Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Article 324
Mains level: Paper 2- Need for clarity on the powers of ECI
The article highlights the issue of lack of clarity on the extent of the power of the Election Commission of India.
Where ECI derives its power from
- Supreme Court held in Mohinder Singh Gill vs Chief Election Commissioner that Article 324 contains plenary powers to ensure free and fair elections.
- These plenary powers are vested in the ECI which can take all necessary steps to achieve this constitutional object.
- Thus, the model code of conduct has been issued in exercise of its powers under Article 324.
- Besides the code, the ECI issues from time to time directions, instructions and clarifications on a host of issues which crop up in the course of an election.
The model code of conduct
- The model code of conduct issued by the ECI is a set of guidelines meant for political parties, candidates and governments to adhere to during an election.
- This code is based on consensus among political parties.
- The model code is observed by all stakeholders for fear of action by the ECI.
- However, there exists a considerable amount of confusion about the extent and nature of the powers which are available to the ECI in enforcing the code as well as its other decisions in relation to an election.
Issues with model code of conduct
1) Issue of enforceability
- As the code of conduct is framed on the basis of a consensus among political parties, it has not been given any legal backing.
- A committee of Parliament recommended that the code should be made a part of the Representation of the People Act 1951.
- However, the ECI did not agree to it on the ground that once it becomes a part of the law, all matters connected with the enforcement of the code will be taken to court, which would delay elections.
- But then the question about the enforceability of the code remains unresolved.
- Paragraph 16A of the Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968 says that the commission may suspend or withdraw recognition of a recognised political party if it refuses to observe the model code of conduct.
- But it is doubtful whether this provision is legally sustainable.
- When the code is legally not enforceable, how can the ECI resort to a punitive action such as withdrawal of recognition?
2) Transfer of officials
- Observers of ECI report to it about the conduct of certain officials of the States where elections are to be held.
- Transfer of an official is within the exclusive jurisdiction of the government.
- It is actually not clear whether the ECI can transfer a State government official in exercise of the general powers under Article 324 or under the model code.
- Transfer of an official is within the exclusive jurisdiction of the government.
- It is actually not clear whether the ECI can transfer a State government official in exercise of the general powers under Article 324 or under the model code.
- Further, to assume that a police officer or a civil servant will be able to swing the election in favour of the ruling party is extremely unrealistic and naive.
3) ECI’s intervention in administrative decisions
- According to the model code, Ministers cannot announce any financial grants in any form, make any promise of construction of roads, provision of drinking water facilities, etc or make any ad hoc appointments in the government. departments or public undertakings.
- These are the core guidelines relating to the government.
- But in reality, no government is allowed by the ECI to take any action, administrative or otherwise, if the ECI believes that such actions or decisions will affect free and fair elections.
- A recent decision of the ECI to stop the Government of Kerala from continuing to supply kits containing rice, pulses, cooking oil, etc is a case in point.
- The Supreme Court had in S. Subramaniam Balaji vs Govt. of T. Nadu & Ors (2013) held that the distribution of colour TVs, computers, cycles, goats, cows, etc, done or promised by the government is in the nature of welfare measures and is in accordance with the directive principles of state policy, and therefore it is permissible during an election.
- So, how can the distribution of essential food articles which are used to stave off starvation be electoral malpractice?
Consider the question “The model code of conduct issued by the Election Commission of India is in the forms of guidelines and lacks legal backing. In light of this, examine the issues that arise due to the lack of legal backing.”
Conclusion
There is no doubt that the ECI, through the conduct of free and fair elections in an extremely complex country, has restored the purity of the legislative bodies. However, no constitutional body is vested with unguided and absolute powers.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
National Green Tribunal has directed Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Delhi Pollution Control Committee (DPCC) to take remedial action against the three waste-to-energy plants in Ghazipur, Okhla and Narela-Bawana.
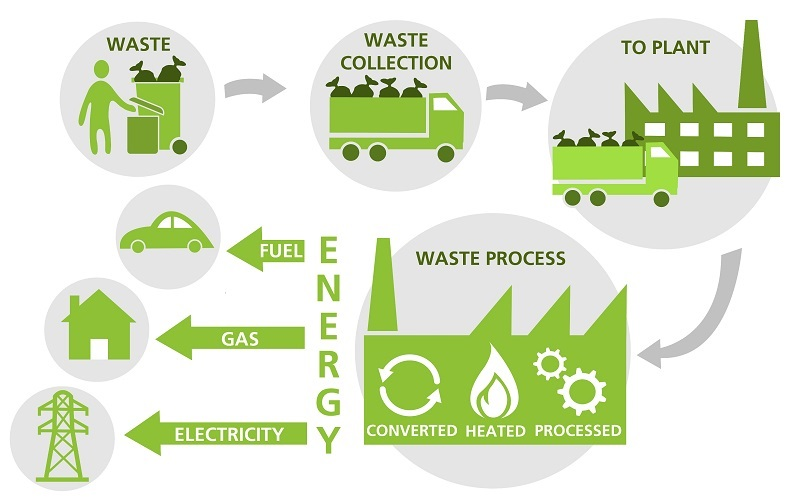
Waste to Energy:
- Waste to Energy or Waste to Power is the process of generating energy in the form of electricity and heat from the primary treatment of waste.
Methods for waste to Power generation:
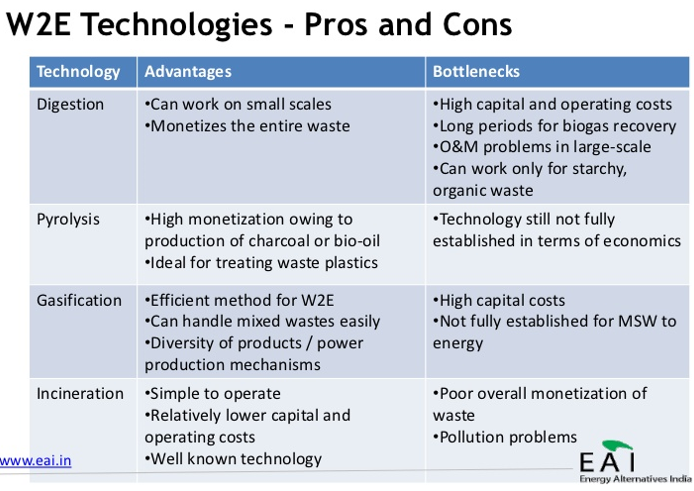
1. Thermal technologies:
- Incineration:
- It is the most common and popular method for waste to energy generation.
- The organics from the waste collected are burnt at high temperatures.
- Gasification: Produces combustible gas, hydrogen, synthetic fuels
- Thermal depolymerization: Produces synthetic crude oil, which can be further refined
- Pyrolysis: Produces combustible tar/bio-oil and chars
- Plasma arc gasification or plasma gasification process (PGP): Produces rich syngas including hydrogen and carbon monoxide usable for fuel cells or generating electricity to drive the plasma arch.
2. Non-thermal technologies:
- Anaerobic digestion: Biogas rich in methane
- Fermentation production: Examples are ethanol, lactic acid, hydrogen
- Mechanical biological treatment: Combines a sorting facility with a form of biological treatment such as composting.
Advantages of WTE plants:
- Decreases quantity of waste
- Efficient waste management
- Production of heat and power
- Reduction of pollution
- Incinerators have filters for trapping pollutants
- Saves on transportation of waste
- Provides better control over odour and noise
- Prevents the production of methane gas
Challenges for India:
- Lack of general awareness on waste management
- Unsegregated waste
- High moisture content
- Unorganized sector
- High wear and tear of equipment due to foreign materials
- Only electricity demand
- Cycle Efficiency is low
- Lack of enforcement of rules / regulations
- Lack of Transparency in plant management
- Lack of adequate waste disposal cost
- Lack of customization of plant and machinery to suit Indian condition
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
To provide relief to stressed companies, the Finance Ministry expanded the scope of a government-guaranteed credit facility to healthcare and stressed sector companies that have loan dues for up to 60 days (or SMA-1 accounts),as against 30 days earlier (SMA-0).

Key highlights:
- This has been expected to provide partial relief to stressed firms facing fresh uncertainty and business risks due to fresh lockdowns and restrictions being imposed by states.
- SMA-1 borrowers in the healthcare sector and 26 other high stress sectorsare now eligible under ECLGS 2.0.
- Companies from hospitality, travel & tourism, and leisure & sportingsectors are expected to benefit from the relaxation in the scheme.
- Accounts that are classified as non-performing assets or where overdueshave crossed 60 days (SMA-II) are not eligible.
- Companies that had loan dues up to 30 days (Special Mention Accounts or SMA-0) as on February 29, 2020, were being provided additional credit of 20 per cent outstanding under the scheme, which will now be given to SMA-1 accounts as well.
- The government has recently extended the ECLGS till June 2021, as against March 31, 2021 earlier.
About the ECLGS scheme:
- The Finance Ministry unveiled a Rs. 20 Lakh Crore comprehensive package, known as the Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS), in view of the economic distress caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- This package is in aid of MSME sector, addressing working capital needs, operational liabilities and restart business impacted due the COVID-19 crisis.
- Borrowers with up to Rs. 25 Crore outstanding as on Feb 29, 2020 and up to Rs. 100 Crore annual turnover for FY 2020 are eligible for this scheme.
- Business Enterprises, MSMEs constituted as Proprietorship, Partnership, registered company, trusts and Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) shall also be eligible.
- Borrower accounts which had NPA or SMA-2 status as on Feb 29, 2020 shall not be eligible under the scheme.
- 20% of the total outstanding credit of borrowers can be sanctioned as a loan under the Guaranteed Emergency Credit Line (GECL), for those who having a loan as on Feb 29, 2020.
Special Mention Accounts:
- SMAs are those assets/accounts that shows symptoms of bad asset qualityin the first 90 days itself or before it being identified as NPA.
- The classification of Special Mention Accounts (SMA) was introduced by the RBI in 2014, to identify those accounts that has the potential to become an NPA/Stressed Asset.
- Logic of such a classification is because some accounts may turn NPA soon.
- An early identification will help to tackle the problem better.
- There are four types of Special Mention Accounts – SMA-NF, SMA 0, SMA1 and SMA 2.
- The Special Mention Accounts are usually categorized in terms of duration.
- For example, in the case of SMA -1, the overdue period is between 31 to 60 days.
- On the other hand, an overdue between 61 to 90 days will make an asset SMA -2.
- But some ‘Special Mention’ assets are identified on the basis of other factors that reflect sickness/irregularities in the account (SMA -NF).
- In the case of SMA -NF, non-financial indications about stress of an asset is considered.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Great Indian Bustard
Mains level: Wildlife conservation efforts
The recent shooting of two Great Indian Bustards (GIBs) in Pakistan’s Cholistan desert has left wildlife activists in Rajasthan shocked and outraged.
Great Indian Bustards
- The GIB is one of the heaviest flying birds and can weigh up to 15 kg which grows up to one metre in height.
- In July 2011, the bird was categorised as “critically endangered” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- It is considered the flagship grassland species, representing the health of the grassland ecology.
- For a long, conservationists have been demanding to secure this population, warning that the bird might get extinct in the coming decades.
- It would become the first mega species to disappear from India after Cheetah in recent times.
- Till the 1980s, about 1,500-2,000 Great Indian Bustards were spread throughout the western half of India, spanning eleven states.
- However, with rampant hunting and declining grasslands, their population dwindled.
Why in news?
- The GIB, which is the state bird of Rajasthan, is considered India’s most critically endangered bird.
- It is one of the most critically threatened species in India, with less than 150 birds left in the wild.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which one of the following groups of animals belongs to the category of endangered species?
(a) Great Indian Bustard, Musk Deer, Red Panda, Asiatic Wild Ass
(b) Kashmir Stag, Cheetah, Blue Bull, Great Indian Bustard.
(c) Snow Leopard, Swamp Deer, Rhesus Monkey, Saras (Crane)
(d) Lion Tailed Macaque, Blue Bull, Hanuman Langur, Cheetah
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GAVI
Mains level: Paper 2- Issues with vaccine diplomacy
Amid the second wave of covid pandemic, India’s decision to supply vaccine to foreign countries has been questioned from various quarters. The article deals with this issue.
Issue of vaccine supply to foreign countries
- While responding to a question Minister of State in the Ministry of External Affairs noted that India was sending these vaccines abroad in the form of grant, commercial sales of manufacturers GAVI’s COVAX facility.
- The supply to GAVI’s COVAX facility is an obligation since India is a member of this multilateral body and also a recipient of vaccines from this body.
- By doing this, India wishes to signal that it is a responsible global power which does not self-obsessively think of itself alone.
- This desire to be a good global citizen can be traced to the Objective Resolution moved by Jawaharlal Nehru in the Constituent Assembly on December 13, 1946.
- The premise of the ideal ‘Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’ is no different to that of the Objective Resolution.
Factors to consider
- The government made estimates of the vaccines that could be sent abroad on the interplay of three factors: domestic production, the demands of the national vaccine programme and requests for vaccines manufactured in India.
- What is not known is how these factors were collectively addressed in the decision-making process.
- It is also argued that it was obligatory to send vaccines contracted under GAVI’s COVAX facility.
- However, sovereign states can always invoke supreme national interest to over-ride obligations.
- Certainly, the vaccines sent as grants were voluntary and the commercial contracts of the company concerned could always be disregarded under existing laws.
Conclusion
The government needs to convince Indians that the vaccine exports have not been made at the cost of their health.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Multipolar global
With the declining American supremacy in the global order, the world is set for new global order led by the developing countries. The article deals with this rise of alternate global order.
Factors that explains decentred and pluralistic global order
- The international order is under threat of the rising economic power of the BRICS nations, with China dominating in its economic and military capacity.
- It is apparent that the future of global politics requires a significant agenda in the hands of the rising powers that are aggressively building a parallel economic order envisaging new centres of hegemonic power.
- It forebodes the final decline of American ascendancy.
- It was the Bandung Conference of 1955, a meeting of Asian and African states, most of which were newly independent, that set the schema for the rise of Asia, politically and economically.
- The confrontational stance was therefore the expected corollary in third world struggles to create a parallel order.
- America will continue to play a prime role in international affairs though its image representing universal brotherhood has sharply declined under the Trump regime.
- The rising tide of far-right ultra-nationalism and ethnic purity experienced in the Brexit phenomena, in Trumpism and in the promotion of the right-wing agenda in India, has set in motion the wearing down of liberal democracy.
- Other threats such as terrorism, ethnic conflicts and the warning of annihilation owing to climate change necessarily demand joint international action where American “exceptionalism” becomes an incongruity and an aberration.
- This indeed has chipped away at the American global supremacy.
- The world is, as a result, witness to a more decentred and pluralistic global order.
New world order led by developing countries
- Though pandemic has ravaged economies such as Brazil, India, Turkey and South Africa into a downward spiral, in the post-pandemic period, these economies would rise to meet the American-led liberal hegemonic world order.
- With China spearheading Asian regionalism, a serious challenge is possible.
- China must strengthen the opposition to the West through the promotion of regional multilateral institutions.
- More than having individual partners or allies, China must embrace and give a push to multilateral affiliations in order to not further exacerbate regional tensions.
- Power rivalry in a multipolar world would remain a possibility with military conflict not ruled out.
- However, the capabilities of the rising economies cannot be underestimated.
- China and India clearly have the age-old potential to lead as, historically, they have been pioneers of some of the oldest civilisations in the world.
- China is indisputably a serious rival to the U.S. in the South China Sea, a world leader in renewable energy, and a formidable actor on the global stage of investment and trade, penetrating India, Israel, Ethiopia and Latin America.
- Thus, a kind of dualism persists in the world order with no clear hegemony that can be bestowed on one single nation.
Conclusion
It is feared that there could be a possibility of a multipolar world turning disordered and unstable, but it is up to the rising nations to attempt to overcome territorial aspirations and strike a forceful note of faith on cultural mediation, worldwide legitimacy, and the appeal of each society in terms of its democratic values.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Currency Manipulation
Mains level: Impact of Currency Manipulation
India is one of the 11 countries on the US Treasury’s ‘Monitoring List’ with regard to their currency practices for the first time in the Biden administration.
What is Currency Manipulation?
- Currency manipulation refers to actions taken by governments to change the value of their currencies relative to other currencies in order to bring about some desirable objective.
- The typical claim – often doubtful – is that countries manipulate their currencies in order to make their exports effectively cheaper on the world market and in turn make imports more expensive.
Why do countries manipulate their currencies?
- In general, countries prefer their currency to be weak because it makes them more competitive on the international trade front.
- A lower currency makes a country’s exports more attractive because they are cheaper on the international market.
- For example, a weak Rupee makes Indian exports less expensive for offshore buyers.
- Secondly, by boosting exports, a country can use a lower currency to shrink its trade deficit.
- Finally, a weaker currency alleviates pressure on a country’s sovereign debt obligations.
- After issuing offshore debt, a country will make payments, and as these payments are denominated in the offshore currency, a weak local currency effectively decreases these debt payments.
US treasury’s criteria
To be labelled a manipulator by the U.S. Treasury:
- Countries must at least have a $20 billion-plus bilateral trade surplus with the US
- foreign currency intervention exceeding 2% of GDP and a global current account surplus exceeding 2% of GDP
Implications for India
- India has traditionally tried to balance between preventing excess currency appreciation on the one hand and protecting domestic financial stability on the other.
- India being on the watch list could restrict the RBI in the foreign exchange operations it needs to pursue to protect financial stability.
- This comes when global capital flows threaten to overwhelm domestic monetary policy.
- The two most obvious consequences could be an appreciating rupee as well as excess liquidity that messes with the interest rate policy of the RBI.
- Indian policymakers have to be sensitive to the unpredictable nature of policy-making in the US under Trump, especially concerning global trade.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Whitest paint and its composition
Mains level: NA
Engineers in the US have created what they are calling the whitest paint yet.
What is the whitest paint?
- The researchers created an ultra-white paint pushing the limits of how white paint can be.
- This older formulation was made of calcium carbonate, while the new one is made up of barium sulphate, which makes it more white.
- The newer paint is whiter and keeps the surface areas it is painted on cooler than the formulation before this could.
- If this new paint was used to cover a roof area of 1,000 square feet, it may be able to get a cooling power of 10 kilowatts.
- Most ovens use up about 2.3 kilowatts to run for an hour and a 3 ton 12 Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) air conditioner uses up about 3 kilowatts to run for an hour.
The researchers have claimed that this paint may be the closest equivalent to the blackest black paint called “Vantablack” which is able to absorb up to 99.9 per cent of visible light.
What determines if a colour absorbs or reflects light?
- To understand how this works one needs to note that whenever an object is seen by the eye, it is either because of sunlight or the artificial light in the room.
- This light is made up of seven different colours (Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red or VIBGYOR).
- Specifically, light is made up of wavelengths of different colours.
- If an individual is looking at a sofa that is green, this is because the fabric or material it is made up of is able to absorb all the colours except green.
- This means that the molecules of the fabric reflect the green coloured wavelengths, which is what the eye sees.
- Therefore, the colour of any object or thing is determined by the wavelength the molecules are not able to absorb.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Rainbow is produced when sunlight falls on drops of rain. Which of the following physical phenomena are responsible for this?
- Dispersion
- Refraction
- Internal reflection
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
What determines which wavelength of light will be reflected and absorbed?
- This is dependent on how electrons are arranged in an atom (the building block of life, an atom is made up of electrons, protons and neutrons.
- These three particles make up everything in the known universe from mountains, planets, humans to pizza and cake).
- In contrast, if an object is black, it is because it has absorbed all the wavelengths and therefore no light is reflected from them.
- This is the reason that darker objects, as a result absorbing all wavelengths tend to heat up faster (during absorption the light energy is converted into heat energy).
So, what makes the paint so white?
There are two features:
- One is the paint’s high concentration of a chemical compound called barium sulfate, which is also used to make photo paper and cosmetics white.
- The second feature is that the team has used different sized particles of this chemical compound, which means different sizes scatter different amounts of light.
In this way, the varying size of particles of the compound makes sure that the paint can scatter more of the light spectrum from the sun.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: La Soufriere
Mains level: Not Much

Sulphur dioxide (SO2) emissions from La Soufriere volcano eruption in the Caribbean have reached all the way to India.
Why in news?
- Its eruption has sparked fear of increased pollution levels in the northern parts of India and acid rain.
- Volcanic plumes can cause aviation and air quality hazards.
La Soufriere
- It is an active stratovolcano on the Caribbean island of Saint Vincent in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
- It is the highest peak in Saint Vincent and has had five recorded explosive eruptions since 1718.
Impact of such eruptions
- Volcanic emissions reaching the stratosphere can have a cooling effect on global temperatures.
- The most significant climate impacts from volcanic injections into the stratosphere come from the conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphuric acid, which condenses rapidly in the stratosphere to form fine sulphate aerosols.
- The aerosols increase the reflection of radiation from the Sun back into space, cooling the Earth’s lower atmosphere or troposphere.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which of the following adds/add carbon dioxide to the carbon cycle on the planet Earth?
- Volcanic action
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
- Decay of organic matter
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cynodonts
Mains level: NA
The Tiki Formation in Madhya Pradesh, a treasure trove of vertebrate fossils, has now yielded a new species and two genera of cynodonts, small rat-like animals that lived about 220 million years ago.
Tiki Formation
- The Tiki Formation is a Late Triassic geologic formation in Madhya Pradesh.
- Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus.
- Phytosaur remains attributable to the genus Volcanosuchus have also been found in the Tiki Formation.
- The genera Tikiodon, Tikitherium and Tikisuchus and species Rewaconodon tikiensis, Hyperodapedon tikiensis and Parvodus tikiensis have been named after the Tiki Formation.
Findings of the new study

- The fossil teeth were studied for size, crown shape, structure of the cusps and compared with previously reported cynodonts.
- Cynodonts are important in evolutionary studies as this group ultimately gave rise to the present-day mammals.
- By studying their molar and premolar teeth, we see how they slowly evolved and modified.
- Their crown shape shows that these animals are actually intermediate forms that are very near to the mammalian line of evolution.
- Cynodonts and living mammals both belong to a group of egg-laying vertebrates (amniotes) called synapsids.
- The close relationship of cynodonts with living mammals is seen in their bones.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GDPR
Mains level: Paper 3- Data governance
The article explains the data governance norms we need to adopt to secure better societal outcomes.
Whatsapp privacy issue
- New terms of service circulated by WhatsApp, caused a stir among the user.
- It informed users that data about chats with business accounts would be shared with Facebook.
- These policies seemed unfair to India as they were not applicable to the European Union (EU), given their strong data protection policies.
Acceptable levels of data exchange
- Default norms provide power to the tech platforms to collect, analyse and monetize data with complete control.
- This undergirds business models that seem undesirable for society—with harms to privacy and free speech.
- Global discussions about alternatives to the “exchange of data for free services” are becoming nuanced.
3 Norms in the data governance
1) Recognition of individual and collective rights related to data
- It was generally accepted that extraction of data to access free services was a fair exchange with individuals.
- Emergence of existential threats related to privacy and democracy have highlighted the role of guaranteeing human and civil rights.
- There has been significant global progress through regulations on individual data rights.
- A United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) report claims that 128 of 194 countries have put in place legislations for data protection and privacy.
- However, this protection is insufficient as it is centered on individuals and does not account for safety of groups.
- The next wave of data governance ideas will seek to protect collective harms and build on the foundation of individual agency and control.
2) Data sovereignty
- One-size-fits all global norms of data governance are changing and being replaced by region-specific ideas.
- Greater acceptance for “data sovereignty” assertions across India and Europe is a welcome shift towards crafting governance that is respectful of local nuances and inclusive of civic participation.
- The EU general data protection regulation (GDPR) had created an early lighthouse example.
- On the other hand, the US has adopted a light regulation approach—there is no comprehensive country-wide data protection law.
- Closer home, India is finalizing the contours of a country-wide and cross-sector personal data protection bill, which reflects local norms.
3) Value creation for all stakeholders
- So far, data economy has operated in a completely unregulated space, creating a “winner takes all” market, with concentrated profits and little contribution to local taxes.
- A healthy economy requires value creation for all stakeholders.
- As tech platforms take up the profitable role of acting as the gateway to all information and social connections, they have a greater accountability and responsibility to contribute to the economy.
- India’s digital tax through the 2% “equalization levy” is an attempt to make the tech giants pay for revenues earned in India.
Consider the question “What should be norms of data governance we must adopt for achieving better societal outcomes?”
Conclusion
Formal adoption of regulations and setting up of enforcement institutions will lead to meaningful progress in the right direction.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Eurasian Economic Union
Mains level: Paper 2- Multipolar world
Four middle powers: India, Japan, China and Turkey anchor the world to multipolarity. The article deals with this issue.
New cold war
- In respect of three crucial relationships, namely China, Russia and Iran, Mr. Biden is following in the footsteps of his predecessor.
- Mr. Biden has also extended his firm backing for the “Indo-Pacific” and the associated alignment — the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, or Quad for short.
- The U.S. continues to view China as its principal adversary on the world stage and that it will use the Quad to challenge China in the Indo-Pacific.
- The U.S.’s hostility for Russia goes back to the latter’s war with Ukraine and the occupation of Crimea in 2014, followed by allegations of Russian cyber-interference in the U.S. presidential elections of 2016.
- U.S. animosity has encouraged China and Russia to solidify their relations.
- The two countries have agreed to harmonise their visions under the Eurasian Economic Union sponsored by Russia and China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- This idea has now been subsumed under the ‘Greater Eurasian Partnership’ to which both are committed.
- Thus, the new Cold War is now being reflected in a new geopolitical binary — the Indo-Pacific versus Eurasia.
How middle powers can play an important role
- Four nations, Japan, Iran, Turkey and India, which, as “middle powers”, have the capacity to project power regionally, build alliances, and support (or disrupt) the strategies
- But all four seems to be already aligned.
- Japan and India are part of the Quad and have substantial security ties with the U.S.
- Iran has found strategic comfort with the Sino-Russian alliance.
- Turkey, a NATO member, has found its interests better-served by Russia and China rather than the U.S. and its European allies.
- So, why the uncertainty? The main reason is that, despite the allure, the four nations are not yet prepared to join immutable alliances.
Why the middle powers are reluctant to join alliances
1) India’s China concerns
- India has been expanding defence ties with the U.S. since 2016, by massive defence purchases and agreements on inter-operability and intelligence-sharing and frequent military exercises, as also the elevation of the Quad to ministerial level.
- This might have signalled to China that India was now irreversibly in the U.S. camp.
- But China has a point: while the Quad has made India a valuable partner for the U.S. in the west Pacific, neither the U.S. nor the Quad can address the challenges it faces at its 3,500-kilometre land border with China.
- Moreover, the U.S.’s intrusive approach on human rights issues ensures that India will need to manage its ties with China largely through its own efforts while retaining Russia as its defence partner.
2) Sino-Japan relations
- Japan has an ongoing territorial dispute with China relating to the Senkaku Islands in the East China Sea.
- But there is more to Sino-Japanese relations: in 2019, 24% of Japanese imports came from China, while 19% of its exports went to China, affirming the adage.
3) Why Iran is reluctant
- The crippling sanctions on Iran and the frequent threats of regime change make it a natural ally of the Sino-Russian axis.
- However, its strategic culture eschews long-term security alignments.
4) Why Turkey is reluctant to join
- Turkey is steady distancing from its western partners and increasing geopolitical, military and economic alignment with Russia and China.
- But Turkey still wishes to keep its ties with the U.S. intact and retain the freedom to make choices.
- Its “New Asia” initiative involves the strengthening of east-west logistical and economic connectivity backed by western powers and China.
Consider the question “What are the factors India need to consider as it deepens its involvement in the Quad?”
Conclusion
As the clouds of the new Cold War gathers over the world, these four nations could find salvation in “strategic autonomy” — defined by flexible partnerships, with freedom to shape alliances to suit specific interests at different times.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pre-pack in IBC
Mains level: Paper 3- Pre-packs for MSME in IBC
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code was amended recently taking into account its creditor centric approach.
Introducing pre-packs for MSMEs
- IBC was amended last week, through an ordinance.
- The amendment sought to address a structural weakness in India’s resolution architecture by introducing the concept of pre-packs for micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs).
- The pre-packaged framework involves a privately negotiated contract between the promoters of a financially distressed firm and its financial creditors to restructure the company’s obligations.
- This contract is negotiated within the IBC architecture but before the commencement of insolvency proceedings.
- Once accepted by creditors, the plan must be presented to the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) for approval.
How this framework is different from the existing framework
- A firm’s promoters could have submitted a resolution plan even after it enters the insolvency proceedings, subject to restrictions imposed under Section 29A which clarifies all those who are ineligible for submitting the resolution plan.
- So, the difference in the new framework essentially boils down to the following.
1) Control of the firm
- Under the IBC, upon the initiation of insolvency proceedings, control of a firm is taken away from promoters, and a resolution professional is appointed.
- Now, during the restructuring, the promoter, through the pre-pack, retains control over the firm.
- So effectively, we have transitioned from a “creditor-in-control” model of resolution to a “debtor-in-control” model of restructuring.
- This amendment, which creates a framework for restructuring, without the promoter losing control over the firm, addresses a lacuna in the IBC.
2) Issue of price discovery
- In this arrangement, the is an absence of an open bidding process, such as during the resolution phase.
- This might raise questions over price discovery, especially if value maximisation for creditors is the yardstick to measure the efficacy of IBC.
- This marks a fundamental change in the IBC framework.
Why the changes were needed
- The IBC, while it has strengthened the position of the creditors, had swung to an extreme.
- The resolution architecture as it stood prior to this amendment was perceived as being too creditor-centric.
- Wresting control from the “errant” promoter, comes with its own set of consequences.
- The notion that all business failure is due to the connivance of promoters needs to be reconsidered.
- Firms may be unable to pay their obligations simply because the economic cycle has turned.
- Or projects have not materialised as expected.
- Of the 2,422 cases closed since IBC came into being, 46.5 per cent of the firms have gone into liquidation, while a resolution plan has been accepted in only 13.1 per cent of the cases.
- This indicates liquidation bias.
- At a time when there aren’t enough buyers in the economy, the IBC process would lead to significant value destruction.
How it will benefit both creditor and promotors
- Promoters get to hold on to their firms, and exit the process with more manageable obligations, making this an attractive proposition.
- For creditors, considering the liquidation bias in IBC, as long as the value of the restructured obligation is greater than the liquidation value it makes sense to choose this option.
- Moreover, this entire process remains outside the restructuring framework of the central bank.
- And, considering that the pre-packs encompass all financial creditors, as opposed to RBI’s restructuring schemes which deal only with banks.
- This takes into account the concerns of other financial creditors as well.
Consider the question “How far IBC has succeeded in improving the insolvency regime in India? How the concepts of pre-packs is different from the previous system?
Conclusion
This approach will help clarify issues, bring about greater certainty to the process. And, once the creases are ironed out, it will create a permanent mechanism for restructuring debts.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: State of World Population Report 2021
Mains level: Womens' right issues
The United Nations Population Fund’s (UNFPA) flagship State of World Population Report 2021 titled ‘My Body is My Own’ was recently launched.
State of World Population Report 2021
- The State of World Population report is UNFPA’s annual flagship publication.
- It has been published yearly since 1978.
- It highlights emerging issues in the field of sexual and reproductive health and rights, bringing them into the mainstream and exploring the challenges and opportunities they present for international development.
Key findings of the 2021 report
This is the first time a UN report has focused on bodily autonomy, defined as the power and agency to make choices about your body without fear of violence or having someone else decide for you.
- The report measures both women’s power to make their own decisions about their bodies and the extent to which countries’ laws support or interfere with a woman’s right to make these decisions.
- The data show a strong link between decision-making power and higher levels of education.
The report shows that in countries where data are available:
- Only 55 per cent of women are fully empowered to make choices over health care, contraception and the ability to say yes or no to sex.
- Only 71 per cent of countries guarantee access to overall maternity care.
- Only 75 per cent of countries legally ensure full, equal access to contraception.
- Only about 80 per cent of countries have laws supporting sexual health and well-being.
- Only about 56 per cent of countries have laws and policies supporting comprehensive sexuality education.
In essence, hundreds of millions of women and girls do not own their own bodies. Their lives are governed by others.
The report also documents many other ways that the bodily autonomy of women, men, girls and boys is violated, revealing that:
- Twenty countries or territories have “marry-your-rapist” laws, where a man can escape criminal prosecution if he marries the woman or girl he has raped.
- Forty-three countries have no legislation addressing the issue of marital rape (rape by a spouse).
- More than 30 countries restrict women’s right to move around outside the home.
- Girls and boys with disabilities are nearly three times more likely to be subjected to sexual violence, with girls at the greatest risk.
Solutions: the power to say yes, the right to say no
- The report shows how efforts to address abuses can lead to further violations of bodily autonomy.
- For example, to prosecute a case of rape, a criminal justice system might require a survivor to undergo an invasive so-called virginity test.
- Real solutions, the report finds, must take into account the needs and experiences of those affected.
Indian scenario
- In India, according to NFHS-4 (2015-2016), only about 12% of currently married women (15-49 years of age) independently make decisions about their own healthcare, while 63% decide in consultation with their spouse.
- For a quarter of women (23%), it is the spouse that mainly takes decisions about healthcare.
- Only 8% of currently married women (15-49 years) take decisions on the use of contraception independently, while 83% decide jointly with their spouse.
- Information provided to women about the use of contraception is also limited — only 47% of women using a contraceptive were informed about the side effects of the method, and 54% of women were provided information about other contraceptives.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NPS
Mains level: Various pension schemes in India

The National Pension System (NPS) will no longer compel investors to convert 40% of their accumulated retirement corpus into an annuity.
An annuity is a long-term investment that is issued by an insurance company and is designed to help protect you from the risk of outliving your income. Through annuitisation, your purchase payments (what you contribute) are converted into periodic payments that can last for life.
Why such a move?
- Poor yields on annuities and high inflation are translating into negative returns.
- Since annuities are taxable, deducting the tax and factoring in inflation means annuities are yielding negative returns.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Who among the following can join the National Pension System (NPS)?
(a) Resident Indian citizens only
(b) Persons of age from 21 to 55 only
(c) All-State Government employees joining the services after the date of notification by the respective State Governments
(d) All Central Governments Employees including those of Armed Forces joining the services on or after 1st April 2004
National Pension Scheme (NPS)
- NPS is a government-sponsored pension scheme. It was launched in January 2004 for government employees.
- It was extended to all citizens of Indian on a voluntary basis from May 2009 and to corporates in December 2011 and to Non-Resident Indians in October 2015.
- PFRDA is the statutory authority established by an enactment of the Parliament, to regulate, promote and ensure orderly growth of the NPS and pension schemes to which this Act applies.
- The scheme allows subscribers to contribute regularly in a pension account during their working life.
- On retirement, subscribers can withdraw a part of the corpus in a lump sum and use the remaining corpus to buy an annuity to secure a regular income after retirement.
Who can join NPS?
- Any Indian citizen between 18 and 60 years can join NPS.
- The only condition is that the person must comply with know your customer (KYC) norms.
- An NRI can join NPS. However, the account will be closed if there is a change in the citizenship status of the NRI.
- Now, any Indian citizen, resident or non-resident and OCIs are eligible to join NPS till the age of 65 years.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Azhdarchid pterosaurs
Mains level: Not Much

Azhdarchid pterosaurs, the giant reptiles that flew in the skies nearly 65 million years ago, had necks longer than that of a giraffe (i.e. more than 6fts).
What are pterosaurs?
- Pterosaurs are reptiles that are close cousins of dinosaurs, the first animals after insects to evolve powered flight.
- Some pterosaurs were as large as an F-16 fighter jet, while others were as small as a paper aeroplane.
- Pterosaurs went extinct about 65-66 million years ago (end of the Cretaceous period) and while they did not leave any of their descendants behind.
- One reason for this is that few pterosaurs lived in places where fossils tend to form, because of which their bones are preserved poorly.
Revise the geological timescale from your NCERT textbook.
Azhdarchid pterosaurs
- They are one type of pterosaur and one of the distinguishing characteristics about them is how big they were, especially their long necks.
- Some of these pterosaurs were the largest animals to have flown in the sky, with wingspans greater than 30 feet.
- The name azhdarchid, as per a blog on Scientific American comes from Azhdarcho, a Central Asian form named by Russian ornithologist and palaeontologist in 1984.
What have the researchers found?
- Researchers involved in this study were curious about how the reptile’s long neck functioned and how it was able to support the pterosaur’s body, allowing them to capture and eat heavy prey animals.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NIXI
Mains level: Not Much
The Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) has inaugurated three path-breaking initiatives for the National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI).
What is NIXI?
National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI) is a not-for-profit organization (section 8 of the Companies Act 2013) working since 2003 for spreading the internet infrastructure to the citizens of India through the following activities:
- Internet Exchanges through which the internet data is exchanged amongst ISP’s, Data Centers and CDNs.
- .IN Registry, managing and operation of .IN country-code domain and .भारत IDN domain for India.
- IRINN, managing and operating Internet protocol (IPv4/IPv6).
Which are the three new initiatives?
(1) IPv6 Expert Panel (IP Guru) (https://nixi.in):
- IP Guru is a group to extend support to all the Indian entities who are finding it technically challenging to migrate and adopt IPv6.
- In addition to this, the IPv6 expert group will help in identifying & hiring an agency that will help end customer by providing necessary technical support to adopt IPv6.
- This panel will guide all such Indian entities and help in increasing IPv6 adoption.
Note: An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two main functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing.
(2) NIXI Academy (https://training.nixi.in):
- NIXI Academy is created to educate technical/non-technical people in India to learn and relearn technologies like IPv6 which are normally not taught in Educational Institutes.
- NIXI academy comprises an IPv6 training portal which is developed with the help of various technical experts in order to provide mass training to the community.
- The easy-to-use platform helps network operators and educators understand networking best practices, principles and techniques; manage Internet resources better; and use appropriate Internet technologies more effectively.
(3) NIXI-IP-INDEX (https://ipv6.nixi.in):
- NIXI has developed an IPv6 index portal for the Internet community.
- NIXI-IP-INDEX portal will showcase the IPv6 adoption rate in India and across the world.
- It can be used to compare the IPv6 Indian adoption rate with other economies in the world.
- NIXI will populate this portal with web adoption in IPv6, IPv6 traffic etc. in the coming days.
- This portal will motivate organisations to adopt IPv6, provide inputs for planning by technical organisations and research by academicians.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UNCLOS
Mains level: Paper 2- Understanding the rights of the coastal state under UNCLOS
The explains the issues involved in the recent incident in which US position on freedom of navigation under UNCLOS differed from India’s.
Different positions
- On April 7, the U.S.’s 7th Fleet Destroyer conducted a ‘Freedom of Navigation Operation’ inside India’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- This exercise was conducted without requesting India’s consent.
- Moreover, the U.S. 7th Fleet noted in its press release that India’s requirement of prior consent is “inconsistent with international law”.
- However, India asserted that the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) “does not authorize other States to carry out in the Exclusive Economic Zone and on the continental shelf, military exercises or manoeuvres, in particular those involving the use of weapons or explosives, without the consent of the coastal state”.
- The question is, can countries carry out military exercises in another country’s EEZ and if yes, subject to what conditions?
UNCLOS Provisions for EEZ
- UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) binds all its signatories and customary international law binds all states, subject to exceptions like the doctrine of persistent objector.
- As per the UNCLOS, EEZ is an area adjacent to the territorial waters of a coastal state.
- Under UNCLOS, a sovereign coastal state has rights and duties relating to management of natural resources; establishment and use of artificial islands, installations and structures; marine scientific research; and protection of the marine environment.
- India is a party to the UNCLOS while the U.S. is not.
- Article 87 provides for freedom of the high seas under which all states have the freedom of navigation.
- Apart from that, states enjoy the freedom of overflight and of the laying of submarine cables and pipelines as well as other internationally lawful uses of the sea.
- However, the freedom of navigation is subject to the conditions laid down under the UNCLOS and other rules of international law.
- In addition to it, Article 58 (3) stipulates another qualification: “In exercising their rights and performing their duties under this Convention in the exclusive economic zone, States shall have due regard to the rights and duties of the coastal State and shall comply with the laws and regulations adopted by the coastal State…”.
So, what laws and regulation are adopted by India under Article 58 (3) of UNCLOS
- The relevant Indian law in this regard is the Territorial Waters, Continental Shelf, Exclusive Economic Zone and Other Maritime Zones of India Act, 1976.
- Section 7 sub-section 9 of this Act recognises the freedom of navigation of the ships of all States but makes them subject to the exercise of rights by India within the zone.
- Article 310 of the UNCLOS does permit states to make declarations in order to explain the relationship between the Convention and their own laws.
- The declaration by India in 1995 also states that India “understands that the provisions of the Convention do not authorize other States to carry out in the exclusive economic zone and on the continental shelf military exercises or manoeuvres.
Way forward
- Non-consensual military activities that hinder the lawful enjoyment of rights of coastal states need not be permissible.
- Also, a coastal state is naturally concerned about military exercises and manoeuvres posing a risk to its coastal communities, its installations or artificial islands, as well as the marine environment.
- Thus, any state which wishes to conduct such exercises must do so only in consultation with the coastal state since the coastal state is the best judge of its EEZ.
- Both India and the U.S. should negotiate such concerns for the maintenance of international peace and security.
Consider the question “What are the rights of coastal state on its Exclusive Economic Zone under UNCLOS? “
Conclusion
On a conjoint reading of Articles 58, 87 and 310, it can be argued that freedom of navigation cannot be read in an absolute and isolated manner.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Second wave of covid
The article suggests ways to deal with the second wave of Covid in India.
What explains the bigger second wave
- The size of any epidemic is a function of three things:
- 1) The size of the pool of the susceptible population.
- 2) The pattern of contact between the members of the population (frequency, mix, closeness and duration).
- 3) Probability of spread during that contact (infectiousness of the agent).
Let us have a look at these 3 factors in the current context
- As many people have already been infected in the first wave, the pool of susceptibles should be smaller.
- Serosurveys also support this as they found that about 25 per cent of people had already been infected nationally.
- However, this is an average and hides significant variations by state, age and place of residence.
- Populations with lower seroprevalence become the potential pool for the second wave.
- Given India’s large population base, the actual number of people are sufficiently large to enable multiple waves till we achieve a more even spread of protected people.
- The persistence of protectiveness of antibodies of those already infected and their cross-protectiveness to newer strains is not well established.
- Vaccination would reduce the pool of susceptibles.
- However, the current level of vaccination coverage is not sufficient to make a significant difference to this wave, given the fact that we are already riding it.
- It is a good strategy to prevent the next wave, if we can achieve substantial coverage with it.
- Vaccination also prevents severe disease, and hence reduces the death toll.
- With the removal of most restrictions, the probability of contact between individuals has risen sharply.
Way forward
- What can and should be avoided are super-spreader events like a crowded park, the Kumbh mela, election rallies, etc.
- A much stronger community engagement with a robust communication strategy and lesser emphasis on “criminalising” inappropriate behaviour is required.
- A nuanced communication campaign is the need of the hour and is conspicuous by its complete absence.
- What is urgently needed is a robust evidence-based communication campaign.
- Such a campaign would involve proactive serial assessment of the community perceptions and concerns, testing and refining messages through an evolving campaign.
- A district-specific strategy of “test, trace, treat” along with containment measures (isolation and quarantine) is still the best way to deal with the situation.
- We also need to put a stop to political bickering; it erodes public trust and confidence.
Conclusion
Dealing with the second wave should be based on the experience drawn from dealing with the first wave and complemented by a better communication strategy.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hallmark
Mains level: Not Much

The Centre will go ahead with its plan to mandate hallmarking of gold jewellery from June 1. The plan had been delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Note: Gold hallmarking is a purity certification and is voluntary at present.
What is Hallmark Gold?
- The process of certifying the purity and fineness of gold is called hallmarking.
- Bureau of Indian Standards, the National Standards Body of India, is responsible for hallmarking gold as well as silver jewellery under the BIS Act.
- If you see the BIS hallmark on the gold jewellery/gold coin, it means it conforms to a set of standards laid by the BIS. Hallmarking gives consumers assurance regarding the purity of the gold they bought.
- That is, if you are buying hallmarked 18K gold jewellery, it will actually mean that 18/24 parts are gold and the rest is alloy.
Here are the four components one must look at the time of buying gold (they are mentioned in the laser engraving of a hallmark seal):
- BIS Hallmark: Indicates that its purity is verified in one of its licensed laboratories
- Purity in carat and fineness (corresponding to given caratage KT)
- 22K916 (91.6% Purity)
- 18K750 (75% Purity)
- 14K585 (58.5% Purity)
- Assaying & Hallmarking Centre’s mark
- Jeweler’s unique identification mark
Try this PYQ from CSP 2017:
Q. Consider the following statements:
1. The Standard Mark of the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is mandatory for automotive tyres and tubes.
2. AGMARK is a quality Certification Mark issued by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Why such a move now?
- As per the new rules, if jewellery or an artefact made of 14-, 18- or 22-carat gold is sold without the BIS hallmark, the jeweller could be penalized five times the cost of the object or imprisoned for up to one year.
- About 40% of gold jewellery is sold with a hallmark.
- Mandatory hallmarking would protect the public against lower caratage and ensure consumers did not get cheated while buying gold ornaments and got the purity as marked on the ornaments.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now








