Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NEP 2020
Mains level: Paper 2- NEP 2020's focus on mathematical and computational thinking
The article deals with the issues with the emphasis on the coding instead of understanding the basic algorithmic process.
Issues with focusing on coding in NEP 2020
- The National Education Policy 2020 (NEP) envisages putting greater emphasis on mathematical and computational thinking throughout the school years.
- The framing in the NEP appears to put it at the same level of distinction as the more instrumental ‘coding’, and almost as a mere tool towards the utilitarian goals of artificial intelligence (AI) and data science.
- An overemphasis on learning the nitty-gritty of specific programming languages prematurely — even from middle school — may distract from focusing on the development of algorithmic creativity.
What is coding?
Coding is basically the computer language used to develop apps, websites, and software. Without it, we’d have none of the most popular technology we’ve come to rely on such as Facebook, our smartphones, the browser we choose to view our favorite blogs, or even the blogs themselves. It all runs on code.
About computation and algorithms
- Algorithmics is the abstract process of arriving at a post-condition through a sequential process of state changes.
- It is among the earliest human intellectual endeavours that has become imperative for almost all organised thinking.
- All early learning of counting and arithmetic is method-based, and hence algorithmic in nature, and all calculations involve computational processes encoded in algorithms.
- The core algorithmic ideas of modern AI and machine learning are based on some seminal algorithmic ideas of Newton and Gauss, which date back a few hundred years.
- Though the form of expressions of algorithms — the coding — have been different, the fundamental principles of classical algorithm design have remained invariant.
Algorithms in modern world
- In the modern world, the use of algorithmic ideas is not limited only to computations with numbers, or even to digitisation, communication or AI and data science.
- They play a crucial role in modelling and expressing ideas in diverse areas of human thinking, including the basic sciences of biology, physics and chemistry, all branches of engineering, in understanding disease spread, in modelling social interactions and social graphs, in transportation networks, supply chains, commerce, banking and other business processes, and even in economic and political strategies and design of social processes.
- Hence, learning algorithmic thinking early in the education process is indeed crucial.
So, how coding is different from arithmetics?
- Coding is merely the act of encoding an algorithmic method in a particular programming language which provides an interface.
- AS computational process can be invoked in a modern digital computer.
- Thus, it is less fundamental.
- While coding certainly can provide excellent opportunities for experimentation with algorithmic ideas, they are not central or indispensable to algorithmic thinking.
- After all, coding is merely one vehicle to achieve experiential learning of a computational process.
Way forward
- Instead of focusing on the intricacies of specific programming languages, it is more important at an early stage of education to develop an understanding of the basic algorithmic processes behind manipulating geometric figures.
- Indeed, this is a common outcome of the overly utilitarian skills training-based approaches evidenced throughout the country.
Conclusion
The NEP guideline of introducing algorithmic thinking early is a welcome step, it must be ensured that it does not degenerate and get bogged down with mundane coding tricks at a budding stage in the education process.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MDR, IMPS, RTGS, NEFT
Mains level: Paper 3- Role of NPCI in transforming digital payment infrastructure in India
The article tracks the evolution of digital payments system in India and the transformational role played by the NPCI in it.
Adoption of digital payments in India
- Digital payments have found strong ground in India reducing all other modes of payments to the background.
- Through a faster system of simultaneous debits and credits, the money value is transferred from one account to the other across banks.
- With such versatility and ease of settling financial transactions, the growth of digital payments is going to be phenomenal, supported by banks and Fin-Tech companies.
Evolution of digital payments in India
- A major thrust toward large value payments was effected through the Real Time Gross Settlement System, or RTGS, launched by the RBI in March 2004.
- The large value payments on stock trading, government bond trading and other customer payments were covered under the RTGS.
- It substantially reduced the time taken for settlements.
- Around the same time, the RBI introduced National Electronic Funds Transfer, or NEFT to support retail payments.
- Now, NEFT is available round the clock and RTGS will follow from December 2020 — only a few countries have achieved this.
- These systems were seeded and reinforced with the setting up of the umbrella retail payments institution: National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- NPCI was set up by 10 lead banks at the instance of the RBI in 2009.
- The NPCI as a not-for-profit company
How NPCI transformed retail payment systems in India
- The NPCI’s success against deeply entranced formidable international players, supported by innovative technology, viz. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), is well recognised by central banks in many other countries.
- The Bank for International Settlements’s endorsement of the NPCI model in 2019 is a major accolade.
- With digital payment being a public good like currency notes, it was necessary that the corporation was fully supported by the RBI and the government as an extended arm of the sovereign.
- It was also necessary to contain expectations on profits, avoiding direct or indirect control by powerful private interests could dilute the public good character of the outfit.
Issue of converting NPCI into for-profit
- Converting NPCI intro for-profit company will be a retrograde step with huge potential for loss of consumer surplus along with other strategic implications.
- Instead the strategy should be to assist the NPCI financially, either by the RBI or the government, to provide retail payment services at reduced price (in certain priority areas).
- This may also help support expansion of the payment system network and infrastructure in rural and semi-urban areas in partnership with Fin-Tech companies and banks.
Issue fo MDR
- In Budget 2020-21, the government prescribed zero Merchant Discount Rate (MDR) for RuPay and UPI, both NPCI products.
- Zero MDR on UPI and RuPay will help to popularise digital payments benefiting both customers and merchants.
- There is justification in this zero MDR prescription by the government.
- It is justified because depositors implicitly pay around 3% to banks as net interest margin, being the difference between saving and risk free bond rate, for enjoying certain payments services traditionally.
- When banks enjoy such a huge amount of current account savings account (CASA) deposits, in return, is it not incumbent on them to provide such payment services?
- The government left out other providers of digital payment products from this MDR prescription.
- Taking advantage of this dichotomy, many issuing banks switched to mainly Visa and Master cards for monetary gains.
- As customers were induced by such supplier banks, it created a kind of indirect market segmentation and cartel formation, though there is hardly any quality difference in payment products.
- It may be noted that even the European Central Bank imposed a ceiling on MDR for all, protecting consumer interest.
- It is hoped that the government will take corrective action in the next Budget to ensure a level playing field and to relieve the NPCI from such policy-induced market imperfection.
Pricing for digital payments
- The ideal pricing for digital payments products should be based on an analysis of-(i) producer surplus (ii) consumer surplus (i.e. gain or loss of utility due to pricing) (iii) social welfare for which we need cost-volume-price data.
- A factor which needs to be reckoned is the float funds digital payments allow (cash withdrawal is a drain on the banking system), which is a source of sizeable income for banks.
- The RBI will do well to study and arrive at a rational structure of pricing including MDR (possibly also penalty on default by customer).
Consider the question “Elaborate on how the NPCI has been successful in transforming the digital payment landscape in the country through innovations? What are the challenges facing retail payments infrastructures?”
Conclusion
Given that the digital payment system is like a national superhighway, for which the government has a crucial role to play in protecting consumers against exploitation.
Back2Basics: RTGS and NEFT
- With NEFT (National Electronic Funds Transfer)
you can transfer any amount to the recipient’s account in a one-on-one transfer basis.
- NEFT transactions don’t have a maximum limit for funds that can be transferred in a single day.
- The NEFT system is available round the clock throughout the year on all days (24x7x365).
- Funds are transferred in batches that are settled in 48 half-hourly time slots throughout the day.
- There is no maximum or minimum limit on the amount of funds that could be transferred through NEFT.
RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement)
- Business owners can use RTGS when they need to transfer large amounts instantly.
- One advantage that RTGS has over the other methods is the transaction speed, since the entire amount is transferred in real time.
- The available hours for RTGS transactions vary based on the individual banks and their branches.
- There’s a minimum limit of Rs. 2 lakhs for RTGS transactions, and there’s no maximum limit as such.
What is MDR?
- The merchant discount rate (MDR) is charged to merchants for processing debit and credit card transactions.
- To accept debit and credit cards, merchants must set up this service and agree to the rate.
- The merchant discount rate is a fee, typically between 1%-3%, that merchants must consider when managing business costs
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Infodemic Management
Managing the “infodemic” has been a serious challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic, says a Chief Scientist at World Health Organization (WHO).
Try this question for mains:
Q.‘Infodemic’ management these days has become a greater challenge than the actual course of pandemic management. Discuss.
Defining Infodemic
- Infodemic implies too much information, including false or misleading information, particularly on social media.
- It has led to confusion, risk-taking and ultimately mistrust towards governments and the public health response.
WHO framework for infodemics
- The WHO has a framework for managing the coronavirus infodemic.
- Infodemiology is now acknowledged by public health organizations and the WHO as an important emerging scientific field and critical area of practice during a pandemic.
- From the perspective of being the first “infodemiolgist” who originally coined the term almost two decades ago, the author posts four pillars of infodemic management:
- Information monitoring (infoveillance)
- Building eHealth Literacy and science literacy capacity
- Encouraging knowledge refinement and quality improvement processes such as fact-checking and peer-review
- Accurate and timely knowledge translation, minimizing distorting factors such as political or commercial influences
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Particulate Matter
Mains level: Pollution induced mortality in India

Air pollution now biggest health risk in India, says the State of Global Air 2020 Report.
State of Global Air Report
- The State of Global Air report brings into one place the latest information on air quality and health for countries around the globe.
- It is produced annually by the Health Effects Institute and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s Global Burden of Disease project.
India’s exposure to pollution
- Long-term exposure to outdoor and household air pollution contributed to over 1.67 million annual deaths from stroke, heart attack, diabetes, lung cancer, chronic lung diseases and neonatal diseases in India in 2019.
- Overall, air pollution was now the largest risk factor for death among all health risks, the report noted.
- Outdoor and household particulate matter pollution also contributed to the deaths of more than 1,16,000 Indian infants in their first month of life last year.
- For the youngest infants, most deaths were related to complications from low birth weight and preterm birth.
A comparison with peers
- India faced the highest per capita pollution exposure — or 83.2 μg/cubic metre — in the world.
- It is followed by Nepal at 83.1 μg/cubic metre and Niger at 80.1.
- Countries with the least population exposure are below 8 micrograms (μg) per cubic metre.
Back2Basics: Particulate Matter
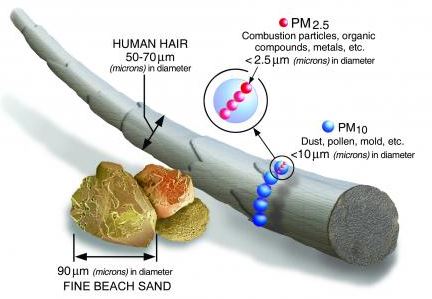
- PM is the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Some particles, such as dust, dirt, soot, or smoke, are large or dark enough to be seen with the naked eye.
- Others are so small they can only be detected using an electron microscope.
- Particle pollution includes:
- PM10 : inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 10 micrometres and smaller; and
- PM2.5: fine inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometres and smaller.
Sources of PM
- These particles come in many sizes and shapes and can be made up of hundreds of different chemicals.
- Some are emitted directly from a source, such as construction sites, unpaved roads, fields, smokestacks or fires.
- Most particles form in the atmosphere as a result of complex reactions of chemicals such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which are pollutants emitted from power plants, industries and automobiles.
Harmful effects of PM
- Particulate matter contains microscopic solids or liquid droplets that are so small that they can be inhaled and cause serious health problems.
- Some particles less than 10 micrometres in diameter can get deep into your lungs and some may even get into your bloodstream.
- Of these, particles less than 2.5 micrometres in diameter, also known as fine particles or PM2.5, pose the greatest risk to health.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kaleshwaram Project, Lift irrigation
Mains level: Kaleshwaram Project

The National Green Tribunal (NGT) wants a relook at Kaleshwaram Project since the Telangana government subsequently changed the design of the project.
Try this question from our AWE initiative:
The Kaleshwaram Project

- The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation System is considered to be one of the world’s largest multi-purpose projects.
- It is designed to provide water for irrigation and drinking purposes to about 45 lakh acres in 20 of the 31 districts in Telangana, apart from Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
- This project is unique because Telangana will harness water at the confluence of two rivers with the Godavari by constructing a barrage at Medigadda in Jayashankar Bhupalpally district.
- It would reverse pump the water into the main Godavari River and divert it through lifts and pumps into a huge and complex system of reservoirs, water tunnels, pipelines and canals.
Records to its glory
- The project has set many records with the world’s longest water tunnels, aqueducts, underground surge pools, and biggest pumps.
- By the time the water reaches Kondapochamma Sagar, the last reservoir in the system, the water would have been lifted to a height of 618 metres from its source at Medigadda.
- The total length of the entire Kaleshwaram project is approximately 1,832 km of which 1,531 km is gravity canals and 203 km comprises water tunnels.
How important is KLIS to Telangana?
- The project will enable farmers in Telangana to reap multiple crops with a year-round supply of water wherein earlier they were dependent on rains resulting in frequent crop failures.
- This year, Telangana farmers have already delivered bumper rabi crops of paddy and maize due to better irrigation facilities and an extended monsoon.
- KLIS covers several districts which used to face rainfall deficit and the groundwater is fluoride-contaminated.
- Apart from irrigation, a main component of the project is the supply of drinking water to several towns and villages and also to twin cities of Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
- Mission Bhagiratha, the Rs 43,000-crore project to supply drinking water to every household in villages, draws a large quantity of water from the KLIS and some quantity from projects on River Krishna.
- There is a burgeoning freshwater fishing industry in the state.
Issues raised by NGT
- The NGT has observed that the Telangana government subsequently changed the design of the project to increase its capacity.
- By increasing its capacity to pump 3 TMC water from 2 TMC, large tracts of forest land and other land was taken over and massive infrastructure was built causing adverse impact on the environment.
- Extraction of more water certainly requires more storage capacity and also affects hydrology and riverine ecology of Godavari River.
- Such issues have to be examined by the statutory authorities concerned.
B2Basics
National Green tribunal
- It is a specialised body set up under the National Green Tribunal Act (2010) for effective and expeditious disposal of cases relating to environmental protection and conservation of forests and other natural resources.
- With the establishment of the NGT, India became the third country in the world to set up a specialised environmental tribunal, only after Australia and New Zealand, and the first developing country to do so.
- NGT is mandated to make disposal of applications or appeals finally within 6 months of filing of the same.
- The NGT has five places of sittings, New Delhi is the Principal place of sitting and Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata and Chennai are the other four.
Structure of NGT
- The Tribunal comprises of the Chairperson, the Judicial Members and Expert Members. They shall hold office for term of five years and are not eligible for reappointment.
- The Chairperson is appointed by the Central Government in consultation with Chief Justice of India (CJI).
- A Selection Committee shall be formed by central government to appoint the Judicial Members and Expert Members.
- There are to be least 10 and maximum 20 full time Judicial members and Expert Members in the tribunal.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Plants mentioned in the newscard
Mains level: NA
This newscard is an excerpt from the original article published in DownToEarth.
Explained below are the medicinal properties of 10 valuable plants known to boost natural immunity:
(1) Abrusprecatorius (Indian liquorice, Ratti)
- The bright red ovoid seeds with a black spot weigh 1/10th of a gram, and were hence used as weighing unit called ‘Ratti’ in ancient India by goldsmiths.
- Its seeds are said to have immune-modulating properties.
(2) Artemisia scoparia (Redstem Wormwood)
- These plants have excellent clinical anti-malarial properties due to the presence of artemisinin.
- They possess potent anti-inflammatory properties and help regulate both innate and adaptive immunity.
(3) Azadirachtaindica (Neem)
- It is a well-known tree used in various systems of traditional medicine since time immemorial. In Sanskrit, it is known as Arishtha, which means ‘reliever of sicknesses’.
- Neem bark is known to have strong immunostimulant Neem oil has been shown to possess activity by selectively activating cell-mediated immune mechanisms.
(4) Boerhaviadiffusa (Punarnava)
- In Ayurveda, Punarnava is included in the category of rasayana herbs that possess anti-ageing properties. It helps prevent diseases.
- This means they increase resistance by providing hepatoprotection (the ability of a substance to prevent damage to the liver) and immune-modulation.
(5) Cardaminehirsuta (Hairy Bitter Cress)
- The plants contain vitamin C, calcium, magnesium, beta carotene, antioxidants and sulfur-containing compounds that boost immunity.
(6) Clerodendrumphlomidis (Sage Glory Bower, Arni, Agnimantha)
- It is an essential medicinal plant that is also mentioned in texts since the Vedic period. It is known to boost the immune system, purify the blood and cure urinary tract infection.
- The decoction made from the whole plant is useful in improving strength and immunity following a bout of fever or other ailments.
(7) Phyllanthus tenellus (Mascarene Island leaf-flower)
- It is an annual herb commonly found near wetlands, ditches, wet places, edges of drains and disturbed places. It is known for immune-modulatory properties.
- Physalis peruviana (Cape Gooseberry, Rasbhari) (Family: Solanaceae): It is used in traditional folk medicines as an immunomodulatory drug. It is rich in vitamin C and helps enhance body immunity.
(8) Portulaca oleracea (Purslane)
- Purslane has been used in folk medicine since ancient times and is included in the World Health Organization’s list of most widely used medicinal plants.
- The leaves of the plant are a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which is important in preventing heart attacks and strengthening the immune system.
(9) Withaniasomnifera (Indian Winter Cherry, Indian Ginseng, Aswagandha)
- Ashwagandha is an important ancient herb and has been used in the indigenous medical system for over 3,000 years.
- It is considered to be one of the best rejuvenating agents in Ayurveda that helps to maintain proper nourishment of the tissues. It possesses antioxidant, mind-boosting and immune-enhancing properties.
Now try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- The Taxus tree is naturally found in the Himalayas
- The Taxus tree is listed in the Red Data Book.
- A drug called “taxol” is obtained from Taxus tree is effective against Parkinson’s disease
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MSP, MIP
Mains level: Fixation of MSP and its legal backing
The Union Cabinet has approved the extension of Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) for apple procurement in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) for the current season.
UPSC can ask a question on the difference between MSP and MIP. All the agricultural and horticultural commodities for which Minimum Support Price (MSP) are not fixed and are generally perishable in nature are covered under Market Intervention Scheme (MIS).
Market Intervention Scheme
- MIS is a price support mechanism implemented on the request of State Governments for the procurement of perishable and horticultural commodities in the event of a fall in market prices.
- It is implemented when there is at least a 10% increase in production or a 10% decrease in the ruling rates over the previous normal year.
- MIS works in a similar fashion to Minimum Support Price based procurement mechanism for food grains but is an ad-hoc mechanism.
- Its objective is to protect the growers of these horticultural/agricultural commodities from making distress sale in the event of the bumper crop.
- Under MIS, support can be provided in some years, for a limited but defined period, in specified critical markets and by purchasing specified quantities. The initiative has to emerge from the concerned state.
Commodities covered
- The MIS has been implemented in case of commodities like apples, garlic, oranges, grapes, mushrooms, clove, black pepper, pineapple, ginger, red chillies, coriander seed, chicory, onions, potatoes, cabbage, mustard seed, castor seed, copra, palm oil etc.
Remuneration under MIS
- MIS provides remunerative prices to the farmers in case of the glut in production and fall in prices.
- Proposal of MIS is approved on the specific request of State/UT Government, if they are ready to bear 50% loss (25% in case of North-Eastern States), if any, incurred on its implementation.
- Further, the extent of total amount of loss shared is restricted to 25% of the total procurement value which includes the cost of the commodity procured plus permitted overhead expenses.
Implementation of MIS
1) Market Intervention Price (MIP)
- The Department of Agriculture & Cooperation is implementing the scheme.
- Under the MIS, a pre-determined quantity at a fixed MIP is procured by NAFED as the Central agency.
- There are other agencies designated by the state government for a fixed period or till the prices are stabilized above the MIP whichever is earlier.
- The area of operation is restricted to the concerned state only.
2) Funds transfer
- Under MIS, funds are not allocated to the States.
- Instead, central share of losses as per the guidelines of MIS is released to the State Governments/UTs, for which MIS has been approved, based on specific proposals received from them.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




