From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Issues with unscientific highway infrastructure
Context
- In a March 2019 circular, the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) raised the subject of premature issuance of completion certificates for national highway works. NHAI had noticed that, in certain cases, completion certificates had been issued even before the completion of works ‘up to the standards and specifications’ prescribed by the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways.
Status of National highways and deaths
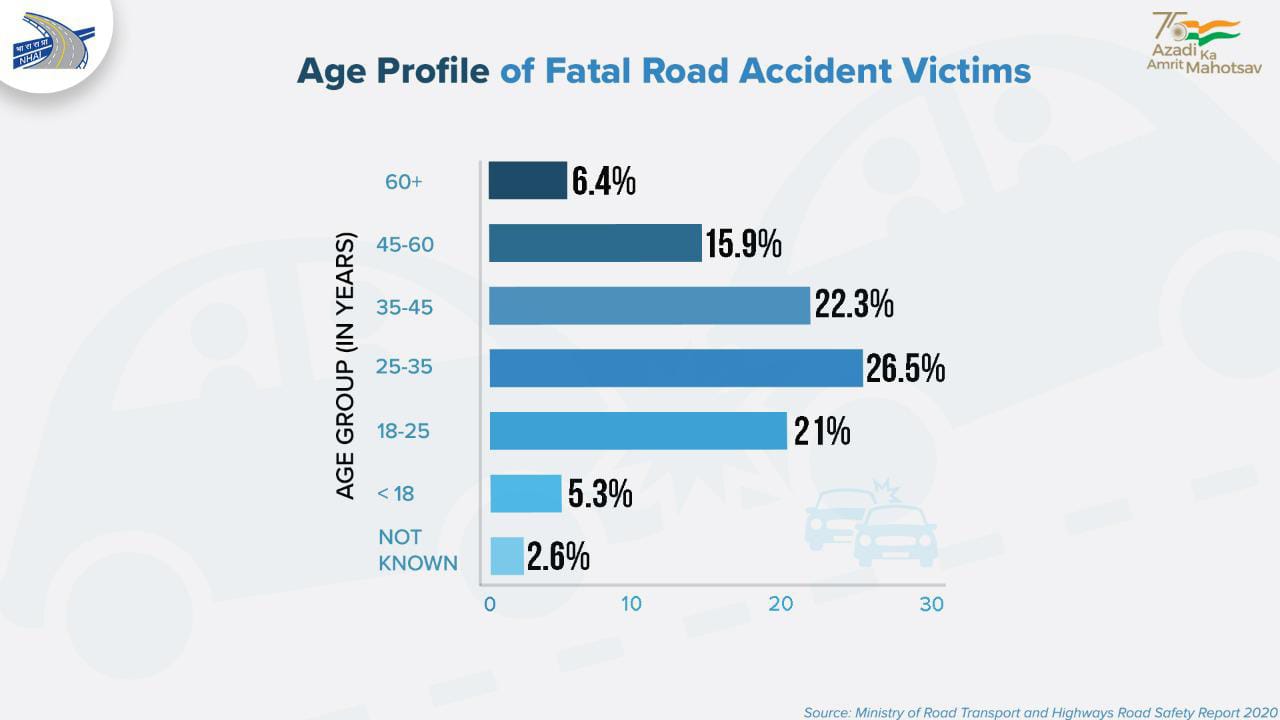
- 35 percent of all road deaths: NHAI is the principal organization responsible for construction of National Highways in India. National highways constitute a mere 2 percent of the country’s road network, but account for close to 35 percent of all road deaths.
- Record 37 kms per day: The ministry has been taking credit for the pace at which national highways are being constructed. In the fiscal year 2021, it reached a record 37 kms per day. This has come down to 19.44 km per day in the first six months of the financial year 2022.
What was the circular issued by NHAI?
- Issuance of completion certificate: The circular forbade the issuance of such certificates, especially if non-completion resulted in ‘material inconveniences to users’ or affected their safety.
- Likely cause of fatalities: Items such as road shoulders, road signs, markings, dressing of slopes, and road furniture were explicitly mentioned. circular was not taken with due seriousness by some authorized engineers. This negligence could have contributed to road crashes, probably resulting in fatalities.
- Dereliction of duty by NHAI’s officials: The NHAI has now warned the delinquents that such behavior would be treated as a serious dereliction of duty and disciplinary action would be taken against officers issuing such certificates to incomplete road works. Additionally, the officers would be held personally liable in case of serious accidents that occur on such unfinished infrastructure.
- Safety is better than pace of construction: The Minister for Road Transport & Highways stressed that it is necessary to build safer roads even if this decelerated the pace of construction.
Case study of NHAI’s road construction?
- Death of Cyrus Mistry: Unfortunately, self-introspection by the NHAI in regard to safety failures and the large number of deaths on national highways was not in evidence in the aftermath of the death of Cyrus Mistry on the Ahmedabad-Mumbai national highway in September 2022.
- Crash was result of poor infrastructure: In this instance, a seven-member forensic investigation team found that the car crash was the result of an infrastructure issue. The car in which Mistry was travelling happened to tragically hit a bridge that was faultily designed.
- Invisible dividers: The bridge parapet was found to be protruding into the shoulder lane. Furthermore, the road with three lanes unexpectedly narrowed to a road with two lanes with a dangerous L-shaped concrete divider that had no proper paint on it.
- Inadequate safety signs: Road signages were grossly inadequate, making that road stretch a ‘black spot’. This epithet is used for a road section where accidents are a frequent occurrence.
- Expressways are constructed for more speed: The accident also raised issues of the excessive speed of the car that crashed. It was said that the car was travelling at a speed in excess of 100 km per hour. However, the minister himself has been in favour of higher speeds on Indian expressways and national highways. He proposed a speed limit of 140 kmph on expressways and at least 100 kmph on four-lane national highways. This, he stated, was advocated on account of considerable improvements in the quality of India’s highways that permit vehicles to go faster than in the past.
- Speed limit safety needs to be revise: The minister was also critical of some judicial rulings that disallowed hiking speeds on national highways. However, in the light of certain facts repeatedly surfacing in regard to safety issues of national highways, it does appear that greater caution in regard to increasing speed needs to be taken.
Critical analysis of NHAI’s road construction and maintenance
- Rains and potholes: While the government claims that they are of international standard, a recent report highlighted the plight of road travelers on national highways post India’s monsoons. The rains have left the country’s arterial network in poor shape as they have become riddled with potholes.
- Higher toll but poor roads: The cited report mentioned the Gurgaon-Jaipur stretch of NH-8, which, despite a hike in toll rates, remains incomplete and terribly potholed. The reason for this sorry state of affairs was revealed in a reply by the government to a parliamentary standing committee.
- Insufficient maintenance: The budgetary provision for maintenance of national highways was a mere 40 percent of their own estimated standards. Clearly, maintenance of national highways was being discounted in favour of more kilometres of road construction. The shortfall of 60 percent of maintenance money was terribly high and resulted in the resources being thinly spread, making adequate maintenance intervention highly unlikely.
- Inadequate budgetary allocation: The parliamentary committee pointed out in its report titled ‘Issues related to road sector’ that the shortfall in sufficient budgetary allocation was echoed in the poor quality of national highways often witnessed across the country. The committee emphasized that the maintenance of national highways was vitally significant in regard to safety and good average traffic speeds and ought to be given high priority. The issue had been repeatedly flagged by the committee.
- NITI Aayog’s acknowledgement of poor infrastructure: Similarly, NITI Aayog, in its report titled ‘Strategy for New India @75’, advised that the government should earmark 10 percent of its annual budget for maintenance of roads and highways and move towards the developed country norm of marking 40 percent of the budget for road upkeep. It is evident that if national highways are not in shape, the economy of the country and the states takes a hit.
Conclusion
-
It is absolutely necessary for citizens to follow road safety norms but government cannot look away from its responsibility. Scientific road construction even at the cost of slow construction rate is non-negotiable for sake of accident prevention. Safety of citizens is prior to any world record.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024