Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Brexit
Mains level: Paper 2- India-U.K. ties
India and the U.K. has shard past, now the present offers an opportunity to strengthen the ties between the two countries.
India-U.K. ties in changing geopolitical landscape
- India has invited the British Prime Minister as chief guest for the Republic Day parade.
- India has a shared past with Britain and needs to chart a different shared future, now that Britain has left the European Union (EU).
- One joint enterprise will be as members of the UN Security Council where Britain has permanent status and India holds a non-permanent seat this year and next.
- Also, this year, the U.K. will be hosting India as an invitee to the G-7, and the UN Climate Change Conference.
Implications of Brexit on the bilateral relations
- For the U.K., Brexit necessitates that every effort be made to seek commercial advantage in Asian countries with high growth rates.
- India has been fruitlessly negotiating a trade agreement with the EU since 2007, during which Britain was considered the main deal-breaker.
- The EU wanted duty reductions on autos, wines and spirits and wanted India to open financial sectors.
- India sought free movement for service professionals.
- The same obstacles with post-Brexit Britain will arise, because the export profile of both countries is predominantly services-oriented.
- In response to free movement for professionals, Britain will refer to its new points-based system for immigrants.
- After withdrawing from the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, and will place greater stress on aspects related to country of origin and percentage of value addition in exports.
- Therefore, while signing agreement two countries will coverge on pharmaceuticals, financial technology, chemicals, defence production, petroleum and food products.
India-U.K. close ties
- One and a half million persons of Indian origin reside in Britain.
- Before COVID-19, there were half a million tourists from India to Britain annually and twice that figure in the reverse direction.
- Around 30,000 Indians study in Britain despite restrictive opportunities for post-graduation employment.
- Britain is among the top investors in India and India is the second-biggest investor and a major job creator in Britain.
- India has a credit balance in total trade of $16 billion, but the level is below India’s trade with Switzerland, Germany or Belgium.
Conclusion
Two countries should strive towards strengthening ties against the backdrop of changing geopolitical circumstances and the Brexit.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Trends in the various data of NFHS
Mains level: Paper 2- Analysis of NFHS-5 data
The article analyses the data of NHFS-5 and try to factors responsible for the outcomes.
Analysing health and nutrition of child through NHFS-5
- The recently released fifth round of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) provide insights into some dimensions of micro-development performance before COVID struck.
- The latest round only has data for 17 states and five Union territories.
- Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu are notable exclusions.
- Many of the child-related outcomes are also determined by state-level implementation, therefore neither success nor failure can be attributed to state or the centre alone.
Let’s understand the data
- The NFHS has 42 indicators related to child’s health and nutrition.
- Indicators fall into nine categories and each of these can be divided into outcomes and inputs.
- For example, neonatal, infant and under-5 mortality rates can be thought of as outcomes.
- Similarly, all the nutrition indicators —stunting, wastage, excess wastage, underweight and overweight can also be classified as outcomes.
- In contrast, the post-natal care indicators relating to visits made by health workers and the extent and nature of feeding for the child can be classified as inputs.
Outcomes of the survey
- On the front of wasting (weight for height of children) these is an improvement because even though the gains were marginal, they reversed a negative trend between 2005 and 2015.
- India continues to be successful in preventing child deaths, but the health and nutrition of the surviving, living child has deteriorated, somewhat worryingly.
- India continued to make progress in preventing child-related deaths (neonatal, infants and under-5).
- The pace of improvement in child mortality slowed down relative to the previous 10 years (Fig.1).
- Figure 2 shows the six indicators where outcomes have deteriorated. These all relate to what happens after survival:
- The health (anaemia, diarrhoea, and acute respiratory illness (ARI)) and nutrition (stunting, and overweight) of the child deteriorated between 2015 and 2019.
- The absolute deterioration in health and nutrition indicators must be seen against the fact that they reversed the historic trends of steady improvements.
What explains the outcomes
- Implementation capacity of individual states probably played an important role.
- Sector-specific factors such as changing diets are also implicated.
- A broader deterioration in outcomes hints at the likelihood of a common factor, namely the macro-economic growth environment, which determines employment, incomes and opportunities.
- At the least, it is safe to conjecture that some of these outcomes are inconsistent with the narrative of a rapidly growing economy.
Conclusion
As discussed in Chapter 5 of the Economic Survey of 2015-16, perhaps the next big welfare initiative of the government should be a mission-mode focus on the well-being of the early child (and of course the mother), from the womb to the first five years, which research shows is critical for realising its long run potential as an individual.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Water usage for agriculture in India
Mains level: Paper 3- Need for RD in agriculture
The article highlight the need for more emphasis on agricultural R&D as a solution to the woes of the farmers.
India needs low-input high-output agriculture
- Amid farmers protest against farm acts, the current debates focus mainly on MSP, reducing farmers’ debt liabilities, reducing post-harvest losses, cash transfers and marketing reforms.
- India with entrenched poverty requires low-input, high-output agriculture; low input in terms of both natural resources and monetary inputs.
- Very little attention is being given to reducing the natural resource inputs — most critical being water —and agricultural R&D.
- This cannot be achieved without science and technology.
Following are the areas in which Indian agriculture needs R&D to reduce agriculture inputs
1) Water usage for agriculture
- India receives around 4,000 billion cubic meters (bcm) of rainfall, but a large part of it falls in the east.
- Moreover, most of the rain is received within 100 hours of torrential downpour, making water storage and irrigation critical for agriculture.
- India has one of the highest water usages for agriculture in the world — of the total 761 bcm withdrawals of water, 90.5 per cent goes into agriculture.
- In comparison, China uses 385.2 bcm (64.4 per cent) out of the total withdrawals of 598.1 bcm for agriculture.
- China’s per-unit land productivity in terms of crop production is almost two to three times more.
- The total estimated groundwater depletion in India is in the range of 122-199 bcm .
- The depletion is highest in Punjab, Haryana, and western UP.
2) Increasing the yields of coarse-grain crops and oilseed crops
- Years of intense research on yield increase and yield protection by breeding varieties and hybrids resistant to pests and pathogens have made wheat, rice and maize stable high yielders.
- Environmentalists suggest replacing rice with coarse grain crops — millets, sorghum etc.
- However, the yields of these crops are not comparable to those of wheat and rice even when protective irrigation is available.
- These crops have a serious R&D deficit leading to low yield potential as well as losses to pests and pathogens.
- This leaves us with pulses and oilseeds.
- In the 2017-18 fiscal year, India imported around Rs 76,000 crore worth of edible oils.
- Three oilseed crops (mustard, soybean, and groundnut) are already grown very extensively.
- Soybean and groundnut are legume crops and fix their nitrogen.
- All three crops not only provide edible oils but are also an excellent source of protein-rich seed or seed meal for livestock and poultry.
- Unfortunately, yields of the three crops are stagnating in India at around 1.1 tons per hectare, significantly lower than the global averages.
3) Genetic improvements of crops
- Pests and pathogens can be best tackled by agrochemicals or by genetic interventions.
- A recent global level study on crop losses in the main food security hotspots for five major crops showed significant losses to pests — on average for wheat 21.5 per cent, rice 20 per cent, maize 22.5 per cent, potato 17.2 per cent, and soybean 21.4 per cent.
- India is one of the lowest users of pesticides.
- In 2014, comparative use of pesticides in kilograms per hectare in some select countries/regions is as following: Africa 0.30, India 0.36, EU countries 3.09, China 14.82, and Japan 15.93.
- A more benign method for dealing with pests is through breeding.
- The Green Revolution technologies were based on the effective use of germplasm and strong phenotypic selections.
- Recombinant DNA technologies since the 1970s have brought forth unprecedented opportunities for genetic improvement of crops.
- Since 2000, genomes of all the major crops have been sequenced.
- The big challenge is in the effective utilisation of the enormous sequence data that is available.
- India’s efforts in all three areas are half-hearted.
Way forward
- Over the last 20 years, India has been spending between 0.7 to 0.8 per cent of its GDP on R&D.
- This is way below the percentage of GDP spent by the developing countries and Asia’s rapidly growing economies.
- There are structural issues like lack of competent human resources and lack of policy clarity.
- However, the biggest impediment to agricultural R&D has been overzealous opposition to the new technologies.
Consider the question “India needs low-input, high-output agriculture. This cannot be achieved without science and technology. In light of this, examine how R&D could play a role in the advancement of agriculture in India.”
Conclusion
Maybe the present crisis in agriculture would lead to a greater appreciation of the need for strong public supported R&D in agriculture.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Central Vista Project
Mains level: Need for new parliament building

The Hon’ble Supreme Court has allowed the central vista project to go ahead.
Try this MCQ first:
Q.The architecture of the present Parliament House of India is inspired from:
a) Ekattarso Mahadeva Temple
b) Virupaksa Temple
c) Dilwara Temples
d) Brihaddeswara Temple
The Central Vista Project

- The project aims to renovate and redevelop 86 acres of land in Lutyens’s Delhi.
- In this, the landmark structures of the government, including Parliament House, Rashtrapati Bhavan, India Gate, North Block and South Block, etc. stand.
- This dream project of redeveloping the nation’s administrative heart was announced by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs on September 13, 2019.
Litigation over the project
- A petition was filed in the Supreme Court in April 2020, challenging the Centre’s change-of-land-use notification of March 2020 with regard to the 86 acres of land.
- The petitioner submitted that the order violated the citizen’s Right to Life guaranteed under Article 21 by depriving people of open and green spaces.
- The petition also argued that the notification violated the Master Plan of Delhi 2021.
- Subsequently, the court heard the challenge on three main grounds: change of land use; violations of municipal law; and violations of environmental law.
What has the court held?
- In a 2:1 majority verdict, the court has held that there are no infirmities in the approvals granted.
- The verdict held that the central government’s change of land use for the project in the Master Plan of Delhi 2021 is also a lawful exercise of its powers.
History of Lutyens’s Delhi
- At his coronation as Emperor of India on December 12, 1911, Britain’s King George V had announced the transfer of the seat of the Government of India from Calcutta to the ancient Capital of Delhi.
- Thereafter, a 20-year-long project to build modern New Delhi was spearheaded by architects Edwin Lutyens and Herbert Baker.
- They built Parliament House, Rashtrapati Bhavan, North and South Blocks, Rajpath, India Gate, National Archives and the princes’ houses around India Gate.
- New Delhi was unveiled in 1931.
Must read:
New Parliament Building
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam
Mains level: Horn of Africa Region

Ethiopia, Sudan and Egypt have agreed on to resume negotiations to resolve their decade-long complex dispute over the Grand Renaissance Dam hydropower project in the Horn of Africa.
Note: You never know when UPSC might switch map based questions away from the Middle East and SE Asia.
Considering this news, the UPSC may ask a prelim question based on the countries swept by River Nile/ various dams constructed/ landlocked countries in the African continent etc.
Also read
[Burning Issue] Ethiopian Crisis and the Geopolitics
Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam
- Spearheaded by Ethiopia, the 145-meter-tall (475-foot-tall) Grand Renaissance Dam hydropower project, when completed, will be Africa’s largest.
- Its construction was initiated in 2011 on the Blue Nile tributary of the river that runs across one part of Ethiopia.
- The Nile is a necessary water source in the region and Egypt has consistently objected to the dam’s construction, saying it will impact water flow.
- The long-standing dispute has been a cause of concern for international observers who fear that it may increase conflict between the two nations and spill out into other countries in the Horn of Africa.
What is the dispute about?
- The Nile, Africa’s longest river, has been at the centre of a decade-long complex dispute involving several countries that are dependent on the river’s waters.
- At the forefront of this dispute are Ethiopia and Egypt, with Sudan having found itself dragged into the issue.
- The main waterways of the Nile run through Uganda, South Sudan, Sudan and Egypt, and its drainage basin runs through several countries in East Africa, including Ethiopia.
Concerns over the dam
- Given the dam’s location on the Blue Nile tributary, it would potentially allow Ethiopia to gain control of the flow of the river’s waters.
- Egypt lies further downstream and is concerned that Ethiopia’s control over the water could result in lower water levels within its own borders.
- In addition, Egypt proposed a longer timeline for the project over concerns that the water level of the Nile could dramatically drop as the reservoir fills with water in the initial stages.
- Sudan’s location between Egypt up north and Ethiopia down south has caused it to become an inadvertent party to this dispute.
- But that isn’t all; Sudan to is concerned that if Ethiopia were to gain control over the river, it would affect the water levels Sudan receives.
Why does Ethiopia want this dam?
- Ethiopia’s goal is to secure electricity for its population and to sustain and develop its growing manufacturing industry.
- Addis Ababa anticipates that this dam will generate approximately 6,000 megawatts of electricity when it is completed, that can be distributed for the needs of its population and industries.
- In addition to its domestic requirements, Ethiopia may sell surplus electricity to neighbouring nations like Kenya, Sudan, Eritrea and South Sudan, that also suffer from electricity shortages, to generate some revenue.
What lies ahead?
- Despite previous talks, the point of contention hasn’t changed: Egypt and Sudan are concerned about the filling and the operation of the dam.
- Ethiopia continues to insist that the dam is required to meet the needs of its population and has said that downstream water supplies will not be adversely affected.
- Cairo insists that the dam would cut its water supplies — concerning for a country that depends on the Nile for approximately 97% of its drinking water and irrigation supplies.
- Sudan believes that the dam will reduce flooding, but is concerned about the path forward if the negotiations end at a stalemate.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Lithium production
Mains level: Lithium ion batteries and their significance
India has inked a pact with an Argentine firm to jointly prospect lithium in the South American country.
Why such a move?
- Currently, India is heavily dependent on import of these cells and the move to ink sourcing pacts for lithium is seen as another salvo in the front against China, a key source of both the raw material and cells.
- India is seen as a late mover as it attempts to enter the lithium value chain, coming at a time when EVs are predicted to be a sector ripe for disruption.
- And 2021 is likely to be an inflexion point for battery technology, with several potential improvements to the Li-ion technology.
About Lithium
- Lithium is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3.
- It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element.
- Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable and must be stored in mineral oil.
- When cut, it exhibits a metallic lustre, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery grey, then black tarnish.
- Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride.
- It is a crucial building block of the lithium-ion rechargeable batteries that power electric vehicles (EVs), laptops and mobile phones.
Global producers of lithium
- Australia and Chile have swapped positions as the world’s leading lithium-producing country over the past decade. In 2019, the world’s Top 5 lithium producers were:
- Australia – 52.9% of global production
- Chile – 21.5%
- China – 9.7%
- Argentina – 8.3%
- Zimbabwe – 2.1%
- The U.S. ranked 7th with 1.2% of the world’s lithium production.
- In 2019, the world’s Top 5 lithium reserves by country were:
- Chile – 55.5% of the world’s total
- Australia – 18.1%
- Argentina – 11.0%
- China – 6.5%
- U.S. – 4.1%
Lithium-ion batteries
- A lithium-ion battery or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery.
- They are commonly used for portable electronics and electric vehicles and are growing in popularity for military and aerospace applications.
- A prototype Li-ion battery was developed by Akira Yoshino in 1985, based on earlier research by John Goodenough, M. Stanley Whittingham, Rachid Yazami and Koichi Mizushima during the 1970s–1980s.
- In 2019, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was given to this trio “for the development of lithium-ion batteries”.
How does it work?

- In the batteries, lithium ions move from the negative electrode through an electrolyte to the positive electrode during discharge, and back when charging.
- Li-ion batteries use an intercalated lithium compound as the material at the positive electrode and typically graphite at the negative electrode.
- The batteries have a high energy density, no memory effect and low self-discharge.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce one of the following as “exhaust”:
(a) NH3
(b) CH4
(c) H2O
(d) H2O2
Limitations
- Despite the improvements in lithium-ion batteries over the last decade, long charging times and weak energy density are still barriers.
- The Li-ion batteries are seen as sufficiently efficient for applications such as phones and laptops, in case of EVs.
- They still lack the range that would make them a viable alternative to internal combustion engines.
- A number of alternatives are being fostered to achieve more optimal options.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PM UJALA scheme
Mains level: Not Much
The Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All (UJALA) Scheme and Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP) marks their sixth anniversary today.
Do not get confused with PM-UJJWALA Scheme.
UJALA Scheme
- Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All (UJALA) was launched by our PM on 1 May 2015, replacing the “Bachat Lamp Yojana”.
- The project is spearheaded by the Energy Efficiency Services Limited.
- In non-subsidized LED lamp distribution projects, this program is considered the world’s largest.
- In May 2017, the Government of India announced that they were expanding the LED distribution project to the United Kingdom.
- Both the programmes are being implemented by Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), a joint venture of PSUs under the Ministry of Power, Government of India since their inception.
A roaring success
- Under UJALA, EESL has distributed over 36.69 crores LED bulbs across India.
- This has resulted in estimated energy savings of 47.65 billion kWh per year with an avoided peak demand of 9,540 MW and an estimated GHG emission reduction of 38.59 million tonnes CO2 per year.
- Additionally, over 72 lakh LED tube lights and over 23 lakh energy efficient fans have also been distributed at an affordable price under this programme.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Unemployment
Mains level: Paper 3- Support to gig workers
With the lack of NREGA equivalent in the urban area government has to find ways to provide income support and employment. The article suggests ways to do the same.
Slowdown in employment recovery
- The Indian economy has been gradually recovering from historic contraction of negative 23.9%.
- This recovery has shifted focus away from the employment question, considered resolved after a sharp rally following the collapse in employment numbers in April.
- More recent data from the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy, however, point to a gradual slowdown in employment recovery.
NREGA: employment support in rural area
- For labour coming back to rural India, employment support came in the form of the National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGA), which witnessed a 243% increase in person workdays.
- This increased dependency on NREGA, has seen the Rural Development Ministry spend nearly 90% of its increased ₹86,4000 crore allocation by the month of November.
- In several Indian cities, however, closed businesses have meant that millions of workers have either had to leave or have had to take up new forms of work.
Supporting gig workers
With no urban equivalent to the NREGA on the horizon, there must be an increased impetus on evaluating, regulating and supporting new forms of employment.
1) Evaluation
- Our current understanding of gig work is based on the limited disclosures made by the platforms themselves.
- Furthermore, most regulators continue to remain in the dark on basic questions surrounding platform labour.
- As of now, there exists no authoritative estimate on the total number of gig workers in India.
- The centralised nature of the platforms and the larger platform labour market should make the collating of this data relatively straightforward for the Labour Ministry.
2) Regulation
- The next step is significantly more sensitive and involves regulation.
- The reason for the sensitivity primarily revolves around the varied nature of gig work.
- While some workers use these platforms as a “side hustle”, for others it continues to serve as a primary source of employment.
- This dynamic is further complicated by the risk of a one-size-fits-all regulatory strategy.
- Such regulatory strategies are unintentionally hurting the similar, yet distinct, market for highly skilled (and highly paid) freelancers.
Way forward
- A more viable strategy then would involve conditional government partnerships with platforms under some of its flagship schemes.
- The successful pilot of Swiggy’s Street Food Vendors programme under the PM SVANidhi, or PM Street Vendor’s Atma Nirbhar Nidhi scheme, may prove to be an illustrative example.
- Creation of jobs, alongside the voluntary adoption of quality standards, is an example of a mutually beneficial partnership between the state and platforms.
- Similar collaborations on urban employment, that require labour platforms to comply with disclosure norms and worker compensation standards to access government support, could create jobs while ensuring compliance.
- Collaborating with platforms to employ workers, would bring down costs significantly (for both the state and their partners) it would also create an environment where firms would be more likely to cooperate with the state.
Conclusion
Limited fiscal space and a growing need to fuel the country’s consumption base, must push the government to build symbiotic relationships with new partners.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- India-U.S. relations and area of cooperation
The article explores the area of cooperation for India and the U.S. under a new administration in U.S. amid changing geopolitical realities.
China: Shared cause of concern
- The Biden administration’s approach to India will be shaped by its position towards China.
- There is a bipartisan change in the US’s attitude to China.
- The Biden administration will continue Trump administrations trade policy- reducing the trade deficit, ensuring a level-playing field, keeping a keen eye on technology rivalry etc.
- There are parallels in the concerns of India and the U.S. — invigorating the domestic economy and dealing with a rising rival.
- These concerns can translate into opportunities for both countries.
How India and U.S can convert concerns into opportunities
1) Cooperation in healthcare
- Healthcare is clearly an area that India can play up in bilateral relations.
- The two countries can also work with multilateral agencies across the spectrum of vaccine (including Covid vaccine) development, logistics and distribution.
- India produces around 20 per cent of the global requirement for generic drugs by volume and every third tablet of generics consumed in the US.
- The President-elect has indicated his commitment to providing better and affordable healthcare
- This could be an opportunity for the Indian pharma sector to play a role in reducing health costs of the American consumer.
- India can benefit from advancements in medical technologies, devices, new medicines and R&D capabilities, presenting opportunities for American companies.
2) Job creation through trade and exports
- Biden has set an ambitious target for US-India trade.
- Businesses in both countries are also looking for diversifying their manufacturing supply chains.
- This portends well for the creation of employment in manufacturing.
- An area where strategic considerations and imperatives of job creation converge is defence, especially since India has been designated a Major Defence Partner of the US.
3) Focus on infrastructure in both countries
- For the US, this can mean opportunities in India in transportation, power and other urban amenities.
- The US’s renewed focus on climate change should lead to greater cooperation with India in energy-related areas.
- Cooperation in energy-related areas includes more efficient energy dissemination and management (such as smart grids) to renewable energy technologies.
4) Enhance opportunities in 5G tech
- There is potential to enhance mutual opportunities in the 5G tech sector.
- Increased partnership between the two nations can accelerate the development of technology solutions, promote vendors in the 5G open ecosystem and drive economic growth.
- The two countries should engage in shaping the rules of a new order in this space.
- This also has an important strategic element when seen in the light of developments in the Indo-Pacific as well as China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
5) Multilateralism for cooperation in wider areas
- Once the Biden administration assumes office, we should expect the U.S.’s return to multilateralism.
- The Trans-Pacific Partnership aimed to create a rules-based order that all parties could subscribe to.
- With the ascendancy of the Indo-Pacific paradigm and the Quad and Quad Plus, a successor to the TPP could include a wider canvas.
- For India, this could mean cooperation beyond defence and security, including economics, technology and developments pertaining to the regional order.
Conclusion
Both countries should treat the economic and commercial dimension with as much priority as the strategic dimension. Both governments should embrace the prosperity-creating potential of such an approach.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Uranium Enrichment
Mains level: Iran's hostile nuclear ambitions and its global threat
Iran has begun enriching uranium up to 20% at an underground facility and seized a South Korean-flagged oil tanker in the crucial Strait of Hormuz, further escalating tensions in West Asia between Tehran and the West.
Scratch your school basics to answer this PYQ:
Q.The known forces of nature can be divided into four classes, viz, gravity, electromagnetism, weak nuclear force and strong nuclear force.
With reference to them, which one of the following statements is not correct? (CSP 2012)
(a) Gravity is the strongest of the four
(b) Electromagnetism act only on particles with an electric charge
(c) Weak nuclear force causes radioactivity
(d) Strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons inside the nuclear of an atom.
What is Uranium Enrichment?
- Uranium enrichment is a process that is necessary to create an effective nuclear fuel out of mined uranium by increasing the percentage of uranium-235 which undergoes fission with thermal neutrons.
- Nuclear fuel is mined from naturally occurring uranium ore deposits and then isolated through chemical reactions and separation processes.
- These chemical processes used to separate the uranium from the ore are not to be confused with the physical and chemical processes used to enrich the uranium.
- Naturally occurring uranium does not have a high enough concentration of Uranium-235 at only about 0.72% with the remainder being Uranium-238.
- Due to the fact that uranium-238 is fissionable and not fissile, the concentration of uranium-235 must be increased before it can be effectively used as a nuclear fuel.
Why is the West concerned?
- Iran’s decision to begin enriching to 20% purity a decade ago nearly triggered an Israeli strike targeting its nuclear facilities, tensions that only abated with the 2015 atomic deal.
- A resumption of 20% enrichment could see that brinksmanship return as that level of purity is only a technical step away from weapons-grade levels of 90%.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: School Bag Policy, 2020
The Directorate of Education has issued a circular asking school to follow the new ‘School Bag Policy, 2020’ released by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
Q.What are the features of the School Bag Policy, 2020? Discuss how heavy school bags are a serious threat to the health and learning capability of students.
School Bag Policy, 2020
- According to the circular, schoolteachers should inform the students in advance about the books and notebooks to be brought to school on a particular day.
- They frequently need to check their bags to ensure that they are not carrying unnecessary material.
- It adds that the teachers should take the responsibility of checking the weight of school bags of the students every three months on a day selected for the whole class.
- It also holds that any information about heavy bags should be communicated to the parents.
- The circular also says that it is the duty and the responsibility of the school management to provide quality potable water in sufficient quantity.
- It adds that files and thin/light exercise books should be preferred to thick/heavy ones.
Prescribed weights
The weight of the school bags, as per the policy, should be
- 6 to 2.2 kg for students of Classes I and II
- 7 to 2.5 kg for Classes III, IV and V
- 2 to 3 kg for Classes VI and VII
- 5 to 4 kg for Class VIII
- 5 to 4.5 kg for Classes IX and X
- 5 to 5 kg for Classes XI and XII
Why heavy school bags are a curse?
- Heavy school bags are a serious threat to the health and well-being of students.
- A heavy backpack can pull on the neck muscles contributing to headache, shoulder pain, lower back pain and neck and arm pain.
- Not just this, carrying backpacks over one shoulder is a wrong practice as it makes muscles strain.
- The spine leans to the opposite side, stressing the middle back, ribs, and lower back more on one side than the other and this muscle imbalance can cause muscle strain, muscle spasm, and back pain.
- Heavy school bags are also one of the major reasons for cervical and lumbar pains.
- The posture of the body also gets affected to a great extent which in the long term develops imbalances in the body and affects the health of the nervous system.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tide–Rainfall Flood Quotient
Mains level: Flood management
To understand if a coastal city is more prone to floods caused by tidal events or extreme rainfall, a team from the IIT Bombay devised a new metric or measure called the Tide–Rainfall Flood Quotient.
Try this PYQ:
The 2004 Tsunami made people realize that mangroves can serve as a reliable safety hedge against coastal calamities. How do mangroves function as a safety hedge?
(a) The mangrove swamps separate the human settlements from the sea by a wide zone in which people neither live nor venture out
(b) The mangroves provide both food and medicines which people are in need of after any natural disaster
(c) The mangrove trees are tall with dense canopies and serve as art excellent shelter during a cyclone or tsunami
(d) The mangrove trees do not get uprooted by storms and tides because of their extensive roots
Tide–Rainfall Flood Quotient
- Using the past rainfall data, tidal data, and topography of the region one can apply this framework to pinpoint the major factor at play.
- This quotient helps understand the main driver of the flooding events for effective disaster management.
- It considers three geographically diverse flood-prone coastal regions – Mithi Catchment in Mumbai, , Jagatsinghpur District in Odisha, and Greater Chennai to test their new metric.
- The new method helped classify these regions into ‘storm-tide dominated’ or ‘pluvial (rainfall) dominated’ regions.
- In Mithi, they found a devastating impact of storm-tide reaching even up to a distance of 7 km from the coastal boundary.
- It concluded that Mithi catchment was ‘storm-tide dominated’, while Jagatsinghpur and Chennai were ‘pluvial dominated’
A tool for flood management
- This metric can help disaster management experts in framing better flood risk management systems directed towards long term planning.
- For storm-tide dominated regions, severe flood hazard can be alleviated by building coastal defence structures such as closure dams, tide breakers, and storm-surge barriers at appropriate locations.
- The tide and surge forecasting systems in these regions should be equipped with state-of-the-art ocean circulation models.
- On the other hand, for pluvial dominated regions, structural measures such as rainwater storage structures, lakes, and detention basins should be prioritized in the flood management plans.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bird Flu
Mains level: Not Much
An outbreak of bird flu was confirmed in Kerala, Rajasthan and Himachal.
Try this question from our AWE initiative:
There is been an increase in occurance of zoonotic human infectious diseases are zoonotic . Give reasons for this. Also suggest ways to contain and decrease the frequency of such events.(250 Words)
What is Bird Flu?
- Bird flu is an infection caused by avian influenza viruses, which are of different types A, B and C.
- Type A avian influenza viruses are the most frequently associated with avian influenza epidemics and pandemics.
- There are 16 hemagglutinin (H1 to H16) and 9 neuraminidase types (N1 to N9) identified till date.
- There are various modes of transmission of human influenza including inhalation, direct or indirect contact etc. can have manifestations ranging from mild to severe or fatal disease.
- Avian influenza A (H5N1) results in a high death rate amongst infants and young children.
- The first outbreak of human infection by avian influenza viruses (H5N1) was observed in 1997 in Hong Kong. Since then a large number of outbreaks have been reported in different parts of the world.
The H5N8 strain
- The presence of the H5N8 subtype of the Influenza A virus was reported in ducks in parts of Kerala.
- While it can prove lethal for birds, the H5N8 strain of avian influenza has a lower likelihood of spreading to humans compared to H5N1.
- While the source of infection is yet to be pinpointed, the role of migratory birds in passing on the virus is suspected.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India's polar mission
Mains level: Climate change impact on cryosphere

40th Indian Scientific Expedition is set to depart for Antarctica from Mormugao Port, Goa.
Try this question:
Q.How does the cryosphere affect global climate? (150W, CSM 2018)
Indian mission on the Antarctic
- The Indian Antarctic Program is a multi-disciplinary, multi-institutional program under the control of the National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research, Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It was initiated in 1981 with the first Indian expedition to Antarctica.
- The program gained global acceptance with India’s signing of the Antarctic Treaty and subsequent construction of the Dakshin Gangotri Antarctic research base in 1983, superseded by the Maitri base from 1990.
- The newest base commissioned in 2015 is Bharati, constructed out of 134 shipping containers.
Its significance
- This 40th expedition is procuring fuel from India after about 22 years. Till the last expedition, fuel was being obtained from outside the country.
- Indian Oil Co. Ltd. has supplied aviation fuel, Jet A1 in bulk and packed form to a non-aviation customer and is delivered to an ocean-going vessel for the first time.
Why need such a mission?
- Polar Regions are crucially important in answering key questions about global climate change.
- It contributes towards the global sea-level rise, the background aerosol properties, variability in the sea ice cover and phenomena like Antarctic haze and ozone concentrations.
- Attempts to address some of these issues are helping in mitigating several important problems concerning human life and well-being.
Back2Basics: India’s polar missions
- The first Indian expedition to Antarctica sailed from Goa on December 6, 1981, and reached the shores of this polar continent on January 9, 1982.
- India has two stations in the polar continent of Antarctica – Maitri and Bharati, which are being operated under NCPOR, Ministry of Earth Sciences.
Indian mission on the Arctic
- Himadri Station is India’s first Arctic research station located at Spitsbergen, Svalbard, Norway. It is located at the International Arctic Research base, Ny-Ålesund.
- It was inaugurated on the 1st of July, 2008 by the Minister of Earth Sciences. It is followed by IndARC.
- The United States Geological Survey estimates that 22% of the world’s oil and natural gas could be located beneath the Arctic.
- ONGC Videsh has signed joint-venture with Russia for oil exploration there.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Faceless Tax Scheme
Mains level: Ease of IT returns
The government’s faceless tax assessment scheme has managed to deliver about 24,000 final orders since its introduction in August 2020.
Try this PYQ:
Q. With reference to India’s decision to levy an equalization tax of 6% on online advertisement services offered by non-resident entities, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is introduced as a part of the Income Tax Act.
- Non-resident entities that offer advertisement services in India can claim a tax credit in their home country under the “Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements”.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Faceless Tax Scheme
- The Central Government introduced the Faceless Assessment Scheme to provide greater transparency, efficiency and accountability in Income Tax assessments.
- It is an attempt to remove individual tax officials’ discretion and potential harassment for income taxpayers.
- All provisions introduced under Faceless Assessment, under the Income Tax Act, 1961, are introduced to-
- Eliminate the interface between the Assessing Officer and the assesses during the course of proceedings, to the extent that is technologically feasible
- Optimize the utilization of resources through the economies of scale and functional specialization and
- Introduce a team-based determination of arm’s length price with dynamic jurisdiction.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Patent Act 1970
Mains level: Paper 3- Amendment to patent working disclosure rule and its implications
A recent amendment to a unique feature in patent law under which patentee/licensee has to disclose information regarding the extent to which they have worked patent in India, could have several implications.
Why the changes in rules matter
- Indian patent law grants a 20-year patent monopoly to an inventor.
- In exchange for such monopoly, India’s patent law imposes a duty on the patentee to commercially work the invention in India to ensure that its benefits reach the public.
- Accordingly, section 146(2), a unique provision not found in patent laws of most other countries, requires every patentee and licensee to submit to the Patent Office an annual statement (Form 27 format) explaining the extent to which they have worked the invention in India.
- This statement is meant to help the Patent Office, potential competitors, etc. to determine whether the patentee has worked the invention in India and made it sufficiently available to the public at reasonable prices.
- A failure of this duty could trigger compulsory licensing or even subsequent revocation of the patent under the Patents Act, 1970.
- The central government recently amended the format of a statement that patentees and licensees are required to annually submit to the Patent Office.
- The amendment has significantly watered down the disclosure format.
- This could hamper the effectiveness of India’s compulsory licensing regime.
- This in turn could hinder access to vital inventions including life-saving medicines, thereby impacting public health.
- There has been significant pressure from multinational corporations and the United States government to do away with this requirement.
What changes were made through the amendment
- The recent amendment to the form was made in response to a PIL filed by Shamnad Basheer before the Delhi High Court in 2015.
- The PIL brought to the Court’s attention the rampant non-filing and defective filing of Form 27 and sought a direction to strictly enforce the patent working disclosure rules and take action against the violators.
- The PIL also called for a reform of Form 27, arguing that the information it sought was grossly insufficient to ascertain the extent of the working of the patent.
- However, instead of strengthening the form, the amendment has significantly weakened it further, thereby defeating the entire purpose of the amendment exercise.
- The amended form has removed the requirement of submitting a lot of important information.
- It is no longer required to provide any information in respect of the quantum of the invention manufactured/imported into India, the licenses and sub-licenses granted during the year and the meeting of public requirement at a reasonable price.
- It no longer requires quantum or the total units of the invention manufactured/imported in India.
- The deletion of this requirement of its disclosure is shocking.
- This is because, it is the disclosure of this data by Bayer in Form 27 that played a crucial role in grant of India’s first compulsory license to Natco for the anti-cancer drug Sorafenib/Nexavar.
- The removal of the requirement of submitting any licensing information, including the disclosure of even the existence of licenses means that the patentees/licensees can just self-certify that they’ve worked the patent.
- The omission to mandate disclosure of details makes it extremely difficult to ascertain whether the invention has been made available to the public in sufficient quantity and at an affordable price.
Conclusion
The government has significantly weakened the critical duty imposed by the law on patentees/licensees to disclose patent working information. Therefore, the government must reconsider its amendments to the form taking into account the PIL recommendations and re-amend it to restore as well as strengthen its spirit.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Post-covid development model
The article discusses the themes of the post-covid world which will be somewhat more aware and mindful of the dangers of global dimension.
Collaborative model and public-private partnership
- A few weeks back, Prime Minister visited the private companies involved with the formulation of the anti-COVID vaccine.
- The PM’s visit was one more reminder of the critical importance of public-private partnerships.
- The PM signalled the government’s receptivity to external expert advice.
- The CEOs reaffirmed their commitment to partnering with the state to help address not just this medical crisis but also the many other social and humanitarian problems.
- The government has appreciated that the model for sustainable development in a post-COVID world must be a collaborative one.
- Businesses will repurpose their goals and look beyond profits.
Working together to deal with the crises of global dimensions
- COVID-19 was not the first, nor will it be the last crisis of global dimensions.
- The threat of global warming, for instance, hangs over our heads.
- Its impact is less immediate and for the present, at least less palpable.
- But it looms and its consequences are existential.
- COVID has offered, it is the tangible evidence that no one entity or group — the state, markets, businesses, entrepreneurs, scientists — can tackle existing and emergent economic and social problems on their own.
- They have to work together to resolve them.
Business uncertainties
- Businesses has been the uncertainty of operating in the post-COVID digital world.
- Every business leader has, in some form or other, expressed three types of uncertainties.
- 1) Is their business facing a hinge moment, necessitating the reimagining and re-engineering of their strategy and product portfolio?
- Or are they witnessing no more than another turn of the business cycle and that, once the vaccine is developed and distributed, the market will return to business as usual?
- Or will conditions necessitate a middle of the road approach: Stay the pre- COVID course but at the same time, speed up the pivot toward a new business model.
- Most business leaders are adopting this third hybrid path.
- The key to corporate success in a digital world in which a distinct incident could influence it, is the capability of leaders to think out of the box and to handle the unexpected.
- Financial, technological and human resources will be necessary, but they will not be sufficient.
Consider the question “The post-covid development model must be based on the cooperation underscored by the public-private partnership as the challenges that could emerge are not possible to be tackled by any on entitiy. Comment”
Conclusion
COVID has “obliterated the one remaining obstacle to a digital future — human attitudes”. Covid forced them to adopt and adapt. The challenge for our business leaders will be to navigate a pathway that sustains the benefits of these tools but without deepening the existing social and economic inequalities. Life is not digital for millions in our country.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CDS and Department of Military Affairs
Mains level: Paper 3- Creation of Theatre Commands and issues with it
The article examines issues of national security like the recent creation of a Department of Military Affairs (DMA) and a Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and also some focus areas like Threatre Command.
Understanding the significance of DMA and CDS
- Through the creation of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS), the management of the armed forces, so far which was assigned to the civilian Defence Secretary, was brought under a military officer, the CDS.
- The designation of CDS as Secretary DMA made him the first military officer to be recognised as a functionary of the Government of India (GoI).
- With the DMA is now a part of the GoI, it would aid the resolution of organisational, hierarchical and financial issues faced by the military.
Recent steps taken by DMA
- The responsibility for accruing savings to fund defence expenditure has been placed on the DMA.
- DMA has floated two schemes aimed at reducing the defence pensions bill.
- One penalises officers seeking early release from service and another envisages a three-year “Tour of Duty” for jawans.
- Issues with these ideas:
- Penalising officers for early release is likely to harm morale.
- “Tour of Duty” will degrade the military’s combat-capability in today’s technology-intensive battle-space.
- The need here is that DMA must focus on military matters and leave the plans of financing national defence to finance ministry or the Niti Aayog. It will better serve it’s purpose.
Another area of needed reform – Theatre Command
- Theatre Commands stands for jointness and integration in the Indian military are varying degrees of synergy and cross-service cooperation between the military wings of Indian armed forces.
- Objectives of the creation of theatre command should be:
- To hand over the military’s warfighting functions to the Theatre Commanders, while retaining the support functions with service HQs.
- To combine India’s 17 widely-dispersed, single-service Commands into four or five mission/threat-oriented, geographically contiguous “Joint” or “Theatre Commands”.
- To place the appropriate warfighting resources of all three services directly under the command of the designated Theatre Commanders; and
- To achieve efficiency/economy by pooling of facilities and resources of the three services.
Advantages of Theatre Commands
- The Theatre Commanders and their staff will be trained and groomed in jointness.
- With that jointness, they will be able to plan operations and to employ land, maritime and air forces, regardless of the service to which they belong.
- For this to happen, radical changes are required in the content of our system of professional military education.
- The Theatre Commander will also have the benefit of advice from commanders representing each service.
Issues with Theatre Commands
- Two thorny issues are the chain of command of the Theatre Commanders and the relationship of the CDS (or his equivalent) with the service Chiefs.
- To avoid over-concentration of power in any single military functionary, the system followed by the US ensures that the chain of command runs from the President to the Secretary (Minister) of Defence and then, directly to the Theatre Commander.
- In India, the peacetime management of the armed forces is left to the MoD and the Chiefs of Staff Committee (COSC).
- However, during war, strategic guidance to the military, has always come from the PM.
- In the system of higher defence under implementation, ideally, the Defence Minister needs to be brought into the command/operational chain of the Theatre Commanders, with the CDS acting as his adviser.
- Due to frequency of elections and intensity of politics in India that no Defence Minister has had the time or inclination to devote his/her undivided attention to complex national security issues.
Consider the question “Examine the implications of the creation of Theatre Commands. What are the challenges in its creation.”
Conclusion
India’s military reforms are complex, the GoI needs to seriously consider the constitution of a Parliamentary Committee, with military advisers, to oversee and guide this transformational process.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: OECD , various parameters mentioned
Mains level: Concerns of farmers other than MSP
The OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) has provided five sets of data on the issue of agriculture support and India trails on most counts:
The ongoing debate about farmers protest has brought to light some of the key support mechanisms for agriculture in India. And it is being argued that the government has preferred the welfare of Indian consumers over the Indian farmers.
Lets’ have a look at various OECD’s parameters:
(1) Producer Support Estimates (PSE)

- These are transfers to agricultural producers and are measured at the farm gate level.
- They comprise market price support, budgetary payments and the cost of revenue foregone.
(2) Consumer Support Estimates (CSE)

- These refer to transfers from consumers of agricultural commodities. They are measured at the farm gate level.
- If negative, the CSE measures the burden (implicit tax) on consumers through market price support (higher prices), that more than offsets consumer subsidies that lower prices to consumers.
(3) General Services Support Estimates (GSSE)

- GSSE transfers are linked to measures creating enabling conditions for the primary agricultural sector through the development of private or public services, institutions and infrastructure.
- GSSE includes policies where primary agriculture is the main beneficiary but does not include any payments to individual producers.
- GSSE transfers do not directly alter producer receipts or costs or consumption expenditure.
(4) Total Support Estimate (TSE)
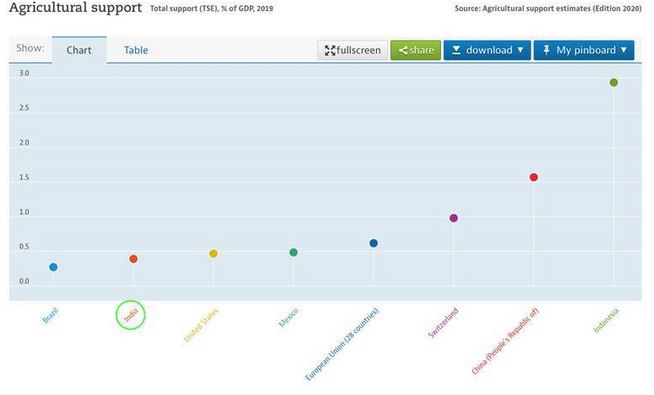
- The TSE transfers represent the total support granted to the agricultural sector, and consist of producer support (PSE), consumer support (CSE) and general services support (GSSE).
(5) Producer protection

- Lastly, the OECD also provides data on “producer protection”.
- The PP is the ratio between the average price received by producers (measured at the farm gate), including net payments per unit of current output, and the border price (measured at the farm gate).
- For instance, a coefficient of 1.10, which China has, suggests that farmers, overall, received prices that were 10% above international market levels.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gilgit-Baltistan Region, CPEC
Mains level: CPEC and India's sovereignty concerns

The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) has turned five.
What is CPEC?
- China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a collection of infrastructure projects that are under construction throughout Pakistan since 2013.
- It is an extension of the Belt and Road Initiative of China.
- It intended to upgrade Pakistan’s required infrastructure and strengthen its economy by the construction of modern transportation networks, numerous energy projects, and special economic zones.
- On 13 November 2016, CPEC became partly operational when Chinese cargo was transported overland to Gwadar Port for onward maritime shipment to Africa and West Asia.
Why in news?
- The viability of some of the CPEC’s projects, and how they were going to be paid for in a pandemic-hit economy, had come under renewed attention in Pakistan.
- China had sought additional guarantees before sanctioning a $6 billion loan for the Main Line-1 (ML-1) project, which includes upgrading a 1,872 km rail line from Peshawar to Karachi.
- This is due to the “weakening financial position of Pakistan” and had “proposed a mix of commercial and concessional loans against Islamabad’s desire to secure the cheapest lending”.
An overrated project
- The CPEC, to some degree, has been a victim of its own hype.
- Its economic figure may never materialise as the plan has been “considerably slimmed-down” from the scope that was first imagined.
- This largely due to the ever-deteriorating financial situation of Pakistan and a visible debt-trap.
- Pakistan had established a CPEC authority to speed up the execution of several projects that were mired in delays (and to give the military a greater role in the project).
Threats of Baloch insurgency
- Gwadar, the heartland of CPEC certainly faces serious threats.
- The city is a prime target for Baloch nationalist insurgents. Hence Pakistan has decided to fence the area.
- This has sparked a new furore among the local residents.
India’s concerns with CPEC
- CPEC passes through Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (Gilgit-Baltistan) which is an Indian territory illicitly occupied by Pakistan.
- Thus CPEC undermines India’s strategic interests and territorial integrity.
- More importantly, with CPEC, China will get access to the western Indian Ocean through Gwadar port.
- This will help China in controlling maritime trade and would affect the freedom of navigation and trade-energy security of India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now











