Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Innovations In AI and tools
Mains level: AI's diverse potential and its application for better governance

Central Idea
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) has gained worldwide attention, and many mature democracies are using it for better legislative procedures. In India, AI can be used to assist parliamentarians in preparing responses for legislators, enhancing research quality, and obtaining information about any Bill, legislative drafting, amendments, interventions, and more. However, before AI can work in India, there is a need to codify the country’s laws, which are opaque, complex, and face a huge translation gap between law-making, law-implementing, and law-interpreting organizations.
- AI is a constellation of technologies that enable machines to act with higher levels of intelligence and emulate the human capabilities of sense, comprehend and act.
- The natural language processing and inference engines can enable AI systems to analyze and understand the information collected.
- An AI system can also take action through technologies such as expert systems and inference engines or undertake actions in the physical world.
- These human-like capabilities are augmented by the ability to learn from experience and keep adapting over time.
- AI systems are finding ever-wider application to supplement these capabilities across various sectors
Need to Codify Laws
- Current laws are complex and opaque: Current laws in India pose many challenges, such as their complexity, opaqueness, and lack of a single source of truth.
- The India Code portal does not provide complete information: The India Code portal is not enough to provide complete information about parent Acts, subordinate legislation, and amendment notifications.
- AI can be used to provide comprehensive information: There is a need to make laws machine-consumable with a central law engine, which can be a single source of truth for all acts, subordinate pieces of legislation, gazettes, compliances, and regulations. AI can use this engine to provide information on applicable acts and compliances for entrepreneurs or recommend eligible welfare schemes for citizens.
Assisting Legislators
- Potential of AI for legislators: AI can help Indian parliamentarians manage constituencies with a huge population by analysing citizens’ grievances and social media responses, flagging issues that need immediate attention and assisting in seeking citizen inputs for public consultation of laws and preparing a manifesto.
- AI-powered assistance: Many Parliaments worldwide are now experimenting with AI-powered assistants.
- For instance:
- Netherlands’s Speech2Write system: The Speech2Write system in the Netherlands House of Representatives, which converts voice to text and translates voice into written reports.
- AI tools Japan: Japan’s AI tool assists in preparing responses for its legislature and helps in selecting relevant highlights in parliamentary debates.
- Brazil: Brazil has developed an AI system called Ulysses, which supports transparency and citizen participation.
- NeVA portal India: India is also innovating and working towards making parliamentary activities digital through the ‘One Nation, One Application’ and the National e-Vidhan (NeVA) portal.
Simulating Potential Effects of Laws
- Dataset modelling: AI can simulate the potential effects of laws by modelling various datasets such as the Census, data on household consumption, taxpayers, beneficiaries from various schemes, and public infrastructure.
- Flag outdated laws: In that case, AI can uncover potential outcomes of a policy and flag outdated laws that require amendment.
- For example: During the COVID-19 pandemic, ‘The Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897’ failed to address the situation when the virus overwhelmed the country. Several provisions in the Indian Penal Code (IPC) are controversial and redundant, such as Article 309 (attempted suicide) of the IPC continues to be a criminal offense. Many criminal legislation pieces enacted more than 100 years ago are of hardly any use today.
Conclusion
- The COVID-19 pandemic has given a strong thrust to the Digital India initiative, and a digitization of services needs to be kept up in the field of law, policy-making, and parliamentary activities, harnessing the power of AI. However, the use of AI must be encouraged in an open, transparent, and citizen-friendly manner, as AI is a means to an end, not an end in itself. Therefore, it is necessary to address the current challenges faced by India’s laws before AI can be effectively used to assist parliamentarians in their legislative duties.
Mains Question
Q. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has gained worldwide attention, and many mature democracies are using it for better legislative procedures. In this light evaluate the potential of AI in assisting Indian parliamentarians.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Private Space companies in news
Mains level: India's space sector and role pf private companies and startups
Central Idea
- India needs an enabling policy and regulatory environment to tap into the potential of the Second Space Age and its rapidly growing space economy.
What is mean by the Second Space Age?
- Commercialization: The Second Space Age refers to the recent era of increased commercialization and private sector involvement in space exploration, which began in the early 2000s.
- Emergence of private space companies: This period has been marked by the emergence of private space companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic, who are investing heavily in space technology and infrastructure.
- Today’s space domain has many more actors once dominated by US and USSR: Compared to the First Space Age dominated by the US and the USSR, today’s space domain has many more actors, with a majority being private companies. Private companies account for 90% of global space launches since 2020, and India is no exception
- Increasing involvement of non-spacefaring nations: The Second Space Age is also characterized by the increasing involvement of non-spacefaring nations in space exploration and the development of technologies that enable greater access to space for both commercial and scientific purposes.
- Exploration: The hope is that this new era will lead to breakthroughs in areas like space tourism, asteroid mining, and Mars colonization, among others.
- India’s journey in space began modestly in the 1960s.
- Societal objectives: Over the decades, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) prioritized societal objectives and benefits, such as developing satellite technology for mass communication, remote sensing for weather forecasting, resource mapping of forests, agricultural yields, groundwater and watersheds, fisheries and urban management, and satellite-aided navigation.
- Enhanced launch capabilities: ISRO also developed satellite launch capabilities, beginning with the SLV-1 in the 1980s, followed by the PSLV series, which has become its workhorse with over 50 successful launches.
Facts for prelims
| Steps taken to promote the space industry in India |
Resulting Outcome
|
| Creation of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in 1969 |
Establishment of a strong foundation for space research and exploration in India |
| Launch of Aryabhata satellite in 1975 |
First satellite successfully launched by India |
| Establishment of the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) in 1972 |
Development of technologies for rocket and satellite launch |
| Launch of Rohini satellite in 1983 |
First satellite launched using an Indian-made launch vehicle |
| Launch of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in 1993 |
Capability to launch smaller satellites into orbit |
| Launch of Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) in 2001 |
Capability to launch larger and heavier satellites into orbit |
| Successful Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) in 2014 |
India became the first country to successfully launch a spacecraft to Mars in its first attempt |
| Formation of NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) in 2019 |
Increased involvement of private sector in space activities and commercialization of space technologies |
| Announcement of Gaganyaan mission in 2018 |
Development of human spaceflight capabilities in India |
India’s Space Potential
- Economy and employment: India’s space economy, estimated at $9.6 billion in 2020, is expected to be $13 billion by 2025. However, with an enabling policy and regulatory environment, the Indian space industry could exceed $60 billion by 2030, directly creating more than two lakh jobs.
- Downstream activities: Downstream activities such as satellite services and associated ground segment are dominant, accounting for over 70% of India’s space economy.
- Media and entertainment segment: Media and entertainment account for 26% of India’s space economy, with consumer and retail services accounting for another 21%.
The Growing Role of the Private Sector
- Increasing space start ups: The Indian private sector is responding to the demands of the Second Space Age, with over 100 space start-ups today. From less than $3 million in 2018, investment in the sector has doubled in 2019 and crossed $65 million in 2021.
- Potential of multiplier effect on economy: The sector is poised for take-off, as a transformative growth multiplier like the IT industry did for the national economy in the 1990s.
Way ahead: Creating an Enabling Environment
- ISRO needs to focus on research and collaborate with the Indian private sector, which has different needs and demands.
- To create an enabling environment for the private sector, India needs a space activity act that provides legal grounding, sets up a regulatory authority, and enables venture capital funding into the Indian space start-up industry.
- Although a series of policy papers have been circulated in recent years, legislation is needed to provide legal backing and create an enabling environment for private sector growth.
Conclusion
- India’s space industry has enormous potential, but realizing it requires an enabling policy and regulatory environment that encourages private sector growth. With a space activity act that provides legal backing, sets up a regulatory authority, and enables venture capital funding, India can take advantage of the Second Space Age and become a major player in the global space economy.
Mains Question
Q. What do you understand by mean Second Space Age? Highlight potential of India’s space industry and growing role of private sector
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Finance Commission
Mains level: Read the attached story
The Union government is gearing up to constitute the Sixteenth Finance Commission in November this year to recommend the formula for sharing revenues between the Centre and the States for the five-year period beginning 2026-27.
What is the Finance Commission?
- The Finance Commission (FC) was established by the President of India in 1951 under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution.
- It was formed to define the financial relations between the central government of India and the individual state governments.
- The Finance Commission (Miscellaneous Provisions) Act, 1951 additionally defines the terms of qualification, appointment and disqualification, the term, eligibility and powers of the Finance Commission.
- As per the Constitution, the FC is appointed every five years and consists of a chairman and four other members.
- Since the institution of the First FC, stark changes in the macroeconomic situation of the Indian economy have led to major changes in the FC’s recommendations over the years.
Constitutional Provisions
Several provisions to bridge the fiscal gap between the Centre and the States were already enshrined in the Constitution of India, including Article 268, which facilitates levy of duties by the Centre but equips the States to collect and retain the same.
Article 280 of the Indian Constitution defines the scope of the commission:
- Who will constitute: The President will constitute a finance commission within two years from the commencement of the Constitution and thereafter at the end of every fifth year or earlier, as the deemed necessary by him/her, which shall include a chairman and four other members.
- Qualifications: Parliament may by law determine the requisite qualifications for appointment as members of the commission and the procedure of selection.
- Terms of references: The commission is constituted to make recommendations to the president about the distribution of the net proceeds of taxes between the Union and States and also the allocation of the same among the States themselves. It is also under the ambit of the finance commission to define the financial relations between the Union and the States. They also deal with the devolution of unplanned revenue resources.
Important functions
- Devolution of taxes: Distribution of net proceeds of taxes between Center and the States, to be divided as per their respective contributions to the taxes.
- Grants-in-aid: Determine factors governing Grants-in-Aid to the states and the magnitude of the same.
- Augment states fund: To make recommendations to the president as to the measures needed to augment the Fund of a State to supplement the resources of the panchayats and municipalities in the state on the basis of the recommendations made by the finance committee of the state.
- Any financial function: Any other matter related to it by the president in the interest of sound finance.
Members of the Finance Commission
- The Finance Commission (Miscellaneous Provisions) Act, 1951 was passed to give a structured format to the finance commission and to bring it to par with world standards.
- It laid down rules for the qualification and disqualification of members of the commission, and for their appointment, term, eligibility and powers.
- The Chairman of a finance commission is selected from people with experience of public affairs. The other four members are selected from people who:
- Are, or have been, or are qualified, as judges of a high court,
- Have knowledge of government finances or accounts, or
- Have had experience in administration and financial expertise; or
- Have special knowledge of economics
Key challenges ahead for 16th FC
- Overlap with GST Council: A key new challenge for the 16th FC would be the co-existence of another permanent constitutional body, the GST Council.
- Conflict of interest: The GST Council’s decisions on tax rate changes could alter the revenue calculations made by the Commission for sharing fiscal resources.
- Feasibility of recommendations: Centre usually takes the Commission’s recommendations on States’ share of tax devolution and the trajectory for fiscal targets into account, and ignores most other suggestions.
Major outstanding recommendations
- Creating a Fiscal Council: The 15th FC has suggested creating a Fiscal Council where Centre and States collectively work out India’s macro-fiscal management challenges, but the government has signalled there is no need for it, he pointed out.
- Creating a non-lapsable fund for internal security: The centre accepted to set up a non-lapsable fund for internal security and defense ‘in principle’, its implementation still has to be worked out.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Article 371, 371F
Mains level: Special provisions for some States

Former Sikkim CM claimed that the Sikkimese people feel betrayed as Article 371F, which guarantees special provisions for Sikkim, was “violated”.
What is Article 371F?
- Article 371F is a special provision in the Constitution of India that was created to provide for the unique status of Sikkim, a state located in the northeastern part of India.
- Sikkim was an independent kingdom until 1975, when it became the 22nd state of India.
- Article 371F was included in the Constitution to ensure that Sikkim’s distinct identity and cultural heritage were protected and preserved after its merger with India.
Special provisions for Sikkim
Under Article 371F, Sikkim has been granted several special provisions that are not available to other states in India. Some of the key provisions of Article 371F are:
- Protection of Sikkimese people: Only the descendants of Sikkim subjects (those who lived in the state before its merger with India) whose names were mentioned in the 1961 register are considered Sikkimese and are entitled to certain benefits, such as the right to own land and get state government jobs. They are also exempted from paying income tax.
- Legislative powers: The Governor of Sikkim has special powers with respect to the Sikkim Legislative Assembly, including the power to nominate one member to the Assembly and the power to give his or her assent to certain bills.
- Constitutional safeguards: Certain constitutional safeguards have been provided to the people of Sikkim to protect their distinct identity and cultural heritage.
- Formation of Committees: The Central Government has the power to appoint a committee of experts to advise on matters related to Sikkim, and the State Government can also appoint committees to examine issues related to the protection of Sikkim’s unique identity.
Why in news?
- The Financial Bill, 2023 redefined Sikkimese as any Indian citizen domiciled in Sikkim, which would extend these benefits to a broader population.
- This move is seen as a violation of Article 371F, which was the basis for Sikkim’s merger with India in 1975.
Concerns highlighted
- The leader claimed that the people of Sikkim feel betrayed by the violation of Article 371F.
- He alleged that Sikkim has become a hotbed for political violence.
- He claimed that unrest in a sensitive border state like Sikkim is not good for national security.
Back2Basics: Article 371
- It is a provision in the Constitution of India that grants special provisions and autonomy to certain states in India.
- It is a set of temporary and transitional provisions that were included in the Constitution to address the specific needs and aspirations of various regions and communities in the country.
- The provisions of Article 371 differ from state to state, depending on the specific needs and demands of the region. For instance:
- Maharashtra and Gujarat: Article 371 provides for special provisions for the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat, which grants certain rights and privileges to the people of the Marathi-speaking areas of Maharashtra and the Gujarati-speaking areas of Gujarat.
- Nagaland: Article 371A provides for special provisions and autonomy for the state of Nagaland. It grants the Nagaland Legislative Assembly special powers with respect to lawmaking, and prohibits outsiders from acquiring land in the state.
- Assam: Article 371B provides for special provisions for the state of Assam, which includes the establishment of a regional council for the state and grants the council certain legislative and executive powers.
- Manipur: Article 371C provides for special provisions for the state of Manipur. It gives the Manipur Legislative Assembly the power to enact laws related to land, forests, and minerals, and also provides for the protection of the rights of the hill tribes in the state.
- Andhra Pradesh: Article 371D provides for the establishment of a special committee to oversee the development of backward regions in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- The provisions are aimed at promoting the development and welfare of the people in these states, while preserving their unique cultural and linguistic identity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rare earth elements
Mains level: Not Much

Scientists at the National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI) in Hyderabad have discovered the presence of rare-earth elements (REEs) in Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh.
What are Rare-Earth Elements?
- Rare-earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 elements, including lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, yttrium, hafnium, tantalum, niobium, zirconium, and scandium.
- These elements are widely used in modern electronics, such as smartphones, computers, jet aircraft, and other products, due to their unique magnetic, optical, and catalytic properties.
- These elements are crucial components in various electronic devices and have industrial applications in sectors like imaging, aerospace, and defense.
SHORE Project and discovery of REEs
- The discovery was part of a study funded by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) under a project called ‘Shallow subsurface imaging Of India for Resource Exploration’ (SHORE).
- NGRI scientists found enriched quantities of REEs in “whole rock analyses”.
- Drilling for at least a kilometer deep will help ascertain the consistency of the elements’ presence underground.
Significance of the discovery
- The discovery of REEs in Anantapur district is significant as these elements are in high demand worldwide, and their supply is limited.
- REEs have become a subject of geopolitical concern due to their increasing demand and limited supply.
- China is currently the world’s largest producer and exporter of rare-earth elements (REEs), accounting for more than 80% of global production.
- The country has significant reserves of REEs and has invested heavily in mining and processing infrastructure.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LIGO
Mains level: Gravitational waves study

India has given the final approval to build its biggest scientific facility, Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), in the Hingoli district of Maharashtra. The facility will join the global project to detect and study gravitational waves.
Gravitation and General Theory of Relativity
- Newton’s law of gravitation, proposed by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century, explains that the force that makes an object fall to the ground is also responsible for making heavenly bodies go around in their orbits.
- However, the theory did not explain the existence of an attractive force between any two bodies or the instantaneous propagation of the gravitational force over large distances.
- In 1915, Albert Einstein proposed the General Theory of Relativity, which altered our understanding of gravitation. Einstein proposed that space-time interacted with matter, was influenced by it, and in turn, and influenced events.
- The curvature in space-time produced by matter was the reason other smaller bodies in the vicinity felt the gravitational pull.
- General Relativity also predicted that moving objects would generate gravitational waves in space-time.
|
What is LIGO?
|
What is it?
|
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) |
| Purpose |
Detect and study gravitational waves |
| Cause |
Ripples in spacetime caused by violent and energetic events in the universe |
| Location |
Livingston, Louisiana and Hanford, Washington |
| Detector |
Michelson interferometer |
| Function |
Measure changes in length caused by passing gravitational waves |
| Benefits |
Improving our understanding of the universe and its origins |
| Discovery |
Detected gravitational waves for the first time in 2015 |
| Significance |
Confirmed a prediction made by Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity |
| Field |
Gravitational wave astronomy |
| Discoveries |
Many exciting discoveries about the nature of the universe |
About LIGO-India
- LIGO-India will be the fifth node of this international network of gravitational wave observatories, and possibly the last.
- The instrument is so sensitive that it can easily get influenced by events like earthquakes, landslides, or even the movement of trucks, and produce a false reading.
- That is why multiple observatories are needed to revalidate the signals.
- India’s involvement in LIGO is crucial to demonstrating its intent and capability to pull-off complex science projects independently.
Significance
- The detection and study of gravitational waves could help in understanding the universe’s structure, the origin of the universe, and the functioning of black holes.
- The LIGO project also has huge spin-off benefits for India’s science and technology sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Uranium isotopes, Radioactivity
Mains level: NA
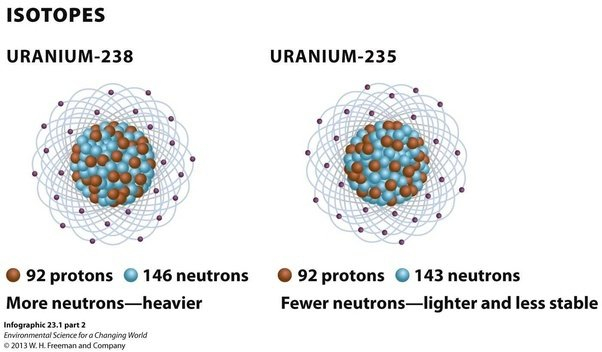
Physicists in Japan have discovered a new isotope of uranium, with atomic number 92 and mass number 241.
Uranium
- Uranium is a naturally occurring chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92.
- It is a heavy metal that is radioactive and found in small quantities in rocks and soils worldwide.
- Uranium has several isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Isotopes of Uranium
The most common isotopes of uranium are uranium-238 and uranium-235.
- Uranium-238: It is the most abundant isotope of uranium, accounting for over 99% of natural uranium. It has 92 protons and 146 neutrons in its nucleus. It is not fissile, which means it cannot sustain a nuclear chain reaction. However, it is fertile, which means it can absorb neutrons and undergo radioactive decay to produce other isotopes such as plutonium-239, which is fissile.
- Uranium-235: It is the second most abundant isotope of uranium, accounting for less than 1% of natural uranium. It has 92 protons and 143 neutrons in its nucleus. Unlike uranium-238, it is fissile, which means it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is used as fuel in nuclear reactors and as the primary material for nuclear weapons.
How are isotopes created?
- Isotopes can be created through natural processes or artificial processes in a laboratory.
- Isotopes are created through natural processes such as radioactive decay, cosmic ray interactions, and nuclear fusion reactions in stars.
- For example, carbon-14 is created in the Earth’s upper atmosphere when cosmic rays interact with nitrogen atoms.
- Isotopes can also be created artificially through nuclear reactions.
- This involves bombarding atoms with particles such as protons, neutrons, or alpha particles, which can change the number of protons and/or neutrons in the nucleus.
How uranium-241 was found?
- To find uranium-241, the researchers accelerated uranium-238 nuclei into plutonium-198 nuclei using the KEK Isotope Separation System (KISS).
- In a process called multinucleon transfer, the two isotopes exchanged protons and neutrons, resulting in nuclear fragments with different isotopes.
- The researchers identified uranium-241 and measured the mass of its nucleus using time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
- Theoretical calculations suggest that uranium-241 could have a half-life of 40 minutes.
Significance of the discovery
- The discovery is significant because it refines our understanding of nuclear physics, particularly the shapes of large nuclei of heavy elements and how often they occur.
- This information helps physicists to design models for nuclear power plants and exploding stars.
Also, what are Magic numbers?
- There is a particular interest in ‘magic number’ nuclei, which contain a certain number of protons or neutrons that result in a highly stable nucleus.
- Lead (82 protons) is the heaviest known ‘magic’ nucleus, and physicists have been trying to find the next element with magic numbers.
- The researchers hope to extend their systematic mass measurements towards many neutron-rich isotopes, at least to neutron number 152, where a new ‘magic number’ is expected.
Conclusion
- The discovery of the new neutron-rich uranium isotope is a major breakthrough in nuclear physics, as it provides essential information for understanding the behavior of heavy elements.
- The researchers’ aim to extend their measurements to other neutron-rich isotopes reflects their commitment to exploring the frontiers of nuclear science and to improve our understanding of the universe.
- Discovering new magic number nuclei through these measurements could have practical applications in designing safer and more efficient nuclear power plants and understanding the properties of exploding stars.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CR Rao
Mains level: Not Much

Central idea: Indian-American statistician Calyampudi Radhakrishna Rao has been awarded the 2023 International Prize in Statistics, which is considered the Nobel Prize for statistics. He is 102 YO.
Who is C. R. Rao?
- R. Rao, is an Indian-American mathematician and statistician.
- He is currently professor emeritus at Pennsylvania State University and Research Professor at the University at Buffalo.
- Rao has been honoured by numerous colloquia, honorary degrees, and festschrifts and was awarded the US National Medal of Science in 2002.
- The American Statistical Association has described him as “a living legend whose work has influenced not just statistics, but has had far reaching implications for fields as varied as economics, genetics, anthropology, geology, national planning, demography, biometry, and medicine.”
- The Times of India listed Rao as one of the top 10 Indian scientists of all time.
Rao’s Groundbreaking Paper
- The research paper, “Information and accuracy attainable in the estimation of statistical parameters,” was published in 1945 in the Bulletin of the Calcutta Mathematical Society.
- The paper provided a lower limit on the variance of an unbiased estimate for a finite sample, which has since become a cornerstone of mathematical statistics.
Key outcomes of his research
Rao’s 1945 paper has three outcomes-
- Cramer-Rao inequality: It provides a lower limit on the variance of an unbiased estimate for a finite sample.
- Rao-Blackwell Theorem: It provides a method to improve an estimate to an optimal estimate.
- Information geometry: It is a new interdisciplinary area called “information geometry,” which integrated principles from differential geometry into statistics, including the concepts of metric, distance, and measure.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PLFS and NSO data
Mains level: Poverty trends and estimates and issues
Central Idea
- The claim of poverty reduction in India during the pandemic year of 2020-21 is contested due to discrepancies in data and survey design. The PLFS data is used to make this claim, and there are recent papers that have come up with divergent claims on trends in poverty, showing both a rapid decline in poverty as well as a sharp increase.
Use of Comparable Estimates
- Poverty estimates in India have always been based on consumption estimates from the NSO, particularly based on the consumption expenditure surveys (CES).
- The last official poverty estimates were for 2011-12, even though a comparable consumption survey was conducted in 2017-18.
What is Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS)?
- PLFS is a large-scale household survey conducted by the National Statistical Office (NSO) of India.
- It collects data on various aspects of the labour force in India, including employment, unemployment, and labour force participation rates. In addition to these labour force indicators, the PLFS also collects data on consumption expenditure, which can be used to estimate poverty levels.
Issue with PLFS Data
- Estimates are not comparable: The PLFS estimates of poverty are not comparable with those from the CES, as the PLFS estimates are based on a single question.
- Consumption estimates: The issue of sensitivity of consumption estimates to survey design, the level of aggregation and details has been extensively written about and was at the heart of the Great Indian Poverty Debate of the early 2000s.
- Details about consumption expenditure is not just relevant: The sensitivity to the details of questions asked to collect consumption expenditure is not just relevant across different surveys but also across different rounds of the PLFS.
Poverty Trends
- The first set of conclusions can be drawn for the period between 2011-12 and 2017-18.
- Using the CES based full schedule and the leaked report for 2017-18, a rise in poverty can be seen.
- For a similar time period, the single question asked in the earlier rounds of PLFS can be compared with the 2014-15 (72nd round) NSO survey on services and durable goods expenditure which had exactly the same question in the same block with the same instructions making them comparable to estimates from the PLFS from 2017-18 to 2019-20.
- These suggest that the poverty headcount ratio was 27 per cent in 2014-15 and rose to 36 per cent in 2017-18, declining to 32 per cent in 2018-19 and remaining at that level in 2019-20.
- Unfortunately, for the period during the pandemic (2019-20 to 2020-21) that the PM paper tries to address, it is difficult to say what happened based on available consumption data because of the questionnaire changes mentioned above.
Impact on Policy
- The absence of official estimates on poverty is also a reflection of the lack of political priority of the government on such a crucial indicator.
- Currently, a survey on consumption expenditure is being canvassed by the NSO which again follows a completely new methodology and schedule. While it may provide another set of estimates of consumption expenditure, it is unlikely to help resolve the poverty debate.
Conclusion
- The issue of what happened to poverty after 2011-12 is crucial for policy. However, frequent interference in the statistical system through changes in survey and questionnaire design, suppression of data, and delaying the release of crucial data are making it difficult to have a correct assessment of reality. The absence of official estimates on poverty is a reflection of the lack of political priority of the government on such a crucial indicator.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Role of compassion in healthcare
Central Idea
- India’s rapid strides in health and healthcare with the help of a digital boom and the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, and the need for compassionate leadership to ensure respectful healthcare.
India’s healthcare sector
- India’s healthcare sector has shown improvement in multiple metrics due to the push for healthcare digitization, infrastructure, coverage, and other inputs.
- However, healthcare is not just about the treatment of diseases or the availability of infrastructure but also about the overall wellness of the person.
- Respectful healthcare that is available, affordable, accessible, and compassionate is a determinant of the quality of care.
Importance of Compassionate leadership
- Respectful and compassionate healthcare is essential: Healthcare is a perpetually evolving, stressful, and high-risk industry that puts a vast burden on healthcare providers. It is essential to navigate and manage the situation compassionately to deliver respectful care.
- Compassion is a beating heart if healthcare: Compassionate leadership is required to build this type of healthcare system, as it is the quiet, beating heart of the entire healthcare system.
Curriculum for compassionate healthcare
- Compassionate curriculum is very necessary: To integrate compassion into the healthcare system at every stage, it is necessary to build a curriculum and deliver it to those responsible for administering healthcare respectfully.
- Curriculum with Dalai Lama’s vision rolled out in Bihar: An eight-stage curriculum, developed by Emory University, that furthers the Dalai Lama’s vision of educating both heart and mind for the greater good of humanity is being rolled out in Bihar.
- Impact: To date, 1,200 healthcare providers across 20 districts have been impacted by the vital components of the cognitive-based compassion training, creating compassionate leaders at every level.
Institutionalizing compassionate healthcare
- Institutionalizing will bring in real change: While the curriculum is a quantum leap towards building compassionate leadership, institutionalizing it will bring in real change.
- Adopting at each level: Every academic institution and every department mandated with the responsibility to deliver health-related learning should develop and adopt compassion-based curricula.
- Building capacity: State and regional health institutions must also be built with the capacity to deliver compassionate leadership. Partnerships with established academia and development sector organizations can enable the organizing of master coaches and master facilitators, thereby creating public goods that can be delivered by all.
Strengthening internal systems
- Making compassion intrinsic to the ethos: All healthcare providers are expected to carry out a wide range of tasks within the system, which often leads to burnout and impacts patient experience adversely. It is vital to strengthen systems internally to make respect and compassion intrinsic to the ethos.
- Building a network: Building a network of compassionate practitioners in every state, district and block hospital is crucial to fan the winds of change by starting with self-compassion first and then moving to compassion for others.
- Valuing and measuring organizational culture: Valuing and measuring organizational culture is just as critical as patient outcomes. Developing sound metrics to measure culture and employee satisfaction, self-compassion, and compassion for the team assumes greater significance to building an institution whose foundation is compassion.
Conclusion
- Respectful healthcare is already mentioned in the National Health Mission (NHM) guidelines, and such guidelines need to be the warp and weft of every policy and every guideline developed by public health authorities to improve patient experience. Compassionate leadership can truly realize India’s historically known values of compassion and bring alive the words of Hippocrates, the father of medicine, “Wherever the art of medicine is loved, there is also a love of humanity”.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: China's attempts to use cartography as a weapon
Central Idea
- The Chinese leadership has been using cartographic deception as a weapon to violate the sovereign national boundaries of its neighbours, and India has been a victim of this deception since Independence. The recent rechristening of villages and areas in Arunachal Pradesh is another example of China’s cartographic deception, and India must remain vigilant against such tactics.
Background: India-China relations
- Historical context:
- India has been a victim of China’s deception since its independence.
- Mao’s Red Army sent messages to Indian Communists promising support in their violent liberation struggle to overthrow the government of Jawaharlal Nehru.
- In the early 1950s, China started staking claims to large parts of Indian territory.
- Cartographic deception used by China:
- Cartographic deception is integral to the Chinese leadership’s machinations.
- China has been indulging in cartographic deception by staking claims to large parts of Indian territory.
- The recent rechristening of villages and areas in Arunachal Pradesh by the Chinese cabinet is another example of that cartographic deception.
- Despite President Xi Jinping’s claims of standing guard over the world order based on international law, China continues to use cartography as a weapon to violate sovereign national boundaries of its neighbours.
How cartography is used as a weapon?
- Deliberate manipulation of maps: The term use of cartography as a weapon refers to the deliberate manipulation of maps for political and strategic purposes. This can involve drawing new borders or redefining existing borders, claiming territory that was previously not contested or that belonged to another country, and renaming places to support these claims.
- Psychological warfare technique: It is often accompanied by historical revisionism, propaganda, and the creation of artificial historical links to justify these claims. This approach can be seen as a form of psychological warfare, intended to create confusion, weaken the opponent’s resolve, and undermine its legitimacy in the eyes of the international community.
Historical background of Arunachal Pradesh
- No contact with China: Historically, Arunachal Pradesh had no contact with China, and there was never any Chinese presence there.
- Shimla Agreement: The McMahon Line, which became the international boundary between India and Tibet through the Shimla Agreement between the British and Tibetan governments in 1914, clearly puts Tawang, which fell south of the McMahon Line, out of Tibetan administrative control.
- Claims over Tawang: Attempts by pro-China historians to claim that parts of Western Arunachal Pradesh like Tawang were under the rule of Lhasa before 1950 are negated by historical records.
Chinese invasion of Arunachal Pradesh in 1962
- During the Chinese invasion of Arunachal Pradesh in 1962, they were extra-cordial with the locals and made special efforts to convince them about the greater racial affinity between them.
- However, despite all the deceptive maneuvers during the 49-day-long occupation, the Chinese could not win over the hearts and minds of the people of NEFA.
Conclusion
- India must remain vigilant against China’s cartographic deception, as it was through a similar deception in 1962 that China annexed territory. India has dismissed the recent rechristening exercise by China, and rightly emphasised that Arunachal Pradesh is, has been, and will always be an integral and inalienable part of India. India must continue to stand firm against China’s attempts to use cartography as a weapon to violate its sovereign national boundaries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cannabis , Marijuana, NDPS Act
Mains level: Legalizing marijuana

Himachal Pradesh CM has announced that the state government is considering legalizing the cultivation of cannabis.
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant used primarily for medical or recreational purposes.
- The main psychoactive component of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD).
- It is used by smoking, vaporizing, within the food, or as an extract.
Prospects of legalizing Marijuana
(1) Health benefits
- The cannabinoids found in Cannabis is a great healer and has found mentioned in Ayurveda.
- It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions like multiple sclerosis, arthritis, epilepsy, insomnia, HIV/AIDS treatment, and cancer.
(2) Ecological benefits
- The cannabis plant and seeds apart from being labelled a ‘super-foods’ as per studies is also a super-industrial carbon-negative raw material.
- Each part of the plant can be used for some industry. Hemp currently is also being used to make bio-fuel, bio-plastics and even construction material in certain countries. The cosmetic industry has also embraced Hemp seeds.
(3) Marijuana is addiction-free
- An epidemiological study showed that only 9% of those who use marijuana end up being clinically dependent on it.
- The ‘comparable rates’ for tobacco, alcohol and cocaine stood at 32%, 15% and 16% respectively.
(4) Good source of Revenue
- By legalizing and taxing marijuana, the government will stand to earn huge amounts of revenue that will otherwise go to the Italian and Israeli drug cartels.
- In an open letter to US President George Bush, around 500 economists, led by Nobel Prize winner Milton Friedman, called for marijuana to be “legal but taxed and regulated like other goods”.
(5) A potential cash crop
- The cannabis plant is something natural to India, especially the northern hilly regions. It has the potential of becoming a cash crop for poor marginal farmers.
- If proper research is done and the cultivation of marijuana encouraged at an official level, it can gradually become a source of income for poor people with small landholdings.
(6) Prohibition was ineffective
- In India, the consumption of synthetic drugs like cocaine has increased since marijuana was banned, while it has decreased in the US since it was legalized in certain states.
- Moreover, these days, it is pretty easy to buy marijuana in India and its consumption is widespread among the youth. So it is fair to say that prohibition has failed to curb the ‘problem’.
(7) Marijuana is less harmful
- Marijuana consumption was never regarded as a socially deviant behaviour any more than drinking alcohol was. In fact, keeping it legal was considered as an ‘enlightened view’.
- It is now medically proven that marijuana is less harmful than alcohol.
Risks of Legalizing Cannabis
(1) Health risks continue to persist
- There are many misconceptions about cannabis. First, it is not accurate that cannabis is harmless.
- Its immediate effects include impairments in memory and in mental processes, including ones that are critical for driving.
- Long-term use of cannabis may lead to the development of addiction of the substance, persistent cognitive deficits, and of mental health problems like schizophrenia, depression and anxiety.
- Exposure to cannabis in adolescence can alter brain development.
(2) A new ‘tobacco’ under casualization
- A second myth is that if cannabis is legalized and regulated, its harms can be minimized.
- With legalization comes commercialization. Cannabis is often incorrectly advertised as being “natural” and “healthier than alcohol and tobacco”.
- Tobacco, too, was initially touted as a natural and harmless plant that had been “safely” used in religious ceremonies for centuries.
(3) Unconvincing Advocacy
- Advocates for legalization rarely make a convincing case. To hear some supporters tell it, the drug cures all diseases while promoting creativity, open-mindedness, moral progression.
- Too much trivialization of Cannabis use could lead to its mass cultivation and a silent economy wreaking havoc through a new culture of substance abuse in India.
Legalization status elsewhere in India
- Several states in India have already legalized cannabis cultivation, including neighboring Uttarakhand, which became the first state in the country to do so in 2017.
- Controlled cultivation is being done in some districts of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh.
Legal Framework for Cannabis Cultivation
- Definition of Cannabis: The Parliament has defined cannabis in the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS), 1985.
- Ban on extracting resin and flowers: While a complete ban has been imposed on extracting the resin and flowers of the cannabis plant, the law determines the method and extent of cultivation of cannabis for medicinal and scientific purposes.
- Authorities to States: Section 10 (a) (iii) of the Act empowers States to make rules regarding the cultivation of any cannabis plant, production, possession, transport, consumption, use, purchase, sale, and consumption of cannabis (except charas).
- Cultivation of hemp: States are also empowered to permit, by general or special order, the cultivation of hemp, only for obtaining fibber or seeds or for horticultural purposes.
What next?
- The government will consider all aspects, including regulatory measures, and study the models followed by other States that have legalized cannabis cultivation, before taking the final call.
- Highlighted that the government is cautious about the potential increase in drug use, and will make a decision only after a thorough study by the committee.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TEMPO Mission
Mains level: Air Pollution monitoring

SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket successfully launched carrying a new NASA device named Tropospheric Emissions Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO) designed to monitor air pollutants and their emission sources across North America from space more comprehensively than ever before.
What is TEMPO?
- TEMPO is an instrument developed by NASA, which will enable scientists to monitor air pollutants and their emission sources from space, down to the neighbourhood level.
- This instrument will measure pollution and air quality across greater North America on an hourly basis during the daytime.
TEMPO’s special features
- TEMPO is unique because it will be hosted on an Intelsat communications satellite in geostationary orbit, about 22,236 miles (35,786 km) above the equator.
- This will allow the instrument to match the rotation of the Earth, meaning it will stay over the same location (North America) at all times.
- It will be able to measure atmospheric pollution down to a spatial resolution of 4 square miles (10 square km), or neighbourhood level.
Applications of TEMPO
- TEMPO will have multiple applications from measuring levels of various pollutants to providing air quality forecasts and helping the development of emission-control strategies.
- The data will be used by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and other agencies responsible for tackling atmospheric pollution.
Importance of the mission
- According to the American Lung Association, more than 40% of the US population, 137 million people, live in places with unhealthy levels of particle pollution or ozone, and air pollution is blamed for some 60,000 premature deaths a year.
- TEMPO will track pollutants like nitrogen dioxide, produced from the combustion of fossil fuels, formaldehyde, and ozone.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mera Gaon Mera Dharohar
Mains level: Not Much

Central idea: The government has identified and documented the unique cultural heritage of more than one lakh villages across the country under the National Mission for Cultural Mapping’s Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar programme.
Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar
- The National Mission for Cultural Mapping aims to develop a comprehensive database of art forms, artists, and other resources across the country.
- The programme was launched by the Culture Ministry in 2017 but was handed over to the Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts (IGNCA) in 2021.
- The programme aims to cover all the 6.5 lakh villages in the country.
Why such a program?
- The program seeks to document the cultural identity at the village level by involving citizens to share what makes their village, block, or district unique.
- The villages have been classified into seven-eight categories based on ecological, developmental, scholastic, historical, and mythological importance.
- The mapping aims to develop a comprehensive database of art forms, artists, and other resources across the country.
Survey process
- The survey process involves a CSC Village Level Entrepreneur (VLE) conducting meetings with locals and then uploading interesting facts about their village, its places of interest, customs and traditions, famous personalities, festivals and beliefs, art and culture, etc., on to a special application.
- The IGNCA plans to create special films on 6,500 village clusters showcasing their unique heritage.
- Short films have been made on 750 cluster villages, which have been shot using drones, and the VLEs would upload these videos on the application as well.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UN Statistical Commission
Mains level: Not Much
Central idea: India has been elected to the UN Statistical Commission for a four-year term.
About United Nations Statistical Commission
- The UN Statistical Commission is the topmost body of the global statistical system, bringing together the Chief Statisticians from member states worldwide.
- Responsibilities of the Commission include setting statistical standards and developing concepts and methods, implemented at national and international levels.
- The Commission was established in 1947 and is headquartered in New York.
- The United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) is overseen by the Commission.
- The Commission is a Functional Commission of the UN Economic and Social Council.
Membership details
- There are 24 member states of the Commission.
- Members are elected by the Economic and Social Council based on equitable geographical distribution, including:
- African States (5)
- Asian States (4)
- Eastern European States (4)
- Latin American and Caribbean States (4)
- Western European and other States (7)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Basic concepts
Mains level: RBI's pause on rate hikes, reasons and implications

Central Idea
- The RBI has decided to not increase the repo rate amid continuing hikes by important central banks such as the US Federal Reserve (Fed) and European Central Bank (ECB), and domestic inflation concerns. However, if incoming data point to rising inflation risks, this decision could prove to be only a pause in the rate hiking cycle.
- The RBI feels that money market rates have effectively risen more than the 250-basis-point yank in the repo rate since May 2022, and hence it decided to pause and assess the impact of rate hikes.
- The key reason behind the MPC decision is the expectation of a decline in inflation to 5.2% in the current fiscal, driven by a healthy rabi crop, normal monsoon, moderating international commodity prices, and the impact of rate hikes.
- The RBI acknowledges the upside risks and stated its readiness to fight any unexpected rise in inflation.
Impact on GDP growth
- The RBI expects GDP growth to slow to 6% from 7% this fiscal as slowing global growth, domestic interest rates, and messy geopolitics bite.
- Slowing global growth will be net negative for India’s exports, and the growing dependence on commodity exports makes India more vulnerable to global growth volatility.
- Fiscal 2024 will, therefore, test the resilience of India’s domestic demand amid rising interest rates.
Reasons for the expected cooling of consumer inflation
- Fuel inflation expected to reduce: Fuel inflation is expected to reduce to 3% from a high of over 10% in the current fiscal because some easing of crude oil prices is likely as global growth slows down.
- Decline in core inflation: Slowing domestic growth will ease core inflation from very sticky levels of over 6% last fiscal to 5.5% in the current one. However, the decline in core inflation will be limited as input cost pressures have not dissipated. To protect their margins, firms will continue to pass on input costs to end-consumer. Services inflation will also continue to exert pressure as the rotation of consumption demand from goods to services continues.
- Moderate food inflation: Food inflation, which has a high weightage in the Consumer Price Index and has driven headline inflation in the past, is projected to moderate to slightly below 5%, assuming a normal monsoon. However, food inflation has always been volatile and carries upside risks largely because of climate-related factors affecting agriculture output and prices.
How slowing global growth will have a negative impact on India’s exports?
- The impact of the growth slowdown in the US and Europe is deeper than the recovery in China: The US and Europe have a combined GDP that is twice that of China. Therefore, the impact of the growth slowdown in the US and Europe will be deeper than the recovery in China. This will have a negative impact on India’s exports to the US and Europe.
- India’s exports to the US and Europe are more than to China by a factor of six: India exports more to the US and Europe than to China by a factor of six. Therefore, the negative impact of the growth slowdown in the US and Europe will be felt more by India than by China.
- India’s growing dependence on commodity exports makes it more vulnerable to global growth volatility: India’s exports of petroleum products and steel are growing, and this makes India more vulnerable to global growth volatility. As global growth slows down, demand for commodities is likely to decline, which will have a negative impact on India’s exports.
External vulnerabilities
- India’s external vulnerability is expected to decline with a narrower current account deficit (CAD) and modest short-term external debt.
- The CAD is expected to narrow to 2% of GDP this fiscal from an estimated 2.5% last fiscal.
Conclusion
- The RBI’s decision to pause on rate hikes is driven by expectations of a decline in inflation. However, inflation risks remain, and the impact of rate hikes on GDP growth is expected to be significant. India’s external vulnerabilities are expected to decline, but the banking turmoil playing out amid interest rate hikes by important central banks and elevated debt levels remains a risk. The RBI’s decision to pause on rate hikes will be closely watched, and further rate hikes may be necessary if inflation risks persist.
Mains Question
Q. Enumerate the factors that led RBI to pause on rate hikes, and discuss the potential risks and impacts on the Indian economy?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: India- Bhutan border and trijunction
Mains level: India- Bhutan relationship

Central Idea
- India-Bhutan’s exemplary relationship has been a key factor in ensuring the stability and security of the region. The recent visit of Bhutan King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck to India was focused on enhancing the bilateral relationship between the two countries. However, the unspoken part of the visit was the Bhutan-China boundary talks, which have gained momentum in recent times.
- Special and strategic relationship: India and Bhutan share a special and strategic relationship with a border of over 600 km. The bond has been strengthened since India’s independence, and it has been a buffer between China and India.
- India is Bhutan’s largest development partner: The relationship is not limited to rhetoric but extends to an institutional and economic framework. India is Bhutan’s largest development partner, and Bhutan is India’s biggest trade partner in the region.
- Hydroelectricity, a crucial factor: Hydroelectricity has become the biggest revenue earner of Bhutan, and India buys power generated in Bhutan. It makes Bhutan the country with the highest per capita income in South Asia today.
- Historical and theological relations: Bhutan is a Buddhist theocracy, monarchy, and modern state. The relationship between India and Bhutan is special from a historical, theological, strategic, and economic perspective.
Bhutan-China Boundary Talks
- Considerable progress but no decision yet: Before the King’s visit to India, Bhutanese Prime Minister Lotay Tshering had said in an interview that Bhutan and China have made considerable progress on demarcating border lines. Bhutan has been having talks with China on the boundary question for years, and there has been no decision yet.
- There will be adjustment of territory: Bhutan and China are adopting a modern methodology to draw boundary lines on the ground, and there may be some adjustment of territory as a result of that.
- India’s strategic interests: India’s strategic interests are involved in the boundary talks between Bhutan and China. China has been seeking a toehold in Bhutan for decades. Bhutan is fully conscious of India’s strategic needs.
- Trijunction: Where Bhutan decides its boundary with China (to the west) is of exceptional relevance to India because that is a trijunction of the three countries.

India’s Strategic Interests
- No compromise on national security: India will not talk about Bhutan-China negotiations publicly; however, when it comes to India’s national security, there will be no compromise.
- Siliguri corridor: Doklam plateau overlooks the Chumbi Valley, which overlooks the chicken’s neck (Siliguri corridor). India says this not because Bhutan is threatening its cooperation with India on this front, but to send a message to China that we will draw a line here in conformity with our national interest.
Why India needs Bhutan?
- Strategic location: Bhutan is strategically located between India and China, which makes it an important buffer state for India. Bhutan’s strategic location ensures India’s security and helps in maintaining regional stability.
- Water resources: Bhutan is the source of several rivers that flow into India, including the Brahmaputra, the Sankosh, and the Manas. India needs access to these rivers for irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and other purposes. India has helped Bhutan in developing its hydropower potential and has signed several agreements for the purchase of hydropower from Bhutan.
- Trade and economic ties: India is Bhutan’s largest trading partner, and Bhutan relies heavily on India for its imports and exports. India provides Bhutan with various economic assistance and has helped Bhutan in its development process.
- Cultural and historical ties: India and Bhutan share a common cultural heritage and have historical ties dating back centuries. India has helped Bhutan preserve its cultural heritage and has supported Bhutan in its efforts to promote tourism.
Why Bhutan needs India?
- Security: Bhutan does not have a large army, and India provides security assistance to Bhutan. India has helped Bhutan in building its border infrastructure and has helped in the development of the Bhutanese army.
- Economic ties: India is Bhutan’s largest trading partner, and Bhutan relies heavily on India for its imports and exports. India provides economic assistance to Bhutan, and Indian companies have invested in various sectors in Bhutan.
- Infrastructure: India has helped Bhutan in building its infrastructure, including roads, airports, and telecommunication networks. India has also helped Bhutan in developing its hydropower potential, and several hydropower projects in Bhutan have been built with Indian assistance.
- Education and healthcare: India has helped Bhutan in the field of education and healthcare. Many Bhutanese students study in India, and India provides scholarships and grants to Bhutanese students. India has also helped Bhutan in building hospitals and providing medical assistance.
- Cultural and historical ties: Bhutan and India share a common cultural heritage and have historical ties dating back centuries. India has helped Bhutan in preserving its cultural heritage and has supported Bhutan in its efforts to promote tourism.
Future of India-Bhutan Relations
- The Bhutan-India relationship has survived because of spiritual underpinnings, geography, economy, and connectivity, all of which strengthen the relationship.
- India and Bhutan have survived mainly because it was built on mutual trust, which means Bhutan has equally driven the relationship. India should pursue this relationship with trust and complete faith.
- India must reach out to the new generation in Bhutan, which is being influenced by social media negativity and wrong information about India.
Conclusion
- The India-Bhutan relationship has been a key factor in ensuring the stability and security of the region. The relationship between the two countries has been built on mutual trust and has been strengthened by an institutional and economic framework. India’s strategic interests are involved in the boundary talks between Bhutan and China. India should pursue the relationship with trust and complete faith and should reach out to the new generation in Bhutan.
Mains Question
Q. Highlight the significance of the India-Bhutan relationship in ensuring regional stability and security? Discuss why India and Bhutan need each other?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Curriculum Framework (NCF)
Mains level: Not Much

The Ministry of Education has released a pre-draft version of National Curriculum Framework (NCF) for School Education.
National Curriculum Framework (NCF)
Features
|
Details
|
| What is it? |
A comprehensive framework for school education in India
Provides guidelines for the development of curricula and syllabi, textbooks, and teaching practices for schools in India |
| Developed by |
National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Education |
| Aim |
To promote a child-centred, activity-based approach to learning that focuses on the development of knowledge, skills, and values |
| Development |
The first NCF was developed in 1986 and subsequently revised in 2000 and 2005.
The latest pre-draft version of NCF for School Education was released by the Ministry of Education in April 2023. |
| Coverage |
For age groups 3 to 18 years
Seeks feedback from various stakeholders |
| National Steering Committee |
Set up by the Ministry to undertake and develop NCFs under the chairmanship of K. Kasturirangan. |
Salient features of NCF
(1) Values and Roots
- A key part of the document is the inclusion of values and its “rootedness” in India.
- The pre-draft says that the framework is deeply rooted in India in content and learning of languages, in the pedagogical approaches including tools and resources, and in philosophical basis — in the aims and in the epistemic approach.
- The document further says that it leans towards making students acquainted with true sources of knowledge, which have been a philosophical preoccupation of ancient Indians.
- These sources focus on six pramanas: pratyaksa, anumana, upamana, arthapatti, anupalabdhi, and sabda.
Six Pramanas
1. Pratyaksha: Interpreted as perception through the five senses
2. Anumana: Uses inferences to come to new conclusions
3. Upamana: Knowing through analogy and comparison
4. Arthapatti: Involves knowing through circumstantial implication
5. Anupalabdhi: Includes perception of non-existence
6. Sabda: Something an individual can only directly know a fraction of all reality through direct experience and inference but must rely on other experts was acknowledged thousands of years ago |
(2) Moral Development
- A part of the document focuses on the moral development of a child through panchakosha vikas or five-fold development.
- The pre-draft recommends developing moral values for the child through a balanced diet, traditional games, yoga asanas, as well as a wide variety of stories, songs, lullabies, poems, and prayers to develop a love for cultural context.
(3) Curriculum revamp
- The pre-draft says that for Grade 10 certification, students will have to take two essential courses from humanities, maths and computing, vocational education, physical education, arts education, social science, science, and interdisciplinary areas.
- In Grade 11 and 12, students will be offered choice-based courses in the same disciplines for more rigorous engagement.
- Arts education will include music, dance, theatre, sculpture, painting, set design, scriptwriting, while interdisciplinary areas will include knowledge of India, traditions, and practices of Indian knowledge systems.
- For Class 11 and 12, the document states that “Modular Board Exams will be offered as opposed to a single exam at the end of the year, and the final result will be based on the cumulative result of each exam.”
- The framework of the social science curriculum emphasizes understanding and appreciating the feeling of Indianess, ‘bhartiyata,’ by valuing the rich cultural heritage and tradition of the country.
- It also stresses on identifying and explaining important phases of the Indian national movement against British rule, with special reference to Gandhian and other subaltern movements.
(4) Social Science Curriculum
- The pre-draft emphasizes understanding and appreciating the feeling of Indianess, “bhartiyata,” by valuing the rich cultural heritage and tradition of the country.
- The pre-draft also stresses on identifying and explaining important phases of the Indian national movement against British rule, with special reference to Gandhian and other subaltern movements.
- It also recommends teaching concepts of Buddhism, Jainism, and Vedic and Confucian philosophies.
(5) Follow-up processes
- As a follow-up to the National Education Policy 2020, development of four National Curriculum Frameworks — NCF for School Education, NCF for Early Childhood Care and Education, NCF for Teacher Education, and NCF for Adult Education — have been initiated.
- The National Steering Committee under the chairmanship of K. Kasturirangan was set up by the Ministry to undertake and develop NCFs.
Controversy over curriculum revamp
- The latest round of textbook rationalisation has resulted in some of the most sweeping changes in the curriculum since the NDA government came to power.
- These changes include removing all references to the 2002 Gujarat riots, reducing content related to the Mughal era and the caste system, and dropping chapters on protests and social movements.
- Many of these changes are seen as ‘political’, however, their earlier introduction into curriculum was also a political move.
The furore over Mughal History
- While some of the content on the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire has indeed been removed from the history textbook for Class 7, the Mughals have not entirely disappeared.
- For instance, the chapter ‘The Mughal Empire’ in the Class 7 history textbook, Our Pasts – II, has undergone deletions — including a two-page table on the milestones and achievements of the reigns of the emperors Babur, Humayun, Akbar, Jahangir, Shah Jahan, and Aurangzeb.
- However, the chapter itself has not been removed.
- Students of Class 7 will continue to learn about the Mughals, though in lesser detail.
Significance
- School textbooks have always been seen as playing a crucial role in shaping national narratives, and as a tool for cultivating a desired national identity.
- NCERT textbooks are read by more than 5 crore students in 18 states around the country, who are seen by political parties as a large captive audience with impressionable minds.
- It’s not just school students either — candidates preparing for competitive exams such as the Civil Services Examination, SSC, JEE, and NEET, also rely on these textbooks.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indian Space Policy, 2023
Mains level: Not Much
Central idea: The Union Cabinet has approved the Indian Space Policy, 2023.
Indian Space Policy, 2023
- It aims to enhance the role of the Department of Space, boost the activities of ISRO missions, and encourage participation from research, academia, startups, and industry.
Salient features
(1) Outlining roles and responsibilities
- The Indian Space Policy, 2023 outlines the roles and responsibilities of various organizations in the space sector.
- The policy includes the responsibilities of ISRO, NewSpace India Limited, and private sector entities.
- This clarity in roles will help in the efficient functioning of the components set up in recent times.
(2) Multistakeholder participation
- The policy aims to boost the space sector by enhancing the role of the Department of Space and encouraging participation from research, academia, startups, and industry.
- This will help in the development of the space segment and create more opportunities for the private sector.
(3) Boosting ISRO Missions
- The Indian Space Policy, 2023 aims to boost the activities of ISRO missions.
- This will help ISRO achieve its objectives more efficiently and effectively.
- It will also help in the development of new technologies and innovative solutions.
(4) Involvement of Private Sector
- The Policy, 2023 recognizes the importance of the private sector in the development of the space sector.
- It encourages the involvement of private sector entities in various aspects of the space segment.
- This will create more opportunities for the private sector and help in the growth of the Indian space industry.
(5) Research and development
- The policy aims to involve research, academia, and startups in the development of the space sector.
- This will help in the development of new technologies, innovative solutions, and talent pool.
- It will also help in the growth of the Indian space industry and create more opportunities for research and development in the sector.
Conclusion
- The Indian Space Policy, 2023 is a comprehensive policy that provides clarity in the roles and responsibilities of various organizations in the space sector.
- The policy aims to boost the space segment, encourage private sector involvement, and involve research, academia, and startups in the development of the sector.
- The policy will help in achieving the objectives of ISRO more efficiently and effectively, and create more opportunities for the private sector and research and development in the space sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Natural Justice, Proportionality
Mains level: Freedom of press

Central idea
A quick recap of the case
- The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB) has earlier refused to renew broadcast license of a Malayalam news channel.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs had declined to grant security clearance to the channel’s promoters citing alleged links between radical groups.
- Hence the news agency approached Kerala High Court, which upheld the ban on February 9, 2022
- The Supreme Court granted temporary relief and allowed it to resume operations.
Supreme Court’s ruling
- The Supreme Court set aside earlier ban orders and upheld the channel’s appeal on two procedural grounds, namely
- Principles of natural justice and
- Proportionality
Articles invoked in the judgment
- The Court stated that the burden shifts on the Centre to prove that the procedure followed was reasonable and in compliance with the requirements of Articles 14 and 21 of the Constitution.
- The Court used the standard of proportionality to test the reasonableness of the procedure in the present case and assessed the validity of public interest immunity claims based on the “structured proportionality standard”.
- The Court found that the reasons for denying security clearance to the channel were not legitimate purposes for the restriction of the right of freedom of speech protected under Article 19(1)(a) of the Constitution.
Key concepts involved
(1) Principles of natural justice
- The principles of natural justice are a set of procedural rules that ensure fairness and justice in administrative and legal proceedings.
- These principles are based on the fundamental idea that everyone is entitled to a fair hearing, and they are aimed at preventing arbitrary or biased decisions by decision-makers.
- The SC bench allowed the challenge to the MHA order and judgment of the High Court on account of the principles of natural justice constitutionalized by its judgment in its 1978 ruling in “Maneka Gandhi vs Union of India”
- Actions which violate procedural guarantees can be struck down even if non-compliance does not prejudice the outcome of the case.
(2) Proportionality
- The principle requires that the decision or action must be proportionate to the objective it seeks to achieve.
- In other words, the means employed to achieve the objective must be no more than necessary to achieve it, and the harm caused by the decision or action must not be excessive in relation to the benefit gained.
- The validity of the claim of involvement of national security considerations must be assessed on the test of whether there is material to conclude that the non-disclosure of information is in the interest of national security.
- Courts can assess the validity of public interest immunity claims based on the “structured proportionality standard”, said the SC.
- The SC observed that sealed cover proceedings infringe the principles natural justice and open justice.
Conclusion
- The Court’s ruling has been welcomed by media organizations and civil society groups as a victory for freedom of speech and expression
- The Court observed that the duty to act fairly derived from common law is not exhaustively defined in a set of concrete principles, and the concept of natural justice “cannot be put into a ‘straitjacket formula’.
- The ruling has been hailed as a victory for freedom of speech and expression, and a blow to attempts to stifle dissent and critical voices in the media.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now















