been nominated by the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunisation (GAVI) as a member of the GAVI Board.
Q.The Covid-19 pandemic has exposed the limitations of global cooperation. Critically analyse.
GAVI
- GAVI is a public-private global health partnership with the goal of increasing access to immunization in poor countries.
- GAVI has observer status at the World Health Assembly.
- GAVI has been praised for being innovative, effective, and less bureaucratic than multilateral government institutions like the WHO.
- Members: the WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank, the vaccine industry in both industrialized and developing countries, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation among others.
- GAVI programs can often produce quantified, politically appealing, easy-to-explain results within an election cycle, which is appealing to parties locked in an election cycle.
Its function
- It currently supports the immunization of almost half the world’s children, giving it the power to negotiate better prices for the world’s poorest countries and remove the commercial risks of manufacturers.
- It also provides funding to strengthen health systems and train health workers across the developing world.
Significance of India’s membership
- The GAVI Board is responsible for the strategic direction and policymaking oversees the operations of the Vaccine Alliance and monitors program implementation.
- With membership drawn from a range of partner organizations, as well as experts from the private sector, the Board provides a forum for balanced strategic decision making, innovation, and partner collaboration.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] PM-JAY SEHAT
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat, PM-JAY SEHAT
Mains level: Not Much

The Prime Minister has launched Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY SEHAT to extend coverage to all residents of Jammu & Kashmir.
Q.Discuss various challenges in ensuring Universal Healthcare in India. (150W)
PM-JAY SEHAT
- The full form of SEHAT is social, endeavor for health, and telemedicine. Under this scheme, the SEHAT card will be distributed to all the eligible beneficiaries.
- All the eligible beneficiaries of Jammu and Kashmir can apply for the Scheme through common service center operators
- Around 1 crore beneficiaries will cover under this scheme. All the eligible citizens of Jammu and Kashmir will get cashless treatment up to Rs 5 lakh under the Scheme.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
No need for a Two-Child Policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: India's population boom
The latest data from the National Family Health Survey-5 (NFHS-5) proves that the country’s population is stabilizing and fears over a “population explosion” and calls for a “two-child policy” is misguided.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Economic growth in country X will necessarily have to occur if
(a) There is technical progress in the world economy
(b) There is population growth in X
(c) There is capital formation in X
(d) The volume of trade grows in the world economy
Two-Child Policy
- The two-child policy is a state-imposed limit of two children allowed per family or the payment of government subsidies only to the first two children.
- A two-child policy has previously been used in several countries including Iran, Singapore, and Vietnam.
- In British Hong Kong in the 1970s, citizens were also highly encouraged to have two children as a limit (although it was not mandated by law), and it was used as part of the region’s family planning strategies.
- Since 2016, it has been re-implemented in China replacing the country’s previous one-child policy.
Present status in India
- There is no national policy mandating two children per family.
- A parliamentarian had tabled a Bill in the Rajya Sabha in 2019 on the matter, proposing incentives for smaller families.
- PM in 2019 had appealed to the country that population control was a form of patriotism.
- Months later, the NITI Aayog called various stakeholders for a national-level consultation on the issue, which was subsequently cancelled following media glare on it.
- In 2020, the PM spoke about a likely decision on revising the age of marriage for women, which many stakeholders view as an indirect attempt at controlling the population size.
Why doesn’t India need it?
- The survey provides evidence of uptake in the use of modern contraceptives in rural and urban areas.
- It gives an improvement in family planning demands being met and a decline in the average number of children borne by a woman.
- The report stated that most States have attained replacement level fertility, i.e., the average number of children born per woman at whom a population exactly replaces itself from one generation to the next.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Dominance of Private healthcare in India & Related issues
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat
Mains level: Paper 2- Importance of public investment in health care
-
Lack of resources such as 1:1,700, doctor: citizen ratio, well below the minimum ratio of 1:1,000 stipulated by WHO.
-
Rural areas and smaller towns of India are the worst sufferers, where even basic health services remain inaccessible, many cases were reported where ward boys and alone found running the primary healthcare center.
-
Inadequate government spending on healthcare and lack of access to health insurance to a large section of society.
-
The quality of public health services in India continues to remain below expectations which hamper the economic growth of the country.
-
Government’s inability to build sufficient capacity and infrastructure, difficulty in reaching out to poor and vulnerable groups.
-
An undersized skilled workforce and the absence of upgraded technology is a major challenge in the health sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Vision 2035: Public Health Surveillance in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ayushman Bharat
Mains level: Importance of Public Health Surveillance
NITI Aayog today released a white paper: Vision 2035: Public Health Surveillance (PHS) in India.
Q.Discuss the role of Public Health Surveillance in the success of Ayushman Bharat Abhiyan.
Vision 2035 for PHS
- It is a continuation of the work on health systems strengthening.
- It contributes by suggesting mainstreaming of surveillance by making individual electronic health records the basis for surveillance.
- Public health surveillance (PHS) is an important function that cuts across primary, secondary, and tertiary levels of care. Surveillance is ‘Information for Action’.
Let’s have a look at the executive summary of the vision document:
PHS in India
- Surveillance is an important Public Health function.
- It is an essential action for disease detection, prevention, and control. Surveillance is ‘Information for Action’.
Why need PHS?
- Multiple disease outbreaks have prompted India to proactively respond with prevention and control measures. These actions are based on information from public health surveillance.
- India was able to achieve many successes in the past. Smallpox was eradicated and polio was eliminated.
- India has been able to reduce HIV incidence and deaths and advance and accelerate TB elimination efforts.
- These successes are a result of effective community-based, facility-based, and health system-based surveillance.
- The COVID19 pandemic has further challenged the country. India rapidly ramped up its diagnostic capabilities and aligned its digital technology expertise.
- This ensured that there was a comprehensive tracking of the pandemic.
Highlights of the vision document
- It builds on initiatives such as the Integrated Health Information Platform of the Integrated Disease Surveillance Program.
- It aligns with the citizen-centricity highlighted in the National Health Policy 2017 and the National Digital Health Blueprint.
- It encourages the use of mobile and digital platforms and point of care devices and diagnostics for amalgamation of data capture and analyses.
- It highlights the importance of capitalizing on initiatives such as the Clinical Establishments Act to enhance private sector involvement in surveillance.
- It points out the importance of a cohesive and coordinated effort of apex institutions including the National Centre for Disease Control, the ICMR, and others.
Gap areas in India’s PHS that could be addressed
- India can create a skilled and strong health workforce dedicated to surveillance activities.
- Non-communicable disease, reproductive and child health, occupational and environmental health and injury could be integrated into public health surveillance.
- Morbidity data from health information systems could be merged with mortality data from vital statistics registration.
- An amalgamation of plant, animal, and environmental surveillance in a One-Health approach.
- PHS could be integrated within India’s three-tiered health system.
- Citizen-centric and community-based surveillance, and use of point of care devices and self-care diagnostics could be enhanced.
- To establish linkages across the three-tiered health system, referral networks could be expanded for diagnoses and care.
Moving ahead
- Establish a governance framework that is inclusive of political, policy, technical, and managerial leadership at the national and state level.
- Identify broad disease categories that will be included under PHS.
- Enhance surveillance of non-communicable diseases and conditions in a step-wise manner.
- Prioritize diseases that can be targeted for elimination as a public health problem, regularly.
- Improve core support functions, core functions, and system attributes for surveillance at all levels; national, state, district, and block.
- Establish mechanisms to streamline data sharing, capture, analysis, and dissemination for action.
- Encourage innovations at every step-in surveillance activity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
National Family Health Survey- 5 Part: I
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NFHS
Mains level: Data on India's health
- Current times require integrated and coordinated efforts from all health institutions, academia and other partners directly or indirectly associated with the health care services to make these services accessible, affordable and acceptable to all.
- The data in NFHS-5 gives requisite input for strengthening existing programmes and evolving new strategies for policy intervention, therefore government and authorities should take steps to further improve the condition of women in India.
The first phase of the fifth National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) has been released.
Do you think that India is still the sick man of Asia?
What is the National Family Health Survey?
- The NFHS is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted in a representative sample of households throughout India.
- Three rounds of the survey have been conducted since the first survey in 1992-93.
- The survey provides state and national information for India on fertility, infant and child mortality, the practice of family planning, maternal and child health, reproductive health, nutrition, etc.
- The Ministry of Health has designated the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) Mumbai, as the nodal agency, responsible for providing coordination and technical guidance for the survey.
Part I of the Survey
- The latest data pertains to 17 states — including Maharashtra, Bihar, and West Bengal — and five UTs (including J&K) and, crucially, captures the state of health in these states before the Covid pandemic.
- Phase 2 of the survey, which will cover other states such as Uttar Pradesh, Punjab and Madhya Pradesh, was delayed due to the pandemic and its results are expected to be made available in May 2021.
Highlights of the NHFS-5
- The NFHS-5 contains detailed information on population, health, and nutrition for India and its States and Union Territories.
- This is a globally important data source as it is comparable to Demographic Health Surveys (DHS) Programme of 90 other countries on several key indicators.
- It can be used for cross country comparisons and development indices.
Good news
- Several of the 22 states and UTs, for which findings have been released, showed an increase in childhood immunisation.
- There has been a drop in neonatal mortality in 15 states, a decline in infant mortality rates in 18 states and an increase in the female population (per 1,000 males) in 17 states.
- Fertility rate decline and increase in contraceptive use were registered in almost all the states surveyed showing trends of population stabilization.
Some bad news
- There has been an increase in stunting and wasting among children in several states, a rise in obesity in women and children, and an increase in spousal violence.
- In several other development indicators, the needle has hardly moved since the last NFHS-4.
(1) Hunger Alarm
- The proportion of stunted children has risen in several of the 17 states and five UTs surveyed, putting India at risk of reversing previous gains in child nutrition made over previous decades.
- Worryingly, that includes richer states like Kerala, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa and Himachal Pradesh.
- The share of underweight and wasted children has also gone up in the majority of the states.
(2) Fertility Rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) is defined as the average number of children that would be born to a woman by the time she ends childbearing.
- The TFR across most Indian states declined in the past half-a-decade, more so among urban women, according to the latest NFHS-5.
- Sikkim recorded the lowest TFR, with one woman bearing 1.1 children on average; Bihar recorded the highest TFR of three children per woman.
- In 19 of the 22 surveyed states, TFRs were found to be ‘below-replacement’ — a woman bore less than two children on average through her reproductive life.
- India’s population is stabilizing, as the total fertility rate (TFR) has decreased across majority of the states.
(3) Under-5 and infant mortality rate (IMR)
- The Under 5 and infant mortality rate (IMR) has come down but in parallel recorded an increase in underweight and severely wasted under 5 children among 22 states that were surveyed.
- These states are Goa, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Maharashtra, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Telangana, Tripura, West Bengal, Lakshadweep and Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
For the first time: Gaps in internet use
- In 2019, for the first time, the NFHS-5, which collects data on key indicators on population health, family planning and nutrition, sought details on two specific indicators: Percentage of women and men who have ever used the Internet.
- On average, less than 3 out of 10 women in rural India and 4 out of 10 women in urban India ever used the Internet, according to the survey.
- First, only an average of 42.6 per cent of women ever used the Internet as against an average of 62.16 per cent among the men.
- Second, in urban India, average 56.81 per cent women ever used the Internet compared to an average of 73.76 per cent among the men.
- Third, dismal 33.94 per cent women in rural India ever used the Internet as against 55.6 per cent among men.
- In urban India, 10 states and three union territories reported more than 50 per cent women who had ever used the Internet: Goa (78.1%), Himachal Pradesh (78.9%), Kerala (64.9%), and Maharashtra (54.3%).
- The five states reporting the lowest percentage of women, whoever used the Internet in urban India were Andhra Pradesh (33.9%), Bihar (38.4%), Tripura (36.6%), Telangana (43.9%) and Gujarat (48.9%).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Healthcare in India & Pandemic
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations
Mains level: Paper 2- Lessons to improve healthcare system
Pandemic has been ravaging the world in a way few could have imagined. It highlighted the flaws in our healthcare system. However, it also offers several important lessons for tackling future pandemics and healthcare emergencies.
Where we stand after 1 year of pandemic
- About a year after the first cases were reported, we are in a different position than at the start.
- Doctors, public health specialists and policymakers have a better sense of the interventions that are required.
- Many treatments initially proposed, based on expert experience, have been tested and removed from management strategies even as modified protocols have improved survival rates.
- Vaccines have moved even faster than drugs with nearly 40 of them undergoing clinical trials, a dozen of which are at the phase three stage, and at least one has been licensed post-phase three trials under conditional emergency use authorisation (EUA).
- This highlights the importance of science, technology, multilateral partnerships such as the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations and the WHO.
- This highlights the importance of science, technology, multilateral partnerships such as the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations and the WHO.
Takeaways from our response to pandemic
1) Increase investment on health services
- The countries which handled the pandemic best (Thailand and Vietnam) have well-functioning health systems designed to deliver primary healthcare services.
- These countries also have strong preventive and promotive health services as well as a dedicated public health workforce.
- Their governments had made sustained investments in health over decades.
- In contrast, countries which focused mainly on hospital centric medical systems struggled.
2) Important role played by health workers
- The role of community health workers in recognising, referring and motivating individuals for therapy was remarkable.
- Healthcare workers, particularly those at the frontline, such as the accredited social health activists (ASHA) who visited hundreds of households repeatedly during the pandemic.
- If we are to build back better, we need to give them better recognition, salaries and career progression.
3) Increase community participation
- Third, community trust and participation is essential for implementation of non-pharmacological interventions.
- Dharavi in Mumbai is an example of the difference community participation can make.
4) Importance of data
- Outside of the immediate response, the need for timely and quality data in a health information system was recognised again during the pandemic.
- Without real time data on testing, disease surveillance and other outcomes, tailored responses are near impossible.
- The solutions that have brought us hope have come from long-term private or public investments in scientific research and developments.
Conclusion
Future readiness needs to start now, and we have the resources and knowledge to do this — all we need is commitment and that is outlined in the recent National Health Policy 2017 and reiterated in the report of the Fifteenth Finance Commission, which for the first time has a dedicated chapter on health.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
UN removes Cannabis from ‘Most Dangerous Drug’ Category
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cannabis
Mains level: Cannabis and its de-regulation
The United Nations Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND) voted to remove cannabis and cannabis resin from Schedule IV of the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, decades after they were first placed on the list.
Q. Too much de-regulation of Cannabis could lead to its mass cultivation and a silent economy wreaking havoc through a new culture of substance abuse in India. Critically analyse.
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant used primarily for medical or recreational purposes.
- The main psychoactive component of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD).
- It is used by smoking, vaporizing, within the food, or as an extract.
UN’s decision and India
- Currently in India, the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985, illegalizes any mixture with or without any neutral material, of any of the two forms of cannabis – charas and ganja — or any drink prepared from it.
- The WHO says that cannabis is by far the most widely cultivated, trafficked and abused illicit drug in the world. But the UN decision could influence the global use of medicinal marijuana,
- India was part of the voting majority, along with the US and most European nations.
- China, Pakistan and Russia were among those who voted against, and Ukraine abstained.
Cannabis in India
In India, cannabis, also known as bhang, ganja, charas or hashish, is typically eaten (bhang golis, thandai, pakoras, lassi, etc.) or smoked (chillum or cigarette).
Under international law
- The Vienna-based CND, founded in 1946, is the UN agency mandated to decide on the scope of control of substances by placing them in the schedules of global drug control conventions.
- Cannabis has been on Schedule IV–the most dangerous category– of the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs for as long as the international treaty has existed.
Fuss over Cannabis
- Cannabis has various mental and physical effects, which include euphoria, altered states of mind and sense of time, difficulty concentrating, impaired short-term memory and body movement, relaxation, and an increase in appetite.
- But global attitudes towards cannabis have changed dramatically, with many jurisdictions permitting cannabis use for recreation, medication or both, despite it remaining on Schedule IV of the UN list.
- Currently, over 50 countries allow medicinal cannabis programs, and its recreational use has been legalized in Canada, Uruguay and 15 US states.
Impact of the decision
- The reclassification of cannabis by the UN agency, although significant, would not immediately change its status worldwide as long as individual countries continue with existing regulations.
- The decision would add momentum to efforts for decriminalizing cannabis in countries where its use is most restricted, while further legalizing the substance in others.
- Scientific research into marijuana’s medicinal properties is also expected to grow.
- Legalising and regulating cannabis will “undermine criminal markets” as well as its smuggling and cultivation.
Risks of Legalizing Cannabis
(1) Health risks continue to persist
- There are many misconceptions about cannabis. First, it is not accurate that cannabis is harmless.
- Its immediate effects include impairments in memory and in mental processes, including ones that are critical for driving.
- Long-term use of cannabis may lead to the development of addiction of the substance, persistent cognitive deficits, and of mental health problems like schizophrenia, depression and anxiety.
- Exposure to cannabis in adolescence can alter brain development.
(2) A new ‘tobacco’ under casualization
- A second myth is that if cannabis is legalized and regulated, its harms can be minimized.
- With legalization comes commercialization. Cannabis is often incorrectly advertised as being “natural” and “healthier than alcohol and tobacco”.
- Tobacco, too, was initially touted as a natural and harmless plant that had been “safely” used in religious ceremonies for centuries.
Way ahead
- It’s important to make a distinction between legalization, decriminalization and commercialization.
- While legalization and decriminalization are mostly used in a legal context, commercialization relates to the business side of things.
- For India to liberalise its policy on cannabis, it should ensure that there are enough protections for children, the young, and those with severe mental illnesses, who are most vulnerable to its effects.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indian Cancer Genome Atlas (ICGA)
Mains level: Burden of non-communicable diseases on India
The Ministry of Science & Technology has inaugurated the 2nd Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) 2020 Conference.
Do you know?
According to the World Cancer Report by the WHO, one in 10 Indians develops cancer during their lifetime and one in 15 dies of the disease!
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) is a landmark project started in 2005 by the US-based National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI).
- The idea was to make a catalogue of the genetic mutations that cause cancer.
- This meant collecting tumour samples and blood samples (known as the germline) from patients and processing them using gene sequencing and bioinformatics.
- The TCGA is a continuing effort even after fifteen years and has generated over 2.5 petabytes of data for over 11,000 patients.
- This data is available to researchers all around the world and has been used to develop new approaches to diagnose, treat and prevent cancer.
Indian Cancer Genome Atlas (ICGA)
- On similar lines, the establishment of an ICGA has been initiated by a consortium of key stakeholders in India led by CSIR in which several government agencies, cancer hospitals, academic institutions and private sector partners.
- It is aimed at improving clinical outcomes in cancer and other chronic diseases.
Why need such Atlas?
- Diverse molecular mechanisms- including genetic and lifestyle factors contribute to cancer, posing significant challenges to treatment.
- Therefore, it is necessary to better understand the underlying factors- patient by patient.
- In this context, it is important to create an indigenous, open-source and comprehensive database of molecular profiles of all cancer prevalent in Indian population.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Swasthya Sathi Health Insurance Scheme
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Swasthya Sathi
Mains level: Ayushman Bharat
West Bengal CM has recently extended the Swasthya Sathi health insurance scheme to cover the entire population of the state.
Do you know?
Delhi, Telangana, Odisha and West Bengal have not implemented the Ayushman Bharat Scheme.
Swasthya Sathi
- The scheme was launched in West Bengal in 2016.
- It is a basic health cover for secondary and tertiary care up to Rs five lakh per annum per family.
- It is quite popular among rural and economically deprived sections of the state’s population.
Highlights of the expanded scheme
- Every family, every citizen irrespective of the age group will be included in this scheme
- This is a basic health cover for secondary and tertiary care up to Rs 5 lakh per annum per family
- The scheme is completely funded by the state government
- To cover the entire population of the state, each and every family will be given one smart card to avail the benefits under this scheme, where they will get cashless treatment
- All state-run and private hospitals are going to come under the Swasthya Sathi
- The card will be issued to the female guardians of families
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Is allowing Ayurvedic doctors to perform surgery legally and medically tenable?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Ways to counter shortage of doctors in India
The Central Council of Indian Medicine, a statutory body set up under the AYUSH Ministry has allowed postgraduate (PG) Ayurvedic practitioners to receive formal training for a variety of general surgery, ENT, ophthalmology and dental procedures.
Debate over Ayurvedic surgeries
- The Indian Medical Association (IMA) decrying it as a mode of allowing mixing of systems of medicine by using terms from allopathy.
- The debate revolves Ayurveda doctors allowing ‘Shalya’ (general surgery) and ‘Shalakya’ (dealing with eye, ear, nose, throat, head and neck, oro-dentistry) to perform 58 specified surgical procedures.
- The AYUSH Ministry has clarified that the ‘Shalya’ and ‘Shalakya’ postgraduates were already learning these procedures in their (surgical) departments in Ayurvedic medical colleges as per their training curriculum.
Broader issue
- The broader issue is the feasiblity of short-term training equip them to conduct surgeries and if this dilutes the medicine standards in India.
- As such, the postgraduate Ayurvedic surgical training is not short-term but a formal three-year course.
- Whether the surgeries conducted in Ayurvedic medical colleges and hospitals have the same standards and outcomes as allopathic institutions requires explication and detailed formal enquiry, in the interest of patient safety.
Why such a move?
- The shortage and unwillingness of allopathic doctors, including surgeons, to serve in rural areas is now a chronic issue.
- The government has tried to address this by mechanisms such as rural bonds, a quota for those who have served in rural service in postgraduate seats.
- However, it would probably still continue to fall short of enough trained specialists in rural areas.
Are there any restrictions on Ayurveda practitioners?
- As of now, no such restriction exists that limits non-allopathic doctors, including those doing Ayurvedic surgical postgraduation, to rural areas.
- They have the same rights as allopathic graduates and postgraduates to practise in any setting of their choice.
Is it sensible to allow Ayurvedic surgeons to only assist allopathic surgeons, rather than perform surgeries themselves?
- The AYUSH streams are recognised systems of medicine, and as such are allowed to independently practise medicine.
- They have medical colleges with both undergraduate and postgraduate training, which include surgical disciplines for some systems, such as Ayurveda.
- There is, however, a difference in approach in the systems of medicine, and hence models, which allow for cross-pathy.
Various risks associated
- An apprenticeship model for Ayurvedic surgeons working with allopathic surgeons might fall into a regulatory grey zone.
- It might require re-training Ayurvedic practitioners in the science of surgical approaches in modern medicine.
- Even then, there might be a limit to what they are allowed to do. Any such experiment can put patient safety in peril, and hence, will need careful oversight and evaluation.
Can this lead to substandard care?
- Many patients prefer to receive treatment exclusively from AYUSH providers, while some approach this form of treatment as a complement to the existing allopathic treatment they are receiving.
- For invasive procedures, like surgery, the risk element can be high.
A matter of rights
- Patients have a right to know and understand who their surgeon would be, what system of medicine they belong to, and their expertise and level of training.
- There should not be a difference in quality of care between urban and rural patients — everyone deserves a right to quality and evidence-based care from trained professionals.
Way forward
- We need to explore creative ways of addressing this gap by evidence-based approaches, such as task-sharing, supported by efficient and quality referral mechanisms.
- The advent of mid-level healthcare providers, such as Community Health Providers in many States, is also an opportunity to shift some elements of healthcare (preventive, promotive, and limited curative) to these providers, while ensuring clarity of role and career progression.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
National Digital Health Mission
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Digital Health Mission
Mains level: Healthcare in India
The National Digital Health Mission will soon be ready for a nationwide roll-out, confirmed the Chairman of National Health Authority and CEO of Ayushman Bharat.
Must read:
[Burning Issue] Rolling-out of National Digital Health Mission
National Digital Health Mission
- Our PM has launched the National Digital Health Mission on 15th August 2020.
- The mission aims to create an integrated healthcare system linking practitioners with the patients digitally by giving them access to real-time health records.
- It is a complete digital health ecosystem. The digital platform will be launched with four key features — health ID, personal health records, Digi Doctor and health facility registry.
- At a later stage, it will also include e-pharmacy and telemedicine services, regulatory guidelines for which are being framed.
Its implementation
- The NDHM is implemented by the National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The National Health Authority (NHA), is also the implementing agency for Ayushman Bharat.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Sex Ratio in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sex Ratio
Mains level: Sex ratio in India

A 2018 report on “vital statistics of India based on the Civil Registration System” shows crucial data of sex ratios of major states in India.
Sex Ratio
- Sex ratio at birth is the number of females born per thousand males.
- Sex ratios are among the most basic of demographic parameters and provide an indication of both the relative survival of females and males and the future breeding potential of a population.
Try this PYQ
Q.Consider the following specific stages of demographic transition associated with economic development:
- Low birth rate with a low death rate
- High birth rate with a high death rate
- High birth rate with a low death rate
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 3, 2 and 1 only
(c) 2, 3 and 1 only
(d) 3, 2 and 1 only
Statewise data
- Arunachal Pradesh recorded 1,084 females born per thousand males, followed by Nagaland (965) Mizoram (964), Kerala (963) and Karnataka (957).
- The worst was reported in Manipur (757), Lakshadweep (839) and Daman & Diu (877), Punjab (896) and Gujarat (896).
- Delhi recorded a sex ratio of 929, Haryana 914 and Jammu and Kashmir 952.
- The number of registered births increased to 2.33 crore in 2018 from 2.21 crore registered births the previous year.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is the Viability Gap Funding (VGF) Scheme?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Viability Gap Funding
Mains level: Not Much
The government has expanded the provision of financial support by means of viability gap funding for public-private partnerships (PPPs) in infrastructure projects to include critical social sector investments in sectors such as health, education, water and waste treatment.
Note the minutes of VGF, its meaning, funding mechanism, various sectors included and its nodal ministry etc. UPSC can ask static statements based question.
What is the move?
- Now, under this scheme, private sector projects in areas like wastewater treatment, solid waste management, health, water supply and education, could get 30% of the total project cost from the Centre.
- Separately, pilot projects in health and education, with at least 50% operational cost recovery, can get as much as 40% of the total project cost from the central government.
- The Centre and States would together bear 80% of the capital cost of the project and 50% of operation and maintenance costs of such projects for the first five years.
Viability Gap Funding (VGF) Scheme
- Viability Gap Finance means a grant to support projects that are economically justified but not financially viable.
- The scheme is designed as a Plan Scheme to be administered by the Ministry of Finance and amount in the budget are made on a year-to-year basis.
- Such a grant under VGF is provided as a capital subsidy to attract the private sector players to participate in PPP projects that are otherwise financially unviable.
- Projects may not be commercially viable because of the long gestation period and small revenue flows in future.
- The VGF scheme was launched in 2004 to support projects that come under Public-Private Partnerships.
Its’ funding
- Funds for VGF will be provided from the government’s budgetary allocation. Sometimes it is also provided by the statutory authority who owns the project asset.
- If the sponsoring Ministry/State Government/ statutory entity aims to provide assistance over and above the stipulated amount under VGF, it will be restricted to a further 20% of the total project cost.
VGF grants
- VGF grants will be available only for infrastructure projects where private sector sponsors are selected through a process of competitive bidding.
- The VGF grant will be disbursed at the construction stage itself but only after the private sector developer makes the equity contribution required for the project.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Strengthening the public health capacities in disasters
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Disaster Management Act 2005
Mains level: Paper 2- Making healthcare disaster prepared
The article highlights the importance of the robust public healthcare system for the disaster preparedness and suggests linking it with the primary healthcare.
Reactive approach to disasters
- In 2005, India enacted the Disaster Management Act, which laid an institutional framework for managing disasters across the country.
- Under the Act, reactive, ad hoc measures applied in the event of a disaster, was to be replaced with a systematic scheme for prevention, mitigation, and responding to disasters of all kinds.
- Disaster management considerations were to be incorporated into every aspect of development and the activities of different sectors, including health.
- While some headway has indeed been achieved, the approach continues to be largely reactive.
- Significant gaps remain particularly in terms of medical preparedness for disasters.
Medical preparedness for disasters
- Two important lessons emerge:-
- First, health services and their continuing development cannot be oblivious to the possibility of disaster-imposed pressures.
- Second, the legal framework for disaster management must push a legal mandate for strengthening the public health system.
Role of private health sector during disaster
- Instances of overcharging during Covid illustrates how requisitioning of private sector services during disasters can hardly be a dependable option in the Indian context.
- This is particularly important since the future development of hospital care services is being envisaged chiefly under publicly financed health insurance, which would very likely be private-sector led.
- The Indian private sector landscape, characterised by weak regulation and poor organisation, is incapable for mounting a strong and coordinated response to disasters.
- During disasters, the limited regulatory ability could be further compromised.
- While publicly financed insurance could be a medium to introduce some order into this picture, a large majority of private hospitals in the country are small enterprises which cannot meet the inclusion criteria for insurance.
- Many of these small hospitals are also unsuitable for meeting disaster-related care needs.
- Punitive action against non-compliant requisitioned hospitals becomes tricky during disasters since health services are already inadequate.
- Private hospitals are known to prefer lucrative and high-end ‘cold’ cases, especially under insurance, and are generally averse to infectious diseases and critical cases with unpredictable profiles.
Need for strong public sector capacities
- Due to the above-cited limitations of the private sector, strong public sector capacities are imperative for dealing with disasters.
- While the Disaster Management Act does require States and hospitals to have emergency plans, medical preparedness is a matter of policy, and, therefore, gaps are pervasive.
- There is a strong case for introducing a legal mandate to strengthen public sector capacities via disaster legislation.
- There is also scope for greater integration of disaster management with primary care.
- Primary care stands for things such as multisectoral action, community engagement, disease surveillance, and essential health-care provision, all of which are central to disaster management.
Way forward
- Evidence supports the significance of robust primary care during disasters, and this is particularly relevant for low-income settings.
- Synergies with the National Health Mission, concurrently with the Disaster Management Act in 2005, could be worth exploring.
- Interestingly, the National Health Mission espouses a greater role for the community and local bodies, the lack of which has been a major criticism of the Disaster Management Act.
- Making primary health care central to disaster management can be a significant step towards building health system and community resilience to disasters.
Consider the question “Robust public healthcare system is indispensable for the disaster preparedness which could be achieved through making the primary healthcare central to the disaster management. Comment.
Conclusion
While the novel coronavirus pandemic has waned both in objective severity and subjective seriousness, valuable messages and lessons lie scattered around. It is for us to not lose sight and pick them up.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
AIDS & India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Gains against HIV
The article highlights the achievement in the fight against AIDS. Most significant are the achievements in the prevention of transmission from mother-to-child.
Significant gains
- As per recently released 2019 HIV estimates by the National AIDS Control Organization (NACO)/Ministry of Health and Family Welfare with the technical support of UNAIDS there has been a 66.1% reduction in new HIV infections among children and a 65.3% reduction in AIDS-related deaths in India over a nine-year period.
- The number of pregnant women living with HIV has reduced from 31,000 in 2010 to 20,000 in 2019.
- Overall, antenatal coverage has expanded, and HIV testing has increased over time and within target range.
- Treatment coverage has also expanded.
Progress in preventing mother to child transmission
- Under the leadership of NACO, a ‘Fast-Tracking of EMTCT (elimination of mother-to-child transmission) strategy-cum-action plan’ was outlined by June 2019.
- The plan entailed mobilisation and reinforcement of all national, State and partners’ collective efforts to achieve the EMTCT goal.
- Additionally, in March 2020, we began efforts to minimise challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- From 2010 to 2019, India made important progress in reducing the HIV impact on children through prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
- This was done through education and communication programmes; increased access to HIV services with innovative delivery mechanisms for HIV testing; counselling and care; and treatment and follow-ups.
- India made HIV testing for all pregnant women free and HIV treatment is offered the same way nationwide without cost to pregnant mothers living with HIV through the national ‘treat all’ policy.
- For two years UNICEF has worked with the World Health Organization and NACO to identify high burden districts (in terms of density of pregnant women living with HIV) as the last mile towards disease elimination.
- Since 2002, when the EMTCT of HIV programmes were launched in India, a series of policy, programmatic and implementation strategies were rolled out so that all pregnant women can access free HIV testing and free treatment regimens for life to prevent HIV transmission from mothers to babies.
- This has been made possible in government health centres and grass-root level workers through village health and nutrition days and other grass-roots events under the National Health Mission.
- Indeed, the approach being promoted by UNICEF in focusing attention and resources in high burden districts is supported by the HIV strategic information division of NACO and UNAIDS to better understand the locations and populations most HIV affected, so that technical support and HIV services can be directed towards these areas.
Conclusion
Using data-driven and decision-making approaches it is certain that AIDS will no longer be a public health threat for children in India by the end of 2030, if not before.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Obesity in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Obesity
Mains level: Obesity in India
Adults in urban India consume much more fat than those in rural areas, found the latest survey by the Indian Council of Medical Research and National Institute of Nutrition.
Do you know?
Over-nutrition is also a form of malnutrition.
‘What India Eats’ Survey
- Adults in India’s urban centres consumed 51.6 grammes fat per day per head on an average. The volume was 36 g in rural areas, according to the survey report What India Eats.
- The report categorised fat into two groups:
- Visible or added fat, comprising oils and fat in preparing food, in fried food and those derived from meat and poultry
- Invisible fat, including fat/oils from rice, pulses, nuts and oilseeds
Urban-Rural data
- 84 per cent of the rural population secured their energy (E) per day requirement from total fats/oils, or visible / added fats.
- On the other hand, less than 20 per cent of the urban population derived their E / day from this category.
- In urban areas of the country, northern India had the highest intake of added fat with 45.9 g / day.
- Southern India reported the lowest per capita consumption of added fat/oils with 22.9 g / day in this segment of the population.
- In the urban region of north India, fat intake (67.3 g) was among the highest; and overweight, obesity and abdominal obesity were highest when compared to other regions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Brucellosis: A bacterial disease
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Brucellosis
Mains level: NA
As the novel coronavirus pandemic continues, the health commission has announced this week that a leak in a biopharmaceutical company last year caused an outbreak of brucellosis disease.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following kinds of organisms:
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Flowering plants
Some species of which of the above kinds of organisms are employed as bio-pesticides?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
What is Brucellosis?
- Brucellosis is a bacterial disease that mainly infects cattle, swine, goats, sheep and dogs.
- Humans can get infected if they come in direct contact with infected animals or by eating or drinking contaminated animal products or by inhaling airborne agents.
- According to the WHO, most cases of the disease are caused by ingesting unpasteurized milk or cheese from infected goats or sheep.
- Symptoms of the disease include fever, sweats, malaise, anorexia, and headache and muscle pain.
- While some signs and symptoms can last for long periods of time, others may never go away. Human to human transmission of the virus is rare.
- These include recurrent fevers, arthritis, swelling of the testicles and scrotum area, swelling of the heart, neurologic symptoms, chronic fatigue, depression and swelling of the liver or spleen.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What counts as ‘Act of God’?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Act of God , Force Majeure clause
Mains level: Not Much
Amid disruptions caused by Covid-19, the Finance Minister has referred to an Act of God while businesses are looking at a legal provision, force majeure, to cut losses.
Note the key differences between the Act of God and Force Majeure.
Evoking “Act of God”
- The force majeure or “Act of God” clause has its origins in the Napoleonic Code.
- The finance ministry had issued an office memorandum inviting attention to the force majeure clause (FMC) in the 2017 Manual for Procurement of Goods issued by the Department of Expenditure.
- It clarified that the pandemic should be considered a case of natural calamity and FMC may be invoked, wherever considered appropriate.
What is a force majeure clause?
- The law of contracts is built around a fundamental norm that the parties must perform the contract.
- When a party fails to perform its part of the contract, the loss to the other party is made good.
- However, the law carves out exceptions when the performance of the contract becomes impossible for the parties.
- A force majeure clause is one such exception that releases the party of its obligations to an extent when events beyond their control take place and leave them unable to perform their part of the contract.
- FMC is a clause that is present in most commercial contracts and is a carefully drafted legal arrangement in the event of a crisis.
- When the clause is triggered, parties can decide to break from their obligations temporarily or permanently without necessarily breaching the contract.
- Companies in such situations use the clause as a safe exit route, sometimes in opportunistic ways, without having to incur the penalty of breaching the contract.
Difference between the two
- Both concepts elicit the same consequences in law.
- Generally, an “Act of God” is understood to include only natural unforeseen circumstances, whereas force majeure is wider in its ambit and includes both naturally occurring events and events that occur due to human intervention.
What situations legally qualify for use of force majeure?
- While some contracts have clauses with standard circumstances, some contracts would have specific circumstances that are more focused.
- For example, a shipping contract would have a force majeure clause that could cover a natural disaster like a tsunami.
- If an event is not described, then it is interpreted in a way that it falls in the same category of events that are described.
- An FMC is negotiated by parties, and events that could potentially hamper the performance of the contract are catalogued.
- It is not invoked just by expressing that an unforeseen event has occurred.
- In case a contract does not have a force majeure clause, there are some protections in common law that can be invoked by parties.
- For example, the Indian Contract Act, 1872 provides that a contract becomes void if it becomes impossible due to an event after the contract was signed that the party could not prevent.
Global precedents dealing with COVID-19 pandemic
- In China, where the Covid-19 outbreak originated, the Council for Promotion of International Trade is issuing force majeure certificates to businesses.
- China’s Supreme People’s Court had recognised the 2002 SARS outbreak as a force majeure event.
- Singapore enacted the Covid-19 (Temporary Measures) Act in April to provide relief to businesses that could not perform their contractual obligations due to the pandemic.
- The Paris Commercial Court in July ruled that the pandemic could be equated to a force majeure event.
- In the UK, the Financial Conduct Authority has brought in a test case before the High Court to look into business insurance contracts and interpret the standard wordings in such contracts.
- The International Chamber of Commerce has developed a Model Code on the force majeure clause reflecting current international practice.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Vitamin-D Deficiency
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vitamin D
Mains level: Not Much
The pandemic-induced lockdown has confined people to their houses for five months now. The resultant lack of sunlight, followed by rains, has brought down the vitamin D levels to the lowest.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2014:
Q.Consider the following pairs:
Vitamin Deficiency:: Disease
- Vitamin C::Scurvy
- Vitamin D:: Rickets
- Vitamin E:: Night blindness
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
What is Vitamin-D?
- Vitamin D is an essential vitamin that has myriad positive effects on several systems in the body.
- Unlike other vitamins, it functions like a hormone and every cell in your body has a receptor for it.
- It is sparsely found in certain fatty fish and fortified dairy products, and it is extremely difficult to get the Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) of 600-800 IU from diet alone.
There are two main forms of vitamin D in the diet:
– Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) — found in plant foods like mushrooms.
– Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) — found in animal foods like salmon, cod and egg yolks.
Common signs and symptoms of the deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is incredibly common and most people are unaware of it, as the symptoms are subtle and nonspecific.
– Getting sick or infected often with common cold and flu, because of a weak immune system.
– Fatigue and tiredness
– Bone and muscle pains
– Depression
– Impaired wound healing
– Bone loss and osteoporosis
Sources of Vit. D
- Sunlight is the best natural source of vitamin D. Sunlight synthesizes cholesterol into Vitamin D3.
- Usually, 20 to 30 minutes of sun exposure between 10 am and 3 pm is adequate to meet daily requirements, in places with minimum pollution levels.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Changing India’s health delivery landscape through NDHM
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NDHM
Mains level: Paper 2- National Digital Health Mission
The National Digital Health Mission promises to transform the Indian healthcare system with the aid of technology. The article highlights the key aspects of the mission.
Building integrated digital health infrastructure through NDHM
- NDHM is based on the principles of health for all, inclusivity, accessibility, affordability, education, empowerment, wellness, portability, privacy and security by design.
- NDHM will build the backbone necessary to create an integrated digital health infrastructure.
- With its key building blocks HealthID, DigiDoctor, Health Facility Registry, Personal Health Records, Telemedicine, and e-Pharmacy, the mission will bring together disparate stakeholders and radically strengthen and, thus change India’s healthcare delivery landscape.
- NDHM is also a purposeful step towards the achievement of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal of Universal Health Coverage.
Importance of digital intervention in health service
- Digital interventions significantly enhance the outcomes of every health service delivery programme.
- Importance of digital intervention is demonstrated in the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana scheme.
- Under PM-JAY, 1.2 crore cashless secondary and tertiary care treatments have been provided using an indigenously developed state-of-the-art IT platform.
- The Arogya Setu mobile app deploys ICT innovations for contract tracing.
Principal highlight of NDHM
1) Voluntary in nature
- HealthID is entirely voluntary for citizens.
- Its absence will not mean denial of healthcare to a citizen.
- They can choose to generate their Health Account or ID using their Aadhaar card or digitally authenticable mobile number and by using their basic address-related details and email ID.
- The use of Aadhaar, therefore, is not mandatory.
2) Data sharing based on consent
- Providing access to and sharing of personal health records is a prerogative of the HealthID holder.
- The consent of the health data owner is required to access this information or a part of it.The consent can be withdrawn anytime.
- The personal health record will enable citizens to store and access their health data, provide them with more comprehensive information and empower them with control over their private health records.
3) Compliance with laws and fundamental rights
- NDHM has been built within a universe of fundamental rights and legislation such as the Aadhaar Act and the IT Act 2008 as well as the Personal Data Protection Bill 2019.
- This project is also informed by the entire gamut of Supreme Court judgments and core democratic principles of cooperative federalism.
- The Mission gets its strategic and technical foundation from the National Digital Health Blueprint, the architectural framework of which keeps the overall vision of NHP 2017 at its core and ensures security and privacy by design.
4) Reaching out to the unconnected population
- NHDM is a digital mission led by technology powered by the internet.
- So, to reach out to and empower the large number of “unconnected” masses specialised systems are being built and off-line modules that will be designed to reach out to the “unconnected”.
5) Partnership with all key stakeholders
- The design of NDHM has been built on the principle of partnership with all key stakeholders — doctors, health service providers, technology solution providers and above all citizens.
- Without their belief, trust, adoption, and stewardship, this mission will not achieve its desired result.
Consider the question “Examine the key aspects of the National Digital Heath Mission and how it could help transform the Indian healthcare landscape?”
Conclusion
NDHM is a mission whose time has come because health is the first step towards self-reliance and only a healthy nation can become Atma Nirbhar.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Reversing health sector neglect with a reform agenda
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2-Universal health coverage in India
The article analyses the issues India could face in implementing the universal health coverage.
Context
- Both India and the U.S. leads the Covid cases in the world and also lack effective universal health coverage (UHC).
What explains the lack of UHC in both the countries
- The lack of UHC is due to multiple long-standing factors and historical reasons that have put a damper on the UHC agenda.
- This long legacy has two important and inter-related implications when it comes to health-care reform.
- 1) Certain foundational aspects of these health systems that have been adopted over decades tend to dictate the terms of further evolution and lead to a number of compromises.
- 2) The long legacy itself comprises a path-dependent trajectory that precludes far-reaching health-care reform.
- This applies both to AB-PM-JAY and NDHM.
India’s attempt at UHC: Ayushman Bharat–Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana
- The government has looked poised to employ Ayushman Bharat–Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PM-JAY) health insurance as the tool for achieving UHC.
- Taking the health insurance route to UHC driven by private players, rather than strengthening the public provisioning of health care, is reflective of the non-negotiability of private health care in India.
- Covering the remaining population under the AB-PM-JAY presents massive fiscal and design challenges.
- Turning it into a contributory scheme based on premium collections would be a costly and daunting undertaking, given the huge informal sector and possible adverse selection problems.
- Distributing benefits among various beneficiary groups, and a formalisation and consolidation of practices in a likely situation of covering outpatient care, are formidable additional challenges.
- One possible advantage for India over the U.S. could be a relative ease of integrating fragmented schemes into a unified system. The AB-PM-JAY has this ability.
Issues with AB-PM-JAY
1) Universal insurance will not be universal access
- In India, almost two-third corporate hospital are located in cities.
- So, such maldistribution of health-care facilities and low budgetary appropriations for insurance could mean that universal insurance does not translate to universal access to services.
- So far, insurance-based incentives to drive private players into the rural countryside have been largely unsuccessful.
2) Lack of regulatory robustness
- AB-PM-JAY is without enough regulatory robustness to handle everything from malpractices to monopolistic tendencies.
- This could have major cost, equity, and quality implications.
National Digital Health Mission (NDHM)
- Integration and improved management of patient and health facility information are sought through NDHM.
- But in the absence of robust ground-level documentation practices and its prerequisites, it would do little more than helping some private players and adding to administrative complexity and costs.
Consider the question “What are the challenges India faces in the implementation of universal health coverage? Suggest the measures to achieve it.”
Conclusion
Upheavals offer a window for reforms. We cannot afford to be complacent and think that the pandemic will automatically change the Indian health-care landscape. It will require mobilising concerted action from all quarters.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is the National Health ID System?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Health ID System
Mains level: Developing digital health infrastructure
In his address to the nation on Independence Day, the PM has launched the National Digital Health Mission which rolls out a national health ID for every Indian.
Try this question for mains:
Q.What is the National Health ID System? How will it benefit transforming healthcare facilities in India?
National Health ID System
- This system finds its roots in a 2018 NITI Aayog proposal to create a centralised mechanism to uniquely identify every participating user in the National Health Stack.
- It will be a repository of all health-related information of a person.
- According to the National Health Authority (NHA), every patient who wishes to have their health records available digitally must start by creating a Health ID.
- Each Health ID will be linked to a health data consent manager — such as National Digital Health Mission (NDHM).
- The Health ID is created by using a person’s basic details and mobile number or Aadhaar number.
- This will make it unique to the person, who will have the option to link all of their health records to this ID.
What was the original proposal for the health ID?
- The National Health Policy 2017 had envisaged creation of a digital health technology eco-system aiming at developing an integrated health information system.
- In the context of this, the central government’s think-tank NITI Aayog, in June 2018, floated a consultation of a digital backbone for India’s health system — National Health Stack.
- As part of its consultation, NITI Aayog proposed a Digital Health ID to greatly reduce the risk of preventable medical errors and significantly increase the quality of care.
Stakeholders in the national health ID
- As envisaged, various healthcare providers — such as hospitals, laboratories, insurance companies, online pharmacies, telemedicine firms — will be expected to participate in the health ID system.
Back2Basics:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: eVIN
Mains level: Vaccination programme in India
The eVIN has reached 32 States and Union Territories (UTs) and will soon be rolled out in the remaining States and UTs of Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Ladakh and Sikkim.
Try this question from CSP 2016:
Q.‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to:
(a) Immunization of children and pregnant women
(b) Construction of smart cities across the country
(c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
(d) New Educational Policy
About eVIN
- The eVIN is an innovative technological solution aimed at strengthening immunization supply chain systems across the country.
- This is being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM) by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It aims to provide real-time information on vaccine stocks and flows, and storage temperatures across all cold chain points in the country.
- This system has been used during the COVID pandemic for ensuring the continuation of the essential immunization services and protecting our children and pregnant mothers against vaccine-preventable diseases.
Components of eVIN
- eVIN combines state-of-the-art technology, a strong IT infrastructure and trained human resource to enable real-time monitoring of stock and storage temperature of the vaccines kept in multiple locations across the country.
- At present, 23,507 cold chain points across 585 districts of 22 States and 2 UTs routinely use the eVIN technology for efficient vaccine logistics management.
Benefits of eVIN
- It has helped create a big data architecture that generates actionable analytics encouraging data-driven decision-making and consumption-based planning.
- It helps in maintaining optimum stocks of vaccines leading to cost savings. Vaccine availability at all times has increased to 99% in most health centres in India.
- While instances of stock-outs have reduced by 80%, the time taken to replenish stocks has also decreased by more than half, on an average.
- This has ensured that every child who reaches the immunization session site is immunized, and not turned back due to unavailability of vaccines.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Private: India’s Ailing Health Sector and Coronavirus
Healthcare is LITERALLY the talk of the town right now. But for all the wrong reasons. Whether it is the lack of beds/ventilators or high cost of treatment, COVID has amplified our present deficiencies. Like rest of the world, Indians are for the first time so singularly focused on healthcare and public health amid this pandemic. And everyone suddenly wants to fix healthcare!

Confucius, it is said, once observed, “a seed grows with no sound, but a tree falls with huge noise. Destruction has noise, but creation is quiet”. As we all know, the world is at a crossroads. With COVID-19, many of our beliefs and the systems we follow are bound to change OR even get collapsed!
Healthcare in India: A Background
- The Indian Constitution has incorporated the responsibility of the state in ensuring basic nutrition, basic standard of living, public health, protection of workers, special provisions for disabled persons, and other health standards, which were described under Articles 39, 41, 42, and 47 in the DPSP.
- Article 21 of the Constitution of India provides for the right to life and personal liberty and is a fundamental right.
- Public Health comes under the state list.
- India’s expenditure on healthcare has shot up substantially in the past few years; it is still very low in comparison to the peer nations (at approx. 1.28% of GDP).
All-time Paradoxes of Indian Healthcare
(1) Healthcare is a fundamental right, but it is not fundamentally right in India:
The Supreme Court has held healthcare to be a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Constitution.
The expenditure on healthcare is one of the lowest in the world, lower than nations with similar economic growth rates. Though our economy has grown robustly post-liberalization, investment in healthcare has consistently hovered around 1% of the GDP. In the 2020-21 Budget, it was 1.02% of overall expenditure.
(2) Sector attracts investments, but delivery remains contentious:
India’s healthcare sector has attracted a steady stream of investments, albeit at the higher end of the value chain — the secondary & tertiary care. Lack of penetration, inflated billing, opaqueness in diagnosis, and poor quality of service has ensured that most Indians get treated below the standards prescribed by the WHO.
(3) Among the cheapest in the world, yet unaffordable for most locally:
Healthcare in India is cheap. For example: Compared to India, the cost of a knee replacement treatment is over twenty times more in the US and double in Malaysia. Yet India has one of the world’s highest rates of out-of-pocket spending in healthcare. There are millions in India who cannot afford these procedures in their own country.
(4) Less than one doctor for 1,000 patients, but medical tourism booms:
- India treated 3.6 lakh foreign patients in 2016 and the country’s medical tourism market is expected to grow to $7-8 billion by 2020.
- The doctor-patient ratio in India is less than the WHO-prescribed limit of 1:1000. There is a dearth of medical schools and clinicians.
- Most hospitals in India are overburdened, understaffed, and ill-equipped. However, all this has not prevented the private healthcare sector to establish sophisticated medical tourism facilities on the plank of ‘world-class service at low cost’.
(5) Stark divergence in healthcare outcomes within the country:
Healthcare being a state subject, the healthcare outcomes have remained divergent based on the quality of the state administration. While North India is the most populated part of India, it has one of the most undeserved healthcare infrastructures in the country.
Is India prepared to face this pandemic?
- Current health infrastructure in India paints a dismal picture of the healthcare delivery system in the country.
- Public health experts believe that India is ill-equipped to handle such emergencies. It is not prepared to tackle health epidemics, particularly given its urban congestion.
- Post unlock, the spread is at a galloping rate.
- The slum clusters all around the cities and the unhygienic growth, poor waste disposal system will only aggravate the situation.
History shows us that “blame” has been a standard human response during pandemics.
These are some issues surfaced during this pandemic ………..
(1) Poor Infrastructure
- In the 2019 Global Health Security Index, which measures pandemic preparedness for countries based on their ability to handle the crisis, India ranked 57, lower than the US at 1, the UK at 2, Brazil at 22, and Italy at 31.
- This is well revealed through indicators like hospital beds per 1,000 people.
- As per the OECD data available for 2017, India reportedly has only 0.53 beds available per 1,000 people as against 0.87 in Bangladesh, 2.11 in Chile, 1.38 in Mexico, 4.34 in China, and 8.05 in Russia.
(2) Fewer doctors per thousand
- The WHO mandates that the doctor to population ratio should be 1:1,000, while India had a 1:1,404 ratio as of February 2020.
- In rural areas, this doctor-patient ratio is as low as 1:10,926 doctors as per National Health Profile 2019.
(3) Denial of healthcare
- Despite private hospitals accounting for 62 percent of the total hospital beds as well as ICU beds and almost 56 percent of the ventilators, they are handling only around 10 percent of the workload.
- Private hospitals are reportedly denying treatments to the poor. Cases of overcharging patients are also being reported in private hospitals.
- This is seen in Bihar, which has witnessed an almost complete withdrawal of the private health sector and has nearly twice the bed capacity of public facilities.
(4) Discrepancy in Testing
- India continues to test less than it should in a post-lockdown scenario where testing is one of the most obvious ways to flatten the curve.
- The Supreme Court, after ruling on April 8 that private labs should conduct free testing, modified its decision five days later to fix the rate of one of the most dependable tests at Rs 4,500.
(5) Negligence for mental healthcare
- The tragic death of an actor and the gloom of the Covid-19 pandemic have led to much-needed conversations on mental health in the country.
- Mental health problems were already a major contributor to the burden of illness in India which usually gets unnoticed.
- The widespread anxiety due to lockdown has frustrated the laborers, farmers, and various vulnerable sections to a great extent due to the fear of impoverishment and loss of livelihoods.
Need of the hour: A tectonic overhaul
(1) Universal health coverage
- Access to healthcare in India is not equitable—the rich and the middle class would survive the COVID-19 or any other crisis but not the poor.
- As part of the SDGs, all countries have pledged to deliver universal health coverage (UHC) by 2030.
- This includes India. But, sadly, nearly 50 percent of the world’s population lacks essential health services.
- If any good comes out of this crisis, then it will be India waking up to the reality that investing in health is not a luxury. It is a basic need.
(2) Increasing healthcare professionals in numbers
- India has handled the COVID-19 pandemic exceptionally well. However, considering the rise in the number of infections, India is in dire need of more medical staff and amenities.
- If India wants to achieve a 1:1,000 ratio, it will need an additional 2.07 million doctors by 2030. For this, the government needs to increase its spending on the health sector.
- It needs to aid attempts at constructing new medical institutes.
(3) Revamping medical education
- If the government wants to stay successful in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic, it needs to rapidly build medical institutions and increase the number of doctors.
- Once COVID-19 is under control, we need to consider the psychological and professional impact of the pandemic on medical professionals.
(4) Helping the downtrodden
- How the poor are going to manage without, or even with, any government insurance scheme is a big question.
- Rather than dumping them on government hospitals only, the private hospitals should be held accountable to take on their treatment.
- They can make up for the loss by cross-subsidizing treatments of patients with premium insurance policies.
(5) Enhancing pandemic preparedness
- With COVID-19 we risk once again falling into the trap of a narrow vertical disease-specific approach.
- Decades of global health experience have revealed the limitations of narrow “vertical” disease-based programs.
- However, there is a need for recognition to combine vertical programs with “horizontal” health system strengthening.
(6) Optimum use of technology
- The COVID-19 crisis has elevated the importance of digital tools and e-health.
- There is a growing use of mobile apps, online consultations, e-pharmacies, and other tools.
- These are all welcome and must be leveraged.
(7) Looping-in private players
- For too long, India has allowed the private health sector to grow, with little regulation.
- The lack of alignment between the public and private sectors has been clearly exposed to COVID-19 testing and treatment in India.
- Time is ripe to loop in private players and promote the industrialization of health-sector.
(8) Learning from the successes
- With crumbling health infrastructure due to overburden, India’s preparedness for handling this epidemic has become a major challenge.
- The world along with India being no exception has responded with extraordinarily aggressive measures such as phased lockdowns, Bhilwara Model, Pathanamthitta Model, Taiwan model, etc.
- The success of these models is attributed to various best practices which are were implemented days before the thought of nationwide lockdown was incepted.
Kindly refer for various success models:
Way Forward
- The aerial spread of the pandemic post unlock poses a threat of rapid dissemination but it can still be contained with an efficient response that combines effective public health, microbiological, clinical, and communication responses.
- While our laboratory network has improved somewhat, but much needs to be done to improve the community facing primary health services and risk communication to the public.
- Kerala’s success in responding swiftly and smartly to the outbreak should be a role model for other states.
Conclusion
India’s healthcare system is too small for such a large population. There seems to be a long battle ahead. The public healthcare system cannot be improved overnight. The country needs all hands on deck during and after this crisis—both public and private sectors must work together and deliver universal health coverage for all citizens.
Ultimately, the onus of governance always rests with the government, which needs to set standards, invest resources, ensure quality, and strategically purchase services from the private sector, as needed.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
India COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health System Preparedness Package
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Coronovirus outbreak and its mitigation
The Centre has approved a centrally funded ‘India COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health System Preparedness Package’ with the objective of strengthening national and state health systems.
About the Package
- The package is 100 per cent centrally funded project under the National Health Mission.
- It will be implemented in three phases from January 2020 to March 2024.
- It aims at strengthening national and state health systems to support prevention and preparedness, procurement of essential medical equipment, consumables and drugs, etc.
- The three phases of the project are Phase – 1 from January 2020 to June 2020, the second phase is from July 2020 to March 2021 and the third phase from April 2021 to March 2024.
What are the major activities planned under this package?
- The key activities to be implemented under Phase -1 includes support to states/UTs for the development of dedicated COVID-19 hospitals and other hospitals, isolation blocks, negative pressure isolation rooms, ICUs with ventilators, the oxygen supply in hospitals etc..
- The central package will also assist the state/ UTs for the Procurement of Personal Protection Equipment (PPE), N95 masks and ventilators, over and above what is being procured and supplied by the govt.
- The activities under the first phase also include the disinfection of hospitals, government ambulances, etc.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Kendriya Bhandar
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kendriya Bhandar
Mains level: Not Much

Kendriya Bhandar which functions under the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) has taken the unique initiative of providing “Essentials Kits” to needy families during the ongoing lockdown.
About Kendriya Bhandar
- The Central Govt. Employees Consumer Cooperative Society Ltd. is popularly known as Kendriya Bhandar.
- It was set up in 1963 as a welfare project for the benefit of Central Govt. employees and public at large.
- It is functioning under aegis of Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions and was registered with Delhi Registrar of Cooperative Societies.
- Subsequently, it was registered with Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies, Govt. of India as a Multi-State Consumer Cooperative Society in September 2000.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Delhi’s ‘5T’ war against virus
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: COVID-19 and its mitigation
Delhi CM has announced a “5T plan” created by his government to contain COVID-19 spread in Delhi. These five Ts are testing, tracing, treatment, teamwork and tracking-monitoring.
5Ts strategy
1)Testing
- Testing when done on a mass scale enables the actual data of people affected by novel coronavirus.
- Like South Korea, Delhi will be testing on a large scale.
- Through rapid testing, the government will also be able to identify COVID-19 hotspots and take necessary action.
2)Tracing
- The second T is tracing, which involves identifying and quarantining people who have come in contact with infected persons.
- Delhi authorities are taking the help of police to trace whether the people who have been advised to self-quarantine are actually doing it or not.
3)Treatment
- The third component is the treatment.
- Serious patients who are suffering from heart diseases and patients above 50 years will be isolated in hospitals and the rest with minor symptoms will be kept in isolation in hotels and dharamshalas.
4)Teamwork
- The fourth element of the five-point plan is teamwork and collective efforts are being made to fight the virus.
- All State governments must learn from each other and work together.
5)Tracking and monitoring
- The fifth T is tracking and monitoring.
- The state should ensure that all these measures are in place and all the systems are functioning smoothly.
Also read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
‘Bhilwara Model’ for containment of coronavirus
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bhilwara Model
Mains level: Agressive strategies to contain covid-19 spread
Bhilwara in Rajasthan was one of the early hotspots of the COVID-19 outbreak. The government responded with extraordinarily aggressive measures — and the ‘Bhilwara model’. The success of the model is attributed to the fact that Bhilwara, which was the first district in Rajasthan to report most number of covid cases has now reported only one positive case since March 30.
What is the Bhilwara Model?
- The Bhilwara COVID-19 containment “model” refers to the steps taken by the administration in Rajasthan’s Bhilwara district to contain the disease, after it emerged as a hotspot for coronavirus positive cases.
- Bhilwara district was among the most-affected places in India during the first phase of the COVID-19 outbreak.
- The measures taken by the state govt. included imposing a curfew in the district which also barred essential services, extensive screening and house-to-house surveys to check for possible cases.
- It went for detailed contact tracing of each positive case so as to create a dossier on everybody they met ever since they got infected.
What did the administration do as part of the containment strategy?
- The “Bhilwara model” of tackling COVID-19 cases involves, simply, “ruthless containment”.
- Within three days of the first positive case the district health administration in Bhilwara constituted nearly 850 teams and conducted house-to-house surveys at 56k houses and of 280k people.
- Thousands were identified to be suffering from influenza-like illness (ILI) symptoms and were kept in home quarantine.
- Intense contact tracing was also carried out of those patients who tested positive, with the Health Department preparing detailed charts of all the people whom they had met since being infected.
- The state also took the help of technology, using an app to monitor the conditions of those under home quarantine on a daily basis along with keeping a tab on them through GIS.
- The administration backed up the surveys by imposing a total lockdown on the district, with the local police ensuring strict implementation of the curfew.
- The patients were treated with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), Tamiflu and HIV drugs.
What were the challenges the administration faced in imposing these extraordinary measures?
- The biggest challenge that the administration faced was containing the rising number of cases after the initial outbreak.
- The doctors of the private hospital who had tested positive had come into contact with numerous people including the staff and patients who visited the private hospital during the period when the doctors were already infected.
- Some of these patients had come from other states and after the first case of COVID-19 was detected.
- The government also had an uphill task ahead of them assembling the teams of doctors, auxiliary nurse and midwives and nursing students who went to conduct the house-to-house surveys.
- Owing to the fact that Bhilwara, a thriving textile city with an estimated population of 30 lakh, it was also a difficult task for the government to strictly impose the curfew uniformly in all areas.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] Centre for Augmenting WAR with COVID-19 Health Crisis (CAWACH)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CAWACH
Mains level: Not Much

Department of Science & Technology has approved setting up of a Centre for Augmenting WAR with COVID-19 Health Crisis (CAWACH).
What is CAWACH?
- CAWACH will help to address various challenges faced by country due to severe impact of COVID-19.
- CAWACH will identify up to 50 innovations and startups that are in the area of novel, low cost, safe and effective ventilators, respiratory aids, protective gears, novel solutions for sanitizers, disinfectants, diagnostics, therapeutics, informatics and any effective interventions to control COVID-19.
- The CAWACH’s mandate will be to extend timely support to potential startups by way of the requisite financial assistance and fund deployment targeting innovations that are deployable in the market within next 6 months.
- The Society for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (SINE), a technology business incubator at IIT Bombay supported by DST has been identified as the Implementing Agency of the CAWACH.
- It will provide access to pan India networks for testing, trial and market deployment of these products and solutions in the identified areas of priority COVID-19 solutions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Drive-through Testing?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Drive-through Testing
Mains level: Coronovirus outbreak and its mitigation
To work around the challenges of home-based testing in the country, a New Delhi based firm has offered ‘drive-through test’ for COVID-19.
Drive-through Testing
- Those who feel sick drive up to a test centre where nurses wearing protective gear collect a nose or throat sample from the car itself.
- Results are mailed or messaged in a day.
- This method of mass testing has allowed reduced contact between patients and healthcare workers, thereby lessening the chances of transmission.
- South Korea has led the world in the number of tests per million to check for coronavirus infection through this method.
Germany: leading through examples
- Germany is conducting around 3,50,000 coronavirus tests a week, far more than any other country.
- It means that more people with few or no symptoms are reported thereby increasing the number of known cases and adequate quarantines.
Limitations (for India)
- We have seen so far is that many are uncomfortable with the home collection process.
- Some people are worried that lab personnel visiting home in full protective gear would scare the neighbours.
- There are also instances when spouses of some healthcare personnel have separated for a while.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
BCG vaccine
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: BCG Vaccine
Mains level: Coronovirus and the hunt for its vaccine
According to a US-based research, a combination of reduced morbidity and mortality could make the Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccination a “game-changer” in the fight against novel coronavirus.
What is BCG Vaccine?
- Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine primarily used against tuberculosis (TB).
- In countries where TB or leprosy is common, one dose is recommended in healthy babies as close to the time of birth as possible.
- In areas where tuberculosis is not common, only children at high risk are typically immunized, while suspected cases of tuberculosis are individually tested for and treated.
How can TB vaccine help fight COVID-19?
- The BCG vaccine contains a live but weakened strain of tuberculosis bacteria that provokes the body to develop antibodies to attack TB bacteria.
- This is called an adaptive immune response, because the body develops a defense against a specific disease-causing microorganism, or pathogen, after encountering it.
- Most vaccines create an adaptive immune response to a single pathogen.
- Unlike other vaccines, the BCG vaccine may also boost the innate immune system, first-line defenses that keep a variety of pathogens from entering the body or from establishing an infection.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Telemedicine/Telehealth as a tool to fight COVID-19
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Telemedicine/Telehealth
Mains level: Telemedicine and its effectiveness

The Medical Council of India and the NITI Aayog have developed new guidelines released on March 25, 2020 for registered medical practitioners to deliver consultations to patients via telemedicine.
Telemedicine
- Telemedicine involves the use of telecom and virtual technology to deliver health care outside of traditional health-care facilities.
- It is the essential delivery of health care services where distance is a critical factor — comes in.
- At least one doctor is needed for a population of 1,000, according to WHO guidelines.
- Telemedicine, thus, holds significance for countries like India that have low doctor-to-patient ratios.
About the guidelines
- The guidelines aim to empower registered doctors to reach out to patients safely using technologies for the exchange of valid information.
- This information can be used for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease and injuries, research and evaluation and for continuing the education of healthcare providers.
- The guidelines have empowered medical practitioners. They have, however, also imposed many restrictions.
- Registered medical practitioners, for instance, have to take the patient’s consent.
- If the patient denies her consent, however, the practitioner cannot insist that the patient to go in for telemedicine.
How telemedicine can help against COVID-19?

- Telemedicine can help bridging the gap between people, physicians and health systems, enabling everyone, especially symptomatic patients, to stay at home and communicate with physicians through virtual channels.
- It thus helps reducing the spread of the virus to mass populations and the medical staff on the frontlines.
- It can help provide routine care for patients with chronic diseases who are at high risk if exposed to the virus.
Limitations
- The out-of-hospital management is has not been yet established in India. Perhaps a ‘crisis-based’ evolution of telemedicine can help find local testing centers and also manage the flow of patients seeking a test.
- However, for a smaller subset of higher risk patients, the clinical course may not be consistent with conventional telemedicine.
- These patients often present with a more serious condition require rapid hospitalization.
- Telemedicine hasn’t traditionally been used in response to public health crises. Many health practitioners are not equipped to deliver care in this way.
- Another issue is access to broadband – some hospitals struggle with running a quality connection within their facilities and now we are faced with taking this to potential new areas of care, such as an outside tent.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[pib] ArogyaSetu App
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ArogyaSetu App
Mains level: Coronovirus outbreak and its mitigation

The Government of India has launched a mobile app ArogyaSetu developed in a public-private partnership to bring the people of India together in a resolute fight against COVID-19.
AarogyaSetu App
- The App enables people to assess themselves the risk of their catching the Corona Virus infection.
- It will calculate this based on their interaction with others, using cutting edge Bluetooth technology, algorithms and artificial intelligence.
- Once installed in a smartphone through an easy and user-friendly process, the app detects other devices with AarogyaSetu installed that come in the proximity of that phone.
- The app can then calculate the risk of infection based on sophisticated parameters if any of these contacts has tested positive.
- The personal data collected by the App is encrypted using state-of-the-art technology and stays secure on the phone till it is needed for facilitating medical intervention.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Supreme Court upholds “Right to discuss COVID-19”
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Right to Discuss, Art. 19
Mains level: Coronovirus outbreak and its mitigation
The Supreme Court has upheld the right to free discussion about COVID-19, even as it directed the media to refer to and publish the official version of the developments in order to avoid inaccuracies and large-scale panic.
Right to Discuss
- The Right to Discuss falls under the purview of the right to freedom of speech and expression.
- Article 19(1)(a) of the Constitution of India states that all citizens shall have the right to freedom of speech and expression.
- It ensures all citizens the liberty of thought and expression.
- The exercise of this right is, however, subject to “reasonable restrictions” for certain purposes being imposed under Article 19(2) of the Constitution of India.
- These restrictions are imposed in the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order, decency or morality or in relation to contempt of court, defamation or incitement to an offence.
Why such a move?
- The court was responding to a request from the Central government that media outlets, in the “larger interest of justice”, should only publish or telecast anything on COVID-19 after ascertaining the factual position from the government.
- Any deliberate or inaccurate reporting by the media, particularly web portals, had the serious and inevitable potential of causing panic in a larger section of the society.
- Any panic reaction in the midst of an unprecedented situation based on such reporting would harm the entire nation.
- Creating panic is also a criminal offence under the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Private: Huntington Disease
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
PM-CARES Fund
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PM-CARES Fund
Mains level: Not Much
Our PM has called for donations to the newly instituted PM-CARES Fund which has been formed on popular demand to help fight the novel coronavirus.
PM-CARES Fund
- The fund will be a public charitable trust under the name of ‘Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund’.
- The PM is Chairman of this trust and members include the Defence Minister, Home Minister and Finance Minister.
- Contributions to the fund will qualify as corporate social responsibility (CSR) spending that companies are mandated to make.
- The Fund accepts micro-donations as well.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
What is Hantavirus?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hantavirus
Mains level: Rise in zoonotic diseases and their possible causes

China has reported the death of a person from Yunnan Province who tested positive for the Hantavirus.
What is Hantavirus?
- The Hantaviruses are a family of viruses spread mainly by rodents. It is contracted by humans from infected rodents.
- Cases of the Hantavirus in humans occur mostly in rural areas where forests, fields and farms offer suitable habitat for infected rodents.
- A person can get infected if he/she comes in contact with a rodent that carries the virus.
- In the US and Canada, for instance, the Hantavirus carried by the deer mouse is responsible for the majority cases of the Hantavirus infection.
- Like this, there are various other kinds of Hantaviruses that find hosts in rodents, like the white-footed mouse and the cotton rat among others that may lead to infections in humans if transmitted.
Its origin
- The Hantavirus is not novel and its first case dates back to 1993, according to the US Centre for Disease Control (CDC).
- In the Americas, the family of viruses is known as ‘New World hantaviruses’.
Symptoms
- A person infected with the virus may show symptoms within the first to eighth week after they have been exposed to fresh urine, faeces or the saliva of infected rodents.
- Symptoms may include fever, fatigue, muscle aches, headaches, chills and abdominal problems.
- Four to ten after being infected, late symptoms of HPS may start to appear, which include coughing and shortness of breath.
Mortality risk
- It is the cause of Hantavirus pulmonary disease (HPS), a severe respiratory disease. The HPS can be fatal and has a mortality rate of 38 per cent.
- It remains unclear whether human-to-human transmission of the virus is possible.
- There have been no reports of human-to-human transmission of Hantavirus in the US.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
PCR Test for Diagnosis of the COVID-19
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Polymerase Chain Reaction Test
Mains level: Coronovirus outbreak and its mitigation

The diagnosis of COVID-19 can be done with the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test which is explained as under:
The PCR Test
- It uses a technique that creates copies of a segment of DNA. ‘Polymerase’ refers to the enzymes that make the copies of DNA.
- Kary Mullis, the American biochemist who invented the PCR technique, was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1993.
- The ‘chain reaction’ is how the DNA fragments are copied, exponentially — one is copied into two, the two are copied into four, and so on.
- However, SARS-COV-2 is a virus made of RNA, which needs to be converted into DNA. For this, the technique includes a process called reverse transcription.
- A ‘reverse transcriptase’ enzyme converts the RNA into DNA. Copies of the DNA are then made and amplified.
- A fluorescent DNA binding dye called the “probe” shows the presence of the virus. The test also distinguishes SARS-COV-2 from other viruses.
Various Stages:
1) Collection and transport
- Testing centre takes swabs from nasal cavities and back of the throat (pharynx), and puts samples in a “virus transport medium”, which contains balanced salts and albumin to prevent the virus from disintegrating.
- Sample is then transported in cold storage to the testing lab.
2) Extraction of viral RNA
- Coronaviruses have large single-stranded RNA genomes.
- Testing lab extracts the RNA from the samples, using commercially available kits.
3) Putting THE RNA in THE PCR mix
- Extracted RNA is added to a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) mix.
- This includes the ‘master mix’, which contains a ‘reverse transcriptase’ enzyme that converts the RNA into DNA.
- Master Mix contains Taq polymerase, the enzyme that creates copies of the DNA, nucleotides, as well as other elements such as magnesium — an ion of which is needed to amplify the DNA.
- The PCR mix also contains ‘reagents’ such as ‘primers’ and ‘probes’.
- Primers are particular strands of DNA that are designed to bind with the DNA that is to be copied; probes are used to detect the specific sequence in the DNA sample.
- Finally, the PCR mix consists of a “housekeeping” gene — a normal human gene (RNAse P) that is used to ensure that samples were properly collected, and RNA extracted.
4) Amplification of the viral DNA
- Sample, in its PCR mix, is put into tubes or plates, which are then put in a thermal cycler machine that is used to conduct the PCR process.
- First, the RNA is converted into DNA. Then the process of copying the genes starts.
- The thermal cycler heats and cools the mixture with the sample, alternating between three temperatures — for melting the DNA to separate the two strands.
- The thermal cycler runs 30-40 such cycles in order to amplify the DNA to check for the virus.
5) Testing against controls
- Amplified DNA is tested against a positive control, which usually consists of genes of the virus cloned into plasmid, and a negative control, which is a ‘known’ sample that has tested negative for the virus earlier.
- RNase P should show amplification, positive control should be positive, negative control should be negative, and then whatever result you get for the specimen, is the correct result.
- In order for a test to be valid before the result is released, certain ‘validity criteria’ have to be met.
- If the housekeeping gene (RNase P) is positive, positive control is positive, negative control is negative, and the sample does not show any PCR positive result, the sample is declared negative.
- If the PCR result is positive, the patient has COVID-19.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Smart-locking India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- Strategies to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic.
Context
Currently, India has entered Stage 2 of the COVID 19 epidemic, but can we do something urgently to halt it before Stages 3 and 4, and prevent it from becoming another China or Italy? Let’s look at what COVID 19 is doing globally and what it has already done in India.
Nature and characteristics of COVID-19
- It belongs to a simple family of cold viruses: Coronavirus 19, which emerged from China but has now spread globally, belongs to a simple family of common cold viruses which look innocent and harmless, unlike the sinister flu.
- Footprints of similar epidemics: It has footprints of two similar epidemics: SARS (2002) and MERS (2012) apart from Ebola, which were contained well globally in the last two decades.
- They are the group of viruses: Coronaviruses are large groups of viruses seen in humans as well as animals like camels, bats, cats, and even cattle, which India should take note of.
- The current COVID 19 appears to be a bat-originated beta variant of the coronavirus.
- Who is the most vulnerable? The human COVID disease is fatal predominantly in elderly or vulnerable groups, such as people with a chronic disease like hypertension, diabetes, cancer or people with suppressed immune systems.
- How it is spread? It is spread via airborne droplets (sneeze or cough) or contact with the surface. It is possible that a person can get COVID-19 by touching a surface or an object that has the virus on it and then touching their own nose, eyes or mouth.
Susceptibility and the measures needed to contain the spread
- Mode of spread: The way virus spreads creates vulnerability and susceptibility of the spread of the virus through airborne droplets and contact surfaces — which are now, therefore, targets of public hygiene for preventing the spread.
- Why India is more vulnerable? We are vulnerable due to the large population constantly travelling and working: This needs immediate containment to halt the virus spread. We are a ticking time bomb now with less than 30 days to explode in Stage 3, which will be the virus getting deeper into communities, and which will then be impossible to contain.
- Poor public hygiene in India: Public hygiene in India is poor despite the “Swachh Bharat (Clean India)” movements. We need to have legislation with a penalty to stop spitting in public as well as private spaces.
- Past performance: India has done very well to contain both SARS and the novel Nipah viral spread very well.
Should India shut down the cities?
- From China to global spread: The COVID 19 virus possibly came from the Wuhan epicentre of central China. Subsequent it assumed a large enough proportion to be called a pandemic. It rapidly transitioned across different geographies of the world including Korea, Japan, Iran, Italy and others for the WHO to declare it as a pandemic.
- Neighbouring countries shutting down the cities: neighbouring countries like Thailand and Singapore shut down their major cities and towns for a few weeks to stop it from moving onto the next stages.
- Should India shut down the cities? The big question today is, should the Indian government and the state governments stop the virus spread from Stage 2 to 3 by totally shutting down cities and towns when the economy is already fragile and on the brink?
- From cluster to community spread: India had its first case diagnosed on January 30, from a student who returned from China. Later, it had a very slow spread despite the global transit involved. Such individual cases will become small clusters.
- These clusters will then spread to communities.
- We must halt the community-wide spread: Currently, we have just moved from case to clusters, but we must halt the community-wide spread.
- Biphasic or dual-phase infection: COVID 19 usually follows what is known as a biphasic or dual-phase infection, which means the virus persists and causes a different set of symptoms than observed in the initial bout.
- Also, sometimes, the recovered person can relapse.
- The possibility of “super spreader”: Currently, the cases and clusters in India are simple spreaders which means an infected person with normal infectivity.
- What is it? But COVID 19 can also have a “super spreader”, which means an infected person with high infectivity who can infect hundreds in no time.
- This was reportedly seen in Wuhan where a fringe group spread the virus via a place of worship in Korea, infecting almost 51 cases.
- India saw a mini spurt of cases on March 4, and then again between March 10 and 13, when cases jumped from 23 to 35, yet no super spreader was present.
- We need to halt transition from stage 2 to stage 3: Now we have almost crossed a hundred cases and we must be vigilant.
- As we enter Stage 2, we will now see a geometric jump in the number of cases which will put us at risk of rapidly transitioning from Stage 2 to 3 like Italy, which we need to halt urgently.
Conclusion
The ICMR has rightly advised the government to go into partial shutdown but is it too little too late now? It’s time to halt COVID 19 by smartly locking the country at home so that we can have a better tomorrow. This needs a political will which we currently have.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Tracking the big three
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2-Key areas India needs to focus on to achieve good health and well being.
Context
The article focuses on the top three Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations, namely poverty elimination, zero hunger, and good health and well-being by 2030.
India’s record on extreme poverty, hunger and health
- Decline in extreme poverty: The World Bank’s estimates of extreme poverty- measured as $1.9/per capita/per day at purchasing power parity of 2011- show a secular decline in India from 45.9 per cent to 13.4 per cent between 1993 and 2015.
- Elimination of extreme poverty 2030: If the overall growth process continues as has been the case since, say, 2000 onwards, India may succeed in eliminating extreme poverty by 2030, if not earlier.
- Zero hunger by 2030: Given the overflowing stock of food grains with the government, and a National Food Security Act (NFSA) that subsidises grains to the tune of more than 90 per cent of its cost to 67 per cent of the population, there is no reason to believe that India can also not attain the goal of zero hunger before 2030.
- Health- a real challenge: The real challenge for India, is to achieve the third goal of good health and well-being by 2030. India’s performance in this regard, so far, has not been satisfactory. as per the National Family Health Survey (NFHS 2015-16)-
- In 2015-16, almost 38.4 per cent of India’s children under the age of five years were stunted.
- 8 per cent were underweight.
- 21 per cent suffered from wasting (low weight for height).
- The situation in some states like Bihar, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh is even worse.
- Global Hunger Index ranking of India: No wonder, the Global Hunger Index (GHI) ranks India at 102 out of 117 countries in terms of the severity of hunger in 2019.
What are the various targets set on the nutrition problem?
- Target on reducing the problems of underweight children: The National Nutrition Strategy, 2017, aims to reduce the prevalence of underweight children (0-3 years) by three percentage points every year by 2022 from NFHS 2015-16 estimates.
- Why this is an ambitious target? This is an ambitious target given the decadal decline in underweight children from 42.5 per cent in 2005-06 to 35.8 per cent in 2015-16 amounts to less than 1 per cent decline per year.
- Targets set in National Nutrition Mission: Similar targets have been set by the National Nutrition Mission (renamed as POSHAN Abhiyaan), 2017.
- To reduce stunting by 2 per cent.
- Under-nutrition by 2 per cent.
- Anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) by 3 per cent.
- Low birth weight by 2 per cent.
Four areas India needs to focus to achieve the set targets
- India has to focus on four key areas: If India has to make a significant dent on malnutrition by 2030.
- First- Mother’s education.
- Multiplier effect: It is one of the most important factors that have a positive multiplier effect on child care and access to healthcare facilities.
- Increases awareness: It also increases awareness about the nutrient-rich diet, personal hygiene, etc. This can also help contain the family size in poor, malnourished families.
- Thus, a high priority to female literacy, in a mission mode through liberal scholarships for the girl child, would go a long way towards tackling this problem.
- Second- Access to improved sanitation and safe drinking water.
- The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan and Jal Jeevan Mission would have positive outcomes in the coming years.
- Third-shift in dietary pattern
- Shift from cereals to more nutritious food: There is a need to shift dietary patterns from cereal dominance to the consumption of nutritious foods such as livestock products, fruits and vegetables, pulses, etc.
- But they are generally costly and their consumption increases only by higher incomes and better education.
- Diverting the food subsidy to nutritious foods: Diverting a part of the food subsidy on wheat and rice to more nutritious foods can help.
- Fourth- Adoption of new agricultural technology
- Adopt bio-fortifying cereals: India must adopt new agricultural technologies of bio-fortifying cereals, such as zinc-rich rice, wheat, iron-rich pearl millet, and so on.
- The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has to work closely with the Harvest Plus programme of the Consultative Group of International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) to make it a win-win situation for curtailing malnutrition in Indian children at a much faster pace — and, at a much lower cost than would be achieved under a business as usual scenario.
Examples from the world
- Right public policies make the difference: Global experience shows that with the right public policies focusing on agriculture, improved sanitation, and women’s education, one can have much better health and well-being for its citizens, especially children.
- China’s example: In China, it was agriculture and economic growth that significantly reduced the rates of stunting and wasting among the population and lifted millions of people out of hunger, poverty and malnutrition.
- Brazil and Ethiopia example: According to FAO, Brazil and Ethiopia have transformed their food systems: They have targeted their investments in agricultural R&D and social protection programmes to reduce hunger in the country.
Conclusion
Despite India’s improvement in child nutrition rates since 2005-06, it is way behind the progress experienced by China and many other countries. According to the Global Nutrition Report, 2016, at the present rates of decline, India will achieve the current stunting rates of China by 2055. India can certainly do better, but only if it focuses on this issue.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
State lethargy amidst cough syrup poisoning
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- Need of the policy and standard guidelines for the drug recall.
Context
A few days ago, 12 children died in Udhampur district of Jammu due to poisoned cough syrup (Coldbest-PC).
Fourth mass glycol poisoning
- What was the cause of the poisoning? A team of doctors at the Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research, Chandigarh, attributed the deaths to the presence of diethylene glycol in the cough syrup.
- What is Diethylene glycol? It is an anti-freezing agent that causes acute renal failure in the human body followed by paralysis, breathing difficulties and ultimately death.
- This is the fourth mass glycol poisoning event in India that has been caused due to a pharmaceutical drug.
Measures required and example from the US
- Preventing further deaths: The immediate concern for doctors, pharmacists and the drug regulators should be to prevent any more deaths.
- The only way to do so is to account for each and every bottle of the poisoned syrup that has ever been sold in the Indian market and stop patients from consuming this drug any further.
- The US example in such case: United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA), in 1937, when the United States faced a similar situation with glycol poisoning.
- Tracking down every bottle: Entire field force of inspectors and chemists were assigned to the task of tracking down every single bottle of the drug.
- Even if a patient claimed to have thrown out the bottle, the investigators scoured the street until they found the discarded bottle.
- This effort was accompanied by a publicity blitz over radio and television.
- What is being done in India? We do not see such public health measures being undertaken here.
- Seriousness not communicated to the pubic: Authorities are simply not communicating the seriousness of the issue to the general public.
- A general statement: At most, the authorities in Himachal Pradesh (H.P.), who are responsible for oversight of the manufacturer of this syrup, have made general statements that they have ordered the withdrawal of the drug from all the other States where it was marketed.
- Lack of transparency: There is no transparency in the recall process and information about recalls and batch numbers is not being communicated through authoritative channels.
- No public announcement by the DCGI: There is no public announcement by the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI), which is responsible for overall regulation of the entire Indian market.
- The suspect product, although manufactured in H.P., has been sold across the country.
- The website of the DCGI, which is supposed to communicate drug alerts and product recalls, has no mention of Coldbest-PC as being dangerous as of this writing.
Need for the recall policy
- No rules or binding guidelines on recall: One of the key reasons why the DCGI and state drug authorities have been so sloppy is because unlike other countries, India has not notified any binding guidelines or rules on recalling dangerous drugs from the market.
- Warnings to the DGCI on lack of framework: The 59th report of the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Health as well as the World Health Organization (in its national regulatory assessment) had warned the DCGI on the lack of a national recall framework in India.
- A set of recall guidelines was drafted in 2012 but never notified into law.
Conclusion
The drug regulator needs to take the urgent steps to avoid the repeat of such tragedies in the future and formulate a policy on the drug recall at the earliest.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Spontaneous Regression
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Spontaneous healing/regression
Mains level: Not Much
Patients sometimes make ‘miraculous’ recoveries from severe ailments. This is called spontaneous healing or spontaneous regression.
Spontaneous healing/regression
- A patient improves unexpectedly from a disease that usually progresses, such as cancer, and at times is even cured.
- Such cases notwithstanding, the medical fraternity is often sceptical and takes “miraculous” recoveries as flukes.
- A research explores patterns behind healing illnesses such as the deadliest kinds of cancers, and lays out physical and mental principles associated with recovery.
- These include physically healing diets and immune systems, and mentally healing stress responses and identities.
How does it occur?
- The research states that much of our physical reality is created in our minds and perception changes our experiences, sometimes to the point of changing our bodies.
- Therefore it argues that healing our identities may be a key tool to recovery.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Powering the health-care engine with innovation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- Adoption of innovation in improving the healthcare system in India.
Context
India needs to tap the potential of the health-care start-ups in India and make the necessary provision to deal with the problems in the adoption of innovations in health-care.
Expanding the supply side
- Need to increase the hospital empanelled: As the scale of this scheme grows, a key area of focus is-
- To expand the secondary and tertiary hospitals empanelled under PM-JAY and
- To ensure their quality and capacity while keeping the costs down.
- The ratio of doctors and beds: At present, there is one government bed for every 1,844 patients and one doctor for every 11,082 patients.
- 3% hospitalisation under the scheme: In the coming years, considering 3% hospitalisation of PM-JAY-covered beneficiaries, the scheme is likely to provide treatment to 1.5 crore patients annually.
- This means physical and human infrastructure capacity would need to be augmented vastly.
- Need for more beds: Conservative estimates suggest that we would need more than 150,000 additional beds, especially in Tier-2 and -3 cities.
- Long-term strategy: While a comprehensive long-term strategy will focus on expanding hospital and human resources infrastructure, an effective near-term approach is needed to improve efficiencies and bridge gaps within the existing supply and likely demand.
- Mainstreaming innovation: A strong, yet under-tapped lever for accelerating health system efficiency and bridging these gaps is mainstreaming innovation in the Indian health system.
Transformative solutions
- India’s burgeoning entrepreneurial spirit combined with a systematic push for the development of a start-up ecosystem has led to a plethora of innovations in health care.
- It is estimated that there are more than 4,000 health-care technology start-ups in India.
- How do start-ups help? Today, start-ups are working to bring-
- Innovative technologies and business models that leapfrog infrastructure.
- Human resources.
- Cost-effectiveness and efficiency challenges in Tier-2 and -3 cities.
- How other innovations could help?
- Artificial Intelligence platforms that aid in rapid radiology diagnoses in low resource settings.
- Tele-ICU platforms to bridge the gap in high-skilled critical care personnel.
- Centralised drone delivery of blood, medicines and vaccines to reach remote locations cost-effectively and reliably are all no longer just theoretical ideas.
- Time to implement transformative solutions: It is high time for transformative solutions to make their way into our hospitals, especially in Tier-2 and -3 cities, to turbocharge the way health care is delivered at scale.
Challenges in mainstreaming healthcare innovations
- Lack of uniform regulatory standards: One challenge is non-uniform regulatory and validation standards.
- Regulations evolving in India: Regulatory requirements, specifically for biomedical start-ups, are still evolving in India.
- As a result, hospitals often rely on foreign regulatory certifications such as FDA and CE, especially for riskier devices and instruments.
- Government to overhaul standards: The government is now pushing ahead to overhaul Indian med-tech regulatory standards and product standards which will help bridge this trust-deficit.
- Difficulty in the promotion of start-ups: Another problem in promoting start-ups is the operational liquidity crunch due to a long gestation period.
- Health-care start-ups spend long periods of time in the early development of their product, especially where potential clinical risks are concerned.
- Long gestation period: The process of testing the idea and working prototype, receiving certifications, performing clinical and commercial validations, and raising funds, in a low-trust and unstructured environment makes the gestational period unusually long thereby limiting the operational liquidity of the start-up.
- Lack of framework to adopt innovation: Another hurdle is the lack of incentives and adequate frameworks to grade and adopt innovations.
- Health-care providers and clinicians, given limited bandwidth, often lack the incentives, operational capacity, and frameworks necessary to consider and adopt innovations.
- This leads to limited traction for start-ups promoting innovative solutions.
- Procurement challenges: Start-ups also face procurement challenges in both public and private procurement.
- They lack the financial capacity to deal with lengthy tenders and the roundabout process of price discovery.
- Private procurement is complicated by the presence of a fragmented customer base and limited systematic channels for distribution.
Way forward
- Identify promising market-ready products: To accelerate the process of mainstreaming innovations within the hospital system in India-
- We need to focus on identifying promising market-ready health-care innovations that are ready to be tested and deployed at scale.
- Facilitate standard operational validation studies: There is a need to-
- Facilitate standardised operational validation studies that are required for market adoption.
- To help ease out the start-up procurement process such that these solutions can be adopted with confidence.
- This, in effect, will serve the entire ecosystem of health-care innovators by opening up health-care markets for all.
- Need to develop an interface between hospital and start-ups: A strong theme in mature health-care systems in other parts of the world is a vibrant and seamless interface between hospitals and health-care start-ups.
- Through Ayushman Bharat, India has the unique opportunity to develop a robust ecosystem where-
- Hospitals actively engage with health-care start-ups by providing access to testbeds, communicating their needs effectively and adopting promising innovations.
- Start-ups as collaborators: Start-ups can be effective collaborators for the most pressing health-care delivery challenges faced by hospitals.
Conclusion
The dream of an accessible, affordable and high-quality health-care system for all, will be achieved when we work in alignment to complement each other and jointly undertake the mission of creating an Ayushman Bharat.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
A mix Indian health care can do without
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- Will allowing participation of private sector in the public healthcare system beneficial for India?
Context
In India, multiple policy pronouncements over the last few years have expressed an implicit intent to emulate certain features of the U.S. health system which is one of the most prodigal health systems, and it is a well-known reality that it is infamously poor-performing.
Emulating the U.S. health system in India and problems in this approach
- Implicit intent to emulate the U.S. system: In India, multiple policy pronouncements over the last few years have expressed an implicit intent to emulate certain features of the U.S. health system like-
- Enhance private initiative.
- And uphold the insurance route as the way to go for health care.
- AB-NHPS scheme: These are being largely envisaged while riding on the back of the Ayushman Bharat-National Health Protection Scheme (AB-NHPS).
- AB-NHPS aims to provide insurance cover to nearly 50 crores poor Indians.
- The mechanism to check insurance frauds: The AB-NHPS affirmed strong mechanisms to check insurance fraud which was commonplace in its precursor programme, the Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana (RSBY).
- New of fraud in AB-NHPS: Recently, 171 hospitals were reported to have been de-empanelled from the AB-NHPS on charges of fraud.
- How are the frauds in AB-NHPS sought to be tackled? The response to these has been envisaged through an unprecedented bolstering of administratively-heavy and technology-driven mechanisms.
- Anti-fraud units: National- and state anti-fraud units have been established and partnerships with fraud control companies conceived.
- One would ask this question: what is wrong in all of this?
- What is wrong with this approach? Let us return to the U.S. once again.
- Administrative intensive: Multiple layers of complex arrangements and concomitant complex regulatory provisions have made the U.S. system one of the most administratively and technologically intensive systems in the world.
- 50% spending going for the wages: More than 50% of health-care spending in the U.S. in 2010 went into health worker’s wages, with a large chunk of the growth in health-care labour taking place in the form of non-clinical workers.
- Very little going into improving health: What this entails is that for every penny spent on health care, very little goes into actually improving health.
What are the concerns in emulating the U.S. system?
- Sub-satisfactory operations at the large cost: The new system necessitates-
- A battery of new structures.
- Personnel cadres.
- Data systems.
- And working arrangements only in order to sub-satisfactorily operate an insurance scheme that would cover less than half the population.
- Disregarding the death spiral that policy-driven over-reliance on private health care could lead to considerable costs which would not primarily contribute to improving health outcomes.
- Ethical concerns over unnecessary spending: While a besottedness with cutting-edge technology and state-of-the-art systems can help garner eyes and promote businesses, each unnecessary penny incurred this way raises significant ethical concerns.
- Problems of inadequate funding
- Funding sufficient only for a quarter of beneficiary: Gupta and Roy have shown how the allocation for the AB-NHPS for 2019-20 would have covered less than a quarter of the targeted beneficiaries.
- Paltry increase in allocations: For 2020-21, there has been a paltry increase in health-care sector allocation (5.7% above 2019-20 RE), while the allocation for the AB-NHPS is unchanged.
- It is very possible that the AB-NHPS continues to remain insufficiently funded and incapable of extending considerable financial risk protection to the poor.
- Diversion of limited funds to wasteful areas
- Attractive on face: Embracing the complexities associated with robust regulation of the insurance programme and making the requisite technological and administrative investments appear attractive and commendable on the face.
- Diversion of limited fund: However, these complexities entail diverting highly limited resources towards wasteful and dispensable high-end areas.
- These funds could have been set aside for much more pressing and productive domains, such as public hospitals and health centres.
- Improvements in these areas would have strongly reflected in terms of tangibly better health outcomes.
- AB-NHPS reinforcing contradictions: Rather, the AB-NHPS appears attuned to reinforcing a stark contradiction wherein trailblazing but unproductive high-end structures thrive alongside decrepit but potentially fructuos basic structures.
Conclusion
The fanfare with which AB-NHPS was launched, can hide the pressing concerns which lie underneath. The government must ensure that every penny spent on improving healthcare is used in the most optimal way and ensure that India’s AB-NHPS won’t end up the US healthcare way.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Why emergency response units are needed to ensure safety of sanitation workers
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Read the attached story
Mains level: Upliftment of the manual scavengers
- The Maharashtra government has directed all civic bodies in the state to set up Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs) to ensure safeguards for sanitation workers who clean manholes and sewers.
- This move is in response to the multiple cases which were reported of workers dying from suffocation or inhalation of hazardous gases.
PEMSR ACT, 2013
- The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (PEMSR) Act came into force in 2013.
- The law prohibits employing manual scavengers, manual cleaning of sewers and septic tanks without protective equipment and construction of insanitary latrines.
- Those violating the law and getting sewers and septic tanks cleaned without protective equipment can face imprisonment of up to two years or a fine of up to Rs 2 lakh, or both.
- Repeat offenders will face imprisonment of up to five years or a fine of up to Rs 5 lakh, or both.
The Supreme Court judgment
- While hearing a case on manual scavenging in 2014, the Supreme Court had stated, “If the practice of manual scavenging has to be brought to an end, and also to prevent future generations from the inhuman practice… rehabilitation of manual scavengers will need to include steps to avoid sewer deaths.”
- The court had said that making a sanitation worker enter sewer lines without safety gear should be a crime even in emergency situations.
- In such instances, if a sanitation worker died due to the unsafe conditions, a compensation of Rs 10 lakh has to be given to the family of the deceased, stated the court.
- The court had also directed authorities to identify the family members of sanitation workers who died while cleaning manholes and septic tanks since 1993, and give a compensation of Rs 10 lakh to them.
Directives by National Commission for Scheduled Castes
- To ensure effective implementation of the law banning manual scavenging, the commission issued various directives.
- It said workers have to be fully equipped with safety apparatus and oxygen masks in case they have to clean sewers manually.
- A first information report has to be lodged against officials or contractors responsible for sending a worker to clean sewers manually, without proper gear.
- The commission also made it mandatory for all municipal corporations to get an insurance policy of Rs 10 lakh per worker, as per the Supreme Court’s directions.
- The employers, in this case the civic bodies, will have to pay the policy premium.
Emergency Response Sanitation Unit (ERSU)
- In its directive on the setting up of ERSUs, the state government said the municipal commissioner of the civic body concerned will be the Responsible Sanitation Authority (RSA).
- The ERSU should be headed by a senior civic officer and other civic officers should be on the ERSU advisory board to decide the standard operating procedure (SoP) for workers who enter manholes for cleaning purposes.
- The civic body will also have to set up a dedicated toll-free number for the ERSU. The unit will impart training to sanitation workers.
- Only workers trained and certified by an ERSU will be able to clean sewers, but the priority will be on using machines to get such work done.
- In case a worker dies while cleaning a sewer, the civic body will have to hold an inquiry and register a police complaint.
Workshop on creating awareness on the issue
- All civic bodies have been asked to hold workshops to raise awareness on this issue in their respective jurisdictions.
- The workshops are going to focus on latest technology for cleaning sewers and septic tanks, and the final objective is to find a way to clean septic tanks or manholes with machines.
- The workshops will have sessions on laws pertaining to sanitation workers, the establishment of ERSUs and their roles, presentations on the latest equipment, machines and protective gear.
- Sanitation workers, NGOs, social organisations, housing society members and government officials have to participate in the workshops.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Euthermia: the anomaly of human body temperature
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Euthermia
Mains level: Not Much

Euthermia refers to normal body temperature. The thermometer reading of 98.6°F has been a gold standard for a century and a half, ever since a German doctor laid it down as the “normal” body temperature. A new research has found that body temperatures have, in fact, been declining over the last two centuries.
Why we follow 98.6°F?
- In 1851, Carl Reinhold August Wunderlich pioneered the use of the clinical thermometer.
- It was a rod a foot long, which he would stick under the armpits of patients at the hospital attached with Leipzig University, and then wait for 15 minutes (some accounts say 20 minutes) for the temperature to register.
- He took over a million measurements of 25,000 patients, and published his findings in a book in 1868, in which he concluded that the average human body temperature is 98.6°F.
- Most modern scientists feel Wunderlich’s experiments were flawed, and his equipment inaccurate.
- Another study concluded that the average human body temperature is closer to 98.2°F, and suggested that the 98.6°F benchmark be discarded.
The body is cooler
- The Stanford University the researchers confirmed some known trends — body temperature is higher in younger people, in women, in larger bodies and at later times of the day.
- Additionally, they found that the bodies of men born in the early to mid-1990s is on average 1.06°F cooler than those of men born in the early 1800s.
- And the body temperature of women born in the early to mid-1990s is on average 0.58°F lower than that of women born in the 1890s.
- The calculations from the research correspond to a decrease in body temperature of 0.05°F every decade.
Why there’s decrease in body temperature?
- The researchers have proposed that the decrease in body temperature is the result of changes in the environment over the past 200 years, which have in turn driven physiological changes.
- The decrease in average body temperature in the US, they said, could be explained by a reduction in metabolic rate, or the amount of energy being used.
- The environment that we’re living in has changed, including the temperature in our homes, our contact with microorganisms and the food that we have access to.
- Actually the human body is changing physiologically.
So what’s the normal temperature?
- The strong influences of age, time of day, and genders determine the healthy body temperature.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Global Report on Medical Data Leak
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Report on Medical Data Leak
Mains level: Medical administartion in India and its loopholes
Medical details of over 120 million Indian patients have been leaked and made freely available on the Internet, according to a recent report.
Global Report on Medical Data Leak
- It is published by Greenbone Sustainable Resilience, a German cybersecurity firm.
- The first report was published in October 2019 in which Greenbone revealed a widespread data leak of a massive number of records, including images of CT scans, X-rays, MRIs and even pictures of the patients.
- The follow-up report, which was published, classifies countries in the “good”, “bad” and “ugly” categories based on the action taken by their governments after the first report was made public.
- India ranks second in the “ugly” category, after the U.S.
Highlights of the report
- As per the follow-up report, Maharashtra ranks the highest in terms of the number of data troves available online, with 3,08,451 troves offering access to 6,97,89,685 images.
- The next is Karnataka, with 1,82,865 data troves giving access to 1,37,31,001 images.
- The number of data troves containing this sensitive data went up by a significant number in the Indian context a month after the initial report was published.
- It is a notable fact for the systems located in India, that almost 100% of the studies (data troves) allow full access to related images stated the report.
What led to the leaks?
- Greenbone’s original report says the leak was facilitated by the fact that the Picture Archiving and Communications Systems (PACS) servers, where these details are stored.
- These servers are not secure and linked to the public Internet without any protection, making them easily accessible to malicious elements.
Impact of leaks
- The leak is worrying because the affected patients can include anyone from the common working man to politicians and celebrities.
- In image-driven fields like politics or entertainment, knowledge about certain ailments faced by people from these fields could deal a huge blow to their image.
- The other concern is of fake identities being created using the details, which can be misused in any possible number of ways.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[op-ed of the day] Equity’s weak pulse and commodified medicine
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- Lack of coverage of the public health system, Role of private sector and regulation.
Context
As the government tries to overhaul the public health system in India, its time to take into account the advent and the role played by the private sector and its implications.
The advent of the private sector
- Increase in the role of the private sector in the post-Independence era: Post-Independence, the private sector increased its footprint in India.
- Perpetual sub-optimal investments in public health allowed the private sector to capitalise, flourish, and increasingly gain the confidence of the masses.
- The private sector went from having about 1,400 enterprises in 1950 to more than 10 lakh in 2010-11.
- To doctors, this promised greater professional liberty, lesser restrictions, and higher incomes.
- After liberalisation, the greater focus shifted to the lucrative tertiary-care sector and led to an onslaught of sophisticated private health care in cities.
The dominance of the private sector and malpractices
- The scale of dominance: Private sector has over 70% of the health-care workforce and 80% of allopathic doctors, has meant that it is scarcely possible for a health-care provider to function in defiance of its norms.
- Pervasive malpractices: The pervasiveness of malpractices in this market has come to ensure that few could survive without condoning them.
- Nexus of the private players: Players in this market, in much of their malpractices, have also learnt to function as a harmonious family.
- Organised form to safeguard interest: The family plays its role in safeguarding its members, acquainting them with its norms and interests, and leveraging the power of its patriarchs to defend its interests in society.
- Standards of success dictated by the markets: It is little wonder that the market has also come to dictate the avenues of aggrandisement and yardsticks of professional success for health-care professionals.
- Benchmark of quality changed: Business finesse and social adroitness rather than clinical excellence and empathy become the touchstones of calibre in this market.
Failure of the government
- Absence of national system: The larger chunk of Indian health care (and health workforce) could not be brought under a “national system” having some form of overarching state control or involvement.
- If such a system existed it could avail of essential health care without most people having to rely on a vagarious market, except as a luxury.
- Example of the UK’s NHS: The National Health Service of the United Kingdom, remains the single largest health-care provider.
- NHS employs nearly the entire health-care workforce.
- NHS makes essential health care available to all practically free at the point of service.
- Consequences of the absence of such system: The absence ensures is that the profit-driven private sector, the minor component, caters mainly to the affluent lot as largely a matter of deliberate choice rather than desperate compulsion.
- Hopes of benefits of free-market belied: The Indian example, much like the United States’, bespeaks the failure of the idea that a free market will compel players to be more efficient.
- The exploitation of the loops by the private players: Rather than increasing efficiency, the players have found it expedient to scrupulously exploit the prevailing cracks in the system and employ devious methods in order to maximise profits.
Conclusion
- Health-care providers, just like others, are moulded by their social surroundings. When necessary controls are loosened, the connatural vices are let loose; when the habitat is conducive to values, the right traits develop.
- A system that starts off with health care as an overt tradable commodity it threatens the development of virtues in the system.
- On the other hand, a system founded on the concept of equity cultivates a totally different culture of patient care.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
Yada Yada Virus
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Yada Yada
Mains level: NA
A new virus detected in Australian mosquitoes has been provisionally named the Yada Yada virus (YYV).
Yada Yada
- It is an alphavirus, a group of viruses that the researchers described as small, single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses.
- It includes species important to human and animal health, such as Chikungunya virus and Eastern equine encephalitis virus.
- They are transmitted primarily by mosquitoes and (are) pathogenic in their vertebrate hosts.
- Unlike some other alphaviruses, Yada Yada does not pose a threat to human beings.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
National Policy for the treatment of 450 ‘Rare Diseases’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rare Diseases
Mains level: Highlights of the saif policy for ‘Rare Diseases’
The Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has published a national policy for the treatment of 450 ‘rare diseases’.
About the Policy
- The Centre first prepared such a policy in 2017 and appointed a committee in 2018 to review it.
- It was created on the direction of the Delhi High Court to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- This was in response to writ petitions for free treatment of such diseases, due to their “prohibitively” high cost of treatment.
- Hence, a policy was deemed necessary to devise a “multipronged” and “multisectoral” approach to build India’s capacity for tackling such ailments.
Why need such a policy?
- As per the policy, out of all rare diseases in the world, less than five per cent have therapies available to treat them.
- In India, roughly 450 rare diseases have been recorded from tertiary hospitals, of which the most common are Haemophilia, Thalassemia, Sickle-cell anemia, auto-immune diseases, Gaucher’s disease, and cystic fibrosis.
Features of the policy
- While the policy has not yet put down a detailed roadmap of how rare diseases will be treated.
- It has mentioned some measures, which include creating a patient registry for rare diseases, arriving at a definition for rare diseases that is suited to India, taking legal and other measures to control the prices of their drugs etc.
- It intends to kickstart a registry of rare diseases, which will be maintained by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- Under the policy, there are three categories of rare diseases — requiring one-time curative treatment, diseases that require long-term treatment but where the cost is low, and those needing long-term treatments with high cost.
- Some of the diseases in the first category include osteopetrosis and immune deficiency disorders, among others.
- As per the policy, the assistance of Rs 15 lakh will be provided to patients suffering from rare diseases that require a one-time curative treatment under the Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi scheme.
- The treatment will be limited to the beneficiaries of Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana.
What are rare diseases?
- Broadly, a ‘rare disease’ is defined as a health condition of low prevalence that affects a small number of people when compared with other prevalent diseases in the general population. Many cases of rare diseases may be serious, chronic and life-threatening.
- While a majority of rare diseases are believed to be genetic, many — such as some rare cancers and some autoimmune diseases — are not inherited, as per the NIH.
- According to the policy, rare diseases include genetic diseases, rare cancers, infectious tropical diseases, and degenerative diseases.
Definition
- India does not have a definition of rare diseases because there is a lack of epidemiological data on its incidence and prevalence.
- While there is no universally accepted definition of rare diseases, countries typically arrive at their own descriptions, taking into consideration disease prevalence, its severity and the existence of alternative therapeutic options.
- In the US, for instance, a rare disease is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people.
- The same definition is used by the National Organisation for Rare Disorders (NORD) in India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
[op-ed snap] Horror in Kota
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2-Issues relating to development and management of Social sector/services relating to health,education, Human resources.
Context
Death of 100 children in the month of December at a Government Hospital in Kota highlights the state of the public health system in India.
Public health as a political agenda
- After the incident of a large number of children in such a short span, Rajasthan CM appealed not to politicise the issue.
- But it is high time the issue is in fact politicised.
- The issue of public health needs to be pushed at the top of the political agenda.
- Citizens must hold political parties accountable for the state of healthcare in the country.
Poor infrastructure
- Until the number of deaths crosses a certain threshold the poor state of infrastructure fails to attract the attention of the authorities.
- This hospital came to light like Gorakhpur Medical college where scores of children had died only after media reports of 963 child deaths.
Conclusion
Every single death in a hospital ought to be seen as a failure that needs to be addressed urgently. For that, the government needs to make public health a priority.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Health Sector – UHC, National Health Policy, Family Planning, Health Insurance, etc.
2020 as the “Year of the Nurse and Midwife”
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: WHO
Mains level: Role of nurses and midwives , ASHA
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has selected the year 2020 as the international “Year of the Nurse and Midwife”.
Year of the Nurse and Midwife
- It was decided in the honour of 200th birthday of Florence Nightingale.
- WHO said that nurses and midwives are the people who devote their lives to caring for children and mothers, looking after senior citizens and giving lifesaving immunizations.
- The declaration will help to strengthen nursing and midwifery for Universal Health Coverage.
- The declaration will also help to endorse “The NursingNow!” a three-year campaign (2018-2020) to improve health globally by raising the status of nursing.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024





























































Whеn а реrsоn nееds tо tаkе mоrе аnd mоrе сocaine tо ехреrіеnсе thе sаmе lеvеl оf hіgh, thеу аrе buіldіng uр а tоlеrаnсе fоr thе drug. Іf thеу stор smоkіng сrасk аnd bеgіn fееlіng wіthdrаwаl sуmрtоms, іnсludіng nаusеа, vоmіtіng аnd dіаrrhеа, thеіr bоdу іs dереndеnt оn thе drug.
https://www.addictionrehabcenters.com/drug-addiction/cocaine-abuse-addiction/