Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: The post of CDS and its responsibilities.
Mains level: Paper 3-Security forces and their mandates.
Context
Recently Chief of Defence Staff post was created by the Government. The utility of this post and the problem it could create are debated.
History leading to the post
- First World War brought to the fore the command and control dilemmas of concurrent conflicts.
- During the colonial years of Great Britain, an issue that received consideration was the British higher command and control structures.
- With the declaration of the Second World War, the responsibility of higher command fell on War Cabinet serviced by the Chiefs of Staff Committee.
- Winston Churchill as prime minister given the supreme power but remained responsible to the parliament.
- After the U.S. entered the war, a unified command required a single commander.
- After the war ended and the Cold War started, Eisenhower became the supreme commander of NATO.
- While political powers were vested in the NATO council.
- Despite the experience of the World Wars the U.S. has not created CDS.
- In the U.S., the military chain of command runs directly from theatre commanders to civilian secretaries to the President.
- Britain, however, created the post of the Chief of Defence Staff.
The outline for India
- The three-tier defense management structure was adopted by Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Cabinet Committee on security has served India for well over the years.
Role of CDS
- Department of Military Affairs, headed by CDS will deal with the Army, Navy and Air force and The Territorial Army.
- Works related to procurement related exclusively to the services except for capital acquisition.
- He will also act as a Principal Military Advisor to the Defence Minister.
- CDS will not exercise any military command, including the three Service Chiefs, so as to be able to provide impartial advice to the political leadership.
A subordination
- There would be an implied subordination of the three service chiefs to the CDS notwithstanding any declaration to the contrary.
- CDS is tasked with facilitating the restructuring of military commands.
- Bringing about jointness in operations including through the establishment of joint/ theatre command.
- This could encroach upon the domain of the service chiefs.
- The CDS would outrank the three service chiefs even though all are four-star.
- CDS could override the Service Chiefs on critical tactical and perhaps even strategic issues.
Conclusion
- The Department of Military Affairs would exercise control over the three services and also most problematic is the erosion of the civilian supremacy which could result with the creation of the post.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- International relations.
Context
The raging fire in Australia gives provides an opportunity for India and Australia to deepen their dialogue including on energy.
Scope for the two countries
- At this moment India and Australia have a rare opportunity to translate their converging interests into a partnership.
- At Australia India Leadership Dialogue last month in Melbourne, the breadth and depth of the relationship was evident.
- As a consequence of the bushfires, the debate on global warming, climate change and fossil fuels is going to intensify in the weeks ahead.
- Environmental activism has gained ground throughout Australia.
- Indian Ocean Dipole may have triggered the drought that is related to the fires.
- The campaign against fossil fuels and the export of coal is sure to intensify.
- India and Australia are two economies with a great stakeholding in fossil fuels.
- It is critical for India and Australia to ensure that their dialogue on energy acquires momentum.
- Both countries must simultaneously strengthen the International Solar Alliance and the search for other alternative green fuels.
Common threat of China
- Leadership Dialogue also recognised that we are living through a period of immense turbulence, disruption, and even subversion.
- Presence of assertive China is the single biggest challenge to our two countries.
- In India, there is a consensus that the Australia-India relationship is an idea whose time has well and truly come.
Area of coordination
- India and Australia can work on the area of water management to trauma research to skill and higher education.
- Both the countries can also work in the area of maritime security, cybersecurity, counterterrorism,
- In a survey, Indians ranked Australia in the top four nations towards which they feel most warmly.
- Both have a strategic interest in ensuring a free, open, inclusive and rules-based Indo-Pacific region.
- Indians are today the largest source of skilled migrants in Australia.
- there is need for an early conclusion of a bilateral Free Trade Agreement.
Conclusion
There is a large scope for both countries to coordinate on wide issues like energy, research, security and work together for the benefit of both countries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- Health.
Context
The deaths of nearly 200 children in Kota, from largely preventable diseases, lays bare the condition of the healthcare system in India.
Where does India stand?
- According to UNICEF’s ‘State of World’s Children 2019’ report, India reported the maximum number of deaths of children under five in the world in 2018.
- 8,82,000 children under five died that year.
- That means around 2,416 deaths per day.
- The death of children due to largely-preventable illnesses is a matter of serious concern and calls for urgent introspection.
Factors that govern child health
- Most of the children who died in Gorakhpur, Muzaffarpur and Kota belong to the lowest strata of the society.
- It won’t be wrong to conclude that they were victims of structural violence.
- This structural violence is unleashed through a multitude of social, political and economic factors apathy of healthcare professionals, poor health services/infrastructure
- And low rates of female literacy, economic inequality, the rigid caste system, social apartheid, lack of political will and patriarchy play role.
- As a society, we have stopped looking at the deaths of our citizens through the prism of compassion and concern.
- Structural violence influences the nature and distribution of extreme suffering.
What is being done in the wrong way?
- The government is considering the takeover of 750 district hospitals by private medical colleges through a public-private partnership (PPP) model.
- This, despite ample evidence about the failure of the model in the country’s healthcare system.
- Nobel laureate Kenneth Arrow demonstrated that profit and private involvement in healthcare lead to an erosion of trust.
- An Individual’s demand for medical services is irregular and unpredictable, the involvement of a private market model for such services can be disastrous.
- The U.S.’s experiences in the PPP model in healthcare have shone a light on the deficits in transparency and highlighted the lack of care of vulnerable groups.
Conclusion
- What urgently a sincere engagement by the state in matters concerning peoples’ health.
- We need to question the government’s priorities in a country where nearly a million children die every year
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GDP, GNP, GVA etc.
Mains level: First Advance Estimates
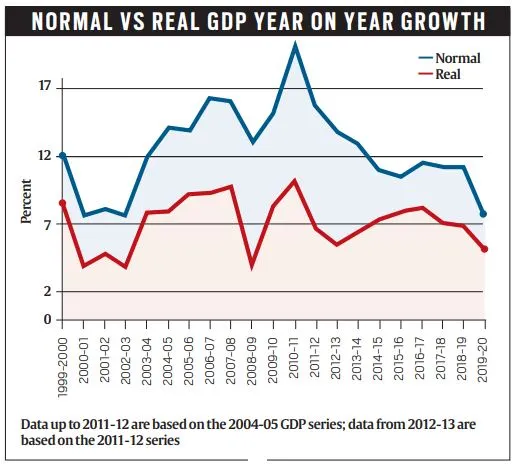
The First Advance Estimates (FAE) were recently released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
The First Advance Estimates and their significance
- The First Advance Estimates (FAE) extrapolate a variety of data, such as the Index of Industrial Production (IIP), the financial performance of listed companies, first advance estimates of crop production etc., for the first 7 to 8 months to arrive at the annual figure.
- The significance of the FAE is that this is the final bit of official data before the government presents its next Budget.
- The sector-wise Estimates are obtained by extrapolation of indicators like-
- IIP of first 7 months of the financial year,
- financial performance of Listed Companies in the Private Corporate sector available upto quarter ending September, 2019
- 1st Advance Estimates of Crop production,
- accounts of Central & State Governments, information on indicators like Deposits & Credits, Passenger and Freight earnings of Railways, Passengers and Cargo handled by Civil Aviation, Cargo etc., available for first 8 months of the financial year”.
Estimates for 2018-19
- It estimated India’s GDP will grow by just 5 per cent in the current financial year (2019-20). Last financial year, 2018-19, the Indian economy grew at 6.8 per cent.
- The gross value added (GVA), which maps the economic activity from the income side as against the GDP which maps it from the expenditure side, is expected to grow by 4.9 per cent in 2019-20 as against 6.6 per cent in 2018-19.
Drivers of the GDP
There are four main drivers of the GDP:
- One, the private consumption expenditure – that is the expenditure that you and I make in our personal capacity. This category has grown by just 5.7 per cent in 2019-20 while it grew by 8 per cent last financial year.
- The second driver is the expenditure made by the Government. This grew by 10.5 per cent, which is higher than the rate of growth (9.2 per cent) in the last financial year.
- But the most disappointing number is the deceleration in business investments in the economy.
- This driver, which is the key to sustainable long-term growth, grew by less than 1 per cent; last financial year it grew by 10 per cent.
- This shows that while the private consumption demand is tepid, businesses have completely turned off the tap on new investments despite the government making a once-in-generation cut in corporate taxes.
Performance in terms of GVA
- The GVA data provides a detailed picture. Given that the overall GVA has decelerated sharply, almost all sectors have witnessed slower growth in economic activity.
- Only “Public Administration, Defence and Other Services,“ which essentially measures how the government did, grew by 9.1 per cent.
- All other sectors saw a GVA growth that was slower than the average growth in the last financial year.
- The worst performing sectors are ‘Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing’, ‘Mining and Quarrying’, ‘Manufacturing’ and ‘Construction’, which are expected to see a GVA growth of 2.8 per cent, 1.5 per cent, 2.0 per cent and 3.2 per cent respectively.
Back2Basics
Real vs. Nominal GDP
- GDP is the total market value of all goods and services produced in the economy during a particular year, inclusive of all taxes and subsidies on products.
- The market value taken at current prices is the nominal GDP.
- The value taken at constant prices — that is prices for all products taken at an unchanged base year (2011) — is the real GDP.
- In simple terms, real GDP is nominal GDP stripped of inflation.
- Real GDP growth thus measures how much the production of goods and services in the economy has increased in actual physical terms during a year.
- Nominal GDP growth, on the other hand, is a measure of the increase in incomes resulting from rise in both production and prices.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GOCO Model
Mains level: Various investment models
Indian Army has initiated the process of identifying potential industry partners to implement the Government Owned Contractor Operated (GOCO) model for its base workshops and ordnance depots intended to improve operational efficiency.
GOCO model
- The GOCO model was one of the recommendations of the Lt. Gen. DB Shekatkar (Retd.) committee to enhance combat capability and re-balancing defence expenditure.
- In GOCO model, the assets owned by government will be operated by the private industries.
- Under the GOCO model, the private companies need not make investments on land, machinery and other support systems.
- The missions are set by government and the private sectors are given full independence in implementing the missions using their best practices.
- The main advantage of the model is that the targets are achieved in lesser time frame. Also, it will boost competitiveness among the private entities paving way to newer technologies.
Who will be eligible under the mode?
- The service provider should be an Indian registered company with at least 10 years of working experience in related domains and have an average annual turnover of ₹50 crore for each of the last three financial years.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Op Twist, Yeild Curve
Mains level: Outcomes of the Op Twist
Reserve Bank of India Governor has informed that the market’s reaction to Operation Twist was on expected lines.
Operation Twist
- The simultaneous buy-sell of government bonds, known as Operation Twist, was conducted to bring down long-term interest rate while allowing short term rates to inch up.
- The move was aimed at addressing liquidity, which is assymetric — abundant at the shorter end but not on the longer end. The move will help in monetary transmission.
- The central bank has so far carried out three rounds of simultaneous bond buy-and-sell via open market operations.
For more reading, navigate to the page:
Operation Twist
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Indian diaspora in Gulf region
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has announced a five-year multiple-entry visa scheme for all nationalities, in a move that is geared towards promoting tourism in the country.
What is UAE’s new visa scheme?
- According to the Dubai-based Gulf News, prior to this, tourists could get single or multiple-entry visas for a duration of 30 or 90 days.
- In the new five-year multiple-entry system, visa holders may be allowed to stay for six months at a stretch.
- The details of the scheme are yet to be announced. The country’s Federal Authority for Identity and Citizenship will be implementing the decision.
- Travellers from Africa, some South American countries, Arab states outside the Gulf, and European states from outside the European Union and the former Soviet Union previously needed visas.
- The UAE currently receives more 2.1 crore tourists annually, and has recently increased its pace of rolling out policies to boost its trade and tourism sectors.
Other reforms
- In July 2019, the UAE allowed women employed in the country to sponsor work permits for their husbands, fathers, and adult children, and reduced the fees for obtaining work permits by 50 per cent to 94 per cent for 145 services and transactions.
- In the same month, the Emirate of Dubai said it would accept the Indian rupee (INR) for transactions at duty-free stores.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SASE
Mains level: Not Much
Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment (SASE) has issued an Avalanche warning to Leh in Ladakh region.
SASE
- SASE is a laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO)
- It is located near Manali, Himachal Pradesh.
- Its primary function is research in the field of snow and avalanches to provide avalanche control measures and forecasting support to Armed forces.
- Leh is important as it has two passes namely Chang La and Khardung La with world’s highest motorable roads through them with several avalanche-prone zones.
- Its utility is also meant for the soldiers in the worlds highest battle filed Siachen, in the region.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Great Indian Bustard
Mains level: Protection measures for GIB

Since June last year, nine GIB eggs collected from the Desert National Park in Jaisalmer where a conservation centre has been set up, have hatched, and the chicks are reported to be doing well.
Great Indian Bustard
- The Great Indian Bustard, one of the heaviest flying birds, can weigh up to 15 kg and grow up to one metre in height.
- It is considered the flagship grassland species, representing the health of the grassland ecology.
- For long, conservationists have been demanding to secure this population, warning that the bird might get extinct in the coming decades.
- It would become the first mega species to disappear from India after Cheetah in recent times.
- Till 1980s, about 1,500-2,000 Great Indian Bustards were spread throughout the western half of India, spanning eleven states.
- However, with rampant hunting and declining grasslands, their population dwindled.
- In July 2011, the bird was categorised as “critically endangered” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Various threats to GIBs
I. General threats to GIB
- Habitat loss & fragmentation, change of land use pattern, desertification, ill-thought plantation of exotic & invasive species in grassland ecosystems are some of the generic causes.
- Neglect of state institutions due to classification of ‘grasslands’ as ‘wastelands’, conversion of grasslands to agriculture lands due to increasing irrigation potential and decline of nature/GIB-friendly agrarian practices, are all commonly and correctly blamed for the steady decline in India’s GIB population.
II. Role of Noise Pollution
- Noise pollution affects the mating and courtship practices of the GIB.
- The male GIB inflates his ‘gular’ pouch (near the neck) which almost touches the ground, in order to produce a large booming sound which reverberates across the grassland.
- The male GIB does this to attract GIB females and to inform them of his exact location in the vast expanse of the grassland.
- Thus, the sound of the male GIB should be loud enough to transcend the walls of the sanctuary and be audible to female GIBs in the fields nearby.
- The noise generated by human activities, whether be it by vehicles, tractors, music during processions, firecrackers, may interfere with the GIB’s mating call and drown it out.
III. Other threats
- The rate of reproduction amongst GIBs is very low; the female GIB lays only one egg per year.
- This solitary egg is under threat from natural predators of the grasslands such as jackals, hyenas or foxes or invasive species such as crows or feral dogs.
- In such a scenario, every opportunity the GIBs lose to mate pushes the species closer to extinction.
Protection Measures
- Birdlife International uplisted this species from Endangered to Critically Endangered (2011)
- Protection under CITES Appendix I
- Protection under Schedule I Wildlife (Protection) Amendment Act 2002
- Project Great Indian Bustard (Rajasthan): aims at identifying and fencing off bustard breeding grounds in existing protected areas as well as provide secure breeding enclosures in areas outside protected areas.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now


