Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MGNREGA, Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan
Mains level: MGNREGA, Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan
- One-third of the way through the financial year, government data shows that the MGNREGA scheme has used up almost half its allocated funds.
- Its spending has been more than ₹48,500 crores out of the expanded ₹1 lakh crore allocations announced following the COVID-19 outbreak.
Try this question for mains:
Q.Discuss how the MGNREG Scheme has been providing a minimum basic income since the Covid pandemic. Also discuss how it can prove to be a game-changer if coupled with Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
About MGNREGA
- The MGNREGA stands for Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act of 2005.
- This is labour law and social security measure that aims to guarantee the ‘Right to Work’.
- The act was first proposed in 1991 by P.V. Narasimha Rao.
Its objectives
- To enhance the livelihood security of the rural poor by generating wage employment opportunities.
- To create a rural asset base which would enhance productive ways of employment, augment and sustain a rural household income.
Features of the Scheme
- MGNREGA is unique in not only ensuring at least 100 days of employment to the willing unskilled workers, but also in ensuring an enforceable commitment on the implementing machinery i.e., the State Governments, and providing a bargaining power to the labourers.
- The failure of provision for employment within 15 days of the receipt of job application from a prospective household will result in the payment of unemployment allowance to the job seekers.
- Employment is to be provided within 5 km of an applicant’s residence, and minimum wages are to be paid.
- Thus, employment under MGNREGA is a legal entitlement.
Also read:
[Burning Issue] Reorienting MGNREGA in times of COVID
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Demo 2 Mission
Mains level: Commercial space flights

Two NASA astronauts returned to Earth from the International Space Station (ISS) in a dramatic, retro-style splashdown, their capsule parachuting into the Gulf of Mexico to finish an unprecedented test flight.
We can get a match the pair type question in prelims asking various space missions and their purposes. Make note of similar space missions from here.
Crew Dragon
- Crew Dragon is a part of the Dragon 2, a class of reusable spacecraft developed and manufactured by American aerospace manufacturer SpaceX.
- It is the fifth class of US spacecraft to take human beings into orbit, after the Mercury, Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle programs.
- The rocket, named Falcon 9, which carried the spaceship into the orbit, was also built by SpaceX.
- It is done under the Demo-2 Mission of NASA and SpaceX.
Demo-2: What is the mission?

- The Demo-2 mission is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program with the aim of developing reliable and cost-effective access to and from the ISS.
- Essentially, the lift-off is a flight test to certify if SpaceX’s crew transportation system can be used to ferry crew to and from the space station regularly.
What makes it a special event?
- It was the first splashdown by U.S. astronauts in 45 years, with the first commercially built and operated spacecraft to carry people to and from orbit.
- The last time NASA astronauts returned from space to water was on July 24, 1975, in the Pacific to end a joint U.S.-Soviet mission known as Apollo-Soyuz.
- The return clears the way for possible tourist flights in the near future.
Back2Basics: SpaceX
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp., trading as SpaceX, is a private American aerospace manufacturer and space transportation Services Company headquartered in Hawthorne, California.
- It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the goal of reducing space transportation costs to enable the colonization of Mars.
- It has developed several launch vehicles and the Dragon spacecraft.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Time capsules
Mains level: NA

Ahead of the laying of the foundation stone for a temple, claims and denials have emerged about plans to put in a time capsule, or ‘Kaal Patra’.
Do you know?
A rubidium standard or rubidium atomic clock is the most inexpensive, compact, and widely produced atomic clock, used to control the frequency of television stations, cell phone base stations, in test equipment, and global navigation satellite systems like GPS.
What is a Time Capsule?
- It is a container of any size or shape, which accommodates documents, photos and artefacts typical of the current era and is buried underground, for future generations to unearth.
- The time capsule requires special engineering so that the contents don’t decay, even if pulled out after a century.
- Material such as aluminium and stainless steel are used for the encasing, and documents are often reproduced on acid-free paper.
- While the term “time capsule” was coined in the 20th century, among the earliest examples of one dates back to 1777, found by historians inside the statue of Jesus Christ in Spain during its restoration.
There’s a global society:
International Time Capsule Society
- The International Time Capsule Society (ITCS), based in the US and formed in 1990, is now defunct but continues estimating the number of time capsules in the world.
- As per its database, there are “10,000-15,000 times capsules worldwide”.
Are there any time capsules in India?
- There have been a number of prominent examples.
- One time capsule, outside the Red Fort and placed underground in 1972 by then PM Indira Gandhi, was dug out by the subsequent government.
- Other time capsules are at a school in Mumbai, IIT-Kanpur, LPU in Jalandhar, and Mahatma Mandir in Gandhinagar.
- The Red Fort time capsule was supposed to be dug out after 1,000 years.
Significance of time capsules
- Historians often criticize the idea of being motivated.
- This exercise is inevitably a subjective exercise, geared towards glorification not to construct the real picture.
- All historians look at this time capsule exercise with suspicion.
- It’s not a valid historical method — who decides what matter, what artefacts, written documents are going into it?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NTPS
Mains level: Regulation of forest produce in India
Environment Minister has launched piloting of the National Transit Pass System for seamless movement of forest produce.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The National Transit Pass System (NTPS) recently seen in news is related to:
(a) Transport of Forest Produces
(b) Transport through National Waterways
(c) Inter-state transport during restrictions
(d) None of these
About National Transit Pass System
- The NTPS is an online system for issuing transit permits for timber, bamboo and other forest produce.
- This system helps in monitoring and keeping records of transit permits for inter-state and intra-state transportation of timber and bamboo from private lands/government/private depot and other minor forest produce.
- E-pass will be issued for transit through the desktop-based web portal as well as a mobile application.
- It will bring ease of business and expedite the issuance of transit permits for timber, bamboo and other minor forest produce without physically going to forest offices.
- It will be functional in Madhya Pradesh and Telangana for now on a pilot basis.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: eVIN
Mains level: Vaccination programme in India
The eVIN has reached 32 States and Union Territories (UTs) and will soon be rolled out in the remaining States and UTs of Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Ladakh and Sikkim.
Try this question from CSP 2016:
Q.‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to:
(a) Immunization of children and pregnant women
(b) Construction of smart cities across the country
(c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
(d) New Educational Policy
About eVIN
- The eVIN is an innovative technological solution aimed at strengthening immunization supply chain systems across the country.
- This is being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM) by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It aims to provide real-time information on vaccine stocks and flows, and storage temperatures across all cold chain points in the country.
- This system has been used during the COVID pandemic for ensuring the continuation of the essential immunization services and protecting our children and pregnant mothers against vaccine-preventable diseases.
Components of eVIN
- eVIN combines state-of-the-art technology, a strong IT infrastructure and trained human resource to enable real-time monitoring of stock and storage temperature of the vaccines kept in multiple locations across the country.
- At present, 23,507 cold chain points across 585 districts of 22 States and 2 UTs routinely use the eVIN technology for efficient vaccine logistics management.
Benefits of eVIN
- It has helped create a big data architecture that generates actionable analytics encouraging data-driven decision-making and consumption-based planning.
- It helps in maintaining optimum stocks of vaccines leading to cost savings. Vaccine availability at all times has increased to 99% in most health centres in India.
- While instances of stock-outs have reduced by 80%, the time taken to replenish stocks has also decreased by more than half, on an average.
- This has ensured that every child who reaches the immunization session site is immunized, and not turned back due to unavailability of vaccines.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Contempt of Court
Mains level: Contempt of Court and associated issues
Contempt of court, as a concept is back in the news after the proceeding by the Supreme Court of India, on its own motion, against a senior Delhi-based advocate-activist.
Try this question for mains:
Q.What is Contempt of Court? Discuss, how free speech can lead to the contempt of courts?
What is Contempt of Court?
- It seeks to protect judicial institutions from motivated attacks and unwarranted criticism, and as a legal mechanism to punish those who lower its authority.
How did the concept of contempt come into being?
- The concept of contempt of court is several centuries old.
- In England, it is a common law principle that seeks to protect the judicial power of the king, initially exercised by him, and later by a panel of judges who acted in his name.
- Violation of the judges’ orders was considered an affront to the king himself.
- Over time, any kind of disobedience to judges, or obstruction of the implementation of their directives, or comments and actions that showed disrespect towards them came to be punishable.
What is the statutory basis for contempt of court?
- There were pre-Independence laws of contempt in India. Besides the early High Courts, the courts of some princely states also had such laws.
- When the Constitution was adopted, contempt of court was made one of the restrictions on freedom of speech and expression.
- Separately, Article 129 of the Constitution conferred on the Supreme Court the power to punish contempt of itself.
- Article 215 conferred a corresponding power on the High Courts.
- The Contempt of Courts Act, 1971, gives statutory backing to the idea.
What are the kinds of contempt of court?
The law codifying contempt classifies it as civil and criminal.
- Civil contempt is fairly simple. It is committed when someone willfully disobeys a court order or wilfully breaches an undertaking given to the court. However, Criminal contempt is more complex.
- It consists of three forms: (a) words, written or spoken, signs and actions that “scandalise” or “tend to scandalise” or “lower” or “tends to lower” the authority of any court (b) prejudices or interferes with any judicial proceeding and (c) interferes with or obstructs the administration of justice.
- The rationale for this provision is that courts must be protected from tendentious attacks that lower its authority, defame its public image and make the public lose faith in its impartiality.
- The punishment for contempt of court is simple imprisonment for a term up to six months and/or a fine of up to ₹. 2,000.
What does not account to contempt?
- Fair and accurate reporting of judicial proceedings will not amount to contempt of court.
- Nor is any fair criticism on the merits of a judicial order after a case is heard and disposed of.
Is truth a defence against a contempt charge?
- For many years, the truth was seldom considered a defence against a charge of contempt.
- There was an impression that the judiciary tended to hide any misconduct among its individual members in the name of protecting the image of the institution.
- The Act was amended in 2006 to introduce truth as a valid defence if it was in the public interest and was invoked in a bonafide
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Asiatic Society William Jones
Mains level: Linguistic study of ancient India
This newscard is an excerpt from the original article published in the Indian Express.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2016:
Q.Who of the following had first deciphered the edicts of Emperor Ashoka?
(a) Georg Buhier
(b) James Prinsep
(c) Max Muller
(d) William Jones
William Jones
- William Jones was appointed as a judge on the Supreme Court of Judicature at Fort William in Bengal,
- In the next couple of years, Jones established himself as an authority on ancient Indian language and culture, a field of study that was hitherto untouched.
- He is particularly known for his proposition of the existence of a relationship among European and Indo-Aryan languages, which he coined as Indo-European.
- He is also credited for establishing the Asiatic Society of Bengal in the year 1784.
His linguistic studies
- Jones’ was the first to suggest that Sanskrit, Greek and Latin languages had a common root and that indeed they may all be further related, in turn, to Gothic and the Celtic languages, as well as to Persian.
- He also suggested that Sanskrit ‘was introduced to India by conquerors from other kingdoms in some very remote age’ displacing ‘the pure Hindi’ of north India
- His claim rested on the evidence of several Sanskrit words that had similarities with Greek and Latin.
Some examples of his propositions
- As he studied the languages further, it became clearer that apart from Greek and Latin, Sanskrit words could be found in most other European languages.
- For instance, the Sanskrit word for ‘three’, that is ‘trayas’, is similar to the Latin ‘tres’ and the Greek ‘treis’. Similarly, the Sanskrit for ‘snake’, is ‘sarpa’, which shares a phonetic link with ‘serpens’ in Latin.
- For instance, ‘mata’ or mother in Sanskrit, is ‘mutter’ in German. ‘Dan’ or ‘to give’ in Sanskrit is ‘donor’ in Spanish.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Galapagos Islands
Mains level: Not Much

Chinese ships are frequently entering Ecuador’s waters for commercial fishing near the Galapagos Islands.
Try this question from CSP 2018:
Q.Which one of the following can one comes across if one travels through the Strait of Malacca?
(a) Bali
(b) Brunei
(c) Java
(d) Singapore
The Galapagos Islands
- Renowned worldwide for its unique species, the islands host a wide array of aquatic wildlife, including marine iguanas, fur seals, and waved albatrosses.
- The giant tortoises found here – ‘Galápagos’ in old Spanish– give the islands its name.
- Ecuador made a part of the Galapagos a wildlife sanctuary in 1935, and the sanctuary became the Galapagos National Park in 1959.
- In 1978, the islands became UNESCO’s first World Heritage Site.
- It was here that the British naturalist Charles Darwin made key observations in 1835 that shaped his theory of evolution. Darwin described the islands as a “world in itself”.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dhole and thier significance
Mains level: Wildlife conservation and various policy efforts

Karnataka, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh rank high in the conservation of dhole in India, according to a new study.
Dhole
- The dhole is a canid native to Central, South, East Asia, and Southeast Asia.
- India perhaps supports the largest number of dholes, with key populations found in three landscapes — Western Ghats, Central India and Northeast India.
- It is a highly social animal, living in large clans without rigid dominance hierarchies and containing multiple breeding females.
- It is listed as ‘Endangered’ by the IUCN as populations are decreasing and are estimated at fewer than 2,500 adults.
- Factors contributing to this decline include habitat loss, loss of prey, competition with other species, persecution due to livestock predation and disease transfer from domestic dogs.
Their significance
- Dholes play an important role as apex predators in forest ecosystems.
- Besides the tiger, the dhole is the only large carnivore in India that is under IUCN’s ‘endangered’ category.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hoolock Gibbons
Mains level: Wildlife conservation and various policy efforts

Hoolock Gibbons, the only species of apes found in India, are threatened with extinction in the Ukhrul and Kamjong districts of Manipur, a report has claimed.
Try this PYQ from CSP2013:
Q.Consider the following pairs:
Protected area:: Well-known for
- Bhitarkanika, Orissa:: Salt Water Crocodile
- Desert National Park, Rajasthan:: Great Indian Bustard
- Eravikulam, Kerala:: Hoolock Gibbon
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Hoolock Gibbons
- The two districts used to be covered with dense, tropical rainforests, which provided ideal tree canopies for the arboreal, brachiating ape species.
- Rampant deforestation for timber, forest fires and indiscriminate hunting had led to the decline in their population.
- Without the tree canopies, the gibbons cannot swing from branch to branch and stake out their territories.
- They also cannot adapt to living on the ground and cannot bear the high temperatures brought about by the loss of green cover.
Conservation status (a/c to WWF India)
- The gibbon has a much wider range, as it is found in all the states of the north-east, restricted between the south of the Brahmaputra River and east of the Dibang River.
- Outside India, it is found in eastern Bangladesh and north-west Myanmar.
- The eastern hoolock gibbon inhabits specific pockets of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India, and southern China and north-east Myanmar.
- Of the two, the western hoolock is listed as Endangered in the IUCN Redlist, while the eastern hoolock is listed as Vulnerable.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bharat Air Fibre Services
Mains level: Digital India

The Union Ministry of Communications has inaugurated “Bharat Air Fibre Services” at Akola in Maharashtra.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2018:
Q: Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of “Digital India” plan of the Government of India?
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like china did.
- Established a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect big data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the internet and bring WiFi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Bharat Air Fibre Services
- The Bharat Air Fibre services are introduced by BSNL as part of Digital India initiates by the GoI.
- It aims to provide Wireless Connectivity in the range of 20 KMs from the BSNL Locations.
- It provides internet connectivity upto 100 Mbps speed.
- It is completely wireless and offers broadband up to 10Mbps up to a distance of 5 Kms.
- These services are special and different from other operators as BSNL is providing unlimited free voice calling.
- Customers at remote places also will be benefitted as BSNL comes with the cheapest services with the support of Telecom Infrastructure Partners (TIPs).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UPI
Mains level: Paper 3- Examining the success of UPI
The UPI sets the template for India in its journey toward digitalisation. This article by WhatsApp head Will Cathcart explains the success story of UPI and the future scope to build on its success.
The success story of UPI
- The UPI system set a national open standard for all of India’s banks, more than 155 of which have adopted it.
- UPI is open standard that technology companies can adopt on an equal and level-playing field.
- This means that no one company, foreign or domestic, can write the rules for the other.
- Since its launch, the UPI system has grown to manage a 100 million-strong user base.
- NPCI has also set a goal to increase UPI’s user base to 500 million by 2022, which if achieved, would be a true game-changer for Digital India.
What the success of UPI means
- UPI has set important new frameworks around security and efficiency.
- Because of the strong rules that India has put in place, payment transaction information remains with the banks and within the country.
- And as a platform built on Indian technology and governed by Indian rules, UPI benefits Indians now and holds great potential for further innovation and commerce.
Future scope for UPI
- It is imperative more tech companies are able to leverage the power of UPI to expand the digital ecosystem to accelerate financial inclusion.
- UPI can also anchor a broader suite of fintech applications like micro-pensions, digital insurance products, and flexible loans.
- These are custom solutions created by Indian technology companies, on the public infrastructure of UPI.
- These solutions will first solve large social, business and financial problems in India and then become templates for other countries to deploy.
- COVID-19 has only underscored the importance of these tools that will serve as critical lifelines for small and micro-enterprises and individuals as they look to recover.
Consider the question “Within a short period from its launch the UPI has transformed the payment landscape in India. Examine the factors that contributed to the success of UPI and elaborate on its future scope.”
Conclusion
With courage, ambition, and boundless potential, India can emerge from this pandemic stronger than ever before — a leading democratic digital powerhouse that will lead the world in the 21st century.
B2BASICS
What is Unified Payments Interface (UPI)?
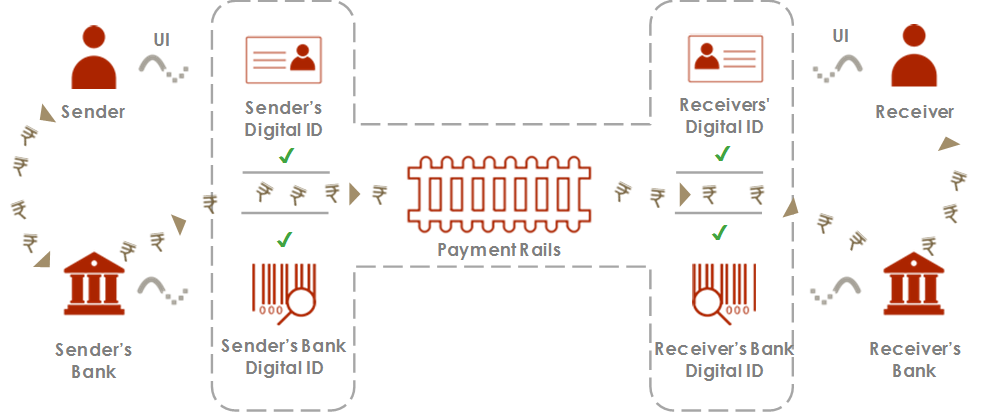
- It was launched in April 2016 and in the last two years, the platform has emerged as a popular choice among users for sending and receiving money.
- UPI is a payment system that allows money transfer between any two bank accounts by using a smartphone.
- UPI allows a customer to pay directly from a bank account to different merchants, both online and offline, without the hassle of typing credit card details, IFSC code, or net banking/wallet passwords.
- It also caters to the “Peer to Peer” collect request which can be scheduled and paid as per requirement and convenience.
Original article:
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/coronavirus-india-economy-poverty-digital-payment-bhim-upi-6533171/
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Issues in National Education Policy
The article critically examines the various aspects of the National Education Policy 2020 and the issue of flexibility and exams has been analysed closely.
Context of scepticism
- The New Education Policy is a forward-looking framework for transforming Indian education.
- But the past record on implementation of polity raises the concern that the New Education Policy should not turn out to be just “another document”.
- Also, the emphasis in the document on critical thinking and free inquiry is entirely well placed.
- But universities are being intimidated into political and cultural conformity.
- The document lays down objectives; the strategy has yet to come.
Walking the tightrope
- On the language issue it prefers the long-standing recommendation of primary education in the mother tongue.
- But does not categorically recommend curb English.
- On the basic architecture of delivery, policy does not show an inclination towards public or private education both in school and higher education.
School education: Most promising part
- The policy focus on early child development, learning outcomes, different forms of assessment, holistic education, and, recognises the centrality of teacher and teacher education.
- The document recognises that “the very highest priority of the education system will be to achieve universal foundational numeracy and literacy.”
- The suggestions for school education are ambitious, centred on the students, cater to their pedagogical diversity, and take on board the world of knowledge as it is now emerging.
Multidisciplinary education
- The document mentions the word multidisciplinary a bit too much, without explicating what it means.
- One way of thinking about this is not in terms of multiple subjects.
- It is reorienting education from disciplinary content to modes of inquiry that allow students to access a wide variety of disciplines.
Two concerns
1) Flexibility issue
- Under the policy, students might need different exit options.
- But it is unclear if the diploma or early exit options all be made available within a single institution, or different institutions.
- If it is within single institutions, this will be a disaster.
- Because structuring a curriculum for a classroom that has both one-year diploma and four-year degree students takes away from the identity of the institution.
- There is also a risk that without adequate financial support, the exercising of exit options will be determined by the financial circumstances of the student.
- The flexibility offered through multidisciplinary education is against the principle that different institutions have a different characters and strengths.
- A healthy education system will comprise of a diversity of institutions, not a forced multi-disciplinarity.
2) Issue of exams conundrum
- The document rightly emphasises that focus needs to shift from exams to learning. But it contradicts itself.
- Exams are burdon because of competition and cost in terms of opportunities.
- So the answer to the exam conundrum lies in the structure of opportunity.
- This will require a less unequal society both in terms of access to quality institutions.
- Exams are also necessary because in a low trust system people want objective measures of commensuration.
- So the policy reintroduces exams back into the picture by recommending a national aptitude test.
- But the idea that this will reduce coaching is wishful thinking, as all the evidence from the US and China is showing.
Consider the question “The National Education Policy 2020 moves away from rigidity and offers flexibility in many ways. In light of this examine the flexible dimensions offered in the policy and issues with it.”
Conclusion
The policy is commendable for focussing on the right questions. But the hope is that with this our education policy can be transformed into a treat, not another trick.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Metropolitan cities of India suffers from various issues. This article analyses such issues and suggests some steps to deal with them.
Inadequate public health infrastructure
- India’s public health expenditure in 2018 was a mere 1.28% of GDP.
- According to the World Bank, India’s out-of-pocket health expenditure was 62.4% in 2017, against the world average of 18.2%.
- Manpower in the health sector is low with India’s doctor-population ratio being 1:1,457 against WHO norm of 1:1,000.
Governance issues
- Factors underlying city governance include spatial planning, municipal capacities, empowered mayors and councils and inter-agency coordination, and ward-level citizen participation.
- Twenty-seven after the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act, these reform agendas continue to be slow in implementation.
- India’s metropolitan cities have weak capacities in finance and staffing.
- Bengaluru’s average percentage of own revenue to total expenditure is 47.9%, Chennai 30.5%, Mumbai 36.1% and Kolkata at 48.4%.
- According to ASICS 2017, Mumbai has the highest number of officers per lakh population at 938 in the country.
- Yet it is abysmally low compared to global cities such as Johannesburg with 2,922 and New York with 5,446 officers per lakh population
Limited powers of mayors
- The leaders steering India’s metropolitan cities are toothless.
- No big metropolitan cities with 10 million-plus population has a directly-elected Mayor.
- Mumbai’s Mayor has a tenure of 2.5 years, Delhi and Bengaluru, a mere one year.
- Mayors do not have full decision-making authority over critical functions of planning, housing, water, environment, fire and emergency services in most cases.
- Our metropolitan cities are far from being local self-governments.
- Parastatal agencies for planning, water and public transport report directly to State governments.
- The State government also largely controls public works and police.
- Globally, metropolitan cities are steered by a directly-elected leader.
- Evolved examples include the Tokyo metropolitan government and recent experimental models such as combined authorities in the United Kingdom and Australia.
Suggestions
- India needs home-grown solutions suited to its context and political realities while imbibing lessons on institutional design from global examples.
- It is time the Central and State governments lead efforts towards a metropolitan governance paradigm.
- The first steps should include empowered Mayors with five-year tenure, decentralised ward level governance, and inter-agency coordination anchored by the city government.
Lack of transparency, accountability and citizen participation
- Transparent cities with institutional platforms encouraging citizen participation improve urban democracy.
- No metropolitan has functional ward committees and area sabhas.
- An absence of citizen participation is worsened by poor transparency in finance and operations.
- As per ASICS 2017, India’s big metropolitan cities on average score 3.04/10 in transparency, accountability and participation.
Significance of smaller cities
- A World Bank report notes that despite the emergence of smaller towns, the underlying character of India’s urbanisation is “metropolitan”.
- Under this metropolitan character, new towns emerge around existing large cities.
- According to a McKinsey report, in 2012, 54 metropolitan cities and their hinterlands accounted for 40% of India’s GDP.
- The report also estimates that by 2025, 69 metropolitan cities, combined with their hinterlands, will generate over half of India’s incremental GDP between 2012 and 2025.
- Despite this, India is yet to begin an active discourse on cohesive metropolitan governance frameworks.
- Studies by the Centre for Policy Research point that India’s spatial feature exhibits the growth of small towns beyond the economics of large agglomerations.
- This indicates that while India’s urban vision should focus on its metropolitan cities to reap the benefit of scale, it shouldn’t ignore smaller cities.
Consider the question “Examine the issues in the governance of metropolitan cities. To what extent the limited power of mayors contributes to the issues of the metropolitan cities in India?”
Conclusion
India should use the current pandemic as an opportunity to introspect and reform the way its metropolises are governed.
Back2Basics: ASICS 2017
- The Annual Survey of India’s City-Systems (ASICS) 2017 evaluates quality of governance in cities, covering 23 major cities in India across 20 states based on 89 questions.
- Indian cities scored between 3.0 and 5.1 on 10, with Pune topping the charts for the first time.
- Other cities that came in the top five include Kolkata, Thiruvananthapuram, Bhubaneswar and Surat, with scores in the range of 4.6 to 4.5.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Anti-defection law
Mains level: Issues over Anti-defection law
A political party is trying to win back its defected MLAs in Rajasthan. This has raised a new question- “Does the anti-defection law apply here?”
Try this question for mains:
Q.“Time and again, the courts have spoken out against the Governor acting in the capacity of an all-pervading super-constitutional authority.” Analyse.
What does “merger” mean a/c to Tenth Schedule?
- The Tenth Schedule of the Constitution prohibits defection to protect the stability of governments but does not prohibit mergers.
- Paragraph 4(2) of the Tenth Schedule, dealing with mergers, says that only when two-thirds of the members agree to “merge” the party would they be exempt from disqualification.
- The “merger” referred to in Paragraph 4(2) is seen as a legal fiction, where members are deemed to have merged for the purposes of being exempt from disqualification, rather than a merger in the true sense.
The ‘merger’ Politics
- The political party is arguing that a state unit of a national party cannot be merged without the party being merged at the national level.
- However, the Tenth Schedule identifies this dichotomy between state units and national units.
- As per Paragraph 4(2), “merger” of a party means merger of a legislative party of that House.
- In this case, it would be the Rajasthan Legislative unit of the BSP and not the BSP at the national level.
- Paragraph 1 of the Tenth Schedule which defines terms specified in the context of the anti-defection law states this clearly.
- “Legislature Party” for the purposes of Paragraph 4 (which deals with mergers) means the group consisting of all the members of that House for the time being belonging to that political party in accordance with the said provisions.
Role of Whip
- Every legislative party identifies the party’s whip at the beginning of the Assembly’s term and conveys this to the Speaker.
- A national leader’s direction cannot be considered a whip in the context of the anti-defection law.
On what grounds is the case-based?
- The contention is that the merger is illegal and unconstitutional because, for a national party, such merger has to take place at the national level.
- Supporting this argument, there are two decisions of the Supreme Court: the 2006 Jagjit Singh v State of Haryana, and the 2007 ruling in Rajendra Singh Rana and Ors vs Swami Prasad Maurya.
- In these cases, the SC ruled that the split cannot be recognised primarily because not all these MLAs split at once.
- The key aspect is that these cases deal with splits where when one-third of the members of a legislative party split; they could not attract disqualification as per Paragraph 3 of the Tenth Schedule.
Row over one-third
- In 2003, through the 91st Constitutional Amendment, Paragraph 3 was deleted from the Tenth Schedule.
- The amendment was made as the one-third split rule was grossly misused by parties to engineer divisions and indulge in horse-trading.
- One-third was regarded as an easy target to achieve and the law now exempts defection only when it is at two-thirds (in a merger).
Are there any such precedents?
- In July 2019, 10 of the 15 one party’s MLAs in Goa joined the other taking the ruling party’s tally to 27 in the 40 member House.
- Since they formed two-thirds of the strength of the legislative party unit, they are exempt from disqualification.
- However, the Speaker’s decision not to disqualify them is under challenge before the Supreme Court.
- Similarly in Telangana in 2016, two years after the 12 out of 15 of MLAs joined the ruling party.
- The Speaker recognised the defection as a merger since more than two-thirds had moved.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UNFAO
Mains level: Assurance of Food Security
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has unveiled a new platform to help accelerate the global reduction in food loss and waste.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2016:
Q. The FAO accords the status of ‘Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS)’ to traditional agricultural systems. What is the overall goal of this initiative?
- To provide modern technology, training in modern farming methods and financial support to local communities of identified GIAHS so as to greatly enhance their agricultural productivity.
- To identify and safeguard eco-friendly traditional farm practices and their associated landscapers, agricultural biodiversity and knowledge systems of the local communities.
- To provide Geographical Indication status to all the varieties of agricultural produce in such identified GIAHS.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
About the Platform
- The Technical Platform on the Measurement and Reduction of Food Loss and Waste brings together information on measurement, reduction, policies, alliances, actions and examples of successful models applied to reduce food loss and waste across the globe.
- The platform will contain information on measurement, reduction policies, alliances, actions and examples of successful models applied to reduce food loss and waste.
- The platform will be officially launched on the first International Day of Awareness of Food Loss and Waste on 29 September 2020.
How will it work?
- The platform is as a gateway to information on food loss and waste from various resources, including the largest online collection of data on what food is lost and wasted.
- Links to related portals from development partners are also provided.
Why need such a portal?
- Food loss and waste is a sign of food systems in distress. Nutritious foods are the most perishable, and hence, the most vulnerable to lose.
- Not only food is being lost, but food safety and nutrition are being compromised as well.
- At least 14 per cent of food is lost (food wastage and food loss together), valued at $400 billion annually.
- In terms of greenhouse gas emissions, the food that is lost is associated with around 1.5 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent.
- Major losses are seen in roots tubers and oil-bearing crops (25 per cent), fruits and vegetables (22 per cent), and meat and animal products (12 per cent).
- Reducing food loss and waste can bring about many benefits: more food available for the most vulnerable; a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions; less pressure on land and water resources; and increased productivity and economic growth.
Food loss vs food wastage
- There is a difference between food wastage and food losses.
- Food is wasted when it is discarded by consumers or is disposed of in retail due to its inability to meet quality standards.
- Food loss, on the other hand, occurs when it is spoilt or spilt before reaching the final product or retail stage.
- For example, dairy, meat, and fish can go bad in transit because of inadequate refrigerated transport and cold storage facilities.
Back2Basics: Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO)
Objective: Lead international efforts to defeat hunger
Members: FAO has 194 Member Nations, two associate members and one member organization, the European Union
Headquarters: Rome, Italy
Year Founded: Established in 1945
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Commonwealth of Nations
Mains level: Abolition of modern slavery
The CHRI has released a report on “Eradicating Modern Slavery: An assessment of Commonwealth government progress”.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2012:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- The Commonwealth has no charter, treaty or constitution
- All the territories/countries once under the British Empire (jurisdiction/rule/mandate) automatically joined the Commonwealth as its members
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
About the report
The report was released on the occasion of World Day Against Trafficking in Persons by the Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative (CHRI) and an international anti-slavery organisation Walk Free.
Highlights of the report
- The report assessed the progress made by Commonwealth countries on the promises made in 2018 to end modern slavery by 2030 and achieve the SDGs of ending forced labour, human trafficking and child labour.
- The report found that one-third of the Commonwealth countries had criminalised forced marriage, while 23 had not criminalised commercial sexual exploitation of children.
- Commonwealth countries have made little progress towards their commitment to eradicate modern slavery by 2030.
- One in every 150 people in the Commonwealth is living in conditions of modern slavery.
- Out of 54 countries, only four engage with business to investigate supply chains, and all countries report gaps in victim assistance programs
- None of the Asian countries in the group had implemented laws against forced labour in supply chains.
India is the worst performer
- India had fared the worst in terms of coordination with no national coordinating body or National Action Plan in place.
- India, like all other Commonwealth countries in Asia, had not ratified the International Labour Organization’s 2011 Domestic Workers Convention or the 2014 Forced Labour Protocol.
- The report said India accounted for one-third of all child brides in the world.
- Despite being the largest country in the region, India has the weakest response on national coordination, with no national coordinating body or National Action Plan in place.
Back2Basics: Commonwealth of Nations

- The Commonwealth of Nations is an intergovernmental organisation of 53 member states that are mostly former territories of the British Empire.
- It dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonization of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories.
- It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nation through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalized by the UK through the Statute of Westminster in 1931.
- The current body was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernized the community, and established the member states as “free and equal”.
- The symbol of this free association is Queen Elizabeth II, who is the Head of the Commonwealth.
- The Queen is head of state of 16 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 32 other members are republics and five others have different monarchs.
- Member has no legal obligations to one another. Instead, they are united by language, history, culture and their shared values of democracy, human rights and the rule of law.
Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative (CHRI)
- It is an independent, non-partisan & nonprofit international NGO which works towards the practical realization of human rights in the countries of the Commonwealth.
- It was founded in 1987 and is headquartered at New Delhi.
- CHRI’s objectives are to promote awareness and adherence to the Commonwealth’s Harare Declaration, to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, to other internationally recognised human rights instruments.
- The organisation specializes in transparency and accountability issues, with a focus on access to justice and access to information.
- The organisation mainly works in South Asia, East Africa, and Ghana region.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Smog towers
Mains level: Air pollution in Delhi
In January this year, the Supreme Court has directed that two smog towers should be installed in the capital by April on a pilot project basis considering a proposal by the IIT-Bombay.
Try this question from CS Mains 2015:
Q.Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata are the three mega cities of the country but the air pollution is much more serious problem in Delhi as compared to the other two. Why is this so?
What is a ‘Smog Tower’?
- A smog tower is a structure designed to work as a large-scale air purifier, fitted with multiple layers of filters which trap fine dust particles suspended in the air as it passes through them.
- Air is drawn through fans installed at the top of the tower, passed through filters, and then released near the ground.
- The large-scale filters expected to be installed in the towers in Delhi would use carbon nanofibres as a major component.
- It would be fitted along the peripheries of the towers and the height would be 20 metres.
How does it work?
- The 20-metre (65 feet) high tower will trap particulate matter of all sizes suspended in the air.
- Large-scale air filters shall draw in the air through fans installed at the top before passing it through the filters and releasing it near the ground.
- The filters installed in the tower will use carbon nanofibres as a major component and will be fitted along its peripheries. The tower will focus on reducing particulate matter load.
Has anyone else experimented with a smog tower?
- Yes, smog towers have been experimented with in recent years in cities in the Netherlands, China, South Korea and Poland.
- The first such tower was erected in 2015, in Rotterdam, Netherlands, created by Dutch artist Daan Roosegaarde.
- The towers to be installed in Delhi are to be the result of a collaboration between the IITs at Mumbai and Delhi, and the University of Minnesota.
Why New Delhi?
- Air pollution in the national capital has been an issue of concern for quite some time as Delhi and its suburbs have ranked among the most polluted cities in the world frequently.
- In 2014, the World Health Organisation (WHO) had declared Delhi the most polluted city in the world.
- Pollution levels in Delhi increase dramatically during winter — on some days to nearly 10 times above the limits prescribed by WHO, posing a serious risk to vulnerable and also healthy populations.
- This is large because sources of emissions — construction work, industrial and vehicular pollution — in and around the city remain more or less consistent.
- The situation is aggravated at the start of winter by smoke from stubble-burning in northwestern states, coupled with unfavourable meteorological conditions, such as calm winds, low temperatures, and fewer sunny days.
How effective are smog towers?
- An estimate on air quality shows that a tower would reduce 50% of the particulate matter load in an area of 1 kilometre in the direction of the wind, as well as 200 metres each along the sides of the tower and against the direction of the wind.
- In an open field in calm weather, it can reduce the particulate matter of 10 micrometres (PM10) up to 45%, and PM2.5 levels up to 25% in an area of 20 metres around the tower, as per details on the ENS Clean Air website.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Black Rain
Mains level: Hiroshima and Nagasaki Bombings by US
Ahead of the 75th anniversary of Hiroshima, a Japanese court has recognised 84 survivors of the post-nuclear explosion “black rain” as the atomic bomb survivors. This would enable them to avail free medical benefits.
Try this question from CSP 2011:
Q.Acid rain is caused by the pollution of the environment by:
(a) Carbon dioxide and nitrogen
(b) Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide
(c) Ozone and carbon dioxide
(d) Nitrous oxide and Sulphur dioxide
What is Black Rain?
- An estimated 69 per cent of the buildings in Hiroshima were destroyed by the atomic bomb.
- The debris and soot from this, mixed with the radioactive fallout from the bomb, raised high into the atmosphere in the form of a mushroom cloud.
- This material combined with the vapour in the atmosphere and came down as dark drops of liquid that have been called black rain.
- Survivors of the black rain described it as consisting of large, greasy drops that are much heavier than normal raindrops.
- It is full of highly radioactive material, and studies have shown that exposure to it can result in serious illnesses.
What was its effect?
- A study conducted in the year 1945 itself showed that black rain had come down as far as 29 km away from ground zero.
- The rain contaminated everything it came in contact with, and dead fish were reported floating in water bodies and severely ill cattle were seen lying in the fields.
- It has caused acute radiation symptoms (ARS) in many who were exposed to it, with reports of people suffering from nausea and diarrhoea for weeks.
- Other ARS include fever, sore throat and loss of hair. Over time, many people who were exposed to black rain have developed cancer.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Finance Commission
Mains level: Finance Commission, Its evolving role in fiscal federalism
The High-Level Group on Agricultural Exports set up by the Fifteenth Finance Commission has submitted its report to the Commission.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2019
Q.In India, which of the following reviews the independent regulators in sectors like telecommunications, insurance, electricity, etc.?
- Ad Hoc Committees set up by the Parliament
- Parliamentary Department Related Standing Committees
- Finance Commission
- Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission
- NITI Aayog
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2 and 5
Why focus on Agri-exports?
- India’s agricultural export has the potential to grow from USD 40 billion to USD 70 billion in a few years.
- The estimated investment in agricultural export could be in the tune to USD 8-10 billion across inputs, infrastructure, and processing and demand enablers.
- Additional exports are likely to create an estimated 7-10 million jobs.
- It will lead to higher farm productivity and farmer income.
Highlights of the report
(A) The HLEG has made its recommendations, major among which are:
- Focus on 22 crop value chains – demand-driven approach.
- Solve Value Chain Clusters (VCC) holistically with a focus on value addition.
- Create a State-led export plan with participation from stakeholders.
- Private Sector should play an anchor role.
- The centre should be an enabler.
- The robust institutional mechanism to fund and support implementation.
(B) State-led Agri Exports
The Group has recommended a State-led Export Plan – a business plan for a crop value chain cluster. It will lay out the opportunity, initiatives and investment required to meet the desired value chain export aspiration.
The Group has also said that for its success, the following factors needed to be considered:-
- Plans should be collaboratively prepared with private sector players and Commodity Boards.
- Leveraging of state plan guide and value chain deep dives.
- The private sector should play an anchor role in driving outcomes and execution.
- The centre should enable state-led plans.
- Institutional governance should be promoted across the state and centre.
- Funding through the convergence of existing schemes, Finance Commission allocation and private sector investment.
Back2Basics: Finance Commission (FC)
- The FC is a constitutionally mandated body that decides, among other things, the sharing of taxes between the Centre and the states.
- Article 280 (1) requires the President to constitute, “within two years from the commencement of this Constitution.
- And thereafter constitute FC at the expiration of every fifth year or at such earlier time as the President considers necessary.
- An FC “which shall consist of a Chairman and four other members”.
Divisible Pool of Taxes
- Under Article 280(3) (a) the FC must make recommendations to the President “as the distribution between the Union and the States of the net proceeds of taxes which are to be, or maybe, divided between them under this Chapter and the allocation between the States of the respective shares of such proceeds”.
- Accordingly, the FC determines a formula for tax-sharing between the states, which is a weighted sum of the states’ population, area, forest cover, tax capacity, tax effort and demographic performance, with the weights expressed in percentages.
- This crucial role of the Commission makes it instrumental in the implementation of fiscal federalism.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now









