Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Patent Act 1970
Mains level: Paper 3- Amendment to patent working disclosure rule and its implications
A recent amendment to a unique feature in patent law under which patentee/licensee has to disclose information regarding the extent to which they have worked patent in India, could have several implications.
Why the changes in rules matter
- Indian patent law grants a 20-year patent monopoly to an inventor.
- In exchange for such monopoly, India’s patent law imposes a duty on the patentee to commercially work the invention in India to ensure that its benefits reach the public.
- Accordingly, section 146(2), a unique provision not found in patent laws of most other countries, requires every patentee and licensee to submit to the Patent Office an annual statement (Form 27 format) explaining the extent to which they have worked the invention in India.
- This statement is meant to help the Patent Office, potential competitors, etc. to determine whether the patentee has worked the invention in India and made it sufficiently available to the public at reasonable prices.
- A failure of this duty could trigger compulsory licensing or even subsequent revocation of the patent under the Patents Act, 1970.
- The central government recently amended the format of a statement that patentees and licensees are required to annually submit to the Patent Office.
- The amendment has significantly watered down the disclosure format.
- This could hamper the effectiveness of India’s compulsory licensing regime.
- This in turn could hinder access to vital inventions including life-saving medicines, thereby impacting public health.
- There has been significant pressure from multinational corporations and the United States government to do away with this requirement.
What changes were made through the amendment
- The recent amendment to the form was made in response to a PIL filed by Shamnad Basheer before the Delhi High Court in 2015.
- The PIL brought to the Court’s attention the rampant non-filing and defective filing of Form 27 and sought a direction to strictly enforce the patent working disclosure rules and take action against the violators.
- The PIL also called for a reform of Form 27, arguing that the information it sought was grossly insufficient to ascertain the extent of the working of the patent.
- However, instead of strengthening the form, the amendment has significantly weakened it further, thereby defeating the entire purpose of the amendment exercise.
- The amended form has removed the requirement of submitting a lot of important information.
- It is no longer required to provide any information in respect of the quantum of the invention manufactured/imported into India, the licenses and sub-licenses granted during the year and the meeting of public requirement at a reasonable price.
- It no longer requires quantum or the total units of the invention manufactured/imported in India.
- The deletion of this requirement of its disclosure is shocking.
- This is because, it is the disclosure of this data by Bayer in Form 27 that played a crucial role in grant of India’s first compulsory license to Natco for the anti-cancer drug Sorafenib/Nexavar.
- The removal of the requirement of submitting any licensing information, including the disclosure of even the existence of licenses means that the patentees/licensees can just self-certify that they’ve worked the patent.
- The omission to mandate disclosure of details makes it extremely difficult to ascertain whether the invention has been made available to the public in sufficient quantity and at an affordable price.
Conclusion
The government has significantly weakened the critical duty imposed by the law on patentees/licensees to disclose patent working information. Therefore, the government must reconsider its amendments to the form taking into account the PIL recommendations and re-amend it to restore as well as strengthen its spirit.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Post-covid development model
The article discusses the themes of the post-covid world which will be somewhat more aware and mindful of the dangers of global dimension.
Collaborative model and public-private partnership
- A few weeks back, Prime Minister visited the private companies involved with the formulation of the anti-COVID vaccine.
- The PM’s visit was one more reminder of the critical importance of public-private partnerships.
- The PM signalled the government’s receptivity to external expert advice.
- The CEOs reaffirmed their commitment to partnering with the state to help address not just this medical crisis but also the many other social and humanitarian problems.
- The government has appreciated that the model for sustainable development in a post-COVID world must be a collaborative one.
- Businesses will repurpose their goals and look beyond profits.
Working together to deal with the crises of global dimensions
- COVID-19 was not the first, nor will it be the last crisis of global dimensions.
- The threat of global warming, for instance, hangs over our heads.
- Its impact is less immediate and for the present, at least less palpable.
- But it looms and its consequences are existential.
- COVID has offered, it is the tangible evidence that no one entity or group — the state, markets, businesses, entrepreneurs, scientists — can tackle existing and emergent economic and social problems on their own.
- They have to work together to resolve them.
Business uncertainties
- Businesses has been the uncertainty of operating in the post-COVID digital world.
- Every business leader has, in some form or other, expressed three types of uncertainties.
- 1) Is their business facing a hinge moment, necessitating the reimagining and re-engineering of their strategy and product portfolio?
- Or are they witnessing no more than another turn of the business cycle and that, once the vaccine is developed and distributed, the market will return to business as usual?
- Or will conditions necessitate a middle of the road approach: Stay the pre- COVID course but at the same time, speed up the pivot toward a new business model.
- Most business leaders are adopting this third hybrid path.
- The key to corporate success in a digital world in which a distinct incident could influence it, is the capability of leaders to think out of the box and to handle the unexpected.
- Financial, technological and human resources will be necessary, but they will not be sufficient.
Consider the question “The post-covid development model must be based on the cooperation underscored by the public-private partnership as the challenges that could emerge are not possible to be tackled by any on entitiy. Comment”
Conclusion
COVID has “obliterated the one remaining obstacle to a digital future — human attitudes”. Covid forced them to adopt and adapt. The challenge for our business leaders will be to navigate a pathway that sustains the benefits of these tools but without deepening the existing social and economic inequalities. Life is not digital for millions in our country.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CDS and Department of Military Affairs
Mains level: Paper 3- Creation of Theatre Commands and issues with it
The article examines issues of national security like the recent creation of a Department of Military Affairs (DMA) and a Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and also some focus areas like Threatre Command.
Understanding the significance of DMA and CDS
- Through the creation of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS), the management of the armed forces, so far which was assigned to the civilian Defence Secretary, was brought under a military officer, the CDS.
- The designation of CDS as Secretary DMA made him the first military officer to be recognised as a functionary of the Government of India (GoI).
- With the DMA is now a part of the GoI, it would aid the resolution of organisational, hierarchical and financial issues faced by the military.
Recent steps taken by DMA
- The responsibility for accruing savings to fund defence expenditure has been placed on the DMA.
- DMA has floated two schemes aimed at reducing the defence pensions bill.
- One penalises officers seeking early release from service and another envisages a three-year “Tour of Duty” for jawans.
- Issues with these ideas:
- Penalising officers for early release is likely to harm morale.
- “Tour of Duty” will degrade the military’s combat-capability in today’s technology-intensive battle-space.
- The need here is that DMA must focus on military matters and leave the plans of financing national defence to finance ministry or the Niti Aayog. It will better serve it’s purpose.
Another area of needed reform – Theatre Command
- Theatre Commands stands for jointness and integration in the Indian military are varying degrees of synergy and cross-service cooperation between the military wings of Indian armed forces.
- Objectives of the creation of theatre command should be:
- To hand over the military’s warfighting functions to the Theatre Commanders, while retaining the support functions with service HQs.
- To combine India’s 17 widely-dispersed, single-service Commands into four or five mission/threat-oriented, geographically contiguous “Joint” or “Theatre Commands”.
- To place the appropriate warfighting resources of all three services directly under the command of the designated Theatre Commanders; and
- To achieve efficiency/economy by pooling of facilities and resources of the three services.
Advantages of Theatre Commands
- The Theatre Commanders and their staff will be trained and groomed in jointness.
- With that jointness, they will be able to plan operations and to employ land, maritime and air forces, regardless of the service to which they belong.
- For this to happen, radical changes are required in the content of our system of professional military education.
- The Theatre Commander will also have the benefit of advice from commanders representing each service.
Issues with Theatre Commands
- Two thorny issues are the chain of command of the Theatre Commanders and the relationship of the CDS (or his equivalent) with the service Chiefs.
- To avoid over-concentration of power in any single military functionary, the system followed by the US ensures that the chain of command runs from the President to the Secretary (Minister) of Defence and then, directly to the Theatre Commander.
- In India, the peacetime management of the armed forces is left to the MoD and the Chiefs of Staff Committee (COSC).
- However, during war, strategic guidance to the military, has always come from the PM.
- In the system of higher defence under implementation, ideally, the Defence Minister needs to be brought into the command/operational chain of the Theatre Commanders, with the CDS acting as his adviser.
- Due to frequency of elections and intensity of politics in India that no Defence Minister has had the time or inclination to devote his/her undivided attention to complex national security issues.
Consider the question “Examine the implications of the creation of Theatre Commands. What are the challenges in its creation.”
Conclusion
India’s military reforms are complex, the GoI needs to seriously consider the constitution of a Parliamentary Committee, with military advisers, to oversee and guide this transformational process.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: OECD , various parameters mentioned
Mains level: Concerns of farmers other than MSP
The OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) has provided five sets of data on the issue of agriculture support and India trails on most counts:
The ongoing debate about farmers protest has brought to light some of the key support mechanisms for agriculture in India. And it is being argued that the government has preferred the welfare of Indian consumers over the Indian farmers.
Lets’ have a look at various OECD’s parameters:
(1) Producer Support Estimates (PSE)

- These are transfers to agricultural producers and are measured at the farm gate level.
- They comprise market price support, budgetary payments and the cost of revenue foregone.
(2) Consumer Support Estimates (CSE)

- These refer to transfers from consumers of agricultural commodities. They are measured at the farm gate level.
- If negative, the CSE measures the burden (implicit tax) on consumers through market price support (higher prices), that more than offsets consumer subsidies that lower prices to consumers.
(3) General Services Support Estimates (GSSE)

- GSSE transfers are linked to measures creating enabling conditions for the primary agricultural sector through the development of private or public services, institutions and infrastructure.
- GSSE includes policies where primary agriculture is the main beneficiary but does not include any payments to individual producers.
- GSSE transfers do not directly alter producer receipts or costs or consumption expenditure.
(4) Total Support Estimate (TSE)
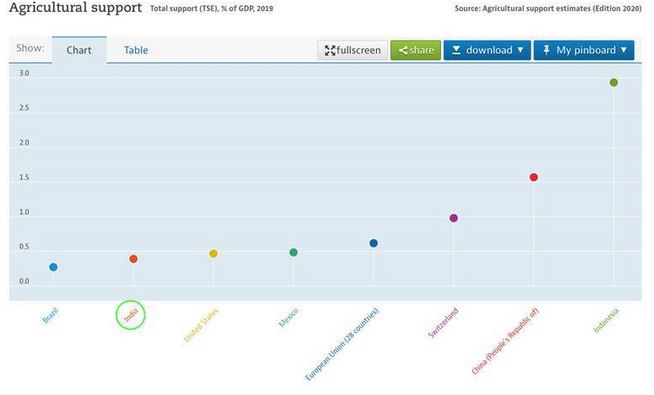
- The TSE transfers represent the total support granted to the agricultural sector, and consist of producer support (PSE), consumer support (CSE) and general services support (GSSE).
(5) Producer protection

- Lastly, the OECD also provides data on “producer protection”.
- The PP is the ratio between the average price received by producers (measured at the farm gate), including net payments per unit of current output, and the border price (measured at the farm gate).
- For instance, a coefficient of 1.10, which China has, suggests that farmers, overall, received prices that were 10% above international market levels.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gilgit-Baltistan Region, CPEC
Mains level: CPEC and India's sovereignty concerns

The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) has turned five.
What is CPEC?
- China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a collection of infrastructure projects that are under construction throughout Pakistan since 2013.
- It is an extension of the Belt and Road Initiative of China.
- It intended to upgrade Pakistan’s required infrastructure and strengthen its economy by the construction of modern transportation networks, numerous energy projects, and special economic zones.
- On 13 November 2016, CPEC became partly operational when Chinese cargo was transported overland to Gwadar Port for onward maritime shipment to Africa and West Asia.
Why in news?
- The viability of some of the CPEC’s projects, and how they were going to be paid for in a pandemic-hit economy, had come under renewed attention in Pakistan.
- China had sought additional guarantees before sanctioning a $6 billion loan for the Main Line-1 (ML-1) project, which includes upgrading a 1,872 km rail line from Peshawar to Karachi.
- This is due to the “weakening financial position of Pakistan” and had “proposed a mix of commercial and concessional loans against Islamabad’s desire to secure the cheapest lending”.
An overrated project
- The CPEC, to some degree, has been a victim of its own hype.
- Its economic figure may never materialise as the plan has been “considerably slimmed-down” from the scope that was first imagined.
- This largely due to the ever-deteriorating financial situation of Pakistan and a visible debt-trap.
- Pakistan had established a CPEC authority to speed up the execution of several projects that were mired in delays (and to give the military a greater role in the project).
Threats of Baloch insurgency
- Gwadar, the heartland of CPEC certainly faces serious threats.
- The city is a prime target for Baloch nationalist insurgents. Hence Pakistan has decided to fence the area.
- This has sparked a new furore among the local residents.
India’s concerns with CPEC
- CPEC passes through Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (Gilgit-Baltistan) which is an Indian territory illicitly occupied by Pakistan.
- Thus CPEC undermines India’s strategic interests and territorial integrity.
- More importantly, with CPEC, China will get access to the western Indian Ocean through Gwadar port.
- This will help China in controlling maritime trade and would affect the freedom of navigation and trade-energy security of India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trans fats
Mains level: Health threats posed by Trans Fats
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has capped the amount of trans fatty acids (TFA) in oils and fats to 3% for 2021 and 2% by 2022 from the current permissible limit of 5%.
New FSSAI norms
- FSSAI has acted in response to the amendment to the Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restriction on Sales) Regulations.
- The country’s food regulatory body notified the amendment on December 29, more than a year after it issued a draft on the subject for consultation with stakeholders.
- The revised regulation applies to edible refined oils, vanaspati (partially hydrogenated oils), margarine, bakery shortenings, and other mediums of cooking such as vegetable fat spreads and mixed fat spreads.
- It was in 2011 that India first passed a regulation that set a TFA limit of 10% in oils and fats, which was further reduced to 5% in 2015.
What are Trans Fats?

- Artificial Trans fats are created in an industrial process that adds hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils to make them more solid.
- Since they are easy to use, inexpensive to produce and last a long time, and give foods a desirable taste and texture, they are still widely used despite their harmful effects being well-known.
Why such a regulation?
- Trans fats are associated with increased risk of heart attacks and death from coronary heart disease.
- As per the WHO, approximately 5.4 lakh deaths take place each year globally because of intake of industrially-produced trans-fatty acids.
- The WHO has also called for global elimination of trans fats by 2023.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ramsar Convention, Wetlands
Mains level: Ramsar wetlands in India

Assam has prohibited community fishing at Deepor Beel, a wetland on the south-western edge of Guwahati and it’s the only Ramsar site.
Try this PYQ:
In which one among the following categories of protected areas in India are local people not allowed to collect and use the biomass?
(a) Biosphere reserves
(b) National parks
(c) Wetlands declared under Ramsar convention
(d) Wildlife sanctuaries
Deepor Beel
- Deepor Beel is located to the south-west of Guwahati city, in Kamrup district of Assam, India.
- It is a permanent freshwater lake, in a former channel of the Brahmaputra River, to the south of the main river.
- It is a wetland under the Ramsar Convention which has listed since November 2002, for undertaking conservation measures on the basis of its biological and environmental importance.
- Considered as one of the largest beels in the Brahmaputra valley of Lower Assam, it is categorised as a representative of the wetland type under the Burma monsoon forest biogeographic region.
- It is also an important bird sanctuary habituating many migrant species.
- Freshwater fish is a vital protein and source of income for these communities; the health of these people is stated to be directly dependent on the health of this wetland ecosystem.
Back2Basics: Ramsar Convention
- The Convention on Wetlands of International Importance (better known as the Ramsar Convention) is an international agreement promoting the conservation and wise use of wetlands.
- It is the only global treaty to focus on a single ecosystem.
- The convention was adopted in the Iranian city of Ramsar in 1971 and came into force in 1975.
- Traditionally viewed as a wasteland or breeding ground of disease, wetlands actually provide fresh water and food and serve as nature’s shock absorber.
- Wetlands, critical for biodiversity, are disappearing rapidly, with recent estimates showing that 64% or more of the world’s wetlands have vanished since 1900.
- Major changes in land use for agriculture and grazing, water diversion for dams and canals and infrastructure development are considered to be some of the main causes of loss and degradation of wetlands.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Natural Gas
Mains level: Natural gas as an alternative fuel

PM will today dedicate the Kochi – Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline to the nation.
Try this PYQ:
Q. Consider the following statements:
- Natural gas occurs in the Gondwana beds.
- Mica occurs in abundance in Kodarma.
- Dharwars are famous for petroleum.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) None
Kochi – Mangaluru Pipeline
- The 450 km long pipeline has been built by GAIL (India) Ltd.
- It has a transportation capacity of 12 Million Metric Standard Cubic Metres per day.
- It will carry natural gas from the Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Regasification Terminal at Kochi (Kerala) to Mangaluru (Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka).
- It will pass through Ernakulam, Thrissur, Palakkad, Malappuram, Kozhikode, Kannur and Kasaragod districts.
Its significance
- The event marks an important milestone towards the creation of ‘One Nation One Gas Grid’.
- The pipeline will supply environment-friendly and affordable fuel in the form of Piped Natural Gas (PNG) to households and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) to the transportation sector.
- It will also supply Natural Gas to commercial and industrial units across the districts along the pipeline.
- Consumption of cleaner fuel will help in improving air quality by curbing air pollution.
Back2Basics: Natural Gas
- Natural gas is a fossil fuel source consisting primarily of methane.
- It is the cleanest among all the available fossil fuels.
- It is used as a feedstock in the manufacture of fertilizers, plastics and other commercially important organic chemicals as well as used as a fuel for electricity generation, heating purpose in industrial and commercial units.
- Natural gas is also used for cooking in domestic households and a transportation fuel for vehicles.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now









