Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Hijab Row

The Supreme Court has delivered a split verdict in the Karnataka hijab ban case with one of the two judges on the Bench upholding the March 15 order of the Karnataka HC validating the government’s ban, and the other set aside the HC ruling.
What lies next?
- With the divided bench, the matter has now been directed to be placed before Chief Justice of India (CJI).
What is a Split Verdict?
- A split verdict is passed when the Bench cannot decide one way or the other in a case, either by a unanimous decision or by a majority verdict.
- Split verdicts can only happen when the Bench has an even number of judges.
- This is why judges usually sit in Benches of odd numbers (three, five, seven, etc.) for important cases, even though two-judge Benches — known as Division Benches — are not uncommon.
After the verdict
- In case of a split verdict, the case is heard by a larger Bench.
- The larger Bench to which a split verdict goes can be a three-judge Bench of the High Court, or an appeal can be preferred before the Supreme Court.
- In the case of the hijab verdict, the CJI, who is the ‘master of the roster’, will constitute a new, larger Bench to hear the matter.
Earlier cases with a split verdict
- In May, a two-judge Bench of the Delhi HC delivered a split verdict in a batch of petitions challenging the exception provided to marital rape in the Indian Penal Code (IPC).
- Justice Rajiv Shakdher held that the exception under Section 375 (which deals with rape) of the IPC is unconstitutional, while Justice C Hari Shankar held that the provision is valid.
About the ‘split’ ruling
- While Justice Hemant Gupta dismissed the appeals challenging the Karnataka High Court order, Justice Sudhanshu Dhulia allowed them.
- In his judgment, Justice Dhulia referred to the Bijoe Emmanuel case, saying it “squarely covers the issue”.
What is the Bijoe Emmanuel verdict?
- The Bijoe Emmanuel case came before up a Bench comprising Justices O. Chinnappa Reddy and M M Dutt in 1986.
- The court granted protection to three children of the Jehovah’s Witness sect who did not join in singing the national anthem at their school.
- The court held that forcing the children to sing the national anthem violated their fundamental right to religion.
- V J Emmanuel, the father of the children pleaded with the court that for the Jehovah’s Witnesses, only Jehovah should be worshipped.
- Since the anthem is a prayer, the children would stand up in respect when it was playing. However, their faith did not allow them to sing it.
- The Supreme Court had said that while the Kerala HC had examined whether or not the national anthem contained any word or thought, which could offend anyone’s religious susceptibilities, it had misdirected itself as that was not the question at all.
Why the hijab case should be heard by a larger Bench?
First and foremost, the matter should be heard by a larger Bench preferably 5 judges as-
- It has to be decided whether the right to practice religion can intertwine with the right and autonomy of educational institutions to decide their uniform.
- While private institutions have the autonomy to decide on the uniform, the court needs to study and decide whether such issues should be looked at in a uniform manner.
- Considering the complexities of the matter which also involves several issues such as female dignity, freedom of expression, and the school’s right to decide on the uniform.
- A Constitution Bench would also have the right to re-examine the Emmanuel verdict which was delivered by a two-judge Bench.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Krishi Satellite Program
Mains level: Space applications for agriculture

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has proposed dedicated satellites for supporting the country’s agriculture sector.
Bharat Krishi Satellite Programme
- Minimum of two satellites are stipulated to guarantee adequate coverage of the entire agricultural area of the country.
- They will aid a gamut of farm-related activities related to crop forecasting, pesticide application, irrigation, soil data, and generation of critical data related to drought.
- The satellites will be owned by the Department of Agriculture and not by ISRO. The ISRO will provide the technical support.
- An ‘Earth Observation Council’ be created for addressing the current deficiencies in earth observation capabilities and data utilisation.
- Such a council can tackle shortcomings in this area in a centralised manner.
Why need such program?
Current deficiencies include:
- Discontinuity in earth observation missions
- Low utilisation of available remote sensing data
- Technology gaps and
- Absence of a streamlined mechanism for data processing and dissemination as required by the industry
Applications of space for agriculture

Satellites in use
| Satellite Type |
Satellite |
Objectives |
| Multispectral imaging satellite |
Resourcesat-2 & Resourcesat-2A |
Multispectral imaging for crop production forecast, land, water and natural resource inventory and management, and disaster management support |
| Cartography satellite |
Cartosat-1 |
High resolution cartographic mapping, digital elevation mapping – drainage and irrigation networks, topographic mapping and contouring |
| Radar imaging |
RISAT-1 |
All weather imaging capability targeted for kharif crop (June to November) during south-west and north-east monsoon seasons. Flood and natural disaster management |
| Meteorological forecasting |
Kalpana-1 |
Comprehensive weather status reporting and forecasting |
| Meteorological observation |
INSAT-3D & INSAT-3DR |
Improved meteorological observations including vertical – temperature and humidity–atmosphere weather forecasting and disaster warning |
Issues in harmonizing space technology
- India’s satellite data is sequestered within the government.
- The private sector has limited access to it, even though it plays an increasing role in the country’s agriculture value chain.
Various govt programs
- Following are some of the programs that are functioning in full spirit-
- In 2017, these insular projects were integrated into a single entity, the National Programme on use of Space Technology for Agriculture (NPSTA).
| NPSTA Constituent Programmes |
Goals of the constituent Programme |
| National Programme on use of Space Technology for Agriculture (NPSTA) |
Forecasting Agricultural output using Space, Agro-meteorology and Land-based observations (FASAL) |
Crop Forecasting |
| National Agricultural Drought Assessment and Monitoring Systems (NADAMS) |
Drought Assessment |
| Coordinated programme on Horticulture Assessment and Management using Geoinformatics (CHAMAN) |
Horticulture assessment and development |
| C(K)rop Insurance using Space technology and Geoinformatics (KISAN) now incorporated into Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojna |
Crop Insurance |
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GHGs relased by Stubble Burning
Mains level: Delhi Air Pollution issue

To prevent stubble burning, the Union Environment Ministry announced a ₹50 crore scheme on to incentivise industrialists and entrepreneurs to set up paddy straw pelletization and torrefaction plants.
What is Stubble Burning?
- Stubble (parali) burning is a method of removing paddy crop residues from the field to sow wheat from the last week of September to November.
- It is usually required in areas that use the combined harvesting method which leaves crop residue behind.
- This practice mostly carried out in Punjab, Haryana and UP contributes solely to the grave winter pollution in the national capital.
Emissions from stubble burning
- The process of burning farm residue is one of the major causes of air pollution in parts of north India, deteriorating the air quality.
- Stubble burning is a significant source of carbon dioxide (CO2), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides (NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC).
Despite emissions, why do farmers burn stubble?
- Crop residue burning is practised by the farmers to prepare the land for the next cultivation.
- The major reason behind the stubble burning is the short time available between rice harvesting and sowing of wheat as delay in sowing wheat affects the wheat crop.
- Between the harvesting of the paddy crop and the sowing of the next crop, there is only a two to three weeks’ time window is left.
- Even though farmers are aware that the burning of straw is harmful to health, they do not have alternatives for utilizing them effectively.
- The farmers are ill-equipped to deal with waste because they cannot afford the new technology that is available to handle the waste material.
- Therefore, stubble burning is considered one of the cheapest methods to clean the field after the harvesting season.
Impact of stubble burning
- Air Pollution: Stubble burning emits toxic pollutants in the atmosphere containing harmful gases like Carbon Monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, volatile organic compounds (VOC). These pollutants disperse in the surroundings and eventually affect air quality and people’s health by forming a thick blanket of smog. Along with vehicular emissions, it affects the Air Quality Index (AQI) in the national capital and NCR.
- Soil degradation: Soil becomes less fertile and its nutrients are destroyed when the husk is burned on the ground. Organic content of soil is completely destroyed. Stubble burning generates heat that penetrates into the soil, causing an increase in erosion, loss of useful microbes and moisture.
Alternative solutions
- Power generation: The available paddy straw can be effectively used for power generation, which will go a long way towards overcoming the problem of disposal of crop residues and power deficit in the region.
- In-situ decomposition: Suitable machinery for collection, chopping and in situ incorporation of straw is required. We can use Pusa Biodecomposer, Biomethanation etc.
- Organic manuring: Convert the removed residues into enriched organic manure through composting.
Conclusion
- Unless financial assistance is to be provided by the Centre for boosting farm mechanization, it is difficult to completely stop stubble burning.
- States need to make alternative arrangements for the consumption of paddy straw into the soil as per the directions of the NGT.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NGLV, PSLV, SSLV, GSLV
Mains level: Not Much
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is developing a Next-Gen Launch Vehicle (NGLV), which will one day replace operational systems like the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
What is the news?
- PSLV, often dubbed the ‘trusted workhorse’, “will have to retire” one day, said ISRO chairman.
What is NGLV?
- NGLV will feature a simple, robust design that allows bulk manufacturing, modularity in systems, sub-systems and stages and minimal turnaround time.
- Potential uses will be in the areas of launching communication satellites, deep space missions, future human spaceflight and cargo missions.
What all modifications would be required?
- In NGLV, ISRO is understood to be looking at a cost-efficient, three-stage, reusable heavy-lift vehicle with a payload capability of 10 tonnes to Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- NGLV will feature semi-cryogenic propulsion for the booster stages which is cheaper and efficient.
- For that, at least 10 tonne capability to GTO is needed.
- Correspondingly, the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) capability will be twice that.
- However, payload capability will be lower when the rocket is reusable.
Back2Basics: Various satellite launch vehicles in India

UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rythu Bharosa
Mains level: Read the attached story

Ethiopian Agricultural Minister is in Andhra Pradesh (AP) to study the first-of-its-kind Rythu Bharosa Kendras (RBKs).
What are Rythu Bharosa Kendras?
- Set up for the first time in the country, the RBKs are unique seeds-to-sales, single-window service centres for farmers that have been set up across the state.
- They are a one-stop solution to all farmers’ needs and grievances. RBKs sell pre-tested quality seeds, certified fertilisers and animal feed.
- Farmers can purchase or hire farm equipment, and even sell their produce at the prevailing MSP in the RBKs.
- The RBKs provide services like soil testing and make recommendations — on which crops to sow, and quantity and type of fertiliser to be used.
- The state government also pays crop insurance, procures grains and makes payments to farmers through the RBKs.
Have the RBKs proved to be helpful to farmers?
- RBKs facilitate interaction between farmers, agriculture scientists, and agriculture extension officers right at the village level.
- Apart from providing services and items for sale, RBK officials demonstrate new farm equipment and provide training to farmers.
- Based on inputs provided by officials after soil testing and weather conditions, many farmers have changed their cropping patterns and benefited immensely.
- The RBKs have been responsible for elimination of spurious seeds and uncertified and dangerous fertilisers, which can cause crop damage and failures.
- The RBKs, staffed by agriculture and horticulture graduates, help farmers decide the crops they should cultivate in a scientific manner.
How has it been received by the Centre?
- The Centre has recently nominated the RBK concept for the Food and Agriculture Organisation’s “Champion’’ award.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Official language , Eight schedule
Mains level: Read the attached story
The 11th volume of the Report of the Official Language Committee headed by Home Minister submitted to President has triggered angry reactions from the CMs of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, who have described the Report as an attempt to impose Hindi on non-Hindi-speaking states.
About the Official Language Panel (for Hindi)
- The Committee of Parliament on Official Language was set up in 1976 under Section 4 of The Official Languages Act, 1963.
- Section 4 of the Act says there shall be constituted a Committee on Official language, on a resolution to that effect being moved in either House of Parliament.
- It should have the previous sanction of the President and passed by both Houses.
Terms of reference of the committee
- The Committee is chaired by the Union Home Minister, and has, in accordance with the provisions of the 1963 Act, 30 members — 20 MPs from Lok Sabha and 10 MPs from Rajya Sabha.
- The job of the Committee is to review the progress made in the use of Hindi for official purposes, and to make recommendations to increase the use of Hindi in official communications.
History of its establishment
- With the active promotion of Hindi being mandated by Article 351 of the Constitution, the Official Language Committee was set up to review and promote the use of Hindi in official communications.
- The first Report of the Committee was submitted in 1987.
Issues with the committee
- The name of the Committee is a little misleading.
- This is because unlike the other Parliamentary panels, the Committee on Official Language is constituted by the Home Ministry.
- It does not submit its report to Parliament like other Committees of Parliament.
- The contents of the report submitted are not in the public domain.
- The panel has the largest representation from the ruling majority party. This has made states more furious.
What has the Shah panel recommended in its latest (2021) report?
- Medium of instruction: The panel has made around 100 recommendations, including that Hindi should be the medium of instruction in IITs, IIMs, and central universities in the Hindi-speaking states.
- Administrative communication: The language used for communication in the administration should be Hindi, and efforts should be made to teach the curriculum in Hindi, but the latter is not mandatory.
- Hindi translation of HC verdicts: High Courts in other states, where proceedings are recorded in English or a regional language can make available translations in Hindi, because verdicts of High Court of other states are often cited in judgments.
- Mandate for govt. officials: The panel wants state governments to warn officials that their reluctance to use Hindi would reflect in their Annual Performance Assessment Report (APAR).
Why are these recommendations under criticism?
The crux of the recommendations is being ‘perceived’ that-
- There is a deliberate attempt to reduce the usage of the English language in official communication and to increase the usage of Hindi.
- Knowledge of Hindi would be compulsory in a number of government jobs.
Is this the first time that such recommendations have been made?
- The makers of the Constitution had decided that both Hindi and English should be used as official languages for the first 15 years of the Republic.
- But in the wake of intense anti-Hindi agitations in the south, the Centre announced that English would continue to be used even after 1965.
- On January 18, 1968, Parliament passed the Official Language Resolution to build a comprehensive program to increase the use of Hindi for official purposes by the Union of India.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Equitable delivery

Context
- 15th Finance commission on horizontal devolution agreed that the Census 2011 population data better represents the present need of States, to be fair to, as well as reward, the States which have done better on the demographic front, Finance commission has assigned a 12.5 per cent weight to the demographic performance criterion. Population, area, forest and ecology, demographic performance, tax efforts, income and distance are the criteria for horizontal distribution of funds.
Why equitable delivery is necessary in the country?
- To fulfil the need of basket of Goods: There is a basket of goods and services that should be delivered by the State. It is best not to call them public goods, since “public goods” have a specific meaning for economists and this basket has items that are typically collective private goods.
- To achieve Aantodaya approach (last person): Curlew Island is in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Until the 2011 Census, it had a population of two. Pulomilo Island, also in Andaman and Nicobar, had a population of 20 in 2011. At the time of elections, we read of astounding attempts made, so that voters in remote locations can vote. No one should be disenfranchised because of remoteness of location. By the same token, a resident, regardless of location, must be entitled to that basket.
- To achieve poverty alleviation: The quality of public services affects economic growth via its impact on poverty alleviation, human capital formation and corruption.

- High cost of delivery: States can have differential sources of revenue. Alternatively, the cost of delivering that basket may vary across geographical zones.
- Problems associated with migration: Over time, villages of course get depopulated. They are reclassified, get absorbed into larger agglomerations, or disappear because of migration.

How equitable delivery can be achieved?
- State need to take honest responsibility: The State cannot abdicate its responsibility of providing the basket.
- Economic compulsion: Migration is a voluntary decision, often driven by the pull (and push) of economic forces. That voluntary decision cannot be replaced by fiat.
- Dividing the pool between the governments: The Union Finance Commission has a vertical task, dividing the divisible pool between the Union government and states.
- Adjusting to the criteria set by FC: It also has a horizontal task, dividing State share between different states. Accordingly, from the 1st to the 15th, Finance commission have adopted different formulae, with an attempt to also create incentives, by attaching weights to fiscal efficiency and even demographic performance.
- This leaves variables like population, geographical area, income distance, infrastructure distance and forest cover:
- expenditure equalisation based on needs/costs of public services;
- Revenue equalisation measured by the ability of the state to raise revenue from one or more sources; and
- Macro indicators covering broader economic or non-economic indicators that approximate fiscal capacity, where data constraints make it difficult to apply the other approaches.
- Addressing Geographic area and population: Needs/costs are sought to be measured through geographical area and population. All Finance Commissions have used area as another criterion in the devolution formula on the ground of need — the larger the area, greater is the expenditure requirement for providing comparable services.
Conclusion
- Equitable access to public goods and services in low income and inequal (economic inequality) country like India is cumbersome task. Finance commission is trying their best for equitable allocation of resources.
Mains Question
Q. How Equity is different from equality? What is the finance commission’s criteria for horizontal allocation of resources among the states ?
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Central Information Commission
Mains level: RTI Act,amendments,pending complaints ,Delay in the process, Credibility of the CIC

Context
- The number of information officers and first appellate authorities in the Central government has remained stagnant in the last few years. In contrast, the new Right to Information (RTI) applications filed as well as pending applications are increasing every year. Worryingly, the Central Information Commission and State Information Commissions, the final recourse in matters concerning RTI, also face manpower shortage. As a result, appeals and complaints are piling up.
- RTI is an act of the parliament that sets out the rules and procedures regarding citizens’ right to information.It replaced the former Freedom of Information Act, 2002.
- Time bound response: Under the provisions of RTI Act, any citizen of India may request information from a “public authority” (a body of Government or “instrumentality of State”) which is required to reply expeditiously or within 30.
- Immediate Information in an urgent petition: In case of a matter involving a petitioner’s life and liberty, the information has to be provided within 48 hours.
- Digitization of records: The Act also requires every public authority to computerize their records for wide dissemination and to proactively publish certain categories of information so that the citizens need minimum recourse to request for information formally.

Implementation of RTI
- The RTI Act is implemented using a three-level structure.
- Public Information Officer: At the first level is the Central Assistant Public Information Officer/Central Public Information Officer (CAPIO/CPIO). Once an RTI query reaches the CAPIO/CPIO, they are expected to reply within 30 days.
- First Appellate Authority (FAA): If the reply is not satisfactory or does not arrive on time, a first appeal can be made to the First Appellate Authority (FAA).
- Central Information and State Information Commissions: If the FAA does not answer or if its answer is not satisfactory, the Central Information and State Information Commissions can be approached.
What are the vacancy related issues?
- Low Performance of Information Commissions: A report released in October by the Satark Nagrik Sangathan, titled ‘Report Card on the Performance of Information Commissions in India,2021-22’,states that the number of appeals and complaints pending before the Central and State Information Commissions as of June 30, 2022 was 3,14,323. The figure is based on data gathered from 26 Information Commissions obtained through 145 RTI applications.
- Increase in the pending appeals: There is an Increase in the number of pending appeals and complaints from 2.18 lakh to3.14 lakh in the last three years.
- Leading states in pending complaints: Maharashtra tops the list with nearly 1 lakh appeals and complaints pending followed by Uttar Pradesh (44,482) and Karnataka (30,358). Data were not available for Tamil Nadu State Information Commission. The Commissions in Jharkhand and Tripura were defunct.
- Substantial delay in reply: The Sangathan assumed that appeals and complaints would be disposed of in a chronological order. It would take the West Bengal State Information Commission 24 years and 3 months to dispose of a complaint filed on July 1, 2022. A similar analysis in Odisha and Maharashtra showed that it would take five years. Only Meghalaya and Mizoram showed no waiting time(not plotted on the tree map).

What is the recent amendment?
- Parity with CEC broken: So far, the CIC received the same salary and perks as that of the Chief Election Commissioner or a judge of the Supreme Court.
- Now on par with Cabinet Secretary: The new rules make the CIC an equivalent of the cabinet secretary and central information commissioners the same as secretary to the government in terms of salary. In the states, the downgrading will be to the level of a secretary to the government, and additional secretary respectively.
- Tenure: The tenure has been reduced from 5 years to 3.
- Power of ICs undermined: The CICs and ICs at both the Centre and the states have the power to review the functioning of government public information officials, and intervene on behalf of citizens seeking information about decisions of the government. This stands undermined.
- Lack of enforcing powers: these officials have zero powers to enforce their orders, except the imposition of a fine for non-compliance.
- Authority exercised: Over the years, government departments coughed out information because they were seen in the same league and of the same authority as the CEC and Supreme Court judges.

Conclusion
- The RTI has unquestionably proved to be one of the significant milestones and a major step towards ensuring the participatory and transparent development process in the country. Dilution of RTI is like downgrading the participation of citizens in public affairs. Government should strengthen the RTI instead of weakening.
Mains Question
Q. Discuss the dilution of RTI through 2019 amendments. How vacancies affect the time bound replies under the RTI Act 2005?
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Appointment of Judges
Mains level: NJAC,Collegium system and related issues.

Context
- Once again, the Collegium of the Supreme Court of India is in the news, and once again for the wrong reasons. This time, it is because of the difficulty hat its five judges have in getting together for one meeting. Justice Chandrachud and Justice Nazeer withhold approval.Apparently, they do not object to the names but object to the procedure of circulation.
What is Collegium system?
- The Collegium of judges is the Indian Supreme Court’s invention.
- It does not figure in the Constitution, which says judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts are appointed by the President and speaks of a process of consultation.
- In effect, it is a system under which judges are appointed by an institution comprising judges.
-
After some judges were superseded in the appointment of the CJI in the 1970s, and attempts made subsequently to affect a mass transfer of High Court judges across the country.

What was the perception around Independence of judiciary under threat?
- There was a perception that the independence of the judiciary was under threat. This resulted in a series of cases over the years.
- First Judges Case (1981): SC ruled that the “consultation” with the CJI in the matter of appointments must be full and effective. However, it rejected the idea that the CJI’s opinion, albeit carrying great weight, should have primacy.
- Second Judges Case (1993): Introduced the Collegium system, holding that “consultation” really meant “concurrence”. It added that it was not the CJI’s individual opinion, but an institutional opinion formed in consultation with the two senior-most judges in the Supreme Court.
- Third Judges Case (1998): On a Presidential Reference for its opinion, the Supreme Court, in the Third Judges Case (1998) expanded the Collegium to a five-member body, comprising the CJI and four of his senior-most colleagues.
- Emphasis on Seniority principle: Collegium system emphasizes excessively on seniority.
- No discussion on merit and objectivity: However, following the seniority convention offers a semblance of certainty and transparency, even though it takes away from selecting judges on other objective criteria such as merit and competence.
- Collegium changes its own decision: At times, the sanctity of Collegium’s own decisions no longer stands. Its own previous decision to appoint other persons to the Supreme Court was reversed, without any explanation or justification.
- Lack of procedure: Besides this, no one knows how judges are selected, and the appointments made reek of biases of self-selection and in-breeding.
- Widely known Nepotism: Sons and nephews of previous judges or senior lawyers tend to be popular choices for judicial roles.
- Lack of checks and balances: With its ad hoc informal consultations with other judges, which do not significantly investigate criteria such as work, standing integrity and so on, the Collegium remains outside the sphere of legitimate checks and balances.
- Opaque system: The lack of a written manual for functioning, the absence of selection criteria, the arbitrary reversal of decisions already taken, the selective publication of records of meetings.

Collegium system is blessing in disguise
- Protect independence of judiciary: The framers of the Constitution were alive to the likely erosion of judicial independence.
- On May 23, 1949, K T Shah stated that the Judiciary, which is the main bulwark of civil liberties, should be completely separate from and independent of the Executive, whether by direct or by indirect influence.
- NJAC Declared unconstitutional: In 2016, the Supreme Court struck down a constitutional amendment for creating the National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC).
- Distrust on political executive: The SC strongly disapproved of any role for the political executive in the final selection and appointment of judges. The SC said that “reciprocity and feelings of payback to the political executive” would be disastrous to the independence of the judiciary.
What is National Judicial Appointment Commission (NJAC)?
- What is NJAC?
- guarantee the independence of the system from inappropriate politicisation,
- Strengthen the quality of appointments,
- Enhances the fairness of the selection process,
- Promotes diversity in the composition of the judiciary, and
- Rebuilds public confidence in the system.
- NJAC was missed opportunity of reforms: The SC in its majority decision declared the NJAC unconstitutional and missed an opportunity to introduce important reformatory changes in the functioning of the judiciary.
- Judicial majority could have been discussed: According to the experts, the Supreme Court could have read down the law, and reorganised the NJAC to ensure that the judiciary retained majority control in its decisions. However, it did not amend the NJAC Act to have safeguards that would have made it constitutionally valid.
- No reforms in the collegium system: It also did not reform the Collegium in any way to address the various concerns voiced by one and all, including the Court itself, Instead, to the disappointment of all those who hoped for a strong, independent and transparent judiciary, it reverted to the old Collegium based appointments mechanism.

Conclusion
- Appointments to the top court seem to be the preserve of judges from the High Court with a handful of appointments from the Bar. Surely some nodding acknowledgement should be given to a specific provision made by the founding fathers in the Constitution. Judges appointing the judges is not a sustainable practice for future of judiciary.
Mains Question
Q.What is NJAC? Why Collegium system is blessings in disguise? Explain the Collegium system of appointments.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Article 66A
Mains level: Read the attached story

The Supreme Court has ordered States and their police forces to stop prosecuting free speech on social media under Section 66A of the Information Technology Act which was declared unconstitutional by the court in a judgment seven years ago.
What did Section 66A do?
- Introduced in 2008, the amendment to the IT Act, 2000, gave the government power to arrest and imprison an individual for allegedly “offensive and menacing” online posts, and was passed without discussion in Parliament.
- Section 66A empowered police to make arrests over what policemen, in terms of their subjective discretion, could construe as “offensive” or “menacing” or for the purposes of causing annoyance, inconvenience, etc.
- It prescribed the punishment for sending messages through a computer or any other communication device like a mobile phone or a tablet, and a conviction could fetch a maximum of three years in jail.
- In 2015, the apex court struck down the law in the landmark case Shreya Singhal v. Union of India, calling it “open-ended and unconstitutionally vague”, and thus expanded the contours of free speech to the Internet.
Why was the law criticized?
- The problem was with the vagueness about what is “offensive”.
- The word having a very wide connotation was open to distinctive, varied interpretations.
- It was seen as subjective, and what might have been innocuous for one person, could lead to a complaint from someone else and, consequently, an arrest arbitrarily.
So, how did 66A come under the Supreme Court’s scrutiny?
- The first petition came up in the court following the arrest of two girls in Maharashtra by Thane Police in November 2012 over a Facebook post.
- The girls had made comments on the shutdown of Mumbai for the funeral of a political leader.
- The arrests triggered outrage from all quarters over the manner in which the cyber law was used.
- The petition was filed by Shreya Singhal, then a 21-year-old law student.
What were the grounds for the challenge?
- The objective behind the 2008 amendment was to prevent the misuse of information technology, particularly through social media.
- The petitioners argued that Section 66A came with extremely wide parameters, which allowed whimsical interpretations by law enforcement agencies.
- Most of the terms used in the section had not been specifically defined under the Act.
- The law was a potential tool to gag legitimate free speech online and to curtail freedom of speech and expression guaranteed under the Constitution, going far beyond the ambit of “reasonable restrictions” on that freedom.
What did the Supreme Court decide?
- In March 2015, a bench of Justices J. Chelameswar and R.F. Nariman ruled in Shreya Singhal v. Union of India declared Section 66A unconstitutional for “being violative of Article 19(1)(a) and not saved under Article 19(2).”
- Article 19(1)(a) gives people the right to speech and expression whereas 19(2) accords the state the power to impose “reasonable restrictions” on the exercise of this right.
- The decision was considered a landmark judicial pushback against state encroachment on the freedom of speech and expression.
- The bench also read down Section 79– now at the centre of the ongoing “intermediary liability” battle between the Centre and micro-blogging platform Twitter– defining key rules for the relationship between governments and commercial internet platforms.
- Section 79 says that any intermediary shall not be held legally or otherwise liable for any third party information, data, or communication link made available or hosted on its platform.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Flex Fuel
Mains level: Ethanol blended petrol (EBP) Program

The auto sector is testing many new technologies to reduce carbon emissions. Flex fuel is one technology that has gained currency.
What are Flex Fuel Vehicles?
- Like traditional vehicles, flex fuel vehicles have an internal combustion engine, but instead of regular petrol, it can run on blended fuel—petrol with ethanol or methanol.
- The ethanol mix can vary between 20% and 85%.
- The vehicle has additional sensors and different programming of the engine control module to assess the blend of the fuel and adjust accordingly.
- Unlike electric hybrid vehicles, no bulky parts need to be added to the basic gasoline vehicle architecture.
- Upgrading existing vehicles to run on high blend of ethanol fuel, however, is possible but expensive and not considered feasible.
Are they better than traditional vehicles?
- Flex fuel vehicles are seen as a one-shot solution for multiple problems—pollution, oil import bill and glut in sugar production.
- According to the US department of energy, they have lower overall greenhouse gas emissions, between 40-108%, depending on the feedstock used to produce them.
- It could also help bring down India’s crude oil import bill.
- Further, India also suffers from a glut in sugar production of 6 million tonnes and in sugar season 2020-21, about 2.4 million tonne was diverted to produce 302 litres of ethanol for blending.
- India has set a target of 20% blending rate for 2025.
Is there a catch in flex-fuel technology?
- There is unlikely to be any direct benefit to the consumer.
- Though ethanol costs much lower than petrol at ₹47-64/ltr depending on the sugarcane source, oil marketing companies are expected to pocket the cost differential.
- It is also controlled by the government. So, chances of frequent revision are high.
- On the contrary, the fuel economy is likely to fall by 4-8%.
What are the challenges?

- For mass adoption, an adequate supply of different types of ethanol blends is needed across the country.
- This would have to be in addition to the existing network as current vehicles on the road would have to be supplied with fuel that has only 10% ethanol blending.
- This means significant investment in infra by oil firms.
- At the same time, a constant supply of ethanol would have to be ensured.
- Since this largely comes from sugarcane in India, which is a water-guzzling crop, any drought could have an impact on blending rates.
How do they fit in with carbon neutrality?
- With electrification already on the horizon, flex fuel vehicles are seen as a stop-gap arrangement.
- The benefit for the environment is less as compared to battery EVs or hydrogen fuel cell vehicles of the future.
- With much lower cost of running, they also offer better economy for consumers.
- The Toyota pilot project notwithstanding, there is also resistance from the industry.
- They want to prioritize investments and not get stretched thin between hybrid and battery electric, fuel cell and flex fuel technologies.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Jaiprakash Narayan-JP
Mains level: Not Much
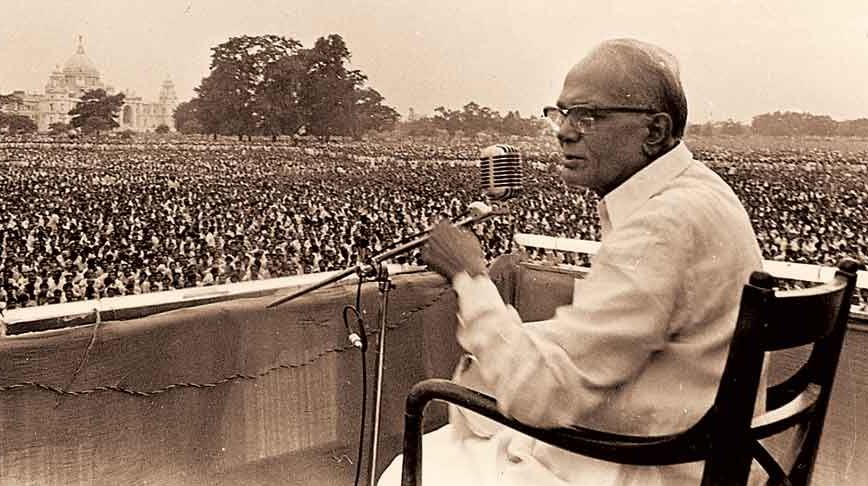

Union Home Minister unveiled a 15-foot statue of Jayaprakash Narayan or JP on his 120th birth anniversary at the socialist icon’s birthplace, Sitab Diara village in Bihar’s Saran district.
Who was Jayaprakash Narayan?
- JP was born in 1902 in Bihar’s Sitab Diara, a village prone to frequent-flooding, after which his family moved to a village in Uttar Pradesh’s Balia district.
- He quit college to join the non-cooperation movement, before going to study at the University of California, Berkeley, where he was influenced by the ideas of Karl Marx.
Political affiliations
- JP returned to India in 1929 and joined the freedom struggle and the Indian National Congress, upon the invitation of Jawaharlal Nehru and drawn by a speech by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad.
- He went on to become the founding members of the Congress Socialist Party (CSP).
- However after independence took it out of the Congress and formed the Socialist Party, which was merged with J B Kripalani’s Kisan Mazdoor Praja Party to form the Praja Socialist Party.
Dissociation from active politics
- While Nehru was keen on JP joining the Union government, JP sought to distance himself from electoral politics, opting to focus on social causes instead.
- He was disillusioned with political parties and called for communitarian democracy.
- Parties, he believed, were centralized and susceptible to moral and financial corruption.
The JP movement
- Students in Gujarat began demonstrating in late 1973, in response to mounting mess bills.
- The protests became widespread in the state, with workers, teachers and several other groups joining in the movement, calling for a change in government.
- JP saw the youth of Gujarat that had been able to bring about political change as an alternative route from electoral.
- The protests against corruption grew widespread, and students of Bihar began their movement in March 1974.
- The students approached JP, who left his self-imposed political exile and led the movement. At a rally in Patna he called for Sampoorna Kranti (Total Revolution).
Opposition to the Emergency
- When Indira Gandhi imposed an Emergency on June 25, 1975, JP shifted his focus to opposing the authoritarian rule and opposition parties looked to him for leadership.
- The Socialists were naturally drawn to him ideologically, while the RSS and its political front the Jana Sangh sought to return to the mainstream, and were happy to be dissolved into the Janata Party that JP had formed.
- JP is celebrated for launching a popular, mass movement against the Indira Gandhi government, which led to the formation of the Janata Party government in the 1977 general election.
- This was the first non-Congress government in the country.
Try this PYQ:
Who among the following were the founders of the “Hind Mazdoor Sabha” established in 1948?
(a) B. Krishna Pillai, E.M.S. Namboodiripad and K.C. George
(b) Jayaprakash Narayan, Deen Dayal Upadhyay and M.N. Roy
(c) C.P. Ramaswamy Iyer, K. Kamaraj and Veeresalingam Pantulu
(d) Ashok Mehata, T.S. Ramanujan and G.G. Mehta
Post your answers here.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sloth Bear
Mains level: NA

The first World Sloth Bear Day was observed yesterday to generate awareness and strengthen conservation efforts around the unique bear species endemic to the Indian subcontinent.
Sloth Bear
- The sloth bear (Melursus ursinus) is an important species and endemic to the Indian subcontinent with small populations in Nepal and Sri Lanka.
- Classified as “vulnerable” on the IUCN Red List, sloth bears are endemic to the Indian sub-continent and 90% of the species population is found in India.
- Listed under Schedule I of the (Wildlife Protection) Act of India, 1972, the species has the same level of protection as tigers, rhinos and elephants.
- Commercial international trade of the sloth bear (including parts and derivatives) is prohibited as it is listed in Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES).
- The sloth bears are omnivorous and survived on termites, ants and fruits.
Why protect sloth bears?
- For a long time, sloth bears were exploited as dancing bears. Though the practice has been banned there are still a few cases of rescue.
- Sloth bears are one of the most aggressive extant due to large human populations often closely surrounding reserves that hold bears.
- Aggressive encounters and attacks are relatively frequent, though in some places, attacks appear to be a reaction to encountering people accidentally.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Right to Information
Mains level: Read the attached story

A good 17 years after India got the Right to Information (RTI) Act, the transparency regime in the country remains a mirage with nearly 3.15 lakh complaints and appeals pending with 26 information commissions across India.
RTI Pendency in India
- According to a report by Satark Nagrik Sangathan, the backlog of appeals or complaints is increasing in commissions every year.
- The number of appeals and complaints pending in 2021 was 2,86,325 with data from 26 commissions and in 2022, it was 3,14,323.
- The highest number of pending cases was in Maharashtra at 99,722, followed by UP at 44,482, Karnataka at 30,358, the Central Information Commission at 26,724 and Bihar at 21,346.
What is the Right to Information?
- RTI is an act of the parliament that sets out the rules and procedures regarding citizens’ right to information.
- It replaced the former Freedom of Information Act, 2002.
- Under the provisions of RTI Act, any citizen of India may request information from a “public authority” (a body of Government or “instrumentality of State”) which is required to reply expeditiously or within 30.
- In case of a matter involving a petitioner’s life and liberty, the information has to be provided within 48 hours.
- The Act also requires every public authority to computerize their records for wide dissemination and to proactively publish certain categories of information so that the citizens need minimum recourse to request for information formally.
What led to the introduction of RTI in India?
There has been a variety of internal and external pressures on governments to adopt RTI.
- Corruption and scandals: The crisis was brought into force due to a lack of transparency in the working of the government.
- Modernization and the Information Society: The expansion of the Internet into everyday life has increased the demand for more information by the public, businesses and civil society groups.
- International pressure: The World Bank, the IMF and others have pressed countries to adopt laws to reduce corruption and to make financial systems more accountable.
- Wider recognition of Public Interest: Public interest is a nebulous concept, not defined in any freedom of information laws, understandably so, as it is a very subjective concept.
Governing of the RTI
The Right to information in India is governed by two major bodies:
- Central Information Commission (CIC) – Chief Information commissioner who heads all the central departments and ministries- with their own public information officers (PIO)s. CICs are directly under the President of India.
- State Information Commissions (SIC)– State Public Information Officers or SPIOs head over all the state department and ministries. The SPIO office is directly under the corresponding State Governor.
State and CIC are independent bodies and CIC has no jurisdiction over the SIC.
(1) Central Information Commission
- The Commission consists of a Chief Information Commissioner and not more than ten Information Commissioners.
- At present (2019), the Commission has six Information Commissioners apart from the Chief Information Commissioner.
- They are appointed by the President on the recommendation of a committee consisting of the PM as Chairperson, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and a Union Cabinet Minister nominated by the PM.
- The CIC/IC shall hold office for such term as prescribed by the Central Government or until they attain the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier. They are not eligible for reappointment.
Power and functions
- It is the duty of the Commission to receive and inquire into a complaint from any person regarding information request under RTI, 2005.
- The Commission can order an inquiry into any matter if there are reasonable grounds (suo-moto power).
- While inquiring, the Commission has the powers of a civil court in respect of summoning, requiring documents etc.
(2) State Information Commission
- The Commission consists of a State Chief Information Commissioner and ten State Information Commissioners.
- They are appointed by the Governor on the recommendation of the committee consisting of the CM as Chairperson, the Leader of the Opposition in the Legislative Assembly and a state Cabinet Minister nominated by the CM.
- They should be a person of eminence in public life and should not hold any other office of profit or connected with any political party or carrying on any business or pursuing any profession.
- Terms of service are similar to that of CIC.
Constitutional backing of the RTI
- The Indian constitution has an impressive array of basic and inalienable rights termed as fundamental rights contained in part-III.
- These include the right to equal protection of the laws and the right to equality before the law, the right to freedom of speech and expression also the right to life and personal liberty.
- Since RTI, is implicit in the Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression under Article 19 of the Indian Constitution, it is an implied FR.
- These are backed by the right to constitutional remedies that is, the right to approach the supreme court and high court under Article 32 and 226 respectively in case of infringement of any of FRs.
- The state is not only under an obligation to respect the FRs of the citizens but also equally under an obligation to ensure conditions under which the right can be exercised.
- The objective of the right to information act is to protect these constitutional rights.
Benefits of RTI
- Greater accessibility of information: A person can seek information from any public authority in the form of copies, floppy disks, sample material etc under RTI.
- Efficient governance: RTI Act helps us in knowing the efficiency of the government functioning.RTI has become a reality consistent with the objectives of having a stable, honest, transparent and efficient government.
- Citizen’s participation: Information under RTI can be sought easily by requesting the public officer and assistant public officer in any public authority.
- Government obligation: Obtaining information from any public authority is obligatory for them.
- Maintenance of public record: Under RTI Act, it is the duty of public authorities to maintain records for easy access and to publish within 120 days the name of the particular officers who should give the information and in regard to the framing of the rules, regulations etc.
- Empowerment of Citizens: Every citizen has been empowered to be informed about anything that affects their life directly or indirectly.
Limitations to the RTI
- Not an absolute right: The RTI and Right to Privacy are not absolute rights, both the rights, one of which falls under Article 19(l)(a) and the other under Article 21 can obviously be regulated, restricted and curtailed in the larger public interest.
- Subjected to restrictions: The RTI, being integral part of the right to freedom of speech, is subject to restrictions that can be imposed upon that right under Article 19 (2).
- Limitations under the rules: Rule 4 of RTI Act puts word limit (No. of words needed in different language is different to express the same idea) as 250 words. Word Limit, The Hidden power of Information Officer, is the cause of rejection of an application.
- Only information already available on record is accessible: The RTI Act provides access only to that information that existent and is available in records of the public authorities.
- Certain information may constitute contempt of court: Any information, the disclosure of which is expressly barred by any Court of law or tribunal or, which may constitute contempt of Court under the Contempt of Court Act, 1971, cannot be released.
- Information causes a breach of privilege: The Constitution of India provides some privileges to the Parliament and the State Legislature, so it is clear that such information cannot be issued by the public authority.
- Information relating to Intellectual Property and trade secrets: Any information, including commercial confidence, trade secrets or intellectual property cannot be disclosed.
Challenges in exercising RTI
- Information explosion: Different types of information is sought which has no public interest and sometimes can be used to misuse the law and harass the public authorities e.g. asking for desperate and voluminous information.
- Popular (mis)use: Some chauvinists file RTI to attain publicity. It is often used as a vindictive tool to harass or pressurize the already burdened public authorities.
- Rising cases of non-disclosure: Some provisions of Indian Evidence Act provide to hold the disclosure of documents. Similar is the case with the Official Secrets Act, 1923.
- Limited ambit of RTI: While the office of the CJI is now under the RTI’s ambit, the CBI is exempt.
- Threats to whistleblowers: There are rising cases of intimidation, threat and murders of RTI activists. There are no safeguards against the victimisation of the person who makes the complaint.
Significance of RTI
- The RTI Act, 2005 did not create a new bureaucracy for implementing the law. Instead, it tasked and mandated officials in every office to change their attitude and duty from one of secrecy to one of sharing and openness.
- RTI has been seen as the key to strengthening participatory democracy and ushering in people-centred governance.
- Access to information has empowered the poor and the weaker sections of society to demand and get information about public policies and actions, thereby leading to their welfare.
- It showed an early promise by exposing wrongdoings at high places, such as in the organisation of the Commonwealth Games, and the allocation of 2G spectrum and coal blocks.
Way Forward
It is well recognized that RTI is pathbreaking, but has not proved sufficient, to improve governance in its capacity due to various shortcomings. We need to improvise a lot on various parameters as discussed under:
- Speedy disposal: The increasing backlog of cases is exacerbated by the fact that most Commissions are functioning at reduced capacity. The government must ensure the timely appointment of chiefs and members of ICs.
- Prioritization of cases: There should be a prioritization of cases dealing with information related to life and liberty. Information regarding matters like food distribution, social security, health and other priority issues should be proactively disclosed.
- Digitalization: Governments should put in place a mechanism for online filing of RTI applications and bring all authorities under one platform.
- Reducing technicalities: The technicalities of filing an RTI application should be more simplified. The literacy rate of rural India is quite low and thus they find it quite difficult to comply with the procedural.
- Protecting whistleblowers: There is an urgent need to protect the whistle blowers who are targeted or attacked so easily. The impending bill should be passed or else an ancillary strict measure should be taken in this regard.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mission Millets
Mains level: Mission Millets .Advantages of Millets Crop

Context
- International Year of Millets in 2023 was approved by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) in 2018 and the United Nations General Assembly has declared the year 2023 as the International Year of Millets. The Odisha Government had launched Odisha Millet Mission (OMM), which aims to bring millets back to its fields and food plates by encouraging farmers to grow the crops that traditionally formed a substantial part of the diet and crop system in tribal areas.

Importance of millets
- Nutrition rich: Millet is a good source of protein, fibre, key vitamins, and minerals. The potential health benefits of millet include protecting cardiovascular health, preventing the onset of diabetes, helping people achieve and maintain a healthy weight, and managing inflammation in the gut.Millet is fibrous in content, has magnesium, Niacin (Vitamin B3), is gluten-free and has a high protein content.
- Requires less water: Millet’s comprise a significant staple in the semiarid tropic and guarantee food and nutritional security for needy individuals, who can’t develop other food crops because of poor rainfall and soil fertility. They are profoundly nutritious and are utilized by people in the rural area.
- Requires Moderate fertile soils: They can grow in low to medium fertile soils and in areas of low rainfall. Jowar, Bajra, and Ragi are the significant Millet’s developed in India.
- Profitable crop: Millets are the good choice for farmers to achieve primary goals of Farming e.g., profit, versatility, and manageability.
- Drought resistant and sustainable: Millet’s are the ‘marvel grains’ of the future as they are drought resistant which need few external inputs. Due to its high resistance against harsh conditions, millets are sustainable to the environment, to the farmer growing it, and provide cheap and high nutrient options for all.
- Long shelf life: Nearly 40 percent of the food produced in India is wasted every year. Millets do not get destroyed easily, and some of the millets are good for consumption even after 10-12 years of growing, thus providing food security, and playing an important role in keeping a check on food wastage.

What is Odisha Millet mission (OMM) and its impact?
- Promotion of millets: OMM promotes production and consumption of seven millets. But so far, focus has been on ragi, which has accounted for 86 per cent of the total area under millets, according to data on the OMM website. In contrast, little millet, foxtail millet, sorghum, pearl millet, kodo millet and barnyard millet cover less than 13 per cent of the area.
- Non ragi millets: Mission aimed at looking for high-yielding seeds for non-ragi millets. Farmers are urged to plant some non-ragi millets
- Limited procurement: In 2020-21, the state government procured slightly more than 20 million kg of ragi. However, this accounts for only 27 per cent of the total ragi produced, as OMM procures only 500 kg of ragi per ha and leaves the rest for farmers to consume.
- Millets in diet for complete nutrition: This practice has prompted farmers to consume more millets in all seasons, shows a mid-term evaluation by NCDS in 2019-20. But given that average yield is 1,500 kg per ha, much of the produce does not get procured and farmers are forced to sell it at distressed rate. OMM officials also admit that despite ragi being distributed in PDS and as a mix through anganwadi centres in two districts, its consumption has not picked up in a significant manner.
- Diverse products of Millets: OMM also sells millet products, such as cookies, savoury snacks, vermicelli and processed millets, under a brand called “Millet Shakti” through food trucks, cafés, kiosks and other outlets.
- Food processing chain using SHGs: Women self-help groups (SHGs) have been kept at the centre of the programme. They do not just pay a major role in manufacturing biological inputs to improve millet yields and undertake processing of the produce, but also operate the millet-based cafés and outlets.The full potential of SHGs, though, has not yet been realised. So far, only three women’s SHGs manufacture and process Millet Shakti products, which limits the volume available, income generated, and consumption.
- Market linkage by FPOs: OMM also leverages farmer-producer organisations (FPOs) to provide better marketing linkages. Until now, OMM has tapped into existing FPOs to sell processed millets in the open market or aggregate produce for Tribal Development Co-operative Corporation of Odisha Limited; if a block does not have an FPO, an SHG or community group is registered as one.
- Current status of FPO’S: Currently, there are 76 FPOs under OMM. But some of them are engaged only in minor processing and aggregation, without plans of scaling up market linkages. Encouraging FPOs with better incentives and benefit-sharing will help them compete in the market

What are other government efforts to promote millet crops?
- Smart food campaign: Smart Food with the tagline ‘good for you, good for the planet and good for the smallholder farmer’ is an initiative that will initially focus on popularising millets, and sorghum and has been selected by LAUNCH Food as one of the winning innovations for 2017.
- Popularising the millets: Smart Food will be taken forward as a partnership and many organisations have already teamed up to popularise millets. In India, this includes Indian Institute of Millet Research (IIMR), National Institute of Nutrition (NIN), MS Swaminathan Research Foundation (MSSRF) and Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA).
Conclusion
- One way to double farm incomes and encourage farm diversification is to make millet production attractive by introducing millet cultivation in areas where farmers’ distress is visible.Dedicated programmes with proper training and capacity-building initiatives that urge farmers to move away from loss-making crops toward diversification via millets can be a timely method to pull farmers away from the region’s distress.
Mains Question
Q.why millets cultivation is suitable for geographic conditions of India? Analyse the various efforts by government to promote the millets.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Space technology Developments
Mains level: Space,Space security and Sustainability.

Context
- World Space Week this year is themed around ‘Space and Sustainability’. Among other things, the 2022 theme seeks to specifically inspire focus on the challenges the world faces to keep space safe and sustainable.
What is mean by Space?
- Space is an almost perfect vacuum, nearly void of matter and with extremely low pressure. In space, sound doesn’t carry because there aren’t molecules close enough together to transmit sound between them. Not quite empty, bits of gas, dust and other matter floats around “emptier” areas of the universe, while more crowded regions can host planets, stars and galaxies.
- From our Earth-bound perspective, outer space is most often thought to begin about 62 miles (100 kilometers) above sea level at what is known as the Kármán line. This is an imaginary boundary at an altitude where there is no appreciable air to breathe or scatter light. Passing this altitude, blue starts to give way to black because oxygen molecules are not in enough abundance to make the sky blue.

What is mean by Space sustainability?
- Space sustainability is ensuring that all humanity can continue to use outer space for peaceful purposes and socioeconomic benefit now and in the long term. This will require international cooperation, discussion, and agreements designed to ensure that outer space is safe, secure, and peaceful.
What necessitate the sustainable space technology debate?
- Mounting challenge of Space debris: Challenges are endless in both quantitative and qualitative terms, i.e., they are several and severe, ranging from satellite crowding and collision risk to space debris in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- Ever increasing satellites: The sense of urgency around space sustainability is already skyrocketing—more than 80 countries currently contribute to the over 6,800 active satellites in orbit, of which many are used for both civilian and military purposes, as well as over 30,000 pieces of orbital debris.
- Militarization of space: Given the development of new and emerging space technologies, the rapid militarisation and securitisation of space, and the growing distrust amongst nations in the domain, space activity is only set to increase and acquire a more national security-oriented focus.
- Large scale Development of ASAT: This is already visible in several countries around the world. There has been a recent uptick in the development and testing of destructive anti-satellite (ASAT) weapons, with 26 tests in the past two decades conducted by the four countries that have access to these weapons (US, Russia, China, and India).
- Massive investment into military space capability: France, which is currently leading the European Council, has also invested several billion euros into military space capabilities, and regularly emphasises the security importance of space for other EU countries.
- Increasing Defence space commands: Australia set up its Defence Space Command in early 2022 to increase its strategic potential in space, and South Korea deployed a spy satellite to better monitor North Korea in June 2022, giving its military space plan a huge push.
- However, none of these countries have a sustainability provision in their defence space operations or programmes.

- Dichotomy in Security and sustainability: Sustainability and security are two sides of the same coin, but as a result of this inherent dichotomy, they are often juxtaposed against each other.
- Keeping Security is the priority: The contrast between highly motivated and funded national security efforts and the relatively non-prioritised international engagements around space sustainability is an example of a larger trend of indifference towards sustainable development in favour of higher military spending.
- SDG on backburner: To substantiate this point, funding for the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) was adversely affected due to COVID-19 in 2021, and this reportedly dramatically pushed back progress on the SDGs, but the global military expenditure has consistently been on an upward incline and crossed the US$2 trillion mark for the first time in the same year.
- Securitization of space: The trade-off between security and sustainability can jeopardise sustainable development within a plethora of issue domains, thus, increasing the likelihood of exhausting limited resources. This in turn could exacerbate the risk of conflict due to the resulting scarce resources, ultimately creating a vicious cycle of securitisation and conflict.
- Rat race in Space : As a case in point, the incumbent space race has always been marked by competing security and commercial interests, which has resulted in a constant escalation of global government spending on space programmes to its record value of US$98 billion in 2021. Space sustainability, on the other hand, has only seen activity recently, and primarily in an international and voluntary set-up.

What regulations are needed for Sustainable Space?
- Prioritising peaceful use of space: A Working Group on the Long-term Sustainability of Outer Space Activities was set up by the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) in 2010, which has 95 UN member states taking part in it. The Group adopted a set of guidelines by consensus in 2019, although it failed to make these guidelines or any other regulations legally binding. It agreed to work over it for 5 years from 2022 onwards, but since the Group uses a consensus-based approach to reach agreements, it is difficult to expect more stringent or extensive regulatory frameworks to emerge from it.
- Consensus is difficult but necessary: Consensus-based approaches in multilateral forums, especially related to arms or other security objectives, often contrast with individual national security interests of its member states and have been criticised for their slow or ineffective progress.
- Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons: Another example of this is the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons’ (CCW) Group of Government Experts (GGE) meetings on lethal autonomous weapons systems (LAWS), which have only produced a set of 11 non-binding guiding principles since deliberations around LAWS began in 2014.
- Space sustainable ratings should be developed: The World Economic Forum, for instance, introduced a new standard called the Space Sustainability Rating (SSR), in 2022, which aims to recognise, reward, and encourage space actors to design and implement sustainable and responsible space missions. It remains to be seen whether countries will respond favourably to tools like the SSR, which are based on a positive reinforcement model, to be more space sustainability-conscious.
Conclusion
- space sustainability is only at the cusp of becoming actionable. When space experts, intergovernmental organisations, or countries themselves conclude that sustainability should be a part of their space mandate, and when they devise possible methods to help achieve this, they cannot do so in a vacuum. Space sustainability should not become the political football like climate change.
Mains Question
Q.What are the threats to sustainable space technology? Comment on various laws, regulations, forums on sustainable space technology.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Holistic decriminalisation Bill
Mains level: Holistic decriminalisation Bill ,advantages and MSME's,Ease of doing business

Context
- The government’s proposal to bring a “holistic decriminalisation” bill in the Winter Session of Parliament, If gets enacted into law, it will be one of India’s greatest reforms since 1991. One of the objectives of this proposed law is to “end harassment and reduce compliance burden on businesses.
What is Holistic decriminalisation Bill?
- A new holistic decriminalisation bill is set to amend burdensome provisions in laws related to businesses.
- Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Piyush Goyal said that the Decriminalising sections of various laws will end the harassment faced by businesses and reduce compliance burden. Seeking quick industry feedback on problematic areas that can be covered in the proposed Bill.
What is the status of existing laws in India?
- Burden of Imprisonment clauses: Business regulatory universe comprises 1,536 laws, of which more than half, or 843 laws, carry imprisonment clauses. Under these laws, there are 69,233 compliances businesses face as an aggregate, of which almost two out of five, or 26,134, carry imprisonment clauses.
- Union and state legislations on the compliance: Of the 843 laws with imprisonment clauses, 28.9 percent, or 244 laws, have been enacted by Parliament; the rest by State legislatures and rules. Of the 26,134 compliances that carry imprisonment clauses, a fifth, or 5,239 clauses are situated in Union laws.
- No institutional support for informal sector: Of the 69 million enterprises in India, only 1 million are formal employers; as a result, the remaining informal enterprises get no access to institutional capital, talent, or supply chains.
- Smaller the better attitude: India’s predatory and rent-seeking policy infrastructure ensures that businesses choose to remain under the regulatory radar—small may not be beautiful but it is certainly safe. For instance, a small business with 150 employees or more has to deal with 500 to 900 compliances a year, on which it can end up spending up to INR 12-18 lakhs by hiring consultants to be compliant with labour laws, taxes, factories, and so on.
- Burden of compliance is cost-effective: Creating a regulatory bias against small businesses once a line of scale is crossed, managing a compliance department becomes cost-effective; until then, for the small business owner-manager, compliances becomes a risk-management strategy, almost an economic activity.

Why such reforms in business laws are necessary?
- To attract more investment: When viewed through the lens of the government’s intention to make India an investment destination for global and domestic capital, it would be a reform that should end the endemic of harassment, corruption, and rent-seeking by officials of the Union government.
- To end corruption at state level: Corruption by officials of state governments will end when criminal provisions in State laws and rules get similarly rationalised; some of these will get rationalised with amendments to Union laws that are enforced by state governments.
- Encouraging the entrepreneurial spirit: Regulatory framework is cumulative policy actions of the three arms of the State the executive, the legislature, and the judiciary using instruments of legislations, rules, regulations, or orders, to create or raise barriers to a smooth flow of ideas, organisation, money, and, most importantly, the flow of the entrepreneurial spirit.

What are the recommendations for Holistic decriminalization?
- Amend the overreaching laws: Reform all compliances with overarching legislation, across ministries and departments. Smaller steps being taken to ease doing business in India, such as shifting the responsibility under the Legal Metrology Rules from directors to executives, should converge into this single bill.
- There should be Justifiable imprisonment: Use criminal penalties in business laws with extreme restraint the idea of using a criminal clause as a default option should be done away with and replaced by a justification for imprisonment, including the term in jail.
- Ending the criminalisation: End the criminalisation of all compliance procedures such as filing on a wrong form or mislabelling.
- Introducing new laws: Introduce sunset clauses for all imprisonment clauses this needs a new enabling law as a precursor.
- Bringing extensive Digitisation: Digitise all compliance filings, as has been done by the income tax department.
- Focus on paperless work: Convert every department that acts as a regulatory body to go paperless and faceless. This should look beyond merely creating a website and uploading records. This will enable automated record reconciliation, identify leakages, detect frauds, and flag discrepancies.
- More such steps in the right direction: By reducing the compliance burden such that it ends harassment, the government is moving in the right direction. To prevent any policy holes left after the passage of the bill into an act, this is a law that needs to be studied hard, debated well, and only then enacted. Of course, there will be political opposition. It is up to the government to ignore the rhetoric and embrace the solutions for the greater good of the country.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
- The country is getting ready for third-generation reforms. Among them are reforms that rationalise compliances and imprisonment clauses—retain a handful, reduce or remove most, compound the rest and turn physical imprisonment into financial penalties. The Inspector Raj, expressed through the colonial, corrupt, and rent-seeking policy infrastructure, must be disassembled and jobs, wealth, and large enterprises created.
Mains Question
Q. Why current industrial policy and laws are causing the harassment of entreprenuers? Discuss the reforms needed in the light of proposed “ Holistic Discrimination” Bill.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Appointment of CJI
Mains level: Issue of Tenure of CJI

Chief Justice of India U.U. Lalit nominated Justice D.Y. Chandrachud as his successor. He will be 50th CJI.
How is CJI selected?
- Justice U.U. Lalit is the senior-most judge in the Supreme Court now.
- The ‘Memorandum of Procedure of Appointment of Supreme Court Judges’ says “appointment to the office of the CJI should be of the seniormost Judge of the SC considered fit to hold the office”.
- The process begins with the Union Law Minister seeking the recommendation of the outgoing CJI about the next appointment.
What is the time frame?
- The Minister has to seek the CJI’s recommendation at the “appropriate time”.
- The Memorandum does NOT elaborate or specify a timeline.
Making final appointment
The Memorandum says:
- Receipt of the recommendation of the CJI
- The Union Minister of Law, Justice and Company Affairs will put up the recommendation to the PM
- PM will advise the President in the matter of appointment
- The President of India appoints the CJI
Chief Justice of India: A brief background
- The CJI is the chief judge of the Supreme Court of India as well as the highest-ranking officer of the Indian federal judiciary.
Appointment
- The Constitution of India grants power to the President to nominate, and with the advice and consent of the Parliament, appoint a chief justice, who serves until they reach the age of 65 or until removed by impeachment.
- Earlier, it was a convention to appoint seniormost judges.
- However, this has been broken twice. In 1973, Justice A. N. Ray was appointed superseding 3 senior judges.
- Also, in 1977 Justice Mirza Hameedullah Beg was appointed as the chief justice superseding Justice Hans Raj Khanna.
Qualifications
The Indian Constitution says in Article 124 (3) that in order to be appointed as a judge in the Supreme Court of India, the person has to fit in the following criteria:
- He/She is a citizen of India and
- has been for at least five years a Judge of a High Court or of two or more such Courts in succession; or
- has been for at least ten years an advocate of a High Court or of two or more such Courts in succession; or
- is, in the opinion of the President, a distinguished jurist
Functions
- As head of the Supreme Court, the CJI is responsible for the allocation of cases and appointment of constitutional benches which deal with important matters of law.
- In accordance with Article 145 of the Constitution and the Supreme Court Rules of Procedure of 1966, the chief justice allocates all work to the other judges.
On the administrative side, the CJI carries out the following functions:
- maintenance of the roster; appointment of court officials and general and miscellaneous matters relating to the supervision and functioning of the Supreme Court
Removal
- Article 124(4) of the Constitution lays down the procedure for removal of a judge of the Supreme Court which is applicable to chief justices as well.
- Once appointed, the chief justice remains in the office until the age of 65 years. He can be removed only through a process of removal by Parliament as follows:
- He/She can be removed by an order of the President passed after an address by each House of Parliament supported by a majority of the total membership of that House and by a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members of that House present.
- The voting has been presented to the President in the same session for such removal on the ground of proven misbehavior or incapacity.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Swiss Banks
Mains level: Black Money Issue

India has received the fourth set of Swiss Bank account details of its nationals and organizations as part of annual information exchange, under which Switzerland has shared particulars of nearly 34 lakh financial accounts with 101 countries.
How India gets such information?
Ans. Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI) Agreement
- In an effort to bring in transparency and restrict money laundering, the Swiss Federal Office gives a detailed account of the massive AEOI exchange.
- This is the fourth tranche of information that India has received from Switzerland since the two countries entered into an Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI) agreement in January 2018.
- The first such exchange with India took place in 2019.
- Some countries which have been added to the Swiss AEOI list for the first time are Turkey, Peru and Nigeria.
- The Swiss Federal Tax Administration office has also informed that with 74 of these 101 countries, the information exchange was reciprocal.
What is the volume, nature of data?
- In 2019, prior to India receiving its first batch of banking information via the AEOI, India would be among 73 countries that would be receiving the data.
- In India’s case “several dispatches” would be required, giving an indication of the large volume of account holders.
Guidelines for exchange of such sensitive banking information
- The guidelines and parameters for the AEOI are set by the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), the Paris-based international body.
- The annual exercise of AEOI exchange, such as the current Swiss bonanza of banking details, is strictly meant for “tax only” purposes and in India.
- This data is kept in the custody of and for action by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT).
- Under the OECD’s guidelines, details of the quantum of funds or the names of account holders cannot be publicised.
What is the scope of India’s AEOI network?
- Under the OECD umbrella of AEOI, India presently shares bulk financial and banking information with 78 countries.
- It receives the same from 107 countries, with Switzerland known to be sharing some of the most voluminous data.
Institutional mechanism in India
- Primarily to the large volume of FI data coming in from now a 100 countries, the CBDT last year set up a network of Foreign Asset Investigation Units (FAIUs) in 14 of its investigation wings.
- The information of a region which has reached India via the AEOI route is transmitted in a secure manner.
- It is the FAIUs that do the follow-up probe of the such data, and to begin with, investigate whether the taxpayer has declared the foreign bank account/s in tax returns or not.
Why do people park their money in Swiss Banks?
- As wealth became easily mobile across international borders, the safety and stability of Swiss banks, located in a peaceful country presented an irresistible attraction for the super-rich.
- Switzerland itself is a politically neutral country.
- Swiss bank accounts are attractive to depositors because they combine low levels of risk with very high levels of privacy.
- The Swiss economy is extremely stable, and the banks are run at very high levels of professionalism.
- Opening an account is not difficult, and requires not much more than basic KYC, including a proof of identity such as a passport.
Question of Black Money
- “Black money” allegedly stashed away by Indians in Swiss banks is a political issue in India.
- Leaders and political functionaries have often made promises to “bring it back” and credit 15 Lakh Rupees in every Indian’s account.
- Swiss authorities have maintained that they cooperate with the Indian government to fight tax evasion and fraud.
Also read:
What are Swiss Banks?
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Israeli region for mapping
Mains level: Not Much
Israel has reached a US-brokered agreement with Lebanon to settle their long-disputed maritime border. This has been seen as a historic deal.
Israel-Lebanon Boundary Issue
- The draft agreement aims to settle Israel and Lebanon’s competing claims over offshore gas fields in the region.
- A major source of friction was the Karish gas field, which Israel insisted fell entirely within its waters and was not a subject of negotiation.
- The issue is a little over a decade old, after the two countries declared overlapping boundaries in 2011 in the Mediterranean Sea.
- Since both countries have been technically at war, the United Nations was asked to mediate.
- The issue gained significance after Israel discovered two gas fields off its coast a decade ago, which experts had believed could help turn it into an energy exporter.
Key terms of the Agreement
- The agreement seeks to resolve a territorial dispute in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, in an area that Lebanon wants to explore for natural gas.
- The gas field in question is located on the maritime boundary between the two countries and this agreement would allow both countries to get royalties from the gas.
- It also sets a border between the maritime waters of Lebanon and Israel for the first time.
Why is this agreement signed?
- Averting terror threats: The agreement is expected to avert the immediate threat of conflict between Israel and Hezbollah militants in Lebanon, after fears of escalation if negotiations fell apart.
- Energy exploitation: The agreement will create new sources of energy and income for both countries, particularly important for Lebanon, which is facing a crippling energy and financial crises.
- Alternative energy for Europe: It could also have a potentially wider impact: it would likely provide Europe with a potential new source of gas amid energy shortages caused by the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
What the agreement does not address?
Ans. Blue Line Issue
- The agreement does not touch on the shared land border between Israel and Lebanon, which is still disputed, but where both countries are committed to a ceasefire.
- This border is also called the Blue Line, a boundary that was drawn up by the UN after Israel withdrew from southern Lebanon in 2000.
- This land border is currently patrolled by the United Nations forces.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now



































 Conclusion
Conclusion

