Indian Navy Updates
INS Varsha Naval Base
Why in the News?
India is set to operationalise INS Varsha, a highly strategic naval base designed specifically to house nuclear-powered submarines, on the eastern coast near Rambilli in Andhra Pradesh by 2026.
About INS Varsha
- INS Varsha is being developed as a specialized base to house India’s growing fleet of nuclear-powered submarines, including both Nuclear-Powered Ballistic Missile Submarines (SSBNs) and Nuclear-Powered Attack Submarine (SSNs).
- It will be situated near the coastal village of Rambilli, about 50 km south of Visakhapatnam, home to the Eastern Naval Command.
- The naval bases lies on the confluence of Sarada and Varaha rivers.
- The facility will have underground pens and tunnels to ensure stealthy operations for nuclear submarines.
- This design will allow submarines to enter and exit the base undetected, maintaining their stealth, particularly important for SSBNs which carry nuclear missiles during long patrols.
- The base will cover an area of 20 square kilometers and is designed to accommodate at least 10 nuclear submarines.
- Like China’s nuclear submarine base at Hainan Island (in the South China Sea), INS Varsha will be situated in waters that allow submarines to operate without detection from satellite surveillance.
Project Varsha
|
| [UPSC 2016] Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently?
(a) Amphibious warfare ship (b) Nuclear-powered submarine (c) Torpedo launch and recovery vessel (d) Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Exercise ‘AIKEYME’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Aikeyme
Why in the News?
India is set to strengthen its military and maritime ties with African nations through two significant initiatives—Exercise Aikeyme (Africa-India Key Maritime Engagement) and IOS Sagar (Indian Ocean Ship Sagar).
About Exercise Aikeyme
- Aikeyme is India’s first-ever multilateral naval exercise with 10 African nations, aimed at improving maritime cooperation, enhancing maritime security, and addressing regional threats.
- It will be held off Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania, from April 13 to 18, 2025.
- The nations taking part include Tanzania (co-host), Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles, and South Africa.
- It is aimed at increasing interoperability between the Indian Navy and African navies, with a focus on combating common threats like piracy and drug trafficking.
- The goal is to make this exercise a biennial event and expand participation in future editions to include West African nations.
- Key Features:
- Visit Board Search and Seizure (VBSS) drills.
- Arms firing exercises.
- Helicopter operations.
- Search and rescue missions.
- Table-top and command post exercises on anti-piracy operations and information-sharing.
IOS Sagar (Indian Ocean Ship) Initiative
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Exercise Varuna
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Varuna
Why in the News?
India and France recently conducted the 23rd edition of Exercise Varuna, a key bilateral naval exercise aimed at enhancing interoperability and combat readiness between the two countries’ naval forces.
About Exercise Varuna
- Exercise Varuna is a bilateral naval exercise between India and France.
- It was first initiated in 1993 and officially named Varuna in 2001.
- The exercise focuses on enhancing combat readiness, improving interoperability, and deepening maritime security cooperation between the two nations.
- It spans multiple domains, including air, surface, and sub-surface operations, with a strong emphasis on anti-submarine warfare (ASW) and air combat drills.
- Key Highlights:
- The 2025 edition took place from March 19-22 off the coast of Goa, with participants such as INS Vikrant (India) and Charles de Gaulle (France).
- This year’s exercises included aircraft carrier operations, ASW drills, and joint surface warfare operations.
- Rafale-M (French Navy) and MiG-29K (Indian Navy) fighters participated in advanced air defence and mock air-to-air combat scenarios.
- Indian Scorpene-class submarines acted as aggressors, while French and Indian frigates protected high-value assets, including the French oiler Jacques Chevallier.
- These drills enhanced underwater domain awareness and improved ASW tactics.
Other Notable India-France Military Exercises:
|
| [UPSC 2024] Which of the following statements about ‘Exercise Mitra Shakti-2023’ are correct?
1. This was a joint military exercise between India and Bangladesh. 2. It commenced in Aundh (Pune). 3. Joint response during counter-terrorism operations was a goal of this operation. 4. Indian Air Force was a part of this exercise. Select the answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 1 and 4 (c) 1 and 4 (d) 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] TROPEX-25
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TROPEX-25
Why in the News?
The 2025 edition of TROPEX is currently underway in the Indian Ocean Region, involving all operational Indian Naval units along with significant participation from the Indian Army, Indian Air Force (IAF), and the Indian Coast Guard (ICG).
About Theatre Level Operational Exercise (TROPEX)
- TROPEX is the Indian Navy’s flagship biennial operational-level exercise, designed to test and enhance India’s maritime defense capabilities.
- It is conducted in the Indian Ocean Region with participation from the Indian Navy, Indian Army, Indian Air Force (IAF), and Indian Coast Guard (ICG).
- It was first held in April 2005.
- TROPEX-25 is being conducted over a three-month period from January to March 2025 in multiple phases:
- Harbour Phase: Focuses on strategic planning, joint training, and coordination before moving to sea operations.
- Sea Phase: Simulates real-time combat scenarios to assess the Navy’s operational readiness.
- Cyber and Electronic Warfare Operations: Integrates modern cybersecurity and electronic warfare tactics to counter digital threats.
- Live Weapon Firings: Includes real-world missile and torpedo firings to test combat effectiveness.
- Amphibious Exercise (AMPHEX): Conducts joint land-sea operations, involving amphibious landings and coastal defence drills.
Mandate and Significance of TROPEX-25
TROPEX-25 plays a pivotal role in:
- Strengthening India’s maritime dominance in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Enhancing interoperability and joint warfighting capabilities among the Navy, Army, Air Force, and Coast Guard.
- Testing real-world combat readiness in dynamic operational environments.
- Securing national maritime interests through proactive military preparedness.
- Projecting India’s naval power to safeguard maritime trade routes and counter emerging threats.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Commissioning of INS Nilgiri, INS Surat, and INS Vaghsheer
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Features of the Ships/Vessels

Why in the News?
Three frontline combatants—INS Nilgiri, INS Surat, and INS Vaghsheer—were commissioned into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai.
About the Ships/Vessels
| Details | |
| INS Nilgiri |
|
| INS Surat |
|
| INS Vaghsheer |
|
PYQ:[2016] Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (a) Amphibious warfare ship |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
What is Coastal Security Scheme (CSS)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Coastal Security Scheme
Why in the News?
Non-operational patrolling boats, insufficient funds for training, and manpower shortages are among the challenges highlighted by 13 coastal states and Union Territories during a review of the Coastal Security Scheme (CSS) phases I and II.
What is the Coastal Security Scheme?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Commissioning of INS TUSHIL
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS TUSHIL

Why in the News?
INS Tushil, a multi-role stealth guided missile frigate, is set to be commissioned by the Indian Navy at Kaliningrad, Russia.
About INS Tushil:
| Details |
Development of INS Tushil:
|
| Special Features |
|
| Significance |
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
India and Japan sign agreement for UNICORN masts for naval warships
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UNICORN Mast
Why in the News?
India and Japan have signed a Memorandum of Implementation (MoI) for the co-development and co-production of the UNICORN (Unified Complex Radio Antenna) mast for Indian Naval warships.
What is the UNICORN Mast?
|
Objectives behind the Mission:
- Enhance Naval Stealth: Improve stealth by reducing electronic and radar signatures.
- Strengthen Defence Ties: Foster India-Japan collaboration in co-developing advanced defence systems.
- Increase Operational Efficiency: Improve radar and communication for better detection and readiness.
- Promote Indigenous Development: Support India’s self-reliance in defence tech with BEL involvement.
Significance of this Mission:
- Japan’s first defence tech export to India under the 2015 agreement.
- Equips Indian Navy warships with advanced stealth technology.
- Enhances regional maritime security and deterrence in the Indo-Pacific.
- Promotes technology sharing and innovation in India’s defence sector, boosting indigenous production.
PYQ:[2016] Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (a) Amphibious warfare ship |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise SIMBEX 2024
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise SIMBEX 2024
Why in the News?
The 31st edition of the Singapore India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX) is being held at the Eastern Naval Command in Visakhapatnam.
About Exercise SIMBEX:
| Details | |
| History |
|
| Evolution | Progressed from anti-submarine warfare to include maritime security, anti-air, and anti-surface warfare. |
| Objectives | • Strengthen strategic partnership between India and Singapore • Enhance interoperability and maritime domain awareness • Foster cooperation to tackle shared maritime challenges. |
| Phases | Harbour Phase: • Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEEs) for knowledge sharing • Cross-deck visits and sports fixtures • Pre-sail briefings between both navies Sea Phase: • Advanced naval drills including live weapon firings • Anti-submarine warfare (ASW) training • Anti-surface and anti-air operations • Seamanship evolutions and tactical manoeuvres. |
| Significance |
|
PYQ:[2024] Which of the following statements about the Exercise Mitra Shakti-2023 is/ are correct?
Select the answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 1 and 4 (c) 1 and 4 (d) 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Second edition of Navika Sagar Parikrama
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Navika Sagar Parikrama
Why in the News?
The second edition of Navika Sagar Parikrama, a global circumnavigation by sailboat was flagged off by Navy Chief at INS Mandovi in Goa.

About Navika Sagar Parikrama:
| Details | |
| Expedition |
|
| Objective | Promotes women’s empowerment, gender equality, oceanic research, and Indian maritime traditions. |
| First Edition |
|
| Second Edition | Launched on October 2, 2024, with two women officers, Lieutenant Commander Dilna K. and Lieutenant Commander Roopa A., setting sail from INS Mandovi, Goa. |
| Agencies Involved |
|
| Route | Divided into five legs with four stopovers: 1. Goa to Fremantle, Australia 2. Fremantle to Lyttleton, New Zealand 3. Lyttleton to Port Stanley, Falkland Islands 4. Port Stanley to Cape Town, South Africa 5. Cape Town to Goa, India |
PYQ:[2016] Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (a) Amphibious warfare ship (b) Nuclear-powered submarine (c) Torpedo launch and recovery vessel (d) Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
INS Arighat: India’s second nuclear sub
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About INS Arighaat;
Why in the News?
India’s second nuclear submarine, the Arighaat, was officially commissioned into the Indian Navy in Visakhapatnam, following rigorous trials conducted over the past few months.
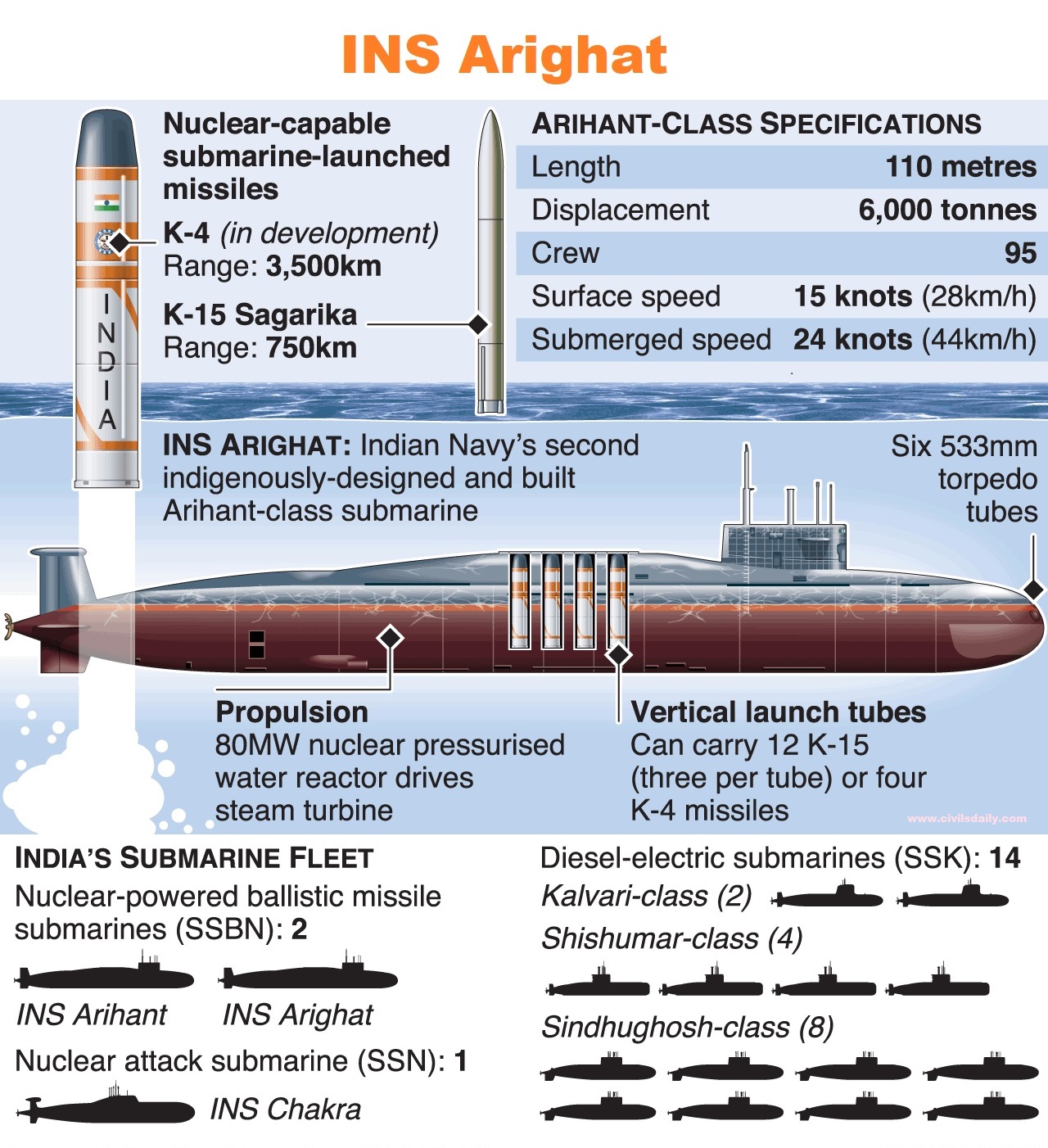
Status of Navy’s Submarines in India:
|
About the newly inducted INS Arighaat
- INS Arighaat is a 6,000-tonne Arihant-class ballistic missile submarine, which will join its predecessor, INS Arihant, as a vital component of India’s nuclear triad.
- The submarine can carry up to 12 K-15 SLBMs with a range of approximately 750 km or four K-4 SLBMs exceeding 3,500 km.
- It is powered by an 83 MW pressurized light-water nuclear reactor, allowing it to remain submerged for extended periods without surfacing compared to the diesel-electric submarine.
- It will enhance India’s nuclear deterrence, support strategic balance in the region, and play a crucial role in national security.
How does it significantly strengthen India’s nuclear triad?
- Enhances Second-Strike Capability: With two nuclear submarines now operational, India can maintain a constant presence of a submarine patrolling its waters, ready to launch a nuclear strike at short notice in retaliation.
- Expands Missile Reach: INS Arighaat is equipped with indigenously developed K-15 missiles with a range of over 700 km and long-lasting availability underwater due to a nuclear-powered engine without surfacing.
- From the South China Sea, these submarines can potentially target locations in China, including its capital Beijing.
- Both of this major developments will provide India with a more balanced and robust nuclear deterrent capability across all three domains – land, air, and sea.
Way forward:
- Indigenous Submarine Development: Accelerate the development and commissioning of indigenous SSBNs (Submersible Ship Ballistic Missile Nuclear) and advanced SLBMs (Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles) to further strengthen India’s strategic autonomy and ensure sustained deterrence capabilities.
- Strategic Partnerships and Modernization: Enhance collaboration with global naval powers for technology transfers and expertise while modernizing the current submarine fleet to ensure continued operational readiness and address emerging maritime security challenges.
Mains PYQ:
Q What are the maritime security challenges in India? Discuss the organisational, technical and procedural initiatives taken to improve maritime security. (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] INS SHALKI
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS SHALKI
Why in the News?
- Indian Navy’s submarine INS Shalki, recently docked at Colombo Port on its two day visit to Sri Lanka.
- This visit comes against the backdrop of China’s persistent attempts to enhance its strategic and military influence over the island nation.
About INS SHALKI
- INS Shalki is a Shishumar class diesel-electric submarine, commissioned into the Indian Navy on 07 Feb 1992.
- Shishumar class submarines are an Indian variant of the Type 209 submarines developed by the German yard Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft under the internal designation “Type 1500”.
- This is the first ever submarine to be built in India.
- It was constructed under licence by the Mazgaon Dock Limited, Mumbai.
Significance of Sri Lanka Visit
- India sends submarines to a handful of countries with whom it has close defence and strategic ties.
- This is the third submarine to visit Sri Lanka after the visit of INS Vagir and INS Karanj in June 2023 and February 2024, respectively.
- India has been expanding its defence and strategic ties with Sri Lanka amid concerns over China’s attempts to increase its military presence in the Indian Ocean.
- Countering Chinese presence:
-
- The docking of the Chinese missile and satellite tracking ship ‘Yuan Wang’ at Hambantota port in August 2022 had triggered a diplomatic row between India and Sri Lanka.
- Another Chinese warship docked at the Colombo port in August last year.
PYQ:[2017] Consider the following in respect of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): 1. Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy. 2. IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] INS Sunayna in Port Victoria, Seychelles
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Sunayna, SAGAR Doctrine
Why in the News?
- INS Sunayna, an Offshore Patrol Vessel based at Southern Naval Command, entered Port Victoria, Seychelles.
- The ship will undertake joint EEZ surveillance with the Seychelles Coast Guard during the deployment.
- The visit is aimed at further strengthening mutual cooperation in line with the vision of SAGAR (Security & Growth for All in the Region).
About INS Sunayna
- INS Sunayna is the second Saryu-class patrol vessel of the Indian Navy launched in 2009.
- It was designed and constructed indigenously by the Goa Shipyard Limited.
- It is designed to undertake fleet support operations, coastal and offshore patrolling, ocean surveillance and monitoring of sea lines of communications and offshore assets and escort duties.
Key operations undertaken
- In June 2018 she was deployed to Yemen’s Socotra Island as part of “Operation Nistar“, an HADR mission to evacuate around 38 stranded Indian nationals in/around Socotra after a cyclone hit the area.
- INS Sunayna, along with INS Chennai, was sent to the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman in June 2019 to protect Indian shipping interests amid tensions in the Strait of Hormuz.
Back2Basics: SAGAR Strategy
The primary objectives of SAGAR include:
|
PYQ:[2022] What are the maritime security challenges in India? Discuss the organisational, technical and procedural initiatives taken to improve maritime security. [2017] Consider the following in respect of the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): 1. Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy. 2. IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Why India needs a third aircraft carrier
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Future Scope and Concerns associated with Indigenous Aircraft Carrier-2 (IAC-2)
Why in the news?
Recent reports from the media suggest that the Indian Navy’s persistent request for a third aircraft carrier is edging closer to reality, as Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) prepares to commence construction on an additional Vikrant-class platform weighing approximately 40,000 tonnes.
About Indigenous Aircraft Carrier-2 (IAC-2)
|
Future Scope
- Operational Versatility: IAC-2 will enhance the Indian Navy’s operational flexibility, enabling it to conduct a wide range of missions including power projection, maritime security, and humanitarian assistance. The carrier’s advanced capabilities and modern technologies will ensure its effectiveness in addressing evolving maritime challenges.
- Strategic Deterrence: IAC-2 will serve as a key deterrent against potential adversaries, bolstering India’s maritime deterrence posture and signalling its commitment to safeguarding its maritime interests. Its presence will reinforce India’s position as a major maritime power in the Indo-Pacific region, contributing to regional stability and security.
- Technological Advancement: The construction and operation of IAC-2 will drive technological innovation and advancement in India’s indigenous defence industry. It will stimulate research and development efforts, fostering self-reliance and technological sovereignty in naval defence capabilities.
Concerns associated
- Budgetary issues: The estimated cost of constructing and operating IAC-2 is high, raising concerns about budgetary constraints and the allocation of resources amidst competing defence priorities.
- Operational Vulnerabilities: IAC-2 may face challenges from evolving anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) strategies employed by potential adversaries such as China and Pakistan. The carrier’s large size and visibility make it susceptible to modern maritime warfare tactics, including advanced missile systems and submarine threats, potentially compromising its operational effectiveness.
- Strategic Alignment: Questions may arise about the carrier’s role and relevance in addressing contemporary security threats and whether alternative defence investments would provide better national security and strategic deterrence returns.
Upgrading Capabilities as a Solution
- Enhanced Airborne Capabilities: The Indian Air Force (IAF) can project maritime power using aircraft like the SEPECAT Jaguar IM/IS and Sukhoi Su-30MKI fighters, which can carry advanced maritime strike weapons. The Su-30MKI squadron, equipped with BrahMos-A supersonic cruise missiles, enhances maritime strike capabilities.
- Strengthening Island Defenses: Upgrading the military capabilities of the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago could create an A2/AD maritime ‘exclusive zone’, deterring Chinese naval activities.
- Balanced Force Development: Diversifying investments to upgrade existing surface combatants, submarines, and air assets can provide a balanced approach to enhancing naval capabilities. Ensuring adequate funding for other critical areas like mine counter-measures, maritime patrol aircraft, and naval utility helicopters is essential for comprehensive maritime security.
Conclusion: While the IAC-2 represents a significant advancement in India’s naval capabilities, addressing financial constraints, strategic vulnerabilities, and diversifying investments in maritime and airborne assets are crucial for achieving a robust and balanced defence strategy.
Mains PYQ:
Q What are the maritime security challenges in India? Discuss the organisational, technical and procedural initiatives taken to improve maritime security. (UPSC IAS/2022)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Launching of LSAM 20 (Yard 130)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LSAM 20;
Mains level: NA
Why in the News?
The Indian Navy has inducted the ‘Ammunition Cum Torpedo Cum Missile Barge, LSAM 20 (Yard 130) into its fleet.
What is LSAM 20?
- LSAM 20 (Yard 130) is the Ammunition Cum Torpedo Cum Missile Barge (Storage) inducted by the Indian Navy. (built by MSME Shipyard, M/s Suryadipta Projects Pvt Ltd, Thane).
- LSAM 20 facilitates transportation, embarkation, and disembarkation of articles/ammunition to IN Ships.
- These Barges are indigenously designed and built under relevant Naval Rules and Regulations of the Indian Register of Shipping.
Objective
- A Torpedo Cum Missile Barge is a specialized vessel used by the Indian Navy to transport various types of ammunition, torpedoes, and missiles to operational areas.
- These barges play a crucial role in providing logistical support to naval vessels by ensuring the uninterrupted transportation of essential military supplies.
PYQ:[2016] Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (a) Amphibious warfare ship (b) Nuclear-powered submarine (c) Torpedo launch and recovery vessel (d) Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] SPACE Testing & Evaluation hub for Sonar Systems
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SPACE Testing, Working of SONAR
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
A state-of-the-art SPACE testing and evaluation hub for sonar systems, designed for the Indian Navy, was inaugurated by DRDO.
About Submersible Platform for Acoustic Characterisation and Evaluation (SPACE)
- The SPACE is located at the Underwater Acoustic Research Facility in Kulamavu, Idukki, Kerala.
- It is developed by the Naval Physical & Oceanographic Laboratory of DRDO.
- It is set to become a premier testing and evaluation hub for sonar systems deployed on various Indian Navy platforms, including ships, submarines, and helicopters.
Key Features of SPACE:
- SPACE comprises two distinct components:
- Floating Platform on the water surface and
- Submersible platform capable of descending to depths of up to 100 meters using winch systems.
- After completing operations, the submersible platform can be winched up and docked with the floating platform, ensuring efficient utilization of resources.
Functions and Capabilities:
- The primary function of SPACE is the evaluation of complete sonar systems, facilitating rapid deployment and retrieval of scientific packages such as sensors and transducers.
- It will serve for surveying, sampling, and data collection of air, surface, mid-water, and reservoir floor parameters utilizing modern scientific instrumentation.
- It will address the data processing and sample analysis requirements, ushering in a new era of Anti-Submarine Warfare research capabilities.
What is SONAR?
Here’s how it works:
|
PYQ:[2020] “The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft,” The experiment in question refers to- (a) Voyager-2 (b) New Horizons (c) LISA Pathfinder (d) Evolved LISA |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise IMT TRILAT- 2024
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise IMT TRILAT- 2024
Mains level: NA
Why in the news-
- INS Tir and INS Sujata are set to participate in the second edition of the India-Mozambique-Tanzania (IMT) Tri-Lateral (TRILAT) Exercise.
Exercise IMT TRILAT- 2024
- It is a biennial exercise conducted by the navies of India, Mozambique and Tanzania.
- The first edition of the exercise took place in October 2022.
- It seeks to enhance India’s commitment to maritime security and cooperation in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Through this joint exercise, the Indian Navy aims to foster mutual trust and understanding with its maritime partners in Mozambique and Tanzania.
Phases of the Exercise
- Harbour Phase: Activities include joint harbour training such as Damage Control, Fire Fighting, Visit Board Search and Seizure procedures, Medical Lectures, Casualty Evacuation, and Diving operations.
- Sea Phase: Focuses on countering asymmetric threats, Visit Board Search and Seizure procedures, boat handling, manoeuvres, firing exercises, and joint EEZ surveillance.
PYQ:
2017: Consider the following in respect of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS):
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Practice MCQ:
Consider the following statements about Exercise IMT TRILAT:
- It is an annual exercise conducted by the navies of India, Mozambique and Tanzania.
- The first edition of the exercise took place in October 2022.
Which of the given statements is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
MH 60R Seahawk: 1st squadron commissioned into Indian Navy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MH 60R Seahawk

In the news
- The Indian Navy describes the commissioning of the MH-60R Seahawk squadron as a pivotal moment in India’s defense modernization journey.
About MH 60R Seahawk
- Maritime Variant: The MH-60R Seahawk is the maritime variant of the Black Hawk helicopter, procured through a 24-aircraft foreign military sales contract with the US government in February 2020.
- Operational Capabilities: It is designed for various operations including anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, search and rescue, and medical evacuation.
- Arsenal: These helicopters offer advanced weapons, sensors, and avionics suite tailored to India’s maritime security needs.
- Armament: Armed with AGM-114 Hellfire missiles, MK 54 torpedoes, and advanced precision weapons, the helicopters provide formidable firepower.
Significance
- Enhanced Blue-Water Capabilities: The commissioning enhances India’s blue-water capabilities, extending operational reach across vast maritime domains.
- Maritime Security: It aligns with the PM’s vision of ensuring security and growth for all in the region (SAGAR), reinforcing the Indian Navy’s dedication to fortifying maritime security.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
INS Jatayu: India’s new Naval Base in Lakshadweep
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Jatayu, Eight Degree Channel
Mains level: Read the attached story
In the news
- The Naval Detachment Minicoy will transition into INS Jatayu, an upgraded naval base, symbolizing India’s commitment to bolstering security infrastructure in the strategic Lakshadweep Islands.
- This development underscores the Indian Navy’s strategic imperative to fortify its presence in the region.
About INS Jatayu
- Upgrade to Naval Base: INS Jatayu will be elevated to a fully-fledged naval base, equipped with essential infrastructure such as an airfield and housing facilities.
- Strategic Location: Situated amidst vital Sea Lines of Communications (SLOCs), the Lakshadweep Islands hold immense strategic importance, serving as a gateway to the Indian Ocean.
- Enhanced Operational Capability: The transformation of Naval Detachment Minicoy into INS Jatayu signifies a significant augmentation of the Navy’s operational capabilities in the region.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: Against the backdrop of evolving geopolitical dynamics, particularly China’s increasing influence in the Indian Ocean Region, the establishment of INS Jatayu assumes greater significance.

A Strategic Asset: Lakshadweep Archipelago
- Geographical Context: Lakshadweep, comprising 36 islands, lies strategically between the Indian mainland and the Maldives, serving as a vital link in India’s maritime security architecture.
- Maritime Highways: Minicoy, in particular, is strategically positioned along key maritime highways, including the Eight Degree Channel and the Nine Degree Channel.
Future Prospects and Challenges
- Operational Implications: The establishment of INS Jatayu will bolster the Navy’s operational reach and responsiveness, enabling effective anti-piracy and anti-narcotics operations in the western Arabian Sea.
- Ecological Considerations: The fragile ecology of the island poses challenges for infrastructure development, necessitating meticulous planning and environmental clearances.
- Operational Expansion: The proposed airfield at INS Jatayu will facilitate operations for various aircraft, bolstering the Navy’s surveillance capabilities and extending its operational reach.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Trilateral Exercise Dosti-16 kicks off
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Dosti
Mains level: Not Much

Introduction
- Indian and Sri Lankan coast guard ships recently arrived in the Maldives to participate in the trilateral coast guard exercise Dosti 16.
Exercise Dosti
- Trilateral Collaboration: Dosti is a trilateral coast guard exercise involving India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives.
- Biennial Event: Conducted biennially, the exercise serves as a platform for enhancing cooperation and interoperability among participating nations.
- Inception: Initiated in 1991 between the Indian and Maldives Coast Guards, with Sri Lanka joining in 2012.
- Previous Editions: The exercise, last held in 2021, focuses on various maritime scenarios, including search and rescue operations and pollution response.
Objectives and Focus Areas
- Enhancing Friendship: Dosti aims to strengthen the bonds of friendship and mutual trust among the coast guards of participating nations.
- Operational Capability: The exercise emphasizes enhancing operational capability and interoperability through joint drills and exercises.
- Maritime Safety: Exercises and drills focus on providing assistance during sea accidents, combating sea pollution, and addressing challenges like oil spills.
Dosti 16: Current Edition
- Edition Details: Dosti 16 marks the 16th edition of the exercise, continuing the tradition of fostering maritime cooperation.
- Participating Forces: The coast guards of India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives, along with observers from Bangladesh, are actively participating.
- Indian Contribution: India’s participation includes vessels like ICGS Samarth (with integral helo), ICGS Abhinav, and ICG Dornier, showcasing its commitment to regional maritime security.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Ram Madhav writes: India, making waves in the Indian Ocean
Central Idea:
The article highlights the historical significance of India’s maritime prowess in the first millennium and its subsequent decline, emphasizing the crucial role of naval power in economic prosperity. It underscores the shift of global power dynamics towards the Indo-Pacific region and the vital importance of the Indian Ocean to India’s trade and security interests. It calls for renewed attention towards leveraging India’s maritime potential and fostering cooperation among Indian Ocean nations to address common challenges.
Key Highlights:
- India’s dominance in the first millennium attributed to maritime strength and extensive trade networks.
- Decline in naval power coincided with economic decline during colonial rule.
- Lack of focus on maritime affairs persists post-independence, hindering India’s maritime capabilities.
- Indo-Pacific region emerges as the new global power center.
- Indian Ocean identified as vital to India’s trade and energy security.
- Indian government takes proactive steps to enhance cooperation and address common challenges in the Indian Ocean region.
Key Challenges:
- Historical neglect of maritime affairs leading to underdevelopment of naval capabilities.
- Competition from other major maritime powers like the United States and China.
- Non-traditional challenges such as climate change and natural disasters impacting maritime security and trade.
Main Terms:
- Maritime prowess
- Indo-Pacific
- Indian Ocean
- Naval power
- Trade routes
- Maritime security
Important Phrases:
- “He who rules on the sea will shortly rule on the land also”
- “Lords of the Sea”
- “Peninsular character”
- “British Lake”
Quotes:
- “He who rules on the sea will shortly rule on the land also.”
- “So far as India is concerned, it should be remembered that the peninsular character of the country and the essential dependence of its trade on maritime traffic give the sea a preponderant influence on its destiny.” – K M Panikkar
Anecdotes:
- Indian rulers’ dominance over the oceans in the first millennium facilitated extensive trade networks and economic prosperity.
- The Portuguese, Dutch, French, and British conquest of the seas in the second millennium challenged India’s maritime dominance.
Useful Statements:
- The Indian Ocean is not just a maritime geography but a civilization, carrying India’s cultural and civilizational influence.
- Eighty per cent of India’s external trade and 90 per cent of its energy trade occur through Indian Ocean routes.
Examples and References:
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
- Fa-Hien’s account of maritime trade in ancient India.
- Establishment of the Royal Indian Navy during British rule.
- K M Panikkar’s warnings about India’s maritime importance.
- The 7th Indian Ocean Conference in Perth, Australia.
Facts and Data:
- India’s share of the world’s GDP was almost 33 per cent in the first millennium.
- The Indian Ocean covers over 74 million square kilometers.
- The Indian Navy has less than 200 combat vessels compared to 400 for the United States and 500 for China.
Critical Analysis:
The article effectively highlights India’s historical maritime prowess and its subsequent decline, emphasizing the importance of reinvigorating India’s naval capabilities in the modern context. It critiques the historical neglect of maritime affairs by Indian leadership and calls for greater attention towards leveraging India’s geostrategic position in the Indo-Pacific region.
Way Forward:
- Prioritize investments in maritime infrastructure and naval capabilities.
- Strengthen cooperation with Indian Ocean nations to address common challenges.
- Increase diplomatic engagement in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Enhance awareness and appreciation of India’s maritime heritage and geopolitical significance among policymakers and the public.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Ram Madhav writes: India, making waves in the Indian Ocean
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
Mains level: India's historical maritime prowess and its subsequent decline
6AIR.jpeg)
Central Idea:
The article highlights the historical significance of India’s maritime prowess in the first millennium and its subsequent decline, emphasizing the crucial role of naval power in economic prosperity. It underscores the shift of global power dynamics towards the Indo-Pacific region and the vital importance of the Indian Ocean to India’s trade and security interests. It calls for renewed attention towards leveraging India’s maritime potential and fostering cooperation among Indian Ocean nations to address common challenges.
Key Highlights:
- India’s dominance in the first millennium attributed to maritime strength and extensive trade networks.
- Decline in naval power coincided with economic decline during colonial rule.
- Lack of focus on maritime affairs persists post-independence, hindering India’s maritime capabilities.
- Indo-Pacific region emerges as the new global power center.
- Indian Ocean identified as vital to India’s trade and energy security.
- Indian government takes proactive steps to enhance cooperation and address common challenges in the Indian Ocean region.
Key Challenges:
- Historical neglect of maritime affairs leading to underdevelopment of naval capabilities.
- Competition from other major maritime powers like the United States and China.
- Non-traditional challenges such as climate change and natural disasters impacting maritime security and trade.
Main Terms:
- Maritime prowess
- Indo-Pacific
- Indian Ocean
- Naval power
- Trade routes
- Maritime security
Important Phrases:
- “He who rules on the sea will shortly rule on the land also”
- “Lords of the Sea”
- “Peninsular character”
- “British Lake”
Quotes:
- “He who rules on the sea will shortly rule on the land also.”
- “So far as India is concerned, it should be remembered that the peninsular character of the country and the essential dependence of its trade on maritime traffic give the sea a preponderant influence on its destiny.” – K M Panikkar
Anecdotes:
- Indian rulers’ dominance over the oceans in the first millennium facilitated extensive trade networks and economic prosperity.
- The Portuguese, Dutch, French, and British conquest of the seas in the second millennium challenged India’s maritime dominance.
Useful Statements:
- The Indian Ocean is not just a maritime geography but a civilization, carrying India’s cultural and civilizational influence.
- Eighty per cent of India’s external trade and 90 per cent of its energy trade occur through Indian Ocean routes.
Examples and References:
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
- Fa-Hien’s account of maritime trade in ancient India.
- Establishment of the Royal Indian Navy during British rule.
- K M Panikkar’s warnings about India’s maritime importance.
- The 7th Indian Ocean Conference in Perth, Australia.
Facts and Data:
- India’s share of the world’s GDP was almost 33 per cent in the first millennium.
- The Indian Ocean covers over 74 million square kilometers.
- The Indian Navy has less than 200 combat vessels compared to 400 for the United States and 500 for China.
Critical Analysis:
The article effectively highlights India’s historical maritime prowess and its subsequent decline, emphasizing the importance of reinvigorating India’s naval capabilities in the modern context. It critiques the historical neglect of maritime affairs by Indian leadership and calls for greater attention towards leveraging India’s geostrategic position in the Indo-Pacific region.
Way Forward:
- Prioritize investments in maritime infrastructure and naval capabilities.
- Strengthen cooperation with Indian Ocean nations to address common challenges.
- Increase diplomatic engagement in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Enhance awareness and appreciation of India’s maritime heritage and geopolitical significance among policymakers and the public.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
INS Imphal: Everything you need to know
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Imphal
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- INS Imphal (Pennant D68), the third ship of the Visakhapatnam class stealth-guided missile destroyers, is set to join the Indian Navy.
- Part of Project 15B, INS Imphal follows the lineage of the Delhi and Kolkata classes of indigenous destroyers.
About INS Imphal
| Details | |
| Ship Name | INS Imphal (Pennant D68) |
| Class | Visakhapatnam class stealth-guided missile destroyer (Project 15B) |
| Commissioning Date | Scheduled for December 26 |
| Builder | Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDSL) |
| Design | Indian Navy’s Warship Design Bureau |
| Propulsion System | Combined gas and gas (COGAG) configuration with four gas turbines |
| Maximum Speed | 30 knots |
| Range | 4000 nautical miles |
| Armament | BrahMos surface-to-surface cruise missiles
Barak-8 surface-to-air missiles 127 mm main gun AK-630 30mm guns Torpedo launchers and anti-submarine rocket launchers |
| Helicopter Facilities | Can operate two multi-role helicopters (Sea King or HAL Dhruv) |
| Strategic Features | Stealth capabilities for reduced radar signature
Advanced combat management system Total atmospheric control system (TACS) for protection against nuclear, biological, and chemical threats |
| Significance | Represents advanced naval warfare capabilities and strategic asset for the Indian Navy |
| Tribute to Northeast India | Named after the city of Imphal, honoring the strategic and historical significance of the Northeast region |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’s Naval Legacy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Maratha Navy
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- On Navy Day, December 4, PM Modi highlighted Chhatrapati Shivaji’s understanding of naval power and announced the incorporation of his emblem on naval officers’ epaulettes.
Indian Navy’s Acknowledgment of Maratha Heritage
- Training Establishment: The Indian Navy’s training facility in Lonavla is named INS Shivaji.
- Administrative Hub: The Western Naval Command’s logistics and administrative center in Mumbai is named INS Angre, after Kanhoji Angre, a prominent Maratha naval commander.
- New Naval Ensign: The Indian Navy’s new Ensign, unveiled in 2022, features the octagonal design of Shivaji’s seal, symbolizing his maritime vision.
About Maratha Navy
| Details | |
| Foundation and Expansion | – Founder: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj
– First Vessel: Built around 1654 near Kalyan – Strategic Naval Bases: Vijaydurg, Sindhudurg, Khanderi, Colaba – Philosophy: Principle of ‘Jalameva yasya, balameva tasya’ (‘He who rules the seas is all powerful’). |
| Composition and Command | – Personnel: Native Konkani sailors and mercenaries
– Notable Commanders: Shivaji Maharaj, Admiral Kanhoji Angre |
| Naval Fleet and Technology | – Ship Types: ‘Gurab’ (large, three-masted) and ‘Galbat’ (smaller, faster), Tarande , Shibad, Pal, Taru, Tirkiti and Machchava.
– Artillery and Arms: Equipped with various cannons, known for innovative naval tactics |
| Tactics and Strategies | – Coastal Dominance: Excelling in coastal defense
– Guerrilla Tactics: Using hit-and-run tactics, exploiting shallow creeks and bays |
| Major Conflicts and Battles | – Against European Powers: Engagements with the British and Portuguese
– Conflict with the Siddis: Ongoing conflicts with the Siddis of Janjira |
| Decline and Legacy | – Reasons for Decline: Internal strife, technological advancements by Europeans, rise of British naval power
– Legacy: Remembered for resisting colonial powers, protecting the western coast of India |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise MILAN
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise MILAN
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Scheduled for February 2024, Exercise MILAN is set to be India’s largest multilateral naval exercise, with over 50 countries expected to participate.
Exercise MILAN
- Origin: Biennial exercise initiated by the Indian Navy in 1995 at the Andaman and Nicobar Command.
- Initial Participation: Began with four countries – Indonesia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Thailand in 1995.
- Growth over Years: The exercise has significantly grown in the number of participants and the complexity of exercises.
- Expansion with Policies: Expanded under India’s ‘Act East policy’ and the SAGAR initiative.
- Broader Inclusion: Now includes island nations in the Western Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and IOR littoral states.
Significance of Exercise MILAN
- Showcasing Naval Strength: This exercise reflects the Indian Navy’s growing engagement and capability to assist as a first responder and Preferred Security Partner in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Enhanced Operational Reach: The Indian Navy’s increasing presence and operational reach through Mission Based Deployments and other engagements underscore India’s commitment to strong defense ties.
- Importance of Naval Exercises: Conducting 17 multilateral and 20 bilateral exercises annually, these events are crucial for operational capability enhancement, interoperability, and strengthening diplomatic and maritime security ties.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Maritime Infrastructure Perspective Plan (2023-37)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Maritime Infrastructure Perspective Plan (2023-37)
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Maritime Infrastructure Perspective Plan (MIPP) 2023-37 was unveiled at the Naval Commanders Conference.
- It signifies a forward-looking strategy aimed at fostering sustainable maritime architecture.
About MIPP
- Aligned with the overarching vision of the PM Gati Shakti project, this comprehensive plan was introduced by the Minister of State for Defence.
- The plan’s objectives span over the next 15 years and strive to synergize the Navy’s infrastructure requirements in a dynamic and encompassing model.
Features of the MIPP
- Synchronizing Infrastructure Needs:
- The MIPP 2023-37 envisions an integrated approach to address the Navy’s infrastructure requirements.
- It aims to harmonize naval infrastructure development over the next 15 years through a meticulously designed perspective plan.
- Compliance with Broader Policies:
- The plan adheres to the broader policy directives of the PM Gati Shakti Project, Disaster Resilience, and Transition to Net Zero, among others.
- Sustainability and compliance with national policy priorities are key principles underpinning the plan’s formulation.
- Modernization Efforts:
- To accommodate technological advancements and promote self-reliance, the revised “IRS Rules and Regulations Handbook for Construction and Classification of Naval Combatants” was introduced.
- This handbook reflects the naval shipbuilding industry’s growth and aligns with the philosophy of ‘AatmaNirbharta’ (self-reliance).
- Transformational Initiatives:
- The release of the “Family Logbook for Defence Civilian Personnel of the Indian Navy” serves as a milestone in maintaining personal records efficiently.
- The launch of the “Electronic Service Document Project” is poised to revolutionize HR record-keeping within the Navy.
Facts/Terms for UPSC Prelims
- PM Gati Shakti Project: A government initiative aimed at enhancing infrastructure connectivity and development across various sectors, contributing to economic growth and national development.
- Indian Register for Shipping (IRS): An organization responsible for ship classification and certification in India, ensuring that ships comply with international standards for safety and environmental performance.
- Blue Economy: Economic activities related to oceans and water bodies, including fisheries, aquaculture, tourism, and shipping, which contribute significantly to a nation’s economy.
- Geoeconomics: The study of how economic factors and policies influence international relations and geopolitics.
- Geopolitics: The study of political and territorial issues influenced by geographical factors and international power dynamics.
Conclusion
- The Maritime Infrastructure Perspective Plan 2023-37 stands as a blueprint for India’s maritime progress, exemplifying the commitment to self-reliance, sustainability, and modernization.
- With a focus on comprehensive development and adherence to national policies, the plan charts a course towards a stronger, more resilient naval infrastructure.
- It aligns with the evolving security landscape and the broader objectives of the nation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
INS Vindhyagiri and Project 17A
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Vindhyagiri, Project 17A
Mains level: Naval fleet modernization

Central Idea
- President’s launch of INS Vindhyagiri, the final vessel in the Project 17A (Alpha) frigates series, marked a significant milestone for India’s maritime strength and self-reliance.
- The launch of INS Vindhyagiri, the sixth vessel in the Project 17A Frigates series, carries forward India’s naval legacy.
About INS Vindhyagiri
- INS Vindhyagiri is the sixth ship of the Project 17A Frigates series, showcasing India’s commitment to indigenous defense technology and self-reliance.
- After INS Nilgiri, Udaygiri, Himgiri, Taragiri, and Dunagiri, INS Vindhyagiri derives its name from a mountain range in Karnataka.
- These frigates are a follow-on class of the Project 17 (Shivalik Class) Frigates, integrating improved stealth, advanced weapons, and cutting-edge sensors.
- It is built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata, India.
Key features
- Employs a cutting-edge propulsion system enabling speeds of over 28 knots, ensuring rapid response and agility in various operational scenarios.
- Equipped with state-of-the-art stealth features, enhancing its ability to operate discreetly and minimize detection.
- Over 75% of the equipment and systems used are sourced from indigenous firms, including Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
Back2Basics: Project 17A
- Project 17 Alpha frigates (P-17A) were launched by the Indian Navy in 2019.
- The first stealth ship launched was the Nilgiri, launched in 2019.
- The project was launched to construct a series of stealth guided-missile frigates, which are currently being constructed by two companies:
- Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders (MDL) and
- Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE).
- These guided-missile frigates have been constructed with a specific stealth design, which has radar-absorbent coatings and is low-observable which can make its approach undetectable for the enemies.
- The new technology also reduces the infrared signals of the ship.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
New Scorpene Class Submarines for Navy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Project-75, Scorpene Submarines
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Procurement Announcement: The three additional Scorpene submarines will be procured under the Buy (Indian) category. The Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in Mumbai will build the submarines.
Scorpene Submarines and Project-75
- Project-75: MDL is already building six Scorpene class submarines under Project-75, with technology transfer from the French defense firm.
- Commissioned Submarines: Five out of the six Scorpene submarines have been commissioned, with the final one expected to be commissioned early next year.
- Delays and Challenges: Project-75 faced significant delays, as the first submarine was originally scheduled for delivery in 2012.
Need for Additional Submarines
- Addressing Delays and Fleet Strength: The procurement of three additional submarines is necessary to compensate for the delayed deliveries under Project-75 and strengthen India’s submarine fleet.
- Current Fleet Status: The Indian Navy currently operates 16 conventional submarines, but it needs a minimum of 18 submarines to carry out its full spectrum of operations.
- Refit Challenges: Around 30% of submarines are under refit at any given time, further reducing the number of operational submarines.
- Employment Opportunities: Procuring additional submarines with higher indigenous content will create employment opportunities and enhance MDL’s submarine construction capabilities.
Capabilities of Scorpene Submarines
- Attack Submarines: Scorpene submarines are designed as conventional attack submarines to target and sink enemy naval vessels.
- Weapons and Surveillance: They can launch a variety of torpedoes and missiles, equipped with surveillance and intelligence-gathering systems.
- Specifications: Scorpene submarines are approximately 220 feet long, with a height of about 40 feet. They have a top speed of 11 knots when surfaced and 20 knots when submerged.
- Diesel-Electric Propulsion: These submarines use diesel-electric propulsion systems, providing an endurance of around 50 days.
Comparison with Nuclear Submarines
- India’s Current Nuclear Submarines: India currently operates two nuclear-powered submarines (SSBMs) of the Arihant class.
- Endurance and Speed: Nuclear submarines have theoretically unlimited endurance and can operate for up to 30 years without refuelling. They can also achieve higher speeds.
- Cost and Expertise: Nuclear submarines are expensive and require specialized expertise to operate.
- Advancements in Conventional Submarines: Diesel-electric technology has significantly improved the range and stealth of conventional submarines.
- Air Independent Propulsion (AIP): Retrofitting Scorpene submarines with AIP systems will enhance their endurance and stealth capabilities.
Conclusion
- India’s decision to procure three additional Scorpene submarines enhances its naval capabilities and strengthens the indigenous manufacturing sector.
- The addition of these submarines will help meet the requirements of a growing fleet and improve operational readiness.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Varunastra: Indigenous Heavy Weight Torpedo
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Varunastra
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Test-firing achievement: The indigenously designed and developed heavy weight torpedo (HWT) Varunastra was successfully test-fired by the Indian Navy, targeting an undersea target with a live warhead.
Varunastra: Feature Details
- Advanced features: Varunastra is a ship-launched anti-submarine torpedo equipped with low drift navigational systems, acoustic homing, advanced acoustic countermeasures, autonomous guidance algorithms, an insensitive munitions warhead, and a GPS-based recovery aid for practice torpedoes.
- Designed and developed by NSTL: Varunastra was designed and developed by the Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL) based in Vizag under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Manufacturing by BDL: Bharat Dynamics Ltd (BDL) is responsible for the manufacturing of Varunastra.
Technical Specifications and Capabilities
- Speed, depth, and range: Varunastra boasts a maximum speed of 40 knots and a maximum operating depth of 600 meters. It has long-range and multi-manoeuvering capabilities.
- Acoustic homing and tracking: The torpedo features acoustic homing with a wide look angle, allowing it to track silent targets effectively.
- Advanced guidance and navigational systems: Varunastra incorporates autonomous advanced guidance algorithms and drift navigational systems, enabling precise targeting and long-endurance operations.
Significance of the test fire
- Mainstay of anti-submarine warfare: Varunastra is set to become the primary anti-submarine torpedo for all naval warships, replacing older torpedoes capable of firing HWT.
- Enhanced anti-submarine warfare: The induction of Varunastra as the mainstay anti-submarine torpedo strengthens the Indian Navy’s capabilities in countering underwater threats.
- Self-reliance and indigenous development: The successful development and deployment of Varunastra highlight India’s progress in indigenous defence technologies and reduce dependence on imports.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Golden Globe Race: Voyage of mad men
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Abhilash Tomy, Golden Globe Race
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Abhilash Tomy, a former Commander in the Indian Navy, has achieved the remarkable feat of completing a solo circumnavigation worldwide by finishing second at the Golden Globe Race (GGR), 2022.
- He achieved this record under even more challenging circumstances than his previous record-breaking feat of going worldwide on a sailboat solo and unassisted back in 2013.

What is Golden Globe Race?
- The Golden Globe Race is a non-stop, solo, unassisted yacht race around the world which was held for the first time in 1968-69.
- The race requires contestants to use boats designed to prescribed premodern specifications and rely entirely on sextants and paper charts.
- Satellite phones are available for extremely restricted use, and the use of modern navigational gear is not allowed.
- The sailing would be along a stipulated route, rounding the three great capes (Cape of Good Hope in South Africa, Cape Leeuwin in Western Australia, and Cape Horn in Chile).
His return to GGR
- After several injuries, in 2021, Tomy began to look for sponsors and boats to participate in GGR-2022.
- He announced his participation in the race on the Bayanat in March 2022, sponsored by a UAE-based company in the field of geospatial artificial intelligence.
- However, just three weeks before the race, the boat collided with a ship and required massive repairs.
Significance of his achievement
- Only three of the 11 contestants of GGR-2022 lasted the course of the race, with Kirsten Neuschafer becoming the first woman to win a solo around-the-world yacht race.
- Tomy’s boat was the most ‘repaired’ boat in the race and it was all carried out by the sailor fighting unimaginable sea conditions and lack of sleep.
- In the end, Tomy became the first Asian to complete the 30,000-mile GGR by finishing second after Neuschafer.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise Konkan, 2023
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Konkan
Mains level: NA
Ex Konkan, the annual bilateral maritime exercise between the Indian Navy and the Royal Navy, was recently held off the Konkan coast in the Arabian Sea.
Exercise Konkan 2023
- Konkan exercise is the annual bilateral maritime exercise between the Indian Navy and the UK’s Royal Navy.
- INS Trishul, a guided missile frigate, and HMS Lancaster, a Type 23 guided missile frigate, participated in this edition.
- They undertook multiple maritime drills to enhance interoperability between the two forces and imbibe best practices.
- The exercises covered all domains of maritime operations, air, surface, and sub-surface.
- It included gunnery shoots on the surface inflatable target ‘Killer Tomato’, helicopter operations, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare drills, Visit Board Search and Seizure (VBSS), ship maneuvers, and exchange of personnel.
- The exercise will help the Indian Navy and Royal Navy work together to improve maritime security and maintain a rules-based order in the region.

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
INS Vagir commissioned into the Indian Navy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Vagir
Mains level: Not Much

The fifth Scorpene class conventional submarine was commissioned into the Indian Navy as INS Vagir.
INS Vagir
- The latest submarine gets its name from the erstwhile Vagir, a submarine that served the Navy between 1973 and 2001 and undertook numerous operational missions.
- The construction of the new Vagir began in 2009 and it took its maiden sea sortie in February last year.
- Also known as Sand Shark, the submarine was delivered to the Indian Navy in December 2022.
Class: Kalvari
- In maritime parlance, a class of ships is a group of vessels which have the same make, purpose and displacement.
- Vagir is a Kalvari-class submarine, which includes other vessels, such as the INS Kalvari, INS Khanderi, INS Karanj, INS Vela and INS Vagsheer.
- Of these, Kalvari and Khanderi were commissioned in 2017 and 2019, and Vela and Karanj were inducted in 2021.
- Vagir has now been commissioned and Vagsheer was launched in 2022 and is expected to be inducted next year.
- The submarines in the current Kalvari-class take their names from erstwhile decommissioned classes of submarines named Kalvari, which included Kalvari, Khanderi, Karanj and Vela classes — comprising Vela, Vagir, Vagshir.
Capabilities and technical details of INS Vagir
- The Kalavari class of submarines have an estimated endurance of approximately 50 days.
- They also have the capability of operating in a wide range of Naval combat including anti-warship and anti-submarine operations, intelligence gathering and surveillance and naval mine laying.
- These submarines are around 220 feet long and have a height of 40 feet. It can reach the highest speeds of 11 knots (20 km/h) when surfaced and 20 knots (37 km/h) when submerged.
- The modern variants of the Scorpene class of submarines have what is called Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) which enables non-nuclear submarines to operate for a long time without access to surface oxygen.
Strategic importance
- Currently, India has less number of submarines than what is required with some more of those from both types being at various stages of construction.
- India operates one submarine in the nuclear-powered class of Chakra and two other nuclear-powered vessels in Arihant.
- There are in addition to submarines belonging to three classes of Diesel Electric category — Kalvari, Shishumar and Sindhughosh, some of which are ageing.
- The nuclear-powered and diesel-electric submarines have their designated roles in the Carrier Battle Groups, which are formations of ships and submarines with Aircraft Carriers in the lead role.
- As per the basic principles of submarine deployment and minimum requirement for India to create a strategic deterrence, there is a specific number of submarines of both types that India needs to have in active service.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Underwater combat drones: Indian Navy’s readiness
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Deployment of AI powered underwater drones and associated challenges
Context
- India is on a drive to induct unmanned combat systems into the military. Months after the Indian Army announced the induction of swarm drones into its mechanized forces, the Navy chief, Admiral R Hari Kumar, reiterated the importance of autonomous systems in creating a future-proof Indian Navy (IN).
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Indian Navy’s expanding surveillance and reasons for doing so
- The IN, indeed, has been on a mission to expand surveillance in India’s near-seas: Two years after it leased MQ-9B Sea Guardian drones from the US, the navy, in July 2022, released an unclassified version of its unmanned roadmap for the induction of remote autonomous platforms including undersea vehicles.
- Maritime deterrence in the Eastern Indian Ocean: A key driver for the enterprise is underwater domain awareness, deemed an increasingly vital component of maritime deterrence in the Eastern Indian Ocean.
- Chinas undersea presence in the Indian ocean: In the aftermath of the conflict in Ladakh in June 2020, there is a growing sense among Indian experts and military planners that China’s undersea presence in the Indian Ocean is on the cusp of crossing a critical threshold.
- Recent reports of sighting of Chinese drones in the waters of Indonesia: Recent reports of the sighting of Chinese drones in the waters off Indonesian islands suggest the Peoples Liberation Army Navy has been studying the operating environment of the Indian Ocean.
- China already deployed vessels around Andaman in the name of research: Already, there has been a rise in the deployment of Chinese research and survey vessels in the waters around India’s Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Recognizing the threat, Indian Navy sought acquire to own AUV: Ever more alive to the dangers posed by foreign undersea presence in Indian waters, the IN sought to acquire its own autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) with twin surveillance and strike capabilities.
Analysis: The navy’s interest in armed underwater drones
- Underwater vehicles never viewed as warfighting assets: Despite being widely used in underwater search and exploration, underwater vehicles have never quite been viewed as warfighting assets by India’s military establishment.
- Never sought deploying underwater drones in combat roles: Notwithstanding the AUVs’ utility in tasks such as mine detection and ship survey, India’s naval planners have traditionally desisted from deploying undersea drones in a combat role.
- Acknowledging war fighting capabilities and need of the hour: Indian analysts and decision-makers seem to be belatedly acknowledging the warfighting abilities of underwater autonomous platforms powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
- Getting ready for the new era warfare: With the fourth industrial revolution (4IR) shaping a new era in warfare, Indian observers are beginning to recognise the likely impact of disruptive technologies on the maritime domain. AI powered by deep learning, data analytics, and cloud computing, many say, is poised to alter the maritime battlefront, potentially triggering a revolution in naval affairs in India.
Challenges to harness the disruptive technologies in maritime combat
- Ethical paradox: There is an ethical paradox that typifies artificially intelligent combat systems.
- Imported AI tech algorithms cannot be under user control: Despite rendering warfare more deadly, AI compromises the control, safety, and accountability of weapon systems it also enhances the risk of shared liability between networked systems, particularly when weapon algorithms are sourced from abroad, and when the satellite and link systems that enable combat solutions are not under the control of the user.
- Predisposition of data in AI can undermine the decision making: AI is characterised by a predisposition to certain kinds of data. Biases in the collection of data, in the set of instructions for data analysis, and in the selection of probabilistic outcomes muddle rational decision-making, undermining confidence in automated combat solutions.
- The doctrinal paradox is equally troubling: There is no easy way of incorporating AI-fuelled warfighting approaches into doctrine, particularly when many technologies are in a nascent stage of development, and there is little clarity about how effective AI could be in combat.
- Capacity limitation that restricts the development of AI: While technology absorption in the navy has matured in certain areas over a period of time, a large gap still exists in the development of critical technologies, which are system engineering, airborne and underwater sensors, weapon systems, and hi-tech components.
The critics of AI in warfare
- Technology without comprehensive testing is risky: That fielding nascent technologies without comprehensive testing puts both military personnel and civilians at risk.
- Probabilistic assessment by computers not always provide optimal solution: A system of targeting human beings based on probabilistic assessments by computers that act merely on machine-learned experiences, is problematic because the computer neither has access to all relevant data to make an informed decision nor recognizes that it needs more information to come up with an optimal solution.
- Shaping policy to account for AI is challenging: That is because military doctrine is premised on a traditional understanding of conflict. If war is a normative construct, then there are rules and codes to be followed, and ethical standards to be met.
- AI could be inconsistent with the laws of war: What is more, AI seemingly automates weapon systems in ways that are inconsistent with the laws of war.
Legality issues of underwater combat drones
- Status by UNCLOS is not yet clear: It is not yet clear if unmanned maritime systems enjoy the status of ships under the UN convention of the laws of the sea; even if they do, it is unlikely that they can be classified as warships.
Way ahead
- Notwithstanding the announcement of multiple AI projects, the navy remains focused on using AI in noncombat activities such as training, logistics, inventory management, maritime domain awareness, and predictive maintenance.
- India’s maritime managers recognize that the IN is still at a place on its evolutionary curve where incorporating AI in combat systems could prove risky. An incremental approach, many believe, is the best way forward.
Conclusion
- It is worth acknowledging that AI in warfare is not just a matter of combat effectiveness but also of warfighting ethics. AI-infused unmanned systems on the maritime battlefront pose a degree of danger, making it incumbent upon the military to deploy its assets in ways that are consistent with national and international law. India’s naval leadership would do well if it takes careful and calculated steps in developing AI-powered underwater systems.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Missile destroyer INS Mormugao commissioned into Indian Navy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Mormugao
Mains level: Indian navy modernization

Indian Naval Ship (INS) Mormugao (Pennant 67), a P15B stealth-guided missile destroyer was commissioned into the Indian Navy.
INS Mormugao
- This was the second ship to be inducted as a part of the four ‘Visakhapatnam’ class destroyers.
- It is indigenously designed by the Navy’s in-house organisation Warship Design Bureau and constructed by Mazagaon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in the country’s financial capital Mumbai.
- The ship was named after a key port in the Indian state of Goa, it was inducted on the eve of Goa Liberation Day.
- The ship was first launched in September 2016 and began sea trials last year on December 19 which coincided with the day that Goa was liberated from Portuguese rule six decades earlier with December 18 marking the launch of Operation Vijay by the Indian Armed Forces in 1961.
- Singh also paid tributed former defence minister, the late Manohar Parrikar who had launched INS Mormugao in 2016.
Features of INS Mormugao
- The ship measures 163 metres by 17 metres and has the ability to fight in nuclear, biological, as well as chemical (NBC) warfare due to its total atmospheric control system (TACS).
- Additionally, with a displacement of 7,400 tonnes, the INS Mormugao is loaded with state-of-the-art weapons.
- It will be operated by a crew of at least 350 which would include 50 officers and 250 sailors.
- Over 75 per cent of the ship’s content was manufactured and developed in India, either directly or designed and developed by Indian Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) or through strategic tie-ups.
- It is capable of achieving speeds of 30 knots (55 km/hour) as it is propelled by four powerful gas turbines in a ‘combined gas and gas’ (COGAG) configuration.
Combat weaponry
- INS Mormugao includes weapons like BrahMos surface-to-surface missiles and Barak-8 surface-to-air missiles.
- It is also fitted with a modern surveillance radar which helps provide target data to the ship’s weapon system.
- Additionally, the ship’s weaponry also includes indigenously-developed rocket launchers, torpedo launchers and ASW helicopters like Sea King or HAL Dhruv.
Historic significance of Mormugao Port
- Even as a port, Mormugao has contributed significantly to the growth of India’s maritime trade.
- Even today, it is one of the oldest and largest ports in the country and will retain this special place due to the services it provides be it Mormugao fort or Mormugao port.
- It is landmark since the 17th century Maratha campaign against the Portuguese under Chhatrapati Sambhaji (Ch. Shivaji Maharaj’s son).
Back2Basics: Project PB15
- P15B destroyers is a class of four ships built by the country’s MDSL with INS Visakhapatnam (Pennant D66), commissioned last year in November as the year.
- These ships are set to be more advanced than the Kolkata class under the project named 15A which comprised INS Kolkata, INS Kochi, and INS Chennai.
- The contract for the ships was signed back in 2011 and under Project 15B they were to be named after four major Indian cities like Visakhapatnam, Mormugao, Imphal, and Surat.
- A group of ships with similar tonnage, usage, capabilities, and weaponry are referred to as a ship’s ‘class’.
- P15B destroyers incorporate new design concepts for improved survivability, seakeeping and manoeuvrability.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
In news: Exercise ‘Sea Vigil’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ex Sea Vigil
Mains level: Holistic security of India's maritime domain
In a related development, the third edition of the ‘pan-India’ coastal defence Exercise ‘Sea Vigil-22’ is scheduled to be held on November 15 and 16.
Ex- Sea Vigil-22
- The Exercise was conceptualised in 2018 to validate various measures that have been instituted towards enhancing maritime security since ‘26/11’.
- The exercise aims to test its preparedness along the entire 7,516.6 km-long-coastline and exclusive economic zone of the country.
- It aims to comprehensively and holistically validate the efficacy of the measures taken since 26/11.
- It aims to simultaneously activate the coastal security mechanism across all 13 coastal States and Union Territories.
- This involves the evaluation of critical areas and processes, including inter-agency coordination, information sharing and technical surveillance.
- Multi agency audit and identification of gaps, shortfalls and incorporation of lessons learnt into Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) are also the desired outcomes.
Role of Indian Navy
- Post 26/11, the Navy was designated as the agency responsible for overall maritime security, including offshore and coastal security.
- The Coast Guard was designated as the agency responsible for coastal security in territorial waters.
- A multi-tiered patrol and surveillance mechanism with focus on technical surveillance and augmenting Maritime Domain Awareness through the coastal radar chain was adopted.
- Progress has been made in real-time information sharing through the National Command Control Communication and Intelligence (NC3I) Network and improving intelligence and operational coordination.
Significance of the exercise
- The exercise is a build up towards the major Theatre Level Readiness Operational Exercise (TROPEX), which the Indian Navy conducts every two years.
- Sea Vigil and TROPEX together will cover the entire spectrum maritime security challenges.
Progress till now
- Verification and monitoring of a large number of fishing vessels in India has been greatly eased by the creation of the online ReALCraft (Registration and Licensing of Fishing Craft).
- The process of installing transponders on sub-20 metre boats commenced with a pilot project in Tamil Nadu for 5,000 vessels is underway.
- To allay the concerns of fishermen, the transponders with GPS have been modified into a two-way communication system.
- An Automatic Identification System (AIS) was made compulsory for all vessels above 20 metres after the 2008 terrorist attacks in Mumbai.
- Trials were conducted in association with the ISRO on one of their communication satellites last year along the coasts of Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
SLBM launch by INS Arihant
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SLBM, INS Arihant
Mains level: India's nuclear triad

The indigenous ballistic missile nuclear submarine INS Arihant has successfully launched a nuclear capable Submarine Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM) in the Bay of Bengal with very high accuracy.
About INS Arihant
- Launched in 2009 and Commissioned in 2016, INS Arihant is India’s first indigenous nuclear powered ballistic missile.
- It is capable submarine built under the secretive Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) project, which was initiated in the 1990s.
- INS Arihant and its class of submarines are classified as ‘SSBN’, which is the hull classification symbol for nuclear powered ballistic missile carrying submarines.
- While the Navy operates the vessel, the operations of the SLBMs from the SSBN are under the purview of India’s Strategic Forces Command, which is part of India’s Nuclear Command Authority.
Its role in India’s nuclear triad
- In November 2019, after INS Arihant completed its first deterrence patrol, the government announced the establishment of India’s “survivable nuclear triad”.
- It completed India’s capability of launching nuclear strikes from land, air and sea platforms.
- This places India in the league of the few countries that can design, construct and operate Strategic Strike Nuclear Submarines (SSBN).
Significance of the test
- The SLBM was launched from the country’s first indigenous Strategic Strike Nuclear Submarine INS Arihant.
- The test is significant for the nuclear ballistic submarine, or SSBN, programme, which is a crucial element of India’s nuclear deterrence capability.
Submarine Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs)
- The SLBMs, sometimes called the ‘K’ family of missiles, have been indigenously developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The family is codenamed after Dr APJ Abdul Kalam, the centre figure in India’s missile and space programmes who also served as the 11th President of India.
- Because these missiles are to be launched from submarines, they are lighter, more compact and stealthier than their land-based counterparts.
- They are lighter compared to the Agni series of missiles which are medium and intercontinental-range nuclear-capable ballistic assets.
Marine Version of SLBM: Sagarika
- Part of the K family is the SLBM K-15, which is also called B-05 or Sagarika.
- It has a range of 750 km.
- INS Arihant can carry a dozen K-15 missiles on board. India has also developed and successfully tested K-4 missiles from the family, which have a range of 3,500 km.
- It is also reported that more members of K-family — reportedly carrying the code names K-5 and K-6, with a range of 5,000 km and 6,000 km respectively — are under development.
Strategic significance of the launch
- The capability of being able to launch nuclear weapons submarine platforms has great strategic significance in the context of achieving a nuclear triad.
- This is especially in the light of the “No First Use” policy of India.
- The sea-based underwater nuclear capable assets significantly increases the second strike capability, and thus validates the nuclear deterrence.
- These submarines can not only survive a first strike by the adversary, but can also launch a strike in retaliation, thus achieving ‘Credible Nuclear Deterrence’.
Message to our hostile neighbours
- The development of these capabilities is important in the light of India’s relations with China and Pakistan.
- India’s capacity building on the nuclear powered submarines and of the nuclear capable missile which can be launched from them is crucial for nuclear deterrence.
- China has deployed many of its submarines, including some that are nuclear-powered and nuclear-capable.
Conclusion
- In an era such as this, credible nuclear deterrence is the need of the hour.
- The success of INS Arihant gives a fitting response to those who indulge in nuclear blackmail.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Indian Navy participates in Exercise Kakadu hosted by Australia
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ex Kakadu
Mains level: NA
INS Satpura and a P8 I Maritime Patrol Aircraft of the Indian Navy reached Darwin in Australia on for participation in the multinational Exercise Kakadu – 2022, hosted by the Royal Australian Navy.
Exercise KAKADU
- Exercise KAKADU, which started in 1993, is the premier multilateral regional maritime engagement exercise hosted by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and supported by the Australian Air Force.
- The exercise is held biennially in Darwin and the Northern Australian Exercise Areas (NAXA).
- It derives its name from Kakadu National Park, which is a protected area in the northern territory of Australia, 171 km south-east of Darwin
- During the exercise, professional exchanges in harbour and diverse range of activities at sea, including complex surface, sub-surface and air operations would enable sharing of best practices and honing of operational skills.
India’s presence at the exercise
- Indian Navy’s participation in KAKADU provides an excellent opportunity to engage with regional partners and undertake multinational maritime activities ranging from constabulary operations to high-end maritime warfare in a combined environment
- It is aimed at enhancing interoperability and developing of common understanding of procedures for maritime operations gaining importance with the Indo-Pacific narrative.
Also read:
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Exercise Vostok-22
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vostok 2022
Mains level: India-Russia Relations
Russia is holding Vostok exercises. However, India has only sent its army contingent of the 7/8 Gorkha Rifles, and will not take part in the maritime section of the two-part event.
Vostok-2022
- It is an annual, multilateral, strategic and command exercise hosted by Russia.
- This year it will see the participation of more than 50,000 troops from 13 countries such as India, China, Algeria, India, Laos, Mongolia, Nicaragua, Syria and many more.
- While the exercises in Vostok-2022 are routine, they are the first such multilateral exercises to be held since the Russian war in Ukraine began.
Why in news now?
- India has only sent its army contingent and will not take part in the maritime section of the two-part event.
- This is because the maritime part of the exercises would be held in the Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan.
- These are near the disputed South Kuril Islands.
- India’s decision not to take part in the naval exercises is believed to be in deference to Tokyo’s sensitivities.
What does India’s participation mean?
By sending an army contingent to join Russian and Chinese troops in the exercises at this time, New Delhi is aiming to send a four-pronged message:
- Continuing relationship with Russia despite the Ukraine war: The Modi government has decided not to join the Western sanctions regime, or to curb oil imports and other economic engagement with Moscow.
- Signal balance and non-alignment in the current crisis: India has mostly abstained from votes at the United Nations seeking to criticise Russia.
- India also takes part in routine Indo-Pacific exercises: This is with its Western partners including the Quad, as well as in bilateral exercises, like the India-US Ex. Yudh Abhyas.
- Willingness to conditional engagement with China: The message the government continues to give is that it is willing to engage with China on a number of fronts, even as military talks at LAC (Line of Actual Control) remain stuck.
Conclusion
- There might be some discomfort for Indian soldiers in dealing with their counterparts at a time when they are facing each other off along the LAC.
- But that’s a small price to pay if it means keeping India-Russia ties on an even keel.
- India needs to start communicating its intent better.
- Strategic communication is an art. It’s time to master it.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
INS Vikrant: All about India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Vikrant
Mains level: Indian navy modernization

The nation’s first Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC-1) , INS Vikrant is set to be commissioned on September 2, the Indian Navy has announced.
About INS Vikrant
- The name ‘INS Vikrant’ originally belonged to India’s much-loved first aircraft carrier, a source of immense national pride over several decades of service before it was decommissioned in 1997.
- The original ‘Vikrant’, a Majestic-class 19,500-tonne warship, which was acquired from the UK in 1961, played a stellar role in the 1971 War with Pakistan.
- The IAC-1 is 262 m long and 62 m wide ‘Vikrant’ displaces approximately 43,000 tonnes when fully loaded, and has a maximum designed speed of 28 knots (about 52 km/h) with an endurance of 7500 NM.
- It has around 2,200 compartments designed for a crew of around 1,600, including specialised cabins to accommodate women officers and sailors.
Why is it important for India to have an aircraft carrier?
- An aircraft carrier is one of the most potent marine assets for any nation.
- It enhances a Navy’s capability to travel far from its home shores to carry out air domination operations.
- Having an aircraft carrier as essential to be considered a “blue water” navy — that is, a navy that has the capacity to project a nation’s strength and power across the high seas.
- An aircraft carrier generally leads as the capital ship of a carrier strike/ battle group.
Why is it a big deal that this warship has been Made in India?
- Only five or six nations currently have the capability of manufacturing an aircraft carrier, and India has joined this prestigious club now.
- India has demonstrated the capacity and self-reliance to build what is considered to be one of the most advanced and complex battleships in the world.
- India has had aircraft carriers earlier too — but those were built either by the British or the Russians.
- The ‘INS Vikramaditya’, which was commissioned in 2013 and which is currently the Navy’s only aircraft carrier, started out as the Soviet-Russian warship ‘Admiral Gorshkov’.
- India’s two earlier carriers, the ‘INS Vikrant’ and the ‘INS Viraat’, were originally the British-built ‘HMS Hercules’ and ‘HMS Hermes’.
- These two warships were commissioned into the Navy in 1961 and 1987 respectively.
What indigenous components does the new ‘Vikrant’ have?
- The indigenous content of the project is approximately 76%.
- The warship-grade steel was indigenised through Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) in collaboration with Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL).
- It includes 23,000 tonnes of steel, 2,500 km of electric cables, 150 km of pipes, and 2,000 valves.
- It also includes a wide range of finished products including rigid hull boats, galley equipment, air-conditioning and refrigeration plants, and steering gear.
What weapons and equipment will the new ‘Vikrant’ have?
- The new warship can carry up to 34 aircraft, including both fighter jets and helicopters.
- It will be capable of operating 30 aircraft including MiG-29K fighter jets, Kamov-31 Air Early Warning Helicopters, MH-60R Seahawk multi-role helicopters, as well as the Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH).
- Using a novel aircraft-operation mode known as Short Take Off But Arrested Recovery (STOBAR), the IAC is equipped with a ski-jump for launching aircraft.
What else will be there on the new INS Vikrant?
- The carrier is designed with a very high degree of automation for machinery operations, ship navigation and survivability.
- The carrier is equipped with the latest state of the art equipment and systems.
- It boasts a fully-fledged state of the art medical complex with the latest medical equipment facilities..
Now that India has shown the capability, will it build more carriers?
- Since 2015, the Navy has been seeking approval to build a third aircraft carrier for the country, which, if approved, will become India’s second Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC-2).
- This proposed carrier, to be named ‘INS Vishal’, is intended to be a giant 65,000-tonne vessel, much bigger than both IAC-1 and the ‘INS Vikramaditya’.
- The Navy has been trying to convince the government of the “operational necessity” of having a third carrier.
- Also, it is argued that now that India has developed the capability to build such vessels, it should not be whittled away.
- The expertise gained by the Navy and the country over the past 60 years in the art of maritime aviation should not be wasted either.
Significance of the induction
- Vikrant is the largest warship to have ever been built in India, and the first indigenously designed and built aircraft carrier for the Indian Navy.
- It puts India in an elite club of nations that have the capability to design and build these giant, powerful warships.
- The indigenisation efforts led to the development of ancillary industries, and generated employment opportunities for 2,000 CSL personnel and about 13,000 employees in ancillary industries.
- This bolstered plough-back effect on the nation’s economy. That is, it pushed all money back that it consumed.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
INS Vikrant inducted into Indian Navy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Vikrant
Mains level: Indigenization of defense production

The Indian Navy took delivery of IAC-1 the ‘Vikrant’, the nation’s first indigenously built aircraft carrier from its manufacturer, Cochin Shipyard Ltd.
Vikrant
- INS Vikrant also known as Indigenous Aircraft Carrier 1 (IAC-1), is an aircraft carrier constructed by the Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) for the Indian Navy.
- It is the first aircraft carrier to be built in India.
- It is named ‘Vikrant’ as a tribute to India’s first aircraft carrier, Vikrant (R11).
- The name Vikrant means “courageous” in Sanskrit.
- Work on the ship’s design began in 1999, and the keel was laid in February 2009.
- The carrier was floated out of its dry dock on 29 December 2011 and was launched on 12 August 2013.
Why is it important for India to have an aircraft carrier?
- An aircraft carrier is one of the most potent marine assets for any nation, which enhances a Navy’s capability to travel far from its home shores to carry out air domination operations.
- Many experts consider having an aircraft carrier as essential to be considered a “blue water” navy — that is, a navy that has the capacity to project a nation’s strength and power across the high seas.
- An aircraft carrier generally leads as the capital ship of a carrier strike/ battle group.
- As the aircraft carrier is a prized and sometimes vulnerable target, it is usually escorted in the group by destroyers, missile cruisers, frigates, submarines, and supply ships.
And why is it a big deal that this warship has been Made in India?
- Only five or six nations currently have the capability of manufacturing an aircraft carrier, and India has joined this prestigious club now.
- Experts and Navy officials said India has demonstrated the capacity and self-reliance to build what is considered to be one of the most advanced and complex battleships in the world.
- India’s has had aircraft carriers earlier too — but those were built either by the British or the Russians.
- The ‘INS Vikramaditya’, which was commissioned in 2013 and which is currently the Navy’s only aircraft carrier, started out as the Soviet-Russian warship ‘Admiral Gorshkov’.
- India’s two earlier carriers, the ‘INS Vikrant’ and the ‘INS Viraat’, were originally the British-built ‘HMS Hercules’ and ‘HMS Hermes’.
- These two warships were commissioned into the Navy in 1961 and 1987 respectively.
Why will this new warship be named ‘INS Vikrant’?
- IAC-1 — as the carrier is currently codenamed — has been designed by the Indian Navy’s Directorate of Naval Design (DND), and built at Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- Once commissioned, it will be called ‘INS Vikrant’, the name that originally belonged to India’s much-loved first aircraft carrier.
- It was a source of immense national pride over several decades of service before it was decommissioned in 1997.
- The original ‘Vikrant’, a Majestic-class 19,500-tonne warship, which was acquired from the UK in 1961, played a stellar role in the 1971 War with Pakistan.
What weapons and equipment will the new ‘Vikrant’ have?
- The new warship is comparable to India’s existing carrier ‘INS Vikramaditya’, which is a 44,500-tonne vessel and can carry up to 34 aircraft, including both fighter jets and helicopters.
- The Navy had earlier said that once commissioned, IAC-1 will be “the most potent sea-based asset”, which will operate the Russian-made MiG-29K fighter aircraft and Kamov-31 Air Early Warning Helicopters.
- The new ‘Vikrant’ will also operate the soon-to-be-inducted MH-60R Seahawk multirole helicopter manufactured by the American aerospace and defence company Lockheed Martin.
- It will also take onboard the Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) built by Bengaluru-based Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Next-Generation Corvettes for Indian Navy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Corvettes
Mains level: Indian navy modernization

The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has given the Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for the procurement of next-generation Corvettes for the Indian Navy at an approximate cost of Rs 36,000 crore.
What is a Corvette?
- A Corvette is the smallest class of naval ships and it falls below the warship class of a frigate.
- These are highly agile ships and are categorised as missile boats, anti-submarine ships, coastal patrol crafts and fast attack naval vessels.
- The word corvette itself is derived from French and Dutch origin.
- During World War II, the term Corvette was used to describe vessels which had anti-submarine roles assigned to them.
- Modern Corvettes can go up to 2,000 tons in displacement which helps in keeping them agile.
What kind of Corvettes does the Indian Navy possess?
- The Indian Navy at present has the Kamorta Class Corvettes, which are also known as Project 28.
- These ships have an anti-submarine role and are manufactured at Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers in Kolkata.
- The four Kamorta Class Corvettes that the Indian Navy possesses are named INS Kamorta, INS Kadmatt, INS Kiltan and INS Kavaratti.
- The first of these was commissioned in 2014 and the last one in 2020.
What new capabilities will the new generation Corvettes have?
- The next-generation Corvettes will be manufactured for various roles like surveillance missions, escort operations, deterrence, surface action group operations, search and attack and coastal defence.
- It is worth noting that these roles will be in addition to the anti-submarine roles being already performed by the existing Corvettes in the Navy.
- Corvettes will be constructed based on new in-house design of the Indian Navy using latest technology of ship buildings.
- They would contribute to further the government’s initiative of Security and Growth for all in the region (SAGAR).
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
France pulls out of P-75I Project
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: P-75 I
Mains level: Indian navy modernization
Ahead of PM Modi’s scheduled visit, France has denounced its participation in the P-75 India (P-75I) project under which six conventional submarines are to be built in India for the Indian Navy.
Why did France pull out?
- The reason was that the Request for Proposal (RFP) requires that the fuel cell AIP be sea proven, which not the case is for us yet since the French Navy does not use such a propulsion system.
- AIP refers to Air-Independent Propulsion, a technology for conventional — that is, non-nuclear — submarines.
Backgrounder: Project 75
- Project 75 India is a part of India’s thirty-year-old submarine building plan by which all the six submarines which are under the project should already be sailing and it should have been followed by the submarines now for which the RFP has been issued.
- It is a long-awaited and long-overdue project.
- This should have happened way back but it got delayed because it was difficult to find a strategic partnership model.
What is P-75I?
- The Project 75I-class submarine is a follow-on of the Project 75 Kalvari-class submarine for the Indian Navy.
- In the late 1990s, around the time of Kargil war, a three-decade plan took shape for indigenous construction of submarines.
- It was known to have two separate series of submarine building lines – codenamed Project 75 and Project 75I — in collaboration with foreign entities.
- Under this project, the Indian Navy intends to acquire six diesel-electric submarines, which will also feature advanced air-independent propulsion systems.
- This is for enabling them to stay submerged for longer duration and substantially increase their operational range.
What is the status of the project?
- The navy is slightly behind the curve on P-75I.
- The project faces choppy waters; the Naval Group has already announced it is pulling out, and sources said the Russian and Spanish companies might also not proceed with their bids.
- Among the concerns, is the requirement to demonstrate a sea-proven fuel cell AIP.
- While some manufacturers may have the technology, it may not have been proven at sea yet.
- Another problem for the OEMs is the transfer of technology, which is built into the process.
Why does the Navy want AIP subs?
- Simply put, AIP technology allows a conventional submarine to remain submerged for much longer than ordinary diesel-electric submarines.
- All conventional submarines have to surface to run their generators that recharge the batteries that allow the boat to function under water.
- However, the more frequently a submarine surfaces, the higher the chances of it being detected.
- AIP allows a submarine to remain submerged for more than a fortnight, compared to two to three days for diesel-electric boats.
- IP has a force multiplier effect on lethality of a diesel electric submarine as it enhances the submerged endurance of the boat several folds.
What submarines does India have now?
- India has 16 conventional diesel-electric submarines, which are classified as SSKs.
- After the last two Kalvari Class subs are commissioned under P-75, this number will go up to 18.
- India also has two nuclear ballistic submarines, classified SSBN.
Strategic importance of submarines development
- Ageing arsenal: Currently, India has less number of submarines than what is required with some more of those from both types being at various stages of construction.
- Combat roles in near future: The nuclear powered and diesel-electric submarines have their designated roles in the Carrier Battle Groups, which are formations of ships and submarines with Aircraft Carriers at the lead role.
- Strategic deterrence: As per the basic principles of submarine deployment and the minimum requirement for India to create a strategic deterrence, there is a specific number of submarines of both types that India needs to have in active service.
Significance of P-75 I
- ‘Make in India’ Projects: It will serve to facilitate faster and more significant absorption of technology and create a tiered industrial ecosystem for submarine construction in India.
- Self-Reliance: From a strategic perspective, this will help reduce current dependence on imports and gradually ensure greater self-reliance and dependability of supplies from indigenous sources.
- Securing Indo-Pacific: China is increasing its presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and this is creating pressure on the Indian Navy in sprucing up the submarine arm.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
INS Vagsheer: Key features, capabilities
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Vagsheer
Mains level: Project P 75I

The sixth and last of the French Scorpene-class submarines, INS Vagsheer, was launched into water at the Mazagon Docks in Mumbai.
Launch of INS Vagsheer
- It was launched by Veena Ajay Kumar (wife of Union Defence Secretary), in keeping with the naval tradition of launch and naming by a woman.
- The six submarines were being built under Project-75 by the Mazagon Docks under technology transfer from the Naval Group as part of a $3.75-billion deal signed in October 2005:
- INS Kalvari was commissioned in December 2017;
- INS Khanderi in September 2019;
- INS Vagir in November 2020;
- INS Karanj in March 2021; and
- INS Vela in November 2021.
- P 75 is one of two lines of submarines, the other being P75I, as part of a plan approved in 1999 for indigenous submarine construction with technology taken from overseas firms.
Why ‘Vagsheer’
- Vagsheer is named after the sand fish, a deep sea predator of the Indian Ocean.
- The first submarine Vagsheer, from Russia, was commissioned into the Indian Navy on December 26, 1974, and was decommissioned on April 30, 1997.
- The new Vagsheer will be officially named at the time of its commissioning.
Specifications
- Vagsheer can take up to eight officers and 35 men.
- It is 67.5 metres long and 12.3 metres high, with a beam measuring 6.2 metres Vagsheer can reach top speed of 20 knots when submerged and a top speed of 11 knots when it surfaces
- It has four MTU 12V 396 SE84 diesel engines, 360 battery cells for power, and a silent Permanently Magnetised Propulsion Motor.
- The hull, fin and hydroplanes are designed for minimum underwater resistance and all equipment inside the pressure hull is mounted on shock-absorbing cradles for enhanced stealth.
Features
- Vagsheer is a diesel attack submarine, designed to perform sea denial as well as access denial warfare against the adversary.
- It can do offensive operations across the spectrum of naval warfare including anti-surface warfare, anti-submarine warfare, intelligence gathering, mine laying and area surveillance.
- It is enabled with a C303 anti-torpedo counter measure system.
- It can carry up to 18 torpedoes or Exocet anti-ship missiles, or 30 mines in place of torpedoes.
- Its superior stealth features include advanced acoustic absorption techniques, low radiated noise levels, hydro-dynamically optimised shape.
- It has the ability to launch a crippling attack using precision guided weapons, underwater or on surface.
Road ahead
- Vagsheer will be commissioned into the Indian Navy’s Western Command after 12 to 18 months when sea trials end.
- It will be based with Western Naval Command, mostly in Mumbai.
- The submarine will undergo a very comprehensive and rigorous set of tests and trials, for more than a year, to ensure delivery of a fully combat worthy submarine.
Back2Basics: Various classes of Submarines in India
In maritime terms, a class of ships is a group of vessels that have the same make, purpose and displacement.
- Chakra Class: Under a 10-year lease from Russia since 2012
- Arihant Class: Nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines
- Shishumar Class: Diesel-electric attack submarines Indian variant of the Type 209 submarines developed by the German Navy
- Kalvari Class: Diesel-electric attack submarines designed by French company DCNS
- Sindhughosh Class: Kilo-class diesel-electric submarines built with the help of Russia
- Scorpene-Class: French submarines that can undertake various types of missions such as anti-surface warfare, anti-submarine warfare, intelligence gathering, mine laying, area surveillance etc.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
In news: P-8I Aircraft
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: P-8I Aircraft
Mains level: Indian Naval Arsenal

Aviation and defence colossus Boeing delivered India’s 12th maritime surveillance and anti-submarine warfare P-8I aircraft.
P-8I Aircraft
- It is a multi-mission aircraft with state of the art sensors, proven weapons systems, and a globally recognised platform.
- The first aircraft produced by Boeing flew in 2009, and has been in service with the US Navy since 2013, the same year as the Indian Navy.
- Apart from India and the US, it has been chosen by six other militaries in the world.
- The aircraft has two variants — the P-8I, which is manufactured for the Indian Navy, and the P-8A Poseidon.
- The aircraft is designed for long-range anti-submarine warfare (ASW), anti-surface warfare (ASuW), and intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) missions.
Naval operations
- While the Indian Navy uses it for maritime operations, the aircraft was also used in eastern Ladakh in 2020 and 2021, when the standoff with China was at its peak.
- The aircraft for the Indian Navy are called P-8I, and have replaced the ageing Soviet/Russian Tupolev Tu-142s.
Specifications and features
- The P-8I can fly as high as 41,000 feet, and has a short transit time, which reduces the size of the Area of Probability when searching for submarines, surface vessels or search and rescue survivors.
- The aircraft has two engines, and is about 40 metres long, with a wingspan of 37.64 metres.
- Each aircraft weighs about 85,000 kg, and has a top speed of 490 knots, or 789 km/hour.
- It requires a crew of nine, and has a range of 1,200+ nautical miles, with 4 hours on station, which means about 2,222 km.
- According to Boeing, more than 140 P-8 aircraft have “executed more than 400,000 mishap-free flight-hours around the globe”.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
What is Presidential Fleet Review?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fleet Review
Mains level: Indian Naval Arsenal

The President of India recently took part in the Indian Navy’s 12th Presidential Fleet Review.
What is the President’s Fleet Review?
- In simplest terms, it is the country’s President taking stock of the Navy’s capability.
- It showcases all types of ships and capabilities the Navy has.
- It takes place once under every President, who is the supreme commander of the armed forces.
- The President is taken on one of the Naval ships, which is called the President’s Yacht, to look at all the ships docked on one of the Naval ports.
- The yacht will be distinguished by the Ashoka Emblem on her side and will fly the President’s Standard on the Mast”.
Importance of Presidential Fleet Review
- A fleet review is usually conducted once during the tenure of the President.
- So far, 11 Presidential Fleet Reviews have been conducted since Independence, of which two have been International Fleet Reviews, in 2001 and 2016.
- In terms of significance, the Navy’s Presidential review is second only to the Republic Day Parade.
- The President will be given a 21-gun salute before embarking on the yacht.
Do all naval ships participate?
- The idea is to showcase not all the Navy’s ships, but every type of ship — and the kind of capabilities it has at that time.
- The review also includes merchant ships as well.
What else happens in the fleet review?
- In this most formal of naval ceremonials, each ship dressed in full regalia will salute the President as he passes.
- The President will also be reviewing the Indian Naval Air Arm in a display of spectacular fly-past by several helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft.
- In the final stage of the review, a mobile column of warships and submarines will steam past the Presidential Yacht.
How many of these reviews have been held?
- There have been 11 President’s Fleet Reviews since Independence.
- The first was conducted in 1953, under Dr Rajendra Prasad.
- The next one was done not by the President but by the then Defence Minister, Y B Chavan, in 1964.
- Since then, it has been the President reviewing the fleet.
- The longest gap between reviews was of 12 years — between 1989 (President R Venkatraman) and when 2001 (President K R Narayanan).
- The last one was done in 2016, under President Pranab Mukherjee.
Significance of the event
- It is one of the most important events for the Navy, which is essentially showing its allegiance and commitment to defending the country.
- It is a long-standing tradition followed by navies across the world, and according to Navy officials it is a strong bond that links seafarers of the world.
- Historically, a Fleet Review is an assembly of ships at a pre-designated place for the purpose of displaying loyalty and allegiance to the Sovereign and the state.
- In turn, the Sovereign, by reviewing the ships, reaffirms his faith in the fleet and its ability to defend the nation’s maritime interest.
- It is perhaps conceived as a show of naval might. Though it still has the same connotation, assembling of warships without any belligerent intentions is now the norm in modern times.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
In news: Exercise Milan 2022
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Milan
Mains level: NA
Exercise Milan as well as the Fleet Review by President is scheduled to be held this month for which 46 countries have been invited.
Exercise Milan
- Milan began in 1995 and is held biennially and brings together Navies of all the countries in the region.
- It has so far been held at Port Blair in Andaman and Nicobar but is now being shifted to Visakhapatnam which offers more infrastructure as well as sea space for the exercise.
- It has several themes such as anti-submarine warfare among others along with deliberations, including by subject matter experts.
What is Fleet Review?
- A Fleet Review is usually conducted once during the tenure of the President.
- The first PFR was held in 1953 for the first President Dr. Rajendra Prasad.
- Since Independence 11 PFRs have been conducted by the Navy, of which two have been International Fleet Reviews in 2011 and 2016.
- In terms of significance, the Navy’s Presidential review is second only to the Republic Day Parade.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Exercise Sea Dragon 22
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ex Sea Dragon 22
Mains level: Maritime cooperations for Indo-Pacific
India is among the six Indo-Pacific nations participating in Exercise Sea Dragon 22.
Sea Dragon 22
- It is a multi-lateral anti-submarine warfare exercise in the Pacific Ocean hosted by the US.
- The exercise includes the navies of India, Australia, Canada, Japan, the US and South Korea.
- India, Japan, Australia and America are also part of the Quad, and also participate in the Malabar exercise.
- It includes in-flight training, ranging from tracking simulated targets to the final problem of tracking a live US Navy submarine.
Significance of the exercise
- The exercise is significant as almost all of the participating countries have strained relations with China.
- China is expanding its prowess in the Indo-Pacific under its Look West Policy.
Also, take time to read about all major exercises:
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Trilateral Exercise ‘Dosti’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Dosti
Mains level: Not Much
The 15th edition of the biennial trilateral coast guard exercise ‘Dosti’ involving India, the Maldives and Sri Lanka is underway in the Maldives.
Exercise Dosti
- The aim of this exercise is to further fortify the friendship, enhance mutual operational capability, and exercise interoperability and to build cooperation.
- Both the Maldives and Sri Lanka are of strategic importance to New Delhi and to its maritime security interests.
- 2021 marks 30 years since these exercises were first launched.
Significance of the exercise
- These exercises help during joint operations and missions undertaken by countries and also help enhance interoperability.
- Although piracy is not a major issue in this part of the Indian ocean, these kinds of exercises also help coast guards with training for possibilities.
- These exercises help develop a better understanding of the other nation’s coast guard operations and how to enhance coordination during different kinds of missions.
What it involves
- The scope of these exercises are wide-ranging.
- India, Sri Lanka and the Maldives have agreed to work on what they called the “four pillars” of security cooperation.
- These involved the areas of marine security, human trafficking, counter-terrorism and cyber security.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise Malabar
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ex Malabar
Mains level: QUAD security Dialogue
Indian Naval Ships Shivalik and Kadmatt have arrived at Guam, an Island Territory of the USA to participate in the annual Exercise MALABAR-21.
Also read:
Ex Malabar
- MALABAR series of maritime exercises commenced in 1992 as a bilateral IN-USN exercise and has grown in stature over the years to include four prominent navies in the Pacific and Indian Ocean Region.
- It is carried out between navies of Australia, India, Japan, and the USA
- The exercise provides an opportunity for common-minded navies to enhance inter-operability, gain from best practices and develop a common understanding of procedures for Maritime Security Operations.
Significance
- The exercise will see the participation of all four Quad countries.
- Indian Navy also conducted a number of Passage Exercises (PASSEX) with navies from Japan, Australia and the US.
Another Exercise in news: Ex Konkan 2021
- Exercise Konkan 2021 was held between INS Tabar and HMS Westminster on 16 Aug 21 in the English Channel.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Back2Basics: Quad Security Dialogue
- QSD is a strategic dialogue between the United States, Japan, Australia and India that is maintained by talks between member countries.
- The dialogue is paralleled by joint military exercises of an unprecedented scale, titled Exercise Malabar.
- Quad is widely viewed as a response to increased Chinese economic and military power.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Exercise Al–Mohed Al–Hindi
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Al–Mohed Al–Hindi
Mains level: NA
The maiden bilateral naval exercise between India and Saudi Arabia named ‘AL–Mohed AL–Hindi’ has got underway.
Must read:
Ex Al-Mohed AI-Hindi 2021
- This is the first edition of a bilateral naval exercise between India and Saudi Arabia.
- It comprises several shore and sea-based drills between the two navies.
- It reflects the growing defense ties between the two nations in the wake of the Indian Army chiefs’ first visit to the West Asian country last year.
- INS Kochi is the Indian warship participating in the exercise.
- The exercise is being held against the backdrop of growing tensions in the Persian Gulf following a drone attack on the tanker MV Mercer Street off Oman.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise Cutlass Express 2021
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Cutlass Express
Mains level: Not Much
Indian Naval Ship Talwar is participating in Exercise Cutlass Express 2021, being conducted along the East Coast of Africa.
Exercise Cutlass Express
- The exercise is an annual maritime exercise conducted to promote national and regional maritime security in East Africa and the Western Indian Ocean.
- Indian Navy is participating in the exercise in a ‘trainer role’.
The 2021 edition of the exercise involves the participation of:
- 12 Eastern African countries, US, UK, India
- Various international organizations like International Maritime Organization (IMO), United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), Interpol, European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR), Critical Maritime Routes Indian Ocean (CRIMARIO), and EUCAP Somalia
Focus of the exercise
- The exercise focuses on East Africa’s coastal regions.
- It is designed to assess and improve combined maritime law enforcement capacity, promote national and regional security and increase interoperability between the regional navies.
- As part of the exercise, the Indian Navy, together with other partners, shall undertake the training of contingents from various participating countries in various fields across the spectrum of maritime security operations.
Must read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
What is Project Seabird?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Project Seabird
Mains level: Need for a naval base
Defence Minister has recently visited the Karwar Naval Base in Karnataka to inspect infrastructure development under Phase II of “Project Seabird”.
Project Seabird
- The largest naval infrastructure project for India, Project Seabird involves the creation of a naval base at Karwar on the west coast of India.
- INS Kadamba is an Indian Navy base located near Karwar in Karnataka.
- The first phase of construction of the base was code-named Project Seabird and was completed in 2005.
- INS Kadamba is currently the third-largest Indian naval base and is expected to become the largest naval base in the eastern hemisphere after the completion of expansion Phase IIB.
Why need such a base?
- During the Indo-Pakistan War of 1971, the Indian Navy faced security challenges for its Western Fleet in Mumbai Harbour due to congestion in the shipping lanes from commercial shipping traffic, fishing boats and tourists.
- At the end of the war, various options were considered on addressing these concerns
- Upon completion, it will provide the Indian Navy with its largest naval base on the west coast and also the largest naval base east of the Suez Canal.
- The Navy’s lone aircraft carrier INS Vikramaditya is based at Karwar.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise EUNAVFOR
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise EUNAVFOR
Mains level: NA
Indian Navy is participating in the maiden IN – EUNAVFOR Joint Naval Exercise in the Gulf of Aden.
Exercise EUNAVFOR
- EUNAVFOR is a multilateral naval exercise comprising of Italian Navy, Spanish Navy, and French Navy.
- Ships of the four navies will endeavor to enhance and hone their war-fighting skills and their ability as an integrated force to promote, peace, security, and stability in the maritime domain.
- EUNAVFOR and the Indian Navy converge on multiple issues including counter-piracy operations and protection of vessels deployed under the charter of the World Food Programme (UN WFP).
- Indian Navy and EUNAVFOR also have regular interaction through SHADE (Shared Awareness and De-confliction) meetings held annually in Bahrain.
- This engagement showcases increased levels of synergy, coordination, and inter-operability between India and EUNAVFOR.
- It also underscores the shared values as partner navies, in ensuring freedom of seas and commitment to an open, inclusive and rules-based international order.
Mark the nations along the Gulf of Aden:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Seven Indian Navy Ships Deployed for Op Samudra Setu II
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Operation Samudra Setu
Mains level: Paper 3- Operation Samudra Setu II
Operation Samudra Setu II
- In support of the nation’s fight against Covid-19 and as part of operation ‘Samudra Setu II’, seven Indian Naval ships have been deployed for shipment of liquid medical oxygen-filled cryogenic containers and associated medical equipment from various countries.
- Indian Navy also has the surge capability, to deploy more ships when the need arises to further nation’s fight against COVID-19.
- It is pertinent that the ships are combat ready and capable of meeting any contingency in keeping with the attributes of versatility of sea power.
Operation Samudra Setu I
- It may be recalled that Operation Samudra Setu was launched last year by the Navy and around 4000 Indian citizens stranded in neighbouring countries, amidst COVID 19 outbreak, were successfully repatriated back to India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Induction of INS Dhruv
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Dhruv
Mains level: India's naval arsenal

India Navy is set to commission INS Dhruv to track satellites, strategic missiles and map the Indian Ocean bed later this year.
INS Dhruv is no ordinary vessel for the Indian Navy. Read its stealth capabilities and utilities.
INS Dhruv
- INS Dhruv has been developed with the help of the DRDO and Indian Navy with India’s Strategic Force Command and National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO) as main intelligence consumers.
- The indigenously-developed surveillance ship has been built by Hindustan Shipyard Ltd at its Visakhapatnam facility under the Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan initiative.
- The 15,000-tonne ship, part of a classified project, will not only create maritime domain awareness for India in the Indian Ocean but also act as an early warning system for adversary missiles headed towards India.
Stealth capabilities
- INS Dhruv is equipped with active electronically scanned array radars, or AESA considered a game-changer in radar technology.
- It can scan various spectrums to monitor satellites of adversaries that are watching over India.
- It can also understand the range and true missile capability of adversary nations that it finds in the Indo-Pacific.
Benefits offered
- Once the vessel is commissioned, India will be the only country outside the P-5 – the US, the UK, China, Russia and France – to have this capability
- It will act as a major force multiplier to India’s ocean surveillance capabilities.
- It will be able to provide the Indian Navy with an “ECG of the Indian Ocean”.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Mission Sagar-IV
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mission SAGAR
Mains level: Not Much
As part of Mission Sagar-IV, Indian Naval Ship Jalashwa has arrived at Port Anjouan, Comoros to deliver 1,000 Metric Tonnes of rice.
Mission SAGAR, unlike other missions, can create confusion with the name and its purpose. It is not a military exercise. Make note of such special cases. UPSC can ask such questions as one-liner MCQs.
Also note the location of the island country Comoros and its geostrategic significance.
Mission Sagar
- SAGAR is a term coined by PM Modi in 2015 during his Mauritius visit with a focus on the blue economy.
- It is a maritime initiative that gives priority to the Indian Ocean region for ensuring peace, stability and prosperity of India in the Indian Ocean region.
- The goal is to seek a climate of trust and transparency; respect for international maritime rules and norms by all countries; sensitivity to each other`s interests; peaceful resolution of maritime issues; and an increase in maritime cooperation.
- It is in line with the principles of the Indian Ocean Rim Association.
Earlier such missions
- This is the second visit of an Indian Navy ship to the island country within a span of one year.
- Earlier, as part of Mission Sagar-I, in May-June 2020, the Indian Navy had delivered essential medicines to the nation.
- Mission Sagar-II was undertaken in May-June 2020, wherein India reached out to Maldives, Mauritius, Seychelles, Madagascar and Comoros, and provided food aid and medicines.
- Sagar-III was undertaken in Sihanoukville Port, Cambodia.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] INS Karanj – A Kalvari Class Submarine
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Karanj, Various classes of Submarines
Mains level: NA

Indian Navy’s third stealth Scorpene-class Submarine INS Karanj has been commissioned into the Indian Navy. It also completed the trials of the Indigenous Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) System jointly developed by Naval Materials Research Laboratory (NMRL) and DRDO.
In a rare case, we would see a question based on various classes of Indian Submarines in the CSP. However, we can expect a question based on the AIP system in the CSP and CAPF exam.
INS Karanj
- INS Karanj is the third submarine of the first batch of six Kalvari-class submarines for the Indian Navy.
- It is a diesel-electric attack submarine based on the Scorpene-class, designed by French naval defence and energy group DCNS and manufactured by Mazagon Dock Limited, an Indian shipyard in Mumbai.
What is AIP?
For this, we have to understand how a submarine works. Traditionally we hear about two types of submarines- Nuclear and Diesel Electric.
Diesel Electric Submarines
- While Nuclear Submarines can stay submerged for a prolonged period and remain undetected, Diesel Electric submarines cannot do so, and they must surface after a stipulated time interval.
- Their Diesel Propulsion would need air to run the engine like any other Vehicle or Aircraft engines and for this, they would need oxygen which is not available underwater.
- Hence they have to move closer to the surface so that their engines can breathe air through their snorkels.
So, these diesel turbines charge the batteries available in the submarine and once the batteries are fully charged, the submarine goes underwater where the propeller shaft, as well as other systems, runs on the power stored in the batteries.
- This makes the Submarine very much vulnerable to threats from Air, Sea or even underwater.
- Not only has this, but the storage of excessive fuel also reduced the overall performance and weapon holding of the submarine too.
Why don’t we can induct only the Nuclear Submarines in the Navy?
- Though nuclear submarines can stay underwater for months, they cannot do so with total stealth.
- While a diesel-electric submarine (while underwater) is making no noise, Nuclear submarines have a lot of vibrations that are generated from the coolant pumping system of their reactors which must run nonstop.
- This makes even nuclear submarines vulnerable to depth sonars.
- Moreover, the manufacturing cost of these submarines is several times higher than those of diesel-electric ones.
- So, the most effective and commercially viable solution is a diesel-electric submarine with AIP.
What is AIP, then?
- Over the years the biggest challenge before the mariners was to ensure that the submarines can sustain underwater for a prolonged time.
- AIP is any marine propulsion technology that allows a non-nuclear submarine to operate without access to atmospheric oxygen (by surfacing or using a snorkel).
- While there are different types of AIP systems being pursued internationally, the DRDO has applied fuel cell-based AIP using hydrogen onboard.
- Fuel cell-based AIP has merits in performance compared to other technologies
- While the first two submarines (INS Kalvari & INS Khanderi) are equipped with French-made AIPs, the rest of the submarines will be equipped with an Indian system.
Note: The Project 75I-class submarine is a follow-on of the Project 75 Kalvari-class submarine for the Indian Navy.
Significance for India
- With this induction, India has joined the club of six other elites who have the capacity to design and install such complex systems.
- These countries are France, China, Spain, Sweden, Germany and Russia.
- Indian AIP system is unique. It is one of the most advanced AIP systems of the world where Fuel Cell technology is used to generate onboard power.
- With indigenous AIP, submarines can stay underwater for more than 3 weeks in low consumption mode, more than 2 weeks in endurance mode and 2-4 days in max power mode.
Back2Basics: Various classes of Submarines in India
In maritime terms, a class of ships is a group of vessels that have the same make, purpose and displacement.
- Chakra Class: Under a 10-year lease from Russia since 2012
- Arihant Class: Nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines
- Shishumar Class: Diesel-electric attack submarines Indian variant of the Type 209 submarines developed by the German Navy
- Kalvari Class: Diesel-electric attack submarines designed by French company DCNS
- Sindhughosh Class: Kilo-class diesel-electric submarines built with the help of Russia
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Malabar Naval Exercises
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Malabar Exercises
Mains level: Not Much
The 24th edition of Malabar maritime exercise, hosted by Indian Navy in 2020, witnessed the participation by Indian Navy, United States Navy, Japan Maritime Self Defence Force and Royal Australian Navy.
Such news is nothing but the repetitive chunk that occurs every year with few or no new developments. Still, they are significant for the sake of information as Australia has joined it after several apprehensions.
Question can be expected in CAPF, CDS or AFCAT exams.
About Ex. Malabar
- Exercise Malabar is a trilateral naval exercise involving the US, Japan and India as permanent partners.
- This year Australia has joined as a permanent partner.
- Originally begun in 1992 as a bilateral exercise between India and the United States, Japan became a permanent partner in 2015.
- Past non-permanent participants are Australia and Singapore.
- The annual Malabar series began in 1992 and includes diverse activities, ranging from fighter combat operations from aircraft carriers through Maritime Interdiction Operations Exercises.
Significance of Australia’s inclusion
- Earlier, India had concerns that it would give the appearance of a “quadrilateral military alliance” aimed at China.
- Now both look forward to the cooperation in the ‘Indo-Pacific’ and the strengthening of defence ties.
- This has led to a convergence of mutual interest in many areas for a better understanding of regional and global issues.
- Both are expected to conclude the long-pending Mutual Logistics Support Agreement (MLSA) as part of measures to elevate the strategic partnership.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
India’s efforts in increasing Maritime domain awareness
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Regional Maritime Information Fusion Centre (RMIFC)
Mains level: Paper 3- Increasing maritime domain awareness
The article analyses India’s efforts in increasing the maritime domain awareness while increasing the cooperation with the neighbourhood and other countries.
Indian Navy improving domain awareness
- The enemy at sea is often unrecognisable — a terrorist, a pirate, a criminal or a sea robber.
- Of late, the Indian Navy has been on a drive to improve domain awareness in the Indian Ocean.
- The Indian Navy’s efforts seem focused primarily on monitoring Chinese activity in the Eastern Indian Ocean, particularly in the seas around the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- The Navy is seeking to expand India’s surveillance footprint by setting up radar stations in the Maldives, Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- Mauritius, the Seychelles and Sri Lanka have already integrated into the wider coastal radar chain network.
Increasing international cooperation
- Seven Indian Ocean countries — Bangladesh, Myanmar, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, Mauritius and the Seychelles — will soon post Liaison Officers at the Indian Navy’s Information Fusion Centre-Indian Ocean Region in Gurugram.
- France already has an officer at the IFC.
- Four other Indo-Pacific navies — Australia, Japan, the U.K and the U.S. — have also agreed to position officers at the centre.
- As a result of such cooperation, IFC is fast emerging as the most prominent information hub in the Eastern Indian Ocean.
- India is increasing engagement in the Western Indian Ocean by positioning a Liaison Officer at the Regional Maritime Information Fusion Centre (RMIFC) in Madagascar.
- India has also posted an officer at the European Maritime Awareness in the Strait of Hormuz (EMASOH) in Abu Dhabi to assist in the monitoring of maritime activity.
Stronger partnership with France
- Delhi’s moves in the Western and South-Western littorals have been facilitated by France.
- Two countries have signed a logistics agreement in 2019.
- France is keen for a stronger partnership in the maritime commons.
- France has been instrumental in securing ‘observer’ status for India at the Indian Ocean Commission and is pushing for greater Indian participation in security initiatives in the Western Indian Ocean.
- However, the Indian Navy’s priority remains South Asia, where the naval leadership remains focused on underwater domain awareness in the Eastern Indian Ocean.
Concerns over increasing Chines presence
- There is concern that the Chines navy may be poised to develop a generation of quieter submarines that would be hard to detect.
- As a result, India has moved to expand its underwater detection capabilities in the Eastern chokepoints.
- India might also partner Japan in installing an array of undersea sensors near the Andaman Islands to help detect Chinese submarines.
India as a security provider: Manifestation of SAGAR
- India’s initiatives in the maritime domain are motivated by more than just strategic considerations.
- Shipping agreements with 21 countries in the Indian Ocean have enabled a comprehensive picture of maritime traffic.
- Efforts are under way to help smaller island states build capacity to combat regional threats.
- India’s military satellite (GSAT-7A) may soon facilitate a real-time sharing of maritime information with partners.
- These endeavours are a manifestation of Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) that advances the idea of India as a ‘security provider’ and ‘preferred partner’ in the Indo-Pacific region.
Challenges
- Indian initiatives, however, are yet to bring about an alignment of objectives and strategies of regional littoral states.
- While cooperative information sharing allows for a joint evaluation of threats, countries do not always share vital information timeously.
Conclusion
To bring real change, India must ensure seamless information flow, generating operational synergy with partners, and aim to expand collaborative endeavours in shared spaces.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Information Management and Analysis Centre (IMAC)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IMAC
Mains level: India's maritime security
India is looking at integrating more countries into coastal radar network IMAC.
What is IMAC?

- The Indian Navy’s IMAC located in Gurugram which was set up after the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks is the nodal agency for maritime data fusion.
- It functions under the National Maritime Domain Awareness (NMDA) Project.
- The NMDA project was launched in accordance with the vision of PM on SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- The IMAC monitors movement of more than 120,000 ships a year passing through the Indian Ocean.
- The cargo carried by these ships accounts for 66 per cent of world crude oil, 50 per cent of container traffic and 33 per cent of bulk cargo.
- Thus, IMAC performs a very crucial role in collecting shipping information, analysing traffic patterns and sharing the inputs with the user agencies.
Mission SAGAR, unlike other missions, can create confusion with the name and its purpose. Make note of such special cases. UPSC can ask such questions as one liner MCQs.
Expanding IMAC
- It is meant to enable real-time monitoring of the high seas for threats as also expand India’s assistance for capacity building to Indian Ocean littoral states.
- Efforts are in advanced stages to set up coastal radar stations in Maldives, Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- Mauritius, Seychelles and Sri Lanka have already been integrated into the country’s coastal radar chain network.
- Similar plans are in the pipeline with Maldives and Myanmar and discussions are ongoing with Bangladesh and Thailand.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
What is Project 17A?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Project 17A
Mains level: India's maritime capability

Himgiri, the first of the three stealth frigates being built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, under Project 17A for the Navy, was launched into the water.
Try this question:
Q“To be secure on Land, we must be Supreme at Sea”. In this context, discuss why India is primarily a Maritime Nation?
Project 17A
- The coveted ‘Project 17A’ was cleared by the govt back in 2015.
- It involves the building of seven stealth frigates at an estimated cost of Rs 50,000 crore.
- Of these seven, the contract for three frigates was awarded to GRSE while the contract for another four frigates was awarded to Government-owned Mazagon Docks Limited (MDL) which is based in Mumbai.
- These frigates will come armed with advanced state-of-the-art sensors and boast of top-notch stealth features.
- They will represent the most advanced class of major surface warships for the Indian Navy in a decade, also featuring BrahMos supersonic surface-to-surface missiles.
- These will also have torpedoes and rockets to hit submarines and rapid-fire guns to destroy anti-ship missiles as well as a heavy main gun to engage ships and coastal target.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Operation Trident and its significance
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Operation Trident
Mains level: Liberation of Bangladesh

Every year, India celebrates December 4 as Navy Day to commemorate Operation Trident – a key offensive during the 1971 India-Pakistan War. This year, it is the 50th anniversary of the victory in the 1971 War.
This newscard is crucial for the CAPF aspirants. It hardly holds any importance for CS prelims. But the grit, glory and honour of our armed forces is a matter of pride that every CS aspirants should know.
Operation Trident
- The India-Pakistan War of 1971 had begun on December 3, when the Pakistan Air Force launched pre-emptive strikes on airfields in Western India.
- Following the Battle of Longewala, the Indian Navy inflicted heavy damage on Pakistani vessels in Karachi harbour.
- India responded by formally declaring war in the wee hours of December 4.
- On December 4, under Operation Trident, the Indian Navy sank three vessels near the Pakistani port city of Karachi.
- The Indian Air Force also played a crucial role, when Karachi’s Kemari oil tanks were strafed by the IAF on the same day in an independent operation which it did not claim.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
To be taken seriously, Quad needs military heft
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Quad needs naval heft
The article suggests projection of naval power to ensure the stability in the Indian Ocean.
Quad conducts Malabar exercise
- In November, the Quad converged to continue the Malabar series, with a total of just eight ships.
- The idea of Quad is to form a grouping of democratic nations in the Indian Ocean, and use naval power to convey a message to Beijing.
- The message a grouping of eight ships would convey to a nation thinking in terms of five aircraft carriers remains would not be taken seriously.
Importance of naval power in ensuring oceanic stability
- There is no substitute for naval power to ensure oceanic stability, but one alternative lies in the area of Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA).
- Perhaps, some thought may already have been given to MDA in the twin agreement to BECA (Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement), and Maritime Information Sharing Technical Agreement (MISTA) signed between India and the US.
- There is little information available in the public domain about MISTA.
- But MISTA should cover an omnibus agreement for Maritime Patrol Aircraft (MPA) operating and information sharing for the entire Indo-Pacific.
- The Pacific has a high density of MPA assets, while they are sparse in the Indian Ocean, particularly the western Indian Ocean.
- The Australians can cover the Malacca Straits, but for the west Indian Ocean, the US will probably have to base a squadron of P-8 aircraft at Masirah or Diego Garcia.
- Today, the primary weapon system of most warships is the surface-to-surface missile, with ranges of up to 200 km.
- The ships’ sensor range is only up to 100 km.
- So, accurate target information has to be supplied beyond 100 km by aircraft or helicopters in what is called Over the Horizon Targeting (OTHT).
- With the Indo-Pacific fully covered by the MPAs of the Quad, a PLAN ship in the Indian Ocean is in imminent danger of being sunk at will
Conclusion
A public announcement of a division of the Indo-Pacific into areas of responsibility for MDA, between members of the Quad will send an unmistakable signal to Beijing. With a desultory Quad naval exercise, once a year of a few ships, Beijing will only be amused that a “threat” exists to its ambition to become a global power.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
National Maritime Domain Awareness Centre (NMDAC)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IMAC, NMDAC
Mains level: India's maritime security
The Navy’s Information Management and Analysis Centre (IMAC), the nodal agency for maritime data fusion will soon become a National Maritime Domain Awareness (NMDA) centre.
Try this question:
Q“To be secure on Land, we must be Supreme at Sea”. In this context, discuss why India is primarily a Maritime Nation?
What is IMAC?
- The IMAC monitors movement of more than 120,000 ships a year passing through the Indian Ocean.
- The cargo carried by these ships account for 66 per cent of world crude oil, 50 per cent of container traffic and 33 per cent of bulk cargo.
- Thus, IMAC performs a very crucial role in collecting shipping information, analysing traffic patterns and sharing the inputs with the user agencies.
- It tracks vessels on the high seas and gets data from the coastal radars, white shipping agreements, Automatic Identification Systems (AIS) transponders fitted on merchant ships, air and traffic management system and global shipping databases.
Transforming to NDMAC
- The IMAC will soon transform into a national NMDA centre, wherein it will be a multi-agency centre.
- The NMDA project was launched in accordance with the vision of PM on SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- Approved by the Defence Acquisition Council in 2012, the IMAC became operational in 2014 and is located in Gurugram.
- It is the nodal centre of the National Command Control Communication and Intelligence System (NC3I), which was established to link the Navy and the Coast Guard.
Why such a move?
- India has a coast line of about 7500 km and an Exclusive Economic Zone(EEZ) of over 2 million sq kms.
- In addition, we are endowed with abundant oceanic wealth comprising a large number of island territories and vast sea bed area, over 97 % of our national trade is carried by sea routes.
- It is therefore, imperative that we modernize the Navy which always has to be in a high state of preparedness.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
MQ-9B Sea Guardian Unarmed Drone
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MQ-9B, BECA
Mains level: India-US defense cooperation

The Indian Navy has inducted two MQ-9B Sea Guardian unarmed drones procured from the U.S. on lease.
Try this question from CSP 2018:
Q.What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news?
(a) An Israeli radar system
(b) India’s indigenous anti-missile programme
(c) An American anti-missile system
(d) A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea
MQ-9B Sea Guardian
- The Guardian, which is the maritime variant of the Predator MQ-9 UAV, has a maximum endurance of 40 hours and a maximum flying altitude of 40,000 feet.
- It has 360-degree maritime surveillance radar and optional multimode maritime surface search radar.
- The drone can perform over-the-horizon long-endurance, medium-altitude Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) missions.
- The recently released Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020 has introduced an option for leasing military platforms.
- The Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement for Geo-Spatial Cooperation (BECA) has simplified such high- technology cooperation.
About BECA
- BECA will help India get real-time access to American geospatial intelligence that will enhance the accuracy of automated systems and weapons like missiles and armed drones.
- Through the sharing of information on maps and satellite images, it will help India access topographical and aeronautical data, and advanced products that will aid in navigation and targeting.
- This could be a key to Air Force-to-Air Force cooperation between India and the US.
- BECA will provide Indian military systems with a high-quality GPS to navigate missiles with real-time intelligence to precisely target the adversary.
- Besides the sailing of ships, flying off aircraft, fighting of wars, and location of targets, geospatial intelligence is also critical to the response to natural disasters.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Exercise SITMEX-20
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise SITMEX
Mains level: NA
The second edition of the India, Thailand and Singapore trilateral naval exercise SITMEX-20 has concluded in the Andaman Sea.
Exercise SITMEX-20
- The SITMEX series of exercises are conducted to enhance mutual inter-operability and imbibing best practices between IN, Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN) and Royal Thai Navy (RTN).
- The first edition of SITMEX, hosted by Indian Navy, was conducted off Port Blair in September 2019.
- The 2020 edition of the exercise is being hosted by RSN.
- The maritime drill witnessed a variety of exercises including naval manoeuvres, surface warfare exercises and weapon firings.
- Besides improving inter-operability, SITMEX series of exercise also aims to strengthen mutual confidence and develop common understanding and procedures towards enhancing the overall maritime security in the region.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Project-75
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Arsenal of Indian Navy
Mains level: Modernisation of Indian Navy

The fifth Scorpene submarine of Project-75 named ‘Vagir’ has been launched at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in Mumbai.
In a rare case we would see a question based on various classes of Indian Submarines in the CSP. However, we can expect a question based on Project-75 in the CSP and CAPF exam very well.
About Vagir
- Vagir, ex-Russia, named after the Sand Fish, a deadly deep-sea predator of the Indian Ocean, was commissioned into the Indian Navy on December 3, 1973, and was decommissioned on June 7, 2001.
- In true nautical tradition, it is refurbished under the same name – Vagir.
- It is rebuilt with superior stealth features (such as advanced acoustic absorption techniques, low radiated noise levels, hydro-dynamically optimized shape etc.) and precision-guided weapons.
- The attack can be launched with both torpedoes and tube-launched anti-ship missiles, whilst underwater or on the surface.
What is Project-75?
- The Project 75I-class submarine is a follow-on of the Project 75 Kalvari-class submarine for the Indian Navy.
- In the late 1990s, around the time of Kargil war, a three-decade plan took shape for indigenous construction of submarines.
- It was known to have two separate series of submarine building lines – codenamed Project 75 and Project 75I — in collaboration with foreign entities.
- Under this project, the Indian Navy intends to acquire six diesel-electric submarines, which will also feature advanced air-independent propulsion systems.
- This is for enabling them to stay submerged for longer duration and substantially increase their operational range.
Submarines commissioned till date
- The submarines in the current Kalvari-class take their names from erstwhile decommissioned classes of submarines named Kalvari.
- It included Kalvari, Khanderi, Karanj and Vela class — which included Vela, Vagir, Vagsheer.
- Two submarines of the ongoing project, Kalvari and Khanderi, have been commissioned into the Indian Navy.
- The third submarine, Karanj, is in the last phase of rigorous sea trials.
- The fourth Scorpene, Vela, has commenced her sea trials, whilst the sixth and last submarine, Vagsheer, is being readied for boot together.
Strategic importance of these submarines
- India currently operates one submarine each in nuclear-powered Classes of Chakra and Arihant and in addition to 14 submarines belonging to three classes of Diesel Electric category — Kalvari, Shishumar and Sindhughosh, some of which are ageing.
- The nuclear powered and diesel-electric submarines have their designated roles in the Carrier Battle Groups, which are formations of ships and submarines with Aircraft Carriers at the lead role.
- As per the basic principles of submarine deployment and the minimum requirement for India to create a strategic deterrence, there is a specific number of submarines of both types that India needs to have in active service.
- Currently, India has less number of submarines than what is required with some more of those from both types being at various stages of construction.
Back2Basics: Classes of Submarines in India
- In maritime terms, a class of ships is a group of vessels which have the same make, purpose and displacement.
- In the Navy and Coast Guard in India, the ships belonging to a particular class are named in a specific manner.
- Many times the names have the same first letters, prefixes, similar meanings or the names belong to a particular type of words for example names of cities, persons, mythological concepts, animals, rivers, mountains, weapons, etc.
- The class is generally named after the first vessel in the category. In some cases, a particular class of vessels takes their names from an earlier class of vessels which are now decommissioned.
- Like Kalvari – which means Tiger Shark, Vagir has been named after a Sand Fish, a predatory marine species.
- Khanderi has been named after an Island Fort built by Chhatrapati Shivaji, which played a key role in his Navy. Karanj has also been named after an Island located South of Mumbai.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Malabar Naval Exercise
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Countries participating in exerciese
Mains level: Paper 3- Defence exercises
Upping the ante against China amid the ongoing LAC confrontations, Australia has formally accepted India’s invite for the upcoming Malabar Exercise.
About Ex. Malabar
- Exercise Malabar is a trilateral naval exercise involving the United States, Japan and India as permanent partners.
- Originally begun in 1992 as a bilateral exercise between India and the United States, Japan became a permanent partner in 2015.
- Past non-permanent participants are Australia and Singapore.
- The annual Malabar series began in 1992 and includes diverse activities, ranging from fighter combat operations from aircraft carriers through Maritime Interdiction Operations Exercises.
Significance of Australia’s inclusion
- Earlier, India had concerns that it would give the appearance of a “quadrilateral military alliance” aimed at China.
- Now both look forward to the cooperation in the ‘Indo-Pacific’ and the strengthening of defence ties.
- This has led to a convergence of mutual interest in many areas for a better understanding of regional and global issues.
- Both are expected to conclude the long-pending Mutual Logistics Support Agreement (MLSA) as part of measures to elevate the strategic partnership.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise SLINEX-20
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SLINEX
Mains level: Not Much
The Eighth Edition of annual Indian Navy (IN) – Sri Lanka Navy (SLN) bilateral maritime exercise SLINEX-20 is scheduled off Trincomalee.
About SLINEX-20
- SLINEX-20 aims to enhance inter-operability, improve mutual understanding and exchange best practices and procedures for multi-faceted maritime operations between both navies.
- In addition, the exercise will also showcase the capabilities of our indigenously constructed naval ships and aircraft.
- SLINEX series of exercise exemplifies the deep engagement between India and Sri Lanka which has strengthened mutual cooperation in the maritime domain.
- Interaction between the SLN and IN has also grown significantly in recent years, in consonance with India’s policy of ‘Neighbourhood First’ and the vision of ‘Security and Growth for all in the Region (SAGAR)’.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Dismantling INS Viraat
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INS Viraat
Mains level: Not much
Decommissioned aircraft carrier INS Viraat is set to be scrapped at a ship breaking yard at Alang in Gujarat soon.
In rarest case we would see a question based on this in CSP. However, we can expect a question based on INS Viraat in the CAPF exam very well.
INS Viraat
- Viraat, a Centaur class aircraft carrier weighing 27,800 tonnes, served in the British Navy as HMS Hermes for 25 years from November 1959 to April 1984.
- It was commissioned into the Indian Navy in May 1987 after refurbishment and had operated Harrier fighter jets.
- It was decommissioned from in March 2017, and the Navy had been incurring expenditure since then on its upkeep, such as the provision of electricity and water, and repairs.
- In 2018, the Maharashtra Cabinet approved a proposal to convert the carrier into a museum and hospitality centre on a PPP basis and had invited bids. But there were no takers.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
What are MK 54 torpedoes, AGM-84L Harpoon missiles that US has cleared for sale to India?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Read the attached story
Mains level: India-US arms trade
The US has approved a military sale to India of 16 MK 54 all round up lightweight torpedoes and ten AGM-84L Harpoon Block II air-launched missiles. India plans to use the equipment requested in both the deals on the Indian Navy’s Boeing P-8I maritime aircraft.
What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)” , sometimes seen in the news? (CSP 2018) .
MK 54 lightweight torpedo

- The MK 54 lightweight torpedo is known as the Lightweight Hybrid Torpedo (LHT).
- It weighs around 608 pounds, while its warhead weighs around 96.8 pounds and is highly explosive.
- The primary use of this equipment is for offensive purposes when deployed by anti-submarine warfare aircraft and helicopters, and for defensive purposes when deployed by ships and against fast, deep-diving nuclear submarines and slow-moving, quiet, diesel-electric submarines.
AGM-84L Harpoon Block II air-launched missiles

- The Harpoon missile system will be integrated into the P-8I aircraft to conduct anti-surface warfare missions in defence of critical sea lanes.
- It uses GPS-aided inertial navigation to hit the designated target.
- Its warhead weighs over 500 pounds and is capable of delivering lethal firepower against targets, including land-based targets, coastal defence sites, surface-to-air missile sites, exposed aircraft and industrial or port facilities.
About P-8I aircraft

- Boeing’s P-8s are designed for long-range anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare and intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance missions.
- The P-8s India version is called the P-8I, and helps the Indian Navy carry out important maritime operations.
- According to Boeing, the aircraft can surpass 25,000 flight hours, and gives the Navy a significant edge in the strategically important Indian Ocean.
- India currently has eight of these aircraft and is scheduled to receive four more by 2022.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Bay of Bengal Offshore Sailing Expedition (BBSE)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bay of Bengal Offshore Sailing Expedition (BBSE)
Mains level: Not Much
Indian Naval Sailing Vessels Mhadei and Tarini set sail for the Bay of Bengal Offshore Sailing Expedition from the Indian Naval Ocean Sailing Node at Goa.
BBSE
- This would be the maiden major mixed crew sailing expedition of the Indian Navy with crew composition of five naval officers including two women officers in each boat.
- It would be covering a total distance of 6,100 Nautical miles each and will be at sea for 55 days.
- The prolonged voyage of nearly three months during this expedition would showcase harnessing of renewal energy namely wind energy to propel the boats.
- The expedition is also in pursuance of the GOI mission of ‘Nari Shakti’ providing opportunity to women officers at par with men.
- The sailing vessels as part of the expedition would make replenishment halts at ports of Phuket, Yangon, Chittagong and Colombo.
About the vessels
- Mhadei and Tarini inducted in the Indian Navy on 08 February 2009 and 18 February 2017 respectively have been the vessels of choice for the naval expeditions in various sailing expeditions, including three circumnavigations and thus have thousands of miles tucked under their belt.
- Mhadei has successfully completed two circumnavigations, three Cape to Rio trans-Atlantic races and several other expeditions around various continents.
- The vessel has covered in excess of 1,36,000 nautical miles.
- Tarini created history in 2017-18 when six Indian Naval women officers sailed the vessel on maiden circumnavigation voyage titled Navika Sagar Parikrama.
- She thereafter also participated in mixed crew Kochi to Seychelles sail training expedition during the 10th-anniversary celebration of the IONS.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Operation Vanilla
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HADR, Op Vanila
Mains level: NA
Indian navy will perform HADR operations in Madagascar under ‘Operation Vanilla’.
Operation Vanilla
- Indian Navy Ship Airavat whilst mission deployed in the Southern Indian Ocean has been diverted to Antsiranana based on request recieved from Madagascar.
- The ship will undertake Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) mission as part of ‘Operation Vanilla’.
- It has been launched to provide assistance to the affected population of Madagascar post devastation caused by Cyclone Diane.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
Exercise ‘Sahyog-Kaijin’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise ‘Sahyog-Kaijin’
Mains level: NA
Exercise ‘Sahyog-Kaijin’
- Indian and Japanese coast guards participated in a joint exercise ‘Sahyog-Kaijin’ on January 16.
- The aim behind ‘Sahyog-Kaijin’ is to strengthen the bond between the two countries.
- One ship of the Japanese Coast Guard and four ships and an aircraft of the Indian Coast Guard participated in the joint exercise.
- The drill is a five-day event.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Exercise MILAN 2020
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ex Milan
Mains level: Not Much
Visakhapatnam is set to host an International Naval event ‘MILAN’ in March 2020.
MILAN 2020
- It is a multilateral naval exercise aimed to enhance professional interaction between friendly foreign navies and learn from each other’s strengths and best practices in the maritime domain.
- The Exercise with the theme ‘Synergy Across the Seas’ would provide an excellent opportunity for Operational Commanders of friendly foreign navies to interact with each other in areas of mutual interest.
- Of the 41 navies invited, confirmations from over 30 navies have been received towards their participation in MILAN 2020.
In continuity with:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Indian Navy Updates
[pib] Operation Sankalp
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Op Sankalp
Mains level: Safeguards against the ongoing turmoil in the Gulf
Indian Navy has commenced Maritime Security Operations, code named Op SANKALP, in the Gulf region to ensure safe passage of Indian Flag Vessels transiting through the Strait of Hormuz.
Op Sankalp
- Indian Navy warships and aircraft were deployed to establish presence, provide a sense of reassurance to the Indian merchantmen, monitor the ongoing situation and respond to any emergent crises.
- The operation is being progressed in close coordination with all stakeholders including Ministry of Defence, Ministry of External Affairs, Ministry of Shipping, Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas and DG, Shipping.
- The Navy continues to monitor the situation in the Gulf region and is maintaining presence in the region to ensure security of our sea borne trade and the safety of Indian Flag Merchant Vessels transiting through the region.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024








