Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LTRO
Mains level: Paper 3- Stance of MPC amid rising inflation
The article analyses the implications of the recently concluded MPC meeting and predicts the trends for the future.
Highlights of the MPC meeting
- In the October meeting of the monetary policy committee (MPC), repo rate were kept unchanged at 4%, with a continuation of an accommodative stance.
- It chose to ignore elevated levels of CPI inflation as transitory and maintaining focus on supporting growth.
- It appears that the MPC would maintain a status quo on rates through this fiscal year.
- The scope for further easing is anyways limited to 0.50%, as any more easing may affect household financial savings and endanger financial stability.
Ensuring the rate transmission
- With unchanged repo rates, the focus of the liquidity measures announced by the RBI is to further improve transmission of previous rate cuts across a spectrum of market rates and other instruments.
- The RBI Governor assured market participants that the large supply of government bonds in the second half along with a likely pick-up in credit demand, would be accommodated through open market purchases of government bonds.
Reducing the cost of borrowing
- The RBI may have to buy bonds worth ₹1,000 to 1,500 billion in these operations over 2HFY21 keeping pressure on yields [which affects interest rates].
- In a related move, to reduce the cost of borrowings for state governments, the RBI for the first time will buy state government bonds, as a special case for this year.
Other measures
- The extension of enhanced Held to Maturity (HTM) limit of banks on their government bonds portfolio to March 2022.
- A new on-tap targeted LTRO window was announced, for banks to borrow up to ₹1,000 billion from the RBI at a floating rate linked to the repo rate, and invest in corporate paper issued by specific sectors and to provide loans to them.
- In effect, the aim of the central bank is to ensure that lower policy rates determined by the macro-economic fundamentals, are reflected in lower cost of borrowings for the Centre, states and corporates.
Containing inflation
- Inflation outlook for this fiscal and projections for next year indicate that CPI inflation would ease, from an average of 6.8% in Q2 to 4.5% in Q4 and 4.1% by Q4FY22.
- Headline inflation is expected to fall, as supply conditions normalize with progressive unlocking and another year of bumper farm output helps pull down food inflation.
- Higher fuel taxes and import duties are expected to provide an upward push though.
- Effective supply management will therefore be crucial in controlling food inflation and ensuring that it does not turn persistent and feeds into non-food inflation.
Conclusion
- The role of monetary policy in the is limited and the RBI focus will remain on improving transmission of policy signals through banking, bond and credit market channels.
Back2Basics: LTRO
- Long-Term Repo Operation (LTRO) was introduced by the Reserve Bank in February, 2020.
- Through this policy, the central bank would provide liquidity support to commercial banks for a period of 1 to 3 years at the current repo rate, and would accept government securities as collateral in return.
- This is in contrast to the other measures it was providing such as Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) and Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) which provide cash to banks for a period of 1 to 28 days only.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Definition of urban area
Mains level: Paper 2- Need for new definition of urban area
The article the need for liberal and realistic definition of the ‘urban’ area in the next Census and mention the implications of such change.
2 ways to define urban areas
1) Statutory town
- These towns are defined by state governments and place India’s urbanisation rate at 26.7%.
- A statutory town includes all places with a municipality, corporation, cantonment board or notified town area committee.
2) Census-based criteria
- Census adopts three criteria to define what is urban.
- The three criteria are:
- i) a minimum population of 5,000;
- ii) at least 75% of the male main working population engaged in non-agricultural pursuits, and
- iii) a density of population of at least 400 persons per sq km
- This, coupled with statutory towns, pegs India’s urbanisation rate at 31%.
- Total number of towns (state and census) stands at 7,933, together constituting a 377-mn population.
Why there is a need for changing the definition of ‘urban’
- There is growing evidence—mostly from satellite imagery—that India is way more urban than the 2011 Census estimate.
- This is quite plausible because there is a large sum of money allocated for rural development, and it is in the interest of state governments to under-represent urbanisation.
- Besides, the Census’s stringent definition was first carved out in 1961 which do not reflect the realities of the 21st century.
- India won’t be alone in changing these definitions for Census 2021.
- Many countries, such as China, Iran, the UK, among others, have changed the definition of ‘urban’ from one census to another.
Getting the right picture of urbanisation
- A more liberal and realistic definition in the upcoming census will present the actual picture of urbanisation.
- For instance, if we just use the population density criteria like 37 other countries, with the 400 people per sq km threshold, we will add around 500 mn people to the urban share of the population.
- This pegs the urbanisation rate at over 70%!
What will be its implications?
- First, the budgetary allocation will reflect the reality and scales will balance between rural and urban areas.
- Second, the urban areas will not be governed through rural governance structures of Panchayati Raj Institutions.
- Third basic urban infrastructure like sewerage networks, fire services, building regulations, high-density housing, transit-oriented development, piped drinking water supply.
- Fourth, these newly defined urban areas could act as a new source of revenue for funding local infrastructure development.
- This would ease pressure on state finances.
- Lastly, the rethink of urban definition would have an impact on the regional and national economy.
- These newly defined urban areas will open them to new infrastructure such as railway lines, discom services, highway connectivity, creation of higher education institutes which will together increase the connectivity and resource capability at the local level.
- This will not only boost the local economy but also ease pressure on bigger cities and help in cluster level development.
Conclusion
A rethink of urban definition in Census 2021, particularly with some degrowth in urban areas due to Covid, will bode well for India for coming decades in more ways than one.
Source:-
https://www.financialexpress.com/opinion/redefining-cities-a-new-urban-consensus/2102154/
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various GHGs
Mains level: Hazards of N2O pollution
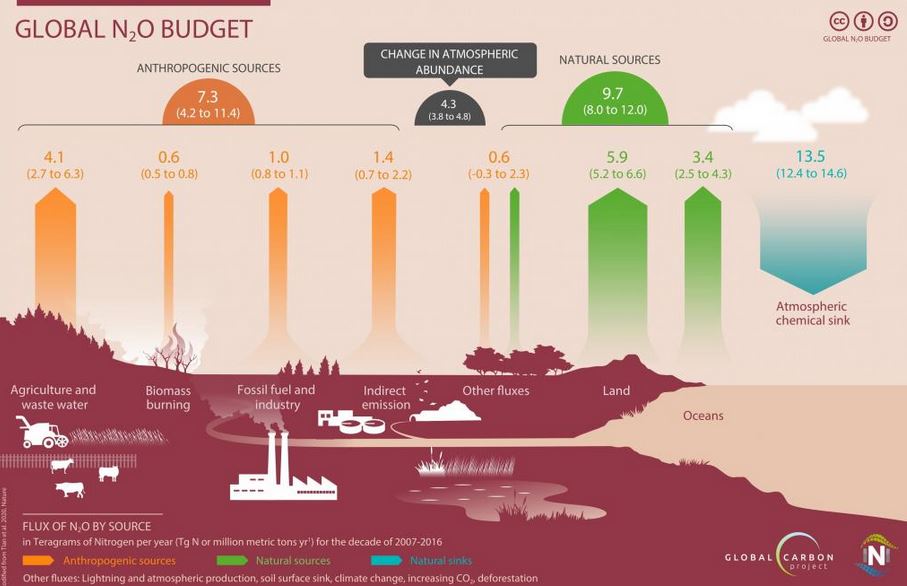
Human emissions of nitrous oxide (N2O) — a greenhouse gas 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) — increased by 30 per cent between 1980 and 2016.
Observe the above image carefully and try to find out the major contributor of nitrous oxide emission in the Global N2O Budget.
What is Nitrous oxide?
- Nitrous oxide is a dangerous gas for the sustainable existence of humans on Earth.
- It has the third-highest concentration — after CO2 and methane — in our atmosphere among greenhouse gases responsible for global warming.
- N2O can live in the atmosphere for up to 125 years.
- Most N2O emissions have come from emerging countries like India, China and Brazil.
About the research
- Nitrous oxide global concentration levels have increased from 270 parts per billion (ppb) in 1750 to 331 ppb in 2018 — a jump of 20 per cent.
- The growth has been the quickest in the past five decades because of human emissions.
- The research was conducted through an international collaboration between the International Nitrogen Initiative (INI) and the Global Carbon Project of Future Earth, a partner of the World Climate Research Programme.
Why N2O matters?
- N2O is also the only remaining threat to the ozone layer, for it accumulates in the atmosphere over a long period of time, just like CO2.
- The increase in its emissions means that the climatic burden on the atmosphere is increasing from non-carbon sources as well, while the major focus of global climate change negotiations is currently centred on carbon.
- A major proportion of the N2O emissions in the last four decades came from the agricultural sector, mainly because of the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers.
- The growing demand for food and feed for animals will further increase global nitrous oxide emissions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SVAMITVA
Mains level: Land records management in India

Our PM has launched the physical distribution of Property Cards under the SVAMITVA Scheme.
Try this MCQ:
Q.The SVAMITVA Scheme sometimes seen in news is related to:
Urban Employment/ Land records management/ Child Adoption/ None of these
About SVAMITVA
- SVAMITVA stands for Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas.
- Under the scheme, the latest surveying technology such as drones will be used for measuring the inhabited land in villages and rural areas.
- The mapping and survey will be conducted in collaboration with the Survey of India, State Revenue Department and State Panchayati Raj Department under the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- The drones will draw the digital map of every property falling in the geographical limit of each Indian village.
- Property Cards will be prepared and given to the respective owners.
Significance of the scheme
- The scheme paves the way for using the property as a financial asset by villagers for taking loans and other financial benefits.
- Also, this is the first time ever that such a large-scale exercise involving the most modern means of technology is being carried out to benefit millions of rural property owners.
Various benefits
- The scheme will create records of land ownership in villages and these records will further facilitate tax collection, new building plan and issuance of permits.
- It will enable the government to effectively plan for the infrastructural programs in villages.
- It would help in reducing the disputes over property.
Back2Basics: E-Gramswaraj Portal
- E Gram Swaraj portal is the official portal of central govt for the implementation of Swamitva scheme.
- By visiting this portal people can check their Panchayat profile easily. It will also contain the details of ongoing development works and the fund allocated for them.
- Any citizen can create his or her account on the portal and can know about the developmental works of villages.
- The user of E Gram Swaraj portal can also access all work of the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- This single interface will help speed-up the implementation of projects in rural areas from planning to completion.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Calcium Nitrate
Mains level: India's import dependence of fertilizers
Union Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers has launched an indigenous variety of fertilizers- ‘Calcium Nitrate’ & ‘Boronated Calcium Nitrate’.
Try this PYQ:
Why does the Government of India promote the use of ‘Neem-coated Urea’ in agriculture?
(a) Release of Neem oil in the soil increases nitrogen fixation by the soil microorganisms
(b) Neem coating slows down the rate of dissolution of urea in the soil
(c) Nitrous oxide, which is a greenhouse gas, is not at all released into atmosphere by crop fields
(d) It is a combination of a weedicide and a fertilizer for particular crops
What is Calcium Nitrate?
- Calcium nitrate is used as a water-soluble fertilizer in agriculture. In addition, this product is also used in wastewater treatment and to increase the strength of cement concrete.
- Last year, around 1.25 lakh metric tons (1,23,000 tons) of Calcium Nitrate was imported in the country.
- Of this, 76% was imported from China and the rest from other countries like Norway and Israel.
- These indigenous varieties will provide a quality product at a cheaper rate to the farmer community in the country than imported ones.
Uses of Calcium nitrate
- The fertilizer grade calcium nitrate is popular in the greenhouse and hydroponics. It is also used to control certain plant diseases.
- Calcium nitrate is also used in wastewater pre-conditioning for odour emission prevention.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Verticillium lecanii
Mains level: NA
Indian researchers have successfully developed new Aqueous Suspension formulation technology of bio-pesticide based on entomopathogenic fungus Verticillium lecanii.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Recently, there was a growing awareness in our country about the importance of Himalayan nettle (Girardinia diversifolia) because it is found to be a sustainable source of
(a) anti-malarial drug
(b) biodiesel
(c) pulp for paper industry
(d) textile fibre
Verticillium lecanii
- This bio-pesticide formulation has been found very effective in controlling various insects in seed spice crops (fenugreek, cumin, and coriander).
- It has a good shelf life, safe to user & environment and it may be effectively used for controlling different agricultural insects especially in seed spice crops.
- This bio-pesticide may be used as a safer alternative to chemical pesticides to minimize pesticide residue problem.
- Besides, it may be used as a key input for crop protection from insects pest in organic agriculture and Integrated Pest Management.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: RudraM-I
Mains level: India's missile arsenal

A New Generation Anti Radiation Missile (NGARM), RudraM-I, was successfully flight-tested by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
Try this MCQ:
Q.The RudraM-I recently seen in news is an:
Ans: Anti-satellite missile/ Anti-radiation Missile/ Anti-tank mine/ Submarine Torpedo
RudraM-I
- RudraM-I is an anti-radiation missile can locate and target any radiation-emitting source like enemy radars, communication sites and other Radio Frequency (RF) emitting targets.
- It is being developed by Defence Research Development Laboratory (DRDL), Hyderabad, as the nodal agency.
- It is a joint effort involving several DRDO labs, the IAF, the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and several public and private sector enterprises.
- This is the first indigenous anti-radiation missile of the country. It has a range of up to 200 km depending upon the launch conditions.
- It can be launched from altitudes of 500 m to 15 km and speeds of 0.6 to 2 mach.
- It can play a key role in neutralizing any jamming platforms of the enemy or take out radar stations thereby clearing a path for own fighters to carry out an offensive and also prevent own systems from being jammed.
How does it work?
- Anti-radiation missiles are designed to detect, track and neutralize the adversary’s radar, communication assets and other radio frequency sources, which are generally part of their air defence systems.
- Such a missile’s navigation mechanism comprises an inertial navigation system — a computerised mechanism that uses changes in the object’s own position — coupled with GPS, which is satellite-based.
- For guidance, it has a “passive homing head” — a system that can detect, classify and engage targets (radio frequency sources in this case) over a wide band of frequencies as programmed.
- Once the RudraM missile locks on the target, it is capable of striking accurately even if the radiation source switches off in between.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: World Food Programme
Mains level: Not Much
The Nobel Peace Prize was awarded to the World Food Programme (WFP) for feeding millions of people from Yemen to North Korea, with the coronavirus pandemic seen pushing millions more into hunger.
Tap here to read more about Nobel Prizes here at:
Nobel and other Prizes
World Food Programme
- The WFP is the food-assistance branch of the United Nations and the world’s largest humanitarian organization focused on hunger and food security.
- Founded in 1961, it is headquartered in Rome and has offices in 80 countries.
- In addition to emergency food aid, WFP focuses on relief and rehabilitation, development aid, and special operations, such as making food systems more resilient against climate change and political instability.
- It is an executive member of the United Nations Development Group, which collectively aims to fulfil the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), and has prioritized achieving SDG 2 for “zero hunger” by 2030.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National butterflies
Mains level: Not Much

A citizen poll to identify the national butterfly concluded with three species garnering the highest number of votes.
Try this PYQ:
Q.With reference to India’s Biodiversity, Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith barbet, Gray-chinned minivet and White-throated redstart are-
(a) Birds
(b) Primates
(c) Reptiles
(d) Amphibians
Which are the three species?
(1) Indian Jezebel
- Blessed with a vibrant colour pattern, including vermilion (Haldi – kumkum), the Indian Jezebel (or Common Jezebel) is known to deter its predators with its flashy wing colours.
- Regarded as soldiers of farmers, they also prey on parasites that infest fruit-bearing plants.
- Widely distributed, the species can be spotted in gardens and other lightly wooded areas.
(2) Krishna Peacock
- It is a flagship species for biodiversity and conservation, generally found in large numbers in the Himalayas.
- Possessing a peculiarly large swallowtail, its iridescent green scales diffract light to coat itself in radiance.
(3) Orange Oakleaf
- It is commonly known as ‘dead leaf’ for its ability to camouflage as a dry autumn leaf while striking a stationary pose with its wings closed.
- The masquerade enables the species to prevent it from being devoured by birds in the moist forests of the northern Western Ghats, central, northern and northeastern parts of India where they are generally found.
- Besides, the Oakleaf is also known to exhibit polyphenism as it assumes specific colour and size during dry and wet seasons.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CAG's role
Mains level: Paper 2- Role of CAG in the pandemic
The article highlights the importance of CAG in times of disasters to ensure check and balances.
Context
- With the nation spending substantial resources to manage the pandemic, the role of Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has come into prominence.
Opportunity for corruption in pandemic
- Allegations of siphoning off of funds to purchase the inferior quality at prices higher than those prevailing in the market are made.
- The opportunity to indulge in corruption exists in disaster management.
- Emergency procurement to save lives and reduce sufferings are a chance to obfuscate rules and procedures and can happen in all three tiers of governance.
Role of the CAG
- If all the major purchases by governments are audited by the CAG, there can be substantial improvement in disaster management.
- It will usher in better transparency, integrity, honesty, effective service delivery and compliance with rules and procedures and governance.
- The CAG has issued an order creating a new vertical — health, welfare and rural development, restructuring the office of the Director General of Audit, Central Expenditure.
- It is necessary that the CAG undertakes performance audits of COVID-19 related procurements, the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) and Employee State Insurance (ESI) hospitals.
- A beneficiary survey will become part of the audit process to bring out efficacy of service delivery and the availability and quality of drugs.
- Audit recommendations can contribute improvements in various aspects of disaster preparedness, management and mitigation.
Benefits of audit
- The statutory responsibility of CAG includes appraising disaster preparedness, ensuring that management, mitigation operations, procedures are complied with, and proper internal controls are in place.
- Ensuring that there are proper records, documentation, authentic, accurate, reliable and complete information and data.
- Providing assurance to people’s representatives, tax payers and the public at large that government resources are being used prudentially as per the law and regulations and safeguarded.
- Providing assurance that risks are assessed, identified and minimised with established disaster management process and procedures.
- Offering assurance that resources are being used economically efficiently and effectively for achieving the planned objectives and that benefits have gone to the targeted beneficiaries.
Conclusion
All public entities management must be accountable and ensure that resources are managed properly and used in compliance with laws and regulations; programmes are achieving their objectives; and services are being provided efficiently, effectively, and economically.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ART Bill
Mains level: Paper 2- Concerns with the ART Bill
There are several issues with the Assisted Reproductive Technology Bill and these issues need consideration before the passage of the Bill.
What the Bill aims to achieve
- Union Health Minister introduced the Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Bill, 2020 (Bill) in the Lok Sabha.
- Its aim is to regulate ART banks and clinics, allow safe and ethical practice of ARTs and protect women and children from exploitation.
- The Bill was introduced to supplement the Surrogacy (Regulation) Bill, 2019 (SRB), which awaits consideration by the Rajya Sabha after review by two parliamentary committees.
Concerns with the Bill
1) Exclusion in the access of ART
- .The Bill allows for a married heterosexual couple and a woman above the age of marriage to use ARTs.
- It excludes single men, cohabiting heterosexual couples and LGBTQI individuals and couples from accessing ARTs.
- This violates Article 14 of the Constitution and the right to privacy jurisprudence of Puttaswamy, where the Supreme Court held that “ the liberty of procreation, the choice of a family life” concerned all individuals irrespective of their social status and were aspects of privacy.
- In Navtej Johar case, Justice Chandrachud exhorted the state to take positive steps for equal protection for same-sex couples.
- Unlike the SRB, there is no prohibition on foreign citizens accessing ARTs.
- Foreigners can access ART but not Indian citizens in loving relationships.
- This fails to reflect the true spirit of the Constitution.
2) Consent
- The ART Bill does little to protect the egg donor.
- Harvesting of eggs is an invasive process which, if performed incorrectly, can result in death.
- The Bill requires an egg donor’s written consent but does not provide for her counselling or the ability to withdraw her consent before or during the procedure.
- She receives no compensation or reimbursement of expenses for loss of salary, time and effort.
- Failing to pay for bodily services constitutes unfree labour, which is prohibited by Article 23 of the Constitution.
- The commissioning parties only need to obtain an insurance policy in her name for medical complications or death; no amount or duration is specified.
- The egg donor’s interests are subordinated in a Bill proposed in her name.
- The Bill restricts egg donation to a married woman with a child (at least three years old).
3) Threat of eugenics
- The Bill requires pre-implantation genetic testing.
- If the embryo suffers from “pre-existing, heritable, life-threatening or genetic diseases”, it can be donated for research with the commissioning parties’ permission.
- These disorders need specification or the Bill risks promoting an impermissible programme of eugenics.
4) Overlap with Surrogacy Regulation
- There is considerable overlap between ART and SRB sectors. Yet the Bills do not work in tandem.
- Core ART processes are left undefined; several of these are defined in the SRB.
- Definitions of commissioning “couple”, “infertility”, “ART clinics” and “banks” need to be synchronised between the Bills.
- A single woman cannot commission surrogacy but can access ART.
- The Bill designates surrogacy boards under the SRB to function as advisory bodies for ART, which is desirable.
- However, both Bills set up multiple bodies for registration which will result in duplication or lack of regulation (e.g. surrogacy clinic is not required to report surrogacy to National Registry).
- Also, the same offending behaviours under both Bills are punished differently + punishments under the SRB are greater.
- Offences under the Bill are bailable but not under the SRB.
- Finally, records have to be maintained for 10 years under the Bill but for 25 years under the SRB.
- The same actions taken by a surrogacy clinic and ART clinic attract varied regulation.
Other concerns
- Children born from ART do not have the right to know their parentage, which is crucial to their best interests and protected under previous drafts.
- There is no distinction between ART banks and ART clinics, given that gamete donation is not compensated, economically viability of ART Banks raises a question.
- In previous drafts, gametes could not be gifted between known friends and relatives if this is not changed, gamete shortage is likely.
- The Bill’s prohibition on the sale, transfer, or use of gametes and embryos is poorly worded and will confuse foreign and domestic parents relying on donated gametes.
- Unusually, the Bill requires all bodies to be bound by the directions of central and state governments in the national interest, friendly relations with foreign states, public order, decency or morality — being broadly phrased, it undermines their independence.
Way forward
- The Bill to maintain a grievance cell but clinics must instead have ethics committees.
- Mandated counselling services should also be independent of the clinic.
- The poor enforcement of the PCPNDT Act, 1994, demonstrates that enhanced punishments do not secure compliance — lawyers and judges also lack medical expertise.
- Patients already sue fertility clinics in consumer redressal fora, which is preferable to criminal courts.
Conclusion
The Bill raises several constitutional, medico-legal, ethical and regulatory concerns, affecting millions and must be thoroughly reviewed before passage.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Declining private investment in the infrastructure and ways to boost it
Declining private investment in the infrastructure needs policy overhaul. The article suggests the changes in the policy and approach on the part of the government to achieve the sustainable 40 per cent private investment in the infrastructure.
Declining private investment in infrastructure
Currently, private financing into the infrastructure sector has declined to around 20 per cent of the total funding.
Reasons for the decline are-
- 1) the crisis in the non-banking finance sector.
- 2) the financial challenges faced by infrastructure companies.
- 3) the inadequately developed Indian market for infrastructure financing.
- The Economic Survey 2017-18 has assessed India’s infrastructure financing needs at $4.5 trillion by 2040.
- Reviving private investment flows into infrastructure to around 40 per cent will be key to attaining this threshold.
Actions need to be taken to revive the private investment in infrastructure
- The Vijay Kelkar committee had put out a balanced report in 2015 on overhauling the PPP ecosystem, including governance reform, institutional redesign, and capacity-building.
Ramping up private investments in infrastructure will need action on two fronts:
- 1) Refreshing institutions and policies for channelling financing.
- 2) Providing a stable, durable, and empowering ecosystem for private players to partner with government entities.
1) Institutions and policies for channelling financing
- Due to long-duration profitability cycles of infrastructure projects, successful PPP requires stable revenue flow assurances and a settled ecosystem to investors over long periods.
- This could be achieved means of policy stability, assurances possibly secured by law.
- PPP contracts also need to provide for mid-course corrections to factor in uncertainties including utilisation patterns, as well as the creation of competing infra assets.
- Government partners in PPP arrangements need to ensure that open-ended arrangement that might entail unforeseeable risk are minimised for the private investor, including aspects such as land availability and community acceptance.
2) Institution and policies for financing
- There is a need to change the culture and attitude towards the conjoining of government entities and private partners.
- Kelkar committee has stated that there needs to be an approach of “give and take” and the Government should avoid a purely transactional approach.
- Government should avoid trying to minimise risk to themselves by passing on uncertain elements in a project — like the land acquisition risk — to the private partner.
- This attitudinal change can be achieved by amending the Prevention of Corruption Act to encompass modern-day requirements, including factoring in the need for government agents to take calibrated risks while engaging with the private sector.
- The private partners also need to be incentivised to focus on project outcomes, with guard-rails in place to discourage rent-seeking behaviour.
- In sum, risk avoidance by the public entity and rent-seeking by the private partner are the twin challenges that need to be carefully addressed.
- On the regulatory front, a compelling need would be to promulgate a PPP legislation which can provide a robust legal ecosystem and procedural comfort.
Consider the question “Declining private investment in the infrastructure has several implications for the economy. In ligh of this, examine the factor for such decline and suggest the measures to boost the private investment in the infrastructure.”
Conclusion
After we emerge out of this pandemic, a focus area for public policy has to be the creation of a modern-day, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. . Designing a fresh approach and creating a stable policy environment that provides comfort and incentives to private investors will be key to attaining this goal.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TRP, BARC
Mains level: TRAI and its regulations of telecom services
Mumbai police are investigating the alleged manipulation of Television Rating Points (TRP) by an extremely right-wing opinionated news reporter.
Try this question:
Q.What do you mean by “TRP Journalism”? Discuss the loopholes in the present system of self-regulation in Indian media.
What is TRP?
- In simple terms, anyone who watches television for more than a minute is considered a viewer.
- The TRP or Target Rating Point is the metric used by the marketing and advertising agencies to evaluate this viewership.
- In India, the TRP is recorded by the Broadcast Audience Research Council (BARC) using Bar-O-Meters that are installed in televisions in selected households.
- As on date, the BARC has installed these meters in 44,000 households across the country. Audio watermarks are embedded in video content prior to broadcast.
- These watermarks are not audible to the human ear, but can easily be detected and decoded using dedicated hardware and software.
- As viewing details are recorded by the Bar-O-Meters, so are the watermarks.
What is BARC?
- It is an industry body jointly owned by advertisers, ad agencies, and broadcasting companies, represented by The Indian Society of Advertisers, the Indian Broadcasting Foundation and the Advertising Agencies Association of India.
- Though it was created in 2010, the I&B Ministry notified the Policy Guidelines for Television Rating Agencies in India on January 10, 2014, and registered BARC in July 2015 under these guidelines, to carry out television ratings in India.
How are the households selected?
- Selection of households where Bar-O-Meters are installed is a two-stage process.
- The first step is the Establishment Survey, a large-scale face-to-face survey of a sample of approximately 3 lakh households from the target population. This is done annually.
- Out of these, the households which will have Bar-O-Meters or what the BARC calls the Recruitment Sample are randomly selected. The fieldwork to recruit households is not done directly by BARC.
- The BARC on its website has said that the viewing behaviour of panel homes is reported to BARC India daily. Coincidental checks either physically or telephonically are done regularly.
Vigilance activities by BARC
- Certain suspicious outliers are also checked directly by BARC India.
- BARC India also involves a separate vigilance agency to check on outliers that it considers highly suspicious.
- And as per the guidelines of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, these households rotate every year.
- This rotation is in such a manner that older panel homes are removed first while maintaining the representativeness of the panel.
- The Ministry guidelines further say that the secrecy and privacy of the panel homes must be maintained, and asked the BARC to follow a voluntary code of conduct.
What are the loopholes in the process?
- Several doubts have been raised on many previous occasions about the working of the TRP.
- As per several reports, about 70% of the revenue for television channels comes from advertising and only 30% from subscriptions.
- It is claimed that households were being paid to manipulate the TRP.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GRAP
Mains level: Not Much
The Supreme Court has directed Delhi and neighbouring States to implement air pollution control measures under “very poor” and “severe” category air quality of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP).
Note the various measures under the GRAP under various grades of Air Quality.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- In 2014, when a study by the WHO found that Delhi was the most polluted city in the world, panic spread in the Centre and the state government.
- Approved by the Supreme Court in 2016, the plan was formulated after several meetings that the Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA) held with state government and experts.
- The result was a plan that institutionalized measures to be taken when air quality deteriorates.
- GRAP works only as an emergency measure.
How does it work?
- As such, the plan does not include action by various state governments to be taken throughout the year to tackle industrial, vehicular and combustion emissions.
- When the air quality shifts from poor to very poor, the measures listed under both sections have to be followed since the plan is incremental in nature.
- If air quality reaches the severe+ stage, GRAP talks about shutting down schools and implementing the odd-even road-space rationing scheme.
Measures taken under GRAP
1)Severe+ or Emergency
(PM 2.5 over 300 µg/cubic metre or PM10 over 500 µg/cu. m. for 48+ hours)
- Stop entry of trucks into Delhi (except essential commodities)
- Stop construction work
- Introduce odd/even scheme for private vehicles and minimise exemptions
- Task Force to decide any additional steps including shutting of schools
2) Severe
(PM 2.5 over 250 µg/cu. m. or PM10 over 430 µg/cu. m.)
- Close brick kilns, hot mix plants, stone crushers
- Maximise power generation from natural gas to reduce generation from coal
- Encourage public transport, with differential rates
- More frequent mechanized cleaning of road and sprinkling of water
3) Very Poor
(PM2.5 121-250 µg/cu. m. or PM10 351-430 µg/cu. m.)
- Stop use of diesel generator sets
- Enhance parking fee by 3-4 times
- Increase bus and Metro services
- Apartment owners to discourage burning fires in winter by providing electric heaters during winter
- Advisories to people with respiratory and cardiac conditions to restrict outdoor movement
4) Moderate to poor
(PM2.5 61-120 µg/cu. m. or PM10 101-350 µg/cu. m.)
- Heavy fines for garbage burning
- Close/enforce pollution control regulations in brick kilns and industries
- Mechanized sweeping on roads with heavy traffic and water sprinkling
- Strictly enforce a ban on firecrackers
Has GRAP helped?
- The biggest success of GRAP has been in fixing accountability and deadlines.
- For each action to be taken under a particular air quality category, executing agencies are clearly marked.
- In a territory like Delhi, where a multiplicity of authorities has been a long-standing impediment to effective governance, this step made a crucial difference.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Quad Group
Mains level: Deterrence in Australia-China Ties
Australia and China’s cordial economic ties, established over the last three decades, have been soured this year over several points of friction.
Try this question
Q. Discuss the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (or the Quad) and its purpose to establish “Asian Arc of Democracy”.
Various points of friction
(1) Australia’s Covid-19 inquiry
- Australia’s appeal for an independent global inquiry into the origins and initial response of Covid-19 created fury in Beijing.
- China alleged that Australia was teaming up with the US to spread “anti-China propaganda”.
(2) Tension over journalists
- The second diplomatic spat began with the detention of an Australian news anchor based in Beijing by the Chinese authorities after she was suspected of “criminal activities” that endangered China’s national security.
- The Australian government said the journalist was held under “residential surveillance” at an unknown location.
- Following this, the journalists sought refuge in Australian diplomatic missions, as they were not allowed to leave the country.
(3) Ideological issues
- The two countries have also been at loggerheads on other ideological issues previously too.
- After reports of China keeping Uighur Muslims in state-run detention camps surfaced, Australia was swift to respond and expressed “deep concern” over the “human rights situation.”
- Australia also supported Hong Kong’s autonomy cause. It decided to extend visas for Hong Kong residents.
- In both instances, China responded staunchly and asked Australia to not meddle in its “internal matters.”
(4) Economic dependence
- China is Australia’s largest trading partner in terms of both exports and imports.
- China’s share in Australia’s exports reached a record A$117 billion, or 38 per cent, in 2019, more than any other country.
- Australian sectors like mining, tourism, education benefit from trade with China. China even imports products such as milk, cheese, wine and meat.
- Over the years, it has been increasing its investment in Australian infrastructure and real estate products too.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Abortelphusa Namdaphaensis
Mains level: Eastern Himalayas and its biodiversity

A crab specie was recently named after Arunachal Pradesh’s pristine forests on the edge of a small stream in Namdapha Tiger Reserve.
Try this question from CSP 2020:
Q.With reference to India’s Biodiversity, Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith barbet, Gray-chinned minivet and White-throated redstart are:
(a) Birds
(b) Primates
(c) Reptiles
(d) Amphibians
Abortelphusa Namdaphaensis
- The species, a small freshwater crab species, is a tribute to Namdapha, the largest protected area in the Eastern Himalayan Biodiversity Hotspot and the Abor Hills.
- It is the first Gecarcinucidae to be found in the Himalayan region. Freshwater crabs are divided into two families/categories: Potamidae and Gecarcinucidae.
- Both differ in abdomen shape and size. Potamidae species have a broad triangular abdomen, whereas, in Gecarcinucidae, the abdomen is mostly T-shaped.
- While the Gecarcinucidae is found in the peninsular region, the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, Potamidae are found in the Himalayan region.
What makes it special?
- The new species was found in a dry area, despite being a “freshwater” crab.
- Freshwater crabs use their gills to absorb dissolved oxygen from water, but for food, breeding, and other purposes, they do not need water, and thus roam on the land near water.
- The only reason it was possible to spot this on land is that the habitat around the water body has been preserved, untouched even.
- Of the 125 freshwater crabs in India, the north-east accounts for 37. Arunachal Pradesh has 15 and Assam has 21.
- The discovery highlights the potential of Arunachal Pradesh as one of the richest biodiversity hotspots in the country.
Back2Basics: Namdapha
- Namdapha (named a National Park in 1983) is known for its rich biodiversity and believed to be the rare area that harbours four large cats: tigers, snow leopards, clouded leopards and leopards.
- The Abor Hills, bordered by the Mishmi Hills and Miri Hills, is historically known for the Abor Expedition.
- It is a punitive expedition against the Abors in the North-Eastern Frontier Agency (which corresponds to parts of present-day Assam and Arunachal Pradesh) from October 1911 to April 1912.
- The expedition had thrown up a plethora of new floral and faunal species, making it a zoological and botanical expedition as well.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: WPI and CPI, MPC inflation targeting framework etc
Mains level: Paper 3- Role of MPC and inflation targeting issue
The article analyses the challenge faced by the Monetary Policy Committee in wake of a pandemic where falling growth is accompanied by the rising inflation.
Dilemma with inflation targetting in pandemic
- After the RBI’s adoption of a flexible inflation targeting framework from August 2020, it became even more focused on anchoring inflation and inflation expectations than ever before.
- But the COVID pandemic has created a dilemma for the RBI.
- Higher-than-anticipated inflation compelled the monetary policy committee (MPC) to hold policy rates despite the contraction in April-June GDP by 23.9 per cent.
CPI vs. WPI: Which should be focused for inflation targeting?
- Inflation-targeting framework based on one narrow nominal consumer price index (CPI) has highlighted the challenges of conducting monetary policy in a severe growth shock scenario.
- Inflation targeting is particularly challenging if it coincides with a sharp increase in headline CPI inflation as in the current period.
- The current framework has led to an excessive and obsessive emphasis on point CPI estimates, at the cost of ignoring other indicators.
- WPI core inflation, which essentially represents the manufacturing sector, is below 1 per cent but this does not find much mention.
- This is strange because ultimately, the GDP deflator is calculated using both CPI and WPI inflation, with the latter having a greater weight.
- This should be taken into consideration, while reviewing the existing monetary policy framework.
- Given the composition of the current CPI basket, RBI’s monetary policy actions can at best impact only 41.35 per cent of the overall items.
- Food and beverages, fuel items, gold and silver tobacco/intoxicants are items over which the RBI does not have any control.[58.65 per cent of the overall items]
This is a different time
- In normal times, a sustained increase in food and fuel prices can lead to a generalised increase in prices.
- But this argument is not valid in the current context where a large number of people have lost their jobs or have seen fall in incomes.
- In the current context, higher food and fuel prices would lead to reduction in expenditure on discretionary items.
- So there will be only a relative shift in prices, without any fear of a generalised spiral, as households will not be in any position to demand higher wages to compensate for the increase in prices of food and fuel items.
- Given the amount of slack in the economy, a scenario of sustained generalised increase in prices seems unlikely over the next 6-9 months.
How to measure the success of inflation targeting
- The CPI inflation targeting framework has helped to reduce inflation expectations during FY17-FY21 on average (9.3 per cent) compared to the previous period of FY12- FY16 (12.8 per cent).
- However, the gap between inflation expectations and actual CPI inflation has remained unchanged at 5.1 per cent during these two periods.
- The success of the inflation-targeting framework should not only be judged by the actual CPI inflation trend, but also in terms of gap between the two.
How RBI performed without inflation targeting framework in the past
- Even without any formal inflation-targeting framework, India had successfully managed to keep inflation low during FY02-FY06.
- The RBI’s stance then was based on a multiple-indicator approach to conduct monetary policy.
- First factor that made it possible was the increase in minimum support prices of food-grains was kept below 3 per cent on average.
- Second factor was the composition of growth which was better during this period with investment growth surpassing consumption growth by several percentage points.
- It is for this reason that CPI inflation remained contained at 4 per cent on average during this period even with 7 per cent real GDP growth.
Risk of structural increase in inflation
- In the current cycle, investment growth is likely to be impacted more severely than consumption growth.
- Given the acute weakness in the demand side of the economy, persistent problems in the real estate sector, continued deleveraging of the NBFC sector and significant job losses structural increase in inflation is limited.
What should be the policy response
- The scope for rate cuts remains dim in the near-term.
- But the RBI to remain active with a host of unconventional measures, which will likely include more proactive bond purchases to ensure that market interest rates do not rise significantly due to fiscal and market borrowing-related concerns.
Conclusion
Given the prevailing unholy mix of growth and inflation, it is tempting to categorise India’s economic situation as one of “stagflation”. But, in our view, it is too early to conclude decisively on this matter, given the fluid nature of things.
Back2Basics: Inflation expectations
- Inflation expectations are what people expect future inflation to be, and they matter because these expectations actually affect people’s behavior.
- If people expect inflation to be lower and they act on those beliefs, they could, in fact, cause inflation to be lower.
- If businesses expect lower inflation, they may raise prices at a slower rate; they don’t want the prices of their items to look too out of line with those of their competitors.
- If workers expect lower inflation, they may ask for smaller wage increases.
- The combination of businesses and workers acting in this manner will result in the economy experiencing lower inflation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Provision in labour codes
Mains level: Paper 2- Provisions for gig workers and platform workers in the labour codes
The article examines the provision made for the platform workers and the gig workers in the labour codes passed by the Parliament recently and explains the issues with it.
Context
- The three new labour codes passed by Parliament recently acknowledge platform and gig workers as new occupational categories in the making.
Definition issue
- The specific issues of working in factories, the duration of time needed on a factory floor, and associated issues are recognised as the parameters for defining an ideal worker.
- The Code on Wages, 2019, tries to expand this idea by using ‘wages’ as the primary definition of who an ‘employee’ is.
- Yet, the terms ‘gig worker’, ‘platform worker’ and ‘gig economy’ not defined with in connection with their wages.
- The new Code on Social Security allows a platform worker to be defined by their vulnerability — not their labour, nor the vulnerabilities of platform work.
Issues with the code
- Since the laws are prescriptive, what is written within them creates the limits to what rights can be demanded, and how these rights can be demanded.
- Platform delivery people can claim benefits, but not labour rights.
- This distinction makes them beneficiaries of State programmes.
- This does not allow them to go to court to demand better and stable pay, or regulate the algorithms that assign the tasks.
- This also means that the government or courts cannot pull up platform companies for lapses[ ex. choice of pay, work hours etc].
Benefits with no guarantee
- In the Code on Social Security, 2020, platform workers are now eligible for benefits like maternity benefits, life and disability cover, old age protection, provident fund, employment injury benefits, and so on.
- None of these are secure benefits.
- This means that from time to time, the Central government can formulate welfare schemes that cover these aspects of personal and work security, but they are not guaranteed.
- Actualising these benefits will depend on the political will at the Central and State government-levels and how unions elicit political support.
- The language in the Code is open enough to imply that platform companies can be called upon to contribute either solely or with the government.
Consider the question “What are the provisions for gig workers and platform workers in the new labour code? What are the issues with the provision?”
Conclusion
The ‘platform worker’ identity has the potential to grow in power and scope, but it will be mediated by politicians, election years, rates of under-employment, and large, investment- heavy technology companies that are notorious for not complying with local laws.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: H-1B term
Mains level: Paper 2- H-1B visa issue
Trump administration’s two moves on the visa could have implication for both India and corporate America. It needs to be seen whether the situations will remain the same after the Presidential elections in the U.S.
Context
- The U.S. President announced a hike in the salaries for those arriving in the U.S. on H-1B or skilled-worker visas.
Implications for India
- This hike is expected to cut visa applications by around 33%.
- Trump administration has in its earlier executive actions banned the issuance of new skilled worker visas and new green cards.
- India’s export of services to the U.S. is estimated to be at $29.6 billion in 2018, 4.9% more than in 2017, and 134% more than 2008 levels.
- The U.S. has been issuing 85,000 H-1B visas annually, of which 20,000 are given to graduate students and 65,000 to private sector applicants, approximately 70% of which are granted to Indian nationals.
- The visa issuance ban, combined with the mandatory salary floor soon to be instituted, will seriously hit U.S. imports of services from India.
Criticism of the move
- A federal judge in the Northern District of California blocked the enforcement of the new visa ban, ruling that the President “exceeded his authority” under the U.S. Constitution.
- Google CEO hit out at the ban, saying, “Immigration has contributed immensely to America’s economic success, making it a global leader in tech, and also Google the company it is today.”
Consider the question “What makes the H-1B visa important for India? What are the implications of the recent rise in the salary floor by the U.S. for the visa on India?”
Conclusion
While the ban and floor limit on salary come in the election milieu, India should prepare for the after election scenario.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Right to Protest
Mains level: Right to Protest and restrictions over it

The Supreme Court has found the indefinite “occupation” of a public road by the Shaheen Bagh protestors unacceptable.
Right to Protest
- The right to protest is the manifestation of the right to freedom of assembly, the right to freedom of association, and the right to freedom of speech.
- The Constitution of India provides the right of freedom, given in Article 19 with the view of guaranteeing individual rights that were considered vital by the framers of the constitution.
- The Right to protest peacefully is enshrined in Article 19(1) (a) guarantees the freedom of speech and expression; Article 19(1) (b) assures citizens the right to assemble peaceably and without arms.
- Article 19(2) imposes reasonable restrictions on the right to assemble peaceably and without arms.
What did the Court say?
- The court said the protest, considered an iconic dissent mounted by mothers, children and senior citizens of Shaheen Bagh against the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, became inconvenient to commuters.
- The judgment upheld the right to peaceful protest against the law but made it unequivocally clear that public ways and public spaces cannot be occupied, and that too indefinitely.
- Democracy and dissent go hand in hand, but then the demonstrations expressing dissent have to be in designated places alone.
- The present case was not even one of the protests taking place in an undesignated area but was a blockage of a public way which caused grave inconvenience to commuters.
Reasonable restrictions do exist in practice
- Fundamental rights do not live in isolation. The right of the protester has to be balanced with the right of the commuter. They have to co-exist in mutual respect.
- The court held it was entirely the responsibility of the administration to prevent encroachments in public spaces.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






