Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Finance Commission and its recommendations
Mains level: Paper 2- Fifteenth Finance Commission report and federalism
The article analyses the recommendations of fifteenth Finance Commission and their implications for the federalism in India.
Major recommendations accepted by the government
- Report of the fifteenth Finance Commission (XVFC) was laid before the Parliament.
- The finance minister announced the acceptance of its recommendation of retaining the share of states in central taxes at 42 per cent.
- She also stated that on its recommendation revenue deficit grants of Rs 1.18 lakh crore to the states have been provided for in the budget.
- Some of the recommendations, however, have far-reaching implications on government finances, both of the Centre and the states.
- Keeping in view the extant strategic requirements for national defence in a global context, XVFC has, in its approach, recalibrated the relative shares of the Union and the states in gross revenues receipts.
Issues with the recalibration for national defence
- Recalibration enables the Union to set aside resources for special funding on defence.
- The states have been made to pay Rs 7,000 crore to bridge [the] Centre’s gap between projected budgetary requirements and budget allocation for defence and internal security defence.
- But this is an expenditure that the Centre is obliged to fund.
- For the first time, a finance commission has carved out resources meant for distributable statutory grants and dipped into the states’ revenue share, as against the tax share, in order to finance the Centre’s exclusive expenditure obligation.
- What has been done is not in line with the system envisaged in the Constitution.
- This move will eventually put the fiscal federal system under systemic strain.
- In operational terms, too, this move is a significant departure.
- So far, the Centre has been used to pre-empting resources from the kitty to be distributed among the states but only to finance expenditures in areas earmarked for states.
- This was done through the centrally-sponsored schemes, but at least the states’ money was being used in the states, even if on a discretionary rather than a criteria basis.
- Now, with this move of earmarking and financing of funds for sectors, it is the states’ money that is being used to finance the Centre’s expenditure.
- This is certainly not cooperative federalism.
Changes in horizontal distribution: More weightage to efficiency and performance
- In horizontal distribution, the criteria used by successive finance commissions for devolving taxes across states have always been linked to need — based on equity, tempered by efficiency.
- From 92.5 per cent of funds to a state being devolved based on need and equity, the XVFC has reduced these two components to 75 per cent.
- The remaining 25 per cent are to be devolved on considerations of efficiency and performance.
- This is the lowest weightage for equity, making the XVFC transfers potentially the least progressive ever.
Structural changes not taken into account
- The Finance Commission has not even made any serious effort to review the existing scheme of transfers in light of the changed federal landscape.
- The existing criteria for the devolution have evolved in, and for, a production-based tax system.
- The XVFC should have reformulated the distributional criteria for a consumption-based tax system [GST].
- The structural change from production to consumption will make a significant difference to distribution as well as the need, nature and distribution of equalising grants.
- This is the same manner in which the revenue deficit grants have been carried forward.
- Ideally, the “gap-filling” approach should have been redesigned in light of the compensation law providing a minimum-guaranteed revenue of 14 per cent to every state.
Consider the question “For the first time, a finance commission has carved out resources meant for distributable statutory grants and dipped into the states’ revenue share, as against the tax share, in order to finance the Centre’s exclusive expenditure obligation. What are the issues with this move?”
Conclusion
The Fifteenth Finance Commission report is not aligned with the new landscape of federalism and does not address the key issues.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Agri-marketing reforms and water accounting to solve the problems of agriculture
China and Israel offer two important lessons for India to transform its agriculture: agri-market reforms and water accounting.
Lessons from Israel and China
- India, China and Israel — started off their new political journey in late 1940s, but today China’s per capita income in dollar terms is almost five times that of India, and Israel’s almost 20 times higher than India.
- China produces three times more agri-output than India from a smaller arable area.
- China started off its economic reforms in 1978 by taking up agriculture first.
- It dismantled its commune system of land holdings and liberated agri-markets that allowed farmers to get much higher prices.
- As a result, in 1978-84, farmers’ incomes in China increased by almost 14 per cent per annum, more than doubling in six years.
- Israel cultivates high-value crops for exports (citrus fruits, dates, olives) by using every drop of water and recycling urban waste water for agriculture, by de-salinisation of sea waters.
- Water accounting in Israel is something exemplary.
Need for agri-reform in India
- The average holding size in China was just 0.9 ha in 2016-18, smaller than India’s 1.08 ha in 2015-16.
- So there is no doubt that small holders can do wonders, if they are given the right incentives, good infrastructure and research support, and the right institutional framework to operate.
- In India, the 1991 reforms did not include agriculture.
- Indian agri-food policies remained more consumer-oriented with a view to protect the poor.
- Export controls, stocking limits on traders, movement restrictions, etc all continued at the hint of any price rise.
- The net result of all this was farmers’ incomes remained low and so did those of landless agri-labourers.
Way forward
- India needs to change its policy framework from being subsidy-led to investment-driven, from being consumer-oriented to producer-oriented, and from being supply-oriented to demand-driven by linking farms with factories and foreign markets, and, finally, from being business as usual to an innovations-centred system.
- Until India breaks away from the policy of free power for agriculture, there would be no incentive for farmers to save water.
- In a state like Punjab where almost 80 per cent of blocks are over-exploited or critical, meaning the withdrawal of water is much more than the recharge.
- Highly subsidised urea and open-ended procurement have become a deadly cocktail that are eating away the natural wealth of Punjab.
- Out-of-box thinking is needed to break this regressive cycle for a brighter future for Punjab, for our own children.
Consider the question “What are the implications of subsidy oriented policies for Indian agriculture.”
Conclusion
Lessons from China and Israel suggest that India need reform in agri-food policies and water accounting to address several issues plaguing agriculture.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Interstate boundary disputes in India

Andhra Pradesh recently held panchayat elections in three villages in the Kotia cluster, which is at the centre of a dispute between Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
Do you know?
Sukma district of Chhattisgarh borders with Odisha (Malkangiri district), Telangana (Bhadradri Kothagudem district) and Andhra Pradesh (East Godavari district).
You got it right. Thers’ a junction. AP and Telangana , both borders with Chhattisgarh.
Andhra-Odisha Boundary Dispute
- Prior to April 1, 1936, villages under Kotia panchayat were part of Jeypore Estate.
- In the Constitution of Orrisa Order, 1936, published in the Gazette of India on March 19 that year, the GoI demarcated Odisha from the erstwhile Madras Presidency.
- In 1942, the Madras government contested the boundary and ordered re-demarcation of the two states.
- When the state of Andhra Pradesh was created in 1955, the villages were not surveyed by the state government either.
Details of the villages
- These villages, with a population of nearly 5,000, are located on a remote hilltop on the inter-state border and are inhabited by Kondh tribals.
- The region, once a Maoist hotbed which still reports sporadic incidents of violence, is also rich in mineral resources like gold, platinum, manganese, bauxite, graphite and limestone.
What is the judicial reaction?
- In the early 1980s, Odisha filed a case in the Supreme Court demanding right and possession of jurisdiction over the 21 villages.
- In 2006 the court ruled that disputes belonging to the state boundaries are not within the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court.
- The matter can only be resolved by Parliament and passed a permanent injunction on the disputed area.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Migration trends in India
This newscard presents data on India’s internal migration considering the mass exodus which was visible during the lockdowns.
The displacement of people during the imposition of lockdown has been described as the second-largest since the Partition of the country.
Also read:
[Burning Issue] Migrant workers amid COVID-19 outbreak
India’s internal migration
(1) Number of migrants
- As of 2020, India has an estimated 600 million migrants. Roughly half of India is living in a place where it wasn’t born.
- It would be roughly double the size of the fourth-largest nation on the planet — the United States.
(2) Nature of migration
- The bulk of the internal migration in India is within one district itself. An estimated 400 million Indians “migrate” within the district they live in.
- The next 140 million migrate from one district to another but within the same state.
- And only about 60 million — that is, just 10% of all internal migrants — move from one state to another.
(3) Type of Migration
- There are other misconceptions as well. Typically, it is thought that most migration happens when people from rural areas move to urban areas.
- That is incorrect. The most dominant form of migration is from rural to rural areas.
- Only about 20% of the total migration (600 million) is from rural to urban areas.
- In fact, 20% of the total migration is from one urban area to another urban area.
- As such, urban migration (rural to urban as well as urban to urban) accounts for 40% of the total migration.
(4) Comparison with other countries
- India’s proportion of internal migrants (as a percentage of the overall population) is much lower than some of the comparable countries such as Russia, China, South Africa and Brazil.
- All have much higher urbanisation ratios, which is a proxy for migration level.
- In other words, as India adopts a strategy of rapid urbanisation, levels of internal migration will increase further.
Impact of COVID
The reality of a migrant worker’s existence is much more complicated than those sharply defined numbers.
Not all migrants were equally affected
- The worst-hit were a class of migrants that felt under the group “vulnerable circular migrants”.
- These are people who are “vulnerable” because of their weak position in the job market and “circular” migrants because even though they work in urban settings, they continue to have a foothold in the rural areas.
- Such migrants work in construction sites or small factories or as rickshaw pullers in the city but when such employment avenues dwindle, they go back to their rural setting.
- In other words, they are part of the informal economy outside agriculture.
“Data insufficient”
- The truth is that even now all the estimates mentioned above are individual estimates.
- The official data — be it the Census or the National Sample Survey — is more than a decade old.
- In fact, Census 2011 migration data was made publicly available only in 2019.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mechanophotonics, Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Mains level: Not Much
Crystals are normally rigid, stiff structures, but researchers from the University of Hyderabad have shown how crystals can be sliced and even bent using atomic force microscopy. They have named this technique as “mechanophotonics”.
The newscard discusses an out of the box technology which if brought to reality in practical use, can create immense disruptions in the technology market.
Manipulating light through crystals
- Manipulating them with precision and control comes in very useful in the field of nanophotonics, a qualitative, emerging field.
- The aim is to go beyond electronics and build-up circuits driven entirely by photons (light).
If the technique can be successfully developed, this can achieve an unprecedented level of miniaturisation and pave the way to all-optical-technology such as pliable, wearable devices operated by light entirely.
What Indian researchers have achieved?
: Bending light path
- Light, when left to itself moves along straight paths, so it is crucial to develop materials and technology that can cause its path to bend along what is required in the circuits.
- This is like using fibre optics, but at the nanoscale level using organic crystals.
- The Hyderabad group has demonstrated how such crystals can be lifted, bent moved, transferred and sliced using atomic force microscopy.
: How?
- Researchers add a crucial piece to the jigsaw puzzle of building an “organic photonic integrated circuit” or OPIC.
- Generally, millimetre- to centimetre-long crystals were bent using hand-held tweezers.
- This method lacks precision and control. Also, the crystals used were larger than what was required for miniaturisation.
- The atomic force microscopy (AFM) cantilever tip could be used to lift a crystal, as crystals tend to stick to the tip due to tip–crystal attractive forces.
- Thus they demonstrated the real waveguiding character of the crystal lifted with a cantilever tip.
In 2014, for the first time, the group led by Rajadurai Chandrasekar of the Functional Molecular Nano/Micro Solids Laboratory in University of Hyderabad demonstrated that tiny crystals could be lifted and moved with precision and control using atomic force microscopy.
What is Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)?
- AFMs are a type of electron microscope used for the observation at an atomic level.
- It is commonly used in nanotechnology.
- The AFM works by employing an ultra-fine needle attached to a beam.
- The tip of the needle runs over the ridges and valleys in the material being imaged, “feeling” the surface.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: nORF
Mains level: Not Much
A team from the University of Cambridge set out to find whether new genes emerge in the genome of living organisms and if they do, how they do so. They have now catalogued 1,94,000 novel regions.
Genes/Genomes/DNA/RNA is all-time favourite of UPSC. You can easily find 1-2 questions every year since 2017 in Prelims.
Novel genomic regions
- The ‘novel’ genomic regions cannot be defined by our current ‘definition’ of a gene.
- Hence, researchers call these novel regions – novel Open Reading Frames or as nORFs.
- Researchers found that the mutations in nORFs do have physiological consequences and a majority of mutations that are often annotated as benign have to be re-interpreted.
What novel did the researchers find?
- nORF regions were uniquely present in the cancer tissues and not present in the control tissue.
- They found that some nORF disruptions strongly correlated with the survival of patients.
- nORFs proteins can form structures, can undergo biochemical regulation like known proteins and be targeted by drugs in case they are disrupted in diseases.
- The researchers also identified these nORFs in Plasmodium falciparum, the parasite which causes the deadliest form of malaria.
Connected to disease
- The research found that these regions are also broadly involved in diseases.
- The nORFs were seen as dysregulated in 22 cancer types.
- Dysregulated is a term which means that they could either be mutated, upregulated, or downregulated, or they could be uniquely present.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Malwares
Mains level: Cyber attacks and the treats posed to national security
This newscard is an excerpt from the original article published in The Hindu.
Try this question from CSP 2018:
Q.The terms ‘WannaCry, Petya, Eternal Blue’ sometimes mentioned news recently are related to
(a) Exoplanets
(b) Crypto currency
(c) Cyber attacks
(d) Mini satellites
What is NetWire?
- NetWire, which first surfaced in 2012, is a well-known malware.
- It is also one of the most active ones around.
- It is a remote access Trojan, or RAT, which gives control of the infected system to an attacker. Such malware can log keystrokes and compromise passwords.
Threats posed
- This malware essentially does two things:
- One is data exfiltration, which means stealing data. Most anti-virus software is equipped to prevent this.
- The other involves infiltrating a system, and this has proven to be far more challenging for anti-virus software.
- NetWire is described as an off-the-shelf malware, while something like Pegasus, which used a bug in WhatsApp to infiltrate users’ phones in 2019, is custom-made and sold to nations.
Back2Basics: Classification of malicious softwares
Viruses
- A computer virus is a type of malware that propagates by inserting a copy of itself into and becoming part of another program.
- It spreads from one computer to another, leaving infections as it travels.
- Viruses can range in severity from causing mildly annoying effects to damaging data or software and causing denial-of-service (DoS) conditions.
- Almost all viruses are attached to an executable file, which means the virus may exist on a system but will not be active or able to spread until a user runs or opens the malicious host file or program.
- When the host code (alternative word for a computer program) is executed, the viral code is executed as well.
Ransomware
- Ransomware is a type of malicious software that threatens to publish the victim’s data or perpetually block access to it unless a ransom is paid.
- While some simple ransomware may lock the system in a way that is not difficult for a knowledgeable person to reverse, more advanced malware uses a technique called cryptoviral extortion.
- This encrypts the victim’s files, making them inaccessible, and demands a ransom payment to decrypt them.
Worms
- Computer worms are similar to viruses in that they replicate functional copies of themselves and can cause the same type of damage.
- In contrast to viruses, which require the spreading of an infected host file, worms are standalone software and do not require a host program or human help to propagate.
- To spread, worms either exploit the vulnerability on the target system or use some kind of social engineering to trick users into executing them.
- A worm enters a computer through a vulnerability in the system and takes advantage of file-transport or information-transport features on the system, allowing it to travel unaided.
- More advanced worms leverage encryption, wipers, and ransomware technologies to harm their targets.
Trojans
- A Trojan is a harmful piece of software that looks legitimate.
- After it is activated, it can achieve any number of attacks on the host, from irritating the user (popping up windows or changing desktops) to damaging the host (deleting files, stealing data, or activating and spreading other malware, such as viruses).
- Trojans are also known to create backdoors to give malicious users access to the system.
- Unlike viruses and worms, Trojans do not reproduce by infecting other files nor do they self-replicate.
- Trojans must spread through user interaction such as opening an email attachment or downloading and running a file from the Internet.
Bots
- “Bot” is derived from the word “robot” and is an automated process that interacts with other network services.
- Bots often automate tasks and provide information or services that would otherwise be conducted by a human being.
- A typical use of bots is to gather information, such as web crawlers, or interact automatically with Instant Messaging (IM), Internet Relay Chat (IRC), or other web interfaces.
- They may also be used to interact dynamically with websites.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mandarin Duck, Dibru Saikhowa NP
Mains level: Not Much

A rare Mandarin duck was observed floating in the Maguri-Motapung beel (or wetland) in Assam’s Tinsukia district for over a week is spectacular.
Mandarin duck
IUCN status: Least Concerned
- Considered the most beautiful duck in the world, the Mandarin duck, or the (Aix galericulata) was first identified by Swedish botanist, physician and zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758.
- The eBird website, a platform that documents birds world over, describes it as a “small-exotic looking bird” native to East Asia.
- It’s very beautiful, with majestic colours and can be spotted from a distance.
Its habitat and breeding
- The migratory duck breeds in Russia, Korea, Japan and northeastern parts of China. It now has established populations in Western Europe and America too.
- In 2018, when a Mandarin duck was spotted in a pond in New York City’s Central Park, it created a flutter among local residents.
- It was recorded in 1902 in Dibru River in the Rongagora area in Tinsukia.
About Maguri beel

- The Maguri Motapung wetland is an Important Bird Area as declared by the Bombay Natural History Society.
- It is located close to the Dibru Saikhowa National Park in Upper Assam.
- The entire ecosystem is very important as it is home to at least 304 bird species, including a number of endemic ones like Black-breasted parrotbill and Marsh babbler.
- In May 2020, the beel was adversely affected by a blowout and fire at an Oil India Limited-owned gas well.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fastag
Mains level: Fastag and its benefits for speedy transport
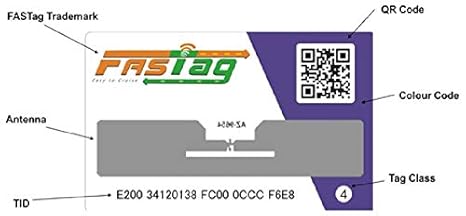
Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has decided that all lanes in the fee plazas on National Highways shall be declared as “FASTag lane of the fee plaza”.
Fastag went unnoticed this year. The RFID technology deployed in this holds an intuition for its relevance in CS prelims and many forthcoming exams.
What is ‘FASTag’?
- FASTags are stickers that are affixed to the windscreen of vehicles and use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to enable digital, contactless payment of tolls without having to stop at toll gates.
- The tags are linked to bank accounts and other payment methods.
- As a car crosses a toll plaza, the amount is automatically deducted, and a notification is sent to the registered mobile phone number.
How does it work?
- The device employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for payments directly from the prepaid or savings account linked to it.
- It is affixed on the windscreen, so the vehicle can drive through plazas without stopping.
- RFID technology is similar to that used in transport access-control systems, like Metro smart card.
- If the tag is linked to a prepaid account like a wallet or a debit/credit card, then owners need to recharge/top up the tag.
- If it is linked to a savings account, then money will get deducted automatically after the balance goes below a pre-defined threshold.
- Once a vehicle crosses the toll, the owner will get an SMS alert on the deduction. In that, it is like a prepaid e-wallet.
Must read:
[Burning Issue] Implementation of FASTags
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




