Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3- PDS and issue of excess food stock with FCI.
Context
A substantial rise in consumer food price inflation to 14.12% in December 2019, the highest ever in the past six years, has driven the retail price inflation in this country.
Discrepancies in the fiscal deficit
- Policy dilemma for the RBI: Though the CPI was at 14.12% in December but with the core inflation rate still not overshooting the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) medium-term target of 4(+/- 2)%.
- Speculations hover as to whether the RBI monetary policy committee will go for another rate cut in the coming month.
- This is a policy dilemma for the central bank
- Why is the dilemma? The dilemma is because the moot issues regarding the government’s key economic estimates, such as the fiscal deficit, largely remain unresolved.
- Discrepancies flagged by the CAG: The CAG has stated that the current figures on deficit have been kept at a 1.5% to 2% low by not including the government’s off-budget borrowings from public accounts, such as the National Small Savings Fund (NSSF).
- According to media reports, such off-budget expenditure of the current government stands at ₹1.5 lakh crore in 2019–20.
- The major portion of off budged expenditure on food subsidy: About three-fourths of the incremental off-budget expenditure is on account of under-recoveries in food subsidies of the Food Corporation of India (FCI).
- Low allocation but high expenditure on food subsidy: For instance, the 2019–20 Union Budget had provisioned food subsidy at₹1.84 lakh crore.
- While the overdue of the FCI is already at₹1.86 lakh crore.
- For these burgeoning overdue, FCI’s off-budget borrowings from the NSSF have been on the rise.
Excessive stock by the government and rising inflation
- Issue of supply management: The issues of agricultural supply management are relegated to the background by the standard causality argument of “crop damages” caused by excessive rains and that the inflation will ease out once the new harvest comes in.
- This argument can hold some water for horticulture crops like onions that saw an almost 200% rise in price in November and December.
- Unable to explain inflation in wheat and other cereals: This argument may not find traction in explaining the price inflation of wheat and other cereals.
- holding the excessive cereal stock: With the government currently stocking much higher quantities of cereals at the FCI than the buffer norms.
- 45.8 million tonnes of wheat as against the buffer norm of 27.5 million tonnes and nearly double the amount of rice vis-à-vis the buffer norm of 13.5 million tonnes.
- India is now a cereal surplus economy.
- Why then the inflation in cereal prices? Is this artificially created by the government through its irrational stocking practice?
- Some fundamental concerns are triggered at this juncture.
- Concerns with excess stocks
- First-Higher stock means higher subsidy bill-With the economic costs of the FCI being 12 times or more than the allocation cost of the grains through the public distribution system-higher stocks would imply higher subsidy bills.
- Second–No benefit of the stock: In tandem with the first, ad hoc releasing of the stocks will not bring about any major changes in the situation.
- Third–Hiding fiscal deficit from the public: In this context, off-budget borrowing can serve various politically expedient purposes.
- It has enabled the government to showcase a consistently low share (below 1%) of subsidies in national income.
- Thereby diverted the public attention from two critical facts: the FCI’s tipping financials and the country’s (grossly) underestimated fiscal deficit.
Conclusion
The government must recall that the “illusion” of this acceptable limit of inflation potentially rests upon the savings of the common consumers, which is being unduly misemployed by the government.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3- Face recognition technique, its uses and related issue.
Context
Facial recognition technology is set to become an integral part of the law enforcement toolkit, but we should regulate this technology before it pervades our public spaces.
What are the issues with the use of facial recognition?
- Enormous possibilities for law enforcement agencies:
- Detectives have been using facial recognition to solve crimes for almost as long as the camera has been in existence.
- Use of AI for facial recognition: It is but a logical extension of the modern crime solver’s toolkit to use artificial intelligence (AI) on the most identifiable physical feature of people, their face.
- Screening faces within hours: An image captured at the scene of a crime can now be screened against photographs of entire populations for a match within a matter of hours.
- Uneasiness with being watched: The idea of being watched by devices linked to vast databases far out of sight makes liberal societies uneasy.
- Invasion of privacy: The intrusion that is causing alarm, however, has nothing to do with the technology itself, and everything to do with the all-pervasive surveillance it enables.
Should there be no rules governing it?
- Issue of accuracy: How accurately faces are identified by machines is a major point of concern. Deployed in law enforcement, false matches could possibly result in a miscarriage of justice.
- Judicial scrutiny: Even a low rate of error could mean evidence faces judicial rejection. It is in the judiciary’s interest, all the same, to let technology aid police-work.
- Racial bias: First up for addressal is the criticism that facial recognition is still not smart enough to read emotions or work equally well for all racial groups.
- With iterative use, it will improve.
- Mala fide use: Since such tools can be put to mala fide use as-rogue drones equipped with the technology, for example, should never be in a position to carry out an assassination.
- Nor should an unauthorized agent be able to spy on or stalk anyone.
- Caution in the developed countries: Apart from California, the European Union has also decided to exercise some caution before exposing people to it.
- Privacy as fundamental rights in India: India, which has recently accepted privacy as a fundamental right, would do well to tilt the Western way on this.
Conclusion
- We need regulations that restrict the use of facial recognition to the minimum required to serve justice and ease commercial operations. For the latter, customer consent should be mandatory.
- There will be some overlaps. Its use at an aerobridge to board an aircraft, for example, could serve the interests of both state security and the airline, but data-sharing could risk leakage.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- India-US ties, what are the issues that introduces friction in the ties between the two.
Context
Persistent in their efforts to remake their countries and their engagement with the world, Mr Modi and Mr Trump are shaking up the bilateral ties between the two countries, and the resultant flux could outlive their tenures.
The emergence of both the leaders on similar promises
- Improvements over the legacy of their predecessors: Both leaders continuously reiterate that their predecessors were incapable of protecting national interest.
- The compulsion to reframe the national interest: Such premises commits them both to reframe the national interest, and both have articulated it with clarity and force.
- For instance, Mr Modi, in Houston in September 2019 and Mr Trump in Davos this week, went great lengths to lay out figures that presented their respective regimes as the most effective guardians.
- Both have cultural and economic agenda: Both dispensations believe that “the people” had been given a raw deal by earlier regimes.
- Both have a cultural and economic agenda.
- National awakening: They are now leading a national reawakening, and working hard for the hard-working people.
- Both believe that cultural nationalism is a force for the good.
- Securing borders and entry barriers: Both believe that national borders need to be strengthened by stricter monitoring and setting new bars for entry.
- Renegotiating the treaties: Both leaders try to renegotiate the contract between the union and the States, and between citizens and the state within their respective countries.
- The supremacy of executive: They assert the supremacy of the executive over the legislature and the judiciary.
- Shared values: The notion of shared values of India and the U.S. has acquired a whole new meaning under Mr Trump and Mr Modi.
Politics and governance
- Hopes of status-quo in bilateral relations shattered: It was hoped that the stronger U.S.-India ties- that have autonomous drivers of convergence-would not be impacted by the nationalist politics of these two leaders.
- But both leaders have been remarkably true to their politics in their governance.
- Current tumult in the India-US ties: Shared values notwithstanding, national interests as perceived by these leaders have several points of divergence and therein lies in the current tumult in India-U.S. ties.
- Opposition to the “world order”: Mr Trump has been outspokenly confrontational with the “world order” that he says has worked against American interests.
- Dismantling the treaties: America under Mr Trump has wrecked treaties such as the Paris climate agreement and institutions such as the World Trade Organization and the United Nations, disrupting the “rule-based order”.
- India’s relations with Bangladesh: India’s spirited outreach in the neighbourhood is still playing out. India’s historically warm ties with Bangladesh have been frayed after CAA.
- India’s ambitions on the global level
- The seat at the UNSC: India under continues to push for more space for itself in global affairs by seeking a permanent seat in the UN Security Council and membership.
- NSG membership: India is also pushing for the membership of the Nuclear Suppliers Group.
- The US actions at global levels
- Expansion of the principle of the pre-emptive strike: America expanded the principle of pre-emptive strike to include the assassination of a senior official of Iran.
- Renegotiating the treaties: After dismantling the North American Free Trade Agreement, Mr Trump forced Mexico and Canada to accede to his demands in a new trade deal.
- The India-US relations and impact of U.S. relations with other countries
- Impact on India-US ties: India’s ties with the U.S. are impacted by America’s ties with India’s adversaries and neighbours, China and Pakistan.
- Hopes of alignment in the Indo-US ties: Mr Trump’s bluster against both had lit hope that there would finally be a near-complete alignment between India and the U.S. on strategy.
- US-Iran conflict: Despite Mr Trump’s avowed opposition to America’s endless wars in West Asia, the US is going against Iran headlong, which is not in India’s interest.
- Relations with Gulf Countries: Trump and Mr Modi share a strong bonding with the Gulf Cooperation Council kings, but their courses in the region are diverging.
- US-Pakistan coming closer once again: The American President’s impatience to get out of Afghanistan has already pushed his administration closer to Pakistan, which is now further necessitated by his adventurist Iran policy.
- The US disregard for China’s expansionist policies: Mr Trump has been singularly focused on one question-trade. He cares little about China’s expansionism and at any rate that is not a factor in his ties with other Asian countries.
India-US ties- Points of fission
- On the trade front: Mr Trump has bracketed India and China as two countries that have duped his predecessors to gain undue advantage. Which is far from seeing India as deserving special concessions to counterbalance China as old wisdom demanded.
- Ending GSP: The US ended India’s status under the World Trade Organization’s Generalized System of Preferences and took other punitive measures.
- India trying to decrease the trade surplus: By increasing hydrocarbon imports from the U.S., the government is trying to reduce India’s trade surplus.
- Restrictions on H1-B visa: The US has tightened the restrictions on the H1-B visa which is used by the Indian companies.
- Decreasing bipartisan support in the US: The mobilisation of Indian diaspora in America by the government has resulted in the inevitable blowback.
- Diaspora divided and bipartisan support waning: The diaspora has been divided, and the bipartisan support for India is now squandered. Progressive sections on the Democratic side and religious libertarians and evangelicals on the Trump side are both concerned over India’s actions back home.
Conclusion
Partnership with America is critical to India. India must take the steps to align the interest but whenever it diverges India must take measures to minimise its impact on India while furthering its interests.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India's Forex reserves, SDR, Reserve tranche
Mains level: Forex Reserves and its significance
India’s foreign exchange reserves rose by $943 million to touch a lifetime high of $462.16 billion according to the latest data from the RBI.
Forex reserves of India
- They are holdings of cash, bank deposits, bonds, and other financial assets denominated in currencies other than Indian rupee.
- The reserves are managed by the Reserve Bank of India for the Indian government and the main component is foreign currency assets.
- They act as the first line of defense for India in case of economic slowdown, but acquisition of reserves has its own costs.
- They facilitate external trade and payment and promote orderly development and maintenance of foreign exchange market in India.
- They act as a cushion against rupee volatility once global interest rates start rising.
Composition of Forex
- Reserve Bank of India Act and the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 set the legal provisions for governing the foreign exchange reserves.
- RBI accumulates foreign currency reserves by purchasing from authorized dealers in open market operations.
- The Forex reserves of India consist of below four categories:
- Foreign Currency Assets
- Gold
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs)
- Reserve Tranche Position
What is Reserve tranche?
- Reserve tranche is a portion of the required quota of currency each member country must provide to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) that can be utilized for its own purposes.
What are Special Drawing Rights?
- The SDR is an international reserve asset, created by the IMF in 1969 to supplement its member countries’ official reserves
- The SDR is neither a currency nor a claim on the IMF.
- Initially SDR was defined as equivalent to 0.888671 grams of fine gold, which at the time, was also equivalent to one U.S. dollar.
- After the collapse of the Bretton Woods system, the SDR was redefined as a basket of currencies.
- This basket Includes five currencies—the U.S. dollar, the euro, the Chinese renminbi, the Japanese yen, and the British pound sterling.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Shola Forests
Mains level: Western Ghats and its biodiversity richness

Shola Forests
- The Shola forests of South India derive their name from the Tamil word solai, which means a ‘tropical rain forest’.
- Classified as ‘Southern Montane Wet Temperate Forest’ the Sholas are found in the upper reaches of the Nilgiris, Anamalais, Palni hills, Kalakadu, Mundanthurai and Kanyakumari in the states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- These forests are found sheltered in valleys with sufficient moisture and proper drainage, at an altitude of more than 1,500 metres.
Vegetation
- The upper reaches are covered with grasslands, known as Shola grasslands.
- The vegetation that grows in Shola forests is evergreen. The trees are stunted and have many branches. Their rounded and dense canopies appear in different colours.
- Generally, the leaves are small in size and leathery. Red-coloured young leaves turning into different colours on maturity is a prominent characteristic of the Shola forests.
- Epiphytes like lichens, ferns and bryophytes usually grow on the trees.
- The occurrence of Himalayan plants like rhododendron in these Shola forests is a mystery.
Significance of Sholas
- Sholas thus act as ‘overhead water tanks’. They play a major role in conserving water supply of the Nilgiris’ streams.
- The trees are slow-growing varieties which produce timber of little or no value and probably take at least a century to mature.
- The rolling grasslands found on top of the Western Ghats, enhance the beauty of the region. Usually, Shola forests and grasslands are found in a ratio of 1:5.
- The rain received from the Southwest and Northeast monsoons is harvested by the Shola forest-grassland ecosystem, leading to the formation of the Bhavani river that finally drains into the Cauvery.
- Thus, the Shola forest-grassland ecosystem of the Nilgiris, also supports the prosperity of Cauvery delta farmers.
- As tree species of the montane, evergreen forests are flammable, regeneration of any Shola tree species is completely prevented except for Rhododendron nilagiricum, the only Shola tree that can tolerate fire.
Threats to Sholas
- Unfortunately, the Sholas have begun to gradually shrink due to the introduction of alien plant species and annual fire occurrences.
- Alien species like Sticky Snakeroot, Gorse and Scotch Broom introduced during British rule, have encroached upon the grasslands.
- During 1840, tree species such as Acacia and Eucalyptus were introduced from Australia.
- Afterwards, between 1886 and 1891, Pine and Cypress were introduced, again from Australia. As the alien species grew, the forests and grasslands gradually became degraded and shrank.
- In addition, unscientific agricultural practices like growing tea on the slopes, cattle grazing and fuel wood collection have become serious causes for degradation.
- Unregulated tourism has created concrete jungles, traffic congestion and caused the generation of garbage.
Wrath of Eucalyptus
- During 1849, the extent of Shola forests was 8,600 hectares (ha), grasslands 29,875 ha and agriculture was 10,875 ha.
- No wattle or eucalyptus was planted in the area at that time.
- The comparison of the results of the 1849 and 1992 studies shows that cultivation of tea, wattle and eucalyptus has reduced the Shola forest-grassland ecosystem to a great extent.
Protective measures
- After realizing the seriousness of the situation, the government banned the planting of wattle and eucalyptus completely in 1987.
- Ecological restoration and biodiversity conservation were given importance.
- Under the Hill Area Development Programme since the mid-1980s, seedlings have been planted in degraded patches and protected with chain-link fences to restore the forests.
- Special Shola forest protection committees were formed involving teachers, nature lovers, ecologists, environmentalists, students and villagers in the Nilgiris.
- They were motivated to remove plastic garbage from the nearby forests, protect Shola trees, remove alien species and learn about the importance of the Sholas.
- Presently, the Tamil Nadu forest department is now focusing on eradicating wattle, providing fencing and planting shola seedlings in degraded shola forests.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ICDS and its components
Mains level: Forms of malnutrition in urban areas and their preventive measures

Centre seeks to revamp the ICDS scheme in urban areas. For this NITI Aayog will develop draft policy, which will be circulated to the Ministries for consultations.
Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)
- The ICDS is a government programme in India which provides food, preschool education, primary healthcare, immunization, health check-up and referral services to children under 6 years of age and their mothers.
- The scheme was launched in 1975, discontinued in 1978 by the government of Morarji Desai, and then relaunched by the Tenth Five Year Plan.
- Tenth FYP also linked ICDS to Anganwadi centres established mainly in rural areas and staffed with frontline workers.
- The ICDS provide for anganwadis or day-care centres which deliver a package of six services including:
- Immunization
- Supplementary nutrition
- Health checkup
- Referral services
- Pre-school education(Non-Formal)
- Nutrition and Health information
Implementation
- For nutritional purposes ICDS provides 500 kilocalories (with 12-15 grams of protein) every day to every child below 6 years of age.
- For adolescent girls it is up to 500 kilo calories with up to 25 grams of protein every day.
- The services of Immunisation, Health Check-up and Referral Services delivered through Public Health Infrastructure under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Revamp for Urban Areas
- Health and ICDS models that work in rural areas may not work in urban areas because of higher population density, transportation challenges and migration.
- Children in urban areas were overweight and obese as indicated by subscapular skinfold thickness (SSFT) for their age.
- The first-ever pan-India survey on the nutrition status of children, highlighted that malnutrition among children in urban India.
- It found a higher prevalence of obesity because of relative prosperity and lifestyle patterns, along with iron and Vitamin D deficiency.
- According to government data from 2018, of the 14 lakh anganwadis across the country there are only 1.38 lakh anganwadis in urban areas.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Association for Democratic Reforms
Mains level: De-criminalization of politics in India

The Supreme Court has agreed to examine a proposition made by the Election Commission (EC) to ask political parties to not give a ticket to those with criminal antecedents.
Cleansing of Political Parties
- The judgment had urged Parliament to bring a “strong law” to cleanse political parties of leaders facing trial for serious crimes.
- The ruling concluded that rapid criminalisation of politics cannot be arrested by merely disqualifying tainted legislators but should begin by “cleansing” the political parties.
- The court had suggested that Parliament frame a law that makes it obligatory for political parties to remove leaders charged with “heinous and grievous” crimes like rape, murder and kidnapping, only to a name a few, and refuse ticket to offenders in both parliamentary and Assembly polls.
- It had also issued guidelines, including that both the candidate and the political party should declare the criminal antecedents of the former in widely-circulated newspapers.
Why such move?
- 46% of Members of Parliament have criminal records.
- A move to steer politics away from the denizens of the criminal world would definitely serve national and public interest.
- The EC had tried several measures to curb criminalisation of politics but failed.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NAVIC, IRNSS
Mains level: Utility of NAVIC
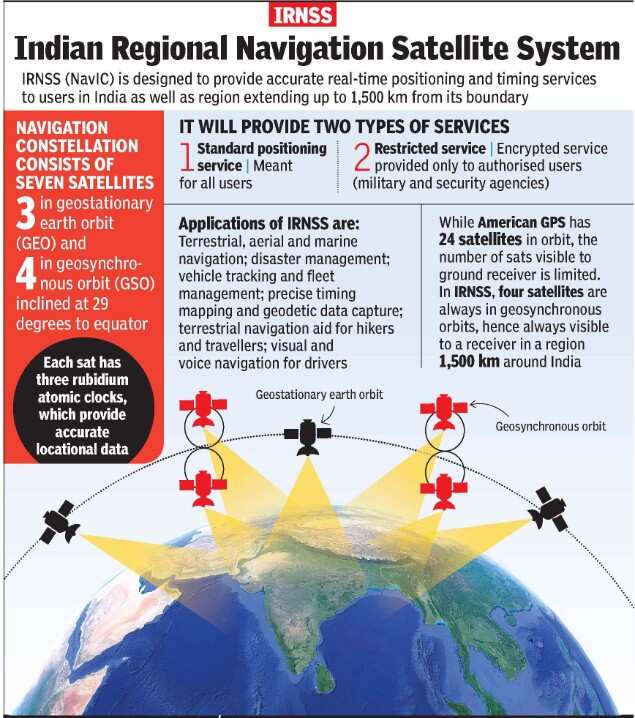
Qualcomm Technologies has released chipsets, supporting India’s own GPS system ‘Navigation with Indian Constellation’ (NavIC).
New androids to be equipped with NavIC
- The Qualcomm chipsets now supports up to 7 satellite constellations at the same time, including the use of all of NavIC’s operating satellites.
- These enhancements will enable select mobile, automotive and IoT platforms to better serve key industries and technology ecosystems in the region.
- It will help improve user experience for location-based applications especially in dense urban environments where geolocation accuracy tends to degrade, said the company earlier.
About NavIC
- The name NavIC was given by Prime Minister Narendra Modi after successful launch of the seventh navigation satellite, in April, 2016.
- To date, ISRO has built a total of nine satellites in the IRNSS series, of which eight are currently in orbit.
- The constellation is designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1,500 km from its boundary, which is its primary service area.
- It is designed to provide two types of services – Standard Positioning Service (SPS), which is provided to all users and Restricted Service (RS), which is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users.
- The system is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
For more readings about NAVIC, navigate to the page:
NAVIC (Navigation in Indian Constellation)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Natrialba Swarupiae, Sambhar Lake
Mains level: Not Much
- Scientists at the National Centre for Microbial Resource — National Centre for Cell Science (NCMR-NCCS) in Pune have reported a new archaeon (a kind of microorganism), which they discovered in Sambhar Salt Lake in Rajasthan.
- The new archaeon has been named Natrialba swarupiae, after Dr Renu Swarup, secretary, Department of Biotechnology, for her initiative in supporting microbial diversity studies in the country.
Archaea
- Archaea (singular archaeon) are a primitive group of microorganisms that thrive in extreme habitats such as hot springs, cold deserts and hypersaline lakes.
- These slow-growing organisms are also present in the human gut, and have a potential relationship with human health.
- They are known for producing antimicrobial molecules, and for anti-oxidant activity with applications in eco-friendly waste-water treatment.
- Archaea are extremely difficult to culture due to challenges in providing natural conditions in a laboratory setting.
- As archaea are relatively poorly studied, very little is known about how archaea behave in the human body.
- The organism has potential gene clusters that helps maintain the metabolism of the archaea to survive in extreme harsh conditions.
Search and discovery
- Sambhar Lake has been poorly studied for microbial ecology studies.
- With a salt production of 0.2 million tonnes per annum, it is also a hypersaline ecosystem which provides an opportunity for microbial ecologists to understand organisms that thrive in such concentrations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various chairs named after eminent Women
Mains level: Women empowerment

On the occasion of National Girl Child Day, the Ministry of Women and Child Development has set up 10 Chairs in different fields with an aim to carry out research activities to encourage women.
Chairs named after eminent Women
- The initiative is called “the Establishment of Chairs in the Universities in the name of eminent women administrators, artists, scientists and social reformers”.
- It is being launched with the assistance of University Grants Commission (UGC).
- The main objective is to inspire women to pursue higher education and to achieve excellence in their area of work.
- The financial implications of the proposal is Rs. 50 lakh per Chair per year and the total expenditure for establishing ten Chairs will be approximately Rs. Rs. 5 crore per annum.
- The Chairs are to be established for a period of 5 years initially as per the guidelines.
The chairs proposed by UGC and approved by the Ministry are as under:
| S. No. |
Subject |
Proposed name of chair |
| 1. |
Administration |
Devi Ahilyabai Holkar |
| 2. |
Literature |
Mahadevi Varma |
| 3. |
Freedom Fighter (North East) |
Rani Gaidinliu |
| 4. |
Medicine & Health |
Anandibai Gopalrao Joshi |
| 5. |
Performing Art |
Madurai Shanmukhavadivu Subbulakshmi |
| 6. |
Forest/Wildlife Conservation |
Amrita Devi (Beniwal) |
| 7. |
Mathematics |
Lilavati |
| 8. |
Science |
Kamala Sohonie |
| 9. |
Poetry & Mysticism |
Lal Ded |
| 10. |
Educational Reforms |
Hansa Mehta |
Functions of these chairs
- Academic functions of the Chairs will be to engage in research and, in turn, contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the area of the study, strengthen the role of university/academics in public policy making etc.
- The University will review the progress of the Chair annually and submit a final report on the activities and outcome of the Chair to the UGC after five years.
- However, the UGC may undertake the exercise of reviewing the Chair for its continuance, at any stage.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now



