Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2-Pandemic and SDGs
Context
- As lockdown eases, return to business as usual is unimaginable in Asia and Pacific which was already off track to meet the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Efforts to respond to the pandemic have revealed how many people in our societies live precariously close to poverty and hunger.
Progress towards SDGs in pandemic
- The SDGs can serve as a beacon in these turbulent times.
- SDGs are a commitment to eradicate poverty and achieve sustainable development, globally, by 2030.
- The pandemic has exposed fragility and systemic gaps in many key systems.
- Countries have used workable strategies during pandemic to accelerate progress related to development goals and strengthen resilience.
- Countries have taken steps to extend universal health care systems and strengthen social protection systems.
- Accurate and regular data have been key to such efforts.
- Innovating to help the most disadvantaged access financing and small and medium-sized enterprise credits have also been vital.
- Several countries have taken comprehensive approaches to various forms of discrimination, particularly related to gender and gender-based violence.
- Partnerships with the private sector and financing institutions, have played a critical role in fostering creative solutions.
Focus on green recovery in Asia-Pacific countries
- Countries in Asia and the Pacific are developing ambitious new strategies for green recovery and inclusive approaches to development.
- South Korea recently announced a New Deal based on two central pillars: digitisation and decarbonisation.
- Many countries in the Pacific are focusing on “blue recovery,” which promote more sustainable approaches to fisheries management.
- India recently announced operating the largest solar power plant in the region.
- China is creating more jobs in the renewable energy sector than in fossil fuel industries.
Suggestions for policymaking
- We need a revolution in policy mindset and practice- following are part of the transformations needed.
- 1) Inclusive and accountable governance systems.
- 2) Adaptive institutions with resilience to future shocks.
- 3) Universal social protection and health insurance.
- 4) Stronger digital infrastructure.
Consider the question “Pandemic has highlighted the fragility of our systems. But it also emphasised the need to strive to achieve the SDGs. Comment.”
Conclusion
With the onslaught of pandemic disrupting us, we should base our recovery and progress trajectory firmly towards achieving SDGs.
Back2Basics: SDGs
Sustainable Development Goals and India
- The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), otherwise known as the Global Goals, are a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity.
- The 17 Goals build on the successes of the Millennium Development Goals, while including new areas such as climate change, economic inequality, innovation, sustainable consumption, peace and justice, among other priorities.
- The goals are interconnected – often the key to success on one will involve tackling issues more commonly associated with another.
- The SDGs work in the spirit of partnership and pragmatism to make the right choices now to improve life, in a sustainable way, for future generations.
- They provide clear guidelines and targets for all countries to adopt in accordance with their own priorities and the environmental challenges of the world at large.
The SDGs are an inclusive agenda. They tackle the root causes of poverty and unite us together to make a positive change for both people and planet. “Poverty eradication is at the heart of the 2030 Agenda, and so is the commitment to leave no-one behind,” UNDP Administrator Achim Steiner said. “The Agenda offers a unique opportunity to put the whole world on a more prosperous and sustainable development path. In many ways, it reflects what UNDP was created for.”
The Goals

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Contempt of court
Mains level: Paper 2- Contempt of court and issues
The article discusses the issues that law for contempt of the court give rise to. The practice has monarchical origins. Its continuance conflicts with the ideals of democracy.
Objective
- The objective for contempt is stated to be to safeguard the interests of the public if the authority of the Court is denigrated and public confidence in the administration of justice is weakened or eroded.
- Need to “respect the authority and dignity of the court” has monarchical origins.
Issues in India
- With adjudicatory role having been handed over to judges, showing extreme deference to judges does not sit well with the idea of a democracy.
- But the definition of criminal contempt in India is extremely wide, and can be easily invoked.
- Justice V.R. Krishna Iyer famously termed the law of contempt as having a vague and wandering jurisdiction, contempt law may unwittingly trample upon civil liberties.
- Criminal contempt is completely asynchronous with our democratic system which recognises freedom of speech and expression as a fundamental right.
- Excessively loose use of the test of ‘loss of public confidence’, combined with a liberal exercise of suo motu powers, can be dangerous.
- It can amount to the Court signalling that it will not suffer any kind of critical commentary about the institution at all.
Lessons from other democracies
- Contempt has practically become obsolete in foreign democracies.
- Canada ties its test for contempt to real, substantial and immediate dangers to the administration.
- American courts also no longer use the law of contempt in response to comments on judges or legal matters.
- In England, too, the legal position has evolved.
Approach of Indian judiciary
- Truth and good faith were not recognised as valid defences until 2006, when the Contempt of Courts Act was amended.
- Indian courts have not been inclined to display the same maturity and unruffled spirit as their peers in the other democracies.
Consider the question “A law for criminal contempt is completely asynchronous with our democratic system which recognises freedom of speech and expression as a fundamental right. Examine the issue in India context and suggest the major to strike the balance.”
Conclusion
Besides needing to revisit the need for a law on criminal contempt, even the test for contempt needs to be evaluated. If such a test ought to exist at all, it should be whether the contemptuous remarks in question actually obstruct the Court from functioning. It should not be allowed to be used as a means to prevent any and all criticism of an institution.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Information war against India
Information war waged against India from across the border needs consideration. Three factors have triggered the war in the realm of information. This article examines the way in which it is perpetrated.
Factors
- Following three triggers are responsible for Pakistan’s information war.
- 1) The Balakot attack of February 2019.
- Balakot demolished Pakistan’s presumed nuclear equivalence that guaranteed that India would not retaliate against terrorist attacks
- 2) The return of the BJP government in the May 2019 elections-which signalled that India would follow aggressive muscular policy.
- 3) The August 2019 revision of Article 370.
- The Article 370 decision demolished the centrepiece of Pakistan’s nationalism build on Kashmir.
- The move also raised apprehensions about India’s plans for Pakistan Occupied Jammu and Kashmir.
- These developments have forced it to shift the emphasis of its anti-India strategy from fomenting terrorism supported by an information war component to an information war supported by terrorism.
How the information war is waged
- The ISI and the Inter-Services Public Relations (ISPR) two main instruments for the furtherance of this policy.
- The ISPR has, over the years, recruited thousands of youth, trained them in the mechanics of social media and used them to project anti-India themes.
- The core Pakistani objective is to demolish “Brand India” by attacking its key components — an inclusive and secular society, democratic polity, decisive government, a developing economic powerhouse and strong foreign policy.
- The expectation is that such a strategy would adversely impact India’s secular and democratic credentials, scare foreign investment and lead to questions about its international image.
- The key platforms for this strategy are Twitter, WhatsApp, YouTube and Facebook.
- A large number of fake social media accounts, especially on Twitter, have been created.
- The use of handles with phoney Middle Eastern identities is the latest addition to its bag of tricks.
Themes of information war
- Internal developments and dissent in India have been manipulated, packaged and used to develop a narrative damaging India’s social fabric.
- On J&K, the key themes are: Kashmir is a “disputed territory” awaiting solution under the UN resolutions; India needs to talk to Pakistan to resolve the issue and since India refuses to talk, there must be international intervention, the Indian Army is violating the human rights of Kashmiris.
Consider the question “Internet has made waging information war easier. Examine the threat posed by the information war to Indian polity. Suggest the measures to contain the threat emanating from the information war.”
Conclusion
Even though the Indian polity is strong, such persistent venomous attacks can temporarily damage our social fabric. We must not allow ourselves, wittingly or unwittingly, to fall prey to such machinations to polarise society, even temporarily.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Discretionary powers of Governor
Mains level: Speaker vs Governor Tussle
A Constitution Bench judgment of the Supreme Court has held that a Governor is bound to convene a meeting of the Assembly for a floor test on the recommendation of the Cabinet.
Try this question for mains:
Q. “Time and again, the courts have spoken out against the Governor acting in the capacity of an all-pervading super-constitutional authority.” Analyse.
Resolving the deadlock
- The judgment is significant in the present deadlock between the CM and the Governor over the summoning of an Assembly session for a floor test.
- The Governor can summon, prorogue and dissolve the House only on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers with the Chief Minister as the head.
The Nabam Rebia Case
- The five-judge Constitution Bench judgment of the Supreme Court cited the Nabam Rebia versus Deputy Speaker on July 13, 2016.
- It held that a Governor cannot employ his ‘discretion’, and should strictly abide by the “aid and advice” of the Cabinet to summon the House.
- It held that the discretionary power of the Governor is extremely limited and entirely liable to judicial review.
- The judgment was a consequence of then Arunachal Pradesh Governor J.P. Rajkhowa’s decision to advance the Assembly session, a move which led to unrest in the State and resulted in the President’s rule.
- The Constitution Bench held Mr. Rajkhowa’s decision to be a violation of the Constitution.
Governor’s discretion: Limited to specified areas
- The Supreme Court highlighted that Article 163 of the Constitution does not give the Governor a “general discretionary power to act against or without the advice of his Council of Ministers.
- The court said the Governor’s discretionary powers are limited to specified areas like giving assent or withholding/referring a Bill to the President or appointment of a CM or dismissal of a government which has lost of confidence but refuses to quit, etc.
Back2Basics: Governor’s Discretionary Powers
The governor can use his/her discretionary powers:
- When no party gets a clear majority, the governor has the discretion to choose a candidate for the chief minister who will put together a majority coalition as soon as possible.
- He can impose president’s rule.
- He submits reports on his own to the president or on the direction of the president regarding the affairs of the state.
- He can withhold his assent to a bill and send it to the president for his approval.
- During emergency rule per Article 353, he can override the advice of the council of ministers if specifically permitted by the president.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Landfills
Mains level: Social and environmental threats posed by Landfills
The Ghazipur landfill site rises by nearly 10 metres a year and is expected to surpass the height of Qutub Minar and other vertical structures in the country.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2016:
Q.What can be the impact of excessive/inappropriate use of nitrogenous fertilizers in agriculture?
- Proliferation of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in soil can occur.
- Increase in the acidity of soil can take place.
- Leaching of nitrate to the ground-water can occur.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
What are Landfills?
- A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials.
- Some landfill sites are also used for waste management purposes, such as temporary storage, consolidation and transfer, or for various stages of processing waste material, such as sorting, treatment, or recycling.
Threats posed by landfills
Landfills have the potential to cause a number of issues. Infrastructure disruption, such as damage to access roads by heavy vehicles, may occur amongst others.
1) Leachate
- When precipitation falls on open landfills, water percolates through the garbage and becomes contaminated with suspended and dissolved material, forming leachate.
- If this is not contained it can contaminate groundwater.
2) Decomposition gases
- Rotting food and other decaying organic waste create decomposition gases, especially CO2 and CH4 from aerobic and anaerobic decomposition, respectively.
- Both processes occur simultaneously in different parts of a landfill.
3) Other threats
- Poorly run landfills may become nuisances because of vectors such as rats and flies which can spread infectious diseases.
- The occurrence of such vectors can be mitigated through the use of daily cover.
- Other potential issues include wildlife disruption due to occupation of habitat and animal health disruption caused by consuming waste from landfills, dust, odour, noise pollution, and reduced local property values.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Seismic noise
Mains level: Seismic activity and thier monitoring
The seismic noise level has dropped by as much as 50 per cent between March and May due to lockdowns this year, according to researchers.
Ever heard of space-based monitoring of seismic activities? This topic creates a scope for potential prelims question…
What is Seismic Noise?
- Seismic noise refers to vibrations within the Earth, which are triggered by natural and man-made phenomena like earthquakes, volcanoes and bombs.
- Seismometers, specialised devices that record ground motions, also capture seismic noise.
- Everyday human activity — such as road traffic, manufacturing in factories, the sound produced by planes roaring overhead, or simply people walking down the street.
- The sound signals created by human beings are often referred to as anthropogenic seismic noise.
- Seismic noise acts almost like background sound for seismologists — it is the unwanted component of signals recorded by a seismometer.
Variations in noise levels
- The level of anthropogenic seismic noise recorded varies based on a number of factors.
- Highly-populated urban areas will generate more vibrations from human activity than less densely populated regions.
- Timing too plays an important role. The degree of seismic noise is found to be much lower during public holidays.
Why is this important to record this noise?
- Due to this, scientists will be able to spot weaker signals.
- Such small signals tell us about a geological fault making seismic hazard assessment more accurate.
- This means that scientists will have a better shot at monitoring a whole range of seismogenic behaviour, including the smallest earthquakes or the early signs of a volcanic eruption.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kashmir Saffron
Mains level: Not Much

The J&K administration has issued the certificate of geographical indication (GI) registration for saffron grown in the Kashmir Valley.
Must read:
GI Tags in news for 2020 Prelims
All time GI tags in news
Kashmir saffron
- It is cultivated and harvested in the Karewa (highlands) in some regions of Kashmir, including Pulwama, Budgam, Kishtwar and Srinagar.
- It is a very precious and costly product. Iran is the largest producer of saffron and India is a close competitor.
- It rejuvenates health and is used in cosmetics and for medicinal purposes.
- It has been associated with traditional Kashmiri cuisine and represents the rich cultural heritage of the region.
- Saffron cultivation is believed to have been introduced in Kashmir by Central Asian immigrants around 1st Century BCE. In ancient Sanskrit literature, saffron is referred to as ‘bahukam’.
3 Types
The saffron available in Kashmir is of three types —
- ‘Lachha Saffron’, with stigmas just separated from the flowers and dried without further processing;
- ‘Mongra Saffron’, in which stigmas are detached from the flower, dried in the sun and processed traditionally; and
- ‘Guchhi Saffron’, which is the same as Lachha, except that the latter’s dried stigmas are packed loosely in air-tight containers while the former has stigmas joined together in a bundle tied with a cloth thread
Whats’ so special about Kashmir Saffron?
- The unique characteristics of Kashmir saffron are its longer and thicker stigmas, natural deep-red colour, high aroma, bitter flavour, chemical-free processing, and high quantity of crocin (colouring strength), safranal (flavour) and picrocrocin (bitterness).
- It is the only saffron in the world grown at an altitude of 1,600 m to 1,800 m AMSL (above mean sea level), which adds to its uniqueness and differentiates it from other saffron varieties available the world over.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ravines, Chambal River
Mains level: Features of badland topography
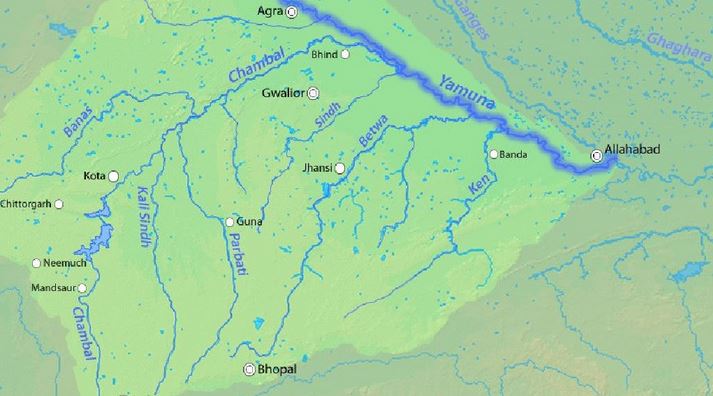
Union Minister of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare held a meeting with World Bank representatives to bring large Ravines of Gwalior–Chambal region under agriculture.
Try this question for mains:
Q.What is Badland Topography? Discuss the scope of their utilization as arable land in India.
What are Ravines?

- Badland topography is a major feature of the Chambal valley is characterized by an undulating floodplain, gullies and ravines.
- Ravines are a type of fluvial erosional feature and are formed as a result of constant vertical erosion by streams and rivers flowing over semi-arid and arid regions.
How are they formed?
- Researchers consider the regional climate as a major factor in the formation of ravines.
- Climate indeed plays a huge role by supplying the water in the form of rain or snow as well as providing the temperature variations.
- However, the ravines of Chambal are a bit difficult to be explained solely on climatic terms.
- The region through which the Chambal River flows does not receive enough rainfall to create ravines that are 60–80 m deep.
- Researchers have attributed neotectonic activities to the Chambal ravines genesis.
Other factors
- It is well known that rivers are full of energy and actively erode in their initial phases and progressively become passive as they attain their base levels.
- But sometimes, due to tectonic movements, the base level may be lowered further thus energizing the river and reactivating the erosion. This is known as River Rejuvenation.
- Moreover, wind erosion has also contributed to the formation of Chambal ravines.
Back2Basics: What are Badlands?
- Badlands are erosional landforms of highly dissected morphology that are created on soft bedrock in a variety of climate conditions.
- They develop in arid to semiarid areas where the bedrock is poorly cemented and rainfall is generally heavy and intermittent.
- The dry, granular surface material and light vegetation are swept from the slopes during showers, leaving the gullies bare.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




