Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fastag
Mains level: Fastag and its benefits for speedy transport
Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has decided that all lanes in the fee plazas on National Highways shall be declared as “FASTag lane of the fee plaza”.
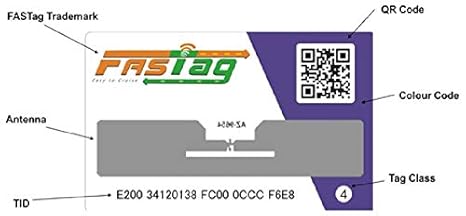
Fastag went unnoticed this year. The RFID technology deployed in this holds an intuition for its relevance in CS prelims and many forthcoming exams.
What is ‘FASTag’?
- FASTags are stickers that are affixed to the windscreen of vehicles and use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to enable digital, contactless payment of tolls without having to stop at toll gates.
- The tags are linked to bank accounts and other payment methods.
- As a car crosses a toll plaza, the amount is automatically deducted, and a notification is sent to the registered mobile phone number.
How does it work?
- The device employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for payments directly from the prepaid or savings account linked to it.
- It is affixed on the windscreen, so the vehicle can drive through plazas without stopping.
- RFID technology is similar to that used in transport access-control systems, like Metro smart card.
- If the tag is linked to a prepaid account like a wallet or a debit/credit card, then owners need to recharge/top up the tag.
- If it is linked to a savings account, then money will get deducted automatically after the balance goes below a pre-defined threshold.
- Once a vehicle crosses the toll, the owner will get an SMS alert on the deduction. In that, it is like a prepaid e-wallet.
Must read:
[Burning Issue] Implementation of FASTags
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: RTE, New Education Policy
Mains level: Paper 2- Impact of pandemic on education of the poor
The article highlights the issue of the decrease in allocation for education and two ways in which the government seeks to plug this gap.
Decrease in allocation to education: Two paradoxical axes
- The government allocated Rs 6,000 crore less on education in Budget 2021 as compared to last year.
- It’s strange that this year’s budget makes no reference to the pandemic and the multiple challenges it has thrown up for the poor.
- Parents who depend on the lowest rung of free government schools are the ones who need maximum state support.
- More recently, the state’s position with regard to the provision of education in general and budgetary allocations to education in particular hinges on two paradoxical axes.
1) Supporting community volunteer
- On one axis, is its appreciation of the commitment and passion of the community volunteers to reach out to children who may not be learning for multiple reasons.
- Acknowledging the contribution of such people, the NEP proposes ideas of “peer-tutoring and trained volunteers” to support teachers to impart foundational literacy and numeracy skills to children in need of such skills.
- While such efforts need to be applauded, they cannot be regarded as substitutes of the formal state apparatus.
- Such a view also de-legitimises the teaching profession-associated qualifications and the training mandated by the state for people to become teachers.
- Salaries and working conditions of the local community, most of whom are unemployed youth and women, are often compromised.
- This is exploitation and needless to say, it also impacts the quality of education for the poor.
2) Public-Private partnership and issues with it
- On the second axis, is the position advocating partnerships between public and private bodies.
- Not that the involvement of private individuals/organisations/schools in education is anything new in India.
- However, in the past, private schools catered to the relatively better-off but now the poor are being targeted for profit.
- This narrative is based on two sources: Poor learning outcomes of children, particularly those studying in government schools as reported by large scale assessment surveys, and large-scale absenteeism/dereliction of duty on the part of government school teachers.
- Reasons for these are attributed to government school teachers having no accountability.
- NEP 2020 also states that the non-governmental philanthropic organisations will be supported to build schools and alternative models of education will be encouraged by making their requirements for schools as mandated in the RTE less restrictive.
- This is clearly problematic but convenient as the justification underlying this position is that one needs to shift focus from inputs to outputs.
- This also indicate that schools can do with lesser financial resources, and compromised inputs may not necessarily lead to compromised outputs.
- The nature of the partnership between public and private has also changed from the private supporting the public to private jostling for space with the public, even replacing them.
- It’s a win-win situation for both — the state gets to spend less and private players make profit.
Consider the question “Examine the impact of a covid pandemic on the education of the poor. Suggest the measure need to be taken by the government to mitigate the impact.”
Conclusion
While money may not ensure quality education, lack of adequate resources will only deepen the social divide between people.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Floods in Uttarakhand and its mitigation
The article explains the relationship between development activities in Uttarakhand and the devastating floods.
Cause of recent flash flood in Uttarakhand
- According to Planet Labs, ice along with frozen mud and rocks fell down from a high mountain inside the Nanda Devi Sanctuary, from a height of 5,600 m to 3,300 m.
- This created an artificial lake within the sanctuary in Rontigad, a tributary of Rishi Ganga.
- Within eight hours, this lake burst open and its water, laden with mud and stones, rushed through the Rishi Ganga gorge which opens near Reni.
- Studies say that the current winter season has seen little rain and snow, with temperatures being highest in the last six decades.
- So, the effects of chemical weathering were much more active in the higher Himalayas.
- There is a possibility of more such events this year.
Factors responsible
1) Development with no regard for the environment
- As a mountain system, the Himalayas have had earthquakes, avalanches, landslides, soil erosion, forest fires and floods, and these are its natural expressions, parts of its being.
- Except for earthquakes, humans have directly contributed towards aggravating all the other phenomena.
- The Ravi Chopra committee formed by the SC recommended closure of all the 24 hydro projects in question by Wildlife Institute of India.
- The SC also formed another committee to look at the impact of the Chaardham road project.
- Road and hydro projects are being operated in the Himalayas with practically no rigorous research on the ecological history of the area, cost-benefit analysis and many other aspects including displacement of communities, destruction of biodiversity, agricultural land, pastures as well as the cultural heritage of the area.
Dilution of Environmental Impact Assessment rules
- Earlier, while independent experts carried out the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), today it is assigned to a government agency, which does the work for other government departments.
- Furthermore, during the lockdown, the government changed the EIA rules and diluted labour laws (most of the workers in both the affected projects belong to unorganised sector) in the name of pandemic measures.
2) Climate change
- Another factor which cannot be overlooked is that of climate change.
- Studies have suggested that the pace of this change is faster in mountains and fastest in the Himalayas.
- While earthquakes and weathering work at their own pace, climate change can contribute towards altering their natural speed.
Need for studying the 2013 calamity
- We can look back at the terrible calamity of 2013, and see how it washed away the encroachments in river areas-dams, barrages, tunnels, buildings, roads.
- The communities paid a much heavier price than what they received in compensation.
- Further, the 2013 calamity has to be studied and understood in all the other regions and river valleys of Uttarakhand, Western Nepal and Himachal.
- It was not specific to Kedarnath, although much of the focus was directed there.
- Till date, we don’t have any white paper on this calamity.
- The India Meteorological Department failed in its prediction and wrongly announced at the end of the first week of June that the monsoon will reach Uttarakhand by June 27-28.
- It reached on June 16-17 with 300-400 per cent more rain, a record never heard of before.
- 24 big and small hydro projects were destroyed.
- The muck created by these projects was also the cause of their destruction.
- The road debris, always dumped in rivers, was another cause.
- The smaller rivers were more aggressive in 2013.
Consider the question “What are the factors responsible for the devastating floods in the Uttarakhand? Suggest the measures for disaster mitigation.”
Conclusion
The Himalayas have been giving us life through water, fertile soil, biodiversity, wilderness and a feel of spirituality. We cannot and should not try to control or dictate the Himalayas.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Farakkha Barrage, Hilsa fish
Mains level: Not Much

It has been reported that an old project to facilitate the movement of Hilsa upstream along the Ganga to its spawning grounds of yore may come to fruition this year.
What is the news?
- Back in February 2019, the government had unveiled a project to redesign the navigation lock at the Farakka Barrage at a cost of Rs 360 crore to create a “fish pass” for the Hilsa.
Hilsa Fish

- In scientific parlance, the Hilsa (Tenualosa ilisha) is an anadromous fish.
- It lives most of its life in the ocean, but during the rainy season, the Hilsa moves towards the estuary, where the rivers of India and Bangladesh meet the Bay of Bengal.
- A large part of the shoal travels upstream in the Padma and the Ganga — some are known to move towards the Godavari, and there are records of Hilsa migration to the Cauvery.
- Culinary lore has it that the fish that travel the farthest upstream have the best combination of the flavours of the sea and the river.
Try this question from CSP 2019:
Q. Consider the following pairs:
| Wildlife |
Naturally found in |
| 1. Blue-finned Mahseer |
Cauvery River |
| 2. Irrawaddy Dolphin |
Chambal River |
| 3. Rusty-spotted Cat |
Eastern Ghats |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Obstructions created by Farakka Barrage
- Historical records also show that until the 1970s, the Hilsa would swim the Ganga upstream to Allahabad — and even to Agra.
- But the Farakka Barrage, which became operational on the Ganga in 1975, disrupted the westward movement of the Hilsa.
- The barrage had a navigation lock that stopped the fish from swimming upstream beyond Farakka.
- In Buxar on the border of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, the last recorded catch of the Hilsa was made 32 years ago.
- The role of the Farakka Barrage in disrupting the Hilsa’s journey is well documented and has been discussed in Parliament as well.
- On August 4, 2016, then Union Water Resources Minister told Lok Sabha about plans to create “fish ladders” to help the fish navigate the obstacle posed by the barrage.
Fish ladders/fishways/fish passes

- Fish passes — also known as fish ladders or fishways — aim to assist fish in crossing obstacles presented by dams and barrages.
- They usually consist of small steps that allow the fish to climb over the obstacles and enable them to reach the open waters on the other side.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Creche scheme
Mains level: Maternity benefits act

The Union Minister of Women and Child Development have given information about the National Creche Scheme to the Lok Sabha.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017?
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months pre-delivery and three months post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother a minimum of six crèche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
National Creche Scheme
- The Ministry of WCD implements the NCS for the children of working mothers as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme through States/ UTs with effect from 01.01.2017.
- It aims to provide daycare facilities to children (age group of 6 months to 6 years) of working mothers.
The Scheme provides an integrated package of the following services:
- Daycare facilities including sleeping facilities.
- Early stimulation for children below 3 years and pre-school education for 3 to 6 years old children
- Supplementary nutrition (to be locally sourced)
- Growth monitoring
- Health check-up and immunization
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dayanand Saraswati
Mains level: Not Much

Information and Broadcasting Minister paid his tributes to Swami Dayanand Saraswati on his birth anniversary.
Dayanand Saraswati (1824-1883)
- Swami Dayanand Saraswati was a philosopher, social leader and founder of the Arya Samaj, a reform movement of the Vedic dharma.
- He was the first to give the call for Swaraj as “India for Indians” in 1876, a call later taken up by Lokmanya Tilak.
- Denouncing the idolatry and ritualistic worship, he worked towards reviving Vedic ideologies.
- Subsequently, the philosopher and then President, S. Radhakrishnan called him one of the “makers of Modern India”, as did Sri Aurobindo.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which among the following event happened earliest?
(a) Swami Dayanand established Arya Samaj
(b) Dinabandhu Mitra wrote Neeldarpan
(c) Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay wrote Anandmath
(d) Satyendranath Tagore became the first India to succeed in the Indian Civil Services Examination
His influence
- Those who were influenced by and followed him included Madam Cama, Shyamji Krishna Varma, Kishan Singh, Bhagat Singh, VD Savarkar, Bhai Parmanand, Lala Hardayal, Madan Lal Dhingra, Ram Prasad Bismil, MG Ranade, Ashfaq Ullah Khan, , Lala Lajpat Rai etc.
Philosophy
- He was ascetic from boyhood and a scholar.
- He believed in the infallible authority of the Vedas.
- He advocated the doctrine of Karma and Reincarnation.
- He emphasized the Vedic ideals of Brahmacharya, including celibacy and devotion to God.
His contribution
- Among Dayananda’s contributions were his promoting of the equal rights for women, such as the right to education and reading of Indian scriptures.
- He wrote his commentary on the Vedas from Vedic Sanskrit in Sanskrit as well as in Hindi.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various provisions of the Juvenile Justice Act
Mains level: Child rights and their protection
The Union Minister of Women and Child Development has given important information regarding the protection of child beggars in India under various acts and ministries.
Q.What are the various legislatures aimed at protecting Child Beggars in India? Discuss their efficacy in the prevention of child begging as well as abuse.
Protection of Child Beggars
(A) JJ Act, 2015
- The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 (JJ Act) is the primary law for children in the country.
- The Section 2 (14) (ii) of the Act, 2015, considers a child being in force or is found begging, or living on the street as a “child in need of care and protection”.
- As per Section 76 of JJ Act, whoever employs or uses any child for the purpose of begging or causes any child to beg shall be punishable with imprisonment.
- The Act provides a security net of service delivery structures along with measures for institutional and non-institutional care, to ensure the comprehensive well being of children in distress situations.
- The primary responsibility of execution of the Act rests with the States/UTs.
(B) Child Protection Services (CPS)
- The Ministry implements a centrally sponsored scheme CPS under the umbrella Integrated Child Development Services scheme.
- It supports the children in difficult circumstances including child beggars and destitute children.
- Under the scheme, institutional care is provided through Child Care Institutions (CCIs), as a rehabilitative measure.
- The programmes and activities in CCIs inter-alia include age-appropriate education, access to vocational training, recreation, health care, counselling etc.
- The scheme supports 24×7 emergency outreach/ helpline service for children in distress conditions.
- The service is accessible through a dedicated toll-free number, 1098 from anywhere in India.
(C) Rehabilitation measures
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, has undertaken a pilot project for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of Persons engaged in the act of begging.
- It is currently held in ten (10) cities; namely Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Ahmadabad, Hyderabad, Bangalore, Lucknow, Patna, Nagpur and Indore.
- The initiative aims for identification, rehabilitation, counselling, skill development of beggars.
- It includes education of children engaged in begging/children of persons engaged in the begging.
The children of today are assets of tomorrow. Yet education, which is a fundamental right to every child in our country, is still a dream for many children in India, especially the ones who are poor, downtrodden and in dire need.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tholpavakkoothu
Mains level: India's puppetry

A shadow leather puppet in Kerala’s famous temple art Tholpavakkoothu is being animated by a robot in Palakkad.
Tholpavakkoothu
- Tholpavakkoothu or shadow puppetry is a temple art form which is prevalent in the Bhagavathy temples (mother Goddess) in Palakkad district and nearby regions in Kerala.
- Tholppava (Thol means leather, Pava means puppet) are moved with the help of strings, and their shadows are depicted on a screen with the help of a row of oil lamps in the background.
- The story of Tholpavakkoothu performance is from the Indian epic, Ramayana.
- In the olden days, it was performed elaborately over a period of forty-one days.
- The narrative used for the performance is a mixture of prose and poetry called Adalpattu.
Try this PYQ:
Q.With reference to Manipuri Sankirtana, consider the following statements:
- It is a song and dance performance.
- Cymbals are the only musical instruments used in the performance.
- It is performed to narrate the life and deeds of Lord Krishna.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3.
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 only
Setup of the art
- Tholppavas are made of the skin of deer and the puppet forms are made by making small holes in the leather that is then attached vertically to a bamboo stick.
- Accompanying instruments include Ezhupara, Chenda and Maddalam.
- The artists have to undergo several years of rigorous training to master this art form.
- The puppetry is staged on a special structure in temple premises called Koothumadam.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: JCPOA
Mains level: Paper 2- The U.S. approach toward JCPOA
The article spells out the U.S.’s foreign policy approach in the changing global order. Though the article doesn’t mention India, the U.S.’s policies and it’s bearing on India need no mention. From that perspective, we should follow their approach.
Decision on the JCPOA
- During the U.S. presidential election campaign, Joe Biden had criticised the U.S. withdrawal from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
- He had then promised that subject to Iran’s compliance with its obligations, the U.S. would re-enter the agreement.
- In office, Mr. Biden has shown little urgency on the JCPOA matter.
- Israel has given the opposite message and said that the nuclear agreement was “bad and must not be allowed”.
- Israel and the U.S.’s Gulf allies, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, have also insisted that they be involved with the discussions with Iran on the revival of the agreement.
U.S.’s Policy approach
- The U.S. policy is likely to show more continuity than change where the U.S.’s core interests are concerned, specifically in its ties with Russia, China and Iran.
- Mr. Biden is likely to reverse his predecessor Donald Trump’s personal accommodative approach towards Russia and adopt the U.S.’s traditional confrontational posture.
- Mr. Biden’s Iran policy is likely to match Mr. Trump’s hardline approach on substantive matters.
- This approach also panders to Iran’s regional rivals who wish to see the Islamic republic weakened and isolated.
- There will thus be no dramatic change in the U.S.’s approach to Iran on the nuclear question.
Regional concerns and role of global powers
- Despite the sanctions, Iran’s regional influence remains significant.
- The Iranian ability to mobilise militants across the region is viewed by Israel and some the Gulf Arab states as threatening their security.
- Gulf states are also concerned about Iran’s influence with their Shia populations.
- The capabilities of Iran’s precision missiles and drones are also a matter of regional anxiety.
- Israel, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates will be in a face-off with Iran and its allies, Iraq, Syria and its Shia militia.
- Alternatively, we could see a genuine regional effort to ease tensions and promote regional confidence, spearheaded by Qatar, working with Russia and, possibly, China.
- Perhaps, Saudi Arabia and the UAE, already facing heat from the Biden administration, will see the value of this approach.
- Russia now an influential player in the region, China, too, with its Belt and Road Initiative, has high stakes in regional stability.
- The Sino-Iran 25 years agreement, envisages their substantial and long-term cooperation in political, security, military, economic, energy and logistical connectivity areas.
Consider the question “How far Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) has been successful in achieving its goals? How peace in the Middle East influence India’s interests?”
Conclusion
The new U.S. administration will thus witness a new world order, shaped by a coalition of Russia, China and Iran, in which the U.S. is no longer the most significant role-player.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IT Act
Mains level: Paper 2- Section 69A of IT Act and issues with it
What is the faceoff about
- Recently, Indian government issued direction to Twitter, ordering it to shut down user accounts connected with farmers’ protests.
- The government has to exercise powers under Section 69A of the Information Technology Act to block user accounts critical of the farm bills.
- The accounts which were sought to be censored are back online.
- This is due to Twitter’s evident refusal to comply with the directions after a constitutional appraisal.
- It has, as per press statements, cited the doctrine of proportionality in its defence.
Concerns with the directive
- This direction presents a clear breach of fundamental rights but also reveals a complex relationship between the government and large platforms on the understanding of the Constitution of India.
- The specific legal order issued is secret.
- This brings into focus the condition of secrecy that is threshold objection to multiple strands of our fundamental rights.
- It conflicts against the rights of the users who are denied reasons for the censorship.
- Secrecy also undermines the public’s right to receive information, which is a core component of the fundamental freedom to speech and expression.
- This is an anti-democratic practice that results in an unchecked growth of irrational censorship but also leads to speculation that fractures trust.
- The other glaring deficiency is the complete absence of any prior show-cause notice to the actual users of these accounts by the government.
- This is contrary to the principles of natural justice.
- This again goes back to the vagueness and the design faults in the process of how directions under Section 69A are issued.
Constitutionality of Section 69A of IT Act
- The secrecy clause represents a failure on the part of the Union executive, which framed the process for blocking websites in 2009.
- he Supreme Court also failed to substantively examine the clause.
- This is despite the opportunity offered by its celebrated judgment Shreya Singhal v. Union of India, when it struck down Section 66A of the IT Act as unconstitutional.
- At the same time, the court stated in Shreya Singhal, that an aggrieved party could approach a court for remedy if their website or user account was blocked under Section 69A.
- More recently, the court, when adjudicating the constitutional permissibility of the telecommunications shutdown in Jammu and Kashmir by its judgment in Anuradha Bhasin v. Union of India directed pro-active publication of all orders for internet shutdowns.
- After this, a decent argument may be made that directions for blocking now need to be made public.
- However, several state governments are actively refusing compliance on the publication of orders on internet shutdowns.
Consider the question “Use of Section 69 of the IT Act to suspend the account of the users on a social media platform has raised concern. Examine these concerns.”
Conclusion
The episode leaves a sense of confusion and wonder about why our own government formed under the Constitution may be failing to fulfil its obligations when strangers who trade in our data for profit are seemingly more eager.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various ports in India
Mains level: Corporatization of ports
Rajya Sabha has passed the Major Ports Authorities Bill 2020 with 88 votes for and 44 against it. The Bill was passed in Lok Sabha in September last year.
Major Ports Authorities Bill 2020: Major: Highlights
- The Bill provides for the regulation of major ports and will replace the Major Port Trusts Act of 1963, and a board of Major Port Authority for each major port will replace the current port trusts.
- The Bill will apply to the major ports of Chennai, Cochin, Jawaharlal Nehru Port, Kandla, Kolkata, Mumbai, New Mangalore, Mormugao, Paradip, VO Chidambaranar and Vishakhapatnam.
Boards to replace trusts
- Under the 1963 Act, all major ports are managed by the respective Board of Port Trusts that have members appointed by the central government.
- The Bill provides for the creation of a Board of Major Port Authority for each major port.
- These Boards will replace the existing Port Trusts.
- It will have a member each from the state governments, the Railways Ministry, the defence ministry, and the customs department.
- The Bill allows the Board to use its property, assets and funds as deemed fit for the development of the major port.
Board has financial powers
- Under the 1963 Act, the Board had to seek the prior sanction of the Centre to raise any loan.
- Under the new Bill, to meet its capital and working expenditure requirements, the Board may raise loans from any scheduled bank or financial institution within India, or any financial institution outside India.
- However, for loans above 50% of its capital reserves, the Board will require prior sanction of the central government.
The board will fix rates
- At present, the Tariff Authority for Major Ports fixes the scale of rates for assets and services available at ports.
- Under the bill, which now awaits President’s accent to become a law, the Board or committees appointed by the Board will determine these rates for services that will be performed at ports.
- The services would include the access to and usage of the port assets, and different classes of goods and vessels, among others.
Punishments
- Under the 1963 Act, there are various penalties for contravening provisions of the Act.
- The penalty for setting up any structures on the harbours without permission, for example, may extend up to Rs 10,000, and the penalty for evading rates may extend up to 10 times the rates.
- Under the new Bill, any person contravening any provision of the Bill or any rules or regulations will be punished with a fine of up to Rs one lakh.
Opposition criticism
- Opposition parties had opposed the legislation terming it the move to privatize ports.
- They said that this Bill is nothing but a retraction of the Singapore model.
- When there were hue and cry that there cannot be the privatization of ports, it adopted a policy of so-called corporatization. Thereafter, it ultimately privatized its ports.
- So, corporatization is the first step. The next in the offing is privatization said the opposition.
What did the govt. say?
- The government has brought in a provision that will allow ports to take their own decisions. To change tariffs, the ports have to now approach the ministry.
- The port sector in the last six years has doubled the profit. Profit has increased, liabilities have come down. For modernization, 300 projects are ongoing.
- This Bill is not to privatize any port, but it is to ensure that our ports can properly compete with private ports.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: OTT
Mains level: Need for OTT media regulation
Online streaming providers have announced the adoption of an ‘implementation toolkit’, under the aegis of the Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI).
What is the news?
- Various OTT platforms say that this is in furtherance to the Universal Self-Regulation Code the body had introduced in September.
- The government had rejected this USRC code.
Q.What is Over the Top (OTT) media services? Critically analyse the benefits and challenges offered by the OTT media services in India.
What are OTT Media?
- An over-the-top (OTT) media service is a streaming media service offered directly to viewers via the Internet.
- OTT bypasses cable, broadcast, and satellite television platforms, the companies that traditionally act as a controller or distributor of such content.
- The term is most synonymous with subscription-based video-on-demand (SVoD) services that offer access to film and television content.
- They are typically accessed via websites on personal computers, as well as via apps on mobile devices (such as smartphones and tablets), digital media players, or televisions with integrated Smart TV platforms.
Regulating OTT
- Currently, there is no law or autonomous body governing digital content. The recent move will give the government control over OTT platforms, which were unregulated till now.
- From time to time, the government had indicated the necessity to monitor these platforms.
- In October 2019, the government had indicated that it will issue the “negative” list of don’ts for the video streaming services like Netflix and Hotstar.
- It also wanted the platforms to come up with a self-regulatory body on the lines of the News Broadcasting Standards Authority.
What is the toolkit about?
- The effort of the signatories, through this toolkit, is to also address feedback received from the ministry of information and broadcasting inter-alia, on the issues of conflict of interest and prohibited content.
The all-inclusive implementation toolkit will assist signatories in a seamless transition to self-regulation and guide them on various dimensions like:
- Relevant laws of the land which will be adhered to by the signatories
- Fair and transparent functioning of the grievance redressal mechanism, with escalation to an advisory panel with independent members
- Training programs for creative and legal teams of OCCPs to enhance the knowledge and nuances of laws that govern content
- Awareness programs for consumers to help increase understanding and use of age rating, content descriptor & parental controls
- Implementation of a detailed audit and compliance mechanism
Why such code?
- The code comes into force at a time when the government has put OTT platforms on the anvil of content regulation after a spate of complaints on the ‘sensitive’ and ‘objectionable’ nature of certain shows.
- Earlier this week, I&B minister has assured the Parliament that guidelines for the regulation of OTTs have been practically hammered out and will be implemented soon.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Critical passes and valleys along the international borders
Mains level: India-China border tensions
In the first major breakthrough in talks China’s Defence Ministry that PLA and Indian troops on the southern and northern shores of Pangong Tso began synchronized and organized disengagement.
This newscard presents a holistic report on the ground situation of Sino-India border disputes in Ladakh.
Also, try this PYQ from CSP 2020:
Q.Siachen Glacier is situated to the
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c)North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley
New plan in eastern Ladakh
- As of now, the disengagement process seems restricted to the north and south banks of Pangong Tso.
- The process has started with the pulling back of certain columns of tanks from the south bank region by both sides.
- At the moment, there is no pullback of troops from the friction points and the heights they are positioned on.
- That will happen in a phased and verified manner.
Disengagement from Pangong Tso
- China will pull its troops on the north bank towards the east of Finger 8.
- Similarly, India will also position its forces at its permanent base near Finger 3.
- Similar action will be taken by both the parties in the south bank area as well.
- Both sides have also agreed that the area between Finger 3 and Finger 8 will become a no-patrolling zone temporarily, till both sides reach an agreement through military and diplomatic discussions to restore patrolling.
- Further, all the construction done by both sides on the north and south banks of the lake since April 2020 will be removed.
Why is this area important?

- The north and south banks of Pangong Tso are two of the most significant and sensitive regions when it comes to the current standoff that began in May 2020.
- What makes the areas around the shores of the lake so sensitive and important is that clashes here marked the beginning of the standoff.
- It is one of the areas where the Chinese troops had come around 8 km deep west of India’s perception of the Line of Actual Control.
- China had positioned its troops on the ridgeline connecting Fingers 3 and 4, while according to India the LAC passes through Finger 8.
Take a glimpse of all friction points along Indian borders:

India is at an advantage
- Further, it is in the south bank of the lake that Indian forces in an action in late August had gained a strategic advantage by occupying certain peaks, outwitting the Chinese.
- Indian troops had positioned themselves on heights of Magar Hill, Mukhpari, Gurung Hill, Rezang La and Rechin La, which were unoccupied by either side earlier.
- Since then, the Chinese side had been particularly sensitive as these positions allowed India to not only dominate Spanggur Gap.
- It is a two-km wide valley that can be used to launch an offensive, as China had done in 1962, they also allow India a direct view of China’s Moldo Garrison.
Why has this taken so long?
- Since September, China has insisted that India first pull its troops back from the south bank of Pangong Tso, and the Chushul sub-sector.
- However, India has been demanding that any disengagement process should include the entire region, and troops should go back to their April 2020 positions.
- However, it seems that for now, both sides have agreed to first disengage from the Pangong Tso area only.
Principles of disengagement
In military and diplomatic discussions with China India expects a solution to the issue on the basis of three principles:
- LAC should be accepted and respected by both parties.
- Neither party should attempt to change the status quo unilaterally.
- All agreements should be fully adhered to by both parties.
Does this mean that the standoff is resolved?
- There are still some outstanding issues that remain regarding deployment and patrolling on LAC.
- The Pangong Tso region is just one of the friction areas. There are other friction points, all north of the Pangong Tso, where the troops have been face-to-face since last year.
- The situation in Depsang Plains continues to be a concern.
- Both sides agree that complete disengagement under bilateral agreements and protocols should be done as soon as possible.
- After the talks so far, China is also aware of our resolve to protect the sovereignty of the country.
Need for confidence building
- Two of the main stumbling blocks in finding a permanent resolution are lack of trust and no clarity on intent.
- Any permanent resolution will include first, disengagement of troops from the frontlines from all friction points.
- Then de-escalation will entail sending the troops from the depth areas to their original bases.
- Both sides have around 50,000 troops in the region, along with additional tanks, artillery and air defence assets.
Conclusion
- A resolution has to include sending these troops and military equipment where they came from on both sides.
- But neither side had been willing to take the first step to reduce their troop or military strength, as it does not trust the other side.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Seaweed Mission
Mains level: Seaweed economy
TIFAC has unveiled a Seaweed Mission for commercial farming of seaweeds and its processing for value addition.
Note the species of edible seaweeds mentioned in the newscard.
Seaweed Mission
The Mission envisages the following activities:
- establishing model demonstration farms over one hectare for the cultivation of economically important seaweeds in nearshore and onshore along the Indian coast
- Kappaphycus all over Indian coast
- Gracilaria dura in Gujarat
- Gracilariaverrucosa in Chilika Lake (Odisha)
- Ulva Linza or Ulva prolife rain Chilika Lake (Odisha)
- Ulva Lactuca or Ulva fasciata or Ulva indica all over India coast
Proposed Sites: Gujarat / Tamil Nadu / Andhra Pradesh / Odisha / Karnataka
Seaweed production in India
- Out of the global seaweed production of ~ 32 million tons fresh weight valued around 12 billion US dollars. China produces ~57 %, Indonesia ~28% followed by South Korea.
- India is having a mere share of ~0.01-0.02%.
- Despite several advantages, commercial seaweeds cultivation has not been taken place in the country at an appropriate scale, as being practised in South-East Asian countries.
- By an estimate, if cultivation is done in ≈10 million hectares or 5% of the EEZ area of India, it can provide employment to ~ 50 million people.
- Seaweed cultivation also enhances ocean productivity, abates algal blooms and sequesters millions of tons CO2.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SAKSHAM portal
Mains level: MSMS sector and its job potential
The Technology Information, Forecasting and Assessment Council (TIFAC) has launched SAKSHAM, a dynamic job portal for mapping the skills of Shramiks.
The name SAKSHAM closely leans towards HRD, Employment and Entrepreneurship developments. Make a note of it. It can create confusion while revision.
SAKSHAM
- SAKSHAM is an acronym for Shramik Shakti Manch.
- The portal with the demand and supply data uses an algorithm and AI tools, for geospatial information on demand and availability of Shramiks, and also provides analysis on skill training programmes of Shramiks.
- It would directly connect Shramiks with MSMEs and facilitate placement of blue-collar jobs.
- The pilot portal originally initiated with two districts is now being launched as an all India portal.
Key features
- A dynamic job portal – an opportunity for Shramiks and MSMEs
- Facilitate the creation of 10 lakh blue-collar jobs
- Direct connect between Shramiks and MSMEs, no middleman in between
- Minimise migration of Shramiks – job opportunity in proximate MSMEs
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Glacial burst
Mains level: Paper 3- Floods in Uttarakhand and steps need to be taken to deal with such disasters
The article discusses the factors that could explain the cause of the recent flash floods in Uttarakhand and suggest the immediate steps to deal with such disasters.
What makes Uttarakhand vulnerable
- Days after a glacier burst in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand caused flash floods, the scientific community is still struggling to understand what triggered the disaster.
- Uttarakhand is located in the midst of young and unstable mountains and is subject to intense rainfall.
- For years experts have voiced their fears about an impending disaster due to climate change, rapid and indiscriminate construction activities, and the subsequent ecological destruction in the region.
- Studies have shown that widespread settlements, farming, cattle grazing and other anthropogenic activities could destroy the natural barriers that control avalanches and floods, thereby enhancing the possibilities of a glacial lake outburst flood.
- The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment Report (2019) had pointed out that one-third of the Hindu Kush Himalaya’s glaciers would melt by 2100 and potentially destabilise the river regime in Asia, even if all the countries in the region fulfilled their commitments under the Paris Agreement.
Possible causes of the current glacial outburst
- The current glacier burst was loosely attributed to erosion, a build-up of water pressure, an avalanche of snow or rocks, landslides or an earthquake under the ice.
- A rock mass, weakened from years of freezing and thawing of snow, may have led to the creation of a weak zone and fractures leading to a collapse that resulted in flash floods.
Issue of construction activity
- Experts and activists have incessantly asked for scrutiny into the construction of hydroelectric power projects in Uttarakhand.
- There have also been allegations about the use of explosives in the construction of dams and other infrastructure.
- In 2014, an expert committee led by Dr Ravi Chopra, instituted to assess the role of dams in exacerbating floods, provided hard evidence on how haphazard construction of dams was causing irreversible damage to the region.
7 Immediate steps
- 1) Investing in resilience planning, especially in flood prevention and rapid response.
- 2) Climate proofing the infrastructure such as by applying road stabilisation technologies for fragile road networks and strengthening existing structures like bridges, culverts and tunnels.
- 3) Strengthening embankments with adequate scientific know-how
- 4) Reassessing development of hydropower and other public infrastructure.
- 5) Investing in robust monitoring and early warning system.
- 6) Establishing implementable policies and regulatory guidelines to restrict detrimental human activities, including responsible eco- and religious tourism policies.
- 7) Investing in training and capacity building to educate and empower local communities to prevent and manage risks effectively.
Consider the question “What are the factors that make Uttarakhand vulnerable to natural disasters? Suggest the measures to prevent and deal with the disasters”
Conclusion
India needs to urgently rise up to the challenge by applying innovative and inclusive solutions that support nature and marginalised communities, to restore and rebuild a resilient future for Uttarakhand.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- MTP (Amendment) Bill and issues with it
The article discusses the provision of the medical board in the MTP (Amendment) Act and issues with it.
Proposal of medical board
- The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Bill (‘MTP Bill’) passed in the Lok Sabha is scheduled to be tabled for consideration in Rajya Sabha.
- The Act prescribes the setting up of medical boards in every state and Union territory (UT), consisting of a gynaecologist, paediatrician, radiologist or sonologist and any other members as proposed by that state or UT.
- Each board will be responsible for diagnosing substantial foetal abnormalities that necessitate termination of pregnancy after a 24-week gestation period.
- Medical boards are a form of third-party authorisation and were not envisaged in the MTP Act, 1971.
Issues with the proposal
- In the context of the current healthcare budgetary challenges, this proposal to set up infrastructure across the country to regulate medical termination of pregnancies is both financially unsound and practically impossible.
- India’s healthcare system has neither the financial investment nor the infrastructure to sustain the operation and functioning of medical boards in every state and UT.
- Due to the weak healthcare infrastructure in the country, it would be practically impossible to constitute these boards with the requisite specialists.
- Even where they are set up, the accessibility of such boards for pregnant persons, especially those living in rural areas, remains a major challenge.
- More importantly, subjecting people to multiple invasive examinations is a grave violation of their rights to privacy and dignity.
- Requiring pregnant persons to navigate a bureaucratic web of authorisation will inevitably lead to delays and thereby impede access to safe and legal abortion services.
Poor public financing and privatisation of healthcare
- At 1.6 per cent of GDP in 2019-20 India’s current level of public financing of health is one of the lowest in the world
- This has meant that most health expenditure in the country is out of pocket (OOP) — borne by patients themselves.
- OOP expenditure on healthcare is recorded at 58.7 per cent as per the National Health Accounts in 2016-17.
- The central government has preferred to incentivise private players to set up or offer services, instead of building infrastructural and professional capacity.
- Privatisation drives up costs of care and the handing over of public facilities to the private sector can have catastrophic consequences.
- They additionally remain non-accountable to state authorities in terms of affordability or transparency for instance, through Right to Information enquiries, or to uphold fundamental rights like non-discrimination in treatment or employment, or even the fundamental right to health.
- The National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO)’s 75th report shows that less than 20 per cent of the population is covered by health insurance in India.
- According to the National Health Profile 2017, India has only one doctor for roughly 10,200 people in the public sector.
Consider the question “Discsss the changes made by the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Bill and the challenges its provision could face.”
Conclusion
Poor public health infrastructure and absence of specialists across the country have meant that most abortions do not happen in the public sector, but at private centres or at home. With overwhelming shortfalls in specialist availability, especially in rural and scheduled areas, it would be impossible to constitute boards with requisite specialist representation as contemplated under the MTP Bill.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Foreign policy challenges India faces
The article explains the various choices India faces in the geopolitical landscape shaped by emergence of two Asian giants.
New challenges and hard choices on geopolitical front
- As it moves to becoming the third largest economy in the world, India needs to have a clear-eyed world view and strategy as it makes hard choices.
- It needs to reject the developing country regional mindset that has shaped India’s national aims and foreign policy.
- We have a “special and privileged strategic partnership” with Russia which provides more than three-quarter of India’s military equipment and a “comprehensive global strategic partnership” with the U.S.
- India’s relationship with the U.S.-led Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad), where the others are military allies, has rightly been cautious, as U.S. President Joe Biden sees China as a ‘strategic competitor’ rather than a ‘strategic rival’.
- Realism dictates that India does not need to compromise on its strategic autonomy.
- India faces two sides of the China conundrum: Defining engagement with its neighbour which is consolidating an expanding BRI while remaining involved with the strategic, security and technological concerns of the U.S.
China’s dominance in financial sphere
- In the financial sphere, there is the real possibility of the Chinese renminbi becoming a global reserve currency or e-yuan becoming the digital payments currency.
- China is the world’s largest trading economy.
- It could soon become the world’s largest economy.
- China has stitched together an investment agreement with the EU and with most of Asia.
- Relative attractiveness will determine when the dollar goes the way of the sterling and the guilder.
- China, facing technological sanctions from the U.S., may well put in the hard work to make this happen soon.
China: Partner, competitor, and economic rival
- Some form of the EU’s China policy of seeing the emerging superpower as a partner, competitor, and economic rival depending on the policy area in question is going to be the global norm.
- This broad perspective is also reflected in India’s participation in both the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, designed to resist the spread of Western interests, and in the U.S.-led Quad, with its anti-China stance.
- Within the United Nations, India’s interests have greater congruence with China’s interests rather than the U.S.’s and the EU’s.
- Sharing the COVID-19 vaccine with other countries distinguishes India, and China, from the rest.
India’s engagement with the U.S.
- The congruence between India and the U.S. lies in the U.S.’s declared strategic objective of promoting an integrated economic development model in the Indo-Pacific as a credible alternative to the BRI, but with a caveat.
- Instead of an alternate development model, India should move the Quad towards supplementing the infrastructure push of the BRI in line with other strategic concerns in the region.
- For example, developing their scientific, technological capacity and digital economy, based on India’s digital stack and financial resources of other Quad members, will resonate with Asia and Africa.
India’s role in global governance
- Another area where India can play a ‘bridging role’ is global governance.
- President Xi Jinping’s “community with shared future for mankind”, and Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s “climate justice” and asking how long India will be excluded from the UN Security Council, challenge the frame of the liberal order without providing specific alternatives.
- With respect to digital data, India has recently expressed that there must be reciprocity in data sharing, and this is the kind of ‘big idea’ for sharing prosperity that will gain traction with other countries.
India’s growing influence
- India’s recent policies are gaining influence at the expense of China and the West, and both know this trend will accelerate.
- The steps to a $5 trillion economy, shift to indigenous capital military equipment, and a new Science, Technology and Innovation Policy underline impact, capacity and interests.
- ASEAN remains keen India re-join its trade pact to balance China.
- It is being recognised that India’s software development prowess could shape a sustainable post-industrial state different to the U.S. and China model.
Consider the question “Examine how India’s foreing policy priorities and its role in global governance is shaped by China’s rise.”
Conclusion
As in the historical past, Asia is big enough for both Asian giants to have complementary roles, share prosperity and be independent of each other and of the West.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Rail Plan in the Budget
Mains level: Paper 3- National Rail Plan
The Budget unveiled the National Rail Plan 2030.
Key provision in the Budget for railways
- First, there is a National Rail Plan (NRP) for 2030.
- Second, the Western dedicated freight corridor (DFC) and the Eastern DFC will be commissioned by June 2022.
- Parts of DFC will be in public-private partnership (PPP) mode.
- Third, there will be an East Coast corridor (Kharagpur to Vijaywada), an East-West corridor (Bhusaval to Kharagpur/Dankuni) and a North-South corridor (Itarsi to Vijayawada).
- Fourth, all broad-gauge routes will be electrified by December 2023.
- Fifth, there will be safety and passenger amenity measures.
National Rail Plan provisions
- The NRP is meant to increase the share of railways in freight, rectifying the pre-Independence and post-Independence bias
- It also aims to develop capacity that will cater to demand in 2050.
- It provides for mapping of the existing railway network on a GIS platform.
- The primary value addition of the NRP is an analysis of the existing network, with expected additions (such as the National Infrastructure Pipeline) also built in.
- NRP bases decision making on objective criteria.
Pricing and cross-subsidy issue
- In 2018-19, as per the NRP, India’s operating ratio (OR) was 0.59 for freight and 1.92 for passenger traffic.
- The problem is low passenger fares and artificially high freight rates required to cross-subsidise those.
- This is not the complete picture since normally, freight and passenger trains share common sections of track and passenger trains are given preference over goods trains in getting a path (route from point A to point B).
- Therefore, the average speed of a freight train is 24 km/hour — average speed is a surrogate indicator.
- A superior indicator is transit time — the time taken for a consignment to reach from one point to another.
Need for decreasing the cost and increasing the average speed
- Indian Railways has a system of HDN and HUN identification for the present network.
- HDNs are high-density routes.
- HUNs are highly-used networks with multiple origins and destinations and no clear single haul corridor.
- HUNs are primarily for passengers.
- For freight, HDNs are important.
- HDNs and HUNs carry 80 per cent of the traffic and there are sections where capacity utilisation is more than 100 per cent.
- With traffic increasing, capacity utilisation will worsen.
- If the intention is to increase rail share in the total freight carried to 44 per cent, the average speed must increase and costs must decline.
- With the Western and Eastern DFCs, both should happen.
Consider the question “What are the factors responsible for preventing the railways from realising its contribution in the development of the country. How far will the National Rail Plan help railways deal with these factors?”
Conclusion
The implementation of the NRP will help railways deal with the issues faced by it.
Back2Basics: Operating Ratio
- The operating ratio shows the efficiency of a company’s management by comparing the total operating expense of a company to net sales.
- An operating ratio that is decreasing is viewed as a positive sign, as it indicates that operating expenses are becoming an increasingly smaller percentage of net sales.
OR = (Operating Expenses + Cost of Goods Sold)/ Net sales
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Division vote
Mains level: Not Much
Parliament saw the first instance of division voting in times of the pandemic, with Major Ports Authorities Bill 2020 passed in Rajya Sabha as members voted through slips in view of social distancing norms in place.
What is the news?
- The Bill provides for the regulation of major ports and will replace the Major Port Trusts Act of 1963, and a board of Major Port Authority for each major port will replace the current port trusts.
- The Opposition has charged that the Bill is aimed at privatization of ports.
- Opposition members said the legislation would adversely affect states’ rights.
What is Division Voting?
- A motion is a binary question raised in Parliament for a decision to be taken by MPs.
- A division is a type of voting which records how each MP voted on a motion.
- There are three methods of holding a Division i.e.
- By operating the Automatic Vote Recorder
- By distributing ‘Ayes’ and ‘Noes’ slips in the House and
- By members going into the Lobbies
- However, the method of recording of votes in Lobbies has become obsolete ever since the installation of Automatic Vote Recording machine.
- This procedure has not been used for the last two decades
Not a usual practice
In spite of the advantages offered by division, it is not the default method of voting in Parliament.
- The division is only mandated for a set of motions which require a special majority of the house to be passed.
- For example, constitutional amendment bills have to be passed by a majority of the total membership of that House and by a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members of the House “present and voting”.
- To ensure that this condition is fulfilled, a division is called for. On other occasions, individual MPs have to ask for a division.
- During the term of the last Lok Sabha (2014-19), voting by division was held only on 108 occasions. Only half of these were asked for by MPs, the other half related to constitutional amendment bills.
What is the preferred method?
- The preferred method for making decisions in Parliament is through a voice vote.
- In this method, MPs orally convey their agreement or disagreement to a motion.
- It clubs the individual decisions of MPs in one loud chorus of “Ayes” or “Noes”.
- Being an oral vote, it does not put on parliamentary record the stand of political parties and individual MPs on contentious political issues.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now









