Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Global coalition of democracies
In the recent speed Mike Pompeo, the US Secretary of State, floated the idea of an ‘alliance of democracies’. This article discusses its implications for India.
Two propositions on China
- The US Secretary of State laid out two propositions.
- One is that nearly five decades of US engagement with China have arrived at a dead-end.
- Second is that the US can’t address the China challenge alone and called for collective action.
- He mused on whether “it’s time for a new grouping of like-minded nations, a new alliance of democracies.”
How it matters for India?
- Both the propositions signal the breakdown of the relationship between the world’s two most important powers.
- They also reflect on the need to create new frameworks to cope with emerging global challenges.
- China, is a large neighbour of India and America, is India’s most important partner makes the new context rather different from the Cold War.
Concerns for India in the propositions
- Many in Delhi would like to know if the current direction of China policy will endure if Joe Biden wins the presidential election in November.
- India must pay close attention to the unfolding China debate in the US.
- India also note the structural changes in American engagement with China over the last two decades.
- Delhi will certainly avoid calling the group proposed by US Secretary of State an “alliance”.
- India would rather have it described as a “coalition of democracies”.
Idea of ‘Coalition of democracies’
- Over the last many years, India has become comfortable with the idea of a political partnership with the world’s leading democracies.
- India also supported past US initiatives like-Clinton Administrations “Community of Democracies”, Bush Administrations democracy promotion fund at the UN.
- Delhi has also welcomed President Trump’s initiative to convene an expanded gathering of the G-7 leaders.
- The idea of democracies working together has an enduring appeal for the US.
- India figures in this American vision is relatively new. So is Delhi’s readiness to reciprocate.
Consider the question “In the ongoing geopolitical situation the U.S. has proposed the idea of ‘alliance of democracies’. Where does India feature in this vision and what are the implications of it for India.”
Conclusion
Constructing a global coalition of democracies will take much work and quite some time. But engaging with that initiative, amidst the rise and assertion of China, should open a whole range of new possibilities for Indian foreign and security policies.
Original article:
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/us-india-democracy-china-cold-war-global-economy-6526409/
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Food security and healthy diet
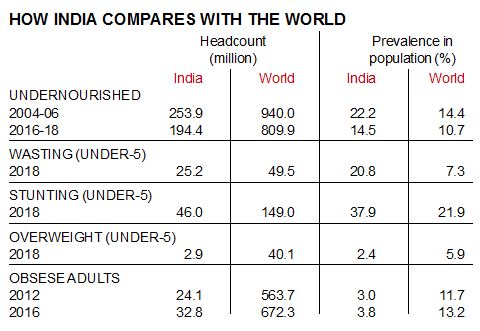
- The “State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World” was recently released.
About the report
- It is published by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and other UN agencies including the WHO.
- The report estimated that 820 million people worldwide did not have enough to eat in 2018, up from 811 million in the previous year.
- At the same time, the number of overweight individuals and obesity continue to increase in all regions.
Highlights of the report
- The number of people going hungry has risen for the third year running to more than 820 million. After decades of decline, food insecurity began to increase in 2015.
- Africa and Asia account for more than nine out of ten of the world’s stunted children, at 39.5% and 54.9% respectively.
- However at the same time, obesity and excess weight are both on the rise in all regions, with school-age children and adults affected particularly.
India scenario
- The number of obese adults in India has risen by a fourth in four years, from 24.1 million in 2012 to 32.8 million in 2016.
- While India’s undernourished population has dropped by roughly the same fraction in 12 years, from 253.9 million in 2004-06 to 194.4 million in 2016-18.
Compared with China
- The report has a section on economic growth in China and India, and its effect on poverty.
- Between 1990 and 2017, the two countries had an average GDP per capita growth rate of 8.6 per cent and 4.5 per cent respectively, the report said, citing World Bank.
- In both countries, the increase in GDP per capita has been accompanied by poverty reduction.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- India's declining soft power in the neighbourhood
The article examines the issue of declining political capital in India’s neighbourhood and the factors responsible for this.
India’s standing in neighbourhood: Past
- Not long ago, India was seen as a natural rising power in South Asia and the Indian Ocean Region.
- It was the de facto leader of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
- It has historical and cultural ties with Nepal.
- It enjoyed traditional goodwill and influence in Sri Lanka and Bangladesh.
- It had made investments worth billions of dollars in Afghanistan and cultivated vibrant ties with the post-Taliban stakeholders in Kabul.
- It had committed itself to multilateralism and the Central Asian connectivity project, with Iran being its gateway.
- It was competing and cooperating with China at the same time.
India’s relations in with the neighbourhood: Present
- India is perhaps facing its gravest national security crisis in 20 years, with China along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- SAARC is defunct.
- Nepal has turned hostile having adopted a new map and revived border disputes with India.
- Sri Lanka has tilted towards China.
- Bangladesh is clearly miffed at the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019.
- When Afghanistan is undergoing a major transition, India is out of the multi-party talks.
- Iran has inaugurated a railway link project connecting the Chabahar port, on the Gulf of Oman, to Zahedan.
What are the factors responsible for this?
When we dig deep, three problems can be found which are more or less linked to this decline.
1) Alignment with US
- As India started moving away from non-alignment, there has been a steady erosion in India’s strategic autonomy.
- India’s official policy is that it is committed to multilateralism.
- When India started deepening its partnership with the United States, New Delhi began steadily aligning its policies with U.S. interests.
- The case of Iran is the best example.
- India’s deepening defence and military ties with the U.S. probably altered Beijing’s assessment of India.
- One of the reasons for the shift could be Beijing’s assessment that India has already become a de facto ally of the U.S.
- The forceful altering of the status quo on the border is a risky message as much to New Delhi as it is to Washington.
2) Domestic politics
- The passing of the CAA is regionalisation of the domestic problems of the countries in India’s neighbourhood.
- Bangladesh took offence at the CAA and the National Register of Citizens, there were anti-India protests even in Afghanistan.
- CAA also drove new wedges between India and the countries that had a Muslim majority and were friendly to India in the neighbourhood.
- The abrogation of the special status of Jammu and Kashmir was another such move.
- But it damaged India’s reputation as a responsible democratic power and gave propaganda weapons to Pakistan.
- The change of status quo in Jammu and Kashmir, could be another factor that prompted the Chinese to move aggressively towards the border in Ladakh.
3) Misplaced confidence
- Great powers wait to establish their standing before declaring that they have arrived.
- China bided its time for four decades before it started taking on the mighty U.S.
- India should learn from at least these modern examples.
- If it did, it would not have used high-handedness in Nepal during the country’s constitutional crisis and caused a traditional and civilisational ally to turn hostile.
- The updated political map which India released in November rubbed salt into the wound on the Nepal border.
Consider the question “India’s standing in its neighbourhood has been on the decline for some time now. Examine the factors responsible for this.”
Conclusion
To address the current crises, India has to reconsider its foreign policy trajectory. It does not lack resources to claim what is its due in global politics. What it lacks is strategic depth.
Original article:
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/needed-a-map-for-indias-foreign-policy/article32206877.ece
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Governor’s Discretionary Powers
Mains level: State legislature issues
Rajasthan Governor returning the fresh proposal by the state Cabinet – seeking to convene a session of the Assembly has raised fresh legal questions on the powers of the Governor.
Try this question for mains:
Q. “Time and again, the courts have spoken out against the Governor acting in the capacity of an all-pervading super-constitutional authority.” Analyse.
Who has the powers to summon the House?
- It is the Governor acting on the aid and advice of the cabinet.
- Article 174 of the Constitution gives the Governor the power to summon from time to time “the House or each House of the Legislature of the State to meet at such time and place as he thinks fit…”
- However, the phrase “as he thinks fit” is read as per Article 163 of the Constitution which says that the Governor acts on the aid and advice of the cabinet.
- Article 163(1) essentially limits any discretionary power of the Governor only to cases where the Constitution expressly specifies that the Governor must act on his own and apply an independent mind.
What has the Supreme Court said in the past about the Governor’s power to summon the House?
- It is settled law that the Governor cannot refuse the request of the Cabinet to call for a sitting of the House for legislative purposes or for the chief minister to prove his majority.
- In fact, on numerous occasions, including in the 2016 Uttarakhand case, the court has clarified that when the majority of the ruling party is in question, a floor test must be conducted at the earliest available opportunity.
- In 2016, the Supreme Court in Nabam Rebia and Bamang Felix vs Deputy Speaker expressly said that the power to summon the House is not solely vested in the Governor.
What did the SC say in the Arunachal case?
- Referring to discussions in the Constituent Assembly, the court noted that the framers of the Constitution expressly and consciously left out vesting powers to summon or dissolve the House solely with the Governor.
- It said that the powers of the Governor were substantially altered to indicate that the framers did not want to give Governors the discretion.
- The Governor can summon, prorogue and dissolve the House, only on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers (CoM) with the Chief Minister as the head and not at his own, said the Court.
When can a Governor use his discretion?
- Article 163(1) of the Constitution says that “there shall be a CoM with the CM at the head to aid and advice the Governor in the exercise of his functions, except some conditions for discretion.
- However, in the 2016 case, the apex court has defined the circumstances if the aid and advice of CoM are binding on the Governor.
- When the chief minister has lost the support of the House and his strength is debatable, then the Governor need not wait for the advice of the CoM to hold a floor test.
Novel situations are created these days
- Generally, when doubts are cast on the chief minister that he has lost the majority, the opposition and the Governor would rally for a floor test.
- The ruling party may attempt to stall the process to buy time and keep its flock together.
- In a puzzling situation, in Rajasthan’s case, despite requests from CM, the Governor has returned requests to call for a session.
- However, in the current case, the rebel MLAs have not defected from their party but have repeatedly stated before the Rajasthan HC that they are merely expressing their dissent within the party.
Back2Basics: Governor’s Discretionary Powers
The governor can use his/her discretionary powers:
- When no party gets a clear majority, the governor has the discretion to choose a candidate for the chief minister who will put together a majority coalition as soon as possible.
- He can impose president’s rule.
- He submits reports on his own to the president or on the direction of the president regarding the affairs of the state.
- He can withhold his assent to a bill and send it to the president for his approval.
- During emergency rule per Article 353, he can override the advice of the council of ministers if specifically permitted by the president.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Interplanetary Contamination
Mains level: Interplanetary Contamination
As ambitious space missions are proliferating, along with advances in commercial space flight, astrobiologists have expressed concerns about possible ‘interplanetary contamination’.
A statements based question can be expected from the two types of interplanetary contamination.
What is Interplanetary Contamination?
- Interplanetary contamination refers to biological contamination of a planetary body by a space probe or spacecraft, either deliberate or unintentional.
- There are two types of interplanetary contamination:
- Forward contamination is the transfer of life and other forms of contamination from Earth to another celestial body.
- Back contamination is the introduction of extraterrestrial organisms and other forms of contamination into Earth’s biosphere. It also covers infection of humans and human habitats in space and on other celestial bodies by extraterrestrial organisms, if such habitats exist.
- The main focus is on microbial life and on potentially invasive species.
- Non-biological forms of contamination have also been considered, including contamination of sensitive deposits (such as lunar polar ice deposits) of scientific interest.
Are there any mechanisms to prevent such contaminations?
- Current space missions are governed by the Outer Space Treaty and the COSPAR (Committee on Space Research) guidelines for planetary protection.
- Forward contamination is prevented primarily by sterilizing the spacecraft.
- According to NASA, the guidelines have had far-reaching implications on human spacecraft design, operational procedures, and overall mission structure.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GFRA
Mains level: Forest conservation in India
India has ranked third among the top 10 countries that have gained in forest areas in the last decade a/c to the latest Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA).

Possible prelim question:
Q.The Global Forest Resources Assessment Report recently seen in news is published by-
a) UN-FAO
b) UN Forum on Forests
c) International Union of Forest Research Organizations
d) None of these
India gains in forest cover
- The top 10 countries that have recorded the maximum average annual net gains in a forest area during 2010-2020 are China, Australia, India, Chile, Vietnam, Turkey, the US, France, Italy and Romania.
- India accounts for two per cent of total global forest area.
- Globally, 12.5 million people were employed in the forestry sector. Out of this, India accounted for 6.23 million, or nearly 50 per cent.
Global prospects
- The Asian continent reported the highest net gain in a forest area in 2010-2020, according to the report.
- It recorded a 1.17 million hectares (ha) per year net increase in forests in the last decade.
- However, the South Asia sub-region reported net forest losses during 1990-2020.
- But, this decline would have been much higher without the net gain in India’s forest during this period, according to FRA 2020.
How did India gain?
- The FRA 2020 has credited the government’s Joint Forest Management programme for the significant increase in community-managed forest areas in the Asian continent.
- The forest area managed by local, tribal and indigenous communities in India increased from zero in 1990 to about 25 million ha in 2015, the assessment said.
- India has been taking up massive afforestation and plantation schemes.
About Global Forest Resources Assessment
- The Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA) reports on the status and trends of the world’s forest resources.
- It is led by the Forestry Department of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN.
- It reports the extent of the world’s forest area as well as other variables, including land tenure and access rights, sustainable forest management (SFM), forest conservation, and sustainable use.
Back2Basics: Defining forests as per FRA
- The definition excludes tree stands in agricultural production systems, such as fruit tree plantations, oil palm plantations, olive orchards, and agroforestry systems when crops are grown under tree cover.
The FAO definition of a forest includes:
- land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 per cent, or trees able to reach these thresholds in situ
- does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban land use
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: KRCNet
Mains level: Not Much

The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) has planned to develop a World-Class Knowledge Resource Centre Network (KRCNet).
Note the salient features of the KRCNet. UPSC may puzzle you asking which of these is/are not a feature of KRCNet.
KRCNet Portal
- KRCs will be connected with each other and integrated into the KRCNet portal.
- It will be a single point entry to the intellectual world of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- The resources and services of the MoES system will be accessible 24X7 through a one-point dynamic, updated and integrated on this portal.
Salient features of the KRCNet:
- Establish a Total Quality Management (TQM) system by securing ISO certification for documenting MoES knowledge resources, its maintenance, easy retrieval and dissemination.
- Collect, collate, analyze, index, store and disseminate the intellectual resources, products and project outputs available in MoES headquarter and its institutes.
- Develop and maintain an up-to-date meta-data of the print & digital resources available in MoES headquarter and MoES institutes, including MoES services.
- Provide 24X7 accesses to the subscribed knowledge contents through the KRCNet portal.
- Application of information-analytical tools & techniques like bibliometrics, scientometrics, big-data analytics, social media analytics etc., for policy formulation, report preparation and information dissemination.
- Periodically organize training workshops to popularize the usage of electronic journals, databases, digital products, data analytics etc.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SWAMIH Fund
Mains level: Housing for all
Union Minister for Finance has informed that so far Rs 8767 crore has been approved for 81 projects under Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH) Investment Fund I.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The SWAMIH Fund recently seen in news is related to:
(a) Higher Education (b) MSMEs (c) Housing (d) Highways
SWAMIH Fund
- In November 2019, the Finance Minister had cleared a proposal to set up a ‘Special Window’ called SWAMIH in to provide priority debt financing for the completion of stalled housing projects.
- SWAMIH Investment Fund has been formed to complete the construction of stalled, brownfield, RERA registered residential developments that are in the affordable housing / mid-income category.
- The Sponsor of the Fund is the Secretary, Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, and Government of India on behalf of the Government of India.
- The fund is set up as a Category-II AIF (Alternate Investment Fund) debt fund registered with SEBI and would be professionally run.
Why need such funds?
- Several real estate projects have suffered due to a combined effect of two changes in the real estate sector.
- On one hand, incremental launches and slow sales have increased unsold inventory in each project.
- While the effect has then got compounded by the fact that consumer preference is now towards completed projects rather than under-construction projects.
- This preference has developed as consumers are largely avoiding taking project completion risk and instead are more inclined to completed projects.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IndSAT
Mains level: Study in India Program

The Ministry of HRD conducted the first-ever Indian Scholastic Assessment (IND-SAT) Test 2020 under its ‘Study in India’ programme.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The INDSAT recently seen in news is a:
a) Free-to-air educational TV channels for school education
b) A satellite for educational purposes
c) IMD weather forecasting system
d) Online examination for foreign students in India
INDSAT Exam
- The Indian Scholastic Assessment or IND-SAT is a standardized online proctored test for students seeking scholarships with Study in India (SII).
- This exam is to gauge the capability and tenacity of students applying to study in India.
- The scores will serve as a criterion to shortlist the meritorious students for the allocation of scholarships for undergraduate as well as postgraduate programmes under ‘Study in India’ programme.
- The exam is conducted in the proctored internet mode by the National Testing Agency.
What makes it special?
- Nearly five thousand candidates from Nepal, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda, Sri-Lanka, Kenya, Zambia, Indonesia and Mauritius appeared for the exam.
About Study in India
- The Study in India is a programme of MHRD under which foreign students come to study in 116 select higher education institutions in India for undergraduate and postgraduate programmes.
- The selection of the students is based on their merit in class 12 / school-leaving exam.
- About top 2000 students are given scholarships, while some others are given fee discounts by the institutions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




