From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Balance of Payment; Current Account deficit; Capital Account Deficit;
Mains level: Impact of BOP on Indian economy;
Why in the news?
India’s current account showed a surplus in Q4 of 2023-24. However, current account surpluses are not always beneficial, and deficits are not inherently detrimental.
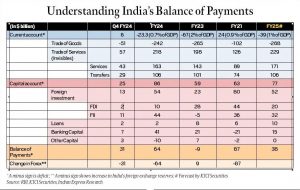
Latest Data from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
|
What is Balance of Payments (BoP)?
- The BoP is a ledger of a country’s transactions with the rest of the world, recording all monetary transactions between residents of a country and the rest of the world.
- It shows the amount of money flowing into and out of the country, indicating the relative demand for the rupee compared to foreign currencies (usually in dollar terms).
Constituents of the BoP
The BoP has two main accounts: the Current Account and the Capital Account.
- Current Account: It covers the trade in goods (exports and imports), trade in services (transportation, tourism, licensing, etc.), Income (wages, interest, dividends, etc.), and current transfers (remittances, foreign aid, etc.).
- Trade of Goods (Merchandise Account): Records export and import of physical goods. A trade deficit occurs when imports exceed exports.
- Invisibles of Trade: Includes services (banking, insurance, IT, tourism), transfers (remittances), and income (earnings from investments). These are transactions not visible like physical goods.
- Net Balance: The sum of the merchandise trade and invisible trade determines the current account balance. Q4 showed a surplus in the current account due to a surplus in invisible despite a trade deficit.
- Capital Account: It covers debt forgiveness, migrants’ transfers of financial assets, taxes on gifts and inheritances, and ownership transfers of fixed assets.
- Investments: Captures transactions related to investments such as Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investments (FII).
- Net Balance: Q4 showed a net surplus of $25 billion in the capital account.
Impact on the Indian Economy:
- Exchange Rate Stability: The current account surplus in Q4 helped stabilize the exchange rate of the rupee. By absorbing excess dollars, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) prevented excessive appreciation of the rupee, which helps maintain the competitiveness of Indian exports.
- Improved Sovereign Ratings: A current account surplus can positively impact India’s sovereign credit ratings, as it indicates stronger external financial health and reduces reliance on foreign borrowing.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: The surplus contributed to an increase in India’s foreign exchange reserves, enhancing the country’s ability to manage external shocks and providing a buffer against global economic uncertainties.
- Investment Climate: A surplus in the capital account, driven by Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investments (FII), indicates investor confidence in the Indian economy, potentially leading to more robust economic growth and development.
- Economic Health Indicators: Despite the Q4 surplus, the annual current account deficit suggests robust domestic demand and investment needs. This aligns with a growing economy that requires imports of capital goods to enhance production capacity and future export potential.
Way forward:
- Enhance Export Competitiveness: India should focus on boosting its export sector by diversifying export products and markets, improving product quality, and providing incentives for export-oriented industries.
- Promote Sustainable Foreign Investment: Encouraging sustainable and long-term foreign investments, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, technology, and renewable energy, can strengthen the capital account.
Mains PYQ:
Q Craze for gold in Indian has led to surge in import of gold in recent years and put pressure on balance of payments and external value of rupee. In view of this, examine the merits of Gold Monetization scheme. (UPSC IAS/2015)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
