Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trends in Bilateral Trades;
Mains level: India- China Bilateral Trade;
Why in the News?
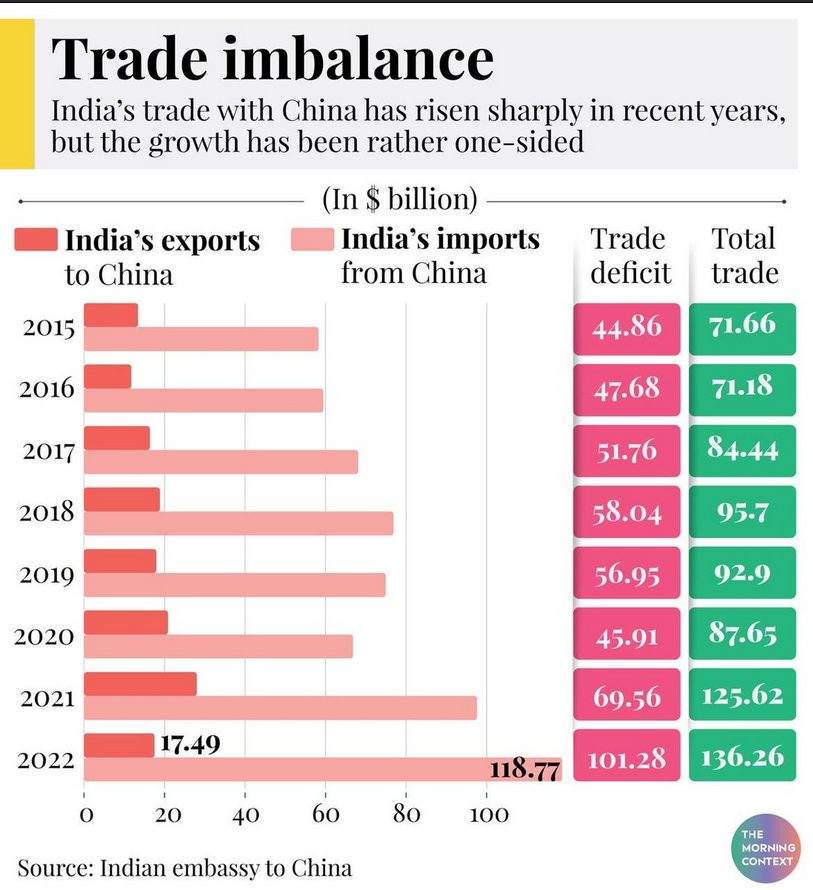
India’s imports from China crossed $101 billion in 2023-24 from about $70 billion in 2018-19, and the country’s share of India’s industrial goods imports has risen from 21% to 30% over 15 years, according to a report by the Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI).
- The data shows, it’s resulting in a cumulative trade deficit exceeding $387 Billion in the last 5 years, which is an alarming situation for the Indian government.
What is meant by Trade Deficit?
|
India’s Industrial Imports from China:
- Electronics and Telecom Sector: During April-January 2023-24, India’s import value for electronics, telecom, and electrical products was $67.8 billion, with China contributing $26.1 billion. (38.4% of the total imports)
- Machinery Sector: China contributed 39.6% of India’s imports in this category. This highlights China’s essential role as a supplier of machinery to India.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sector: India’s chemical and pharmaceutical imports were $54.1 billion, with $15.8 billion coming from China (29.2% of the total).
- MSMEs sector: Products like mobiles and data processing units, are imported by Indian MSMEs. These imports could potentially be produced domestically, highlighting gaps in India’s industrial capabilities.
Current Trade Observations concerning China and other countries:
- Rising Trade Deficit with China: India’s exports to China have stagnated at around $16 billion annually (from 2019 to 2024), while imports from China surged from $70.3 billion in 2018-19 to over $101 billion in 2023-24.
- Growth Rate of Imports: China’s share in India’s industrial product imports increased from 21% to 30% over the last 15 years. China’s exports to India grew 2.3 times faster than India’s total imports from all other countries.
- Diverse Product Imports: Chinese firms are increasingly entering the Indian market, which is expected to accelerate the import of industrial products from China. India’s imports span high to low-technology items, like smartphones, electronics, electric vehicles, and solar energy.
- Strategic Concerns: The growing trade deficit and dependence on China have profound strategic implications, affecting both economic and national security dimensions.
Way Forward:
- Supply chain diversification: India must focus on diversifying its supply chains and reducing dependency on single-country imports, especially from geopolitical competitors like China.
- Boosting R&D: Increase investment in research and development for electronics, semiconductors, and machinery to foster innovation and improve domestic production capabilities.
- Incentivizing Production: Provide tax incentives, subsidies, and grants to local manufacturers of electronics, data processing units, and semiconductor devices to encourage production and reduce import dependency.
Mains PYQ:
Q China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia’, In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbor. (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
