Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chandrayaan-3 Mission
Mains level: Read the attached story
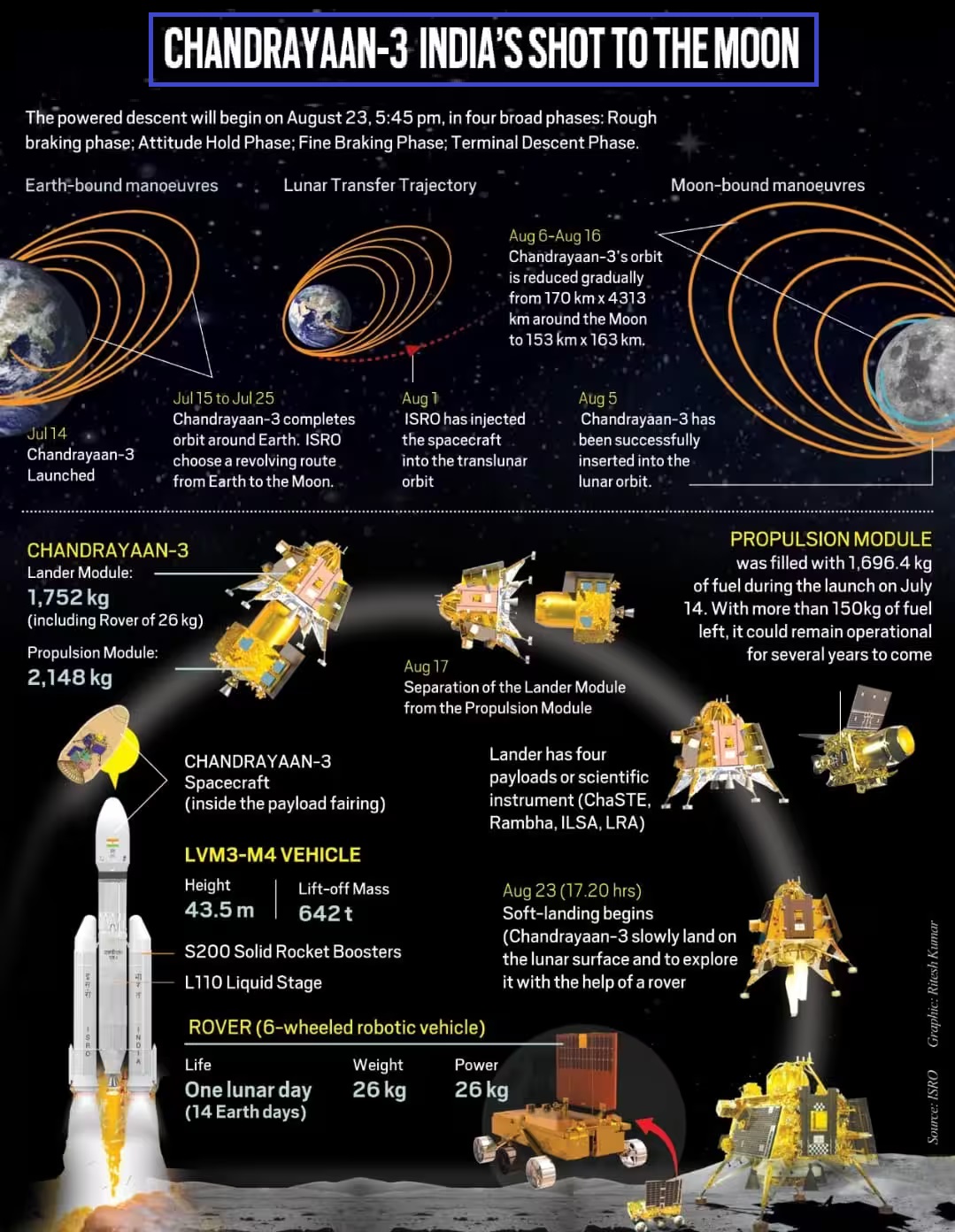
Central Idea
- As Chandrayaan-3 succeeded on its lunar soft landing, its six-wheeled rover begins a journey to unravel the mysteries of the Moon.
- With its payloads and instruments, the mission aims to build on the knowledge gained from its predecessors, investigating lunar quakes, mineral compositions, and water-ice presence.
Chandrayaan-3 Mission: Journey post soft landing
- Rover’s Arrival: The 26-kg rover, launched from the Chandrayaan-3 lander, is poised to cover up to 500 meters, commencing its lunar exploration.
- Duration: The lander and rover, equipped with six payloads, are primed to collect valuable data during the single lunar day (equivalent to 14 Earth days) of operation.
- Studying Lunar Quakes: The Chandrayaan-3 mission seeks to deepen insights into lunar quakes, expanding on the knowledge gained from its predecessors.
- Mineral Composition: The rover’s endeavors include examining the mineral compositions of the Moon’s surface, shedding light on its geological history.
- Electrons and Ions Study: The Radio Anatomy of Moon Bound Hypersensitive ionosphere and Atmosphere (RAMBHA) payload aims to study the behavior of electrons and ions near the lunar surface over time.
- Thermal Properties: Chandra’s Surface Thermo physical Experiment (ChaSTE) will explore the thermal characteristics of the Moon’s Polar Regions.
- Lunar Seismic Activity: The Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA) endeavors to measure lunar quakes and study the Moon’s crust and mantle composition.
- Laser Retroreflector Array: A passive experiment by NASA, the LASER Retroreflector Array (LRA), will serve as a target for precise laser measurements in future missions.
- Chemical Insights: The LASER Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) aboard the rover is designed to identify the chemical and mineral composition of the lunar surface.
- Elemental Analysis: The Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) aims to analyze elements such as magnesium, aluminium, silicon, potassium, calcium, titanium, and iron in lunar soil and rocks.
- Mineral Mapping: The CLASS X-ray Fluorescence experiment, covering nearly 95% of the lunar surface, offers detailed mineral mapping. Oxygen-rich minerals hold potential for future missions as fuel resources.
Earlier Chandrayaan: Pioneering discoveries
- Water Unveiled: Chandrayaan-1 played a pivotal role in uncovering the presence of water and hydroxyl molecules in the Moon’s atmosphere and surface, particularly in its southern polar regions.
- Subsurface Water-Ice: Payloads like mini-SAR and Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3) detected subsurface water-ice deposits within craters near the lunar South Pole.
- Lava Tubes for Habitability: Terrain mapping on Chandrayaan-1 unveiled buried lava tubes that could provide protective habitats for humans, shielding against radiation and extreme lunar conditions.
- Magma Ocean Hypothesis: M3 payload data suggested the possibility of a past magma ocean on the Moon, pointing to its formation and evolution.
- Active Moon: Contrary to previous notions of lunar inactivity, Chandrayaan-1 revealed dynamic lunar processes, including volcanic activity evidenced by lava channels and vents less than 100 million years old.
- Surface-Exosphere Interaction: Measurements indicated that the lunar surface interacts with the exosphere, evident in the emission of carbon dioxide and other gases.
- Solar Mysteries: The Solar X-Ray Monitor on Chandrayaan-2’s orbiter observed solar microflares outside active regions, providing insights into coronal heating mysteries.
Conclusion
- Chandrayaan-3’s scientific journey exemplifies India’s dedication to unraveling the Moon’s mysterious nature.
- As data pours in from its payloads and instruments, the mission builds upon its predecessors, propelling our understanding of lunar geology, composition, and mysteries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fujiwhara Effect
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- In the ever-changing tapestry of Earth’s climate, the Fujiwhara effect has emerged as a captivating and consequential phenomenon.
- With cyclones intensifying due to global warming, this intricate ‘dance’ between cyclones is garnering attention.
Why in news?
- Surprising Weather: Recently, a storm named Hurricane Hilary brought a tropical twist to the US west coast. It’s part of a series of odd weather happenings there.
- Wet Weather: Earlier this year, California had an unexpected rainy season with lots of wet storms, called ‘atmospheric rivers.’
- Fujiwhara Show: During one of these storms, something special occurred—an effect named after a scientist. Let’s dive into the details.
Decoding the Fujiwhara Effect
- Cyclone Waltz: Imagine two cyclones (or big storms) spinning in the same direction. When they get close, they begin a kind of dance around a common center.
- Outcome of the Dance: Depending on the strength of the cyclones, they might merge, spin together, or one might absorb the other.
- Super Cyclone: Rarely, if both cyclones are super strong, they can become one mega cyclone that causes big trouble.
Historical Context and Impact
- Origins and Discovery: The Fujiwhara effect got its name from a Japanese scientist who first talked about it in 1921. It was seen happening for real in 1964.
- Effects Unleashed: This unusual dance can be fierce. It has caused strong winds, broken windows, and power problems in some areas.
- Guessing Game: The Fujiwhara effect is tricky for weather experts. It’s hard to predict what will happen when two cyclones dance together.
Climate Change Connection
- More Frequent Moves: The Fujiwhara effect is showing up more often now. Experts believe it’s because our world is getting hotter and ocean waters are warming up.
- Hotter Waters: Because of global warming, storms are getting stronger. For instance, in Taiwan, typhoons have become 35% stronger since 1977 due to warmer oceans.
Implications
- Nature’s Symphony: The Fujiwhara effect is like a nature’s concert, showing us how everything is connected in our climate.
- Future Twist: As storms get more powerful, the Fujiwhara effect could become even more important and harder to understand.
- Planet’s Dance: The Fujiwhara effect teaches us about our planet’s rhythm and how important it is to take care of our home.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Article 371
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- The Supreme Court recently assured that special constitutional provisions protecting the interests of northeastern states under Article 371 will remain untouched.
- As the Constitution Bench deliberates the challenge to Article 370’s abrogation in Jammu and Kashmir, we delve into the significance of these assurances and their implications.
What is Article 371?
- Article 371 of the Indian Constitution grants special provisions to various states to protect their unique cultural and tribal identities.
- These provisions are aimed at preserving local customs, social practices, and land ownership.
Preserving Tribal Culture
- Context: Article 371 provides special provisions for several states, particularly in the northeast, to safeguard their tribal cultures and unique identities.
- Article 371(A) – Nagaland: Article 371(A) ensures that acts of Parliament do not apply to Nagaland concerning Nagas’ religious and social practices, customary law, civil and criminal justice based on Naga customary law, and land and resource ownership.
- State Assembly’s Role: These provisions only apply to Nagaland after the State Assembly passes a resolution to that effect.
- Development Impediment: Some stakeholders, like Neikiesalie Nicky Kire of the NDPP, argue that Article 371(A) hampers development by preventing the government from carrying out development activities due to landowner preferences.
Similar Provisions in Other States
- Article 371-G – Mizoram: Similar to Nagaland, Article 371-G provides special provisions for Mizoram to protect Mizo religious and social practices, customary law, civil and criminal justice, and land ownership.
- Article 371B – Assam: Article 371B facilitates the creation of the sub-state ‘Meghalaya,’ aiming to provide special provisions with respect to Assam.
State-Specific Provisions
- Article 371C – Manipur: This article addresses special provisions for Manipur, a state that was formed in 1972.
- Article 371F and 371H – Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh: These articles discuss special provisions for Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh, respectively, to address their unique needs.
- Article 371 – Separate Development Boards: Article 371 empowers the President to establish separate development boards for specific regions within Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, promoting balanced growth.
Further State-Specific Provisions except NE
- Articles 371D and 371E – Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Goa: These articles provide special provisions for these states to ensure their cultural and economic development.
- Articles 371J and 371I – Karnataka and Goa: These articles grant special provisions to Karnataka and Goa, respectively, to address their specific requirements.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Astra Missile
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas has achieved another milestone with the successful test firing of the indigenous Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air-to-air missile called Astra.
Indigenous Marvel of Astra Missile
- The Astra missile is an indigenous Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air-to-air missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India.
- The missile is intended for use by both the Indian Air Force (IAF) and the Indian Navy.
Purpose and Capability
- Astra is designed to engage and eliminate high-speed, agile aerial targets in air combat scenarios.
- It boasts advanced air combat capabilities and can engage multiple high-performance targets simultaneously.
Aircraft Integration
- Astra is integrated with various aircraft platforms, including the Su-30MKI fighter jet, Mirage 2000 multi-role combat fighters, Tejas light combat aircraft (LCA), MiG-29 and MiG-21 Bison fighter jets, and the Indian Navy’s Sea Harrier jet fighter.
Features and Specifications
(A) Design:
- The missile is designed for high agility, accuracy, and reliability, ensuring a high single-shot kill probability (SSKP).
- Astra measures approximately 3.8 meters in length and has a diameter of 178mm.
- It has a launch weight of around 160 kilograms.
(B) Advanced Variants:
- DRDO is working on developing an advanced variant called Astra Mk-II.
- Astra Mk-II is expected to have an extended range of 160 kilometers.
(C) Guidance and Warhead:
- The missile utilizes dual-mode guidance for accurate target tracking.
- It is equipped with a high-explosive pre-fragmented warhead for effective engagement against threats.
(D) Propulsion and Performance:
- The Astra missile is powered by a smokeless, single-stage, solid fuel propulsion system.
- It is capable of achieving launch speeds ranging from Mach 0.4 to Mach 2.
(E) Launch Range and Agility:
- The missile’s launch range is approximately 80 kilometers.
- It can execute maneuvers with up to 40 g turns near sea level while engaging moving targets.
Collaborative Development
- Astra Mk-III, a variant of the missile, is being developed in collaboration with Russia.
- This variant employs advanced solid fuel ducted ramjet (SFDR) engine technology.
Back2Basics: LCA Tejas

- Origin: The LCA Tejas is an indigenous light combat aircraft developed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) in collaboration with the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) in India.
- Purpose: LCA Tejas is designed as a multi-role supersonic fighter aircraft for the Indian Air Force (IAF) and the Indian Navy.
- Variants: There are two main variants of LCA Tejas:
- LCA Tejas Mark-I: Developed for the Indian Air Force, it is a single-seat, single-engine aircraft.
- LCA Tejas Mark-I Navy: Designed for the Indian Navy, it is adapted for carrier operations with features like reinforced landing gear and arrestor hook.
- LCA Tejas features a delta wing design for enhanced maneuverability and stability.
- The aircraft incorporates advanced avionics, glass cockpit, and digital fly-by-wire controls.
- It is equipped with modern radar systems, electronic warfare systems, and weapons integration capabilities.
- Powerplant: LCA Tejas is powered by a single engine, the General Electric F404-GE-IN20 turbofan engine.
- Armament: The aircraft can carry a variety of air-to-air and air-to-ground munitions, including missiles, bombs, and rockets.
- Performance:
- The aircraft has a maximum speed of around Mach 1.8 (1,390 mph or 2,240 km/h).
- Its operational range is approximately 500 kilometers (310 miles).
- LCA Tejas has a service ceiling of around 50,000 feet (15,240 meters).
- The LCA Tejas Mark-I was officially inducted into the Indian Air Force in July 2016.
- The aircraft has participated in various national and international airshows, showcasing its capabilities.
- Development and Challenges:
- The development of LCA Tejas faced several challenges, including technical and financial issues, leading to delays.
- However, the successful development and induction of the aircraft marked a significant achievement for India’s aerospace industry.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: BRICS group
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- India, a key member of the BRICS group (Brazil-Russia-India-China-South Africa), has affirmed its endorsement for the bloc’s expansion based on consensus.
BRICS Group
|
| Full Form |
Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa |
| Formation |
Originally “BRIC” in 2001, South Africa joined in 2010 to become BRICS |
| Economic Significance |
Represents significant portion of global population, land area, and economic output |
| Objectives |
Enhance cooperation, dialogue on political, economic, social issues |
| Principles |
Mutual respect, equality, non-interference in internal affairs |
| Summits |
Holds annual summits for leaders to discuss economic, trade, development issues |
| Cooperation Areas |
Finance, trade, investment, technology, energy, agriculture, health, education |
| New Development Bank (NDB) |
Established in 2014, finances infrastructure and sustainable projects |
| Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) |
Established in 2015, provides financial assistance during currency crises |
| Political Dialogue |
Advocates for peace, security, stability, coordinates positions on global issues |
Embracing BRICS Expansion
- Indian Support: PM Modi reiterated India’s full support for the expansion of BRICS membership, emphasizing the need for consensus.
- Collaborative Approach: Modi highlighted the potential for increased collaboration between BRICS countries in fields like space, education, and technology, using India’s expertise as a basis.
- Shared Platforms: Modi offered to share India’s technological platforms with other BRICS members, fostering a cohesive and future-ready organization.
BRICS’ Evolution and Vision
- BRICS Progress: Modi recalled BRICS’ journey, from being defined as “Building Responsive, Inclusive and Collective Solutions” during India’s chairmanship in 2016 to its current vision of “Breaking barriers, Revitalising economies, Inspiring innovation, Creating opportunities, and Shaping the future.”
- Chinese Perspective: Chinese President expressed support for speedy expansion to enhance global governance’s fairness and equity. He emphasized the enthusiasm of developing nations in joining BRICS cooperation.
Ongoing Deliberations on Expansion
- South African Insight: South African President Cyril Ramaphosa noted that discussions on BRICS expansion are ongoing, suggesting that a clear solution will be reached collectively among BRICS leaders.
- Indian Initiative: India’s approach to BRICS expansion was guided by the inclusion of strategic partners as new members, emphasizing consensus and unstructured discussions during leaders’ retreats.
Ensuring Equitable Growth
- Diverse Candidates: Approximately 20 to 30 nations expressed interest in joining BRICS, with leading candidates like Argentina, Egypt, Indonesia, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE. India aims to prevent a China-centric grouping.
- Counterpoint to the West: China aims to expand BRICS as a counterpoint to Western dominance, gaining support from Russia due to diplomatic isolation linked to the Ukraine conflict.
Enhancing BRICS Cooperation
- Modi’s Proposals: Modi emphasized collaboration in space, technology, digital infrastructure, and education among BRICS members.
- BRICS Space Exploration Consortium: Modi proposed creating a Brics space exploration consortium for research and weather monitoring.
- Education and Technology: Modi cited India’s innovative solutions like Diksha and Bhashini for education and the CoWIN platform for vaccination, offering to share these platforms with BRICS partners.
- Skill Mapping and Conservation: Modi proposed skill mapping and cooperation for the preservation of various species of big cats found in BRICS countries.
- Support for African Union: Modi sought BRICS states’ endorsement for India’s proposal to grant the African Union full membership in the G20, reflecting shared commitment and unity within the group.
Conclusion
- As India reaffirms its backing for BRICS expansion, the group’s shared vision of inclusive growth and equitable global governance is reinforced.
- PM Modi proposals highlight the potential for collaboration in diverse domains, harnessing India’s technological prowess to foster a forward-looking and cohesive BRICS organization.
- Amid evolving global dynamics, BRICS’ united stance and collaborative efforts stand to reshape the landscape of international cooperation and equitable development.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: One Health
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- The global spotlight on the ‘One Health’ concept is illuminating India’s strides in integrating this paradigm to enhance its response to health challenges.
- While gaining recent recognition, the One Health approach finds its roots in history.
One Health Approach
- Holistic Vision: The One Health approach acknowledges the intricate linkages between the health of humans, animals, plants, and their shared environment.
- Historical Foundation: Early traces of One Health can be found in the teachings of Hippocrates and later articulated by 19th-century physician Rudolf Virchow, emphasizing unity in animal and human medicines.
Addressing Modern Health Challenges
- Environmental Impacts: Human growth, urbanization, and industrialization contribute to biodiversity and ecosystem disruption, fostering zoonotic diseases.
- Zoonotic Diseases: Roughly 60% of emerging diseases that affect humans are zoonotic, including Ebola, bird flu, and rabies.
- Key Concerns: The rise of antimicrobial resistance, vector-borne diseases, and food safety underscores the need for an integrated approach.
Power of One Health Strategy
- Resource Efficiency: One Health fosters coordination across governmental units, reducing resource demands and promoting cross-sectoral collaborations.
- Economic Benefits: One Health proves economically prudent, potentially saving billions when compared to pandemic management through non-One-Health strategies.
Recent One Health Endeavors in India
- COVID-19 Impact: The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of the One Health approach.
- Indian Initiatives: India established a ‘Standing Committee on Zoonoses’ in 2006 and launched the ‘National One Health Mission’ for coordinated efforts.
The Transformation Process: Four Stages
- Stage 1: Communication: Setting up mechanisms for inter-ministerial communication and stakeholder engagement.
- Stage 2: Collaboration: Exchange of knowledge and expertise, defining roles in zoonoses management.
- Stage 3: Coordination: Long-term routine activities led by a dedicated agency for seamless collaboration.
- Stage 4: Integration: Developing synergies between sectors for streamlined resource sharing and coordinated initiatives.
Facilitating Collaborative Science
- Integrated Research: Beyond office-sharing, integrated research environments are crucial, allowing access to laboratories and biological samples.
- Sample Utilization: Efficient use of expensive and ethical biological samples, such as blood and tissue, enhances collaborative research outcomes.
Conclusion
- India’s embrace of the One Health approach reflects its commitment to holistic well-being.
- By recognizing the interconnectedness of humans, animals, plants, and the environment, India is laying the groundwork for comprehensive health strategies.
- With ongoing initiatives and a vision to seamlessly integrate resources and expertise, India aims to transform its health landscape, ensuring resilience against emerging challenges through a united and holistic approach.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: U.K.-India relationship

What’s the news?
- India, the world’s largest democracy, has taken a momentous stride onto the global stage by hosting the G-20 summit, a pivotal forum fostering international cooperation.
Central idea
- India’s hosting of the G-20 summit takes center stage, as the UK underscores its commitment to free trade and cooperation. The growing Indian middle class emerges as a potential boon for UK businesses. Bilateral trade thrives with an eye on a Free Trade Agreement, while cultural ties and the Alive with Opportunity campaign enrich the partnership.
Growing Indian middle class and bilateral trade relations
- Projected Middle Class Surge: By 2050, India’s middle class is set to expand to a quarter of a billion consumers, signaling a significant opportunity for the UK.
- Thriving Trading Partnership: The UK and India currently enjoy a thriving trading relationship that was valued at £36 billion in the year 2022.
- UK as Top Investment Source: Fresh statistics from the UK’s Department for Business and Trade underscore India’s sustained status as the second-largest source of investment projects for the UK. In the last financial year, 118 new projects emerged, contributing to the creation of 8,384 jobs across the UK.
- Reciprocal Trade and Investment: The partnership between the UK and India goes beyond investment, as the UK is also India’s sixth-largest investor. Over the period from April 2000 to March 2023, the UK invested $34 billion in India through foreign direct investment.
- Mutually Beneficial Business Ventures: The interplay of trade and investment benefits both nations. With 618 UK companies operating in India, the cumulative turnover amounts to approximately $50 billion, and they collectively employ around 466,640 individuals directly as of 2021.
Advancing an Ambitious Free Trade Agreement and Strengthening the Partnership
- Ministerial Meeting: Scheduled discussions with Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal in India focus on progressing an ambitious Free Trade Agreement (FTA) to elevate bilateral trade relations.
- UK’s Negotiating Expertise: Leveraging the UK’s trade negotiation track record, the objective is to expedite the FTA process with India. Addressing complexities in goods, services, and investment is crucial to establishing an encompassing agreement ensuring fairness and mutual benefit.
- Diverse Partnership: Beyond trade, the UK-India partnership extends across culture, sports, education, and tourism, as epitomized by Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s living bridge metaphor.
- Cinematic Bonds: Shared enthusiasm for Bollywood showcases the connection. The UK boasts one of the world’s largest Bollywood audiences. Landmarks like St. Paul’s Cathedral and Blenheim Palace feature in iconic films like Kabhi Khushi Kabhi Gham, cementing the cinematic relationship.
- Vibrant Indian Diaspora: The Indian diaspora, over 1.6 million strong, plays a pivotal role in the UK. Contributions span education to the workforce, with Indian students forming a significant part of the UK’s international student community, reinforcing enduring ties.
Unveiling the Alive with Opportunity Campaign
- Campaign Launch: The UK proudly introduces the £1.5 million Alive with Opportunity marketing campaign, serving as a tribute to the robust bond between the UK and India.
- Celebrating Exchange: This initiative is dedicated to celebrating the perpetual exchange of people, ideas, and culture between the two nations.
- Trade Growth Objective: Aligned with the vision to double trade with India by 2030, the campaign aims to stimulate interest and demand for UK goods and services.
- Business Growth Focus: The campaign also seeks to boost the UK’s potential for business growth through strengthened trade ties with India and by attracting fresh Indian investments.
- Illuminating Connections: Over the course of the upcoming year, the campaign will cast a spotlight on the dynamic business, trade, cultural, and sporting connections between the UK and India across diverse platforms.
- Emphasizing Opportunities: By highlighting these facets, the campaign underscores the significant opportunities embedded within the vibrant partnership.
Conclusion
- The India-UK-UKrtnership stands as a shining example of successful collaboration, underscored by burgeoning trade, investment, and shared values. As both nations continue their journey toward deeper ties, the prospects for mutual growth and prosperity appear brighter than ever.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: biowarfare, Impact on vulnerable genders , emerging technologies and way regulations
Central idea
- In August 2019, the United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research (UNIDIR) convened a conference to deliberate the incorporation of a gender-responsive approach within the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC). The conference centered on the nuanced impact of biowarfare on various genders and the need to comprehend the repercussions of intentional attacks and natural outbreaks on different sexes.
Biological warfare
- Biological warfare, or biowarfare, refers to the strategic use of disease-causing agents like bacteria, viruses, or toxins to harm or incapacitate individuals, populations, or ecosystems for military purposes, potentially causing widespread illness, death, and social disruption.
Gender dynamics in historical biological warfare
- Underrepresentation and Vulnerability: Historical biological warfare highlights gender-specific vulnerabilities, particularly affecting marginalized genders like women due to underrepresentation in research and agent development.
- Apartheid-era South Africa: Deliberate use of biological weapons targeted political opponents; Project Coast attempted infertility in black women.
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases as Weapons: Japan’s 1932-1945 experimentation with sexually transmitted diseases on captives, rape, and forced pregnancy as weapons of war
- Chlamydia and Gender Impact: Chlamydia’s asymptomatic nature categorizes it as a sexually transmitted disease disproportionately impacting women.
- Gender-disparate reactions and anthrax: anthrax disproportionately impacted US biological males (1998–2000). The anthrax vaccine caused stronger reactions in women.
- Anthrax Attacks of 2001: Worst US biological attack, 2001 anthrax attacks resulted in 5 deaths and 17 severe illnesses.
Emerging technology and biological warfare
- Introduction to Emerging Technologies: The rise of gene editing tools, particularly CRISPR, brings novel dimensions to biological warfare, raising concerns and necessitating careful analysis.
- Dual-Use Potential: A 2016 Worldwide Threat Assessment Report categorizes CRISPR as having dual-use potential, with implications for both medical advancements and weaponization capabilities.
- Enhanced Pathogens: CRISPR’s application in gene editing could enhance pathogens by increasing their resistance to treatments and virulence, presenting a novel facet of biowarfare.
- Gender Considerations: The application of CRISPR introduces gender-specific ethical concerns, particularly concerning genetic disorders related to reproductive health and fertility.
- Complex Ethical Landscape: While the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) primarily focuses on offensive research, CRISPR’s versatility demands nuanced evaluation, considering its dual-use potential in both medical research and weaponry.
- Gender and Intersectionality: The impact of CRISPR intersects with gender, ethnicity, and race. It highlights that gender vulnerabilities could be exploited in wartime attacks targeting specific communities, necessitating an intersectional approach.
- Broader Ethical Discourse: The implications of CRISPR’s use within biological warfare extend into a broader ethical and societal conversation, addressing its multifaceted impact and potential consequences.
Enforcement of global biowarfare regulations
- Importance of Enforcement: Enforcing regulations in global biowarfare is paramount to preventing misuse of biological agents. The Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) serves as a key framework, but gender considerations are notably absent.
- Highlighting the Gender Gap: The 2019 UNIDIR conference emphasized the need for gender-responsive strategies within the BWC, underlining the significance of accounting for gender dynamics.
- Broadened Scope: The BWC should expand its purview beyond offensive research to encompass emerging technologies like CRISPR, reflecting the changing landscape of biowarfare threats.
- Collaborative Efforts: Effective enforcement requires collaboration among governments, international organizations, and the scientific community. This collaboration should facilitate research transparency and robust biosecurity measures.
- Preventing Misuse: Gene-editing tools, including CRISPR, must be strictly regulated to prevent their misuse for biowarfare. Stringent controls are vital to avoiding their transformation into tools of destruction.
- Advocacy for Gender-focused Disarmament: Noteworthy figures like Izumi Nakamitsu and countries like Norway advocate for gender-focused disarmament, acknowledging the need for gender considerations in the disarmament discourse.
- UN’s First Committee: Norway’s advocacy within the UN’s First Committee underscores the growing recognition of gender representation in disarmament discussions, signaling progress toward gender-inclusive disarmament policies.
Steps to enhance the gender dimension in biowarfare
- Conduct epidemiological research on the differential impact of biological warfare on victims based on sex and gender.
- Advance understanding of sex-related variations in immune and treatment responses to potential biological agents
- Broaden the scope of biological warfare to encompass emerging technology and agents that can target sex, race, or ethnicity-based victims.
Conclusion
- Governments, international organizations, and the scientific community must collaboratively foster regulations, transparency, and biosecurity to avert the inappropriate utilization of gene-editing tools for biowarfare. Open dialogue and international cooperation stand as linchpins in navigating the ethical and security complexities of the CRISPR and biowarfare intersection.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






