From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SIDS Mapping; Barbados Programme of Action (1994); Mauritius Strategy (2005); and SAMOA Pathway (2014)
Why in the News?
The 4th International Conference on Small Island Developing States (SIDS-4) is underway in Antigua and Barbuda.
What are Small Island Developing States (SIDS)?
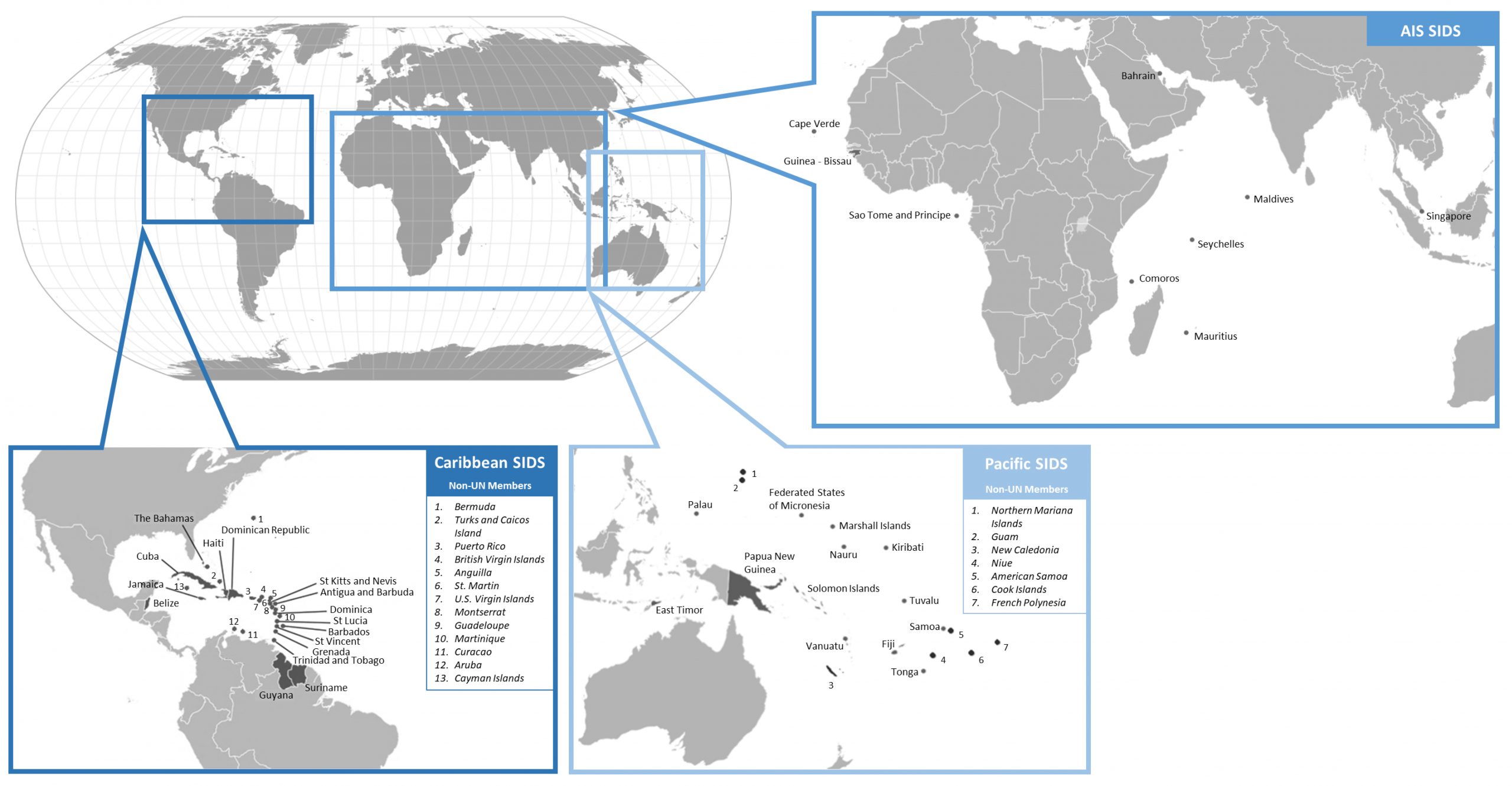
- SIDS encompass 39 States and 18 Associate Members of United Nations regional commissions, facing unique social, economic, and environmental vulnerabilities.
- SIDS are situated across three regions:
- the Caribbean,
- the Pacific
- the Atlantic, Indian Ocean, and South China Sea (AIS).
- Their distinctive challenges were acknowledged at the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
SDGs supporting SIDS
“By 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries from the sustainable use of marine resources, including through sustainable management of fisheries, aquaculture and tourism”. |
Challenges Faced by SIDS:
- Remote geography and reliance on external markets due to narrow resource bases contribute to high import/export costs.
- Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), substantially larger than landmasses, provides vital resources but poses challenges like high transportation costs and vulnerability to economic shocks.
Biodiversity and Economic Significance:
- Biodiversity sustains key industries like tourism and fisheries, often constituting over half of SIDS’ GDP.
- Beyond economic benefits, biodiversity holds aesthetic and spiritual value, providing essential services like food supply, erosion prevention, and protection from natural disasters.
UN Programmes Supporting SIDS:
Priority areas defined by SAMOA Pathway:
|
PYQ:[2021] Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024