
Introduction
- Modern space research in India is traced to the 1920s, when scientist S. K. Mitra conducted a series of experiments leading to the sounding of the ionosphere by applying ground-based radio methods in Kolkata.
- Later, Indian scientists like C.V. Raman and Meghnad Saha contributed to scientific principles applicable in space sciences.
- However, it was the period after 1945 that saw important developments being made in coordinated space research in India.
- Organized space research in India was spearheaded by two scientists: Vikram Sarabhai—founder of the Physical Research Laboratory at Ahmedabad—and Homi Bhabha, who established the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in 1945.
Vision
- The Indian space program is driven by the vision of Vikram Sarabhai, considered the father of the Indian space program.
- Throughout the years, ISRO has upheld its mission of bringing space to the service of the common man, to the service of the Nation.
- In the process, it has become one of the six largest space agencies in the world.
Making of ISRO

- India’s space program began with a vision to harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration
- In this view, the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established in the tenure of PM Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962.
- INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, also under the DAE. This was done keeping in view the urge of scientist Vikram Sarabhai recognizing the need in space research.
- In 1972, GoI set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS) bringing ISRO under the DOS.
- The establishment of ISRO thus institutionalized space research activities in India. It is managed by the DOS, which reports to the PM of India.
Applications of India’s space asset
India’s space mission can be broadly categorized into the following categories:
- Launch vehicle fleet like PSLV, GSLV etc,
- Satellite programs ex. INSAT,
- Satellite Navigation program ex. IRNSSS and NAVIC
- Extraterrestrial exploration like Chandrayaan, Mars Orbiter Mission
- Human Spaceflight Programme viz. Gaganyaan
Telecommunication
- India uses its satellite communication network – one of the largest in the world – for applications such as land management, water resources management, natural disaster forecasting, radio networking, weather forecasting, etc.
- Business, administrative services, and schemes such as the National Informatics Centre (NIC) are direct beneficiaries of applied satellite technology
Military
- Integrated Space Cell, under the Integrated Defence Staff of the Ministry of Defence, has been set up to utilize more effectively the country’s space-based assets for military purposes and to look into threats to these assets.
- This command leverages space technology including satellites.
Telemedicine
- ISRO has applied its technology for telemedicine, directly connecting patients in rural areas to medical professionals in urban locations via satellites.
- Since high-quality healthcare is not universally available in some of the remote areas of India, the patients in remote areas are diagnosed and analyzed by doctors in urban centers in real-time via video conferencing.
Biodiversity Information System
- ISRO has also helped implement India’s Biodiversity Information System, completed in October 2002.
- Based on intensive field sampling and mapping using satellite remote sensing and geospatial modeling tools, maps have been made of vegetation cover on a 1: 250,000 scale.
Significant feats
Disaster Management Support (DMS)

- ISRO’s technologies and applications have always proved useful during natural calamities.
- In 2016, ISRO’s support on this front was significant during the Uttarakhand Forest Fires and floods in the north-eastern states of Manipur and Assam.
Reusable Launch Vehicle – Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD)
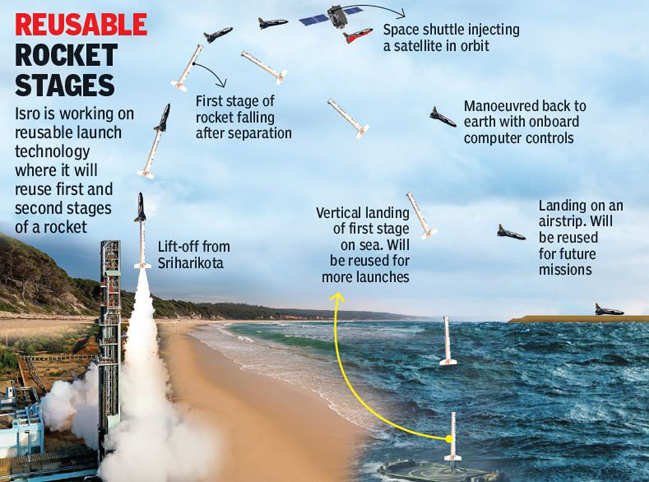
- RLV-TD was successfully flight-tested on May 23, 2016.
- Critical technologies such as reusable thermal protection system, re-entry mission management, guidance & control along with autonomous navigation were tested during the flight.
Launch of Cartosat series

- On June 22, 2016, ISRO put into orbit, India’s Cartosat (Cartosat-2C) earth observation satellite along with 19 other satellites using Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C34) in a single mission.
- Cartosat series of satellites will be used for various strategic and civilian applications. It includes Geographical Information System (GIS), Land Information System (LIS), utility management and precision studies.
- The satellite which has been called ‘India’s eyes in the sky’ by experts due to its high surveillance and monitoring capabilities will assist the other military satellites in the Cartosat series.
104 satellites launch
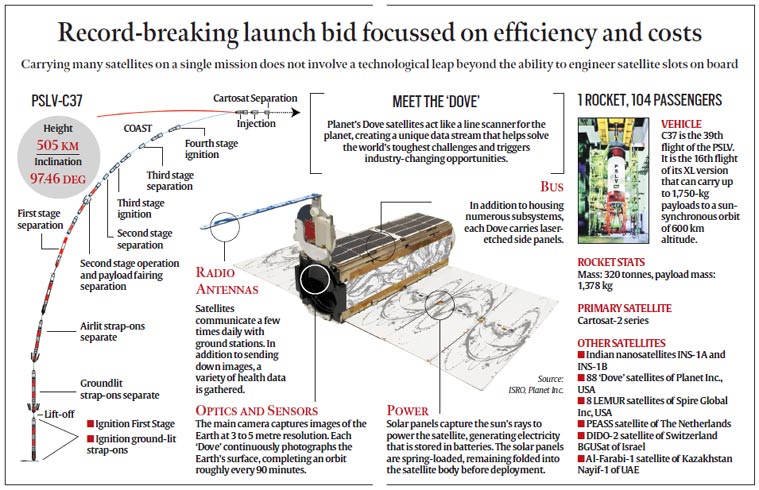
- India created history by successfully launching 104 satellites on a single mission, overtaking the previous record of 37 satellites launched by Russia in 2014.
- PSLV-C37 successfully carried and deployed a record of 104 satellites in sun-synchronous orbits.
Towards Scramjet Engine Technology

- On August 28, 2016, ISRO successfully conducted its first experimental mission of the Scramjet Engine at SDSRC, Sriharikota.
- The flight testing of the Scramjet Engine made India the fourth country to demonstrate such capabilities.
- The technology is expected to radically change the future space transportation systems by ISRO.
- A fully functional Scramjet Engine is expected to reduce the launch costs by half and minimize the chance of engine failure.
Important missions
I. Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM)

- The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) – launched on November 05, 2013 and successfully inserted into Mars orbit on September 24, 2014, has various achievements to its credit.
- It is the first interplanetary mission realized by India and the first Indian spacecraft to incorporate full-scale onboard autonomy to overcome the long distances and the communication gaps due to non-visibility periods.
- Marking India’s first venture into the interplanetary space, MOM will explore and observe Mars surface features, morphology, mineralogy and the Martian atmosphere.
- Further, a specific search for methane in the Martian atmosphere will provide information about the possibility or the past existence of life on the planet.
II. Chandrayaan Mission
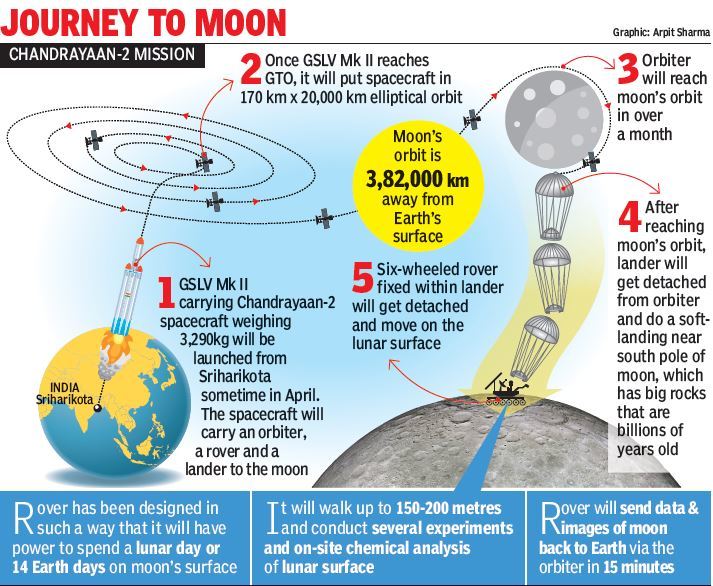
- Chandrayaan Mission-I in 2008 – discovered the presence of water on the surface of the Moon and turned a new chapter in the world’s understanding of Moon.
- Chandrayaan-2 which consisted of an Orbiter, Lander and Rover, was all equipped with scientific instruments to study the moon.
- However, a part of the mission failed as the Vikram lander crash-landed on the lunar surface.
III. Solar Mission

- Aditya-L1 is India’s first dedicated scientific mission to study the sun.
- It is meant to observe only the solar corona- the outer layers of the Sun, extending to thousands of km above the disc (photosphere).
IV. Gaganyaan Mission

- The human spaceflight program will provide a unique micro-gravity platform in space for conducting experiments and testbed for future technologies.
- The program is expected to give impetus to economic activities within the country in terms of employment generation, human resource development, and enhanced industrial capabilities.
- Human Spaceflight capability will enable India to participate as a collaborating partner in future Global space exploration initiatives with long term national benefits.
Developments so far
- ISRO has completed the development of launch vehicle GSLV Mk-III which has the necessary payload capability to launch a 3-member crew module in low earth orbit.
- It has also tested the crew escape system which is an essential technology for human space flight.
- Elements of the life support system and Space suit also have been realized and tested.
- In addition, the orbital & re-entry mission and recovery operations have been flight demonstrated in Space Capsule Re-entry experiment (SRE) mission.
VI. Building own Space station
- India plans to build a space station as a follow-up programme of the Gaganyaan mission.
- ISRO chairman K. Sivan has said that India will not join the International Space Station program and will instead build a 20-tonne space station on its own.
Criticisms of Space Programmes
- For long, India is known to be making investments in the space arena for social, scientific and security purposes. However many fundamentalists see investment in space as a waste of money.
- All previous missions of ISRO are about race for planetary resources. Unfortunately, it has not planned for any missions to asteroids, an ideal bed for mineral mining.
- After Chandrayaan 2 failure there is a danger that future ambitious missions could also end up only as a ‘feel-good program’ with Gaganyaan coming ahead.
A wise investment
- Ironically, one of India’s current challenges is the trickling down effect of investments in technology by the ISRO.
- Many people myopic vision questioned the relevance of space activities in a newly independent nation which was finding it difficult to feed its population.
- Any space exploration mission undertaken by a developing country like India is likely to prompt the argument that such investments need to be redirected in areas that need immediate intervention (ex. education, health).
- One of the simplest ways of resolving this debate is to concretely showcase how technologies developed for space missions like Chandrayaan 2 find their way into the daily lives of citizens.
- However former President APJ Abdul Kalam opined that if Indians were to play a meaningful role in the community of nations, they must be second to none in the application of advanced technologies to their real-life problems.
Why we must explore?
- Curiosity and exploration are vital to the human spirit and accepting the challenge of going deeper into space is the way ahead.
- The intangible desire to explore and challenge the boundaries of what we know and where we have been has provided benefits to our society for centuries.
- Human space exploration helps to address fundamental questions about our place in the Universe and the history of our solar system.
- Through addressing the challenges related to human space exploration we expand technology, create new industries, and help to foster a peaceful connection with other nations.
Way Forward
- Future readiness is the key to maintaining an edge in technology and ISRO endeavors to optimize and enhance its technologies as the needs and ambitions of the country evolve.
- Thus, ISRO is moving forward with the development of heavy lift launchers, human spaceflight projects, reusable launch vehicles, semi-cryogenic engines, single and two stage to orbit (SSTO and TSTO) vehicles, development and use of composite materials for space applications, etc.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indian_Space_Research_Organisation#Applications
http://www.arthapedia.in/index.php?title=Space_Programme_in_India
https://www.dailyo.in/politics/isro-space-research-chandrayaan-antrix/story/1/25922.html
https://debatewise.org/debates/137-space-exploration-is-a-waste-of-money/#yes2
https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/268062-5-reasons-space-exploration-is-more-important-than-ever
