South Korea’s technological advancement and manufacturing capabilities can be helpful in India’s economic growth and human resource development. Seoul’s successful development story of the last few decades can complement Modi’s vision of making a “New India” by 2022.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Debt monetisation, RBI balance sheet etc
Mains level: Paper 3-Ways to raise funds to finance the stimulus package
The article analyses the issues with suggestions like printing of currency and using forex reserves to finance the stimulus. They also lead to an increase in government debts.
Context
- Prime Minister announced a stimulus package of ₹20 trillion to fight the economic fallout of the covid pandemic.
- Since then, several unorthodox ideas have been floated to raise funds for it without straining government finances.
- Among the suggestions are the printing of currency, and using foreign exchange reserves or household gold.
Let’s look at entries in the RBI’s balance sheets
- On the liabilities side of it is the currency in circulation, commercial bank reserves and government reserves.
- On the asset side of it is forex reserves, government securities and gold.
- The balancing item represents the central bank’s equity and accumulated surplus.
Let’s look at 3 options suggested above and issues with them-
1) Printing currency
- Doing this would increase the liabilities of the RBI under “currency in circulation”.
- But it first needs to acquire assets to offset this increase in liability.
- These assets could be government securities, forex reserves or gold.
- Thus, one way for the government to finance its expenditure would be to issue government bonds and ask RBI to print currency with which to subscribe to such bonds.
- This is known as deficit monetization.
- It is important to note that for the central bank to print money, the government would have to issue bonds to it.
- It will increase government debt.
2) Monetisation of gold held by household
- This would first involve the government buying gold from households in exchange for its bonds.
- Then, the accumulated gold would be bought by RBI from the government with newly printed currency.
- In this case, instead of creating new money to acquire government bonds, RBI would be doing the same to acquire gold.
- This too involves the Centre taking on additional debt.
- Moreover, gold monetization schemes in the past have yielded only mild success.
3) Using RBI’s forex reserves
- Against every dollar of forex reserves shown by RBI on the asset side, an equivalent rupee amount has already been created on the liability side.
- This is because whenever RBI acquires foreign currency, it pays for it using the Indian rupee.
- Thus, no additional currency can be printed against such already-acquired reserves.
- The only way our forex reserves can be used for generating additional resources is by pledging them to a third party.
- The pledging of RBI’s assets to raise funds is done only under extreme circumstances, for instance, during the 1991 balance of payments crisis.
- We are certainly not in a situation that warrants a repeat of an exercise where RBI’s assets, be it gold or forex reserves, have to be mortgaged.
So, what is the way out?
- There are only three ways to finance government expenditure: taxes, debt and asset sales.
- Taxes and asset sales can pitch in a bit towards the stimulus bill.
Consider the question “Examine the ways in which government can raise the funds to finance the stimulus package and also discuss the issues with each move.”
Conclusion
There is no escaping the fact that we are staring at a higher build-up of government debt in the future. When we stop harbouring the notion that we can pay the stimulus bill without any deterioration in government finances, we will be able to see the bitter truth: There is no such thing as a free lunch.
Read more about the issue here:
India’s rising Forex Reserves
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AMRUT
Mains level: Paper 1-Urbanisation and issues
The article brings out the issues in the rural-urban binary, which leads to the disparity in the allocation of resources to the urban areas.
Congestion and health issues in cities
- The congestion in large cities has turned out to be their worst enemy during this pandemic.
- Congestion is most evident in slums in large cities and poses a grave health and environmental challenges.
- Yet, the Centre’s allocation for the rural component of the Swachh Bharat Mission is about seven times more than for urban areas.
- Class I cities have 1.4 beds per 1,000 people. (with the population more than 1 lakh)
- However, the urban support under the National Health Mission is just three per cent of the total allocation, while 97 per cent of the funds are set aside for rural areas.
Issues with the present urban development programs
- The Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (2005-2014) allocated the bulk of funds to large cities: 70 per cent to large cities and 30 per cent to smaller towns.
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) and the Smart Cities Mission, focus on Class I cities.
- Both these schemes provide funds for the more developed cities that already have relatively better infrastructure.
- But these schemes overlook the nearly seven crore people who live in smaller towns.
- These are towns that lag behind in services and infrastructure as compared to the big cities.
Consider the question “The rural-urban binary has led to the policy formulation in which there is a huge disparity in the allocation of resources and attention on the urban area. Comment.”
Conclusion
The pandemic has forced us to reflect on the unequal and unplanned development of urban settlements and the absence of infrastructure to provide for the teeming millions. The challenges of urban poverty and congestion cry for more attention, more government support.
Original article:
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/coronavirus-covid-19-pandemic-india-urban-cities-6520574/
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SSC/PC
Mains level: Debate over suitablity of women in combat roles of Indian Army
The Ministry of Defence (MoD) has issued the formal Government Sanction Letter for grant of Permanent Commission (PC) to women officers in the Army.
Try this question for mains:
Q.“Concern for equality of sexes or political expediency should not influence defence policies.” Discuss on lines with the debate over the induction of women in the armed forces.
Also read: https://www.civilsdaily.com/burning-issue-women-in-armed-forces/
Why such an order?
- The order follows a Supreme Court verdict in February that directed the government that women Army officers be granted PC and command postings in all services other than combat.
- Following this, Army Chief had said it was an enabling one and gives a lot of clarity on how to move forward.
- He had stated that the same procedure for male SSC officers will be followed for women to give PC.
Women in Army: Background of the case

- The induction of women officers in the Army started in 1992.
- They were commissioned for a period of five years in certain chosen streams such as Army Education Corps, Corps of Signals, Intelligence Corps, and Corps of Engineers.
- Recruits under the Women Special Entry Scheme (WSES) had a shorter pre-commission training period than their male counterparts who were commissioned under the Short Service Commission (SSC) scheme.
- In 2006, the WSES scheme was replaced with the SSC scheme, which was extended to women officers. They were commissioned for a period of 10 years, extendable up to 14 years.
- Serving WSES officers were given the option to move to the new SSC scheme or to continue under the erstwhile WSES.
- They were to be, however, restricted to roles in streams specified earlier — which excluded combat arms such as infantry and armoured corps.
2 key arguments shot down
- The Supreme Court rejected arguments against a greater role for women officers, saying this violated equality under the law.
- They were being kept out of command posts on the reasoning that the largely rural rank and a file will have problems with women as commanding officers. The biological argument was also rejected as disturbing.
- While male SSC officers could opt for permanent commission at the end of 10 years of service, this option was not available to women officers.
- They were, thus, kept out of any command appointment, and could not qualify for a government pension, which starts only after 20 years of service as an officer.
- The first batch of women officers under the new scheme entered the Army in 2008.
Arguments by the Govt
- The Centre had mentioned several reasons behind the differential treatment of women officers.
- It had proposed that women officers with up to 14 years of service would be granted a permanent commission, while those above 14 years would be permitted to serve for up to 20 years and retire with pension without being considered for permanent commission.
- It also stated that those with more than 20 years of service would immediately be released with pension
- This order did not grant permanent commission to women with over 14 years of service, and hence discriminatory.
- Furthermore, the 2019 order granted permanent commission only for staff appointments and not command appointments.
- The centre justified this by stating that that the units in Army are composed entirely of male soldiers, who are mostly from rural backgrounds and thus, are not mentally prepared to accept women officers in the command of units.
- It also stated that the lower physical capacity of women officers would be a challenge for them to command units wherein officers are expected to lead the men from the front and need to be in prime physical condition to undertake combat tasks.
- The government also stated that the adverse conditions, including two unsettled borders and internal security situations in the northeast and Jammu and Kashmir, have a major bearing on the employment of women officers in light of their physiological limitations.
- Also, it had stated that the isolation and hardships would eat into their resolve and that they have to heed to the call of pregnancy, childbirth and family.
- The government also argued that women ran the risk of capture by the enemy and being taken as prisoners of war.
SC Criticized the Government’s Note
- Reflects Poorly on Women: The note had shown women officers in a poor light, saying isolation and hardships would eat into their resolve and that they would have to heed to the call of pregnancy, childbirth and family. The note had mentioned that women ran the risk of capture by enemy and taken prisoner of war.
- Patriarchal Notion: The court held that the the note reflected the age-old patriarchal notion that domestic obligations rested only with women.
- Sex Stereotype: The court also dismissed the point that women are physiologically weaker than men as a “sex stereotype”.
- Offence to dignity of Indian Army: The court noted that challenging abilities of women on the ground of gender is an offence not only to their dignity as women but to the dignity of the members of the Indian Army – men and women – who serve as equal citizens in a common mission.
Implications of the judgement
- The SC did away with all discrimination on the basis of years of service for grant of PC in 10 streams of combat support arms and services, bringing them on a par with male officers.
- It has also removed the restriction of women officers only being allowed to serve in staff appointments, which is the most significant and far-reaching aspect of the judgment.
- It means that women officers will be eligible to the tenant all the command appointments, at par with male officers, which would open avenues for further promotions to higher ranks for them.
- It also means that in junior ranks and career courses, women officers would be attending the same training courses and tenanting critical appointments, which are necessary for higher promotions.
Back2Basics: Permanent Commission (PC) Vs. Short Service Commission (SSC)
- SSC means an officer’s career will be of a limited period in the Indian Armed Forces whereas a PC means they shall continue to serve in the Indian Armed Forces, till they retire.
- The officers inducted through the SSC usually serve for a period of 14 years. At the end of 10 years, the officers have three options.
- A PC entitles an officer to serve in the Navy till he/she retires unlike SSC, which is currently for 10 years and can be extended by four more years, or a total of 14 years.
- They can either select for a PC or opt-out or have the option of a 4-years extension. They can resign at any time during this period of 4 years extension.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN)
Mains level: Credit facilities for MSMEs
A new credit protocol infrastructure called the OCEN protocol is set to be launched very soon.
Practice question for mains:
Q. What is Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN)? How it is expected to be a gamechanger in the micro-credit facilitation services in India?
Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN)
- OCEN is a credit protocol infrastructure, which will mediate the interactions between loan service providers, usually fintech and mainstream lenders, including all large banks and NBFCs.
- It is developed by a think tank, Indian Software Products Industry Round Table (iSPIRT).
- With this, a credit will become more accessible for a large number of entrepreneurs and small businesses in the country.
- Private equity and venture capital players, angel investors, high net worth individuals and others also could be part of this exercise as investors.
How will it work?
- iSpirit is partnering with key leaders such as SBI, HDFC Bank Ltd., ICICI Bank Ltd., IDFC First Bank Ltd., Axis Bank Ltd. etc. for this new credit rail.
- Account Aggregators which will be using these APIs to embed credit offerings in their applications, and will be called ‘Loan Service Providers’, which will play a crucial role in democratizing access to credit, and lowering interest rates for customers.
Why need OCEN?
- The cost of lending being too high in India, small value loans becomes very unfeasible.
- OCEN which seeks to connect lenders to marketplaces and thereby to borrowers is a technology system.
- If implemented, the technology can democratize lending to micro-enterprises and street vendors in a big way.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bats and thier natural role
Mains level: Illict wildlife trade and its prevention
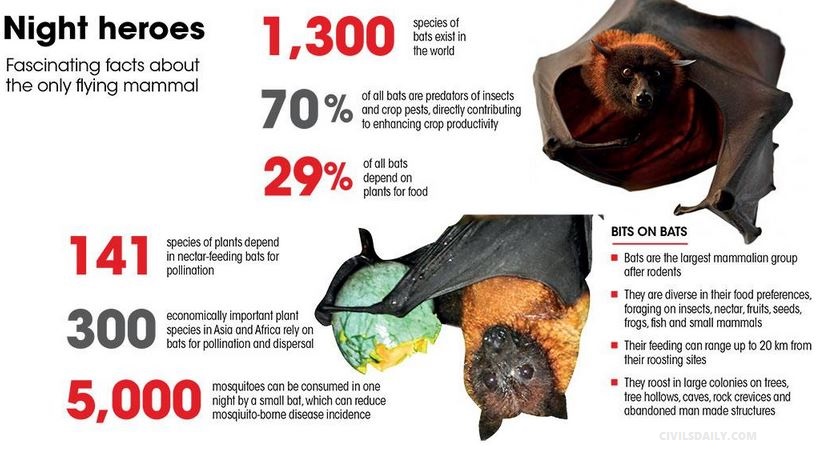
The COVID pandemic has magnified our fear of bats, but their conservation is crucial to prevent such events from arising again.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2014:
Q.Consider the following:
- Bats
- Bears
- Rodents
The phenomenon of hibernation can be observed in which of the above kinds of animals?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) Hibernation cannot be observed in any of the above
Bats
- Bats are the largest mammalian group after rodents, with over 1,300 species making up a quarter of all mammals.
- They occur on all continents except Antarctica and are particularly diverse in South Asia, with 114 species of insect-eating bats and 14 fruit bats, also known as “flying foxes”, occurring in India.
- They roost in large colonies on trees, tree hollows, caves, rock crevices and abandoned manmade structures.
- They play a unique role in maintaining ecosystem structure, making a singular contribution to our food production, economy and well-being.
- They are the only mammals capable of true flight and have a unique sonar-based echolocation mechanism to capture prey at night.
Their significance
1) Seed dispersal
- About 29 per cent of all bats depend upon plants for food.
- The diet of fruit-eating bats consists largely of flowers and fruits such as mangoes, bananas, guavas, custard apples, figs, tamarind and many species of forest trees.
- Therefore, bats play a vital role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration. Studies have shown that seedlings raised from bat dispersed seeds show higher germination and vigorous growth.
2) Pollination
- Studies have found that bats play a vital role in pollination, mainly of large-flowered plants, and in crop protection.
- Fruit bats (Megachiroptera) being large, require big flowers with copious amounts of nectar.
- Bats are major pollinators for many species of mangroves which are important for coastal ecosystems and local livelihoods.
3) Production boost
- Insects are a major problem for agriculture, destroying up to 26 per cent of the annual production of crops worldwide every year, roughly amounting to $470 billion.
- Insectivorous bats, which make up 70 per cent of all bat species, are voracious predators of nocturnal insects and crop pests.
- Some large insectivorous bats are also reported to feed on small rodents. Thus they contribute directly to enhancing the crop productivity with tremendous economic impact.
4) Soil fertility
- Bats contribute significantly to soil fertility and nutrient distribution due to their large numbers, high mobility and varied habitats for roosting and foraging.
- Bat droppings provide organic input to soil and facilitate nutrient transfer, contributing to soil fertility and agricultural productivity. The practice is harmless vis-a-vis human health.
5) Health benefits
- Several species of bats, in fact, contribute to human health by reducing populations of mosquitoes and other insect vectors that spread malaria, dengue, chikungunya and other diseases.
- It is reported that a small bat may feed on almost 5,000 mosquitoes each and every feeding night far more than other measures adopted to eliminate them.
Their conservation
- According to the IUCN, about 5 per cent of bats are categorised as endangered and another 11 per cent are data deficient.
- Further, some species of fruit bats are categorised under Schedule 5 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1973, along with other vermin species like rats, making it difficult to legally conserve them.
Conclusion
- The pandemic has demonstrated that conservation of biodiversity and natural habitats is absolutely essential to prevent such events from arising again.
- Understanding the role played by bats helps us appreciate how their absence can greatly affect all facets of our lives.
- Viruses don’t jump directly from bats or other animals to humans.
- Rather, illicit trade in wildlife, high levels of hunting for the consumption of wild meat, and destruction of natural habitats are responsible for this.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: COVID-19 Law Lab
Mains level: Health Policy measures against COVID-19

The UN agencies have started a portal called the COVID-19 Law Lab to host all recent legal enactments to fight the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic.
Note the following things about COVID-19 Law Lab:
1) It is an online portal and not a cubical laboratory
2) Parent agency includes the UN and WHO
3) It is the first collation of health-related laws and protocols of the countries
COVID-19 Law Lab
- This digital portal hosts all legal steps taken by 190 countries to fight the pandemic.
- The UNDP, the WHO, the Joint UN Programme on HIV/AIDS and the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown University have collaborated for this initiative.
- The collation initiative aims at dissemination of procedures and practices for effective enactment of health-related laws.
- It is expected to be the most expansive collation of laws and procedures related to a health emergency.
Why need such a repository?
- The pandemic has led to confusion over treatment and management protocols.
- Some 220 countries/territories have enacted various procedures backed by various enabling laws related to epidemics and health emergency.
- Laws and policies that are grounded in science, evidence and human rights can enable people to access health services, protect themselves from COVID-19 and live free from stigma, discrimination and violence.
- Sharing medicines and formulae for even general treatment has been a big challenge due to restrictive laws and trade practices.
- As health is global, legal frameworks need to be aligned with international commitments to respond to current and emerging public health risks.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Siddi Tribals
Mains level: NA

The Siddi community gets its first lawmaker in Karnataka. They are included as the Scheduled Tribes in Karnataka.
Try this question from CSP 2019:
Q.Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India:
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Siddi Tribe
- The Siddi also known as Sidi, Siddhi, Sheedi or Habshi, are an ethnic group inhabiting India and Pakistan.
- They are sometimes referred to as Afro-Indians. They are descended from the Bantu peoples of the East African region.
- Similarly, another term for Siddis, habshi, is held to be derived from the common name for the captains of the Abyssinian ships that also first delivered Siddi slaves to the subcontinent.
- They are primarily Muslims, although some are Hindus and others belong to the Catholic Church.
How they came to India?
- The first Siddis are thought to have arrived in India in 628 AD at the Bharuch port. Several others followed with the first Arab conquest of the subcontinent in 712 AD.
- The latter groups are believed to have been soldiers with Muhammad bin Qasim’s Arab army and were called Zanjis.
- In the Delhi Sultanate period prior to the rise of the Mughals in India, Jamal-ud-Din Yaqut was a prominent Siddi slave-turned-nobleman who was a close confidant of Razia Sultana.
- Siddis were also brought as slaves by the Deccan Sultanates. They also served in the Navy of Shivaji Maharaj.
- Several former slaves rose to high ranks in the military and administration, the most prominent of which was Malik Ambar.
- Later the Siddi population was added to via Bantu peoples from Southeast Africa that had been brought to the Indian subcontinent as slaves by the Portuguese.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




