From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Suez Canal
Mains level: The Yemen conflict has seen an alarming erosion in the shipping industry’s confidence in the Suez Canal
Central Idea:
The article discusses the growing relevance of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) in light of the Yemen conflict and its impact on the shipping industry’s confidence in the Suez Canal. The author highlights the potential challenges and geopolitical considerations for IMEC, emphasizing its significance for trade, infrastructure, and strategic partnerships.
Key Highlights:
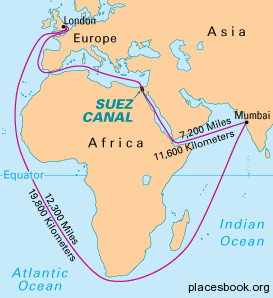
- Shippers are considering alternative routes around Africa due to concerns about the Suez Canal’s reliability amid the Yemen conflict.
- IMEC gains importance as a viable alternative, connecting Saudi Arabia to Israel and potentially transforming trade routes.
- Challenges include geopolitical complexities, opposition from the Arab Street, and alternative proposals by countries like Turkey.
- Existing rail projects in the Middle East, such as Etihad Rail and GCC Railway, align with IMEC’s objectives, targeting ports like Fujairah and Jebel Ali.
- Hydrogen pipelines and containerization through rail and road are proposed components of IMEC, contributing to decarbonization and efficient trade.
Key Challenges:
- Geopolitical hurdles, especially after the Gaza war, may impact the implementation of IMEC.
- Opposition from the Arab Street and concerns about major trade links between Saudi Arabia and Israel pose challenges.
- Turkey’s proposed alternative route and its exclusion from IMEC could complicate regional dynamics.
- The uncertain political landscape and potential changes in U.S. leadership raise questions about the project’s future.

Key Terms/Phrases:
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
- Suez Canal.
- Yemen conflict.
- Gaza war.
- Geopolitics.
- Containerization.
- Hydrogen pipelines.
- Rail freight corridors.
- Decarbonization.
- Strategic partnerships.
Key Quotes:
- “The Yemen conflict has seen an alarming erosion in the shipping industry’s confidence in the Suez Canal.”
- “Critics of IMEC say the Arab Street would simply not allow any major trade link between Saudi Arabia and Israel.”
- “Turkey, which has been explicitly left out of IMEC, has already been expressive about its irritation.”
- “IMEC will be the sort of project that would sync with a business-focused Trump if he were to become President of the U.S. again.”
Key Statements:
- The Yemen conflict has raised concerns about the reliability of the Suez Canal, prompting consideration of alternative routes like IMEC.
- Geopolitical challenges and opposition from the Arab Street may impact the realization of IMEC.
- The exclusion of Turkey and uncertainties in U.S. leadership pose additional complexities for the project.
Key Examples and References:
- Etihad Rail and GCC Railway as existing rail projects aligning with IMEC.
- The Gaza war’s impact on the potential meeting for stakeholders to flesh out IMEC details.
- The Adani stake in Haifa port and its potential role in capacity expansion, drawing parallels with the Colombo deepwater container terminal.
Key Facts/Data:
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) aims to connect Al Haditha in Saudi to Haifa in Israel.
- Containerization through rail and road in IMEC is highlighted as a significant aspect for India’s trade goals.
- IMEC promises to cut delivery schedules by 40%, emphasizing efficiency in trade.
Critical Analysis:
- The article critically evaluates the geopolitical challenges and potential impediments to the successful implementation of IMEC.
- It discusses the impact of recent conflicts and political developments on the project’s feasibility.
- The inclusion of hydrogen pipelines and containerization as components of IMEC is analyzed in the context of global trends and India’s logistics goals.
Way Forward:
- Advocate for addressing geopolitical hurdles and building consensus among stakeholders for IMEC.
- Consider potential modifications to the project to accommodate geopolitical sensitivities, such as involving Turkey.
- Emphasize the importance of IMEC in the context of global trade, decarbonization, and efficiency, especially with changing political landscapes.
- Ensure that key stakeholders, including the U.S., European nations, and Saudi Arabia, remain committed to the project’s financing and implementation.
- Explore opportunities for collaboration and financing models, drawing from successful templates like the United States International Development Finance Corporation funding for the Colombo deepwater container terminal.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
