Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3- India-France relations
Context
Defence cooperation has been one of the fundamentals of the bilateral relationship between India and France, which developed a close and ambitious strategic partnership for over 20 years.
Defence cooperation between France and India
- A long history of cooperation: The defence cooperation between our two countries can be traced back to the first few years following India’s Independence.
- As early as 1953, the Indian Air Force was equipped with a hundred Toofani fighter jets from Dassault, then the Mystère IV, which defended India in tough times.
- This marked the first page in the history of cooperation in military aviation, which also recorded the supply of 60 Mirage 2000s in the 1980s.
- Rafale deal: The ongoing delivery of 36 Rafales is being done as per the schedule.
- The first batch of aircraft, currently being used to train Indian pilots, will land at Air Force Station Ambala within a few months.
- Partnership in maritime domain: Today, the partnership has been deployed in the maritime domain, in support of our joint strategic vision for the maintenance of stability and security in the Indo-Pacific.
- As far as naval equipment is concerned, the Indian Navy has already commissioned two of the six submarines built in Mumbai as part of an industrial partnership between Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and Naval Group.
Industrial cooperation between the two countries
- Support to indigenous production: As for industrial cooperation, the French approach has always been, whenever possible, to offer partial indigenous production in India.
- France was largely a precursor with regard to Make in India, with HAL manufacturing the light helicopters Cheetah and Chetak, and BDL’s Milan anti-tank missile in India in the 1960s.
- It continues this policy today. The plant built under the Dassault Aviation and Reliance joint venture will enable, for example, the complete production of the Falcon 2000 business jet here in India by 2022.
- Transfer of technology: After the delivery of the first two Scorpene submarines, transfers of technology provided by the Naval Group enabled MDL to be solely in charge of building the next four submarines.
- The design of these submarines has thus become largely Indian knowhow.
- Safran will soon inaugurate an aircraft wiring systems factory in Hyderabad and also build another major facility to manufacture LEAP turbofan engine components.
- Thales is investing massively in engineering works in Bengaluru, MBDA is building a plant in Coimbatore and French aeronautical equipment manufacturer Latécoère recently inaugurated a factory in Belgaum.
Opportunities for further cooperation
- Developing the supply chain at all the levels: The French aerospace industries association, GIFAS, and GICAN, the French Marine Industry Group, are organising a seminar focused on this subject during DefExpo.
- Along with the Society of Indian Defence Manufacturers (SIDM), they are exploring opportunities for developing Indo-French industrial partnerships at all stages of the production chain.
- Promoting Make in India: India can count on France being by its side for its Make in India enterprise.
Conclusion
India and France both share the same vision for a new balanced multipolar world, which must be based on the rule of law. They also share the same vision on the main challenges of the times, be they security developments in Asia and the Indo-Pacific, or combating international terrorism. But it is by possessing the capability of ensuring national security and making strategic choices that most efficiently defend their shared principles and visions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3- Expanding the India's sphere of influence in IOR and humanitarian assistance in the region.
Context
Earlier this week, India sent an amphibious warship, INS Airavat, to Madagascar in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) to help in rescue efforts after the island nation was hit by a cyclone.
Humanitarian operations- Key component of peacetime strategy
- A key component in IOR: In recent years, humanitarian operations have emerged as a key component of the Indian Navy’s peacetime strategy in the IOR.
- In March 2019, the Navy deployed four warships for relief operations when Mozambique was hit by Cyclone Idai.
- Indian naval teams played a stellar role in search and rescue operations and even set up medical camps.
- A few months later, the Navy sent two warships to Japan to assist in rescue efforts following Typhoon Hagibis.
- A year earlier, Indian vessels had delivered urgent medical assistance to Sulawesi, Indonesia, after it was struck by a high-intensity earthquake.
- Operation Samudra Maitri was launched after a telephonic conversation between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Indonesian President Joko Widodo, with naval planners mobilising assets and relief material in quick time.
- India’s vision for IOR: The Navy’s new humanitarian approach, many says, is a maritime manifestation of India’s vision for the IOR, christened SAGAR (Security And Growth for All in the Region).
- Lesson’s from tsunami: The Navy’s turn towards human-centred maritime security isn’t recent. It was in the aftermath of the 2004 tsunami that naval commanders first recognised the importance of large-scale relief and rescue missions in the IOR.
- For over a decade, considerable resource and energy have been spent developing specialist capability and skills for naval humanitarian operations.
India- A regional security provider
- What is changing in India’s stance: What’s new today is New Delhi’s resolve to burnish its ‘regional security provider’ credentials.
- The Navy has reached out to countries across the Indo-Pacific region, with greater deployment of assets, personnel and specialist equipment, showcasing an ability to undertake complex and diverse missions.
- The highpoint for India: The highpoint of the Navy’s ‘benign’ efforts was the evacuation of over 1,500 Indian expatriates and 1,300 foreign nationals from Yemen in 2015 amid fighting for control of Aden.
- Three years later, Indian naval ships were in Yemen again, to evacuate 38 Indians stranded in the cyclone-hit Socotra Island.
How the new role could help India?
- India’s desire to be the linchpin of security: The Navy’s humanitarian impulse stems from a desire to be a linchpin of security in the IOR.
- The concept of the first responder: At the core of the evolving operations philosophy is the concept of ‘the first responder’, with the capability and willingness to provide assistance.
- Extension of the sphere of influence: The above approach has the potential to create an extended sphere of Indian influence in the IOR.
- Projection of soft power: Naval leaders recognise that benign missions help project Indian soft power and extend New Delhi’s influence in the littorals.
- Creating goodwill: Prompt response during a humanitarian crisis helps generate political goodwill in the neighbourhood.
Cause for caution with maritime presence
- The issue with prolonged presence: While low-end naval assets in humanitarian mode create strategic equity for India, the prolonged presence of front-line warships in foreign waters has the potential to make partners anxious.
- Shaping perception over naval presence: Naval power, experts underline, must be deployed discreetly, shaping perceptions in subtle ways.
- Need to hide the underlying intent: The key is to not let the underlying intent of a mission appear geopolitical.
- To ensure that motives aren’t misunderstood, and the assistance provided is efficient and cost-effective, it is best to use dedicated disaster-relief platforms.
- India lacking inventory hospital ship: However, unlike the U.S. and China that have in their inventory hospital ships fully equipped for medical assistance, India deploys regular warships and survey ships converted for medical aid.
- India’s improvised platforms do not match the U.S. Navy’s medical ship USNS Mercy or the People’s Liberation Army Navy’s Peace Ark.
Need for greater coordination
- The Navy’s expanding array of humanitarian missions reveals a need for greater coordination with the Indo-Pacific navies
- In particular the U.S. Navy, the Royal Australian Navy and the Japanese Self-Defense Forces- which possess significant experience and assets to mitigate humanitarian threats.
Conclusion
As natural disasters in the IOR become more frequent and intense, India’s regional security role is likely to grow exponentially. At the forefront of disaster scenarios, the Indian Navy and Coast Guard would find themselves undertaking demanding missions. Humanitarian operations could serve as a springboard for a larger cooperative endeavour in the maritime commons.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- India's role and interest's in IMO and consequences.
Context
The International Maritime Organization (IMO), had mandated that merchant ships should not burn fuel with sulphur content greater than 0.5% beginning January 1.
Why the new sulphur content limit matters?
- The previous limit of 3.5 %: Before the ban, fuel had a comfortable sulphur content limit of 3.5%, which was applicable to most parts of the world.
- Problem with low content fuel: Many industry professionals feared that the new very-low-sulphur fuel would be incompatible with the engines and other vessel equipment.
- Problems with past US limits: Past mandates on sulphur limits in American waters had led to many technical problems. There have been instances of ships having been stranded after fine particles separated out from the fuel, damaging equipment and clogging up devices.
How such regulations matter for India?
- Sulphur cap one of the many problems: The global sulphur cap is only one of the many environment-related regulations that have been shaking up the shipping industry.
- The industry is generally risk-averse and slow to accept changes.
- For instance, efforts are ongoing to reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) and ozone-depleting gases.
- IMO project to decarbonise shipping: Further, the IMO has announced an ambitious project to decarbonise shipping in order to reduce carbon emissions.
- How it matters for India? These regulations are triggering massive technological, operational and structural changes.
- They come at a price which will have to be borne to a large extent by developing countries such as India.
- India among 10 countries: The IMO currently lists India as among the 10 states with the “largest interest in international seaborne trade”.
- Inadequate participation of India: But India’s participation in the IMO to advance its national interests has been desultory and woefully inadequate.
- How it could matters: The sulphur cap, for instance-
- Will reduce emissions.
- Reduce the health impact on coastal populations but-
- Ship operational costs are going up since the new fuel product is more expensive.
- Refineries struggling to meet demand: As refineries including those in India struggle to meet the demand, freight costs have started moving up, with a cascading effect on retail prices.
Significance of shipping and the role of IMO
- Significance of shipping: Shipping, which accounts for over 90% by volume and about 80% by value of global trade.
- Role of IMO: It is a highly regulated industry with a range of legislation promulgated by the IMO.
- The IMO currently has 174 member states and three associate members; there are also scores of non-governmental and inter-governmental organisations.
- The IMO’s policies or conventions have a serious impact on every aspect of shipping including the cost of maritime trade.
- How IMO functions
- The IMO, like any other UN agency, is primarily a secretariat, which facilitates decision-making processes on all maritime matters through meetings of member states.
- How treaties are made? The binding instruments are brought in through the conventions -to which member states sign on to for compliance -as well as amendments to the same and related codes.
- Structure of IMO: Structurally, maritime matters are dealt with by the committees of the IMO –
- The Maritime Safety Committee (MSC).
- Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC).
- Technical Cooperation Committee.
- Legal Committee and the Facilitation Committee.
- Each committee is designated a separate aspect of shipping and supported by sub-committees. Working groups and correspondence groups support the subcommittees.
- Role of subcommittees of IMO: The subcommittees are the main working organs, where the proposals from a member state are parsed before they are forwarded to one of the main committees.
- The main committees, thereafter, with the nod of the Assembly, put the approved proposal for enactment through the Convention, amendments, and codes or circulars.
India’s inadequate efforts at protecting the interest
- How other countries deal with the issues: To ensure that their maritime interests are protected, the European countries move their proposals in unison and voting or support are given en bloc.
- Permanent representative: China, Japan, Singapore, Korea and a few others represent their interests through their permanent representative as well as ensuring that a large delegation takes part and intervenes in the meetings.
- How India is falling short? While these countries have fiercely protected their interests, India has not.
- No permanent representative: For example, its permanent representative post at London has remained vacant for the last 25 years.
- Representation at meetings is often through a skeletal delegation
- India’s presentation inadequate: A review of IMO documents shows that the number of submissions made by India in the recent past has been measly and not in proportion to India’s stakes in global shipping.
- “High-Risk Area” demarcation issue: The promulgation of “High-Risk Areas” when piracy was at its peak and dominated media headlines.
- What happened in the issue? The IMO’s demarcation resulted in half the Arabian Sea and virtually the entire south-west coast of India being seen as piracy-infested, despite the presence of the Indian Navy and Coast Guard.
- The “Enrica Lexie” shooting incident of 2012, off the coast of Kerala, was a direct fallout of the demarcation.
- What were the consequences of the demarcation issue?
- Increase in insurance costs: The “High-Risk Area” formulation led to a ballooning of insurance costs; it affected goods coming into or out of India.
- It took great efforts to revoke the promulgation and negate the financial burden.
- The episode highlighted India’s apathy and inadequate representation at the IMO.
- NavIC introduction difficulty: There was also great difficulty in introducing the indigenously designed NavIC (NAVigation with Indian Constellation) in the worldwide maritime navigation system.
- What could be the consequences in future?
- EU’s documented procedure: In contrast, the European Union has a documented procedure on how to influence the IMO.
- Agenda driven by developed countries: New legislative mandates, fitment of new equipment and changes to ship structural designs being brought on have been driven by developed countries.
- Consequences for India: All the issues pushed by developed countries are not entirely pragmatic from the point of view of India’s interests.
- Further, it will not be mere speculation to see them as efforts to push products and companies based in the West.
Conclusion
So far, India’s presence and participation in the IMO has been at the individual level. India should now make its presence felt so that its national interests are served. It is time India regained its status as a major maritime power.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Forest Fire Prevention and Management scheme
Mains level: Forest fires in India
The Minister for Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has informed that area covering 93,273 hectares was affected by forest fires in 2019. Most of the fires have been “ground fires” burning ground vegetation.
Measures to curb Forest fires:
1) National Action Plan on Forest Fires
- The MoEFCC has prepared a National Action Plan on Forest Fires in 2018 after several rounds of consultation with all states and UTs.
- The objective of this plan is to minimize forest fires by informing, enabling and empowering forest fringe communities and incentivizing them to work in tandem with the State Forest Departments.
- The plan also intends to substantially reduce the vulnerability of forests across diverse forest ecosystems in the country against fire hazards, enhance capabilities of forest personnel and institutions in fighting fires and swift recovery subsequent to fire incidents.
2) Forest Fire Prevention and Management scheme
- The MoEFCC provides forest fire prevention and management measures under the Centrally Sponsored Forest Fire Prevention and Management (FPM) scheme.
- The FPM is the only centrally funded program specifically dedicated to assist the states in dealing with forest fires.
- The FPM replaced the Intensification of Forest Management Scheme (IFMS) in 2017. By revamping the IFMS, the FPM has increased the amount dedicated for forest fire work.
- Funds allocated under the FPM are according to the 90:10 ratio of central to state funding in the Northeast and Western Himalayan regions and 60:40 ratio for all other states.
- Nodal officers for forest fire prevention and control have been appointed in each state.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Report on Medical Data Leak
Mains level: Medical administartion in India and its loopholes
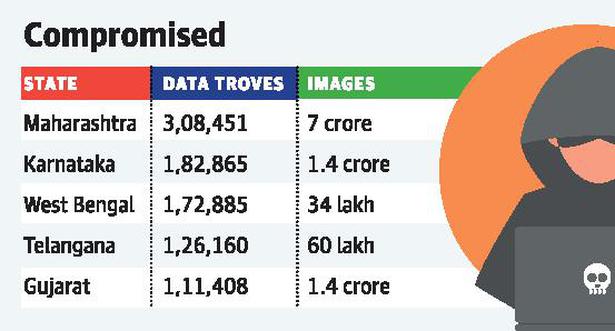
Medical details of over 120 million Indian patients have been leaked and made freely available on the Internet, according to a recent report.
Global Report on Medical Data Leak
- It is published by Greenbone Sustainable Resilience, a German cybersecurity firm.
- The first report was published in October 2019 in which Greenbone revealed a widespread data leak of a massive number of records, including images of CT scans, X-rays, MRIs and even pictures of the patients.
- The follow-up report, which was published, classifies countries in the “good”, “bad” and “ugly” categories based on the action taken by their governments after the first report was made public.
- India ranks second in the “ugly” category, after the U.S.
Highlights of the report
- As per the follow-up report, Maharashtra ranks the highest in terms of the number of data troves available online, with 3,08,451 troves offering access to 6,97,89,685 images.
- The next is Karnataka, with 1,82,865 data troves giving access to 1,37,31,001 images.
- The number of data troves containing this sensitive data went up by a significant number in the Indian context a month after the initial report was published.
- It is a notable fact for the systems located in India, that almost 100% of the studies (data troves) allow full access to related images stated the report.
What led to the leaks?
- Greenbone’s original report says the leak was facilitated by the fact that the Picture Archiving and Communications Systems (PACS) servers, where these details are stored.
- These servers are not secure and linked to the public Internet without any protection, making them easily accessible to malicious elements.
Impact of leaks
- The leak is worrying because the affected patients can include anyone from the common working man to politicians and celebrities.
- In image-driven fields like politics or entertainment, knowledge about certain ailments faced by people from these fields could deal a huge blow to their image.
- The other concern is of fake identities being created using the details, which can be misused in any possible number of ways.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development
Mains level: Dairy sector of India
- The Minister of State for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying has provided certain information in Parliament regarding the ongoing National Programme for Cattle and Buffalo Breeding.
- The scheme is subsumed under Rashtriya Gokul Mission since December 2014.
National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development
- The NPBBDD has been formulated by merging four ongoing schemes of the Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries in the dairy sector.
- It was launched in Feb 2014.
- This merger has been done to integrate milk production and dairying activities in a scientific and holistic manner to meet the increasing demand for milk in the country.
Components of the scheme
NPBBDD has the following three components.
- National Programme for Bovine Breeding (NPBB)
- National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) and
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission.
Differences between all these schemes:
1) National Programme for Bovine Breeding
It aims-
- To arrange quality Artificial Insemination services at farmers’ doorstep
- To bring all breedable females under organized breeding through Artificial Insemination or natural service using germplasm of high genetic merits
2) National Programme for Dairy Development
It aims-
- To create and strengthen infrastructure for the production of quality milk including cold chain infrastructure linking the farmer to the consumer
- To strengthen dairy cooperative societies/Producers Companies at the village level
- To increase milk production by providing technical input services like cattle-feed, and mineral mixture etc.
3) Rashtriya Gokul Mission
It aims-
- To undertake breed improvement programme for indigenous cattle breeds so as to improve the genetic makeup and increase the stock.
- To enhance milk production and productivity of indigenous bovines.
- To upgrade non-descript cattle using elite indigenous breeds like Gir, Sahiwal, Rathi, Deoni, Tharparkar, Red Sindhi.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PTA and its uses
Mains level: Not Much
- During her Budget speech, FM Mrs. Sitharaman said that the government was abolishing in “public interest” an anti-dumping duty that was levied on imports of a chemical called PTA.
- Domestic manufacturers of polyester have called the move a huge relief for the industry, claiming they had been fighting to remove the duty for four-and-a-half years.
What is PTA?
- Purified Terephthalic Acid (PTA) is a crucial raw material used to make various products, including polyester fabrics.
- PTA makes up for around 70-80% of a polyester product and is, therefore, important to those involved in the manufacture of man-made fabrics or their components, according to industry executives.
- This includes products like polyester staple fibre and spun yarn.
- Our cushions and sofas may have polyester staple fibre fillings. Some sportswear, swimsuits, dresses, trousers, curtains, sofa covers, jackets, car seat covers and bed sheets have a certain proportion of polyester in them.
What led to the government decision?
- There has been persistent demand that they should be allowed to source that particular product at an affordable rate, even if it means importing it.
- She had said easy availability of this “critical input” at competitive prices was desirable to unlock “immense” potential in the textile sector, seen as a “significant” employment generator.
- The duty had meant importers were paying an extra $27-$160 for every 1,000 kg of PTA that they wanted to import from countries like China, Taiwan, Malaysia, Indonesia, Iran, Korea and Thailand.
- Removing the duty will allow PTA users to source from international markets and may make it as much as $30 per 1,000 kg cheaper than now, according to industry executives.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About the Project, Indus Water Treaty
Mains level: Indus Water Treaty

The Union government has approved a nearly ₹6,000-crore multi-purpose project for the Ujh multi-purpose project.
Ujh Multi-purpose Project
- The project will store around 781 million cubic meters of water of river Ujh, a tributary of river Ravi.
- It aims to provide uninterrupted water for irrigation to farmers in J&K’s Kathua district and to produce power.
- After completion of the project, utilization of waters of eastern rivers allotted to India as per the Indus Water Treaty would be enhanced by utilising the flow that presently goes across the border to Pakistan.
Back2Basics
Indus Waters Treaty, 1960
- The IWT is a water-distribution treaty between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank signed in Karachi in 1960.
- According to this agreement, control over the water flowing in three “eastern” rivers of India — the Beas, the Ravi and the Sutlej was given to India
- The control over the water flowing in three “western” rivers of India — the Indus, the Chenab and the Jhelum was given to Pakistan
- The treaty allowed India to use western rivers water for limited irrigation use and unrestricted use for power generation, domestic, industrial and non-consumptive uses such as navigation, floating of property, fish culture, etc. while laying down precise regulations for India to build projects
- India has also been given the right to generate hydroelectricity through run of the river (RoR) projects on the Western Rivers which, subject to specific criteria for design and operation is unrestricted.
Present Status of Development
- To utilize the waters of the Eastern rivers which have been allocated to India for exclusive use, India has constructed Bhakra Dam on Satluj, Pong and Pandoh Dam on Beas and Thein (Ranjitsagar) on Ravi.
- These storage works, together with other works like Beas-Sutlej Link, Madhopur-Beas Link, Indira Gandhi Nahar Project etc has helped India utilize nearly entire share (95 %) of waters of Eastern rivers.
- However, about 2 MAF of water annually from Ravi is reported to be still flowing unutilized to Pakistan below Madhopur.
- The three projects will help India to utilize its entire share of waters given under the Indus Waters Treaty 1960:
I. Resumption of Construction of Shahpurkandi project
- It is a dam project under construction on Ravi River.
II. Construction of Ujh multipurpose project
- It is a dam project under construction on Ujh, a tributary of Ravi River.
III. 2nd Ravi Beas link below Ujh
- This project is being planned to tap excess water flowing down to Pakistan through river Ravi, even after construction of Thein Dam.
- It aims constructing a barrage across river Ravi for diverting water through a tunnel link to Beas basin.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Velutheeyam
Mains level: Not Much
A tri-metal sculpture of Jesus Christ( Healing Christ) in Thiruvalla, Kerala has entered the Universal Records Forum’s (URF) book of world records.
Velutheeyam
- The statue was sculpted with an alloy of zinc, copper, and velutheeyam (an alloy of tin and aluminium).
- A URF team adjudged that the 368-cm tall statue, weighing 2,400 kg, is the largest one of its kind in the world.
- It took 18 months for sculpting the statue.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now

