Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Article 21
Mains level: Paper 2- Addressing the issue of undertrials
Context
After the death of Stan Swamy, questions about the conditions of jails and treatment of the incarcerated have been raised anew.
Issue of deaths of prisoners
- The NCRB data reports the death of over 1,800 prisoners in the year 2018. An estimated 70 percent of prison inmates are undertrials.
- Despite constitutional provisions like Article 21, which says, no person shall be denied life or liberty except by the due process of law, the number of undertrials is increasing.
How prisoners are subjected to additional torture
- Overcrowding, delayed medical attention, unhygienic conditions and malnutrition exist in all Indian prisons.
- It is the responsibility of the State and the judiciary to ensure that they are only deprived of their liberty and are not exposed to any additional torture in the form of medical deprivation, unhygienic conditions, bad or inadequate food, etc.
- Yet, thousands are dying every year and the prison authorities are not made accountable.
Way forward
- Acts of extreme neglect that could result in the death of inmates should be acknowledged as extrajudicial torture and made an offense.
- The SC in Sunil Batra (I) v. Delhi Administration (1978), held that “the humane thread of jail jurisprudence that runs right through is that no prison authority enjoys amnesty for unconstitutionality”.
- ARC Recommendations on Prison Reforms: The Union and State Governments should work out, fund and implement at the
earliest, modernization and reforms of the Prison System as recommended by the All India Committee on Jail Reforms (1980-83).
b. The attendant legislative measures should also be expedited.
c. Rules regarding Parole and Remission need to be reviewed.
- Infrastructure: Prisoner Information System, Biometric Identification, facilities for pregnant women, up-gradation of hospitals, etc is needed.
- Strengthening the Open Prison System.
Conclusion
The government needs to take urgent measures to address the issue of additional torture in various forms and the death of prisoners.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ministry for Cooperation
Mains level: Paper 3- Performance of cooperative movement
Context
Two weeks ago, the government created a new Ministry for Cooperation. India is, perhaps, the first country to have such a ministry. The Ministry can play an important role in the transformation of cooperatives in the country.
How 1991 economic reforms benefited agriculture
- On July 24, 1991, India decided to unshackle the spirit of private sector entrepreneurship through the move to de-license industry and reduce tariffs on a host of commodities.
- Trade policy changes improved the terms of trade for agriculture and benefitted millions of farmers.
- Agri-exports increased, but this led to higher domestic prices.
The success story of dairy sector in India
- In 1991, Manmohan Singh, then finance minister wanted to delicense the dairy sector as well, but there was stiff opposition from Verghese Kurien.
- It was after 10 years in 2002 that the dairy sector was fully de-licensed.
- The competition between cooperatives and corporate dairy players has benefitted millions of farmers around the country.
- With the entry of the private sector, the growth of the dairy sector accelerated at double the speed.
- Today, both procure roughly the same quantities and growth in the organised private sector is faster than in cooperatives.
Performance of cooperative movement in India
- India’s experience with the cooperative movement has produced mixed results — few successes and many failures.
- There are cooperatives in the financial sector, be it rural or urban.
- But the performance of these agencies when measured in terms of their share in overall credit, achievements in technology upgradation, keeping NPAs low or curbing fraudulent deals has been poor to average.
- Sugar cooperatives of Maharashtra initially touted as exemplars of the movement, are in the doldrums now.
- Many are being sold to the private sector.
Performance of cooperatives in dairy sector
1) Amul
- The performance of the cooperative champion, Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation (GCMMF) — with its poster brand, Amul — has been most successful.
- During Operation Flood, it received a lot of capital at highly concessional terms.
- But its success is also the result of professionalism, business and, therefore, keeping politics away.
- But despite the grand success of Gujarat’s milk cooperatives in Gujarat, the model did not spread to other states as successfully.
2) Karnataka Milk Federation
- In its eagerness to please milk farmers, the Karnataka Milk Federation (KMF), which sells its products under the brand name of Nandini, gives them Rs 5 to Rs 6 extra per litre.
- This subsidy, given by the state government, cost the exchequer Rs 1,260 crore till 2019-20.
- KMF procures a lot of milk and then dumps it at lower prices in the market for consumers.
- This depresses prices in adjoining states like Maharashtra, affecting the fortunes of Maharashtra milk farmers.
- If Maharashtra and Karnataka were two different countries, Maharashtra would be challenging Karnataka at the WTO.
Way forward
- The new Ministry of Cooperation can work towards ironing out distortions in state price policies due to subsidization such as in Maharastra and Karnatak milk prices.
- Cooperatives desperately need technological upgradation.
- The Ministry of Cooperation can give them soft loans for innovation and technology upgradation.
- But such loans should also be extended to the private sector to ensure a level playing field.
- The Ministry of Cooperation needs to ensure the least political interference in the operation of cooperatives.
Conclusion
The new Ministry of Cooperation can work towards bringing in professionalism in cooperatives and make them more competitive.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Unemployment in India

PM has yet again underscored the importance of a skilled workforce for achieving the goal of becoming Atma-nirbhar Bharat. India still continues to be a country that faces one of the highest shortages of skilled workforce.
Unemployment vs Skills
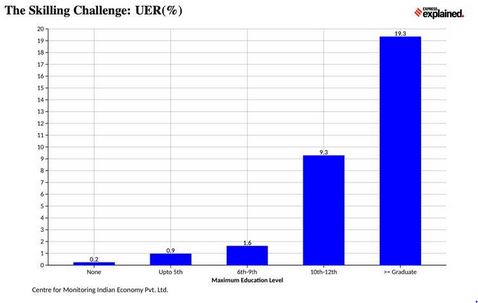
- On one hand, companies in India face an acute shortage of skilled manpower and, on the other, India has millions of educated unemployed.
- The data for this chart is for the January to April 2021 period, when the overall unemployment rate in the country was 6.83%.
- In comparison, those with graduation (or even higher degrees) face almost three times the unemployment level.
- At over 19% unemployment rate, one in every five Indians who graduate (or even better) is unemployed.
What explains this contradiction?
- The lack of skill is definitely the only answer.
What is Skilling?

- National Council of Applied Economic Research, 2018 — aptly titled “No time to lose”.
- This report explains that there are three types of skills.
- Cognitive skills: basic skills of literacy and numeracy, applied knowledge and problem-solving aptitudes, and higher cognitive skills such as experimentation, reasoning, and creativity.
- Technical and vocational skills: physical and mental ability to perform specific tasks using tools and methods in any occupation.
- Social and behavioral skills include working, communicating, and listening to others.
- Different levels of these three types of skills can be combined to further classify skills into foundational, employability, and entrepreneurial skills.
What is the scale of the skilling challenge facing India?
According to the 2018 report by NCAER, India had about 468 million people in its workforce.
- Informal sector: Around 92% of them were in the informal sector.
- Illiteracy: Around 31% were illiterate, only 13% had primary education, and only 6% were college graduates.
- No vocational training: Further, only about 2% of the workforce had formal vocational training, and only 9% had non-formal vocational training.
- Out of more than 5 lakh final year bachelors students aged 18–29 who were surveyed, around 54% were found to be “unemployable”.
Opportunities for India
- India has entered a demographic sweet spot that will continue for another two to three-decade.
- There is a great opportunity for India to improve both its social and economic outcomes if a higher number of workers are productively employed.
What is at stake?
- If the skilling issue is not resolved, India risks forfeiting its so-called “demographic dividend”.
- But whether this will turn into a demographic dividend or not will depend entirely on how many of those in the working-age bracket are working and becoming prosperous.
- If they are not in well-paying jobs, the economy would not have the resources to take care of itself since with each passing year, the proportion of dependents will continue to rise after 2040.
- To put it simply, to attain its rightful place and realize its aspirations, India must become rich before it gets old.
The skilling paradox
- Indians have excelled in technical expertise at the global level — be it medicine or engineering. Then what explains India’s domestic skilling paradox?
- A big part of the trouble is the starting condition. Over 90% of India’s workforce is in the informal sector.
India is trapped in a vicious cycle:
- Greater workforce informality leads to lower incentives to acquire new skills. Faced with inadequately skilled workers, businesses often choose to replace labor with machinery.
- That’s because “skilled labor and technology are complementary, but unskilled labor and technology are substitutes”.
- This, in turn, leads to still fewer formal jobs.
What can be done to break this cycle?
- A distinct disadvantage with India’s approach towards skilling has been to ignore and match the demands of the market.
- For the most part, skills have been provided in a top-down fashion.
- Given the way market demands fluctuate — for instance, how the Covid pandemic has upended supply chains — skilling efforts must try to anticipate the needs of the market.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013
Mains level: Read the attached story
More than two years after the Lokpal came into being, the Centre is yet to appoint a director of inquiry for conducting a preliminary inquiry into graft complaints sent by the anti-corruption ombudsman.
Who is ‘Director of Inquiry’?
- According to the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013, there shall be a director of inquiry, not below the rank of Joint Secretary to the GoI.
- He/ She shall be appointed by the Central government for conducting preliminary inquiries referred to the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) by the Lokpal.
About the Lokpal
- The Lokpal, the apex body to inquire and investigate graft complaints against public functionaries, came into being with the appointment of its chairperson and members in March 2019.
- In March 2019, former SC judge Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose was selected as the first head of the Lokpal.
Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013
- The Lokpal Act 2013 is anti-corruption legislation that seeks to provide for the establishment of the institution of Lokpal.
- It seeks to inquire into allegations of corruption against certain important public functionaries including the PM, cabinet ministers, MPs, Group A officials of the Central Government etc.
- The Bill was introduced in the parliament following massive public protests led by anti-corruption crusader Anna Hazare and his associates.
- The Bill is one of the most widely discussed and debated Bills in India in recent times.
Its history
- The term Lokpal was coined in 1963 by Laxmi Mall Singhvi, a member of parliament during a parliamentary debate about grievance mechanisms.
- The Administrative Reforms Commission (ARC) headed by Morarji Desai submitted an interim report on “Problems of Redressal of Citizen’s Grievances” in 1966.
- In this report, ARC recommended the creation of two special authorities designated as ‘Lokpal’ and ‘Lokayukta’ for redress of citizens’ grievances.
- Maharashtra was the first state to introduce Lokayukta through The Maharashtra Lokayukta and Upa-Lokayuktas Act in 1971.
Also read:
Explained: How Lokpal will form, function
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Need for data localization
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has banned Mastercard from issuing new debit and credit cards to customers in India.
Why such a ban?
- According to the RBI, the US card issuer has failed to comply with the local data storage rules announced by the central bank in 2018.
What is the RBI’s data localization policy?
- In 2018, the RBI had issued a circular ordering card companies such as Visa, Mastercard, and American Express to store all Indian customer data locally.
- This was aimed for the regulator to have “unfettered supervisory access”.
Why such a policy by RBI?
- The reason offered by the RBI was that local storage of consumer data is necessary to protect the privacy of Indian users and also to address national security concerns.
Issues with the policy
- Privacy: Customer privacy and national security are genuine concerns that need to be taken seriously.
- Protectionism: However, data localization rules may sound too stringent and they could simply be used by governments as tools of economic protectionism.
- Security: For instance, it may not be strictly necessary for data to be stored locally to remain protected.
- Formal international laws to govern the storage of digital information across borders may be sufficient to deal with these concerns.
- Discrimination: Governments, however, may still mandate data localization in order to favour local companies over foreign ones.
Implications of the move
- Indian banks that are currently enrolled in the Mastercard network are expected to make alternative arrangements with other card companies.
- The RBI’s data localization policy, as it burdens foreign card companies, may end up favouring domestic card issuers like RuPay, which in turn can lead to reduced competition.
- Mastercard owns about one-third of the market share in India, and the RBI’s ban is likely to significantly benefit its competitors.
- This could mean higher costs and lower quality services for customers.
Conclusion
- In today’s digital economy data have turned out to be a valuable commodity, which companies, as well as governments, have tried to gain control over.
- With no clear rules on who owns customer data and to what extent, conflicts over data ownership are likely to continue for some time.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Moon wobble
Mains level: Moon wobble and climate change

US coastlines will face increasing flooding in the mid-2030s due to a regular lunar cycle called the wobble effect that will magnify rising sea levels caused by climate change.
What is the Moon Wobble?
- The moon wobble is nothing but a regular swaying in the moon’s orbit.
- It was first documented way back in 1728.
- This wobble takes over an 18.6-year period to complete and continues in a cyclic fashion.
How does this wobble occur?
- High tides on this planet are caused mostly by the pull of the moon’s gravity on a spinning Earth. On most beaches, you would see two high tides every 24 hours.
- The moon also revolves around the Earth about once a month, and that orbit is a little bit tilted.
- moon’s orbital plane around the Earth is at an approximate 5-degree incline to the Earth’s orbital plane around the sun.
- Because of that, the path of the moon’s orbit seems to fluctuate over time, completing a full cycle — sometimes referred to as a nodal cycle — every 18.6 years.
- At certain points along the cycle, the moon’s gravitational pull comes from such an angle that it yanks one of the day’s two high tides a little bit higher, at the expense of the other.
- This does not mean that the moon itself is wobbling, nor that its gravity is necessarily pulling at our oceans any more or less than usual.
What impact does this wobble have on Earth?
- Influences the ebb and flow of tides: The moon wobbles impacts the gravitational pull of the moon, and therefore, indirectly influences the ebb and flow of tides here on the Earth.
- One half of the 18.6-year cycle suppresses the tides, which means that the high tides get lower, while the low tides get higher than normal.
- Once this cycle completes, the situation flips—in the subsequent cycle, the tides are amplified, with high tides getting higher and low tides, lower.
- The lunar cycle is expected to shift again by mid-2030, and in the coming phase, the tides will amplify once again.
Moon wobble and climate change
- The upcoming changes in the lunar cycle will pose a serious threat, as the amplified high tides coupled with the rising sea levels will make the risk of flooding far greater across all coastal regions of the globe.
- The study predicts that the high tide-associated floods—also known as nuisance floods or sunny day floods—may occur in clusters that could last for months or even for longer periods!
- This surge will be closely associated with the position of the Moon, Earth and the Sun.
- When the Moon and Earth line up in specific ways with each other and the Sun, the resulting gravitational pull and the ocean’s corresponding response may leave city-dwellers coping with floods every day or two.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Great Barrier Reef
Mains level: Coral Reefs and their significance

Chinese official has said that political tensions between Beijing and Australia were not behind a UNESCO recommendation to place the Great Barrier Reef on its endangered list.
Great Barrier Reef
- The Great Barrier Reef is the world’s largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands.
- It is stretched for over 2,300 kilometres over an area of approximately 344,400 square kilometres.
- The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, Australia.
- It was world heritage listed in 1981 by UNESCO as the most extensive and spectacular coral reef ecosystem on the planet.
Importance of Corals
Coral reefs are some of the most diverse and valuable ecosystems on Earth.
- They support more species per unit area than any other marine environment, including about 4,000 species of fish, 800 species of hard corals and hundreds of other species.
- This biodiversity is considered key to finding new medicines for the 21st century.
- Medical use: Many drugs are now being developed from coral reef animals and plants as possible cures for cancer, arthritis, human bacterial infections, viruses, and other diseases.
- Fisheries: Healthy coral reefs support commercial and subsistence fisheries as well as jobs and businesses through tourism and recreation.
- Local economies receive billions of dollars from visitors to reefs through diving tours, recreational fishing trips, hotels, restaurants, and other businesses based near reef ecosystems.
- Coral reef structures also buffer shorelines against 97 per cent of the energy from waves, storms, and floods, helping to prevent loss of life, property damage, and erosion.
Answer this PYQ in the comment box:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- Most of the world’s coral reefs are in tropical waters.
- More than one-third of the world’s coral reefs are located in the territories of Australia, Indonesia and the Philippines.
- Coral reefs host far more number of animal phyla than those hosted by tropical rainforests.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Back2Basisc: Coral Reef

- Coral reefs are built by and made up of thousands of tiny animals—coral “polyps”—that are related to anemones and jellyfish.
- Polyps are shallow-water organisms that have a soft body covered by a calcareous skeleton. The polyps extract calcium salts from seawater to form these hard skeletons.
- The polyps live in colonies fastened to the rocky seafloor.
- The tubular skeletons grow upwards and outwards as a cemented calcareous rocky mass collectively called corals.
- When the coral polyps die, they shed their skeleton on which new polyps grow.
- The cycle is repeated for millions of years leading to the accumulation of layers of corals shallow rock created by these depositions is called a reef.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pegasus
Mains level: Whatsapp snooping
Telephone numbers of some noted Indian journalists were successfully snooped upon by an unidentified agency using Pegasus software.
Pegasus Spyware
- All spyware do what the name suggests — they spy on people through their phones.
- Pegasus works by sending an exploit link, and if the target user clicks on the link, the malware or the code that allows the surveillance is installed on the user’s phone.
- A presumably newer version of the malware does not even require a target user to click a link.
- Once Pegasus is installed, the attacker has complete access to the target user’s phone.
- The first reports on Pegasus’s spyware operations emerged in 2016, when Ahmed Mansoor, a human rights activist in the UAE, was targeted with an SMS link on his iPhone 6.
What is the new threat?
- Pegasus has evolved from its earlier spear-phishing methods using text links or messages to ‘zero-click’ attacks which do not require any action from the phone’s user.
- This had made what was without a doubt the most powerful spyware out there, more potent and almost impossible to detect or stop.
How do zero-click attacks work?
- A zero-click attack helps spyware like Pegasus gain control over a device without human interaction or human error.
- Zero-click attacks are hard to detect given their nature and hence even harder to prevent.
- Detection becomes even harder in encrypted environments where there is no visibility on the data packets being sent or received.
- Most of these attacks exploit software that receive data even before it can determine whether what is coming in is trustworthy or not, like an email client.
Answer this PYQ from CSP 2018:
Q.The terms ‘WannaCry, Petya, Eternal Blue’ sometimes mentioned news recently are related to
(a) Exoplanets
(b) Crypto currency
(c) Cyber attacks
(d) Mini satellites
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






