Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India-Iran Ties
Mains level: Read the attached story

After months of what appeared to be a go-slow, the Union government has pushed up its interest in using Iran’s Chabahar port to connect to Afghanistan and Central Asia for trade, with the visit of the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways to the port.
Chabahar Port
- In 2016, India signed a deal with Iran entailing $8 billion investment in Chabahar port and industries in Chabahar Special Economic Zone.
- The port is being developed as a transit route to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- India has already built a 240-km road connecting Afghanistan with Iran.
- All this were expected to bring cargo to Bandar Abbas port and Chabahar port, and free Kabul from its dependence on Pakistan to reach the outer world.
- Completion of this project would give India access to Afghanistan and beyond to Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Russia and Europe via 7,200-km-long multi-modal North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
Why is Chabahar back in the news?
- The visit is a chance to strengthen ties and the maritime relationship between the two countries.
- Due to pandemic, there were less number of visits from India to Iran and vice-versa and the pace of the project is also allegedly slower.
- This visit will also highlight the importance of Chabahar as a gateway for Indian trade with Europe, Russia and CIS [Commonwealth of Independent States] countries.
- India is keen in developing the Shahid Beheshti port as a “a transit hub” and link it to the International North South Trade Corridor (INSTC), that also connects to Russia and Europe.
What is India’s strategic vision for Chabahar?

When the first agreement for Chabahar was signed by then PM Atal Bihari Vajpayee in 2003, the plan had a three-fold objective:
- To build India’s first offshore port and to project Indian infrastructure prowess in the Gulf
- To circumvent trade through Pakistan, given the tense ties with India’s neighbour and build a long term, sustainable sea trade route and
- To find an alternative land route to Afghanistan, which India had rebuilt ties with after the defeat of the Taliban in 2001
- Subsequently, PM Manmohan Singh’s government constructed the Zaranj -Delaram Highway in Afghanistan’s South.
- It would help connect the trade route from the border of Iran to the main trade routes to Herat and Kabul, handing it over to the Karzai government in 2009.
- In 2016, PM Modi travelled to Tehran and signed the agreement to develop Chabahar port, as well as the trilateral agreement for trade through Chabahar with Afghanistan’s President Ashraf Ghani.
Commencement of operations
- Since the India Ports Global Chabahar Free Zone (IPGCFZ) authority took over the operations of the port in 2018, it has handled 215 vessels, 16,000 TEUs (Twenty-foot Equivalent Units) and four million tons of bulk and general cargo.
Why is it gaining importance?
- In the last few years, a fourth strategic objective for the Chabahar route has appeared, with China’s Belt and Road Initiative making inroads in the region.
- The government hopes to provide Central Asia with an alternate route to the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) through Iran for future trade.
Why is the Chabahar dream taking so long to realise?
- India’s quest for Chabahar has hit geopolitical road-block after road-block; the biggest issue has been over Iran’s relationship with western countries, especially the United States.
- In years when western sanctions against Iran increased, the Chabahar project has been put on the back-burner.
- However, the nuclear talks resulted in the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) in 2015 came into being, the Chabahar port has been easier to work on.
- In 2018, the Trump administration put paid to India’s plans by walking out of the JCPOA and slapping new sanctions on dealing with Iran.
- This led to the Modi government “zeroing out” all its oil imports from Iran, earlier a major supplier to India, causing a strain in ties.
- India also snapped ties with Afghanistan after the Taliban takeover in August 2021, which put an end to the humanitarian aid of wheat and pulses that was being sent to Kabul via Chabahar.
- When India restarted wheat aid this year, it negotiated with Pakistan to use the land route to Afghanistan instead.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: JCPOA
Mains level: US sanctions on Iran, Nuclear deal

Iran has dropped some of its main demands on resurrecting a deal to rein in Tehran’s nuclear programme, including its insistence that international inspectors close some probes of its program, bringing the possibility of an Iran–US agreement closer.
Which agreement is this article referring to?
- It is an alternative name of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
What demands of Iran are we talking about?
- Iran had already largely relented on its demand that the US lift its designation of the Iran Revolutionary Guard Corps as a foreign terrorist organization (FTO) entity.
- This designation was a more of symbolic move and insulting to Iranian authorities.
- Iran also wanted a guarantee that the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) would close investigations involving unexplained traces of uranium.
- Iran wants guarantees that the IAEA would close all of them.
What is JCPOA?
- The Iran nuclear deal, formally known as the JCPOA is a landmark accord reached between Iran and several world powers, including the United States, in July 2015.
- Under its terms, Iran agreed to dismantle much of its nuclear program and open its facilities to more extensive international inspections in exchange for billions of dollars’ worth of sanctions relief.
Expected outcomes of the deal
- Curb on the nuclear program: Proponents of the deal said that it would help prevent a revival of Iran’s nuclear weapons program.
- Increasing regional engagement: It would thereby reduce the prospects for conflict between Iran and its regional rivals, including Israel and Saudi Arabia.
Background of the JCPOA
- Iran had previously agreed to forgo the development of nuclear weapons as a signatory to the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty, which has been in force since 1970.
- However, after the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979, Iranian leaders secretly pursued this technology.
- In 2007, U.S. intelligence analysts concluded that Iran halted its work on nuclear weapons in 2003 but continued to acquire nuclear technology and expertise.
- Prior to the JCPOA, the P5+1 had been negotiating with Iran for years, offering its government various incentives to halt uranium enrichment.
Issues with the deal
(1) US withdrawal
- The deal has been in jeopardy since President Donald Trump withdrew the US from it in 2018.
- In retaliation for the US, Iran resumed some of its nuclear activities.
(2) Iran’s insistence over sanctions removal
- In 2021, President Joe Biden said the US will return to the deal if Iran comes back into compliance, though Iran’s leaders have insisted that Washington lift sanctions first.
- Iran now has indicated that he will take a harder line than his predecessor in nuclear negotiations.
Who are the participants?
- The JCPOA, which went into effect in January 2016, imposes restrictions on Iran’s civilian nuclear enrichment program.
- At the heart of negotiations with Iran were the five permanent members of the UN Security Council (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and Germany—collectively known as the P5+1.
- The European Union also took part. Israel explicitly opposed the agreement, calling it too lenient.
- Some Middle Eastern powers, such as Saudi Arabia, said they should have been consulted or included in the talks because they would be most affected by a nuclear-armed Iran.
What did Iran agree to?
- Nuclear restrictions: Iran agreed not to produce either the highly enriched uranium or the plutonium that could be used in a nuclear weapon.
- Monitoring and verification: Iran agreed to eventually implement a protocol that would allow inspectors from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), the United Nations’ nuclear watchdog.
What did the other signatories agree to?
- Sanctions relief: The EU, United Nations, and United States all committed to lifting their nuclear-related sanctions on Iran. However, many other U.S. sanctions on Iran, some dating back to the 1979 hostage crisis, remained in effect.
- Weapons embargo: The parties agreed to lift an existing UN ban on Iran’s transfer of conventional weapons and ballistic missiles after five years if the IAEA certifies that Iran is only engaged in civilian nuclear activity.
How has the deal affected Iran’s economy?
- Prior to the JCPOA, Iran’s economy suffered years of recession, currency depreciation, and inflation, largely because of sanctions on its energy sector.
- With the sanctions lifted, inflation slowed, exchange rates stabilized, and exports—especially of oil, agricultural goods, and luxury items—skyrocketed as Iran regained trading partners, particularly in the EU.
- After the JCPOA took effect, Iran began exporting more than 2.1 million barrels per day (approaching pre-2012 levels, when the oil sanctions were originally put in place).
Try this question from CSP 2020:
Q.In India, why are some nuclear reactors kept under “IAEA Safeguards” while others are not?
(a) Some use Uranium and others use thorium.
(b) Some use imported uranium and others use domestic supplies.
(c) Some are operated by foreign enterprises and others are operated by domestic enterprises.
(d) Some are State- owned and others are privately-owned.
Post your answers here.
Back2Basics: International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
- IAEA is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons.
- As the preeminent nuclear watchdog under the UN, the IAEA is entrusted with the task of upholding the principles of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty of 1970.
- It was established as an autonomous organization on July 29, 1957, at the height of the Cold War between the U.S. and the Soviet Union.
- Though established independently of the UN through its own international treaty, the agency reports to both the UN General Assembly and the UNSC.
What are its safeguards?
- Safeguards are activities by which the IAEA can verify that a State is living up to its international commitments not to use nuclear programs for nuclear weapons purposes.
- Safeguards are based on assessments of the correctness and completeness of a State’s declared nuclear material and nuclear-related activities.
- Verification measures include on-site inspections, visits, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation.
Basically, two sets of measures are carried out in accordance with the type of safeguards agreements in force with a State.
- One set relates to verifying State reports of declared nuclear material and activities.
- Another set enables the IAEA not only to verify the non-diversion of declared nuclear material but also to provide assurances as to the absence of undeclared nuclear material and activities in a State.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Preventive fugitive offences
The Finance Ministry has released the Rules for Foreign Exchange Management (Overseas Investment Rules), 2022 subsuming extant regulations for Overseas Investments and Acquisition and Transfer of Immovable Property outside India Regulations, 2015.
What are the news Overseas Investment Rules?
- With an eye on wilful defaulters, the new rules stipulate that:
- Any Indian resident will have to seek an no objection certificate before making any overseas financial commitment:
- Who has an account appearing as a non-performing asset
- Or is classified as a wilful defaulter by any bank
- Or is under investigation by a financial service regulator or by investigative agencies in India
What are the tweaks in overseas investment norms?
- Any resident in India acquiring equity capital in a foreign entity or overseas direct investment (ODI), will have to submit an Annual Performance Report (APR) for each foreign entity, every year by December 31.
- No such reporting shall be required where a person resident in India is holding less than 10% of the equity capital without control in the foreign entity.
- There is no other financial commitment other than equity capital or a foreign entity is under liquidation.
Ceiling on investment
- Any resident individual can make ODI by way of investment in equity capital or overseas portfolio investment (OPI) subject to the overall ceiling under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) of the Reserve Bank.
- Currently, the LRS permits $2,50,000 outward investment by an individual in a year.
- These norms make it easier for domestic corporates to invest abroad.
What are the prohibitions?
- Any Indian resident, who has been classified as a wilful defaulter or is under investigation by the CBI, the ED or the Serious Frauds Investigation Office (SFIO), will have to obtain a no-objection certificate (NOC).
- NOC can be obtained from his or her bank, regulatory body or investigative agency before making any overseas “financial commitment” or disinvestment of overseas assets.
- The rules also provide that if lenders, the concerned regulatory body or investigative agency fail to furnish the NOC within 60 days of receiving an application, it may be presumed that they have no objection to the proposed transaction.
- Additionally, the new rules also prohibit Indian residents from making investments into foreign entities that are engaged in real estate activity, gambling in any form, and dealing with financial products linked to the Indian rupee without the specific approval of the RBI.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: VL-SRSAM
Mains level: Short range missiles development

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Navy has successfully flight-tested the indigenously developed Vertical Launch Short Range Surface-to-Air Missile (VL-SRSAM) from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur off the coast of Odisha.
What is Vertical Launch Short Range Surface-to-Air Missile (VLSRSAM) ?
- VL-SRSAM has been designed and developed jointly by three facilities of the DRDO for deployment of Indian Naval warships.
- The missile has the capability of neutralising various aerial threats at close ranges including sea-skimming targets.
- The tactic of sea skimming is used by various anti-ship missiles and some fighter jets to avoid being detected by the radars onboard warships.
- For this, these assets fly as close as possible to sea surface and thus are difficult to detect and neutralise.
Features of VL-SRSAM
- The missile has been designed to strike at the high-speed airborne targets at the range of 40 to 50 km and at an altitude of around 15 km.
- Its design is based on Astra missile which is a Beyond Visual Range Air to Air missile.
- Two key features of the VL-SRSAM are cruciform wings and thrust vectoring.
- The cruciform wings are four small wings arranged like a cross on four sides and give the projective a stable aerodynamic posture.
- The thrust vectoring is an ability to change the direction of the thrust from its engine control the angular velocity and the attitude of the missile.
- VL-SRSAM is a canisterised system, which means it is stored and operated from specially designed compartments.
- In the canister, the inside environment is controlled, thus making its transport and storage easier and improving the shelf life of weapons
Strategic significance of the missile
- The launch was conducted from a vertical launcher against an electronic target at a very low altitude.
- The flight path of the vehicle along with health parameters was monitored using a number of tracking instruments deployed by ITR, Chandipur.
- The successful testing of these systems was crucial for future launches of the missile from Indian Naval Ships.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: equitable health and education
 Context
Context
- To create the foundation for the next century, we need to invest in equitable education and health care in the next 25 years not just for the elite, but for all.
What is current status of education?
- Expenditure on Education: The expenses on education as a percentage to GDP, India lags behind some developed/ developing nations.
- Infrastructure deficit: Dilapidated structures, single-room schools, lack of drinking water facilities, separate toilets and other educational infrastructure is a grave problem.
- Student-teacher ratio: Another challenge for improving the Indian education system is to improve the student teacher ratio.
What is current status of healthcare?
- Weak delivery: Current health infrastructure in India paints a dismal picture of the healthcare delivery system in the country.
- Unpreparedness: Public health experts believe that India is ill-equipped to handle emergencies.
- Technical glitches in urban areas: It is not prepared to tackle health epidemics, particularly given its urban congestion.
A systemic approach to reforming education system in the country needs
- Dynamic pedagogy: Academic interventions involve the adoption of grade competence framework instead of just syllabus completion.
- Directional efforts: Effective delivery of remedial education for weaker students like after-school coaching, audio-video based education.
- Administrative reforms: that enable and incentivize teachers to perform better through data-driven insights, training, and recognition. Example: Performance based increments in Salary.
 A systemic approach to reforming healthcare system in the country needs
A systemic approach to reforming healthcare system in the country needs
- Universal health coverage: Access to healthcare in India is not equitable—the rich and the middle class would survive the COVID-19 or any other crisis but not the poor.
- Increasing healthcare professionals in numbers: India has handled the COVID-19 pandemic exceptionally well. However, India is in dire need of more medical staff and amenities.
- Revamping medical education: If the government wants to stay successful in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic, it needs to rapidly build medical institutions and increase the number of doctors.
- Cross-subsidization of health-care: How the poor managed without, or even with, any government insurance scheme is a big question. They can make up for the loss by cross-subsidizing treatments of patients with premium insurance policies.
Recent initiatives
- PLI scheme: In view of these challenges, the government announced various policies like PLI scheme for domestic manufacturing of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- National Digital Health Mission: It also announced the National Digital Health Mission.
Way forward
- India’s healthcare system is too small for such a large population.
- There seems to be a long battle ahead. The public healthcare system cannot be improved overnight.
- The country needs all hands on deck during and after this crisis—both public and private sectors must work together and deliver universal health coverage for all citizens.
Conclusion
- Providing expanded access to high quality education and healthcare supports—particularly for those young people who today lack such access—will not only expand economic opportunity for those individuals, but will also likely do more to strengthen the overall state economy.
Mains question
Q. To create the foundation for the next century, we need to invest in education and health in the next 25 years not just for the elite, but for all. Critically examine
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tomato Flu
Mains level: Not Much
With cases of tomato flu reported from at least four states — Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, and Odisha — the Union Health Ministry has issued a set of guidelines on prevention, testing, and treatment of the infection.
Researchers believe that it is a different clinical presentation of hand-foot-and mouth disease (HFMD) caused by a group of enteroviruses (viruses transmitted through the intestine).
What is Tomato Flu?
- Tomato flu or tomato fever is characterized by fever, joint pain, and red, tomato-like rashes usually seen in children below the age of five years.
- This is accompanied by other symptoms of viral fevers such as diarrhoea, dehydration, nausea and vomiting, and fatigue.
- This was thought to be an aftereffect of dengue and chikungunya that is commonly seen in Kerala.
- However, researchers now believe that it is HFMD caused by enteroviruses like Coxsackievirus A-6 and A-16.
Is it very uncommon?
- Tomato flu could be an after-effect of chikungunya or dengue fever in children rather than a viral infection.
- It could also be a new variant of the viral hand, foot, and mouth disease, a common infectious disease targeting mostly children aged 1–5 years and immunocompromised adults.
- HFMD is not a new infection, we have read about it in our textbooks. It is reported from time to time across the country, but it is not very common.
Why is the infection spreading now?
- There actually are more cases or because we are more vigilant about viral infections and testing after Covid-19.
- Since the disease is self-limiting, doctors do not usually test for it.
- There are so many viral infections in children, but we cannot — and there is no need to — test for each and every one of it.
Which pathogen is causing it now? And how is the clinical presentation different?
- The current HFMD cases are mainly caused by Coxsackievirus A-6 and A-16.
- Another pathogen — Enterovirus71 — that also causes the disease is not very prevalent now, according to her.
- This is good because the pathogen was known to lead to severe neurologic symptoms, including fatal encephalitis (brain inflammation).
- In almost all cases, say 99.9% cases, the disease is self-limiting.
- But, in a small number of cases it can lead to CNS (central nervous system) complications.
Is there a treatment for the infection?
- There is no specific treatment or vaccine available for the disease.
- Those with the infection are treated symptomatically, such as prescription of paracetamol for fever.
How can the infection be prevented?
- As it happens mainly in children, the Centre’s advisory focuses on preventions in these age groups.
- As per the advisory, anyone suspected to have the infection should remain in isolation for five to seven days after the onset of the symptoms.
- It states that children must be educated about the infection and asked not to hug or touch other children with fever or rashes.
- The children should be encouraged to maintain hygiene, stop thumb or finger sucking, and use a handkerchief for a running nose, the advisory states.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Data localisation
Mains level: Data diplomacy, Data sovereignty
 Context
Context
- The government has withdrawn the Personal Data Protection Bill from Parliament after several amendments were proposed by the Joint-Parliamentary Committee.
Definition of data
- Data is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted.
What is Data Protection?
- Data protection refers to policies and procedures seeking to minimise intrusion into the privacy of an individual caused by collection and usage of their personal data.
What is data localisation?
- Data localization or data residency law requires data about a nation’s citizens or residents to be collected, processed, and/or stored inside the country, often before being transferred internationally.
What is Data Governance?
- Data governance is a collection of processes, roles, policies, standards, and metrics that ensure the effective and efficient use of information in enabling an organization to achieve its goals. Data governance defines who can take what action, upon what data, in what situations, using what methods.
Interesting facts
- Over 90% of all the data in the world was created in the past 2 years;
- The total amount of data being captured and stored by industry doubles every 1.2 years;
- If you burned all of the data created in just one day onto DVDs, you could stack them on top of each other and reach the moon – twice.
Data sovereignty of India
- Definition: India has placed itself at the heart of the battle, its foreign policy vision fuelled by the principle of ‘data sovereignty’—a broad notion that supports the assertion of sovereign writ over data generated by citizens within a country’s physical boundaries.
- Issues: The ideal of “data sovereignty”, and global attempts to leverage it, has come under heavy criticism from various stakeholders who are of the view that the concept violates the principle of “free and open internet”. They also argue that “data sovereignty” hampers innovation and economic growth, and is a ruse for authoritarian digital governance.
India’s Data Diplomacy: Three Pillars
- Pillar 1: India’s data for India’s development
The flagship ‘Digital India’ programme clearly views data as the cornerstone of India’s socioeconomic future—one where the government leverages the Indian citizen’s data for the benefit of the people themselves, and not solely for profit-making.
- Pillar 2: Cross-border data flows and digital trade
In keeping with its foreign policy tradition of actively shaping debates on global trade rules, India has been an active participant in the ongoing contestation on regulating cross-border data flows.
- Pillar 3: Securitising the economic
The final pillar of India’s data diplomacy has been predicated ostensibly on safeguarding its citizens’ data from external threats.
Why data is important?
- Improve People’s Lives: Data will help you to improve quality of life for people you support: Improving quality is first and foremost among the reasons why organizations should be using data.
- Make Informed Decisions: Data = Knowledge. Good data provides indisputable evidence, while anecdotal evidence, assumptions, or abstract observation might lead to wasted resources due to taking action based on an incorrect conclusion.
- Stop Molehills from Turning into Mountains: Data allows you to monitor the health of important systems in your organization: By utilizing data for quality monitoring, organizations are able to respond to challenges before they become full-blown crisis.
- Get The Results You Want: Data allows organizations to measure the effectiveness of a given strategy: When strategies are put into place to overcome a challenge, collecting data will allow you to determine how well your solution is performing, and whether or not your approach needs to be tweaked or changed over the long-term.
Conclusion
- The fulcrum of India’s data diplomacy should be predicated on the rule of law and the genuine protection of fundamental rights enshrined in the Constitution. A commitment to the rule of law and accountability for all actors sets India apart from present adversaries like China and offers an opportunity to burnish its reputation globally.
Mains question
Q.Data is considered as new gold across the globe in this context analyse data sovereignty along with status of data diplomacy of India.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Article 239AA, Consititution Bench
Mains level: Centre vs. Delhi Govt

A Constitution Bench led by Justice D.Y. Chandrachud will hear the legal battle between the Centre and the Government of Delhi for control over officials in the national capital.
What is a Constitution Bench?
- The constitution bench is the name given to the benches of the Supreme Court of India.
- The Chief Justice of India has the power to constitute a Constitution Bench and refer cases to it.
Constitution benches are set up when the following circumstances exist:
- Interpretation of the Constitution: Article 145(3) provides for the constitution of at least five judges of the court which sit to decide any case “involving a substantial question of law as to the interpretation” of the Constitution of India.
- President of India seeking SC’s opinion: When the President has sought the Supreme Court’s opinion on a question of fact or law under Article 143 of the Constitution. Article 143 of the Constitution provides for Advisory jurisdiction to the SC. As per the provision, the President has the power to address questions to the apex Court, which he deems important for public welfare.
- Conflicting Judgments: When two or more three-judge benches of the Supreme Court have delivered conflicting judgments on the same point of law, necessitating a definite understanding and interpretation of the law by a larger bench.
- The Constitution benches are set up on ad hoc basis as and when the above-mentioned conditions exist.
- Constitution benches have decided many of India’s best-known and most important Supreme Court cases, such as:
- K. Gopalan v. State of Madras (Preventive detention)
- Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala (Basic structure doctrine) and
- Ashoka Kumar Thakur v. Union of India (OBC reservations) etc.
Why in news now?
- A 2018 Constitution bench decision interpreting Article 239AA had not dealt with an aspect having a bearing on the dispute over services, CJI agreed.
- The proceedings have their genesis in the Delhi HC judgment of August 4, 2017, whereby it held that for the purposes of administration, the L-G was not bound by the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers in every matter.
- On appeal, the SC on February 15, 2017, referred the matter to decide on the interpretation of Article 239AA.
What is the 2018 Judgment all about?
- By a majority decision in July, 2018, the Constitution bench upheld the respective powers of the state Assembly and the Parliament.
- It said that while the CoM must communicate all decisions to the L-G, this does not mean that the L-G’s concurrence is required.
- In case of a difference of opinion, the L-G can refer it to the President for a decision.
- The L-G has no independent decision-making power but has to either act on the ‘aid and advice’ of the CoM or is bound to implement the decision of the President on a reference being made.
- The bench, which limited itself to the interpretation of Article 239AA, left individual issues to be decided by regular benches.
When power tussle began?
- Subsequently in 2019, a two-judge bench of the SC dealt with some individual issues arising from the power tussle between the Centre and the NCT government.
- It ruled that the Anti-Corruption Branch of the Delhi government cannot investigate corruption cases against central government officials.
- The power to appoint commissions under the Commission of Inquiry Act, 1952, would be vested with the Centre and not the Delhi government, the judgment said.
Issue over control of administrative services
- The judges, however, differed on who should have control over administrative services.
- This was challenged again in the SC where the Centre contended that the two judges could not take a decision on the question.
- The 2018 Constitution bench judgment had not interpreted the expression “insofar as any such matter as applicable to Union Territories” appearing in Article 239AA.
- The Centre has urged SC CJI Ramana to refer the matter to a five-judge Constitution bench so that the question of law can be settled before the dispute over who has control over services can be looked into.
Article 239AA of the Indian Constitution
- Article 239AA granted Special Status to Delhi among Union Territories (UTs) in the year 1991 through the 69th Constitutional Amendment.
- It provided a Legislative Assembly and a Council of Ministers responsible to such Assembly with appropriate powers.
- That’s when Delhi was named as the National Capital Region (NCT) of Delhi.
- As per this article – Public Order, Police & Land in NCT of Delhi fall within the domain and control of Central Government which shall have the power to make laws on these matters.
- For remaining matters of State List or Concurrent List, in so far as any such matter is applicable to UTs, the Legislative Assembly shall have the power to make laws for NCT of Delhi.
|
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Mains level: Prospects and challenges to CBDC
Reports have said the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) digital rupee — the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) — may be introduced in phases beginning with wholesale businesses in the current financial year.
What is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
- CBDC is a central bank issued digital currency which is backed by some kind of assets in the form of either gold, currency reserves, bonds and other assets, recognised by the central banks as a monetary asset.
- The present concept of CBDCs was directly inspired by Bitcoin, but a CBDC is different from virtual currency and cryptocurrency.
- Cryptocurrencies are not issued by a state and lack the legal tender status declared by the government.
What is Currency chest?
Currency in India is managed by Currency chest. Currency chest is a place where the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) stocks the money meant for banks and ATMs. These chests are usually situated on the premises of different banks but administrated by the RBI.
Why India needs a digital rupee?
- Online transactions: India is a leader in digital payments, but cash remains dominant for small-value transactions.
- High currency in circulation: India has a fairly high currency-to-GDP ratio.
- Cost of currency management: An official digital currency would reduce the cost of currency management while enabling real-time payments without any inter-bank settlement.
Why is CBDC preferred over Cryptocurrency?
- Sovereign guarantee: Cryptocurrencies pose risks to consumers. They do not have any sovereign guarantee and hence are not legal tender.
- Market volatility: Their speculative nature also makes them highly volatile. For instance, the value of Bitcoin fell from USD 20,000 in December 2017 to USD 3,800 in November 2018.
- Risk in security: A user loses access to their cryptocurrency if they lose their private key (unlike traditional digital banking accounts, this password cannot be reset).
- Malware threats: In some cases, these private keys are stored by technical service providers (cryptocurrency exchanges or wallets), which are prone to malware or hacking.
- Money laundering: Cryptocurrencies are more vulnerable to criminal activity and money laundering. They provide greater anonymity than other payment methods since the public keys engaging in a transaction cannot be directly linked to an individual.
- Regulatory bypass: A central bank cannot regulate the supply of cryptocurrencies in the economy. This could pose a risk to the financial stability of the country if their use becomes widespread.
- Power consumption: Since validating transactions is energy-intensive, it may have adverse consequences for the country’s energy security (the total electricity use of bitcoin mining, in 2018, was equivalent to that of mid-sized economies such as Switzerland).
Features of CBDC
- High-security instrument: CBDC is a high-security digital instrument; like paper banknotes, it is a means of payment, a unit of account, and a store of value.
- Uniquely identifiable: And like paper currency, each unit is uniquely identifiable to prevent counterfeit.
- Liability of central bank: It is a liability of the central bank just as physical currency is.
- Transferability: It’s a digital bearer instrument that can be stored, transferred, and transmitted by all kinds of digital payment systems and services.
Key benefits offered
- Faster system: CBDC can definitely increase the transmission of money from central banks to commercial banks and end customers much faster than the present system.
- Financial inclusion: Specific use cases, like financial inclusion, can also be covered by CBDC that can benefit millions of citizens who need money and are currently unbanked or banked with limited banking services
- Monetary policy facilitation: The move to bring out a CBDC could significantly improve monetary policy development in India.
- Making of a regional currency: In the cross border payments domain, India can take a lead by leveraging digital Rupee especially in countries such as Bhutan, Saudia Arabia and Singapore where NPCI has existing arrangements.
Others:
- It is efficient than printing notes (cost of printing, transporting, and storing paper currency)
- It reduces the risk of transactions
- It makes tax collection transparent
- Prevents money laundering
Issues involved with CBDC
- Innovation with centralization: The approach of bringing a sovereign digital currency stands in stark contrast to the idea of decentralization.
- Liability on RBI: when bank customers wish to convert their deposits into digital rupee, the RBI will have to take these liabilities from the books of banks and onto its own balance sheet.
- Inflationary risk: Central banks would indulge in issuing more digital currencies which could potentially trigger higher inflation.
- User adoption: User adoption could also pose a major setback for the smooth roll out of the CBDC in India. The main challenges would always be user adoption and security.
- Reduced savings: Many, including various central bankers, fear that people may begin withdrawing money from their bank accounts as digital currencies issued by Central banks become more popular.
- Volatility: the risk is higher and there is more price volatility and lesser acceptance as a money instrument globally, unless the trust factor and investor protection factors change.
Way forward
- The launch of CBDCs may not be a smooth affair and still requires more clarity in India. There are still a lot of misconceptions about the concept of digital currency in the country.
- The effectiveness of CBDCs will depend on aspects such as privacy design and programmability.
- There is a huge opportunity for India to take a lead globally via a large-scale rollout and adoption of digital currencies.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cloudburst
Mains level: Flash floods and cloudbursts

Over 20 people have been killed in destruction caused by cloudbursts and flash floods in different parts of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand over the last three days.
What are Cloudbursts?
- A cloudburst is a localised but intense rainfall activity.
- Short spells of very heavy rainfall over a small geographical area can cause widespread destruction, especially in hilly regions where this phenomenon is the most common.
- Not all instances of very heavy rainfall, however, are cloudbursts.
- A cloudburst has a very specific definition: Rainfall of 10 cm or more in an hour over a roughly 10 km x 10-km area is classified as a cloudburst event.
- By this definition, 5 cm of rainfall in a half-hour period over the same area would also be categorized as a cloudburst.
How is it different from normal rainfall?
- To put this in perspective, in a normal year, India, as a whole, receives about 116 cm of rainfall over the entire year.
- This means if the entire rainfall everywhere in India during a year was spread evenly over its area, the total accumulated water would be 116 cm high.
- There are, of course, huge geographical variations in rainfall within the country, and some areas receive over 10 times more than that amount in a year.
- But on average, any place in India can be expected to receive about 116 cm of rain in a year.
- During a cloudburst event, a place receives about 10% of this annual rainfall within an hour.
How common are cloudbursts?
- Cloudbursts are not uncommon events, particularly during the monsoon months.
- Most of these happen in the Himalayan states where the local topology, wind systems, and temperature gradients between the lower and upper atmosphere facilitate the occurrence of such events.
- However, not every event that is described as a cloudburst is actually, by definition, a cloudburst.
- That is because these events are highly localized.
- They take place in very small areas which are often devoid of rainfall measuring instruments.
Why are they so destructive?
- The consequences of these events, however, are not confined to small areas.
- Because of the nature of terrain, the heavy rainfall events often trigger landslides and flash floods, causing extensive destruction downstream.
- This is the reason why every sudden downpour that leads to destruction of life and property in the hilly areas gets described as a “cloudburst”, irrespective of whether the amount of rainfall meets the defining criteria.
- At the same time, it is also possible that actual cloudburst events in remote locations aren’t recorded.
Can cloudbursts be forecasted?
- The India Meteorological Department forecasts rainfall events well in advance, but it does not predict the quantum of rainfall — in fact, no meteorological agency does.
- The forecasts can be about light, heavy, or very heavy rainfall, but weather scientists do not have the capability to predict exactly how much rain is likely to fall at any given place.
- Additionally, the forecasts are for a relatively large geographical area, usually a region, a state, a meteorological sub-division, or at best a district.
- As they zoom in over smaller areas, the forecasts get more and more uncertain.
- Theoretically, it is not impossible to forecast rainfall over a very small area as well, but it requires a very dense network of weather instruments and computing capabilities that seem unfeasible with current technologies.
- As a result, specific cloudburst events cannot be forecast. No forecast ever mentions a possibility of a cloudburst.
- But there are warnings for heavy to very heavy rainfall events, and these are routinely forecast four to five days in advance.
- Possibility of extremely heavy rainfall, which could result in cloudburst kind of situations, are forecast six to 12 hours in advance.
Are cloudburst incidents increasing?
- There is no long-term trend that suggests that cloudbursts, as defined by the IMD, are rising.
- What is well established, however, is that incidents of extreme rainfall, as also other extreme weather events, are increasing — not just in India but across the world.
- While the overall amount of rainfall in India has not changed substantially, an increasing proportion of rainfall is happening in a short span of time.
- That means that the wet spells are very wet, and are interspersed with prolonged dry spells even in the rainy season.
- This kind of pattern, attributed to climate change, does suggest that cloudburst events might also be on the rise.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pandurang Khankhoje
Mains level: Ghadr party

Lok Sabha Speaker, who is currently in Canada for the 65th Commonwealth Parliamentary Conference, will travel to Mexico where he will unveil statues of Swami Vivekananda and Maharashtra-born freedom fighter and agriculturalist Pandurang Khankhoje.
Who was Pandurang Khankhoje (1883-1967)?
- Born in Wardha, Maharashtra, in the late 19th century, Pandurang Khankhoje came in contact with other revolutionaries early on.
- As a student, Khankhoje was an ardent admirer of the French Revolution and of the American War of Independence.
- Closer to home, the Hindu reformer Swami Dayanand and his Arya Samaj movement, which called for a spirit of reform and social change, became the hero to a young student group led by Khankhoje.
Revolutionary activities abroad
- Khankhoje decided to go abroad for further training in revolutionary methods and militaristic strategy.
- At this time, the British government’s suspicions of him were also growing due to his anti-government activities.
- Before leaving, he visited Bal Gangadhar Tilak, by whom he was inspired.
- Tilak advised him to go to Japan, which was itself a strong, anti-West Asian imperialistic force then.
- After spending time with nationalists from Japan and China, Khankhoje eventually moved to the US, where he enrolled in college as a student of agriculture.
Participation in the Indian independence movement
- Khankhoje was one of the founding members of the Ghadar Party, established by Indians living abroad in 1914, mostly belonging to Punjab.
- Its aim was to lead a revolutionary fight against the British in India.
- While in the US, Khankhoje met Lala Har Dayal, an Indian intellectual teaching at Stanford University.
- Har Dayal had begun a propaganda campaign, publishing a newspaper that featured patriotic songs and articles in the vernacular languages of India.
- This was the seed from which the Ghadar Party would emerge.
How did Khankhoje reach Mexico?
- At the military academy, Khankhoje met many people from Mexico.
- The Mexican Revolution of 1910 had led to the overthrow of the dictatorial regime, and this inspired Khankhoje.
- He also reached out to Indians working on farms in the US with the aim of discussing the idea of Indian independence with them.
- Along with the Indian workers, militant action was planned by Khankhoje in India, but the outbreak of the First World War halted these plans.
- He then reached out to Bhikaji Cama in Paris, and met with Vladimir Lenin in Russia among other leaders, seeking support for the Indian cause.
Association with Mexico
- As he was facing possible deportation from Europe and could not go to India, he sought shelter in Mexico.
- Soon, in part due to his prior friendship with Mexican revolutionaries, he was appointed a professor at the National School of Agriculture in Chapingo, near Mexico City.
- He researched corn, wheat, pulses and rubber, developing frost and drought-resistant varieties, and was part of efforts to bring in the Green Revolution in Mexico.
- Later on, the American agronomist Dr Norman Borlaug, called the Father of the Green Revolution in India, brought the Mexican wheat variety to Punjab.
- Khankhoje was revered as an agricultural scientist in Mexico.
Return to India
- Both Pandurang and Jean returned to India after 1947.
- His application for visa was initially rejected by the Indian government due to the ban by the British Indian Government, but was eventually overturned.
- He settled in Nagpur and subsequently embarked on a political career.
- Pandurang Khankhoje died on 22 January 1967.
Back2Basics: Ghadar Party
Founder: Sohan Singh Bhakna, 15 July 1913
- The Ghadar Movement was an early 20th century, international political movement founded by expatriate Indians to overthrow British rule in India.
- Earlier activists had established a ‘Swadesh Sevak Home’ in Vancouver and a ‘United India House’ in Seattle to carry out revolutionary activities. Finally, in 1913, the Ghadr was founded.
- The Ghadar Party, originally known as the Pacific Coast Hindustan Association, was founded on July 15, 1913 in the US by Lala Har Dayal, Sant Baba Wasakha Singh Dadehar, Baba Jawala Singh, Santokh Singh, and Sohan Singh Bhakna.
- The Ghadar party drew a sizable following among Indian expatriates in the United States, Canada, East Africa, and Asia.
- It fought against colonialism from 1914 to 1917, with the support of Imperial Germany and the Ottoman Empire, both of which were Central Powers opposed to the British.
- The party was organized around the weekly newspaper The Ghadar, which featured the masthead caption: Angrezi Raj Ka Dushman (an enemy of British rule); “Wanted brave soldiers to stir up rebellion in India,” the Ghadar declared.
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Freedom fighters in news
Mains level: Feminist contribution in freedom struggle
 Context
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Independence Day speech underlined the role of women veeranganas in our freedom movement. The initiative highlighting the brave women of our freedom struggle, under the broader celebration of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, will mark a turning point in Indian feminist history writing from an Indic perspective.
What veerangana means?
- Veerangana means a brave female, someone who can fight for their rights. A strong woman not only protects herself, but protects others too.
Veerangana’s in freedom struggle
Rani Laxmibai
- The queen of the princely state of Jhansi, Rani Laxmibai is known for her role in the First War of India’s Independence in 1857.
- Refusing to cede her territory, the queen decided to rule on behalf of the heir, and later joined the uprising against the British in 1857.
- Cornered by the British, she escaped from Jhansi fort. She was wounded in combat near Gwalior’s Phool Bagh, where she later died.
- Sir Hugh Rose, who was commanding the British army, is known to have described her as “personable, clever…and one of the most dangerous Indian leaders”.
Jhalkari Bai
- A soldier in Rani Laxmibai’s women’s army, Durga Dal, she rose to become one of the queen’s most trusted advisers.
- She is known for putting her own life at risk to keep the queen out of harm’s way.
- Till date, the story of her valour is recalled by the people of Bundelkhand, and she is often presented as a representative of Bundeli identity.
Durga Bhabhi
- Durgawati Devi, who was popularly known as Durga Bhabhi, was a revolutionary who joined the armed struggle against colonial rule.
- A member of the Naujawan Bharat Sabha, she helped Bhagat Singh escape in disguise from Lahore after the 1928 killing of British police officer John P Saunders.
- Later, as revenge for the hanging of Bhagat Singh, Rajguru, and Sukhdev, she made an unsuccessful attempt to kill the former Punjab Governor, Lord Hailey.
Rani Gaidinliu
- Born in 1915 in present-day Manipur, Rani Gaidinliu was a Naga spiritual and political leader who fought the British.
- She joined the Heraka religious movement which later became a movement to drive out the British. She rebelled against the Empire, and refused to pay taxes, asking people to do the same.
- The British launched a manhunt, but she evaded arrest, moving from village to village.
- Gaidinliu was finally arrested in 1932 when she was just 16, and later sentenced for life. She was released in 1947.
- Then PM Nehru described Gaidinliu as the “daughter of the hills”, and gave her the title of ‘Rani’ for her courage.
Rani Chennamma
- The queen of Kittur, Rani Chennamma, was among the first rulers to lead an armed rebellion against British rule.
- Kittur was a princely state in present-day Karnataka.
- She fought back against the attempt to control her dominion in 1824 after the death of her young son. She had lost her husband, Raja Mallasarja, in 1816.
- She is seen among the few rulers of the time who understood the colonial designs of the British.
- Rani Chennamma defeated the British in her first revolt, but was captured and imprisoned during the second assault by the East India Company.
Begum Hazrat Mahal
- After her husband, Nawab of Awadh Wajid Ali Shah, was exiled after the 1857 revolt, Begum Hazrat Mahal, along with her supporters, took on the British and wrested control of Lucknow.
- She was forced into a retreat after the colonial rulers recaptured the area.
Velu Nachiyar
- Many years before the revolt of 1857, Velu Nachiyar waged a war against the British and emerged victorious. Born in Ramanathapuram in 1780, she was married to the king of Sivagangai.
- After her husband was killed in battle with the East India Company, she entered the conflict, and won with support of neighbouring kings.
- She went on to produce the first human bomb as well as establish the first army of trained women soldiers in the late 1700s.
- Her army commander Kuyili is believed to have set herself ablaze and walked into a British ammunition dump.
- She was succeeded by her daughter in 1790, and died a few years later in 1796.
Conclusion
- The veeranganas are a potent symbol of nationalism and patriotism. They can overturn oppressive attitudes towards women in society. Their role and celebration in popular culture also refutes the colonial allegations about the suppression of women throughout Indian history. But it is essential to discover, rewrite and reinterpret the role and representation of these heroic women in the liberation of the motherland.
Mains question
Q. The veerangana’s are a potent symbol of nationalism and patriotism. They can overturn oppressive attitudes towards women in society. Discuss examples of them showing how they inspire women’s today.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kerala Savari
Mains level: Cab aggregators malpractices and their regulation in India

Kerala has soft launched ‘Kerala Savari’, the country’s first online taxi service owned by a State government, to ensure fair and decent service to passengers along with fair remuneration to auto-taxi workers.
What is Kerala Savari?
- Operated by the Motor Workers Welfare Board under the aegis of the Labour Department, the Kerala Savari ensures safe travel for the public at ‘government approved fares’ without any ‘surge pricing’.
- The ‘Kerala Savari’ app would be made available to the public on online platforms shortly as it is under the scrutiny of Google now.
Why such initiative?
- The alleged unfair trade practices and violation of consumer rights by private app-based cab aggregators have come as a major concern for governments.
- Recently, the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) had issued notices to cab aggregators Ola and Uber for unfair trade practices and violation of consumer rights which include:
- Charging exorbitant fares during peak hours
- Unprofessional behaviour from the part of drivers
- Lack of proper response from customer support, and
- Undue levy of cancellation charges despite the cab driver refusing to accept the ride booked by the passenger etc.
- It is against this backdrop that the Kerala government has decided to come up with an app-based platform to offer auto-taxi service for the public.
What are the main attractions of ‘Kerala Savari’?
- There will be no fluctuation in fares on Kerala Savari irrespective of day or night or rain.
- But Kerala Savari only 8% service charge in addition to the rate set by the government, whereas the private cab aggregators charge up to 20 to 30% service charge.
What are the security-related features of ‘Kerala Savari’?
- Kerala Savari is claimed as a safe and reliable online service for women, children, and senior citizens.
- This consideration has been given importance in app designing and driver registration.
- A police clearance certificate is mandatory for drivers joining the scheme apart from the required proper training.
- A panic button system has been introduced in the app.
- It has also been decided to install GPS in vehicles at a subsidised rate.
Will the new government initiative end the monopoly of private cab aggregators?
- Kerala has over five lakh autorickshaws and one lakh cabs.
- The State government plans to bring all auto-taxi workers engaged in the sector under the new platform.
- Since smartphone literacy is high in Kerala, the State is hopeful of bringing them under the scheme in a short span of time.
- In addition, the Kerala government has also decided to provide fuel, insurance, and tyre subsidies for vehicle owners in the future and has already initiated talks with major companies in this regard.
- After the evaluation of the first phase of the project in Thiruvananthapuram, it will be extended to the entire State in a phased manner.
- Kerala Savari is expected to reach Kollam, Ernakulam, Thrissur, Kozhikode, and Kannur municipal limits within a month.
Regulation of Cab Aggregators in India
- The Motor Vehicles Amendment Act 2019 seeks to regulate Cab aggregators in India
- It’s the first time cab aggregators have got statutory recognition as “digital intermediaries” or “transport aggregators”.
- They are now defined as marketplaces that can be used by passengers to connect with a driver for moving from one place to another.
- The Centre will issue broad guidelines from time to time and the states will rely on them to frame their own rules to regulate the industry.
- The aggregators will also have to comply with the provisions of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- This means they will have to follow rules on storing data safely to protect the identity of users.
|
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tigray Crisis
Mains level: Not Much
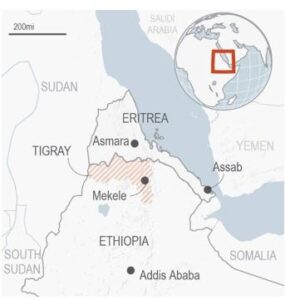
The director-general of the World Health Organization (WHO), described the Tigray crisis region as the “worst humanitarian disaster on earth”.
What is the news?
- Ethiopia has been on the brink of a civil war.
- On Nov 4 2020, Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed declared war on the country’s Tigray region.
- The Tigray region is ruled by the Tigray People’s Liberation Front (TPLF).
- The war was declared in response to the TPLF’s attack on a federal military base in Tigray.
Tigray Crisis: A backgrounder
- The animosity between Tigrayans and Eritrea goes back to the Ethiopian-Eritrean war that occurred between 1998 and 2000.
- It occurred approximately two decades ago was extremely brutal and resulted in the deaths of thousands of soldiers.
- The roots of this crisis can be traced to Ethiopia’s system of government. Since 1994, Ethiopia has had a federal system in which different ethnic groups control the affairs of 10 regions.
- The Tigray People’s Liberation Front (TPLF) – was influential in setting up this system.
- It was the leader of a four-party coalition that governed Ethiopia from 1991, when a military regime was ousted from power.
- Under the coalition, Ethiopia became more prosperous and stable, but concerns were routinely raised about human rights and the level of democracy.
How did it escalate into a crisis?
- Eventually, discontent morphed into protest, leading to a government reshuffle that saw Mr Abiy appointed PM.
- Abiy liberalized politics, set up a new party (the Prosperity Party), and removed key Tigrayan government leaders accused of corruption and repression.
- Meanwhile, Abiy ended a long-standing territorial dispute with neighbouring Eritrea, earning him a Nobel Peace Prize in 2019.
- These moves won Abiy popular acclaim, but caused unease among critics in Tigray.
- Tigray’s leaders see Abiy’s reforms as an attempt to centralize power and destroy Ethiopia’s federal system.
How bad is the humanitarian situation?
- Tigray and its neighbouring regions are facing starvation.
- There is an absence of medical facilities, no access to their own money due to shut-down banking services, ethnic and physical violence, and raids at the hands of warring forces.
- The government declared a ceasefire on humanitarian grounds but in an effort to break the TPLF in June last year, imposed a blockade on Tigray.
- This made it impossible to deliver humanitarian, economic, and medical assistance to Tigrayans.
Also read:
[Burning Issue] Ethiopian Crisis and the Geopolitics
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ICDS
Mains level: Paper 2- Early childhood care and education
 Context
Context
- The economic fallout of COVID-19 makes the necessity of quality public welfare services more pressing than ever.
- The Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) programme is one such scheme.
What is ICDS?
- ICDS caters to the nutrition, health and pre-education needs of children till six years of age as well as the health and nutrition of women and adolescent girls.
What is anganwadi scheme?
- The scheme was started in 1975 and aims at the holistic development of children and empowerment of mother.
- It is a Centrally-Sponsored scheme. The scheme primarily runs through the Anganwadi centre. The scheme is under the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
Need for focus on early childhood care and education (ECCE)
- Low enrolment: The National Family Health Survey-5 (NFHS-5) finds only 13.6 per cent of children enrolled in pre-primary schools.
- Weakest link: With its overriding focus on health and nutrition, ECCE has hitherto been the weakest link of the anganwadi system.
- Low awareness: Unfortunately, due to a lack of parental awareness compounded by the daily stresses of poverty, disadvantaged households are unable to provide an early learning environment.
Data to remember
According to government data, the country has 13.77 lakh Anganwadi centres (AWCs).
A meaningful ECCE programme in anganwadis
- Activity-based framework which reflect local context: To design and put in place a meaningful activity-based ECCE framework that recognises the ground realities with autonomy to reflect the local context and setting.
- Remove non-ICDS work: Routine tasks of anganwadi workers can be reduced and non-ICDS work, such as surveys, removed altogether.
- Extend Anganwadi time: Anganwadi hours can be extended by at least three hours by providing staff with an increase in their present remuneration, with the additional time devoted for ECCE.
- Change in policy mindset: ICDS needs a change in policy mindset, both at central and state levels, by prioritising and monitoring ECCE.
- Engagement with parents: Anganwadi workers must be re-oriented to closely engage with parents, as they play a crucial role in the cognitive development of young children.
Case study / value addition
In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, anganwadi centres have been geotagged to improve service delivery.
Gujarat has digitised the supply chain of take-home rations and real-time data is being used to minimise stockouts at the anganwadi centres.
Way forward
- Government must act on the three imperatives. First, while infrastructure development and capacity building of the anganwadi remains the key to improving the programme, the standards of all its services need to be upscaled.
- Second, states have much to learn from each other’s experiences.
- Third, anganwadi centres must cater to the needs of the community and the programme’s workers.
Conclusion
- Nearly 1.4 million anganwadis of the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) across India must provide ECCE for the millions of young children in low-income households.
Mains question
Q. Some educationists have suggested that owing to the high workload of anganwadi workers, ECCE in anganwadis would remain a non-starter. Critically examine this statement and give dynamic suggestions to improve EECE in anganwadis.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Concept of LiFE
Mains level: Paper 3- LiFE movement
Context
In the midst of a global climate crisis, and as India gets closer to hosting the G20 presidency, it is important to recognise our country’s leadership at both ends of the climate debate: By walking the talk on our climate commitments as well as leading people-powered climate action.
Power of individual and collective action to address the climate change
- Adopting eco-friendly behaviours: According to the United Nation Environment Programme (UNEP), if one billion people out of the global population of close to eight billion adopt eco-friendly behaviours in their daily lives, global carbon emissions could drop by approximately 20 per cent.
- Such eco-friendly behaviours include turning off ACs, heaters and lights when not in use, as this, for instance, can conserve up to 282 kilowatts of electricity per day.
- Avoiding food wastage can reduce an individual’s carbon footprint by 370 kg per year.
The concept of Lifestyle for Environment
- In November 2021, at the CoP 26 in Glasgow, Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in addition to announcing the panchamrit, or five climate-related commitments of the country, also articulated the concept of “Lifestyle for the Environment” (LiFE).
- Mindful and deliberate utilisation: The concept advocate for mindful and deliberate utilisation by people worldwide, instead of “mindful and wasteful consumption”.
- LiFE was launched on June 5, 2022, World Environment Day, by PM Modi, with a vision of harnessing the power of individual and collective action across the world to address the climate crisis.
- The objective of the movement is to nudge individuals and communities to adopt simple and specific climate-friendly behaviours in their daily lifestyles.
- For instance, an individual can carry a reusable cloth bag instead of a plastic bag.
- By making such daily actions an integral part of our collective social norms, LiFE aims to activate a global community of “Pro Planet People” and steer the world towards a sustainable model of development.
- Global precedents: There are already precedents of pro-planet initiatives around the world.
- For example, Denmark promotes the use of bicycles by limiting parking within the city centre and providing exclusive bike lanes.
- Japan has its unique “walk-to-school” mandate, which has been in practice since the early 1950s.
- LiFE, however, is planned as a first-of-its-kind global movement, led by India in partnership with other countries, that will provide the world with a unique people-powered platform to relentlessly focus on bringing individual and collective actions to the core of the climate action narrative.
How the LiFE moment can change people’s behaviour
- 1] Consume responsibly: The prevailing perception that climate-friendly behaviour necessarily implies a frugal lifestyle has played a major role in preventing populations worldwide from adopting a sustainable lifestyle.
- LiFE plans to methodically break down this mental model by nudging the world to consume responsibly, rather than consuming less.
- Using behavioural technique: Building on the unique insights from Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM), LiFE will deploy a range of tested behavioural techniques, including nudges, social and behaviour change communication and norm influencing to make mindful consumption a mass movement.
- 2] Produce responsibly: Our society reflects our markets and vice versa.
- If sustainable choices are not supported from the supply-side, any change in our consumption patterns will only be temporary.
- By nudging the consumption patterns of the society at scale, LiFE can also trigger a huge boost for the sustainability market.
- Several green industries and a large number of jobs are likely to be initiated as a positive externality of LiFE.
- 3] Live responsibly: The Covid pandemic is a wake-up call to all of us that no matter how much technological progress we make as a global society, we all remain at the mercy of the natural world.
- As a global community of people with a shared natural world, a threat to one is a threat to all.
- In this context, through its multi-dimensional, multi-cultural and global approach, the LiFE movement can play a pivotal role in not merely reversing the effects of climate change but, at a broader level, mainstream a harmonious and mindful way of living.
Conclusion
As the world moves in fits and starts towards its shared commitment to achieve ambitious climate goals, the time is ripe for India to lead the LiFE movement and mainstream it into the climate narrative.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rohingyas
Mains level: Global refugee crisis

In a major boost to India’s policy on the Rohingya, the MHA would shift Rohingya refugees to flats meant for EWS in Delhi.
Why in news?
- This is seen as a response to the fundamentalists who claims that the NRC, CAA are against any particular community.
- India respects & follows the UN Refugee Convention 1951 & provides refuge to all, regardless of their race, religion or creed.
Who are the Rohingyas?
- Rohingya, an ethnic group, mostly Muslim, hail from the Rakhine province of west Myanmar, and speak a Bengali dialect.
- They comprise one million out of the 53 million people that live in Myanmar, forming the world’s largest stateless population in a single country.
- Universally reviled by the country’s Buddhist majority, they have been oppressed by the government since the late 1970s when the government launched a campaign to identify ‘illegal immigrants’.
- Serious abuses were committed, forcing as many as 250,000 Rohingya refugees to flee to Bangladesh.
- The 1982 Citizenship Law in former Burma made the Rohingyas stateless people.
- They have often been called the most persecuted minority in the world.
- The 1.1 million Rohingya Muslims squeezed precariously into the northwest state of Rakhine, in mainly Buddhist Burma, bordering majority Muslim Bangladesh, are stateless and unwanted.
Why are they stateless?
- To qualify for citizenship, Rohingya applicants had to renounce their identity and accept being labelled as ‘Bengalis’ on all official documents.
- They also had to prove that they could trace the presence of their family in Rakhine back three generations.
- This is extremely difficult as many Rohingya lack documents or had lost them in 2012.
Why did the Crisis happen?
- Since World War II they have been treated increasingly by Burmese authorities as illegal, interloping Bengalis, facing apartheid-like conditions that deny them free movement or state education.
- The army “clearing operations” sparked the mass exodus of Rohingyas in both October 2016.
- In August 2017, were launched after insurgents known as the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA) attacked several paramilitary check posts.
- Rohingya activists claim the insurgents are mainly young men who have been pushed to breaking point by relentless oppression.
Security Implications
- The Rohingya issue and its spill over impact on Myanmar`s western peripheral region and security implications figured in the discussions is not clear.
- In all probability, the import of the ferment caused by the Rohingya migration, efforts of radical Islamists to influence some of the Rohingya youth, and the Pakistan attempts to capitalise on the situation.
- Rising anger in the Muslim world about the plight of the Rohingya has compounded fears of home-grown militancy as well as support from international jihadists.
- Illegal movement of people, combined with human trafficking and cross-border migration, can weaken Myanmar’s relations with its neighbour Bangladesh and its ASEAN partners.
Where do the Rohingya live in Delhi?
- The Rohingya live in hutments in the densely populated Kalindi Kunj and Madanpur Khadar areas in Delhi which are contiguous with Uttar Pradesh.
- Officially, about 1,200 Rohingya have been identified as among the first batch to have arrived in Delhi in 2012.
- After they protested outside the UNHCR (UN Refugee Agency) office in Delhi, they were provided with refugee cards.
Total Rohingyas in India
- In December 2017, the MHA informed Parliament that there are around 40,000 Rohingya in India, of which around 5,700 are in Jammu and also in Telangana, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi and Rajasthan.
- Of these, only 16,000 are said to be registered with the UN refugee agency.
- The MHA claimed that the exact number is not known as many of them enter the country.
How is the Delhi government involved?
- The Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO), responsible for tracking foreigners and their visas, has been requesting space at a new location for the Rohingya from the Delhi government since 2021.
- The FRRO is under the administrative control of the MHA.
When did the Rohingya come to Delhi?
- A/c to MHA, they first came to Delhi in 2012.
- They were forced to leave Myanmar in large numbers after several waves of violence, which first began in 2012.
- The Myanmar army revived the attacks in 2017 and lakhs took shelter in Bangladesh.
- Around five lakh Rohingya fled to Saudi Arabia in 2012.
What is the process of deportation?
- According to the MHA, illegal immigrants are detected, detained and deported under provisions of the Passport Act, 1920 or the Foreigners Act, 1946.
- Once a ‘foreigner’ has been apprehended by the police for staying illegally, without any document, he or she is produced before the local court.
- The powers to identify and deport them have also been delegated to State governments and UTs.
- If the accused is found guilty, they can be imprisoned for three months to eight years.
- After completing their sentence, the court orders deportation.
Have any Rohingya been deported?
- Any foreign nationals who enter into India without valid travel documents are treated as illegal immigrants.
- In 2018, seven Rohingya were deported to Myanmar.
- It was the first time that Myanmar issued a certificate of identity to the seven Rohingya. They had been picked up in Assam in 2012.
- Many Rohingyas have expressed their desire to return to their country and gave an undertaking that they were returning out of their free will.
India’s stance on Rohingyas
- Amid fears of fresh exodus of Rohingya from Myanmar, the MHA in 2017 cautioned all the States about infiltration from Rakhine State of Myanmar into Indian Territory.
- It cited the burden on the limited resources of the country that aggravates the security challenges especially in the North-East.
- It also said the rise in terrorism in the last few decades is a cause for concern in most nations and that illegal migrants are more vulnerable to getting recruited by terrorist organisations.
What is India’s stand on refugees?
- India is NOT a signatory to the 1951 UN Convention relating to the Status of Refugees and the 1967 Protocol.
- All foreign undocumented nationals are governed as per the provisions of:
- The Foreigners Act, 1946
- The Registration of Foreigners Act, 1939
- The Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920 and
- The Citizenship Act, 1955
Way forward: A humane approach is needed
- India must enact a National Asylum and Deportation Law. Since certain exoduses cannot be prevented due to international pressures.
- We need a proper framework to make sure that refugees can access basic public services, be able to legally seek jobs and livelihood opportunities for some source of income.
- The absence of such a framework will make the refugees vulnerable to exploitation, which is again detrimental to our own national security.
- Our judiciary has already shown the way forward on this: In 1996, the Supreme Court ruled that the state has to protect all human beings living in India, irrespective of nationality since they enjoy the rights guaranteed by Articles 14, 20, and 21 of the Constitution to all, not just Indian citizens.
- The enactment and enumeration of refugee rights will reduce our dependence on judge-centric approaches — or even worse, the whims of Home Ministry bureaucrats, police officers and politicians.
Try this
Q. In the absence of a uniform and comprehensive law to deal with asylum seekers, we lack a clear vision or policy on refugee management. In the context of this, examine the need for law to deal with asylum seeker and suggest the various aspects the law should cover.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Voter List
Mains level: Election reforms in Jammu and Kashmir
Kashmir Voters’ List Upgrade to include Non-Locals
Recently the J&K Chief Electoral Officer (CEO) announced that anyone “who is living ordinarily in J&K” can avail the opportunity to get enlisted as a voter in the Union Territory in accordance with the provisions of the Representation of the People Act.
Why in news?
- Many people who were not enlisted as voters in the erstwhile State of J&K are now eligible to vote after the reading down of Article 370 on August 5, 2019.
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) was expecting an addition of 20-25 lakh new voters in the final list in J&K.
- This has created furore among the out-streamed politicians of the erstwhile state.
What did the EC announce?
- There is no need to have a domicile certificate of J&K to become a voter.
- An employee, a student, a labourer or anyone from outside who is living ordinarily in J&K can enlist his or her name in the voting list.
- Around 25 lakh new voters are expected to be enrolled in J&K, which has 76 lakh voters on the list. The projected 18-plus population of J&K was around 98 lakh.
- After the abrogation of special provisions of Article 370, the Representation of the People Act 1950 and 1951 is applicable in J&K, which allows ordinarily residing persons to get registered in the electoral rolls of J&K.
New Voters in J&K
- Armed forces posted in J&K could also register as voters and could possibly participate in the first ever Assembly polls in the youngest Union Territory (UT) of the country.
- The existing electoral roll is being mapped into the newly delimited Assembly constituencies as per the Delimitation Commission’s final order made applicable by the Union Law Ministry.
Why are electoral rolls being revised?
- The ECI is working on fresh electoral rolls in J&K after the J&K Delimitation Commission carved out seven new Assembly constituencies in the UT earlier this year.
- The Delimitation Commission has re-drawn many constituencies and fresh electoral rolls are essential to prepare the ground for any announcement of elections in J&K.
- The last Assembly elections took place long back in 2014.
- In a latest move, the ECI has decided that it will also include any person who has attained the age of 18 years on or before October 1, 2022 in the fresh electoral rolls.
- The final electoral roll would be published in November.
Why such move?
- Prior to August 5, 2019 when J&K had special constitutional powers, the Assembly electoral rolls in the State were drawn up according to the separate J&K Representation of the People Act 1957.
- Therein only permanent residents of J&K were eligible to get registered in the Assembly rolls.
- To get voting rights, Permanent Resident Certificate and domicile certificates had to be shown.
- Several lakh residents from West Pakistan and Pakistan Occupied Kashmir, who had migrated to J&K and were living there for decades,
- They had no voting rights in Assembly elections till August 5, 2019 but were able to vote in the parliamentary elections.
Why has the ECI announcement caused a furore?
- All pseudo liberal and fundamentalist political parties in J&K have reacted sharply to the ECI announcement.
- J&K’s main regional parties also called Gupkar parties have expressed concerns that the move will open the floodgates and turn locals into an electoral minority.
- Separatists expressed concern that there was a plan to bring 25 lakh non-locals and make them eligible to cast their votes in the next J&K elections.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: FRT system
Mains level: Issues with FRT

A Right to Information (RTI) response revealed that the Delhi Police treats matches of above 80% similarity generated by its facial recognition technology (FRT) system as positive results.
Why in news?
- India has seen the rapid deployment of facial recognition technology (FRT) in recent years, both by the Union and State governments, without putting in place any law to regulate their use.
What is Facial Recognition Technology?
- Facial recognition is an algorithm-based technology that creates a digital map of the face by identifying and mapping an individual’s facial features, which it then matches against the database to which it has access.
- It can be used for two purposes:
(A) 1:1 verification of identity
- Here the facial map is obtained for the purpose of matching it against the person’s photograph on a database to authenticate their identity.
- Increasingly it is being used to provide access to any benefits or government schemes.
(B) One-to-many identification
- There is the one-to-many identification of identity wherein the facial map is obtained from a photograph or video and then matched against the entire database to identify the person in the photograph or video.
- Law enforcement agencies such as the Delhi Police usually procure FRT for 1:n identification.
- It generates a probability or a match score between the suspect who is to be identified and the available database of identified criminals.
- A list of possible matches are generated on the basis of their likelihood to be the correct match with corresponding match scores.
- However, ultimately it is a human analyst who selects the final probable match from the list of matches generated by FRT.
Why is the Delhi Police using facial recognition technology?
- The Delhi Police first obtained FRT for the purpose of tracing and identifying missing children.
- The procurement was authorised under the 2018 direction of the Delhi High Court in Sadhan Haldar vs. NCT of Delhi.
Issues with FRT use
- The use of FRT presents two issues:
- Issues related to misidentification due to inaccuracy of the technology and
- Issues related to mass surveillance due to misuse of the technology
- Extensive research into the technology has revealed that its accuracy rates fall starkly based on race and gender.
- This can result in a false positive rate, where a person is misidentified as someone else, or a false negative where a person is not verified as themselves.
- Cases of a false positive result can lead to bias against the individual who has been misidentified.
- On the other hand, cases of false negative results can lead to exclusion of the individual from accessing essential schemes. Ex. Failure of biometric based authentication under Aadhaar for an 90 YO person.
Authority to Delhi Police
- The Delhi Police is matching the photographs/videos against photographs collected under Section three and four of the Identification of Prisoners Act, 1920.
- This provision has now been replaced by the Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022.
- This Act allows for wider categories of data to be collected from a wider section of people, i.e., “convicts and other persons for the purposes of identification and investigation of criminal matters”.
Why discuss this?
- At present, India does NOT have a data protection law or a FRT specific regulation to protect against misuse.
- In such a legal vacuum, there are no safeguards to ensure that authorities use FRT only for the purposes that they have been authorised to, as is the case with the Delhi Police.
- FRT can enable the constant surveillance of an individual resulting in the violation of their fundamental right to privacy.
- Yet again the nation-security narrative comes into picture which cannot be ignored.
- It is feared that the Act will lead to overbroad collection of personal data in violation of internationally recognised best practices for the collection and processing of data.
- This revelation raises multiple concerns as the use of facial recognition can lead to wrongful arrests and mass surveillance resulting in privacy violations (if used for propaganda politics).
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: FTA
Mains level: India-UK FTA

India and the UK recently revived talks for a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) to encourage trade and investment. The FTA between India and UK is expected to be signed by October.
What is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA)?
- It is an agreement between two or more countries to minimize barriers to imports and exports of products and services among them.
- It includes reducing tariffs, quotas, subsidies or prohibitions which could limit exchange of goods and services across borders.
- The FTA might allow free trade among the two nations with a few exceptions.
- This involves a formal and mutual agreement signed between two or more countries.
- The agreement could be comprehensive and include goods, services, investment, intellectual property, competition, government procurement and other areas.
What is the status of the India-UK FTA?
- India and the United Kingdom have a multi-dimensional strategic partnership and are actively engaged in bilateral trade.
- The two countries agreed to begin formal negotiations for an FTA in January 2022, aiming to advance trade and investment relations between them.
- The fifth round of FTA talks concluded on 29 July, and the expectation is that negotiations would be completed and the stage set for the FTA by October.
- The FTA is important for both countries as it would provide a boost and create a robust framework of overall trade and investment between the two countries.
Which are the countries with which India has FTAs?
- As of April 2022, India had 13 FTAs, including the South Asian Free Trade Area, and with Nepal, Bhutan, Thailand, Singapore, Japan and Malaysia.
- The 13 also include the agreements with Mauritius, UAE and Australia signed during the last five years.
- Additionally, India has also signed six limited Preferential Trade Agreements.
What is the level of India-UK trade?
- Bilateral trade stands at $50 billion (ie approx. $35 billion in services and $15 billion in merchandise).
- India is UK’s 12th largest trading partner and accounts for 1.9% of UK’s total trade in four quarters to the end of 2022.
- UK is the seventh largest export destination for India.
- The trade balance maintained by India with UK has largely been a surplus.
- Top three services exported from India to UK are technical, trade-related and other business services, professional and management consulting services and travel.
How will an FTA with UK benefit India?
- Apart from reducing tariffs, the FTA also looks at lowering non-tariff barriers, particularly technical barriers to trade around rules of origin, investor protection and IPR.
- MoUs on joint recognition of certain educational qualifications and an outline pact on healthcare workforce have already been signed.
- Also, both UK and India have set up panels for a totalization deal being advocated by India and permitting Indian legal services for the UK.
Back2Basics: Types of Trade Agreements
(1) Free Trade Agreement – discussed above
(2) Preferential Trade Agreement
- In this type of agreement, two or more partners give preferential right of entry to certain products.
- This is done by reducing duties on an agreed number of tariff lines.
- Here a positive list is maintained i.e. the list of the products on which the two partners have agreed to provide preferential access.
- Tariff may even be reduced to zero for some products even in a PTA.
- India signed a PTA with Afghanistan.
(3) Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement
- Partnership agreement or cooperation agreement are more comprehensive than an FTA.
- CECA/CEPA also looks into the regulatory aspect of trade and encompasses and agreement covering the regulatory issues.
- CECA has the widest coverage. CEPA covers negotiation on the trade in services and investment, and other areas of economic partnership.
- It may even consider negotiation on areas such as trade facilitation and customs cooperation, competition, and IPR.
- India has signed CEPAs with South Korea and Japan.
(4) Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement
- CECA generally cover negotiation on trade tariff and Tariff rate quotas (TRQs) rates only.
- It is not as comprehensive as CEPA.
- India has signed CECA with Malaysia.
(5) Framework Agreement
- Framework agreement primarily defines the scope and provisions of orientation of the potential agreement between the trading partners.
- It provides for some new area of discussions and set the period for future liberalisation.
- India has previously signed framework agreements with the ASEAN, Japan etc.
(6) Early Harvest Scheme
- An Early Harvest Scheme (EHS) is a precursor to an FTA/CECA/CEPA between two trading partners. For example, early harvest scheme of RCEP has been rolled out.
- At this stage, the negotiating countries identify certain products for tariff liberalization pending the conclusion of actual FTA negotiations.
- An Early Harvest Scheme is thus a step towards enhanced engagement and confidence building.
Also read
[Sansad TV] Perspective: Free Trade Agreement
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now





 Context
Context  A systemic approach to reforming healthcare system in the country needs
A systemic approach to reforming healthcare system in the country needs Context
Context 


 Context
Context 

 Context
Context 

