Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PMP and PLI Scheme
Mains level: Paper 3- Issues with Phased Manufacturing Policy
The Production Linked Incentive Scheme, though ambitious in its goal suffers from several fundamental issues. The article discuses such issues.
Background of the Phased Manufacturing Policy
- The Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP) incentivised the manufacture of low value accessories initially, and then moved on to the manufacture of higher value components.
- This was done by increasing the basic customs duty on the imports of these accessories or components.
- The PMP was implemented with an aim to improve value addition in the country.
- Recently, 16 firms in the mobile manufacturing sector were approved for the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to transform India into a major mobile manufacturing hub.
- The PLI comes on the back of a phased manufacturing programme (PMP) that began in 2016-17.
Issues to consider
1) More imports and less value addition in India
- Firms such as Apple, Xiaomi, Oppo, and OnePlus have invested in India, but mostly through their contract manufacturers.
- As a result, production increased from $13.4 billion in 2016-17 to $31.7 billion in 2019-20.
- But factory-level production data from the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) shows that more than 85% of the inputs were imported.
- UN data for India, China, Vietnam, Korea and Singapore (2017-2019), show that except for India, all countries exported more mobile phone parts than imports.
- More export than import by these countries indicate the presence of facilities that add value to these parts before exporting them.
- India, on the other hand, imported more than it exported.
- Therefore, while the PMP policy increased the value of domestic production, improvement in local value addition remains low.
- The new PLI policy offers an incentive subject to thresholds of incremental investment and sales of manufactured goods.
- Thus, focus remains on increasing value of domestic production, and not local value addition.
2) Shift from China unlikely
- India produced around 29 crore units of mobile phones for the year 2018-19; 94% of these were sold in the domestic market.
- This implies that much of the incremental production and sales under the PLI policy will have to be for the export market.
- Recently, a study by Ernst & Young showed that if the cost of production of a mobile phone is say 100 (without subsidies), then the effective cost (with subsidies and other benefits) of manufacturing mobile phone in China is 79.55, Vietnam, 89.05, and India (including PLI), 92.51.
- So, it may be premature to expect a major chunk of mobile manufacturing to shift from China to India.
3) PLI doesn’t strengthen the current export competitiveness
- India’s mobile phone exports grew from $1.6 billion in 2018-19 to $3.8 billion in 2019-20, but per unit value declined from $91.1 to $87, respectively.
- This shows that our export competitiveness seems to be in mobiles with lower selling price.
- However, for foreign firms chosen under the PLI policy, the incentive will be at and above ₹15,000 ($204.65).
- So, it is clear that the PLI policy does not strengthen our current export competitiveness in mobile phones.
4) Absence of domestic firms
- Domestic firms have been nearly wiped out from the Indian market.
- So, their ability to take advantage of the PLI policy and grab a sizeable domestic market share seems difficult.
- Domestic firms may have the route of exporting cheaper mobile phones to other low-income countries.
- However, their performance in the last couple of years has not been promising.
5) Importance of supply chain colocation
- The six component firms that have been given approval under the ‘specified electronic components segment’do not complete the mobile manufacturing ecosystem.
- For example, when Samsung set up shop in Vietnam, it relied heavily on its Korean suppliers which co-located with it to produce intermediate inputs, so much so that 63 among Samsung’s 67 suppliers then were foreign.
- Though Samsung is invested hugely in India, it has not colocated its supply chain in the country.
- So, the foreign firms chosen under the PLI policy should be encouraged to colocate their supply ecosystems in the country.
6) Complaint at WTO against PMP
- In September 2019, Chinese Taipei contested the raise in tariffs under the PMP.
- If the PMP is found to be World Trade Organization (WTO) non-compliant, then we may be flooded with imports of mobile phones.
- This might make the local assembly of mobile phones unattractive.
- This will affect the operations of the mobile investments done under the PMP.
Conclusion
The PMP policy, since 2016-17 has barely been helpful in raising domestic value addition in the industry even though value of production expanded considerably.
B2BASICS

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Debt-GDP ratio
Mains level: Not Much
India’s public debt ratio, which remarkably remained stable at about 70% of the GDP since 1991, is projected to jump by 17 percentage points to almost 90% a/c to IMF.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- Most of India’s external debt is owed by governmental entities.
- All of India’s external debt is denominated in US dollars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Why such a spike?
- The increase in public spending, in response to COVID-19, and the fall in tax revenue and economic activity, will make public debt jump by 17 percentage points to almost 90% of GDP.
What is Debt-to-GDP Ratio?
- The Debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio between a country’s government debt and its gross domestic product (GDP).
- It measures the financial leverage of an economy.
- A country able to continue paying interest on its debt-without refinancing, and without hampering economic growth, is generally considered to be stable.
- A country with a high debt-to-GDP ratio typically has trouble paying off external debts (also called “public debts”), which are any balances owed to outside lenders.
- In such scenarios, creditors are apt to seek higher interest rates when lending. Extravagantly high debt-to-GDP ratios may deter creditors from lending money altogether.
- A low debt-to-GDP ratio indicates an economy that produces and sells goods and services sufficient to pay back debts without incurring further debt.
- Geopolitical and economic considerations – including interest rates, war, recessions, and other variables – influence the borrowing practices of a nation and the choice to incur further debt.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: FAO
Mains level: India and FAO
On the occasion of 75th Anniversary of Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) on 16th October 2020, PM has released a commemorative coin of Rs 75.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The FAO accords the status of ‘Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS)’ to traditional agricultural systems. What is the overall goal of this initiative?
- To provide modern technology, training in modern farming methods and financial support to local communities of identified GIAHS so as to greatly enhance their agricultural productivity.
- To identify and safeguard eco-friendly traditional farm practices and their associated landscapes, agricultural biodiversity and knowledge systems of the local communities.
- To provide Geographical Indication status to all the varieties of agricultural produce in such identified GIAHS Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
About FAO
- It is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security.
- It was founded in October 1945 and is headquartered in Rome.
- It maintains regional and field offices around the world, operating in over 130 countries.
- It also conducts research, provides technical assistance to projects, operates educational and training programs, and collects data on agricultural output, production, and development.
- Composed of 197 member states, the FAO is governed by a biennial conference representing each member country and the European Union, which elects a 49-member executive council.
- The Director-General serves as the chief administrative officer.
India and FAO
- India has had a historic association with FAO.
- Indian Civil Service Officer Dr Binay Ranjan Sen was the Director-General of FAO during 1956-1967.
- The World Food Programme, which has won the Nobel Peace Prize 2020, was established during his time.
- India’s proposals for the International Year of Pulses in 2016 and the International Year of Millets 2023 have also been endorsed by FAO.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: STARS Project
Mains level: Not Much
The Union Cabinet has approved the sum of Rs. 5718 crore for the World Bank aided project STARS.
Try this MCQ:
Q. The STARS Project recently seen in news is an initiative of:
World Bank/ Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation / UNECOSOC/ UNICEF
STARS Project
- ‘STARS’ is an acronym for Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS).
- The STARS project will be implemented through the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan, the flagship central scheme.
- The six states include- Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha and Rajasthan.
- It will help improve learning assessment systems, strengthen classroom instruction and remediation, facilitate school-to-work transition, and strengthen governance and decentralized management,
- Some 250 million students (between the age of 6 and 17) in 1.5 million schools and over 10 million teachers will benefit from the STARS program.
- STARS will support India’s renewed focus on addressing the ‘learning outcome’ challenge and help students better prepare for the jobs of the future – through a series of reform initiatives.
Major components of the STARS
1) At the national level, the project envisages the following interventions which will benefit all states and UTs:
- To strengthen MOE’s national data systems to capture robust and authentic data on retention, transition and completion rates of students.
- To support MOE in improving states PGI scores by incentivizing states governance reform agenda through SIG (State Incentive Grants).
- To support the strengthening of learning assessment systems.
- To support MOE’s efforts to establish a National Assessment Center (PARAKH).
2) At the State level, the project envisages:
- Strengthening Early Childhood Education and Foundational Learning
- Improving Learning Assessment Systems
- Strengthening classroom instruction and remediation through teacher development and school leadership
- Governance and Decentralized Management for Improved Service Delivery.
- Strengthening Vocational education in schools through mainstreaming, career guidance and counselling, internships and coverage of out of school children
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Thalassemia
Mains level: Not Much
Union Health Ministry has launched the second phase of “Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojna” for underprivileged Thalassemic patients.
Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojna
- This scheme was launched in 2017 under the Coal India CSR funded Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) program.
- It aims to provide a one-time cure opportunity for Haemoglobinopathies like Thalassaemia and Sickle Cell Disease for patients who have a matched family donor.
- The initiative was targeted to provide financial assistance to a total of 200 patients by providing a package cost not exceeding Rs. 10 lakhs per HSCT.
What is Thalassemia?
- Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder characterized by less oxygen-carrying protein (haemoglobin) and fewer red blood cells in the body than normal.
- When there isn’t enough haemoglobin, the body’s red blood cells don’t function properly and they last shorter periods of time, so there are fewer healthy red blood cells travelling in the bloodstream.
- Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, paleness and slow growth.
- Mild forms may not need treatment. Severe forms may require blood transfusions or a donor stem-cell transplant.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Inflation targeting mechanism
Mains level: Paper 3- Issues with the inflation targeting mechanism of the RBI
The article analyses the recent changes signalled by the RBI in its policymaking.
Changes in the economic policymaking
- Recently the U.S. Fed declared that the Fed will not let inflation stand in the way of maximising employment.
- The reason for this was that the Phillips Curve, the relationship between inflation and unemployment, may no longer hold in the U.S. economy.
- This is significant, given that the Anglo-American economics has been dominated by Phillips Curve.
Why there was need for change in inflation targeting
- Data show that the model that currently guides India’s inflation control strategy may be quite irrelevant.
- This is seen in the recent behaviour of inflation.
- We know that output contracted by more than 23% in the first quarter of this year.
- Despite this staggering decline the inflation rate did not change,
- This was contrary to experience that inflation reflects an ‘over heating’ economy, one growing too fast in relation to its potential.
- This view represents the RBI’s official understanding of inflation, and presumably forms the basis of its policy of inflation targeting.
- It was endorsed by the Government of India when it legislated the modern monetary policy framework to enable the RBI to pursue inflation targeting.
- If the Phillips Curve, which the RBI’s approach internalises, exists, inflation should have decreased as India’s economy contracted during the lockdown.
- The current inflation targeting mechanism had been imagined with developing economies in mind.
- Inflation targeting mechanism is based on the idea that food prices are an important determinant of inflation along with imported inflation.
- Accordingly, a macroeconomic contraction need not lower inflation.
Role of food prices in India
- A recent working paper of the RBI’s research department suggested that a more eclectic model than the one that underlies inflation targeting does a better job of forecasting inflation in India.
- This model accepts a role for food prices, a possibility that is missed when embracing economic models developed in the western hemisphere, where food prices have stopped trending upwards over half a century ago.
Conclusion
The RBI shifting away from its rigid inflation targeting policy is in tune with the time and signals that the central bank is finally alive to India’s economy.
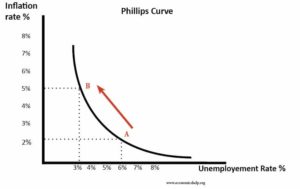
Back2Basics: What is Philips Curve?
- The Phillips curve is an economic concept, stating that inflation and unemployment have a stable and inverse relationship.
- The theory claims that with economic growth comes inflation, which in turn should lead to more jobs and less unemployment.
- However, the original concept has been somewhat disproven empirically due to the occurrence of stagflation in the 1970s, when there were high levels of both inflation and unemployment.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Karman Line, New Sphephard
Mains level: Micro-gravity experimentation

New Shephard, a rocket system meant to take tourists to space successfully completed its seventh test launch.
Note the features of the Karman Line. It is a new terminolgy in our recent space vocab.
What is New Shephard?
- New Shephard has been named after astronaut Alan Shephard, the first American to go to space, and offers flights to space over 100 km above the Earth and accommodation for payloads.
- Essentially, it is a rocket system that has been designed to take astronauts and research payloads past the Karman line – the internationally recognised boundary of space.
- The idea is to provide easier and more cost-effective access to space meant for purposes such as academic research, corporate technology development and entrepreneurial ventures among others.
- It is built by Amazon founder Jeff Bezos’s Space Company called Blue Origin.
- In 2018, Blue Origin was one of the ten companies selected by NASA to conduct studies and advance technologies to collect process and use space-based resources for missions to the Moon and Mars.
How does it work?
- The rocket system consists of two parts, the cabin or capsule and the rocket or the booster.
- The cabin can accommodate experiments from small mini payloads up to 100 kg.
- The cabin is designed for six people and sits atop a 60-feet tall rocket and separates from it before crossing the Karman line, after which both vehicles fall back to the Earth.
- The system is a fully reusable, vertical takeoff and vertical landing space vehicle that accelerates for about 2.5 minutes before the engine cuts off.
- After separating from the booster, the capsule free falls in space, while the booster performs an autonomously controlled vertical landing back to Earth.
- The capsule, on the other hand, lands back with the help of parachutes.
Back2Basics: Karman line
- The Karman line is an attempt to define a boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space.
- The line is named after Theodore von Kármán (1881–1963), a Hungarian American engineer and physicist, who was active primarily in aeronautics and astronautics.
- He was the first person to calculate the altitude at which the atmosphere becomes too thin to support aeronautical flight and arrived at 83.6 km (51.9 miles) himself.
Locating the line
- The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) defines Karman Line as the altitude of 100 kilometres (62 miles; 330,000 feet) above Earth’s mean sea level.
- However, other organizations do not use this definition. There is no international law defining the edge of space, and therefore the limit of national airspace.
- For instance, the US Air Force and NASA define the limit to be 50 miles (80 km) above sea level.
- The line is approximately at the turbopause, above which atmospheric gases are not well-mixed.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zojila Pass
Mains level: Road infrastructure in Himalayas
Union Transport Ministry has launched the first blasting for construction-related work at the Zojila tunnel that will provide all-year connectivity between Srinagar valley and Leh.
These days various Himalayan passes and tunnels are overwhelmingly seen in news. Open your Atlas and try to spot all of them for now and once before the exam.
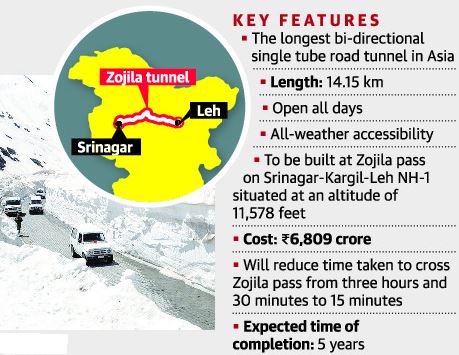
Zojila Tunnel
- The Zojila is set to be Asia’s longest bi-directional tunnel.
- It will connect Srinagar, Dras, Kargil and Leh via a tunnel through the famous Zojila Pass.
- Located at more than 11,500 feet above sea level, the all-weather Zojila tunnel will be 14.15 km long and ensure road connectivity even during winters.
- It will make the travel on the 434-km Srinagar-Kargil-Leh Section of NH-1 free from avalanches, enhance safety and reduce the travel time from more than 3 hours to just 15 minutes.
- The speed limit inside the tunnel is likely to be the same as in the Atal tunnel – 80 kmph.
Its significance
- The project holds strategic significance as Zojila Pass is situated at an altitude of 11,578 feet on the Srinagar-Kargil-Leh National Highway and remains closed during winters due to heavy snowfall.
- At present, it is one of the most dangerous stretches in the world to drive a vehicle and this project is also geo-strategically sensitive.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Export led growth
Mains level: Paper 3- Contribution of export in the growth
To aim for achieving high growth rate by focusing only on the domestic consumption and domestic demand could result in failure. The article argues for the focus on export to achieve the objective of growth.
Domestic-demand led growth and its limitations
- The debate in India has focused on domestic-demand led growth.
- But there is no known model of domestic demand/consumption-led growth, anywhere that has delivered quick, sustained, and high rates of economic growth for developing countries.
- India’s GDP growth of over 6 per cent after 1991 was associated with real export growth of about 11 per cent.
- Moreover, domestic-demand led growth requires more public spending, tax cuts, private investment, and/or financial sector reforms: which is not feasible in the present context due to pandemic.
- Consumption growth will be limited by the fact that household debt has grown rapidly in the last few years.
- Consumption now can grow only if incomes grow.
- Government spending could be a short run option, but COVID has limited that possibility.
Why India should not follow advanced countries’ fiscal policies
- India’s interest rates are not at zero and are unlikely to be so because of persistent inflation.
- India’s borrowing is still considered risky which is reflected in ratings.
- The favourable interest rate-growth differential that supports expansionary policy in the advanced countries is absent in India.
- India may well have scope for expansionary fiscal policy in the short run but not as a medium run growth strategy.
Why India should focus on export
- Given all the above factors, India does not have the luxury of abandoning export orientation because the alternatives are so limited.
- India’s market is too small to sustain any kind of serious import substitution strategy.
- Small size of the market makes it difficult to offer investors the domestic market as bait and incentivising them to export.
- India’s big, unexploited opportunities are in unskilled labour exports.
- India is vastly under-exporting relative to its labour force.
- Because China’s wages are rising as it has become richer, it has vacated about $140 billion in exports in unskilled-labour intensive sectors.
- Post-COVID, the move of investors away from China will probably accelerate to hedge against supply chain disruptions.
- India did not take advantage of the first China opportunity, now, a second opportunity stemming from geo-politics should be seized by India.
- As India contemplates atmanirbharta, two deeper advantages of export orientation are always worth remembering.
- 1) Foreign demand will always be bigger than domestic demand for any country.
- 2) If domestic producers are competitive internationally, they will be competitive domestically and domestic consumers and firms will also benefit.
Why openness of ecnonomy is important
- Exploiting this opportunity in unskilled exports requires more not less openness.
- To be internationally competitive, many parts and components have to be imported from so many different sources.
- One indicator is the foreign or import contribution to exports.
- China and Vietnam at the time of their export boom in textiles and clothing suggests that exports were highly dependent on imports (between 40 and 45 per cent).
- In contrast, India’s import share is about 16 per cent.
- Achieving Chinese and Vietnamese levels of success will therefore require greater imports and openness.
Way forward
- Export success will require genuine easing of costs of trading and doing business in India.
- In the case of clothing, a key policy change in India will be to eliminate tariffs on all inputs.
- It will also require signing free trade agreements with Europe that still impose high duties on India’s clothing export, while Bangladeshi and Vietnamese exports which enjoy preferential access to world markets.
Consider the question “As India contemplates atmanirbharta, we should not forget that export dynamism is essential for the rapid and sustained high economic growth. Comment.”
Conclusion
In sum, resisting the misleading allure of the domestic market, India should zealously boost export performance and deploy all means to achieve that. Pursuing rapid export growth in manufacturing and services should be an obsession with self-evident justification.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now





