Civil Aviation Sector in India
In India, a beginning in the air transport was made in the year 1920, when the government first decided to prepare air routes between Mumbai and Kolkata. The civil aviation work actually started in in 1924-25, but the progress was slow until the outbreak of the second World War.
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited: The Hindustan Aircraft (now Hindustan Aeronautics Limited), was founded in 1940. It was started at Bangalore (now Bengaluru) as a repair, overhauling and assemblage depot, has now grown into an important manufacturing plant. It has designed and manufactured trainer air-crafts. It belongs to the aerospace and defence industry. It is managed by Ministry of Defence.


Civil Aviation Recent Developments: A Snapshot


India is the 9th largest civil aviation market in the world, In FY17, domestic passenger traffic witnessed a growth rate of 21.5 per cent
In FY17, airports in India witnessed a domestic passenger traffic of about 205 million people.
Investments worth US$ 6 billion are expected in the country’s airport sector in 5 years
India’s civil aviation market is set to become the world’s 3rd* largest by 2020 and expected to be the largest by 2030
Growth Potential & Drivers of Indian Aviation Industry

Airport Authority of India

Airports & Airstrips in India

Major Airline Operator in India

Private Sector Participation in Airport Development
Until 2013, AAI was the only major player involved in developing and upgrading airports in India.
Post liberalisation, private sector participation in the sector has been increasing.
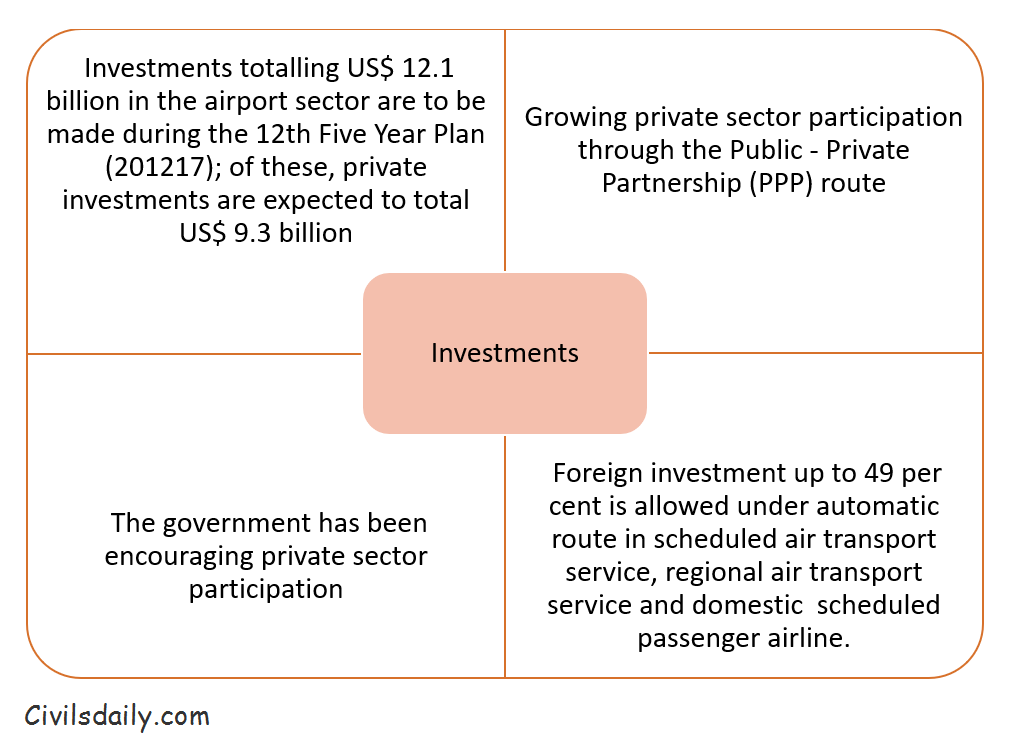
Private sector investment increased to US$9.3 billion during the 12th Five Year Plan from US$ 5.5 billion in the previous plan.


- Recourse to the Public Private Partnership (PPP) model has boosted private sector investments in airports
- PPP route for five international airports (Delhi, Mumbai, Cochin, Hyderabad, Bengaluru) most noteworthy
- In Union Budget 2017, Government of India has decided to develop select airports in tier 2 cities under PPP model in order to attract investments from private players.
- Increasing share of private sector in equity component of major airports:
- 74 per cent private shareholding in IGI Airport (Delhi) – owned majorly by GMR (54 per cent), Fraport AG (10 per cent), Eraman Malaysia (10 per cent); rest of the shares owned by AAI
- 74 per cent private shareholding in CSI Airport (Mumbai) – owned majorly by GVK (50.5 per cent), Bid Services Division (Mauritius) Ltd. (13.5 per cent), ACSA Global (10 per cent); rest of the shares owned by AAI
- 74 per cent private shareholding in RGI Airport (Hyderabad) – owned majorly by GMR (63 per cent), Malaysia Airports Holdings Berhad (11 per cent); rest of the shares owned by Government of India (13 per cent) and Government of Andhra Pradesh (13 per cent)
- 74 per cent shareholding in Kempagowda International Airport (Bengaluru) – owned majorly by Siemens Project Ventures, Germany (40 per cent), Unique (Flughafen Zurich AG) Zurich Airport, Switzerland (17 per cent), L&T, India (17 per cent); rest of the shares owned by AAI (13 per cent) and KSIIDC, which is an agency owned by the state of Karnataka, India (13 per cent).
In March 2017, by selling off 2 offshore bonds, GMR plans to raise US$250-300 million for refinancing their debt. In June 2017, GMR announced plans to refinance loans and divest assets in road and power sectors to cut debt so as to invest up to Rs. 7,400 (US$ 1.15 billion) crore to expand Delhi and Hyderabad airports.
Successful PPP Model Airports in India
Presently India has 5 PPP airports each at Mumbai, Delhi, Cochin, Hyderabad and Bengaluru, which together handle over 55 per cent of country’s air traffic.
Government of India has approved 15 greenfield PPP projects which are expected to increase the air traffic in India. These projects would be setup in Goa, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, Bijapur, Gulbarga, Karnataka, Kerala, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Sikkim, Puducherry and Uttar Pradesh.

Government Initiatives in Civil Aviation Sector





