| PYQ Relevance: Mains: Q) The setting up of a Rail Tariff Authority to regulate fares will subject the cash-strapped Indian Railways to demand subsidy for obligation to operate non-profitable routes and services. Taking into account the experience in the power sector, discuss if the proposed reform is expected to benefit the consumers, the Indian Railways or the private container operators. (UPSC CSE 2014) Q) One of the intended objectives of Union-Budget 15-18 is to ‘transform, energize and clean India’. Analyze the measures proposed in the Budget 15-18 to achieve the objective. (UPSC CSE 2017) Prelims: With reference to bio-toilets used by the Indian Railways, consider the following statements: 1) The decomposition of human waste in the bio-toilets is initiated by a fungal inoculum. 2) Ammonia and water vapour are the only end products in this decomposition which are released into the atmosphere. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (UPSC CSE 2015) (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Note4Students:
Prelims: Government Initiatives for Indian Railways;
Mains: Indian Railways;
Mentor comment: More than 160 years ago, railways were introduced in the Indian subcontinent and were first initiated in 1853. The British Governor-General Lord Dalhousie played the most important part in introducing railways in India. Today, India has the 4th largest railway system in the world (after the US, Russia, and China). The railways operate 13,523 passenger trains and 9,146 freight trains daily. As of Feb 2024, 61,813 km length of the Broad-Gauge network has been electrified. With this, Indian Railways is rapidly progressing towards its target of 100% electrification and becoming the largest green railway network in the world. Indian Railways (IR) is rapidly progressing to accomplish its Mission. However, India during recent times due to the increase in population demand, is unable to cope with priority clauses of maintaining safety and standards.
Let’s learn.
–
Why in the News?
A railway pilot (driver) faced disciplinary action for following safety rules and not speeding to minimize delays to passenger trains after his locomotive failed, highlighting an attitude of prioritizing punctuality over safety in the Indian Railways.
| According to the Performance Audit on Derailment in Indian Railways, nearly 3/4th of 217 consequential train accidents across the country between 2017-18 and 2020-21 were caused by derailments. |
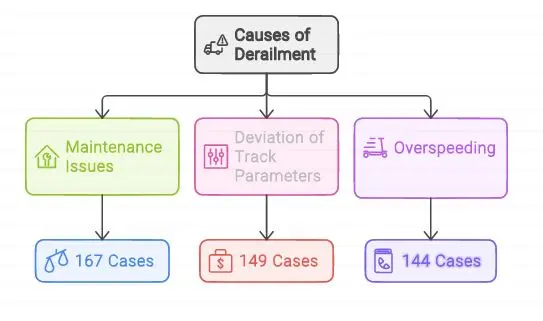
Major challenges of Indian Railway Runways:
- Unmanned level crossings (UMLCs): UMLCs are places where railway tracks are crossed without any barriers or signals to regulate traffic.
- UMLCs accounted for 16% of all train accidents in India (2018-19). Although Indian Railways have eliminated all the UMLCs on broad gauge routes, there are still many Manned Level Crossings (MLCs) that pose a risk of accidents.
- In February 2024, a train consisting of two diesel locomotives (both unmanned), and 53 wagons, with no brakes, rolled out of Kathua station.
- Signal Failures: Signaling failures can lead to trains running on the wrong track, colliding with other trains or stationary objects, or overshooting stations.
- The recent Visakhapatnam-Rayagada train accident was reportedly caused by non-communication and the lack of audio recording of conversations between station masters and loco pilots.
- The media analyzed the accident and highlighted the broader issues with railway safety, such as inadequate signaling and telecommunications infrastructure, and the need for accountability and technological improvements. (In fact, the Right to Information (RTI) Act 2005 denies giving this information)
- Human Errors: According to the Final Report of the CRS (Minister for Railways), railway staff are prone to human errors due to fatigue, negligence, corruption, or disregard for safety rules and procedures.
- It can result in wrong signaling, miscommunication, distraction, overspeeding, or overlooking defects or hazards that affect their performance and coordination.
What are other troubling questions?
- Lack of Professionalism in Railway Accident Investigations: Railway authorities are majorly exposed for unprofessional handling of serious accident investigations. Blaming reckless crew diverts attention from the administration’s role in improper training and ineffective monitoring.
- Issues Concerning Loco Pilots: Nearly 10% of vacancies in the loco pilot cadre, are leading to regular breach of duty hour rules. Continuous night shifts, and inadequate rest, point to the need for focused attention on loco pilots’ issues.
What did the CAG Recommended? (Way Forward)
- Develop a strong monitoring mechanism to ensure timely implementation of maintenance activities, adopting fully mechanized methods and improved technologies.
- Railway administration must follow the guiding principles for the deployment of RRSK (Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh) funds.
- Indian Railways should prepare a Detailed Outcome Framework for each item of safety work.
- Ensure strict adherence to scheduled timelines for conducting and finalizing accident inquiries.


 UPSC 2026 Mentorship - April Batch Launch
UPSC 2026 Mentorship - April Batch Launch