Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kerch Bridge
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Kerch Bridge, linking the Russian mainland to the Crimean Peninsula, suffered an attack by Ukrainian sea drones, leading to retaliatory actions by Russia.
About Kerch Bridge
- The Kerch Bridge, across the Kerch Strait, is 19 km long and has two parallel rail and roadways.
- It was opened in 2018 by Russian President Vladimir Putin with great fanfare, four years after Russia annexed Crimea from Ukraine through a contested referendum.
- It is also a symbol of Russia’s control over Crimea, annexed in 2014.
- It holds symbolic importance for Russia, as it provides direct connectivity between the mainland and the annexed Crimea.
Significance of the Kerch Bridge for Russia
- Establishing Connectivity: Following the annexation of Crimea in 2014, the bridge was constructed to secure a “land bridge” between mainland Russia and Crimea.
- Logistical Supply Link: The bridge plays a critical role in facilitating logistical supplies to Russian troops in southern Ukraine.
- Strategic Vulnerability: The bridge remains within range of Ukrainian fire, making its security vital for Russia’s military operations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Section 69A of IT Act
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The Indian government has exercised its powers under Section 69(A) of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- It requested Twitter and other social media platforms to remove a video depicting the naked parade and sexual assault of two Manipur women.
What is Section 69(A) of the IT Act?
- Empowering Content Takedown: Section 69(A) allows the government to issue content-blocking orders to online intermediaries like ISPs, web hosting services, search engines, etc.
- Grounds for Blocking: Content can be blocked if it is considered a threat to India’s national security, sovereignty, public order, or friendly relations with foreign states, or if it incites the commission of cognizable offenses.
- Review Committee: Requests made by the government for blocking content are sent to a review committee, which issues the necessary directions. Such orders are typically kept confidential.
Supreme Court’s Verdict on Section 69(A)
- Striking Down Section 66A: In the case of Shreya Singhal vs. Union of India (2015), the Supreme Court struck down Section 66A of the IT Act, which penalized the sending of offensive messages through communication services.
- Section 69(A) Validated: The Court upheld the constitutionality of Section 69(A) of the Information Technology Rules 2009, noting that it is narrowly drawn and includes several safeguards.
- Limited Blocking Authority: The Court emphasized that blocking can only be carried out if the Central Government is satisfied about its necessity, and the reasons for blocking must be recorded in writing for legal challenges.
Other Rulings on Section 69(A)
- Twitter’s Challenge: Twitter approached the Karnataka High Court in July last year, contesting the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology’s (MeitY) content-blocking orders issued under Section 69(A).
- Court’s Dismissal: In July of this year, the single-judge bench of the Karnataka HC dismissed Twitter’s plea, asserting that the Centre has the authority to block tweets.
- Extending Blocking Powers: Justice Krishna D Dixit ruled that the Centre’s blocking powers extend not only to single tweets but to entire user accounts as well.
Conclusion
- The application of Section 69(A) has been a subject of legal and societal debate, as it aims to balance national security and public order concerns with the protection of free speech and expression.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Short Duration Discussions
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The Opposition called for the suspension of all other business under Rule 267 to discuss the Manipur issue, while the government preferred a “Short Duration Discussion” under Rule 176.
- Understanding the nuances of these rules and their implications is essential for effective parliamentary discussions.
Rule 267: Suspension of Business
- Overview: Rule 267 allows Rajya Sabha MPs to suspend all listed business and engage in discussions on matters of national importance.
- Consent and Suspension: As per the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Rajya Sabha, any member can seek the Chairman’s consent to suspend the application of a rule related to the day’s listed business.
- Temporary Suspension: If the motion receives approval, the concerned rule is temporarily suspended.
Short Duration Discussions under Rule 176
- Brief Duration Discussions: Rule 176 facilitates short-duration discussions in Rajya Sabha, lasting up to two-and-a-half hours.
- Notice and Explanatory Note: MPs desiring to raise urgent public matters must provide a written notice to the Secretary-General, including an explanatory note justifying the discussion.
- Scheduling and Procedure: The Chairman, in consultation with the Leader of the Council, schedules the discussion without formal motions or voting.
- Statement and Reply: The member who issued the notice presents a brief statement, followed by a concise reply from the Minister.
Contention Surrounding Rule 267
- Opposition’s Discontent: The Opposition expresses discontent as their notices under Rule 267 have not been addressed recently.
- Past Precedents: In the past, several discussions on diverse subjects occurred under this rule during different Chairmen’s tenures.
- Misuse of Rule: Experts suggest that Rule 267 is being misused as a substitute for the adjournment motion in Lok Sabha, where discussions involve motions with elements of censure, which do not apply to Rajya Sabha.
Why discuss this?
- Parliamentary debates hold significant value in addressing pressing public matters and discussing issues critical to the nation.
- They provide a platform for representatives from various political parties to engage in informed discussions, leading to more effective decision-making and improved governance.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: APMCs, NITI Aayog
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- Experts from NITI Aayog have put forth recommendations to revamp the existing Agriculture Produce Marketing Committee (APMC) system in India’s agriculture sector.
NITI Aayog
- NITI Aayog stands for the National Institution for Transforming India. It is a policy think tank and a government institution in India.
- It was established on January 1, 2015, to replace the Planning Commission, which was the central agency responsible for formulating India’s Five-Year Plans.
- PM serves as the ex-officio Chairman of NITI Aayog.
- It has a full-time Vice-Chairperson, who is usually a renowned economist or policy expert, and also includes several full-time members and special invitees.
- Its primary objective is to provide strategic and policy inputs to the central and state governments in India with a focus on sustainable and inclusive development.
|
What is APMC?
- APMCs are created by state governments, reflecting agriculture’s status as a State List subject under the Indian Constitution.
- APMC’s existence aims to safeguard farmers from exploitation by large retailers and maintain reasonable retail price spreads.
- All food produce must first be brought to market yards and then sold through auction as per the Agricultural Produce Marketing Regulation (APMR) Act.
Establishments of APMCs
- British Raj Influence: The regulation of raw cotton under the Hyderabad Residency Order in 1886 marked the beginning of agriculture produce market regulation in India.
- Royal Commission’s Recommendation: The 1928 Royal Commission on Agriculture recommended the regulation of marketing practices and the establishment of regulated markets.
- Model Bill and Independence: The Government of India prepared a Model Bill in 1938, but significant progress was made only after India gained independence.
- Enactment of APMR Acts: During the 1960s and 1970s, most states enacted and enforced Agricultural Produce Markets Regulation (APMR) Acts, bringing primary wholesale assembling markets under their ambit.
Working of APMCs
- APMCs operate on two principles:
- Ensure that farmers are not exploited by intermediaries (or money lenders) who compel farmers to sell their produce at the farm gate for an extremely low price.
- All food produce should first be brought to a market yard and then sold through auction.
- Each state that operates APMC markets (mandis) establish their markets in different places within their borders, geographically dividing the state.
- Farmers are required to sell their produce via auction at the mandi in their region.
- Traders require a license to operate within a mandi.
Key Reforms Suggested by NITI Aayog
(1) Alternative Marketing Options
- App-Based Sales and E-commerce: The experts suggest leveraging technology for app-based sales of farm produce by individual farmers or farmer groups. Additionally, they emphasize the potential of e-commerce and digital commerce as alternative marketing avenues.
- Subsidy Reforms: To address the over-exploitation of groundwater due to free or highly subsidized power, they recommend direct payment of subsidy amounts to farmers and shifting to the metered power supply.
(2) Modernizing Agriculture
- Corporate Investments: The paper highlights that about 80% of investments in agriculture come from private sources, mainly farmers. However, the corporate sector’s involvement remains low, and they believe there is significant potential for corporate expansion in agribusiness.
- Market Integration and Competition: Encouraging corporate investment in areas like warehousing, logistics, cold chain, food processing, and value chain development would improve market integration and competition over time and space.
(3) Enhancing Farmer Income
- High-Value Crops and Livestock Activities: To boost the income of farmers with small land holdings, the experts suggest enabling them to focus on high-value crops and livestock activities while supplementing their agricultural income with non-agricultural sources.
- MSP Reforms: The Minimum Support Price (MSP) system should be designed to avoid market distortions. The paper proposes using a combination of procurement and price deficiency payment to pay MSP to farmers, linked to public distribution system needs, price stability, and strategic stocks.
Earlier reforms: Three Farm Laws
Reforms were passed in the form of three acts in 2020 (later repealed) which led to massive protests.
- Farmers’ Produce Trade and Commerce Act: This act aimed to promote and facilitate trade and commerce of farmers’ produce outside the physical boundaries of APMCs, allowing farmers to sell their produce in other markets and directly to buyers.
- Farmers Agreement on Price Assurance and Farm Services Act: This act empowered farmers to enter into agreements with buyers, ensuring a guaranteed price for their produce and access to various farm services.
- Essential Commodities Amendment Act: This amendment sought to remove restrictions on the movement and storage of essential commodities, promoting a more open market.
Conclusion
- Balancing Farmer Interests and Market Efficiency: While the reforms aim to create a more competitive and liberalized market, it is crucial to address farmers’ concerns and protect their interests.
- Dialogue and Collaboration: To find common ground, constructive dialogue and collaboration between the government and farmers are essential in shaping the future of agricultural reforms.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2022
Mains level: Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2022, Provisions, concerns and way forward

What’s the news?
- The Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2022 is set to be tabled during the monsoon session of the Parliament. Earlier, it was to be discussed in the Lok Sabha on March 29, 2023 but was deferred.
Central idea
- The Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2022, introduced in 2021 seeks to amend the existing Biological Diversity Act, 2002. However, it has faced criticism and reservations due to concerns that certain amendments may favor industry interests and not adequately uphold the principles of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). The bill’s journey so far has raised questions about its potential impact on biodiversity conservation in India.
Objectives of the Bill
- The main objectives of the amendment bill are to ease regulations on wild medicinal plants,
- Promote the Indian system of medicine
- Foster an environment for collaborative research and investments
- Reduce the burden of obtaining permissions from the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) for practitioners and companies producing medicinal products
Controversial Provisions of the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2022
- The bill proposes to de-criminalize violations of biodiversity laws and withdraws the power given to the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) to file a First Information Report (FIR) against defaulting parties.
- The bill allows domestic companies to use biodiversity without seeking approval from biodiversity boards. Only foreign controlled companies are required to acquire permission.
- The bill includes the term codified traditional knowledge, which grants exemptions to users, including practitioners of Indian systems of medicine, from the provisions of approvals for accessing or sharing benefits.
Concerns raised by the activists
- Some critics argue that the proposed amendments may weaken biodiversity conservation efforts in India
- Lack of oversight and accountability may lead to unchecked utilization of biodiversity resources, which could negatively impact ecosystems and biodiversity.
- The codified traditional knowledge may enable profit-seeking domestic companies to exploit traditional knowledge without adequately compensating the communities that have conserved and developed it for generations.
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) emphasizes the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of biodiversity. The proposed amendments may not fully align with these principles.
- While the bill aims to promote traditional medicine and ease regulations, it may not sufficiently address the broader issues of biodiversity loss, habitat degradation, and the need for stronger conservation measures.
- Weakening biodiversity protection and benefit-sharing mechanisms could disproportionately affect indigenous and local communities, which often rely on biodiversity for their livelihoods and cultural practices.
Way forward
- Reassess and redraft the contentious provisions in the bill, particularly those related to decriminalizing violations, exempting domestic companies from seeking permission, and codified traditional knowledge.
- Establish robust and transparent mechanisms for equitable benefit sharing from the use of biodiversity.
- Adequately compensate indigenous communities and traditional knowledge holders for their role in conserving and preserving biodiversity.
- Incentivize businesses that prioritize conservation and sustainable utilization of resources.
- Strengthen enforcement measures to ensure compliance with biodiversity conservation regulations. Establish appropriate penalties for violations to deter non-compliance.
- Align the bill with India’s international commitments, especially those agreed upon during the 15th Conference of Parties to the CBD.
- Strengthen the capacity and authority of biodiversity governance bodies like the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) to effectively regulate and monitor biodiversity-related activities.
Conclusion
- The Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2022 presents a complex dilemma for biodiversity conservation in India. As the bill awaits discussion in the monsoon session, it becomes crucial for policymakers to address the concerns raised by activists and legal experts, ensuring that India’s biodiversity is safeguarded and aligned with global conservation goals.
Also read:
Why is there a controversy on the forest Bill?
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Heatwaves, heat domes ,el nino , ocean warming etc and their interactions and impacts
Mains level: Rising Heatwaves across the globe, factors, impacts and mitigating strategies
What’s the news?
- The average daily global temperature on Thursday was recorded at 17.12 degrees Celsius, encompassing measurements over land, ocean, ice sheets, and mountainous snow regions.
Central idea
- In a concerning announcement, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) declared June as the hottest month ever recorded on Earth since temperature tracking began 174 years ago. The heatwave has persisted into July, with 18 out of the first 20 days witnessing unprecedented average daily global temperatures.
What is Heat-wave?
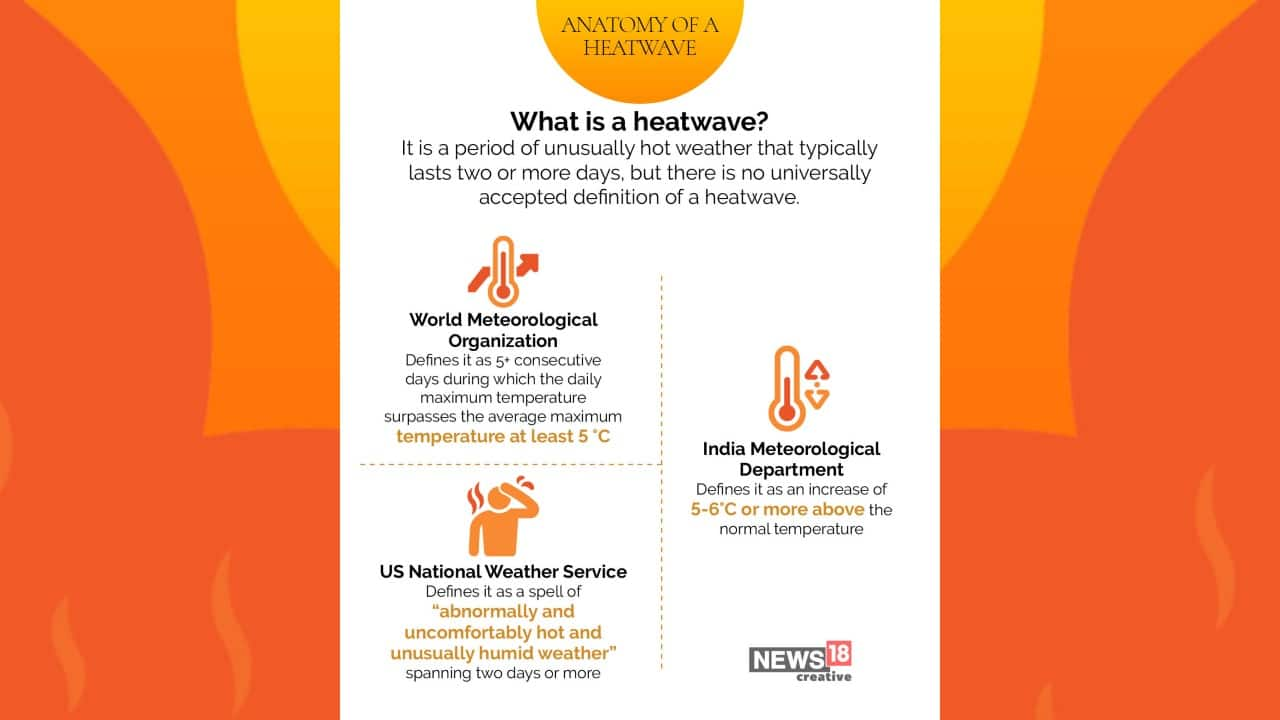
- A heatwave is a prolonged period of abnormally hot weather.
- Heatwaves usually last for several days or weeks and can occur in both dry and humid
- Characterized by temperatures that are significantly higher than the average for a particular region during that time of year.
What are heat domes?

- A heat dome occurs when an area of high-pressure stays over a region for days and weeks. It traps warm air, just like a lid on a pot, for an extended period.
- The longer that air remains trapped, the more the sun works to heat the air, producing warmer conditions with every passing day.
- Heat domes, if they last for a long period, may cause deadly heat waves.
What are Anticyclones?
- An anticyclone, also known as a high-pressure system, is essentially an area of high pressure in which the air goes downwards towards the Earth’s surface.
- As the air sinks, its molecules get compressed, which increases the pressure, making it warmer. This causes dry and hot weather.
- The winds remain calm and gentle during an anticyclone, and there is almost no formation of clouds because here the air sinks rather than rises.
Factors behind this scorching trend?
- Climate change: The primary driver behind the escalating heatwaves and rising global temperatures is human-induced climate change.
- The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial processes, and other human activities release greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat and lead to the greenhouse effect, resulting in the warming of the Earth’s surface.
- El Nino events, characterized by abnormal warming of surface waters in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, can elevate temperatures worldwide and exacerbate heatwaves.
- Heat domes and anticyclones are weather phenomena that can intensify and extend heatwaves.
- Warmer oceans release more heat into the atmosphere, fueling extreme weather events like heatwaves.
- Urban areas with concrete and asphalt surfaces can create heat islands that retain and amplify heat, leading to higher temperatures within cities compared to surrounding rural areas.
- Climate change can trigger feedback loops that amplify its effects. For example, melting ice in the Arctic reduces the Earth’s reflective surface, leading to increased absorption of sunlight and further warming.
*NOTE: Although heat domes and anticyclones don’t occur due to climate change, they have become more intense and longer as a result of soaring global temperatures.
Impact of Heatwaves
1.Human Health Impacts:
- Heat-related Illnesses: Heatwaves can cause heat-related illnesses such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. The elderly, young children, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are more vulnerable.
- Dehydration: High temperatures and excessive sweating can lead to dehydration, especially if individuals do not consume enough fluids.
2.Impact on Agriculture:
- Crop Failure: Prolonged heatwaves can cause damage to crops and reduce agricultural yields due to drought conditions and water shortages.
- Livestock Stress: High temperatures can lead to heat stress in livestock, affecting their productivity and overall health.
3.Environmental Impact:
- Drought: Heatwaves can contribute to drought conditions by increasing evaporation and reducing water availability, leading to water scarcity and affecting ecosystems.
- Wildfires: Hot and dry conditions during heatwaves can increase the risk of wildfires, leading to extensive damage to forests and wildlife habitats.
- Water Quality: Heatwaves can lead to higher water temperatures, which may negatively impact aquatic ecosystems and decrease water quality.
4.Energy Demand and Infrastructure Stress:
- Increased Energy Consumption: Heatwaves result in higher energy demand due to the use of air conditioning and cooling systems, putting strain on the power grid.
- Power Outages: The increased demand for electricity during heatwaves can lead to power outages if the electrical infrastructure becomes overloaded.
5.Social and Economic Impact:
- Disruption of Daily Activities: Heatwaves can disrupt daily life, making it uncomfortable to work, travel, or engage in outdoor activities.
- Economic Losses: Heatwaves can result in productivity losses, increased healthcare costs, and damage to infrastructure, leading to economic impacts on communities and businesses.
Worse affected countries
- United States: North America, particularly the United States, has experienced prolonged heatwaves covering a large swath of the country. States like California, Florida, New Mexico, and Arizona have been experiencing extreme temperatures. Temperature remained around 43.3 degree Celsius.
- Europe: Countries in Europe, such as Italy and Greece, have been gripped by two consecutive heatwaves. Italy’s island of Sardinia saw temperatures reaching 47.7 degrees Celsius, and Greece experienced temperatures exceeding 40 degrees Celsius, leading to wildfires and affecting historical sites.
- Spain: Spain witnessed a temperature of 45.4 degrees Celsius in the town of Figueres, the highest temperature recorded in the country since 1928. It led to dry spells and wildfires.
- Asia: China, Iraq and Saudi Arabia remain some of the worst affected countries. A remote township in China saw temperatures touching 52 degree Celsius
- Algeria: North Africa’s Algeria has reported record-breaking temperatures, with some experts suggesting temperatures exceeding 50 degrees Celsius in certain areas.
- Tunisia: Tunisia has also been impacted by severe heatwaves, with temperatures reaching up to 49 degrees Celsius in some regions.
Mains Marks enhancer: Best Practices in India
- Andhra Pradesh:
- Setting up Heat Action Plans: Cities like Vijayawada have implemented Heat Action Plans that include public awareness campaigns, heat helplines, and designated cooling centers to provide relief to vulnerable populations.
- Telangana:
- Early Warning Systems: The Telangana State Development Planning Society issues heatwave alerts and early warnings to district authorities and the public, allowing them to take precautionary measures.
- Rajasthan:
- Urban Heat Island Mitigation: Cities like Jaipur have implemented measures to reduce the urban heat island effect by promoting green spaces, reflective surfaces, and better urban planning.
- Gujarat:
- Cool Roofs: The Gujarat government has encouraged the use of cool roofs in buildings to reflect sunlight and reduce indoor temperatures during heatwaves.
- Tamil Nadu:
- Heatwave Awareness Programs: The Tamil Nadu government conducts awareness programs through schools, colleges, and community organizations to educate people about heatwave safety and preparedness.
Way forward: Urgent actions needed
- The international community must strengthen and implement the commitments made under climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement.
- Countries should set more ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Provide support to developing nations to enhance climate resilience and adaptation.
- Prioritize the transition to renewable energy sources and invest in clean technologies.
- Develop robust adaptation strategies such as involves establishing heat emergency response plans, cooling centers, and public awareness campaigns.
- Cities should adopt green urban planning practices, incorporating green spaces, green roofs, and sustainable building designs to mitigate the urban heat island effect and promote natural cooling.
- Promote sustainable land management practices, including reforestation and afforestation
- Enhance early warning systems to detect and respond to extreme heat events promptly.
Conclusion
- The alarming surge in global temperatures, culminating in devastating heatwaves across continents, is a potent reminder of the urgency to combat climate change. As nations grapple with the immediate impacts of heatwaves, it is imperative to take collective action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigate the effects of climate change, and safeguard the planet for future generations. The time to act is now; the consequences of inaction are too dire to ignore.
Also read:
Heatwaves in India: Increasing Frequency Needs Range of Measures to Mitigate
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Indo-pacific partnerships and evelopments
Mains level: Indo-pacific and NATO, significance and challenges

What’s the news?
- The Russia-Ukraine conflict has made NATO summits more significant than ever. The wide presence of four Asia-Pacific countries: Australia, New Zealand, Japan, and South Korea has made this year’s summit more prominent especially for Indo- pacific
Central idea
- The recent NATO summit was held in Vilnius, Lithuania, marked a significant turning point for the alliance. The summit showcased NATO’s increasing focus on the Indo-Pacific region, signifying the importance of this area for Euro-Atlantic security.
What is Indo-Pacific?
- The Indo-Pacific is a geographic region interpreted differently by different countries.
- For India, the geography of the Indo-Pacific stretches from the eastern coast of Africa to Oceania whereas, for US, it extends up to the west coast of India which is also the geographic boundary of the US Indo-Pacific command.
NATO’s Historical Background and Pivot Towards Asia
- Founded in 1949, NATO emerged as a response to concerns over expanding Soviet influence in Eastern Europe.
- Originally cantered on trans-Atlantic security, the alliance has evolved to address pressing global security challenges.
- The recent summit’s agenda highlighted issues in the Indo-Pacific, such as North Korea’s nuclear activities, ballistic missile tests, and China’s military expansion and modernization.
Indo-Pacific Partnerships and Collaborations during the summit
- NATO and Japan:
- Individually Tailored Partnership Program between NATO and Japan was signed for the period of 2023-2026- focuses on cooperation in new technologies, space, and supply chain resilience.
- NATO and New Zealand:
- New Zealand was recognized as a valued partner by NATO during the summit.
- The alliance praised the collaboration with New Zealand in various areas, including cyber defense, counter-terrorism, arms control, and new technologies.
- NATO and South Korea:
- A significant agreement was reached between NATO and South Korea further strengthening their collaboration in emerging areas, particularly related to hybrid threats.
- NATO and Australia: Presence of Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese at the NATO summit indicates a willingness to strengthen ties and foster cooperation in areas of common concern
Significance of the Indo-Pacific for NATO
- The Indo-Pacific is home to numerous security challenges that have implications beyond the region.
- These challenges include North Korea’s nuclear and missile activities, China’s military expansion, territorial disputes, and non-traditional security threats such as cyber-attacks and terrorism.
- China’s growing economic, political, and military influence in the Indo-Pacific has global ramifications.
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and its assertive actions in the South China Sea have raised concerns among NATO allies about potential disruptions to regional stability and international norms.
- The Indo-Pacific region is a major driver of the global economy, with many NATO member states heavily reliant on trade and economic ties with countries in the area.
- Ensuring the security of critical sea lanes and trade routes is essential for NATO’s economic interests and stability.
- Collaborating with Indo-Pacific countries can contribute to a rules-based international order and strengthen NATO’s global reach.
Concerns Over NATO’s Role in Indo-Pacific
- Ambiguity and uncertainty within the alliance regarding NATO’s official presence and role in the Indo-Pacific.
- French President Emmanuel Macron’s public opposition to the idea of opening a NATO liaison office in Tokyo highlighted these concerns.
- Establishing an official NATO presence in proximity to China could potentially unsettle the Chinese security establishment and may be perceived as a challenge to China’s regional interests.
- Unease among ASEAN and other South Asian countries with strategic interests in the area.
- Some ASEAN countries’ centrality in the Indo-Pacific being replaced by bloc politics led by NATO.
- It could stretch the alliance’s resources and capabilities- divert attention away from NATO’s core mission in the Euro-Atlantic region.
Interesting read: What is Thucydides’ Trap?
- Thucydides’ Trap is a term derived from the historical work “History of the Peloponnesian War” by the ancient Greek historian Thucydides. Thucydides chronicled the conflict between the city-state of Athens and the rising power of Sparta in the 5th century BC, which eventually led to the Peloponnesian War.
- The central idea behind Thucydides’ Trap is that when a rising power challenges an established power, the competition between the two can lead to conflict or war.
- Thucydides famously wrote, “It was the rise of Athens and the fear that this instilled in Sparta that made war inevitable.” The rising power’s ascent and the fear it generates in the established power create a dangerous and unstable situation that may lead to a conflict as both sides jostle for power and influence.
- In the context of modern times, NATO’s involvement in the region could inadvertently contribute to the Thucydides’ Trap, where a rising power (China) and an established power (United States) risk conflict
- It serves as a warning to policymakers that managing the rise of a new power and avoiding a potential conflict requires careful diplomacy, strategic communication, and the establishment of mechanisms to peacefully resolve disputes
Conclusion
- The recent NATO summit in Vilnius showcased the alliance’s Look East moment, highlighting its increased focus on the Indo-Pacific region. Strengthening ties with Indo-Pacific partners is crucial amid the evolving global strategic landscape. However, NATO must navigate carefully and exercise caution while addressing the challenges of the 21st century and the changing dynamics of the international order.
Also read:
North East as Gateway to Indo-Pacific Strategy
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






