Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Civil Aviation Safety Advisory Council, DGCA and other related departments and mandates
Mains level: Aviation sector, safety concerns and reforms

Central idea
- In 2010, a tragic accident at Mangalore airport claimed the lives of 158 people. Despite prior warnings and PILs filed by the Environment Support Group, the concerned authorities neglected to address safety concerns regarding the airport’s second runway. It highlights the lack of accountability and transparency in the system, the failure to learn from past accidents, and the urgent need for reforms in India’s aviation sector.
Background
- In 1997, the Environment Support Group raised concerns about the inadequacy of Mangalore airport’s second runway during emergencies. However, the PIL filed by the NGO was dismissed by the Karnataka High Court.
- In 2002, another PIL emphasized the potential dangers of the runway, but it faced the same fate. Dissatisfied with the verdict, the group approached the Supreme Court, which ruled that the government must adhere to applicable laws and environmental norms during airport construction
- Following the Mangalore crash, the Ministry of Civil Aviation established the Civil Aviation Safety Advisory Council (CASAC) to identify deficiencies and propose corrective measures.
- CASAC pointed out the court of inquiry’s failure to identify critical errors and suggested improvements, particularly at airports like Mangalore and Calicut. However, their warnings were disregarded by the Ministry and the DGCA.
- The subsequent accident at Calicut on August 7, 2020, claiming 21 lives, further exposed the disregard for safety concerns.
- The recommendations made by the committee formed after the accident remain unimplemented due to prioritizing commercial interests over safety.
Lessons ignored
- Neglecting Compliance with Laws and Norms: Government agencies responsible for airport construction failed to comply with applicable laws and environmental norms, as mandated by the Supreme Court. This negligence resulted in violations that ultimately led to the tragic crash.
- Dismissing Expert Opinions: The Supreme Court’s dismissal of the PIL that highlighted the violations and safety concerns surrounding Mangalore airport indicates a reluctance to hold government agencies accountable. The judiciary’s unwillingness to intervene despite expert opinions undermined the pursuit of justice and prevention of future accidents.
- Lack of Accountability: The blame for accidents was often placed solely on pilots, while the systemic deficiencies and regulatory failures were overlooked. The absence of accountability within the aviation sector perpetuated a culture of negligence and hindered efforts to address underlying safety issues.
- Failure in Accident Investigations: The investigations conducted by the DGCA and AAIB failed to identify the root causes of accidents and provide effective preventive measures. Instead of rectifying systemic shortcomings, investigations often resorted to blaming pilot error, leaving the real issues unresolved.
- Neglecting Recommendations: The warnings and recommendations put forth by the Civil Aviation Safety Advisory Council (CASAC) were disregarded by the Ministry of Civil Aviation and the DGCA. The failure to implement necessary safety measures, such as Runway End Safety Areas (RESA), despite expert advice, highlights a disregard for passenger safety.
- Prioritizing Commercial Interests: Commercial interests were given precedence over safety considerations, as implementing certain safety measures would have affected the runway length and payload. This compromise on safety standards underscores the need to prioritize the well-being of passengers over commercial gains.
Role and responsibilities of Civil Aviation Safety Advisory Council (CASAC)
- Identify Deficiencies: CASAC is tasked with identifying deficiencies in safety measures, regulations, infrastructure, and operational practices across airports, airlines, and regulatory bodies. It conducts thorough assessments and inspections to pinpoint areas where safety standards may be compromised.
- Provide Recommendations: Based on its assessments, CASAC formulates recommendations and proposes corrective measures to address the identified deficiencies. These recommendations cover a wide range of aspects, including operational procedures, infrastructure improvements, training programs, safety audits, and regulatory enhancements.
- Review Reports and Investigations: CASAC reviews accident investigation reports and court of inquiry findings related to aviation accidents and incidents. It examines these reports to determine if proper root cause analysis has been conducted and if adequate preventive measures have been recommended. CASAC ensures that critical errors or safety gaps are identified and addressed in the reports.
- Advise on Safety Enhancements: CASAC advises the Ministry of Civil Aviation on safety enhancements, both immediate and long-term. It provides guidance on the implementation of best practices, industry standards, and international safety protocols. CASAC’s recommendations aim to improve safety outcomes and minimize risks within the aviation sector.
- Monitor Compliance: CASAC monitors the compliance of airports, airlines, and regulatory bodies with recommended safety measures and regulations. It reviews progress reports submitted by stakeholders to assess their adherence to the proposed corrective actions. This monitoring function ensures that safety improvements are implemented effectively.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: CASAC collaborates with various stakeholders in the aviation industry, including airlines, airports, regulatory bodies, industry experts, and international organizations. It engages in discussions, knowledge-sharing, and cooperative initiatives to promote a collective approach to aviation safety.
- Continuous Evaluation: CASAC conducts periodic evaluations and reviews of the aviation sector’s safety performance. It assesses the effectiveness of implemented safety measures, identifies emerging safety concerns, and recommends adjustments or additional measures as required.
Way ahead: The Need for Urgent Action in the aviation sector
- Regulatory Reforms: Initiate comprehensive regulatory reforms to strengthen oversight and enforcement mechanisms. This includes enhancing the authority, capabilities, and resources of regulatory bodies like the DGCA to effectively monitor compliance with safety regulations.
- Transparent and Independent Investigations: Establish an independent and transparent accident investigation process that identifies root causes without bias or external influence. This will enable the implementation of effective preventive measures and foster a culture of learning from past incidents.
- Safety Management Systems: Promote the adoption of Safety Management Systems (SMS) by airlines and airports. An SMS provides a systematic approach to identifying and managing safety risks, ensuring proactive safety measures are in place, and promoting continuous improvement.
- Robust Training and Human Factors Programs: Enhance training programs for aviation personnel, including pilots, air traffic controllers, and maintenance staff, focusing on areas such as emergency procedures, risk management, and human factors. Emphasize the importance of fatigue management and mental well-being to mitigate human error.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Invest in upgrading and modernizing airport infrastructure, including runways, taxiways, and air traffic control systems. Ensure compliance with international safety standards and implement necessary enhancements to address deficiencies.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Foster collaboration and information sharing among industry stakeholders, including airlines, airports, regulators, and international aviation organizations. Establish platforms for regular communication and exchange of best practices to drive collective efforts towards improved safety.
- Accountability and Transparency: Strengthen accountability mechanisms to ensure that responsible individuals and entities are held liable for safety lapses. Foster a culture of transparency, where safety-related information is shared openly, and reporting systems protect whistleblowers.
- Public Awareness and Passenger Education: Increase public awareness about aviation safety and passenger rights through education campaigns. Empower passengers to make informed decisions regarding safety when choosing airlines and demand transparency from regulatory bodies.
Conclusion
- The Mangalore airport crash and subsequent incidents have shed light on the critical need for comprehensive reforms in the aviation sector to ensure the safety of passengers and personnel. The establishment of the CASAC was a step in the right direction. However, to achieve a safer aviation environment it requires collective efforts, commitment, and ongoing vigilance to prevent accidents, learn from past incidents, and ensure the well-being of passengers and personnel in the skies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024 | Schedule your FREE session and get the Prelims prep Toolkit!
Also read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ice-albedo feedback cycle, Climate change, global sea rise
Mains level: Decline in Antarctic sea ice, global sea rise and impact on weather patters, Need of immediate actions

Central Idea
- The recent record-breaking drop in Antarctic Sea ice extent on February 19 has raised significant concerns about the impacts of global warming. This worrying trend, accompanied by rising global temperatures, poses a threat to coastal cities and has far-reaching consequences for weather patterns and underwater ecosystems. As sea ice continues to melt and global sea levels rise, urgent action is needed to address the environmental challenges presented by this alarming decline.
Melting Sea Ice and Rising Sea Levels: A worrying trend
- Over the past six years, the Antarctic Sea ice cover has witnessed substantial declines, resulting in a rise in global sea levels.
- NASA reports that meltwater from Antarctic ice accounts for approximately one-third of the global average sea level rise since 1993.
- The sea ice extent in 2023 has often been notably lower than the levels seen in 2022, which had the second-lowest summer sea ice extent in Antarctica.
- The Antarctic Sea ice extent as of May 21, 2023, has significantly shrunk compared to the median extent between 1981 and 2010
- The April temperature in the Antarctic region in 2023 was 0.93°C higher than the 1910-2000 average for that month, marking the second-highest increase in the millennium.

Impact decline in Antarctic Sea ice on Global Weather and Ecosystems
- Weather Pattern Alterations: The Southern Ocean, surrounding Antarctica, plays a crucial role in transferring heat from the atmosphere to the global oceans. Increased melting of Antarctic sea ice introduces cold, fresh water into the ocean, disrupting the circulation patterns of hot, cold, fresh, and salty water globally. This alteration in temperature and density can subsequently affect weather patterns, including wind patterns, precipitation, and storm formation.
- Oceanic Currents and Nutrient Flows: Changes in water temperature and density due to melting sea ice can disrupt oceanic currents and nutrient flows. These currents are vital for distributing heat, nutrients, and oxygen across the world’s oceans. The disturbance in these flows can have cascading effects on marine ecosystems, impacting the distribution and availability of nutrients for various organisms.
- Impact on Underwater Ecosystems: Sea ice serves as a critical habitat for various organisms, including algae, krill, and other marine life. Diminishing sea ice reduces the availability of food and alters the feeding patterns and reproductive cycles of species dependent on these ecosystems. This disruption can have significant consequences for the entire Antarctic food chain, affecting species such as whales, seals, penguins, and seabirds.
- Altered Albedo Effect: The decline in sea ice coverage reduces the Earth’s albedo effect. Albedo refers to the ability of a surface to reflect sunlight back into space. Sea ice has a high albedo, meaning it reflects a significant portion of incoming solar radiation. As sea ice diminishes, darker ocean water absorbs more solar radiation, leading to increased warming and amplifying the overall warming trend.
- Feedback Loops: The impacts of melting sea ice create feedback loops that exacerbate the effects of climate change. For example, as sea ice melts, more heat is absorbed by the ocean, further accelerating the melting process. These feedback loops contribute to the amplification of warming trends and the intensification of associated environmental changes.
Facts for prelims
What is ice-albedo feedback cycle?
- The ice-albedo feedback cycle, also known as the snow-ice albedo feedback, refers to a positive feedback mechanism that amplifies the effects of global warming. It involves the interaction between ice or snow cover and solar radiation.
- The albedo of a surface refers to its ability to reflect sunlight. Ice and snow have high albedo values, meaning they reflect a significant portion of incoming solar radiation back into space.
- This reflection helps to cool the Earth’s surface. However, when ice or snow melts, it reveals darker surfaces beneath, such as dark ocean water or land, which have lower albedo values. These darker surfaces absorb more solar radiation, leading to increased warming
- The ice-albedo feedback cycle operates in both polar regions, but it is particularly significant in the Arctic and Antarctic regions, where extensive ice and snow cover exist.
- The reduction in sea ice extent and the melting of glaciers and ice sheets contribute to this feedback mechanism, accelerating the warming trend and exacerbating the impacts of climate change.
Understand this way: How do the ice-albedo feedback cycle operate?
- Initial Warming: Due to various factors, including greenhouse gas emissions, the Earth’s temperature increases, leading to the melting of ice and snow cover.
- Reduced Albedo: As ice and snow melt, the reflective white surface is replaced by darker surfaces with lower albedo values. These surfaces absorb more solar radiation rather than reflecting it back into space.
- Increased Heating: The absorption of more solar radiation by darker surfaces results in increased heating of the Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
- Further Melting: The increased heating leads to more melting of ice and snow, further reducing the overall ice and snow cover.
- Amplification of Warming: With less ice and snow cover, more heat is absorbed, contributing to a positive feedback loop. The amplified warming results in further ice and snow melt, creating a cycle of increasing temperatures.
|
Impact of Rising Sea Levels on coastal communities around the worldwide
- Increased Flooding and Erosion: As sea levels rise, coastal areas are more susceptible to storm surges, high tides, and extreme weather events. This puts low-lying regions, including coastal cities and communities, at greater risk of inundation, property damage, and displacement of residents.
- Coastal Infrastructure Vulnerability: Increased flooding and erosion can lead to the degradation and loss of critical infrastructure, disrupting transportation, energy supply, and essential services. This vulnerability can have substantial economic, social, and public safety implications.
- Threat to Freshwater Resources: Rising sea levels can infiltrate freshwater sources and contaminate underground aquifers, particularly in coastal regions where freshwater and saltwater interfaces occur. This intrusion of saltwater can compromise drinking water supplies, agricultural irrigation, and ecosystems dependent on freshwater resources, exacerbating water scarcity issues.
- Displacement of Communities: As coastal areas become uninhabitable due to sea-level rise and increased flooding, communities may face the prospect of forced relocation. This displacement can result in the loss of homes, cultural heritage, and livelihoods, leading to social disruption, economic challenges, and psychological impacts on affected populations.
- Ecological Impacts: Coastal ecosystems, including mangroves, coral reefs, and wetlands, provide critical habitats, buffer against storms, and support biodiversity. Rising sea levels can inundate and degrade these ecosystems, leading to the loss of valuable ecological services, increased vulnerability to coastal hazards, and reduced coastal resilience.
- Economic Consequences: The impacts of sea-level rise and coastal flooding can disrupt tourism, fishing, and shipping industries, leading to economic losses, job displacements, and decreased productivity. Additionally, the costs of coastal protection measures and infrastructure adaptations to rising sea levels can place a significant burden on local economies and governments.
Way Forward
- Strengthening International Cooperation: Collaborate at global forums to address climate change and its impact on Antarctica, emphasizing the need for reduced emissions and sustainable practices.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Research: Invest in further research to understand the dynamics of melting sea ice, its impact on ecosystems, and potential mitigation strategies.
- Promoting Sustainable Practices: Encourage sustainable practices and responsible tourism in the Antarctic region to minimize human impact on the fragile ecosystem.
- Climate Resilience Planning: Develop robust climate resilience plans for coastal cities and communities, considering rising sea levels and potential threats posed by diminishing sea ice.
- Raising Public Awareness: Educate the public about the consequences of melting Antarctic sea ice, fostering a collective sense of responsibility and encouraging individual actions to mitigate climate change.
Conclusion
- The alarming decline in Antarctic sea ice poses grave threats to global sea levels, weather patterns, and underwater ecosystems. Urgent action is required to mitigate climate change, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote sustainable practices. Through international collaboration, research, and public awareness, we can strive to protect the Antarctic region and safeguard coastal communities worldwide from the impacts of melting sea ice. The time to act is now, as the consequences of inaction will be felt by future generations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024 | Schedule your FREE session and get the Prelims prep Toolkit!
Must read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Diversification of religion and caste in contemporary India, new dynamics, challenges and way forrward

Central Idea
- The recent outcome of the Karnataka elections provides an opportunity to broaden our understanding of religion and caste as categories of identity and belief. It is essential to recognize that these identities go beyond mere labels and hold pan-India significance. Amidst the rapid urbanization of Gurugram, the interplay of technology, finance, infrastructure, and land markets has brought about intriguing effects on traditional aspects of life. Notably, the strengthening of caste and religious identities has occurred alongside the transformation of the local landscape
Contemporary dynamics of the religion and caste in society
- Social Media: The emergence and widespread use of social media platforms have significantly influenced the dissemination of information and the expression. Social media platforms have provided individuals with new avenues to express their beliefs, connect with like-minded individuals, and engage in discussions and debates related to religion and caste.
- Leisure Cultures: Changing patterns of leisure activities and cultural practices have contributed to the reshaping of religious and caste identities. The ways in which people engage with leisure, entertainment, and cultural events often intersect with their religious and caste affiliations. These leisure cultures can reinforce existing identities, foster a sense of community, and contribute to the preservation and celebration of religious and caste traditions.
- Globalization of Identities: The increased mobility, migration, and transnational interactions have allowed for the transmission and adoption of religious and caste practices, beliefs, and ideologies across different geographical locations. This globalization of identities has influenced how individuals perceive and express their religious and caste affiliations.
- Emphasis on Heritage: The promotion and celebration of cultural heritage, rituals, and customs have become significant aspects of identity formation and community building. This focus on heritage can reinforce religious and caste affiliations and contribute to the preservation of traditional practices.
Complexities of contemporary identities
- Intersectionality: Contemporary identities are often multifaceted and intersectional, encompassing multiple dimensions such as gender, class, religion, caste, and regional affiliations. Individuals’ identities are shaped by the interaction of these diverse factors, leading to complex experiences and perspectives.
- For example: In the context of Gurugram, caste identities intersect with the effects of urbanization, globalization, and economic transformations, creating intricate social dynamics.
- Shifting Meanings: The meanings attached to religious and caste identities have evolved over time. Globalization, technology, and changing social norms have influenced the ways in which individuals understand and express their religious and caste affiliations. These shifting meanings challenge traditional understandings and necessitate a deeper exploration of the contemporary dynamics surrounding religion and caste.
- Hybridity and Adaptation: As individuals navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing world, they might combine elements of their religious and caste backgrounds with new cultural practices, beliefs, and expressions. This hybridity reflects the fluid nature of contemporary identities and the ways in which individuals negotiate their sense of self within evolving social contexts.
- Global Influences: Increased exposure to diverse cultural and religious influences from around the world can impact individuals’ beliefs, practices, and self-perception. This global exchange of ideas and cultural practices contributes to the complexities of contemporary identities, blurring traditional boundaries and fostering new forms of identity expression.
- Individual Agency: Contemporary identities are influenced by individual agency, as individuals actively construct and negotiate their own sense of self and belonging. People have the autonomy to choose, reinterpret, or reject religious and caste identities based on their personal experiences, beliefs, and aspirations. This individual agency adds complexity to the understanding of contemporary identities and challenges rigid categorizations.
Why religious and caste sentiments thrive despite the seemingly impersonal nature of modern relations?
- Historical Significance: Religion and caste have deep historical roots in India, shaping the social, cultural, and political fabric of the country for centuries. These identities have been intricately woven into people’s lives and community structures, and their significance continues to endure even in the face of modernization. Historical legacies and the sense of identity associated with religion and caste contribute to the persistence of these sentiments.
- Social Cohesion and Belonging: Religion and caste provide individuals with a sense of belonging and community. They offer a framework for social cohesion, providing a sense of identity, support, and solidarity. In an increasingly fragmented and individualistic society, religious and caste affiliations can offer a sense of belongingness and a support system that individuals seek for social integration and a sense of purpose.
- Cultural Identity and Tradition: Religion and caste are deeply intertwined with cultural practices, rituals, and traditions which provide individuals with a connection to their cultural heritage and a sense of continuity with their ancestors.
- Social Networks and Support: Religious and caste communities network foster a sense of mutual aid and communal bonds, creating a support system that individuals rely on in times of need. This social support and network-based assistance further reinforce the importance of religious and caste identities.
- Political and Power Dynamics: Religion and caste continue to play a significant role in political mobilization, electoral strategies, and the distribution of resources and benefits. Political parties often exploit religious and caste identities for electoral gains, further reinforcing their salience and significance in public discourse.
Why the newly emerging religious identities sometimes manifest as hostility towards those of different faiths?
- Identity Assertion: The formation of new religious identities can be driven by a desire to assert and strengthen one’s own religious beliefs and practices. In some cases, this assertion may result in a sense of exclusivity and superiority, leading to hostility towards those who hold different beliefs. Individuals may perceive their newly emerging religious identity as being under threat from other faiths, and this defensive response can contribute to animosity and hostility.
- Socialization and Group Dynamics: If individuals are surrounded by like-minded individuals who reinforce a particular narrative of their religious identity, it can lead to the development of a group mentality that views other faiths with suspicion or hostility. Group dynamics, such as peer pressure, conformity, and the need for social acceptance, can further amplify negative attitudes towards different faiths.
- Perceived Threats and Insecurity: When new religious identities emerge, followers may perceive threats to their beliefs, traditions, or cultural practices from other faiths or societal changes. This perceived threat can evoke a defensive response, fueling hostility towards those seen as posing a challenge to their newly formed religious identity.
- Political Instrumentalization: Political actors may exploit religious sentiments and manipulate the narrative to gain support or advance their agenda. This instrumentalization can create an us versus them mentality, deepening divisions and fostering animosity towards religious groups perceived as adversaries.
- Economic Competition and Social Hierarchies: Economic disparities and perceived inequalities can fuel resentment towards religious groups seen as benefiting disproportionately or hindering one’s own economic advancement. This can result in the projection of animosity onto religious differences.
- Lack of Interfaith Dialogue and Understanding: Insufficient opportunities for interfaith dialogue and understanding can contribute to the persistence of hostility between religious communities. Limited interactions and communication between followers of different faiths may perpetuate stereotypes, misunderstandings, and a lack of empathy. Without platforms for open dialogue and mutual respect, tensions can escalate, leading to hostility.
Way forward: Adopting a forward-looking approach
- Contextual Understanding: Instead of relying solely on historical perspectives, it is crucial to engage with the complexities of the present. This involves analyzing the influence of social media, new leisure cultures, globalization of caste and religious identities, the politics of heritage, and the rise of consumer culture.
- Critical Questions: To address the contemporary manifestations of religious and caste identities, we need to ask fundamental questions. For instance, we must explore why religious and caste feelings gather strength despite the apparent prevalence of impersonal relations in a world organized through contracts and other similar mechanisms.
- Contemporary Relevance: The explanations regarding religious identity and caste should be grounded in the present rather than relying solely on the perspectives of historical figures like Gandhi and Ambedkar. While acknowledging their important contributions, we need to apply their vantage points to analyze and understand the contemporary realities.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Addressing the complexities of caste and religious identities requires an interdisciplinary approach that combines insights from sociology, anthropology, history, political science, and cultural studies, among other disciplines. By bringing together diverse perspectives, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted nature of these identities and their implications for contemporary society.
- Dialogue and Empathy: Encouraging interfaith dialogue, promoting understanding, and fostering empathy are crucial steps towards mitigating hostility and building bridges between different religious communities. Creating platforms for open and respectful discussions can help dispel stereotypes, bridge gaps in understanding, and promote mutual respect.
- Evolving Definitions: Given the altered meanings of caste and religion in a rapidly changing society, it is important to continuously reassess and redefine these concepts. By recognizing the shifting dynamics and meanings associated with caste and religion, we can develop more nuanced perspectives that align with the contemporary reality.
Conclusion
- As we witness the diversification of religion and caste in contemporary India, it is imperative to embrace a nuanced understanding that moves beyond historical interpretations. Recognizing the multifaceted factors influencing modern identities and the complexities of the present allows for a more comprehensive analysis. By exploring the contemporary dynamics and asking pertinent questions, we can better comprehend the changing meanings of religion and caste in today’s society and address the challenges and opportunities they present.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024 | Schedule your FREE session and get the Prelims prep Toolkit!
Also read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: FIPIC
Mains level: Large Ocean Countries

Central Idea: The third summit of Forum for India Pacific Islands Cooperation (FIPIC) was recently held at Port Moresby in Papua New Guinea. It was attended by PM Modi.

What is FIPIC?
- The FIPIC is an intergovernmental forum that facilitates cooperation and dialogue between India and the Pacific island countries (PIC).
- It was established by India in 2014 as a platform to enhance engagement and strengthen ties with the countries of the Pacific region.
- FIPIC serves as a mechanism for mutual collaboration, addressing shared challenges, and promoting development cooperation between India and its Pacific island partners.
Members of FIPIC:
- FIPIC consists of 14 member-countries.
- They are- Fiji, Cook Islands, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Nauru, Niue, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu.
History of FIPIC
- The establishment of FIPIC reflects India’s commitment to deepening its engagement with the Pacific island nations.
- The inaugural FIPIC summit was held in November 2014 in Suva, Fiji, where India and the Pacific island countries came together to discuss bilateral and multilateral cooperation.
- The summit marked a significant milestone in India’s efforts to strengthen relations with the Pacific island states and promote inclusive development in the region.
Key highlights of the Summit
(1) Imbibing perception change
- During the FIPIC-3 summit held in Port Moresby, PM Modi emphasized the importance of recognizing the small island nations of the Pacific Ocean as “large ocean states.”
- PM reiterated India’s commitment to supporting the development goals of the Pacific island states.
(2) Advancing development goals
- India expressed unwavering dedication to supporting Pacific island states in various ways.
- Acknowledged challenges such as climate change, natural calamities, and disruptions in food and fuel supply chains.
- India has been a reliable supplier of essential items, including vaccines, medicines, wheat, and sugar.
(3) Voices to lead Global South
- Prime Minister James Marape of Papua New Guinea urged India to serve as an advocate for the Global South.
- Requested India’s representation in key global forums like the G-7 and G-20.
Why does India need PIC?
- Geopolitical Significance: Strengthening ties in Indo-Pacific to bolster regional influence, promote stability, and shape regional dynamics.
- Maritime Trade Routes: Securing access to vital sea-lanes, ensuring smooth trade flow, and protecting maritime interests.
- Resources: Expanding access to valuable resources such as minerals, hydrocarbons, and fisheries for economic growth and energy security.
- Economic Opportunities: Exploring untapped markets, attracting investments, and fostering trade partnerships for mutual economic benefits.
- Climate Change and Disaster Management: Collaborating on climate resilience strategies, sharing expertise in disaster management, and supporting sustainable development.
- Diplomatic Relations: Establishing strategic alliances, enhancing multilateral cooperation, and strengthening India’s presence in the Pacific region.
- Indian Diaspora: Supporting and engaging with the Indian diaspora, promoting cultural ties, and leveraging their contributions for bilateral cooperation and understanding.
Conclusion
- The FIPIC-3 summit provided a platform for India and Pacific island nations to deepen cooperation and address shared challenges.
- India’s commitment to supporting development goals and its role as a reliable supplier underscores its dedication to the Pacific island states.
- India’s active engagement in global forums and advocacy for the Global South aims to amplify voices and advance interests.
- The summit signifies a strengthened partnership, fostering mutual growth and shared progress.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Comb Jellies, Neurons, Neural Network
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Comb jellies, or ctenophores, are marine animals with jelly-like bodies and iridescent combs.
- They represent an ancient animal lineage and have a distinct nervous system.
- A recent study published in Science examined the comb jelly nervous system and made surprising discoveries.
What are Comb Jellies?
- Comb jellies, also known as ctenophores, are marine animals that belong to the phylum Ctenophora. They are fascinating creatures with a unique and delicate appearance.
- Despite their name, comb jellies are not actually true jellyfish.
- They have a gelatinous, transparent body that is often luminescent and adorned with rows of cilia, or comb-like structures, which give them their characteristic shimmering appearance.
Findings of the new study
- The researchers aimed to investigate how nerve net neurons in comb jellies connect.
- Contrary to expectations, synapses (junctions between neurons) were absent in the nerve net.
- Instead, nerve-net neurons were continuously connected by a single plasma membrane.
Significance of ctenophores
- In the 1950s, electron microscopy confirmed the separate-cell nature of neurons connected by synapses.
- Ctenophores challenge this notion by having a syncytial nerve net, as observed in the new study.
- Ctenophores attracted attention due to their status as a potential early animal lineage.
- Whole-genome sequencing studies supported the theory that ctenophores branched off early in animal evolution.
Evolution of ctenophore nervous systems
- The evolution of ctenophore nervous systems remains unclear to biologists.
- Leonid Moroz proposed a controversial theory of independent nervous system evolution in ctenophores and other animals.
- Ctenophores exhibit a unique nervous system lacking classical neurotransmitter pathways and common neuronal genes.
- The absence of muscle-based movement and reliance on cilia might have driven the evolution of a different signal conduction system.
Questions for further research
- Researchers aim to study the development of nerve net neurons in ctenophores.
- They seek to determine if adult ctenophores retain syncytial nerve nets or develop synapses.
- The uniqueness of ctenophore nervous systems provides valuable insights into the evolution of the nervous system.
- Comparative analyses of unique animal systems like ctenophores aid in understanding neuronal function and treating disorders.
Conclusion
- Understanding the functional and evolutionary significance of syncytial nerve net neurons in ctenophores requires further research.
- This study serves as a crucial foundation for investigating the evolution of nervous systems in animals.
- Comparative studies on small marine creatures like ctenophores offer insights into the fundamental principles of brain function.
Key Terminologies
- Ctenophores: Another term for comb jellies, referring to marine animals belonging to the phylum Ctenophora.
- Nerve Net: The diffuse nervous system found in comb jellies, composed of interconnected neurons.
- Synapses: Junctions between neurons that allow for communication and transmission of signals in most animals, including humans.
- Plasma Membrane: The outer membrane of a cell that separates its internal components from the external environment.
- Neurotransmitter Pathways: The specific chemical signals used by neurons to communicate with each other in the nervous system.
- Syncytial Nerve Net Neurons: Neurons within the nerve net of comb jellies that are interconnected without the presence of synapses.
- Colloblasts: Specialized cells in comb jellies used for capturing prey by producing adhesive substances.
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Antarctic
Mains level: Read the attached story
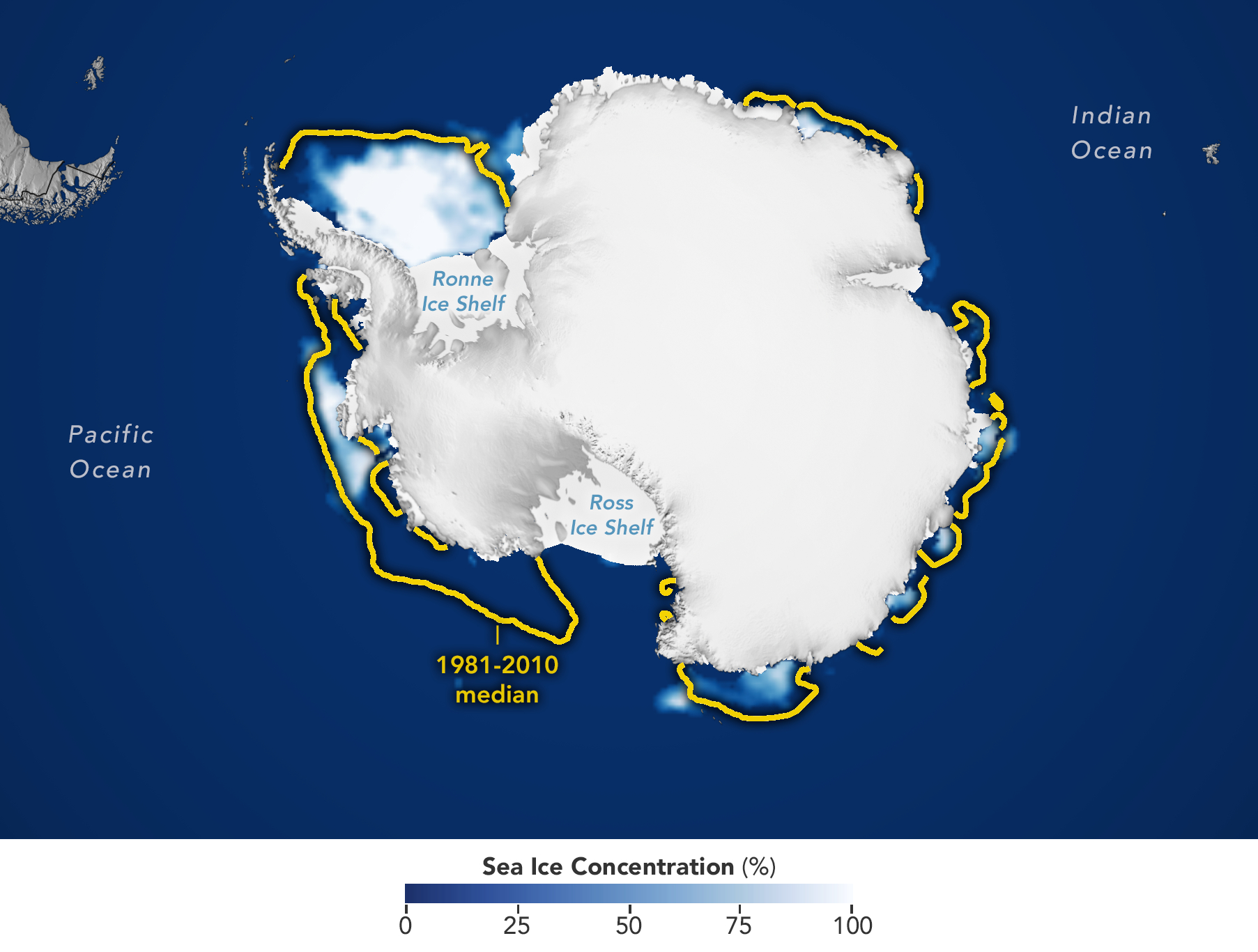
Central Idea
- Sea ice in Antarctica reached its smallest area on record in February for the second consecutive year, continuing a decade-long decline.
Ice cover decline: Key data
(1) Square km decline
- The European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) provided the figures, highlighting the significant decrease in Antarctic sea ice.
- On February 16, the ocean surface covered by ice around Antarctica shrank to 2.09 million square kilometers (800,000 square miles), the lowest level since satellite records began.
(2) Warming trends
- Both the North and South poles have experienced significant warming, with temperatures rising by approximately 3 degrees Celsius compared to late 19th-century levels, three times the global average.
- Arctic sea ice has been diminishing by about 3 percent per year since the late 1970s, while sea ice in Antarctica has remained relatively constant with large annual variations.
(3) Regional variances and vulnerabilities
- Recent ice cover reduction during the southern hemisphere summer has been most pronounced in West Antarctica, which is more vulnerable to the impacts of global warming compared to East Antarctica.
- Antarctica witnessed its first recorded heatwave in 2020, with temperatures 9.2 degrees Celsius above the mean maximum. Unusual temperature spikes have been observed in various parts of Antarctica.
- The Arctic has also experienced significant declines in sea ice, with the record minimum sea ice extent occurring in 2012.
Impact of declining Ice Cover
- Global sea level rise: Melting ice in Antarctica contributes to rising sea levels worldwide.
- Disruption of ecosystems: Declining ice cover disrupts habitats and food sources for ice-dependent species.
- Increased warming: Less ice reflects sunlight, leading to more heat absorption and further ice melting.
- Changes in ocean circulation: Declining ice cover can disrupt currents and impact global climate patterns.
- Release of stored carbon: Melting ice releases trapped carbon, potentially affecting marine ecosystems and contributing to climate change.
- Amplification of global warming: Reduced ice cover creates a positive feedback loop, exacerbating climate change.
- Disruption of biodiversity and food chains: Changing ice conditions impact species relying on ice algae and affect the overall Southern Ocean ecosystem.
Future projections
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) predicted with high confidence that the Arctic Ocean would become practically ice-free in September at least once by mid-century.
- The decreasing trends in both Arctic and Antarctic sea ice highlight the urgent need to address climate change and its impact on the Polar Regions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PARAKH
Mains level: Curriculum harmonization
Central Idea
- The Ministry of Education has organized a workshop in New Delhi to discuss the unification of 60 school examination boards operating across different states and union territories.
- The key component of this plan is PARAKH, the National Assessment Centre established under the National Council of Educational Research and Training.
What is PARAKH?
- PARAKH stands for Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development.
- It is an organization created to bring school boards from various states and union territories onto a unified platform.
- It has been launched as part of the implementation of the National Education Policy (NEP)-2020.
- It acts as a constituent unit of the NCERT.
- It is tasked with holding periodic learning outcome tests like the National Achievement Survey (NAS) and State Achievement Surveys.
- It will work on three major assessment areas: large-scale assessments, school-based assessment, and examination reforms.
Key objectives of PARAKH
- Uniform Norms & Guidelines: Setting comprehensive norms, standards, and guidelines for student assessment and evaluation in all recognized school boards.
- Enhance Assessment Pattern: Encouraging school boards to adopt assessment patterns aligned with the skill requirements of the 21st century.
- Reduce Disparity in Evaluation: Establishing uniformity across state and central boards, which currently employ different evaluation standards, resulting in significant score disparities.
- Benchmark Assessment: Developing a benchmark assessment framework to move away from rote learning and align with the objectives of the NEP 2020.
Outcomes of the recent workshop
(1) Establishing Equivalence of Boards
- The Centre is planning for the equivalence of boards to facilitate seamless transitions for students across different boards or regions.
- The objective is to align curriculum standards, grading systems, and evaluation methodologies to enhance the credibility and recognition of certificates and grades obtained across boards.
(2) Moving away from Rote Examination Culture
- The workshop highlighted the need to reassess the prevailing rote examination culture in the education system.
- There is a growing realization that holistic assessments, considering various dimensions of a student’s abilities and potential, are equally important.
(3) Standardization and Fairness in Assessments
- The discussion emphasized the importance of well-designed and standardized question papers to ensure fairness and consistency across schools and boards.
- Striking a balance between formative and summative assessments was identified as a means to reduce the burden of high-stakes examinations while effectively measuring student progress.
Conclusion
- PARAKH’s significance lies in its potential to bring about transformative change, facilitating collaboration, and benchmarking assessments.
- It is an important step towards creating a standardized and equitable assessment system, providing students with a fair platform to demonstrate their abilities and skills.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now








