Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Guru Nanak and his teachings
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Guru Nanak Jayanti commemorates the birth of Guru Nanak, the founder of Sikhism and the first of its ten Gurus.
- It is celebrated worldwide as Guru Nanak Gurpurab on Kartik Poornima, the full-moon day in the month of Katak (October–November).
Five Key Aspects of Guru Nanak’s Life
[1] Early Life and Philosophical Inclination:
- Born on April 15, 1469, in a Hindu family in Nankana Sahib (now in Pakistan).
- Displayed an early interest in philosophical and spiritual questions.
- Worked as an accountant before embarking on a spiritual journey with a Muslim minstrel, Mardana.
[2] Mystical Experience at Age 30:
- Had a transformative spiritual experience during an early morning ablution by a river.
- Received a divine mission to spread a message of unity and devotion.
- Emerged after three days with the profound declaration, “There is no Hindu, there is no Mussalman.”
[3] Extensive Travels and Interfaith Dialogue:
- Traveled widely, including to Sri Lanka, Baghdad, and Mecca, on journeys called ‘udaasis’.
- Engaged with various religious figures, including Hindu pandits and Sufi saints.
- Advocated for the oneness of God and universal brotherhood.
[4] Preaching the Oneness of God:
- Emphasized the unity of humanity and the presence of one God in all.
- Challenged religious orthodoxy and rituals, promoting a direct connection with the divine.
- His teachings laid the foundation for Sikhism, attracting followers from diverse backgrounds.
- His teachings and hymns are compiled in the Guru Granth Sahib, the holy scripture of Sikhism.
- He wrote in Punjabi, using a script known as Gurmukhi.
[5] Succession and Legacy:
- Spent his final years in Kartarpur, establishing a community with daily prayers and hymns.
- Introduced the practice of ‘langar’, a communal kitchen serving free meals.
- Chose Lehna (later Guru Angad) as his successor, bypassing his own sons.
- Passed away on September 22, 1539, leaving behind a legacy of spiritual and social reform.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rythu Bandhu Scheme
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
Rythu Bandhu Scheme: Key Facts
- The Rythu Bandhu scheme is also known as Farmer’s Investment Support Scheme (FISS).
- It is a welfare programme for farmers started in 2018 by the Telangana government.
- Under the scheme, the state government provided the 58 lakh farmers in Telangana with ₹5,000 per acre of their land as a farm investment for two crops.
- There is no ceiling on the number of acres held by a farmer.
- So, a farmer who owns two acres of land would receive Rs 20,000 a year, whereas a farmer who owns 10 acres would receive Rs 1 lakh a year from the government.
- This investment is made twice a year, once for kharif harvest and once for Rabi harvest.
- It is the country’s first direct farmer investment support scheme where cash is paid directly to the beneficiary.
Reasons for suspension
- The election commission had allowed the disbursement of funds for the rabi harvest this season, provided they are not publicised, in accordance with the model code of conduct.
- However, the model code was violated after the state finance minister made a public announcement of the same.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fibre Optic Technology
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the crucial role of the internet in maintaining global connectivity, facilitated largely by high-speed internet connections.
- These connections, enabling video chats, online payments, and virtual meetings, largely depend on the technology of optical fibers.
Understanding Optical Fibers
- Composition and Size: Optical fibers are thin strands of glass, almost as thin as a human hair, used for transmitting information.
- Information Transmission: They carry various forms of data, including text, images, and videos, at speeds close to that of light.
- Everyday Relevance: Optical fibers play a vital role in everyday communications like text messaging and phone calls.
- Fragility vs. Strength: Despite their thinness, these fibers are strong and durable when encased in protective materials.
- Versatility: They are flexible enough to be laid underground, underwater, or wound around spools.
Historical Perspective
- Charles Kao’s Contribution: About 60 years ago, physicist Charles Kao proposed using glass fibers for telecommunications, a suggestion that earned him a Nobel Prize in 2009.
- Replacing Copper Wires: Kao’s idea was initially met with skepticism but eventually replaced copper wires in telecommunication.
How Optical Fibers Work?
- Light as an Electromagnetic Wave: Light, part of the electromagnetic spectrum, can be controlled and guided through optical fibers.
- Total Internal Reflection: This phenomenon allows light to travel long distances within the fiber with minimal loss of power.
- Fiber Optic Communication System: This system includes a transmitter, the optical fiber, and a receiver to encode, carry, and reproduce information.
Data Transmission and Resistance
- High Data-Transmission Rate: Optical fibers can transmit data at rates of several terabits per second.
- Insensitivity to External Disturbances: Unlike copper cables, they are not affected by external factors like lightning or bad weather.
Development of Fiber Optic Cables
- Early Experiments: The concept of guiding light in transparent media dates back to the 19th century, with demonstrations by Jean-Daniel Colladon and others.
- Medical and Defense Applications: Early glass objects were used in medicine and defense before their adaptation for data transmission.
- Advancements in the 20th Century: Significant progress occurred in the 1950s and 1960s, including the development of glass-clad fibers and the invention of lasers.
Modern Manufacturing
- Fiber-Optic Cable Production: Today, glass fibers are produced using the fiber-drawing technique, ensuring high purity and engineered refractive index profiles.
- Loss Reduction: Modern optical fibers have significantly reduced signal loss, less than 0.2 dB/km.
Future of Fiber Optics
- Expanding Applications: Fiber optics technology is now integral to various fields, including telecommunication, medical science, and laser technology.
- India’s National Mission: The Indian government’s 2020 Union Budget announced a significant investment in quantum technologies and applications, highlighting the future potential of fiber optics.
- Quantum Optics and Communication: The technology stands at the forefront of a new era, with expanding possibilities in quantum optics and home connectivity.
Conclusion
- Impact of Fiber Optics: The evolution of fiber optics has revolutionized communication and connectivity, offering high-speed, reliable data transmission.
- Continued Growth and Innovation: As the technology continues to advance, its applications are likely to expand further, driving innovations in various sectors and enhancing global connectivity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dollarization
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- Argentina faces over 100% inflation and widespread poverty, prompting public support for Milei’s unique economic policies.
- This has prompted the newly elected Javier Milei replacing the peso with the dollar, abolishing the Central Bank, and cutting government spending.
Concept of Dollarization
- Dollarization is the process by which a country adopts a foreign currency in addition to or instead of its national currency.
- Here are 2 types of dollarization:
- Full Dollarization: This occurs when a country adopts a foreign currency (such as the US dollar) as its sole legal tender. In this scenario, the foreign currency completely replaces the domestic currency for all financial transactions.
- Partial Dollarization: In this case, the foreign currency is used alongside the national currency. It often happens unofficially, where residents hold a significant portion of their assets or conduct a large number of their transactions in the foreign currency.
Motive behind Argentine move
- Hyperinflation Solution: Dollarization could break the cycle of rising prices and money supply, as the dollar is not easily manipulated for political gains.
- Growth Potential: By using dollars, economies might focus on exports and attract foreign investment, benefiting from the dollar’s stability.
Potential Challenges
- Loss of Monetary Policy Control: Adopting the dollar means losing the ability to control the money supply through domestic monetary policy.
- Dependence on Export Promotion: Economies must rely solely on export promotion for economic stability, as currency depreciation is no longer an option.
Ecuador’s Experience
- Economic Turnaround: Ecuador, after adopting the dollar, saw significant improvements in GDP growth, poverty reduction, and inflation control.
- Oil and Gas Reserves: Ecuador’s success was partly due to its natural resources, which helped maintain a steady dollar inflow.
- Beyond Dollarization: Ecuador’s economic prosperity was also due to effective fiscal policies and government interventions in the oil sector.
- Social Spending: Increased social spending played a crucial role in translating economic gains into societal benefits.
Comparative Analysis: Greece and the Euro
- Euro Adoption in Greece: Greece’s adoption of the euro initially spurred growth but later limited its fiscal and monetary policy options.
- Austerity Measures: The Eurozone crisis forced Greece into austerity, highlighting the risks of adopting an external currency without policy autonomy.
Conclusion
- Not a Panacea: Dollarization, while potentially stabilizing, is not a standalone solution and requires complementary domestic policies.
- Argentina’s Uncertain Future: With Milei’s intent to slash government spending and abolish the Central Bank, Argentina’s economic future under his administration remains uncertain.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Teenage Galaxies, JWST
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Recently, the James Webb Space Telescope has provided detailed insights into slightly older galaxies, known as ‘teenagers’ in galactic terms, shedding light on their evolution and unique characteristics.
- This research is part of the CECILIA Survey, utilizing Webb to analyze the chemistry of distant galaxies, named after astronomer Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin.
Study of Teenage Galaxies
- Formation Period: The study focuses on galaxies that formed around 2-3 billion years after the Big Bang, which occurred about 13.8 billion years ago.
- Research Methodology: Researchers analyzed light across various wavelengths from 23 such galaxies using Webb, akin to studying their ‘chemical DNA.’
- Key Discoveries: These teenage galaxies exhibit distinct chemical compositions, indicative of intense star formation and rapid developmental phases.
Characteristics of Teenage Galaxies
- Contrast with Modern Galaxies: These galaxies show significant differences in appearance and behavior compared to contemporary galaxies.
- Developmental Mysteries: They undergo crucial, yet not fully understood, processes during this phase, shaping their final structure and nature.
- High Temperatures in Star-Forming Regions: Star-forming areas in these galaxies show temperatures around 24,000 degrees Fahrenheit, much higher than in present-day galaxies.
- Young Stars and Gas Properties: This temperature variation suggests differences in the stars and gas properties of teenage galaxies.
- Detected Elements: Observations identified these galaxies glowing with elements like hydrogen, helium, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, argon, nickel, and silicon.
Significance of Oxygen and Nickel
- Oxygen’s Crucial Role: As a key component of galactic DNA and the third-most abundant element in the universe, oxygen is vital for tracking galaxies’ growth history.
- Nickel – An Unexpected Find: The presence of nickel, usually not bright enough to be observed in nearby galaxies, suggests unique aspects of massive stars in these galaxies.
- Undetected Elements: Astronomers believe that additional elements likely exist in these galaxies but remain undetected due to current technological limits.
Implications of the Findings
- Chemical Immaturity and Rapid Growth: The study indicates that these galaxies are in a phase of rapid formation and are still chemically immature.
- Insights into Star Formation: Understanding the chemical makeup of these galaxies provides valuable information about their star formation history and rate.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HERVH and 'Jumping Genes'
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Recent breakthroughs in genetic research have shed light on the complexities of early embryonic development, particularly focusing on the inner cell mass, a key component in forming the human body.
Embryonic Development Explained
- Life’s Commencement: Life begins with the fusion of sperm and egg, creating a zygote, the first cell of a new individual.
- Cellular Multiplication: The zygote undergoes rapid cell division, marking the onset of embryonic development.
- Diverse Cell Differentiation: As the embryo develops, cells differentiate into various types, leading to the formation of organs and tissues.
- Journey to Birth: This intricate process culminates in the birth of a newborn after nine months of gestation.
Early Stages of Development
- Inner Cell Mass Formation: Early embryonic cells cluster around the inner cell mass, vital for the embryo’s development.
- Pluripotency of Cells: These cells are pluripotent, meaning they can develop into any cell type in the body.
- Scientific Focus: The inner cell mass is a primary subject of study due to its critical role in human development.
Gene Expression in Embryonic Cells
- Analyzing Gene Activity: Researchers study the proteins produced by genes to understand cell-specific gene expression.
- Deciphering Cell Development: This research provides insights into the active genes in each cell, revealing the mechanisms of cell development.
Discoveries in the Inner Cell Mass
- 2016 Research Insights: Manvendra Singh’s reanalysis of gene expression data identified a new group of non-committed cells in the inner cell mass.
- Enigma of Cell Death: These cells, unlike others, do not progress to later developmental stages and are eliminated early on.
HERVH Gene and Cell Survival
- HERVH’s Crucial Function: A 2014 study revealed that HERVH, a gene with virus-like properties, is essential for maintaining pluripotency in embryonic stem cells.
- Gene Expression Variations: Singh’s research showed that while most inner cell mass cells express HERVH, the non-committed cells that eventually die do not.
- Independent Confirmation: This discovery was corroborated by researchers at the University of Spain in lab-fertilized embryos.
Understanding ‘Jumping Genes’
- Transposons in Non-Committed Cells: The non-committed cells express transposons, or ‘jumping genes’, which can cause DNA damage and lead to cell death.
- HERVH’s Protective Role: HERVH protects most cells from the harmful effects of transposons, but cells lacking HERVH expression are vulnerable.
- Natural Selection in Embryos: The early human embryo acts as a selection ground, favoring cells with HERVH expression.
- HERVH’s Unique Nature: Interestingly, HERVH itself is a transposon but functions protectively rather than destructively.
Implications for Placenta and Beyond
- Placental Development: Cells that form the placenta also exhibit transposon activity but manage to survive without HERVH expression.
- Impact on Regenerative Medicine: Understanding HERVH’s role in cell pluripotency has profound implications for regenerative medicine and could influence embryo viability in fertility treatments.Top of Form
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: na
Mains level: constitutional principles in the execution of international obligations
Central idea
Tax treaties or protocols signed by the executive to alter or vary the provisions of the IT Act must withstand the rigours of the constitutional and statutory requirements
Key Highlights:
- Landmark Decision: The Supreme Court’s decision in Assessing Officer (International Tax) vs Nestle SA is a landmark ruling reaffirming the constitutional principle that international obligations assumed by the executive require specific legislative conditions for legal effect.
- Constitutional Framework: The judgment delves into the interplay between domestic law and international law within India’s constitutional framework, emphasizing the need for parliamentary approval when international obligations conflict with domestically enacted laws.
- Article 73 and Article 253: The powers of the Union executive, as per Article 73, are co-terminus with those of Parliament, allowing the executive to assume international obligations without legislation. However, Article 253 emphasizes the dualism between international law and municipal law, requiring a domestic legislative process for conflicting obligations.
- Delegated Powers: Parliament can delegate treaty-making powers to the executive, exemplified by tax treaties under section 90 of the Income Tax (IT) Act. The court clarifies that assuming international obligations and enforcing them domestically are distinct processes.
- Section 90 of IT Act: The judgment interprets section 90, titled “Agreement with foreign countries or specified territories,” emphasizing the necessity of a notification for the implementation of agreements related to the avoidance of double taxation.
- MFN Clauses: Most-Favoured-Nation (MFN) clauses, aimed at altering taxation provisions, must be notified for incorporation into domestic tax law. Failure to do so would create uncertainty in the tax system, with no constitutional or statutory backing for unnotified application.
- Chaos and Uncertainty: Unnotified application of MFN clauses could lead to chaos and uncertainty, with taxpayers and assessing officers interpreting and applying the clauses based on individual understanding, lacking legal foundation.
- Scope of Judgment: The judgment’s scope is limited to the need for a notification for the implementation of MFN clauses, and questions related to diplomatic accountability or the executive’s capacity to prolong the performance of international obligations were not addressed.
- Importance of Constitutional Principles: The Supreme Court’s decision is applauded for upholding democratic principles, ensuring that international obligations assumed by the executive align with constitutional and statutory requirements.
Challenges:
- Future Events Contingency: The activation of MFN clauses contingent upon future events poses challenges in their timely application and raises questions about the executive’s diplomatic accountability.
Key Phrases:
- Dualism of Legal Systems: The constitutional framework recognizes international law and municipal law as separate and distinct legal systems.
- Domestic Legislative Processes: International obligations conflicting with domestic laws must undergo legislative processes for enforceability in courts.
- Separation of Powers: The judgment underscores the importance of the doctrine of separation of powers in judicially incorporating international obligations into domestic law.
Critical Analysis:
The court’s decision provides a robust interpretation of constitutional principles, ensuring that assumed international obligations align with domestic legal processes. The focus on the necessity of notifications for the implementation of MFN clauses reflects the court’s commitment to maintaining clarity and avoiding chaos in the tax system.
Key Examples and References:
- Article 73 and 253 of the Constitution: The judgment extensively refers to constitutional provisions such as Article 73 and Article 253 to establish the legal framework.
Way Forward:
- Legislative Precision: Policymakers should ensure precision in legislative processes, especially concerning the implementation of international obligations, to avoid legal ambiguities.
- Clarity in Notification: The executive should prioritize clarity in notifications, particularly when activating clauses contingent upon future events, to prevent interpretational challenges.
- Review of Existing Treaties: Periodic reviews of existing tax treaties to ensure they align with constitutional and statutory requirements and to address any potential issues related to conflicting obligations.
- Enhanced Diplomatic Engagement: Diplomatic efforts should focus on ensuring that assumed international obligations are seamlessly integrated into domestic legal frameworks to uphold constitutional principles.
The Supreme Court’s judgment serves as a guide for maintaining the sanctity of constitutional principles in the execution of international obligations, particularly in the context of tax treaties.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) JAM Trinity
Mains level: DBT's success
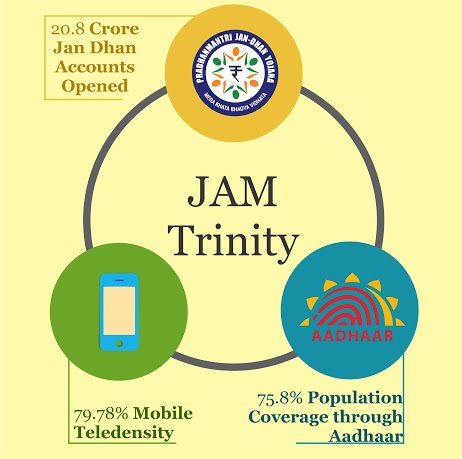
Key Highlights:
- India’s Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system lauded globally as a “logistical marvel.”
- DBT utilizes digital infrastructure to directly transfer government scheme benefits, covering 310 schemes across 53 ministries.
- The JAM Trinity (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, and Mobile) post-2017-18 maximized DBT’s impact.
Dignity of the Poor:
- DBT’s overlooked benefit is its preservation of the dignity of the poor.
- Without corruption or leakages, DBT eliminates the need for the poor to parade for government benefits.
- Shift in approach—government benefits reaching the poor directly without intermediaries.
Poverty Perspectives and Historical Context:
- Discussion on poverty perspectives, referencing Michael Young’s “The Rise of The Meritocracy.”
- Challenge to the prevailing view that poverty is an individual’s fault, offering an alternative, rights-based approach.
- Advocacy for understanding poverty from an individual rights perspective and addressing historical contexts.
Rights-Based Approach to Poverty:
- Recognition of basic security rights for citizens regarding food, shelter, and health.
- Emphasis on shared societal responsibility for poverty, especially by the rich and elite.
- Contrast with technical solutions, highlighting the need to work with the poor.
Preserving Dignity in Design:
- Importance of not just providing benefits but also considering how they are delivered.
- DBT as a mechanism that ensures rightful benefits reach the poor while preserving their dignity.
- Elimination of the poverty parade with the government reaching the poor.
Replicating DBT Success:
- Suggestion to replicate the DBT design in other areas, with a focus on the judiciary.
- Reference to the judiciary’s challenges and an appeal to ensure justice reaches the poor efficiently.
- Call for collective efforts to address complex problems.
Challenges:
- Unquantifiable nature of preserving dignity makes it challenging to measure its impact.
- The need for broader societal shifts in perspectives on poverty and shared responsibilities.
Key Phrases:
- JAM Trinity (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, and Mobile)
- Poverty parade
- Rights-based approach
- Shared societal responsibility
- Technical solutions vs. working with the poor
- Veil of ignorance (Rawlsian perspective)
- Dignity preservation in program design
Critical Analysis:
- Emphasis on the overlooked aspect of preserving dignity brings a unique perspective.
- The article challenges prevailing views on poverty, advocating for a rights-based approach.
- DBT is presented as a successful model, but challenges of replicating its success are acknowledged.
- The article connects poverty perspectives with societal responsibilities and justice delivery.
Key Examples and References for quality enrichment of mains answers:
- Michael Young’s “The Rise of The Meritocracy”
- The Tyranny of Experts by William Easterly
- Reference to the judiciary’s challenges and the appeal of the first woman tribal President.
Key Data and Facts:
- 310 government schemes across 53 ministries utilize DBT.
- Estimated savings of 1.14% of GDP attributed to DBT.
- 79,813 cases pending before 34 judges in the judiciary.
Key Terms:
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT)
- JAM Trinity
- Rights-based approach
- Poverty parade
- Veil of ignorance
- Shared societal responsibility
Way Forward:
- Advocacy for applying DBT’s success in other sectors, particularly the judiciary.
- Acknowledgment of complexity but a call for collective efforts to address challenges.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Composition of Constitution Benches
Mains level: Suggestion to split the Supreme Court into a Final Court of Appeal and a permanent Constitution Bench

Central idea
The article discusses the challenges faced by the Supreme Court of India, the historical proposals for structural changes, and the recent proposal to create Constitution Benches as a permanent feature. It explores the need for regional benches to alleviate the overwhelming caseload and enhance the court’s efficiency, considering historical recommendations and current demands for reform.
Jurisdictions of the Supreme Court:
- Original, appellate, and advisory jurisdictions under the Constitution.
- Functions as a Constitutional Court and Court of Appeal.
Composition of Constitution Benches:
- Typically comprise five, seven, or nine judges.
- Deliberate on issues related to constitutional law.
- Article 145(3) mandates a minimum of five judges for substantial constitutional questions.
Broad Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court:
- Hears cases in Division Benches (two judges) or full Benches (three judges).
- Addresses diverse topics, from film prohibitions to allegations against public officials.
- Notable instances of entertaining frivolous public interest litigations.
Current Caseload and Need for Structural Change:
- 79,813 pending cases before 34 judges, prompting calls for structural reforms.
- CJI D.Y. Chandrachud’s recent announcement on establishing varied-strength Constitution Benches permanently.
Historical Proposals for Structural Change:
- Tenth Law Commission (1984) proposed splitting the Supreme Court into Constitutional and Legal Divisions.
- Eleventh Law Commission (1988) reiterated the need for division, aiming at wider justice availability.
- Bihar Legal Support Society v. Chief Justice of India (1986) expressed the “desirability” of a National Court of Appeal.
- 229th Law Commission Report (2009) recommended regional benches for non-constitutional issues.
Colonial Legacy and Evolution of the Supreme Court:
- Three Supreme Courts during colonial times (Bombay, Calcutta, Madras).
- Indian High Courts Act of 1861 replaced Supreme Courts with High Courts.
- Government of India Act, 1935, created the Federal Court of India.
- The Supreme Court, established on January 28, 1950, under Article 124 of the Constitution.
Increasing Judges and Overburdened Court:
- Evolution of the Supreme Court from eight judges in 1950 to 34 in 2019.
- Overburdened court issuing around 8-10 decisions yearly through Constitution Benches.
- Only four out of 1,263 decisions in 2022 from Constitution Benches.
Critical Analysis:
- Overburdened Judiciary: High number of pending cases (79,813) indicates the burden on the Supreme Court. The overwhelming workload affects the efficiency of the court in delivering timely justice.
- Historical Proposals: Historical proposals, like the Tenth Law Commission’s suggestion in 1984, proposed splitting the Supreme Court into Constitutional and Legal Divisions.The aim was to make justice more accessible and reduce litigants’ fees.
- Regional Benches Proposal: The 229th Law Commission Report (2009) recommended establishing regional benches to hear non-constitutional issues. The proposal aimed to decentralize workload and allow the Supreme Court to focus on constitutional matters.
- Historical Background: Evolution of the Supreme Court from colonial times with the creation of regional Supreme Courts. Transformation from three Supreme Courts (Bombay, Calcutta, Madras) to the current centralized structure.
Key Examples and References:
- Bihar Legal Support Society v. Chief Justice of India (1986) suggested establishing a National Court of Appeal.
- The 229th Law Commission Report (2009) recommended regional benches.
Key Facts:
- The Court sits in benches of varying sizes, as determined by the Registry on the directions of the Chief Justice of India (CJI), who is the Master of the Roster
- The Supreme Court was founded on January 28, 1950, under Article 124 of the Constitution.
- Workforce increased from 8 judges in 1950 to 34 judges in 2019 due to rising caseload.
Way Forward:
- Suggestion to split the Supreme Court into a Final Court of Appeal and a permanent Constitution Bench.
- A Constitution Bench (V. Vasanthkumar v. H.C. Bhatia) analyzing and proposing measures to protect citizens’ access to the Supreme Court.
- Opportunity to address structural gaps by designating appeal benches as regional benches under CJI’s guidance.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






