Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ICMED 13485 PLUS
Mains level: NA
The Quality Council of India (QCI), and the Association of Indian Manufacturers of Medical Devices (AiMeD) have added further features to the ICMED Scheme for Certification of Medical Devices.
ICMED 13485 PLUS
- The ICMED 13485 PLUS, as the new scheme has been christened, will undertake verification of the quality, safety and efficacy of medical devices.
- It was first launched in 2016.
- It has been designed to integrate the Quality Management System components and product-related quality validation processes through witness testing of products with reference to the defined product standards and specifications.
- This is the first scheme around the world in which quality management systems along with product certification standards are integrated with regulatory requirements.
- This scheme will be an end-to-end quality assurance scheme for the medical devices sector in India.
Details of the scheme
- This scheme provides the much-needed institutional mechanism for assuring product quality and safety.
- It will go a long way in assisting the procurement agencies to tackle the challenges relating to the menace of counterfeit products and fake certification.
- This will also help in eliminating the circulation and use of sub-standard medical products or devices of doubtful origin that could prove to be serious health hazards.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Atlas on General Elections
Mains level: Unique features of Indian general elections

The Election Commission of India has released ‘General Elections 2019 – An Atlas’.
Atlas on General Elections
- The Atlas encompasses all the data and statistical figures of this monumental event. It shares interesting facts, anecdotes and legal provisions related to the Indian elections.
- It brings out salient features such as data of the 23 States and Uts where women voting percentage was more than the male voting percentage.
- It has information about the largest & smallest parliamentary constituency in terms of electors, candidates and performance of political parties amongst other parameters.
- The Atlas depicts the elector’s data in different categories and through various comparison charts like Elector Gender Ratio and electors in different age categories.
- This Atlas serves as an informative and illustrative document that brings to light the nuances of the Indian electoral process and empowers readers to analyze trends and changes.
Data on 2019 Elections
- The 2019 General Elections witnessed the lowest gender gap in the history of Indian elections.
- The Elector Gender Ratio which has shown a positive trend since 1971 was 926 in the 2019 General Elections.
- The Atlas also compares the average number of electors per polling station in different states during the 2014 & 2019 General Elections.
- The Election Commission of India set up over 10 lakh polling stations in General Elections 2019 with the lowest number of electors per polling station (365) in Arunachal Pradesh.
Why was such Atlas needed?
- Since the first General Elections in 1951-52, the Commission has been publishing a compilation of electoral data in the form of narrative and statistical books.
- 17th General Elections conducted in 2019 were the largest democratic exercise in human history which witnessed the participation of 61.468 crore voters at 10.378 lakh polling stations spread over 32 lakh sq km.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise EUNAVFOR
Mains level: NA
Indian Navy is participating in the maiden IN – EUNAVFOR Joint Naval Exercise in the Gulf of Aden.
Exercise EUNAVFOR
- EUNAVFOR is a multilateral naval exercise comprising of Italian Navy, Spanish Navy, and French Navy.
- Ships of the four navies will endeavor to enhance and hone their war-fighting skills and their ability as an integrated force to promote, peace, security, and stability in the maritime domain.
- EUNAVFOR and the Indian Navy converge on multiple issues including counter-piracy operations and protection of vessels deployed under the charter of the World Food Programme (UN WFP).
- Indian Navy and EUNAVFOR also have regular interaction through SHADE (Shared Awareness and De-confliction) meetings held annually in Bahrain.
- This engagement showcases increased levels of synergy, coordination, and inter-operability between India and EUNAVFOR.
- It also underscores the shared values as partner navies, in ensuring freedom of seas and commitment to an open, inclusive and rules-based international order.
Mark the nations along the Gulf of Aden:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Regulation of social media and related issues
The article discusses the need for regulation of social media and counters against placing social media on a higher pedestal for the application of reasonable restrictions.
Social media and its regulation
- Social media is a commercial product that connects people all over the globe.
- It allows people to converse with each other through profiles both known and anonymous.
- The object is purely commercial, that is to make money.
- The fact that a commercial product could be used for a social purpose does not make the product a social good.
- The new Information Technology Rules, 2021 formulated by the Government of India attempts to bring in a minimum regulatory standard to social media.
- The present amendment to the rules is to formulate a broad and soft-touch regulation mechanism for use of the product, just like one would for a good like a car or a service like chartered accountancy.
Issues with regulation of social media
1) Immunity from content posted on platforms
- Social media companies enjoy an immunity — they are not considered responsible for the contents posted on them.
- The immunity is granted on the ground that social media is merely a platform or a sort of a glorified postbox.
- It is incorporated under the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines) Rules, 2011 framed under Section 79 of the Information Technology Act.
- This protection is itself unique as it is not extended to newspapers, magazines or even websites.
- This protection is given by the government as an exceptional measure.
- The present amendment to rules only tries to update and make these rules workable considering the latest global developments.
2) Constitution allows for restriction of freedom of speech
- The Constitution itself gives us a restricted right to freedom of speech under Article 19(1)(a) and 19(2).
- The argument that social media is entitled to some form of higher protection because it exists on the internet is an untenable argument.
- The Constitution doesn’t recognise a hierarchy of rights depending on the medium through which the freedom of speech is exercised.
3) Important for political and commercial speech
- Social media has become so crucial to commercial and political speech in this country, there is an urgent need to regulate it.
- It has effectively become a public square in which the most important conversations on politics and society are discussed.
- The function of social media is clearly a public function at the lowest and as a public utility at the high end, and, therefore, automatically subject to regulation and the writ jurisdiction of the courts.
Conclusion
For all its significance and importance, social media needs to be regulated. However, the regulations should not hamper the freedom of expression and free speech.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 3- Increasing the public spending for economic recovery
The article takes an overview of the impact of the second covid wave and suggests the need for more public spending.
Impact of reforms in recovery
- Overlapping State-level lockdowns that started in April have now lasted for almost as long as the nationwide lockdown of 2020, impacting the economy.
- Output may well have contracted in the beginning of this year.
- So, though recovery will eventually come, it could be W-shaped rather than V-shaped.
- It is asserted that the economy will recover due to the reforms planned or already implemented by the government.
- Since 1991, the term ‘reforms’ has been used to mean both policy changes that remove restrictions on private sector activity in certain areas and those that increase profits in existing lines of production.
- Recent examples of such reforms include the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan launched in 2020 and the significant lowering of corporate tax in 2019, respectively.
- However, more reforms may be ineffective in spurring recovery.
- Presently for the private sector is not undertaking investment given their expectation of the state of the economy in the near future, upon which their revenue will depend.
Public expenditure
- In February, believing that the peak of the epidemic had been crossed, the government reverted to fiscal consolidation or the paring down of the fiscal deficit.
- Accordingly, it raised its budgeted expenditure by less than 1% in the last Budget.
- But now, with a possible further contraction of the economy, to continue with the frigid fiscal stance would be disastrous.
- Data from the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy show that unemployment has risen in May, indicating slack demand for output.
- With this knowledge, the private sector is unlikely to respond with alacrity to liberalising reforms.
Way forward
- The objective is to revive the economy, public spending is the instrument and the funding must be found.
- It need not involve money creation.
- India’s public debt is low by comparison with the OECD countries, and debt financing remains an option.
- Even if money financing is adopted, it need not cause accelerating inflation.
- How the expansion is financed is less relevant for inflation at least in the near term.
Consider the question “Are the economic reforms enough to ensure the recovery of the economy? Also, examine the importance of public spending for economic recovery.”
Conclusion
Reforms albeit important for the economy in long run, may not be much effective in an economy battered by the pandemic. What we need is public spending and welfare measures.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Use of disruptive technologies in medical sector
The adoption of technologies such as AI and blockchain has the potential to transform the medical sector.
How new technologies can play important role in medical sector
1) Blockchain technology
- Blockchain technology can help in addressing the interoperability challenges that health information and technology systems face.
- The health blockchain would contain a complete indexed history of all medical data, including formal medical records and health data from mobile applications and wearable sensors.
- This can also be stored in a secure network and authenticated, besides helping in seamless medical attention.
2) Big data analytics
- Big data analytics can help improve patient-based services tremendously such as early disease detection.
- AI and the Internet of Medical Things, or IoMT are shaping healthcare applications.
- IoMT is defined as a connected infrastructure of medical devices, software applications, and health systems and services.
3) Medical autonomous system
- Medical autonomous systems can also improve health delivery to a great extent and their applications are focused on supporting medical care delivery in dispersed and complex environments with the help of futuristic technologies.
- This system may also include autonomous critical care system, autonomous intubation, autonomous cricothyrotomy and other autonomous interventional procedures.
4) Cloud computing
- Cloud computing is another application facilitating collaboration and data exchanges between doctors, departments, and even institutions and medical providers to enable best treatment.
Challenges
- The possible constraints in this effort are standardisation of health data, organisational silos, data security and data privacy, and also high investments.
Using technology for Universal Health Coverage
- According to the World Health Organization, Universal health coverage (UHC) is a powerful social equalizer and the ultimate expression of fairness.
- Studies by WHO show that weakly coordinated steps may lead to stand-alone information and communication technology solutions.
- India needs to own its digital health strategy that works and leads towards universal health coverage and person-centred care.
- Such a strategy should emphasise the ethical appropriateness of digital technologies, cross the digital divide, and ensure inclusion across the economy.
- ‘Ayushman Bharat’ and tools such as Information and Communication Technology could be be fine-tuned with this strategy to promote ways to protect populations.
- Online consultation should be a key part of such a strategy.
Using local knowledge
- In addition to effective national policies and robust health systems, an effective national response must also draw upon local knowledge.
- Primary health centres in India could examine local/traditional knowledge and experience and then use it along with modern technology.
Way forward
- Initial efforts in this direction should involve synchronisation and integration, developing a template for sharing data, and reengineering many of the institutional and structural arrangements in the medical sector.
- Big data applications in the health sector should help hospitals provide the best facilities and at less cost, provide a level playing field for all sectors, and foster competition.
Consider the question “Examine the role technologies such as AI and data analytics could play in the medical sector. What are the challenges in the adoption of such technologies?”
Conclusion
The above-discussed aspects highlight the potential benefits of the adoption of disruptive technologies in the healthcare system. India should embrace it while addressing the concerns with such technologies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Maritime Heritage Complex, Lothal
Mains level: Not Much

In order to showcase the maritime heritage and history of India, a National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) will be developed in the Lothal region of Gujarat.
National Maritime Heritage Complex
- It is to note that the National Maritime Heritage Complex will be made within the ASI site of Lothal that is located 80 km away from Ahmedabad in Gujarat.
- The project, once completed, will be made an international tourist destination in India where people from across the countries can take a look at the maritime heritage of India from ancient to modern times.
- The government is aiming to showcase this via an edutainment approach where the latest technology would be adopted to spread awareness.
- The development will be done in an area expanding 400 acres.
- The complex will have many offerings including National Maritime Heritage Museum, Heritage Theme Park, and Light House Museum.
About Lothal
- Lothal was one of the southernmost cities of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization located in Gujarat.
- Construction of the city began around 2200 BCE.
- According to the ASI, Lothal had the world’s earliest known dock, which connected the city to an ancient course of the Sabarmati river on the trade route between Harappan cities in Sindh and the peninsula of Saurashtra.
- Lothal was a vital and thriving trade Centre in ancient times, with its trade of beads, gems, and valuable ornaments reaching the far corners of West Asia and Africa.
- The techniques and tools they pioneered for bead-making and in metallurgy have stood the test of time for over 4000 years.
- The Lothal site has been nominated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and its application is pending on the tentative list of UNESCO.
Answer this question from CSP 2019 in the comment box:
Q. Which one of the following is not a Harappan site?
(a) Chanhudaro
(b) Kot Diji
(c) Sohgaura
(d) Desalpur
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Neutrinos
Mains level: NA
Indian scientists have shown that the geometry of space-time can cause neutrinos to oscillate.
What are Neutrinos?
- A neutrino is a subatomic particle that is very similar to an electron but has no electrical charge and a very small mass, which might even be zero.
- Since neutrinos are electrically neutral, they are not affected by the electromagnetic forces which act on electrons. Hence, they are also called Ghost Particles.
- Neutrinos are affected only by a “weak” sub-atomic force of a much shorter range than electromagnetism and are therefore able to pass through great distances in matter without being affected by it.
- They are also one of the most abundant particles in the universe. As they have very little interaction with matter, however, they are incredibly difficult to detect.
Answer this PYQ in the comment box:
Q.The known forces of nature can be divided into four classes, viz, gravity, electromagnetism, weak nuclear force and strong nuclear force. With reference to them, which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Gravity is the strongest of the four
(b) Electromagnetism act only on particles with an electric charge
(c) Weak nuclear force causes radioactivity
(d) Strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons inside the nuclear of an atom
Finding of the new research
- Neutrinos are mysterious particles, produced copiously in nuclear reactions in the Sun, stars, and elsewhere.
- They “oscillate”- meaning that different types of neutrinos change into one another – as has been found in many experiments.
- Probing of oscillations of neutrinos and their relations with mass are crucial in studying the origin of the universe.
- Neutrinos interact very weakly with everything else – trillions of them pass through every human being every second without anyone noticing.
- A neutrino’s spin always points in the opposite direction of its motion, and until a few years ago, neutrinos were believed to be massless.
What makes this possible?
- The geometry of space-time can cause neutrino oscillations through quantum effects even if neutrinos are massless.
- Einstein’s theory of general relativity says that gravitation is the manifestation of space-time curvature.
- Neutrinos, electrons, protons and other particles which are in the category of fermions show a certain peculiarity when they move in presence of gravity.
- Space-time induces a quantum force in addition to gravity between every two fermions.
- This force can depend on the spin of the particles and causes massless neutrinos to appear massive when they pass through matter, like the Sun’s corona or the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Something similar happens for electroweak interactions, and together with the geometrically induced mass, it is enough to cause oscillation of neutrinos.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas
Mains level: Desertification of land and preventive measures

The Union Environment Ministry has released the latest version of “Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India.
Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas
- It has been published by Space Application Centre, ISRO, Ahmedabad.
- The Atlas provides a state-wise area of degraded lands for the time frame 2018-19.
- It also provides the change analysis for the duration of 15 years, from 2003-05 to 2018-19.
- It would provide important baseline and temporal data and technical inputs.
Content of the atlas
- This Atlas presents state-wise desertification and land degradation status maps depicting land use, the process of degradation, and severity level.
- This was prepared using IRS Advanced Wide Field Sensor (AWiFS) data of 2011-13- and 2003-05-time frames in the GIS environment.
- The area under desertification/land degradation for both time frames and changes are reported state-wise as well as for the entire country.
- The outputs are helpful in prioritizing areas to be taken up for minimizing the impact of desertification and land degradation.
India and desertification
- Desertification and land degradation are major threats to agricultural productivity in our country.
- India hosted the 14th session of the Conference of Parties (COP 14) of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) in September 2019.
- India is striving towards achieving the national commitments of Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) and restoration of 26 million ha of degraded land by 2030.
- India has been at the forefront of bringing the issue of land degradation to the core of relevant international alliances for the protection and conservation of the environment.
- India has adopted a collective approach for making progress towards achieving the national commitments related to land restoration.
Answer this PYQ from CSP 2016 in the comment box:
Q.What is/are the importance/importances of the ‘United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification?
- It aims to promote effective action through innovative national programmes and supportive inter-national partnerships.
- It has a special/particular focus on South Asia and North Africa regions, and its secretariat facilitates the allocation of major portion of financial resources to these regions.
- It is committed to bottom-up approach, encouraging the participation of local people in combating the desertification.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chennai–Kanyakumari Industrial Corridor (CKIC)
Mains level: Not Much
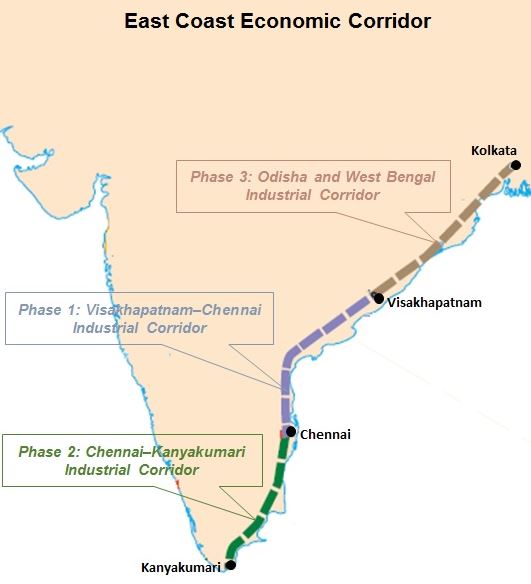
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Centre have signed a $484 million loan to improve transport connectivity and facilitate industrial development in the Chennai–Kanyakumari Industrial Corridor (CKIC).
About CKIC
- CKIC is part of India’s East Coast Economic Corridor (ECEC), which stretches from West Bengal to Tamil Nadu.
- The project will upgrade about 590 km of state highways in the CKIC influence areas that cover 23 of the 32 districts between Chennai and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
- It connects India to the production networks of South, Southeast, and East Asia.
- ADB is the lead partner in developing ECEC.
Answer this PYQ in the comment box:
Q. With reference to Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), consider the following statements:
- AIIB has more than 80 member nations.
- India is the largest shareholder in AIIB.
- AIIB does not have any members from outside Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Significance of CKIC
- The project is part of the priority infrastructure projects identified for corridor development under the ADB-supported CKIC comprehensive development plan.
- Enhanced connectivity of industrial hubs with hinterland and ports will particularly help increase the participation of Indian manufacturing in global production networks and global value chains.
- The project will also strengthen road safety improvement programs through advanced technologies for road monitoring and enforcement.
- In addition, the project will help improve the planning capacity of Tamil Nadu’s Highways and Minor Ports Department.
Back2Basics: Asian Development Bank
- The ADB is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966 which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines.
- The company also maintains 31 field offices around the world to promote social and economic development in Asia.
- From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members.
- The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members’ capital subscriptions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Cooperation among South Asian countries in dealing with pandemic
Pandemic know no borders. So, dealing with it has necessited global cooperation. The article introduce us to some of the cross-country collaborations in dealing with the pandemic, igniting the hope for new era social partnership to the advantage of South Asia.
Regionally-coordinated strategy against pandemic
- Containing Covid pandemic has necessitated global cooperation.
- The deadly pandemic surge in 2021 makes a regionally coordinated, evidence-driven strategy critical.
- It is necessary to construct multi-stakeholder regional coalitions to devise new solutions and frugal innovations that can be applied across South Asia.
- Given our shared and mostly similar social, economic and cultural contexts, local successes must be amplified across South Asia.
- Despite wide variation in how nations have responded to the pandemic, the most successful strategies find commonality in their adherence to science and attention to local context.
How successful interventions could be applied across the subcontinent
- Beliefs, priorities, traditions and aversions to behavioural change are more similar across South Asia.
- This means that interventions that are successful in changing behaviour in one place are highly likely applicable in other parts of the subcontinent.
- For example, Community-Led Total Sanitation (CLTS) campaigns to solve the problem of open defecation, developed by Bangladeshi NGOs in partnership with an Indian consultant is now broadly applied across South Asia and beyond.
- The Grameen Bank microcredit model was an indigenous South Asian innovation that spread rapidly.
- India’s digitised social protection ecosystem with Aadhaar ids and Jan Dhan accounts serves as a model for the region.
Changing social norm around mask-wearing
- The new pan-South Asian consortium in response to Covid-19 evolved out of an experiment conducted in Bangladesh around mask-wearing in rural communities termed as NORM.
- It was observed that a combination of no-cost distribution, information, reinforcing the message, modeling and endorsement by community leaders (NORM) leads to large, sustained increases in mask usage.
- NORM implementation teams based in Lahore, Ahmedabad, Peshawar, Hyderabad, Dhaka, Kathmandu and Delhi are learning from each other’s successes and failures.
- The Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA) quickly implemented the model to reach over one million members in Gujarat.
- Additional 1.5 million masks were shipped from Bangladesh to support SEWA’s outreach to other states.
- Lahore’s commissioner worked with the research team to adapt the NORM model to an urban setting.
- To manage mild and moderate cases of Covid-19 in rural India, where institutional health care access is limited a host of physicians, scientists and community-based organisations created the Swasth Community Science Alliance.
- The Masking-Treatment-Vaccine Preparation (MTV) approach offers a sensible strategy to mitigate the pandemic until universal vaccination is achieved.
Conclusion
We need to come together to solve problems that affect us all. Let the lasting legacy of this pandemic be a new era of partnership in social innovations that can benefit all South Asians.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Right to be forgotten
The article discusses the interplay between right to be forgotten and the right of the public to access courts of record, concepts of fair criticism and accountability.
Context
The Delhi High Court recently ordered the removal of one of its own judgments from easy access. The High Court recognised that the petitioner may have a right to be forgotten, which must be balanced with the right of the public to access courts of record.
Right to be forgotten
- In 2017, the Supreme Court recognised the right to be forgotten as being under the ambit of the right to privacy (specifically, informational privacy) under the Constitution.
- The Supreme Court observed that a lot of personal information may serve no “legitimate interest”, was “incorrect”, or was not “necessary” or “relevant”.
- For now, individuals may request data hosts to take down some content, and it may be taken down based on the policies of the respective hosts.
- There is a general consensus that people should be allowed to modify or delete information uploaded by themselves.
- However, whether this extends to information uploaded by third parties is uncertain.
- The right to be forgotten is, generally, the right to have information about a person removed from public access.
Balancing between right of the public
- The Delhi High Court recognised that the petitioner may have a right to be forgotten, which must be balanced with the right of the public to access courts of record.
- Judgments are published for good reasons.
- Trials held under public scrutiny act as a check against judicial caprices and help in enhancing the confidence of the public in the fairness and objectivity of the administration of justice.
- The Supreme Court has made is clear that the right to be forgotten was subject to reasonable restrictions based on countervailing rights such as free speech.
Consider the question “What is right to be forgotten and how it is related to the right to privacy? Examine the issues related to the implementation of the right to be forgotten.”
Way forward
- The High Court could have ordered that the name and personal details of the petitioner be redacted while maintaining public access to the judgment itself.
Conclusion
The right to be forgotten needs to be studied along with the concepts of fair criticism and accountability.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Direct Taxes
Mains level: Read the attached story
India’s direct tax collections in the first two and a half months of 2021-22 stand at nearly ₹1.86 lakh crore, double the collections over the same period of last year that was affected by the national lockdown.
Surge in direct tax collections
- The jump in the direct tax collections reflects healthy exports and a continuation of various industrial and construction activities.
- This supports our expectation that GDP will record a double-digit expansion.
What are Direct Taxes?
- A type of tax where the impact and the incidence fall under the same category can be defined as a Direct Tax.
- The tax is paid directly by the organization or an individual to the entity that has imposed the payment.
- The tax must be paid directly to the government and cannot be paid to anyone else.
Answer this PYQ in the comment box:
Q.All revenues received by the Union. Government by way of taxes and other receipts for the conduct of Government business are credited to the:
(a) Contingency Fund of India
(b) Public Account
(c) Consolidated Fund of India
(d) Deposits and Advances Fund
Types of Direct Taxes
The various types of direct tax that are imposed in India are mentioned below:
(1) Income Tax
- Depending on an individual’s age and earnings, income tax must be paid.
- Various tax slabs are determined by the Government of India which determines the amount of Income Tax that must be paid.
- The taxpayer must file Income Tax Returns (ITR) on a yearly basis.
- Individuals may receive a refund or might have to pay a tax depending on their ITR. Penalties are levied in case individuals do not file ITR.
(2) Wealth Tax
- The tax must be paid on a yearly basis and depends on the ownership of properties and the market value of the property.
- In case an individual owns a property, wealth tax must be paid and does not depend on whether the property generates an income or not.
- Corporate taxpayers, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), and individuals must pay wealth tax depending on their residential status.
- Payment of wealth tax is exempt for assets like gold deposit bonds, stock holdings, house property, commercial property that have been rented for more than 300 days, and if the house property is owned for business and professional use.
(3) Estate Tax
- It is also called Inheritance Tax and is paid based on the value of the estate or the money that an individual has left after his/her death.
(4) Corporate Tax
- Domestic companies, apart from shareholders, will have to pay corporate tax.
- Foreign corporations who make an income in India will also have to pay corporate tax.
- Income earned via selling assets, technical service fees, dividends, royalties, or interest that is based in India is taxable.
- The below-mentioned taxes are also included under Corporate Tax:
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT): The tax must be paid for any income that is earned via security transactions that are taxable.
- Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT): In case any domestic companies declare, distribute, or are paid any amounts as dividends by shareholders, DDT is levied on them. However, DDT is not levied on foreign companies.
- Fringe Benefits Tax: For companies that provide fringe benefits for maids, drivers, etc., Fringe Benefits Tax is levied on them.
- Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT): For zero tax companies that have accounts prepared according to the Companies Act, MAT is levied on them.
(5) Capital Gains Tax:
- It is a form of direct tax that is paid due to the income that is earned from the sale of assets or investments. Investments in farms, bonds, shares, businesses, art, and home come under capital assets.
- Based on its holding period, tax can be classified into long-term and short-term.
- Any assets, apart from securities, that are sold within 36 months from the time they were acquired come under short-term gains.
- Long-term assets are levied if any income is generated from the sale of properties that have been held for a duration of more than 36 months.
Advantages of Direct Taxes
The main advantages of Direct Taxes in India are mentioned below:
- Economic and Social balance: The Government of India has launched well-balanced tax slabs depending on an individual’s earnings and age. The tax slabs are also determined based on the economic situation of the country. Exemptions are also put in place so that all income inequalities are balanced out.
- Productivity: As there is a growth in the number of people who work and community, the returns from direct taxes also increases. Therefore, direct taxes are considered to be very productive.
- Inflation is curbed: Tax is increased by the government during inflation. The increase in taxes reduces the necessity for goods and services, which leads to inflation to compress.
- Certainty: Due to the presence of direct taxes, there is a sense of certainty from the government and the taxpayer. The amount that must be paid and the amount that must be collected is known by the taxpayer and the government, respectively.
- Distribution of wealth is equal: Higher taxes are charged by the government to the individuals or organizations that can afford them. This extra money is used to help the poor and lower societies in India.
What are the disadvantages of direct taxes?
- Easily evadable: Not all are willing to pay their taxes to the government. Some are willing to submit a false return of income to evade tax. These individuals can easily conceal their incomes, with no accountability to the law of the land.
- Arbitrary: Taxes, if progressive, are fixed arbitrarily by the Finance Minister. If proportional, it creates a heavy burden on the poor.
- Disincentive: If there are high taxes, it does not allow an individual to save or invest, leading to the economic suffering of the country. It does not allow businesses/industry to grow, inflicting damage to them.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ordnance Factory Board (OFB)
Mains level: Defence manufacturing in India
Addressing a long-pending reform, the Union Cabinet has approved a plan to corporatize the Ordnance Factory Board (OFB).
Ordnance Factory Board (OFB)
- OFB consisting of the Indian Ordnance Factories is a government agency under the control of the department of defence production (DDP).
- It is engaged in research, development, production, testing, marketing and logistics of a product range in the areas of air, land and sea systems.
- OFB comprises 41 ordnance factories, nine training institutes, three regional marketing centres and four regional controllers of safety, which are spread all across the country.
Why are OFBs significant?
- OFB is the world’s largest government-operated production organization and the oldest organization in India.
- It has a total workforce of about 80,000.
- It is often called the “Fourth Arm of Defence” and the “Force Behind the Armed Forces” of India.
- OFB is the 35th largest defence equipment manufacturer in the world, 2nd largest in Asia, and the largest in India.
Why corporatization?
- Once implemented, the OFB, the establishment of which was accepted by the British in 1775, will cease to exist.
- It is a major decision in terms of national security and also make the country self-sufficient in defence manufacturing as repeatedly emphasized by PM.
- This move would allow these companies autonomy and help improve accountability and efficiency.
- This restructuring is aimed at transforming the ordnance factories into productive and profitable assets, deepening specialization in the product range, enhancing competitiveness, improving quality and achieving cost efficiency.
Adhering to past recommendations
- There have been several recommendations by high-level committees in the past for corporatising it to improve efficiency and accountability.
What about employees?
- All employees of the OFB (Group A, B and C) belonging to the production units would be transferred to the corporate entities on deemed deputation.
- The pension liabilities of the retirees and existing employees would continue to be borne by the government.
How would this be accomplished?
- The 41 factories would be subsumed into seven corporate entities based on the type of manufacturing.
- The ammunition and explosives group would be mainly engaged in producing ammunition of various calibre and explosives, with huge potential to grow exponentially.
- Similarly, the vehicles group would mainly engage in producing defence mobility and combat vehicles such as tanks, trawls, infantry and mine protected vehicles.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Social media content issue
Twitter has reportedly lost the coveted “safe harbour” immunity in India after failing to appoint statutory officers on time, as mandated by the new Information Technology (IT) Rules, 2021.
What is the news?
- With this, the social media giant becomes the only American platform to have lost the protective shield – granted under Section 79 of the IT Act.
- Its rival platforms such as YouTube, Facebook and WhatsApp remain protected.
- The new development could mean that Twitter’s senior executives that include its India managing director, face legal actions under relevant IPC for ‘unlawful’ activities on the platform – even if conducted by users.
Why such a move?
- Earlier this week, Twitter said it appointed an interim Chief Compliance Officer (CCO), and the details of the officer were not yet shared with the government.
- The company also posted job openings for a Nodal Officer and Resident Grievance Officer – the two key positions mandated by the central government’s IT Rules, 2021.
What is safe harbour protection?
- According to Section 79 of IT Act, 2000, “an intermediary shall not be liable for any third party information, data, or communication link made available or hosted by him,” therefore providing Safe Harbour protection.
- To put it simply, the law notes that intermediaries such as Twitter or your Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are not liable to punishment if third parties (users) misuse the infrastructure, in this case, the platform.
- However, the protection is guaranteed only when the intermediary does not ‘initiate the transmission,’ ‘select the receiver of the transmission,’ and ‘modify the information contained in the transmission.’
- It means that as long as the platform acts just as the medium to carry out messages from users A to user B, that is, without interfering in any manner, it will be safe from any legal prosecution.
Inception of the concept
- In its original form, the IT Act 2000 provided little or no Safe Harbour protection to internet intermediaries as the definition of the intermediary was restricted.
- However, things began changing in 2004, in a case where a student posted an obscene clip for sale.
- The student and the CEO of that company were both held later for letting pornographic material circulate online.
- The CEO challenged the proceedings against him, contending that he could not be personally held liable for the listing and that the MMS was transferred directly between the seller and buyer without the intervention of the website.
- The executive was acquitted, the case eventually resulted in the addition of Section 79 in the IT Act to provide immunity to intermediaries.
Why has Twitter lost the protection?
- Over the years, social media platforms have evolved and often tend to act as gatekeepers.
- For instance, Twitter banning Donald Trump and adding “manipulated media” label on select posts have been questioned by excerpts.
- In other words, an intermediary’s ability to “modify the information contained in the transmission,” opens rooms for revision of the law, experts believe.
- Hence, the government introduced the IT Rules 2021 in December last year and implemented it in May 2021.
- As per the new order, all social media platforms with more than 50 lakh (five million) users will need to appoint a Chief Compliance Officer, a Nodal Contact Person, and a Resident Grievance Officer from India to smoothen the grievance mechanism for citizens.
- The officers will need to acknowledge queries with 24 hours and resolve them in 15 days from the date of receipt.
What can happen next?
- Once a company loses the Safe Harbour protection, technically, officials are liable to punishment if a post even by a third user violates local laws.
- The new IT Rules 2021 do not mention any ban for non-compliance.
- But with an estimated 1.75 crore users in India, Twitter would likely fill key positions soon to comply with the new norms laid by the government.
- As mentioned, the company already appointed an interim Chief Compliance Officer earlier.
- This, according to the government, means that the protection under Section 79 of the Information Technology (IT) Act, accorded to Twitter for being a social media intermediary, now stands withdrawn.
How does this impact Twitter?
- If someone puts out any content on Twitter that leads to some form of violence, or violates any Indian law with respect to content, not only the person that has put out the tweet will be held responsible.
- Even Twitter will be legally liable for the content as it no longer has the protection.
Is there something else that can happen subsequently?
- In the longer run, there is also the theoretical possibility that Twitter might be subjected to the 26 per cent cap of direct foreign investment in media and publishing.
- This in turn means that the platform may be forced to look for an Indian buyer for the remaining 74 per cent stake.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Annual Review of State Laws
Mains level: Not Much
The COVID-19 pandemic and the consequent lockdown had a huge impact on the working of the state legislatures in India. The PRS Legislative Research’s “Annual review of state laws 2020” shows that the productivity and efficacy of State legislatures are poor.
Annual Review of State Laws
- This report focuses on the legislative work performed by states in the calendar year 2020.
- It is based on data compiled from state legislature websites and state gazettes.
- It covers 19 state legislatures, including the union territory of Delhi, which together accounts for 90% of the population of the country.
Highlights of the report
(1) Sittings of states
- Compared with its average number of sitting days of 32 from 2016 to 2019, the Karnataka legislature, which is bicameral, met on 31 days last year, the highest for any State in 2020.
- The southern State was followed by Rajasthan (29 days) and Himachal Pradesh (25 days). For comparison, Parliament met for 33 days last year.
- In 2020, the average number of sitting days for the 19 States was 18, which was 11 less than the four-year (2016-19) average of 29.
- Kerala, which had the distinction of remaining at the top in the four years with an average of 53 days, had only 20 days of sittings of the legislature last year.
(2) Number of bills
- As for the number of Bills passed last year, Karnataka again topped the list with 61 Bills, followed by Tamil Nadu (42) and Uttar Pradesh (37). For this purpose, Appropriation Bills were excluded.
- Among poor performers under this category, Delhi passed only one Bill; West Bengal passed two Bills and Kerala three Bills.
(3) Time taken for passing bills
- On the duration of time taken to pass Bills, the previous year saw 59% of the Bills being passed by the legislature of the States on the day of introduction.
- A further 14% was adopted within a day of being introduced.
- Only 9% of the Bills were passed more than five days after introduction, some of which were referred to committees for further examination.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Deep Ocean Mission
Mains level: Various aspects of DOM

The Union Cabinet has approved the long-pending Deep Ocean Mission since 2018.
Deep Ocean Mission (DOM)
- Nodal Agency: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- The mission proposes to explore the deep ocean similar to the space exploration started by ISRO.
- Underwater robotics and ‘manned’ submersibles are key components of the Mission which will help India harness various living and non-living (water, mineral and energy) resources from the seabed and deep water.
- The tasks that will be undertaken over this period include deep-sea mining, survey, energy exploration and offshore-based desalination.
- These technological developments are funded under an umbrella scheme of the government – called Ocean Services, Technology, Observations, Resources Modelling and Science (O-SMART).
Six major components
(1) Development of Technologies for Deep Sea Mining, and Manned Submersible:
- A manned submersible will be developed to carry three people to a depth of 6000 metres in the ocean with suite of scientific sensors and tools.
- Only a very few countries have acquired this capability.
- An Integrated Mining System will be also developed for mining Polymetallic Nodules from 6000 m depth in the central Indian Ocean.
(2) Development of Ocean Climate Change Advisory Services:
- A suite of observations and models will be developed to understand and provide future projections of important climate variables on seasonal to decadal time scales under this proof of concept component.
- This component will support the Blue Economy priority area of coastal tourism.
(3) Technological innovations for exploration and conservation of deep-sea biodiversity:
- Bio-prospecting of deep-sea flora and fauna including microbes and studies on sustainable utilization of deep-sea bio-resources will be the main focus.
- This component will support the Blue Economy priority area of Marine Fisheries and allied services.
(4) Deep Ocean Survey and Exploration:
- The primary objective of this component is to explore and identify potential sites of multi-metal Hydrothermal Sulphides mineralization along the Indian Ocean mid-oceanic ridges.
- This component will additionally support the Blue Economy priority area of deep-sea exploration of ocean resources.
(5) Energy and freshwater from the Ocean:
- Studies and detailed engineering design for offshore Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) powered desalination plant are envisaged in this proof of concept proposal.
- This component will support the Blue Economy priority area of offshore energy development.
(6) Advanced Marine Station for Ocean Biology:
- This component is aimed at the development of human capacity and enterprise in ocean biology and engineering.
- This component will translate research into the industrial application and product development through on-site business incubator facilities.
- This component will support the Blue Economy priority area of Marine Biology, Blue trade and Blue manufacturing.
Why need such a mission?
- Oceans, which cover 70 per cent of the globe, remain a key part of our life. About 95 percent of the Deep Ocean remains unexplored.
- For India, with its three sides surrounded by the oceans and around 30 per cent of the country’s population living in coastal areas.
- The ocean is a major economic factor supporting fisheries and aquaculture, tourism, livelihoods and blue trade.
- Oceans are also a storehouse of food, energy, minerals, medicines, modulator of weather and climate and underpin life on Earth.
Pre-requisites to this mission
- India has been allotted a site of 75,000 square kilometres in the Central Indian Ocean Basin (CIOB) by the UN International Sea Bed Authority for the exploitation of polymetallic nodules (PMN).
Hunt for PMNs
- These are rocks scattered on the seabed containing iron, manganese, nickel and cobalt.
- Being able to lay hands on a fraction of that reserve can meet the energy requirement of India for the next 100 years.
- It has been estimated that 380 million metric tonnes of polymetallic nodules are available at the bottom of the seas in the Central Indian Ocean.
- India’s Exclusive Economic Zone spreads over 2.2 million square kilometers.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme
Mains level: Fertilizer subsidies in India
The Union Cabinet has approved the proposal of the Department of Fertilizers for fixation of Nutrient Based Subsidy Rates for P&K Fertilizers for the year 2021-22.
Key Points
About Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP):
- DAP is the second most commonly used fertiliser in India after urea.
- Farmers normally apply this fertiliser just before or at the beginning of sowing, as it is high in phosphorus (P) that stimulates root development.
- DAP (46% P, 18% Nitrogen) is the preferred source of Phosphorus for farmers. This is similar to urea, which is their preferred nitrogenous fertiliser containing 46% N.
About Subsidy Scheme for Fertilisers:
-
- Under the current scheme, the MRP of Urea is fixed but the subsidy can vary while MRP of DAP is decontrolled (i.e subsidy is fixed but the MRP can vary).
- All Non-Urea based fertilisers are regulated under Nutrient Based Subsidy Scheme.
About Nutrient-Based Subsidy (NBS) Regime:
-
- Under the NBS regime – fertilizers are provided to the farmers at the subsidized rates based on the nutrients (N, P, K & S) contained in these fertilizers.
- Also, the fertilizers which are fortified with secondary and micronutrients such as molybdenum (Mo) and zinc are given additional subsidy.
- The subsidy on Phosphatic and Potassic (P&K) fertilizers is announced by the Government on an annual basis for each nutrient on a per kg basis – which are determined taking into account the international and domestic prices of P&K fertilizers, exchange rate, inventory level in the country etc.
- NBS policy intends to increase the consumption of P&K fertilizers so that optimum balance (N:P:K= 4:2:1) of NPK fertilization is achieved.
- This would improve soil health and as a result the yield from the crops would increase, resulting in enhanced income to the farmers.
- Also, as the government expects rational use of fertilizers, this would also ease off the burden of fertilizer subsidy.
- It is being implemented from April 2010 by the Department of Fertilizers, Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers.
Issues Related to NBS:
1.Imbalance in Price of Fertilisers:
- Urea is left-out in the scheme and hence it remains under price control as NBS has been implemented only in other fertilizers.
- There is an imbalance as the price of fertilizers (other than urea) — which were decontrolled have gone up from 2.5 to four times during the 2010-2020 decade.
- However, since 2010, the price of urea has increased only by 11%. This has led to farmers using more urea than before, which has further worsened fertilizer imbalance.
2.Costs on Economy and Environment :
Fertilizer subsidy is the second-biggest subsidy after food subsidy, the NBS policy is not only damaging the fiscal health of the economy but also proving detrimental to the soil health of the country.
3.Black Marketing :
- Subsidised urea is getting diverted to bulk buyers/traders or even non-agricultural users such as plywood and animal feed makers.
- It is being smuggled to neighbouring countries like Bangladesh and Nepal.
Implications of Increasing the Subsidy on DAP :
- As farmers will start sowing operations for Kharif Crops, it is highly important for them to get the fertilisers at subsidised rate so as to keep inflation at check.
- Politically, too, to turn down the farmer protests, during the time of the Covid’s second wave, is the last thing the government would want.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Equalisation levy
Mains level: Paper 3- Global minimum tax and issues involve
The article deals with the issue of global minimum tax and how it matters to India in the changing digital landscape where data is the new oil.
Two pillars of global taxation reforms endorsed
- In the just-concluded G7 summit in the UK, the leaders endorsed the global taxation reforms premised on two pillars.
- One, that the multinational companies with at least a 10 per cent profit margin pay tax in countries where they operate and that would be 20 per cent of any profit above the 10 per cent margin.
- Two, a global minimum tax rate that envisages that multinational companies pay a tax of at least 15 per cent in each country they operate.
How companies monetise data
- The concept of tax on electronic transmission of data across borders was expressly prohibited under multiple WTO declarations.
- However, in the changed digital landscape, multinational corporations are mining big data, which has economic value, but not paying their fair share of taxes.
- Many of these tech firms provide their product for free to users, and based on user engagements, create a detailed profile of the user that would be used to sell ad space to the clients.
Efforts to find solution to tax avoidance
- The Union government had rightly introduced an equalisation levy at 2 per cent, targeted at non-resident e-commerce operators with a turnover greater than Rs 2 crore in the Union budget of 2020.
- India had an equalisation levy since 2016, initially at 6 per cent on specified services like online advertisement or provision of digital advertising space and was levied on non-resident firms, deducted by the payer.
- In the case of the amended equalisation levy, the responsibility lay with the operator and was applicable to earnings that have been made by selling advertisements based on the data collected within the country.
- The member-states of the OECD have been trying to find a solution to tax avoidance by multinational corporations under the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting Project since 2015.
- OECD had built a model around two pillars on which the G7 position has been announced.
Way forward for India
- India has to stand its ground.
- With the largest user base for Facebook, WhatsApp and YouTube, India will not be adequately compensated by the above two steps in global minimum tax.
- The government must also pass the Personal Data Protection Bill 2019 quickly so that provisions for data localisation, requiring Indian data to be stored and processed in the country are in place.
- This could be the ideal way to force tech firms to correctly evaluate the revenue generated from our sovereign data and thus tax it.
Consider the question “As the world moves towards the global taxation reforms, what are the factors India needs to consider? Also, mention the previous efforts made to find the solution to tax avoidance by the multinational companies.”
Conclusion
India must negotiate hard to come to an equitable position on the global tax and avoid as it harbours the largest user base of the social media companies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Electoral bond and issues related to it
Mains level: Paper 2- Issues with electoral bond
The article highlights the issues with the political funding through electoral bonds.
Changes made for the electoral bond and issues with them
- Earlier, only profit-making domestic companies could contribute to political parties; now loss-making companies can too.
- Earlier, foreign companies or companies where the controlling stake was held by a foreign company couldn’t contribute; now they can.
- India’s political parties could theoretically be fully funded by a foreign company operating in India or by a foreign entity through a shell company.
- Only the ruling party via the State Bank of India (SBI) has a full account of all donations being made via electoral bonds, to itself and to Opposition parties.
Issues in the Supreme Court verdict
- In March 2021, the Supreme Court refused to stay the sale of electoral bonds before the West Bengal elections.
- Instead, the judgment listed several documents which supposedly establish a paper trail on donations and do some ‘match the following’.
- This is impractical and plainly incorrect.
- The Right to Information (RTI) Act of 2005 enables easier access to information held by public authorities.
- Suggesting a “match the following” is incorrect for three reasons.
1) Full scale of registered entities in unknown
- If we set aside individual donors and focus just on registered entities, we will find that the full scale of registered entities is unknown.
- According to back-of-the-envelope calculations, there are close to 25 lakh potential donors comprising just companies and firms.
- This includes about 12.6 lakh active private limited companies as of January 31, 2021.
- Firms, unlike companies, have no regulatory mandate to submit their annual reports except for filing their annual tax returns, since their functioning is regulated by Acts other than the Companies Act of 2013.
2) No disclosure by companies about donation to political parties
- Even if registered companies filed annual financial statements, many do not disclose political donations.
- Conveniently, the Finance Bill of 2017 amended Section 182 of the Companies Act of 2013 to remove the requirement for declaring disaggregated donations to political parties.
- Even if registered companies filed annual financial statements, many do not disclose political donations.
3) Political parties do not need to disclose their donor
- Crucially, political parties do not need to disclose their electoral bond donors either.
- Strictly speaking, political parties are not even supposed to know their electoral bond donors.
- The only requirement is the annual audit reports with a total of all donations received via electoral bonds.
- These reports are submitted with great delays.
- Even if these reports are submitted on time, there is no way to match a donation of a company to that received by a political party as only aggregate amounts are available.
Implications
- Electoral bonds give political power to companies, wealthy individual donors, and foreign entities, thus diluting the universal franchise of one voter-one vote.
- Every vote is not equally valuable if companies can influence policies through hidden donations.
- The winner of this arrangement is the ruling party, whether at the Centre or in a State, and the loser is the average voter.
Way forward
- Companies and political parties could exercise moral leadership and voluntarily disclose the identity of recipients and donors, as the Jharkhand Mukti Morcha recently did.
Conclusion
Opacity in political funding goes against the basic tenets of democracy. What we need is a system of political funding which is transparent and fair.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






