Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Historical Perspectives on Work
Mains level: Impact of AI on Labour and Work

Central Idea
- Elon Musk’s recent remarks at the Bletchley Park summit on Artificial Intelligence (AI) have stirred discussions about the potential of AI to replace all forms of human labor.
- While such a future may seem theoretical, it raises critical questions about the nature of work, economic paradigms, and societal well-being.
AI’s impact and Labour and Work
- Elon Musk’s Vision: Musk envisions a future where AI replaces all forms of human labor, leaving individuals to seek work solely for personal fulfillment.
- Reality of AI: AI, while capable of substituting certain jobs, also generates new employment opportunities, such as AI programmers and researchers.
- AI’s Self-Awareness: A truly workless future implies AI becoming self-aware, capable of designing, operating, and maintaining itself, a scenario that remains theoretically possible but practically improbable.
Historical Perspectives on Work
- John Maynard Keynes: Keynes believed that reducing working hours would enhance welfare, as work often represented drudgery. He foresaw technological advancements reducing work hours and increasing well-being.
- Karl Marx: Marx viewed work as integral to human identity, providing meaning through material interaction with nature. Capitalism’s exploitation of labor alienates individuals from their work.
- AI’s Impact on Work: Musk’s vision aligns with Keynes’ thinking, suggesting that AI’s advancements could eliminate work, a positive outcome in this context.
Role of Capitalism in a Workless World
- Capitalism and Income: Under capitalism, individuals rely on income from work to access essential resources. Lack of work equals deprivation.
- Access to Resources: Musk’s vision allows for voluntary work but doesn’t address how individuals without work can access basic needs within the capitalist framework.
Imagining a Workless Economy
- Alternative Economic System: A workless world necessitates an economic system with different rules governing production and distribution, possibly involving a universal basic income.
- Institutional Questions: This alternative world raises questions about determining income levels, resource distribution, and balancing future growth with current consumption.
- Challenges of Change: Implementing such a system may be met with resistance within the existing capitalist society marked by rising inequality and a billionaire class.
Conclusion
- While the prospect of a world without work as envisioned by Elon Musk may seem speculative, it underscores the need to understand the potential disruptions caused by technological innovations.
- The impact of AI on work cannot be fully comprehended without considering the economic institutions that shape our society.
- Addressing these challenges requires a thoughtful examination of our current economic system and its adaptability to a rapidly changing technological landscape.
Try this PYQ:
Karl Marx explained the process of class struggle with the help of which one of the following theories?
(a) Empirical liberalism
(b) Existentialism
(c) Darwin’s theory of evolution
(d) Dialectical materialism
Post your answers here.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cyprus Confidential
Mains level: Tax avoidance vs. evasion

Central Idea
- The Cyprus Confidential investigation unveils a web of offshore entities controlled from India, shedding light on financial transactions orchestrated by individuals in India.
Cyprus Confidential and Its Scope
- Global Offshore Probe: Cyprus Confidential explores 3.6 million documents, unveiling companies established in Cyprus by global elites.
- International Collaboration: Over 270 journalists from 60 media outlets across 55 countries and territories participate in this investigation.
- Data Sources: The investigation draws on documents from six offshore service providers in Cyprus, revealing not only Indian investors but also entities formed by prominent business conglomerates to leverage Cyprus’ favorable tax environment.
The Indian Perspective:
Setting Up Offshore Entities in Cyprus
- Indian entities: The investigation aims to lift the secrecy surrounding offshore entities, exposing how they are controlled from India, with financial instructions originating from individuals within the country.
- Legality: Establishing offshore companies in Cyprus is not illegal. India has Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs) with various countries, including Cyprus, offering advantageous tax rates.
- Tax Residency Certificates: Companies utilize tax residency certificates in these countries to legally benefit from reduced tax rates. These jurisdictions are characterized by loose regulatory oversight and stringent secrecy laws.
India’s Tax Treaty with Cyprus
- Pre-2013: Before 2013, India and Cyprus had a tax treaty exempting investors from capital gains tax, attracting substantial investments. Cyprus also had a low withholding tax rate of 4.5%.
- 2013 Onward: India categorized Cyprus as a Notified Jurisdictional Area (NJA) in 2013, leading to higher withholding tax rates and transfer pricing regulations for transactions involving NJA entities.
- Revised DTAA in 2016: A revised DTAA was signed in 2016, rescinding Cyprus from NJA with retrospective effect from November 1, 2013. This treaty introduced source-based taxation of capital gains and a grandfathering clause.
Tax Benefits in Cyprus
- Tax Rates: Offshore companies and branches managed from Cyprus are taxed at 4.25%, while those managed from abroad and offshore partnerships enjoy complete tax exemption.
- Dividends and Capital Gains: No withholding tax on dividends, and no capital gains tax on the sale or transfer of shares in offshore entities.
- Estate Duty Exemption: No estate duty on the inheritance of shares in offshore companies.
- Import Duty Exemption: No import duty on the purchase of vehicles, office, or household equipment for foreign employees.
- Beneficial Owner Anonymity: Ensures anonymity of the beneficial owners of offshore entities.
India-Cyprus DTAA and Its Significance
- Tax Planning: The DTAA enables Cyprus, with its favorable tax regime, to be a jurisdiction for tax planning. Foreign investors often set up investment firms in Cyprus to invest in India and benefit from the DTAA.
- Alternative to Mauritius: Cyprus is now an alternative to Mauritius for establishing offshore entities for Indian investments, as dividends paid from India are subject to withholding tax but not to taxation in Cyprus.
Offshore Trusts in Cyprus
- Cyprus International Trust Law: Offshore trusts under this law are exempt from estate duty and income tax, provided the trustee is Cypriot. Confidentiality is guaranteed.
- Tax Avoidance: Offshore trusts allow businesspersons to avoid taxes they would have paid if income from overseas operations had been remitted to their country of residence.
- Limitations of Indian DTAA: A DTAA does not prevent the Indian Income Tax department from denying treaty benefits if a company is found to have been inserted as a shareowner in India solely to avoid tax. In such cases, the entire transaction may be questioned.
Conclusion
- The India-Cyprus offshore connection is a complex landscape with legal tax planning, secrecy, and regulatory challenges.
- The Cyprus Confidential investigation has brought these nuances to light, prompting scrutiny and raising questions about the intricacies of offshore financial activities.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Leaders’ Week is currently underway in San Francisco, bringing together leaders from the Asia-Pacific region to discuss pressing economic and trade issues.
- Although India is not an APEC member, is participating at the forum.
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC): An Overview
- Founding: APEC, established in 1989, is a regional economic forum aimed at promoting regional economic integration and greater prosperity in the Asia-Pacific region. It consists of 21 member economies, termed “economies” due to their focus on trade and economic matters.
- Member Economies: APEC’s member economies include Australia, Brunei, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Hong Kong (as part of China), the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Singapore, Thailand, Chinese Taipei (Taiwan), China, Japan, South Korea, Russia, Canada, the United States, Mexico, Peru, and Chile, strategically located around the Pacific Ocean.
APEC’s Role over the Years
- Champion of Free Trade: APEC has consistently advocated for free trade, reduction of trade tariffs, and economic liberalization.
- Seoul Declaration: The 1991 Seoul Declaration marked the establishment of a liberalized free trade area around the Pacific Rim as APEC’s primary objective.
- Economic Impact: APEC initiatives have contributed significantly to the development of a growing middle class in the Asia-Pacific region. APEC economies, comprising 2.9 billion citizens, account for approximately 60 percent of global GDP and 48 percent of global trade as of 2018.
India’s Interest in APEC
- Historical Interest: India expressed interest in joining APEC in 1991, coinciding with the initiation of economic reforms for liberalization and globalization.
- Rationale: India’s interest in APEC is based on its geographical location, the potential size of its economy, and its trade interactions with the Asia-Pacific.
- Challenges: APEC has maintained an informal moratorium on expanding membership, despite India’s interest. The US-India Joint Strategic Vision for the Asia-Pacific and Indian Ocean Region in 2015 welcomed India’s interest in joining APEC but no formal progress has been made.
Highlights of APEC Summit 2023
- Biden-Xi Meeting: The meeting between US President Biden and China’s President Xi Jinping is a significant highlight. While it may not result in immediate changes in US-China relations, it reflects ongoing high-level engagements.
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF): The summit will focus on progress related to the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), initiated after the US withdrawal from the Trans-Pacific Partnership. Fourteen members, including Fiji and India, are part of the IPEF, with the rest being APEC members.
Conclusion
- The APEC Summit 2023 brings together leaders from the Asia-Pacific region to address economic and trade issues, with the Biden-Xi meeting and discussions on the IPEF among the key highlights.
- Despite India’s historical interest in APEC, membership expansion remains a challenge, underscoring the importance of regional economic forums in shaping global economic policies and partnerships.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mount Etna
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Volcanic eruptions often make headlines only when iconic volcanoes like Etna, Kilauea, or Eyjafjallajokull erupt.
- However, throughout any given year, our planet witnessed numerous volcanic eruptions, with as many as 50 to 80 occurring worldwide.
About Mount Etna
- Mount Etna, located in Italy, holds the title of Europe’s most active volcano and ranks among the world’s largest.
- Its recorded volcanic activity dates back to 1500 B.C., with over 200 eruptions documented since then.
- Etna’s recent eruptions have disrupted air travel, leading to flight cancellations at the nearby Catania airport.
- Additionally, the accumulation of volcanic ash on roads prompted authorities to temporarily ban the use of cars and motorbikes due to safety concerns.
Volcanic Eruptions this Year
Many of the world’s most active volcanoes are concentrated in the Pacific Ring of Fire, encompassing regions like New Zealand, Southeast Asia, Japan, and the western coast of the Americas. This volatile area also experiences about 90% of all earthquakes globally.
- Kilauea, Hawaii: The Kilauea volcano in Hawaii captivated the world with a nearly nonstop eruption that began in 1983 and continued for an astonishing 35 years until 2018. Remarkably, it rekindled in 2021, with the eruption still ongoing.
- Dukono, Indonesia: Erupting since August 1933, Dukono volcano in Indonesia stands as a testament to long-term volcanic activity, defying the passage of time.
- Santa Maria, Guatemala: The eruption of Santa Maria in Guatemala commenced in June 1922 and persists to this day, underscoring the enduring nature of certain volcanic phenomena.
- Yasur, Vanuatu: Yasur in Vanuatu first erupted around 1270 and has maintained its volcanic activity, continuing as of June 9, 2023.
Understanding Volcanoes
- Volcanoes are geological features characterized by openings or vents through which lava, tephra (small rocks), and steam erupt onto the Earth’s surface.
- They result from both their own eruptions and the broader processes of tectonic plate movement.
- Volcanic eruptions are essentially the result of magma, or molten rock, beneath the Earth’s surface rising, bubbling, and ultimately overflowing, much like boiling milk spilling out of a pot on a stove.
- The magma seeks pathways to vents within the volcano, where it erupts and is expelled across the land and into the atmosphere, a phenomenon referred to as lava.
Types of Volcanoes
|
Appearance |
Formation |
Eruption Style |
Notable Examples |
| Cinder Cones |
Small, steep, conical |
Formed from basaltic magma with high gas content |
Often explosive eruptions with cinders/scoria |
Paricutin (Mexico), Sunset Crater (USA) |
| Composite/Stratovolcanoes |
Tall and symmetrical |
Result from alternating layers of lava, ash, etc. |
Both explosive and effusive eruptions |
Mount St. Helens (USA), Mount Fuji (Japan) |
| Shield Volcanoes |
Broad and gently sloping |
Primarily formed from basaltic magma |
Primarily non-explosive with extensive lava flows |
Mauna Loa, Mauna Kea (Hawaii) |
| Lava Domes |
Rounded dome-like shape |
Formed from slow extrusion of viscous magma |
Typically non-explosive but can be dangerous |
Novarupta Dome (Alaska), Mount St. Helens’ Lava Dome (USA) |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: na
Mains level: criminal justice system

Central idea
The article highlights gender-based challenges in India’s criminal justice system, citing delays and discrimination against women complainants. Despite increased representation and specialized stations, the study in Haryana indicates persistent issues. The central idea emphasizes the need for reforms, gender sensitivity, and equal treatment within the justice system.
Key Highlights:
- Justice System Accessibility: Citizens face challenges accessing the criminal justice system in India due to police station unapproachability, court delays, and outdated forensic equipment.
- Gender Disparities: The study reveals “multi-dimensional discrimination” against women in the justice system, with differential treatment at all stages and levels.
- All-Women Police Stations: Despite efforts, the study, focused on Haryana, suggests that women face delays, dismissals, and lower conviction rates in cases where they are complainants.
- Limited Representation: While more women are joining the justice system, the study emphasizes the need for increased sensitivity and recruitment drives for female officers.
Challenges:
- Police Station Atmosphere: Unfriendly police stations, especially for women, contribute to delays and hinder justice delivery.
- Legal System Inefficiencies: Overworked prosecutors, court delays, and overcrowded prisons impact the overall efficiency of the justice system.
- Gender Bias: Discrimination against women at various stages, including delayed investigations and dismissals, poses a significant challenge.
- Recruitment Delays: Achieving the 33% reservation target for women in police stations may take another decade, delaying the improvement of gender sensitivity.
Key Phrases:
- Multi-dimensional Discrimination: The study identifies pervasive gender-based discrimination throughout the justice system.
- All-Women Police Stations: Initially created to address women’s concerns, the study questions the effectiveness of this approach.
- Delayed Investigations: Cases with women complainants experience longer waiting times and fewer registrations.
- Lower Conviction Rates: Women complainants have a lower chance of seeing the accused being sent to prison.
Analysis:
- Insufficient Gender Sensitivity: Despite efforts to increase women’s representation, the study suggests that sensitivity and fair treatment are lacking in investigations and trials.
- Systemic Inequalities: The research highlights systemic issues leading to dismissals, delays, and lower conviction rates for cases with women complainants.
- Need for Effective Monitoring: Effective monitoring systems are essential to ensure equal treatment for all genders throughout the justice process.
- Research Limitations: While the study raises crucial issues, the lack of validation from police or judicial officers in Haryana raises questions about the data’s accuracy.
Key Data for answer enrichment:
- Representation: Women constitute only around 12% of the police force, emphasizing the need for increased recruitment.
- Conviction Rate: India struggles with less than a 60% conviction rate, reflecting inefficiencies in the justice system.
- Reservation Target: Achieving the 33% reservation target for women in police stations may take another decade.
- Haryana Sample: The study focuses on Haryana, providing insights into the state-specific challenges faced by women in the justice system.
Way Forward:
- Increased Recruitment: Urgent recruitment drives are needed to enhance gender diversity in police stations and improve sensitivity.
- Efficient Justice System: Addressing inefficiencies, overhauling procedures, and providing adequate resources are essential for an accessible and fair justice system.
- Effective Monitoring: Implementing robust monitoring systems ensures consistent and unbiased treatment for all genders.
- Research Validation: Future research should involve direct interactions with police and judicial officers for accurate data validation and a comprehensive understanding of the issues.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Digital Public Infrastructure
Mains level: digital public goods in shaping international development frameworks
Central idea
India’s digital journey, marked by Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), exemplifies a commitment to inclusivity. The article underscores global collaboration, with MOSIP impacting millions, and highlights Norway’s role, advocating for the 50-in-5 campaign. It emphasizes the balance between openness and security in navigating the digital domain.
Key Highlights:
- DPI Transforming India: Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) has transformed India, providing digital identities and access to services for its vast population.
- Global Recognition and Frameworks: India’s G-20 presidency gained global recognition for DPI, setting frameworks for digital public goods and highlighting its development benefits.
- Digital Inclusion Success Stories: MOSIP, developed in Bengaluru, serves as a global blueprint, benefiting over 97 million citizens in diverse countries, showcasing achievements in digital inclusion.
- Comprehensive Development Framework: DPI is a comprehensive framework aligning with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), emphasizing development, inclusion, innovation, trust, and global competition.
Challenges:
- South-South Cooperation Dynamics: The article explores the dynamics of South-South cooperation, especially in the context of MOSIP, showcasing organic global organization.
- Financial Considerations and Privacy: Financial challenges in developing digital protocols and concerns about data privacy are highlighted as critical challenges for the future.
- Safeguarding Digital Sovereignty: Governments and businesses must navigate challenges, ensuring digital sovereignty without compromising an open, free, and secure Internet.
- Balancing Openness and Security: Balancing openness and security is crucial, emphasizing the importance of DPGA’s compass in certifying and pooling digital public goods.
Key Phrases:
- “Leaving no one behind” – Emphasizes the commitment to inclusivity and the challenge in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- “Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)” – Highlights the transformative role of DPI in providing digital identities and access to services.
- “South-South cooperation” – Signifies the collaborative efforts among countries in the global South, exemplified by MOSIP’s impact.
- “Global development architecture” – Describes the role of digital public goods in shaping international development frameworks.
Analysis:
- Global Recognition of DPI: The article analyzes India’s G-20 presidency and its impact on recognizing DPI as part of the international development architecture.
- Challenges in Digital Domain: The challenges of financial considerations, data privacy, and safeguarding digital sovereignty are critically examined.
- Norway’s Digital Contributions: The analysis delves into Norway’s contributions to the digital domain, showcasing its commitment to the 50-in-5 campaign.
- Balancing Openness and Security: The article emphasizes the need to balance openness and security, considering the complexities of the digital domain.
Key Data:
- MOSIP’s Global Reach: Over 97 million people in various countries, including Morocco, Togo, Sri Lanka, and the Philippines, have received IDs through MOSIP.
- Norwegian Digital Goods: Examples include weather services (Yr), health information systems (DHIS2), and contributions targeting SDG2 on ending food hunger.
- 50-in-5 Campaign: Norway pledges to make at least one national digital good available globally in the next five years as part of the 50-in-5 campaign.
- Digital Public Goods Alliance (DPGA): The article highlights the DPGA’s role as a registry of certified digital public goods, shaping the global digital landscape.
Key Facts:
- Digital Inclusion in India: DPI has played a pivotal role in providing digital identities to almost all of India’s 1.4 billion citizens.
- G-20 Framework for DPI: India’s achievement in getting all G-20 countries to agree to the G-20 Framework for Systems of Digital Public Infrastructure is emphasized.
- Norway’s Role in DPGA: Norway is a co-founder and member of the DPGA, contributing to the certification and pooling of digital public goods.
- Digital Goods Addressing Global Challenges: Digital goods like VIPS and DHIS2 contribute to addressing global challenges such as food insecurity and health management.
Key Terms for enriching answer quality:
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- South-South Cooperation
- MOSIP (Modular Open Source Identity Platform)
- G-20 Framework for Systems of Digital Public Infrastructure
- 50-in-5 Campaign
- Digital Public Goods Alliance (DPGA)
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The Way Forward:
- Collaborative Frameworks with India: Encouraging closer collaboration with India within DPGA frameworks is seen as a positive step for advancing global digital initiatives.
- Learning from India’s Digital Journey: Leveraging lessons from India’s digital journey is crucial for inclusive global development, offering insights into effective transformation strategies.
- Balancing Sovereignty and Collaboration: Collaborating with India within the DPGA framework requires a delicate balance, ensuring digital sovereignty while fostering successful global digital initiatives.
- Certification and Pooling for Global Good: Certification and pooling of digital public goods under DPGA’s global leadership provide a compass for future collaborations, emphasizing global cooperation for mutual benefit.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: social justice agenda
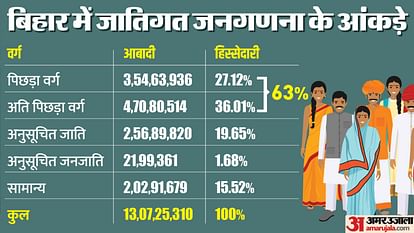
Central idea
Bihar’s caste census is a significant step, yet modernizing caste politics faces hurdles with global economic changes, an authoritative government, and assertive Hindutva ideology. To lead in this complexity, Bihar can pioneer a nuanced, coalition-based approach, reshaping caste politics for the 21st century.
Key Highlights:
- Historic Steps: Bihar takes significant strides in social justice by conducting a caste census and revealing socio-economic data associated with different castes.
- Leadership Challenge: The RJD-JD(U) coalition faces a critical juncture in utilizing caste survey data for an effective social justice agenda, beyond mere reservation expansions.
- Global Economic Situation: Neoliberal policies demand innovative approaches for mass employment (decent work).
- Authoritarian Regime: India experiences an authoritarian shift impacting constitutional norms and federal structures.
- Upper-Caste Hegemony: A visible rise of aggressive north-Indian Hindu upper-caste dominance through Hindutva ideology.
- Internal Differentiations: Complex internal variations within major caste groups challenge traditional one-dimensional caste politics.
Key Data for enhancing answer quality:
- “Formal Sector Jobs”: Despite market-friendly policies, the formal sector of the Indian economy offers less than 8% of all jobs.
- “Reservation Expansion”: Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar’s announcement of expanding reservations to 65%.
- “Resistance Against Hindutva”: Bihar’s historical role in resisting Hindutva politics, along with other states like Karnataka, Kerala, and Rajasthan.
- “Erosion of Indian Federalism”: The resistance against the erosion of Indian federalism, with Bihar contributing to the assertion of State rights.
Key Terms for value addition:
- Caste Census,
- Neoliberal Policies,
- Authoritarian Regime,
- Hindutva Ideology,
- Internal Caste Differentiations,
- Portrait vs. Proxy Model,
- Evolution of Caste Politics,
- State Rights Assertion,
Challenges:
- Neoliberal Constraints: Limited formal sector jobs despite market-friendly policies pose a challenge for reducing caste inequalities.
- Authoritarian Shift: Constitutional norms, checks and balances eroded by an authoritarian regime, altering the Indian state’s shape.
- Hindutva Ideology: Overt and aggressive upper-caste dominance through Hindutva challenges secularism, creating a one-dimensional Hindu identity.
- Internal Caste Differentiations: Diverse class interests within castes require a coalitional approach, potentially leading to unpredictable consequences.
Analysis:
- Changing Caste Politics: The article highlights the need for evolving caste politics beyond automatic association with social justice, considering the complexities of the present context.
- Role of Lower Castes: Lower caste politics can counter Hindutva, even when focused on community interests, offering resistance to the dominance of upper-caste neo-elites.
- State Rights Assertion: Bihar’s resistance against Hindutva and the act of conducting a caste census assert State rights, contributing to the fight against the erosion of Indian federalism.
- Portrait vs. Proxy Model: The caste survey raises questions about representation—whether elected representatives should resemble the population (portrait model) or act on their behalf (proxy model).
The Way Forward:
- Innovative Social Justice: Bihar has the opportunity to pioneer a new form of caste politics, adapting to the present context, breaking from past habits while upholding the core of the social justice agenda.
- Political Representation: The article questions the idea that sharing the same identity is sufficient for representation, emphasizing the need for effective action on behalf of the represented.
- Balancing Identities: Despite the census favoring larger numbers, Bihar can demonstrate that shared identity is a necessary but not sufficient condition for political representation.
- Championing Federalism: Bihar, along with other states, can lead the resistance against the erosion of Indian federalism, emphasizing the importance of locally-relevant policies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Active and Passive Equity Funds
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- Mutual fund investors are currently favouring active equity funds over passive funds, according to a recent study.
Active vs. Passive Equity Funds
|
Active Equity Funds
|
Passive Equity Funds
(Index Funds/ETFs) |
| Investment Strategy |
Actively managed by fund managers |
Passively track a specific benchmark index |
| Research and Analysis |
In-depth research and analysis to select individual stocks |
No active stock selection or market timing; follow benchmark index composition |
| Portfolio Turnover |
Higher turnover; frequent buying and selling of stocks |
Lower turnover; minimal changes to match index composition |
| Fees and Expenses |
Higher management fees and expense ratios |
Lower management fees and expense ratios |
| Performance |
Performance varies widely; aims to outperform the benchmark |
Seeks to match benchmark index performance |
| Diversification |
Diversification depends on the fund’s holdings and strategy |
Offers broad diversification based on benchmark index |
| Tax Implications |
Potential capital gains tax from frequent trading |
Generally lower capital gains tax due to lower turnover |
| Suitability |
Suited for investors seeking potential alpha (outperformance) |
Suited for cost-conscious investors seeking index-like returns |
| Active Management Risk |
Subject to fund manager’s stock-picking skills and market timing |
Minimal active management risk; returns closely track the index |
| Investor Involvement |
Less hands-on; rely on fund manager’s decisions |
Passive investing; no need for frequent monitoring |
| Examples |
Mutual funds with active management |
Index mutual funds, Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) |
| Common Benchmarks in India |
Sensex, Nifty 50, BSE 100, etc. |
Sensex, Nifty 50, Nifty Next 50, etc. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: 2+2 Dialogues Format
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- Indian Defence Minister and External Affairs Minister recently hosted their US counterparts for the fifth annual 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue in New Delhi.
Understanding 2+2 Dialogues
- Purpose: 2+2 dialogues involve the participation of high-level representatives, typically the Ministers of Foreign Affairs and Defence, from two nations. This format aims to expand the scope of dialogue and collaboration between these countries.
- Rationale: Such dialogues enable comprehensive discussions on strategic concerns, mutual sensitivities, and political factors. They facilitate a deeper understanding of each other’s geopolitical perspectives and contribute to the development of stronger, more integrated strategic relationships in an ever-changing global environment.
India’s 2+2 Partners
- United States: The United States is India’s foremost and oldest partner in the 2+2 format. The inaugural 2+2 dialogue took place in September 2018 during the Trump Administration.
- Australia: India engages in 2+2 meetings with Australia, further enhancing bilateral security and defence cooperation.
- Japan: The 2+2 talks with Japan commenced in 2019, with the objective of bolstering strategic depth in security and defence cooperation.
- United Kingdom: In October 2023, India initiated its first 2+2 dialogue with the United Kingdom, signifying the growing importance of this partnership.
- Russia: India and Russia also engage in 2+2 dialogues, fostering a mutually beneficial understanding on various regional and international issues.
Significance of 2+2 Dialogues
- Defence and Strategic Agreements: These dialogues have led to significant bilateral agreements and partnerships. India and the United States, for instance, have signed Troika Pacts like:
- Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA)
- Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA)
- Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement (BECA) for deep military cooperation.
- Addressing Regional Concerns: In the face of common regional concerns, such as China’s increasing assertiveness, 2+2 dialogues have become vital mechanisms for India and its partners to align their strategic interests. This includes cooperation within the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD) forum with Japan, Australia, and the United States.
- Expanding Traditional Alliances: India also values its 2+2 dialogues with Russia, acknowledging shared worldviews and goals in promoting a multipolar world order.
Conclusion
- India’s participation in 2+2 Ministerial Dialogues with key global partners underscores its commitment to fostering robust and multifaceted strategic relationships.
- These dialogues are pivotal in addressing regional and global challenges, strengthening military cooperation, and promoting shared interests in a dynamic world order.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Forest Conservation Amendment Act, 2023
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- The Forest Conservation Amendment Act of 2023 has emerged with limited public discourse, raising concerns about its ramifications for forests and indigenous communities.
- While aimed at addressing climate change and deforestation, the law’s provisions have sparked debates over forest utilization, economic gain, and the rights of forest dwellers, particularly indigenous communities.
Forest Conservation Amendment Act, 2023: Key Provisions
- Focus Areas: The amendment emphasizes climate change mitigation and effective forest management, while also promoting afforestation.
- Jurisdiction Changes: The law restricts its applicability to areas categorized under the 1927 Forest Act and those designated as such after October 25, 1980.
- Exemptions: Forests converted for non-forest use after December 12, 1996, and those within 100 kilometers of the China-Pakistan border for potential linear projects are exempt.
- Security Measures: The central government gains authority to construct security infrastructure in areas up to ten hectares, even extending to vulnerable zones of up to five hectares.
- Economic Initiatives: Initiatives like ecotourism, safari, and environmental entertainment may be implemented to enhance forest-dependent livelihoods.
Motivation behind the Amendment
- Godavarman Thirumulkpad Case: A landmark legal case in 1996 influenced the interpretation of forest land and led to the inclusion of private forests under the 1980 law.
- Industrial Progress: Opposition to the law stemmed from concerns about hindering industrial growth and private landowners’ interests.
- Debate and Controversy: The Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill prompted extensive discussions but was passed with limited opposition, raising concerns among indigenous communities and human rights activists.
Prior Consent and Indigenous Rights
- Amendments in 2016 and 2017: These stipulated mandatory prior consent from tribal grama sabha for non-forest alterations, a provision now removed.
- State-Level Engagement: State governments may involve grama sabhas in decisions related to land acquisition but might be cautious due to perceived hindrance to economic initiatives.
- Impact on Forest Rights Act (FRA): FRA implementation has faced challenges, with governments preferring to limit forest areas rather than amend the Act to address Adivasi claims.
Compensatory Afforestation Concerns
- Ambiguities: Past issues with the Compensatory Afforestation Act have arisen from ambiguities and land shortages.
- Environmental Implications: The new amendment mandates afforestation elsewhere for every parcel of land lost, but lacks specifications, leaving room for discretion.
Forest Governance and Federal Norms
- Afforestation vs. Forest Governance: Financial incentives for afforestation projects clash with forest governance principles, and concurrent list governance practices contradict federal norms.
- Security and Environmental Concerns: While internal environmental security is crucial, it often takes a backseat to external security threats, impacting States prone to natural disasters.
Conclusion
- The Forest Conservation Amendment Act of 2023 raises complex issues related to forest governance, indigenous rights, and environmental security.
- While aimed at addressing critical challenges, its implementation and impact on forest communities warrant careful consideration and debate to ensure a balanced approach to conservation and development.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Euclid Mission, Perseus cluster, Horseshoe Nebula
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- European astronomers have unveiled the first images captured by the newly launched Euclid space telescope.
- These groundbreaking images offer a glimpse into Euclid’s extraordinary capabilities, demonstrating its capacity to observe billions of galaxies situated up to 10 billion light years away.
What is Euclid Mission?
- Euclid’s mission, led by the European Space Agency (ESA) in partnership with NASA, aims to unravel the enigmatic forces of dark matter and dark energy, which together constitute 95% of the universe.
- The Euclid Space Telescope is equipped with a 1.2-meter primary mirror, allowing it to capture detailed observations of galaxies.
- It carries two main scientific instruments: the visible-wavelength camera (VIS) and the near-infrared camera and spectrometer (NISP).
- By mapping the distribution and evolution of galaxies, Euclid aims to shed light on the fundamental forces shaping the cosmos.
(1) Mission Scope and Duration
- Euclid is a space-based mission, equipped with a sophisticated telescope and state-of-the-art scientific instruments.
- The mission is expected to have a nominal operational lifetime of 6 years, during which it will conduct an extensive survey of the sky.
(2) Launch and Spacecraft
- Euclid was launched on July 1, 2023, from Cape Canaveral in Florida using a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
- The spacecraft carries the Euclid Space Telescope, which is designed to observe galaxies across a wide range of wavelengths.
(3) Investigating Dark Energy and Dark Matter
- Dark energy, discovered in 1998, explains the unexpected acceleration of the universe’s expansion.
- Euclid’s mission aims to provide a more precise measurement of this acceleration, potentially uncovering variations throughout cosmic history.
- Dark matter, inferred through the gravitational effects it exerts on galaxies and clusters, plays a vital role in preserving their integrity.
Remarkable Images taken by Euclid

- Sharper and Clearer: These images are touted as the sharpest of their kind, showcasing Euclid’s precision and ability to capture intricate cosmic details.
- Perseus cluster: Euclid’s observations span four regions within our relatively nearby universe, including the massive Perseus cluster, which is located just 240 million light-years away and contains over 1,000 galaxies.
- Horseshoe Nebula: Euclid provided a unique perspective on celestial wonders like the Horsehead Nebula, a region where new stars are born.
- Dark Matter’s Clues: Scientists believe that organized structures like the Perseus cluster could only have formed if dark matter exists. Dark matter is inferred from its gravitational influence on galaxies, including their rotation and the formation of massive cosmic structures.
Unraveling the Dark Universe
- 5% Visible, 95% Dark: The mission emphasizes that our understanding of the universe is limited to merely 5%—the matter we can see. The rest of the universe remains “dark” because it does not emit electromagnetic radiation, but its effects on visible matter are evident.
- Dark Matter’s Role: Dark matter is suspected to influence galaxies’ rotation, galaxy clusters’ cohesion, and the formation of cosmic structures, further validating its existence.
- Dark Energy’s Mystery: Dark energy, an even more enigmatic force, was proposed in the 1990s when the universe’s accelerated expansion was discovered. This mysterious energy was awarded a Nobel Prize in 2011.
Mission Ahead
- Creating a 3D Map: Following its initial commissioning and overcoming technical challenges, Euclid will construct a 3D map covering approximately one-third of the sky. This map will reveal subtle variations attributable to the dark universe.
- Cosmic Web Exploration: By gaining insights into dark energy and dark matter, scientists aim to understand the formation and distribution of galaxies within the cosmic web, a network of cosmic structures that make up the universe.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: counter-terrorism strategy

Central idea
The article explores India’s strategic decision-making in response to terrorism, highlighting the delicate nature of counter-terrorism efforts, the economic consequences of potential military actions, and the significance of thoughtful strategies in shaping international relations. It emphasizes the importance of strategic wisdom over impulsive actions, showcasing India’s nuanced approach to navigating complex geopolitical challenges.
Thomas Friedman’s Praise:
- Columnist’s Perspective: Thomas Friedman commends former PM Manmohan Singh for exercising notable restraint in a recent column.
- Outrage on Social Media: The article triggers heated debates on social platforms, with users expressing strong opinions on India’s past actions.
- Criticizing Past Inaction: Some perceive India’s historical restraint, post-Mumbai attacks, as an act of cowardice, sparking passionate discussions.
Understanding the Context:
- Social Media Dynamics: Vibrant discussions on the Israel-Hamas conflict unfold on social media platforms, reflecting global interest.
- Traumatic Memory: India’s emotional connection to the conflict emerges from the haunting memories of the 2008 Mumbai attacks.
- Opinion Amplification: Thomas Friedman’s praise triggers intense reactions, amplifying opinions on India’s historical decisions.
- National Pride: The ongoing discourse is influenced by national pride, especially in the context of India’s military actions, like the Balakot airstrikes.
Navigating Counter-Terrorism Challenges:
- Delicate Counter-Terrorism: The article underscores the need for nuanced counter-terrorism strategies, cautioning against impulsive actions.
- Hypothetical Scenario: Imagining India’s response post-26/11 prompts consideration of potential nuclear risks and their implications.
- Global Economic Impact: The hypothetical bombing scenario in Pakistan during a global financial crisis raises concerns about broader economic consequences.
- War Consequences: Evaluating the economic aftermath if Pakistan faced aggressive military action underscores the potential disastrous outcomes.
Strategic Thinking and Framing Issues:
- Strategic Counter-Terrorism: Emphasizing the importance of well-thought-out counter-terrorism strategies for effective outcomes.
- International Response: Crafting responses to terrorism globally requires strategic thinking aligned with prevailing economic conditions.
- Alignment with ‘War on Terror’: The consequences of aligning with the global ‘war on terror’ shape international relations and diplomatic considerations.
- Responses Based on Global Conditions: Shaping actions based on economic circumstances highlights the strategic importance of thoughtful decision-making.
Data, Facts, and Economic Consequences:
- Market Crash: The impact of the global financial crisis on India’s stock market and the potential economic fallout from a war.
- Increased U.S. Aid: Rise in U.S. military aid to Pakistan during the ‘war on terror’ and its effects on geopolitical dynamics.
- Pakistan’s Economic Fallout: Examining Pakistan’s economic decline post-2008-09, indicating repercussions of global narratives.
- Investment Decline: The substantial drop in Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan and its significant implications for the nation’s economy.
Emphasizing Key Phrases:
- Delicate Counter-Terrorism Actions: Stressing the importance of sensitive responses in counter-terrorism efforts, emphasizing caution and precision.
- Strategic International Response: Highlighting the significance of thoughtful and planned approaches on the global stage for impactful outcomes.
- Strength in Deliberation: Recognizing the power and effectiveness in well-thought-out actions and decisions for lasting impacts.
Analysis and International Relations:
- Narrative Shift: Changing perceptions of Pakistan as America’s most dangerous ally and the consequential shifts in global narratives.
- Praise for Responsibility: Recognition of India as a responsible nuclear power with global consequences, influencing diplomatic relations.
- Operationalizing Agreements: Timing of the India-U.S. Civil Nuclear agreement and its significance in shaping geopolitical dynamics.
- Economic Consequences: Analyzing the impact on Pakistan’s economic fortunes and India’s sustained growth in the long term.
The Way Forward:
- Importance of Strategy: Emphasizing the critical role of a thoughtful counter-terrorism strategy for effectively addressing future challenges.
- Diplomacy in Action: Acknowledging the instrumental role of diplomatic responses in shaping international outcomes and fostering stability.
- Air Strikes Significance: Recognizing the strategic significance of well-executed airstrikes as a crucial element in diplomatic and military strategies.
- Avoiding ‘Boots on the Ground’: Underlining the strategic approach of avoiding ground invasions, emphasizing the importance of wit and strategic maneuvering in conflict resolution.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Prediabetes
Mains level: Holistic Diabetes Management

Central idea
The article highlights the importance of using precise terms like “remission” rather than “reversal” in discussing diabetes. It introduces the ABCDE criteria for potential remission, emphasizing factors like A1c, BMI, and duration. The author advocates a disciplined approach (ABCD: A1c, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, Discipline) for a healthy life, addressing India’s substantial diabetes challenges.
Key Highlights:
- Redefining ‘Reversal’: Dr. V. Mohan demystifies the trend of claiming ‘diabetes reversal,’ emphasizing the more accurate term ‘remission.’
- Remission: Temporary relief or improvement from diabetes without a permanent cure.
- ABCDE Criteria for Remission: Identification of crucial factors—A1c, BMI, C-Peptide, Duration, and Enthusiasm—that influence the likelihood of remission in type 2 diabetes.
- A1c: Glycated hemoglobin, a measure of average blood sugar levels over the past three months.
- BMI: Body Mass Index, a measure indicating body fat based on weight and height.
- C-Peptide: A marker for insulin secretion, indicating the body’s ability to produce insulin.
- Duration: Period of time since the onset of diabetes.
- Enthusiasm: Eagerness and commitment towards achieving remission.
- Legacy Effect: Recognizing the enduring benefits of achieving even short-term remission in diabetes and its role in preventing complications.
- Legacy Effect: Long-lasting positive impact resulting from past actions or conditions.
- Lifestyle Discipline: Advocating a disciplined lifestyle, with A1c below 7%, controlled blood pressure, and cholesterol as key components for a healthy life with diabetes.
Challenges:
- Deceptive Claims: Cautioning against misleading claims by commercial entities promoting diabetes reversal.
- Individual Variations: Highlighting the diverse likelihoods of achieving remission among individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Post-Remission Severity: Noting the common occurrence of increased diabetes severity upon its recurrence post-remission.
- Post-Remission Severity: Worsening of diabetes conditions after a period of temporary relief.
- Long-term Remission Challenges: Acknowledging the difficulty for a majority in achieving and sustaining long-term remission.
Key Phrases:
- ABCDE Benchmark: Proposing the ABCDE criteria as a pivotal benchmark for assessing the potential for remission in type 2 diabetes.
- Short-Term Remission Benefits: Underlining the lasting benefits, both physical and preventive, derived from short-term diabetes remission.
- Disciplined Lifestyle Advocacy: Advocating for a disciplined lifestyle encompassing A1c control, blood pressure regulation, and cholesterol management.
- Remission Duration Impact: Recognizing that even temporary remission contributes significantly to safeguarding against diabetes-related complications.
Analysis:
- Holistic Diabetes Management: Dr. Mohan stresses the importance of holistic diabetes management that extends beyond the pursuit of remission.
- Holistic Management: Comprehensive and integrated approach addressing various aspects of diabetes care.
- Remission Realities: Acknowledging the challenge for many individuals to achieve and sustain long-term remission in type 2 diabetes.
- Guidelines Adherence: Reinforcing the significance of adhering to ABCD guidelines for a healthy life despite diabetes.
- Balancing Expectations: Encouraging a balanced perspective on diabetes management, considering the varied responses to remission efforts.
Key Data:
- Diabetes Landscape: A snapshot of diabetes prevalence in India, with 101 million people diagnosed and 136 million in the prediabetes stage.
- Diabetes Prevalence: The proportion of the population affected by diabetes.
- Prediabetes Management: Recognizing the potential for delaying the onset of diabetes through lifestyle modifications in individuals with prediabetes.
- Prediabetes: A condition preceding diabetes, indicating higher-than-normal blood sugar levels.
Key Facts:
- Complications Risk: Highlighting the risks of sub-optimal diabetes control, contributing to severe complications.
- Expert Insight Impact: Dr. Mohan’s insights, drawn from extensive experience, underscore the potential for a healthy life despite diabetes.
- National Health Objective: Reinforcing the national health objective of achieving a ‘diabetes complications-free India.
Way Forward:
- World Diabetes Day Pledge: Urging a renewed commitment on World Diabetes Day to prevent diabetes complications and promote overall well-being.
- Dream of Complications-Free India: Aspiring toward realizing a ‘diabetes complications-free India’ by navigating existing challenges with determination and awareness.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Key data
Mains level: Delimitation concept

Central idea
The article discusses the inadequate representation of citizens by Members of Parliament in India, highlighting challenges of malapportionment and proposing solutions such as delimitation, state reorganization, and local governance empowerment. It emphasizes the need for a more representative and efficient electoral system to strengthen India’s democracy.
What is Malapportionment?
- Malapportionment refers to the unequal distribution of representation or political power among different constituencies or districts within a legislative body.
- It occurs when the number of representatives assigned to a particular area is not proportionate to its population or voting strength.
Key Highlights:
- Representation Disparity: The article highlights the disproportionate representation of citizens by Members of Parliament (MPs) in India, compared to the U.S. and other countries.
- Malapportionment Concerns: Malapportionment, favoring certain states, is discussed as a potential issue in India’s political system.
- Delimitation Challenge: The potential consequences of delimitation, freezing the number of Lok Sabha seats until 2031, are examined, considering the changing demographics of states.
- Federalism Promotion: The need for promoting federalism in India’s electoral system is emphasized to give states better representation and a platform to voice their interests.
- Electoral System Reform: Suggestions for electoral system reforms include reconsidering the Rajya Sabha’s representation method and exploring proportional representation for more equitable outcomes.
- State Reorganization Proposal: Proposes the idea of creating more states in India, addressing concerns about governance efficiency and democratic accountability.
Challenges:
- Representation Deficit: India faces a deficit in adequate representation at various levels of governance, impacting the ability to address critical issues and make effective laws.
- Malapportionment Risks: The political system in India is at risk of malapportionment, especially with the growing political culture differences between the south, northeast, and the rest of India.
- Consequences of Delimitation: Delimitation, while necessary, might lead to biases favoring certain regions and political outfits over others.
Key data from article for mains value addition
- An average Indian Member of Parliament (MP) represents approximately 2.5 million citizens.
- In contrast, a U.S. House of Representatives member represents around 700,000 citizens.
- India has around 4,126 Members of the Legislative Assembly.
- Proposed increase in parliamentary seats to at least 848 to avoid any state losing seats during delimitation.
- Potential rise in seats for certain states, e.g., Karnataka by 11%, and for northern states like Uttar Pradesh by 63%.
- Suggests the potential creation of more states, moving from 29 to 50 or even 75 states.
- Calls for a New State Reorganization Commission to evaluate the viability of new states.
- The 2021 Census, delayed and likely to be conducted in 2024, with results potentially published by 2026, provides a window for delimitation.
Key Phrases for improving your mains score:
- Malapportionment in the U.S. Senate.
- Disproportionate allocation of power.
- Consequences of unleashing delimitation.
- Historical form of delimitation.
- Fiscal impact of delimitation on future transfers to States.
- Promotion of federalism.
- Electoral system reforms.
- Proportional representation consideration.
Analysis:
- Representation Deficit Impact: Limited representation in India’s democratic setup is identified as a default preference, impacting the effectiveness of governance.
- Malapportionment Dynamics: India’s heterogeneous political system raises concerns about the potential bias in favor of certain political outfits due to malapportionment.
- Delimitation Challenges: Delimitation is seen as a potential solution but must be approached cautiously to minimize deleterious consequences.
Way Forward:
- Increase in Parliamentary Seats: Proposes a significant increase in the number of seats in Parliament to enhance democratic representation ratios.
- Consideration Beyond Population: Delimitation should consider factors like geographical determinism, economic productivity, linguistic history, and fairness, not solely based on population.
- State Reorganization Commission: Suggests the creation of a new State Reorganization Commission to evaluate the socio-economic and administrative viability of potential new states.
- Empowerment of Local Governance: Advocates for direct elections of mayors in urban areas with enhanced decision-making powers, promoting efficiency and accountability.
- Focus on Local Democratic Representation: Enhancing local democratic representation is seen as a crucial step to strengthen India’s democracy.
In essence, the article emphasizes the need for a more representative and efficient electoral system in India, advocating for reforms in delimitation, federalism promotion, state reorganization, and empowerment of local governance.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aldrovandi's Herbarium
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Researchers have found a 500-year-old herbarium from Italy, particularly Bologna in the north.
- This collection, meticulously crafted by Italian naturalist Ulisse Aldrovandi between 1551 and 1586, offered a window into the past.
Aldrovandi’s Herbarium
- Floristic Changes: The herbarium, containing 5,000 specimens, unveiled a tapestry of historical changes in Italy’s flora over five centuries.
- Human Impact: Clues of human disturbance, habitat loss, transformation, and the invasion of alien species emerged from the pressed and preserved plant specimens.
- Climate Change: The collection allowed insights into the impact of climate change on Italy’s botanical landscape.
- Demographic Trends: European demographic shifts, excluding the European part of the former USSR, were reflected in the herbarium.
- Extinct and Unknown Species: The herbarium hinted at species, both native and alien, that have vanished or remain undiscovered in contemporary times.
Legacy of Transformation
- New World Influence: Aldrovandi’s herbarium holds the memory of Europe’s first encounters with species from the Americas, which later invaded the continent.
- Transforming Flora: It documents the initial signs of a profound transformation in European flora and habitats, paving the way for the introduction of new species and ecological shifts.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ben Gurion Canal Project
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Israel’s aspirations to gain full control over the Gaza Strip and eliminate Hamas may be linked to an ambitious economic opportunity—the creation of the Ben Gurion Canal Project.
Ben Gurion Canal Project
- Vision: Named after Israel’s founding father, David Ben-Gurion, the Ben Gurion Canal Project remains an ambitious infrastructure proposal.
- Route: It envisions cutting a canal through the Negev Desert to connect the Gulf of Aqaba with the Eastern Mediterranean, challenging Egypt’s dominance over the Suez Canal.
- History: A declassified 1963 US government memorandum explored the idea of using nuclear explosives for digging the canal.
- Need: It would offer an alternative route to connect Europe and Asia, bypassing the Suez Canal.
- Transformational Impact: If realized, this project could reshape global trade dynamics by breaking Egypt’s monopoly over the shortest trade route.
Bypassing the Suez
- Historical Significance: The Suez Canal, opened in 1869, revolutionized global maritime trade by reducing travel distances between Europe and Asia.
- Congestion Issues: Despite expansion efforts, the Suez Canal remains congested, causing significant delays and economic losses.
- Political Conflicts: Egypt’s control over the canal has led to conflicts and wars, impacting global geopolitics.
Logistical and Political Challenges
- Complexity and Cost: Building the Ben Gurion Canal is a massive and costly endeavour, potentially exceeding $100 billion.
- Route Length: The proposed canal route is over 100 km longer than the Suez Canal, primarily due to terrain limitations.
- Security Concerns: Constant military threats, such as Hamas rockets or Israeli attacks, would pose a significant challenge to the canal’s operation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2023
Central Idea
- The Information & Broadcasting Ministry recently unveiled the draft Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2023, a transformative legislation designed to modernize and streamline the broadcasting sector in India.
- This bill presents a unified regulatory framework encompassing traditional broadcasting, OTT content, digital news, and current affairs.
Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2023
|
Description |
| What is it about? |
– Replaces outdated laws, including the 1995 Cable Television Networks (Regulation) Act.
– Extends regulatory oversight to emerging broadcasting technologies (OTT, Digital Media, DTH, IPTV). |
| Structure and Definitions |
– Comprises six chapters, 48 sections, and three schedules.
– Provides clear definitions for modern broadcasting terms and formally defines technical terms. |
| Self-Regulation and Advisory Bodies |
– Introduces “Content evaluation committees” for self-regulation within the broadcasting industry.
– Establishes the Broadcast Advisory Council to advise the government on program and advertisement code violations. |
| Penalties and Fairness |
– Operators and broadcasters may face penalties such as advisory warnings, censure, or monetary fines based on the seriousness of offenses.
– Imprisonment and fines are reserved for severe violations and are commensurate with the entity’s financial capacity. |
| Inclusivity for Disabilities |
– Promotes broadcasting accessibility for individuals with disabilities through subtitles, audio descriptors, and sign language.
– Provides for the appointment of a “Disability Grievance Officer” to address disabled individuals’ concerns. |
| Infrastructure Sharing and Dispute Resolution |
– Facilitates infrastructure sharing among broadcasting network operators.
– Streamlines the “Right of Way” section, improving efficiency in addressing relocation and alterations.
– Establishes a structured dispute resolution mechanism. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: White Hole
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- In a discussion with a theoretical physicist, we explore the intriguing concepts of white holes, the nature of time, and their profound implications for our comprehension of the cosmos.
- We delve into theories, from the transition of black holes to white holes to the fundamental granularity of space-time, providing a glimpse into the forefront of contemporary physics.
White Holes and Their Significance
- Reverse of Black Holes: White holes are essentially the opposite of black holes, with objects entering them behaving like a reversed movie.
- Simplicity in Behavior: White holes exhibit a straightforward behaviour: objects fall in, rebound, and ascend along the same path with reduced velocity.
- Quantum Mechanics Role: Quantum mechanics introduces the concept of a bounce within black holes, resulting in the formation of white holes.
- Altering Space-Time: White holes challenge conventional notions of space-time, suggesting that it undergoes quantum leaps and is not uniform or local.
Universe Emerging from a White Hole
- Analogous to a Bouncing Ball: The transition from a black hole to a white hole shares similarities with a ball bouncing back from the ground, albeit with reduced energy.
- Energy Dissipation: Energy dissipates as heat during this transition, a concept pioneered by Stephen Hawking known as Hawking radiation.
- Black Hole to Big Bang: The theory posits that a universe entering a black hole could bounce and generate an event akin to the Big Bang, potentially leading to the creation of our universe.
Understanding Time
- Relativity of Time: Time does not progress uniformly for all observers; it varies based on factors such as velocity.
- Einstein’s Insight: Albert Einstein introduced the idea that time is not a fixed entity like a clock but rather a flexible concept, akin to a stretchable rubber band.
- The Time Field: Einstein envisioned time as an integral component of a gravitational field, influenced by mass and gravity.
- Granular Space-Time: Combining quantum mechanics and gravity suggests that space-time is granular, consisting of discrete “time-steps,” challenging the notion of continuous space-time.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PM-Kisan Bhai Scheme
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- In a bid to empower small and marginal farmers and break the influence of traders in price determination, the Indian government is poised to launch the PM-Kisan Bhai (Bhandaran Incentive) scheme.
PM-Kisan Bhai Scheme
- This scheme aims to incentivize farmers to retain their produce for a minimum of three months post-harvest, granting them the autonomy to decide when and where to sell their crops.
- It seeks to break the monopoly of traders in setting crop prices, giving farmers greater control over their produce.
- This initiative grants farmers the autonomy to decide when to sell, in contrast to the current practice where most crops are sold around harvest, typically spanning 23 months.
Implementation of the scheme
- Initial Rollout: The scheme may be piloted in states such as Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Two Key Components:
- Warehousing Rental Subsidy (WRS): Small farmers and farmer producer organizations (FPOs) can avail a WRS benefit of ₹4 per quintal per month for a maximum of three months, irrespective of warehousing charges.
- Prompt Repayment Incentive (PRI): The government proposes to extend a 3% additional interest subvention under the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme for farmers pledging their produce and obtaining loans at subsidized interest rates.
- The government has proposed that the storage incentive will be provided for a maximum of three months.
- Besides, produce stored for 15 days or less will not be eligible for the subsidy.
- The incentive will be calculated on day to day basis.
Benefits offered
- Resisting Price Dictation: With monetary support for storage during the harvest season, farmers can refuse prices dictated by buyers.
- Access to a Wider Market: Promoting e-Negotiable Warehouse Receipt (eNWR) trade through platforms like e-National Agriculture Market (e-NAM) will connect farmers to a broader range of buyers across the country.
Need for such a scheme
- Pledge Finance Facility: While a pledge finance facility is currently available to farmers, its effectiveness is limited due to high carryover costs on farmers and credit risk to bankers.
- Incentivizing Scientific Warehousing: The scheme aims to incentivize the storage of farmers’ produce in scientifically built warehouses, reducing interest rates on pledge finance.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: State vs . Governor Row

Central Idea
- In a significant ruling, the Supreme Court has asserted that a State Governor cannot obstruct crucial bills passed by a State Legislature.
- The court delivered this verdict in response to a writ petition filed by the Punjab government.
- The Punjab government approached the Supreme Court, challenging Governor Banwarilal Purohit’s decision to withhold some bills, alleging the legislative session’s illegitimacy.
SC Ruling on Governors Bill Withholding
- Court’s Warning: The court sternly warned the Governor that he was “playing with fire” and directed him to make a decision regarding these pending bills presented to him for assent.
- Power of Elected Representatives: Emphasizing the supremacy of elected representatives in a parliamentary democracy, the court highlighted that real power resides with them.
- Governor’s actual Role: The court underscored that the Governor’s role is that of a constitutional statesman guiding the government on constitutional matters.
Governor’s Grounds for Delay
- Governor’s Grounds: Governor Purohit contended that the Assembly session was “patently illegal” because the Speaker had adjourned the Budget Session sine die in March without proroguing it.
- Special Assembly Sitting: He refused to consider the proposed laws passed in a special June sitting, arguing that they were in breach of Punjab Vidhan Sabha Rules.
- Court’s Disagreement: The court disagreed with the Governor’s claims, stating that the Speaker acted within his rights in adjourning the House sine die.
- Constitutional Validity: The court upheld the Speaker’s authority and stressed that it was not constitutionally valid for the Governor to question how the Speaker conducted the House’s affairs.
Court’s Disagreement with the Governor
- House’s Autonomy: The court affirmed that each legislative house has the right to be the sole judge of the legality of its own proceedings.
- Legitimate Session: It found that the June 19-20 legislative session adhered to Rule 16 of the Punjab Vidhan Sabha Rules, rejecting any doubts cast on its legitimacy.
- Democratic Peril Warning: The court cautioned that any attempts to challenge the legislative session could pose a grave peril to democracy.
Governor’s Role Defined
- No Judgment on Prorogation: The court questioned the Governor’s right to sit in judgment on whether the session was prorogued and emphasized that the Speaker’s decisions on adjournments governed the House.
- Avoiding Perpetual Session: While acknowledging the Speaker’s authority, the court cautioned against exploiting the sine die adjournment to perpetually avoid prorogation.
Conclusion
- The Supreme Court’s verdict reiterates the importance of upholding legislative proceedings and the authority of elected representatives.
- It underscores that Governors should respect the autonomy of legislative houses and not obstruct the passage of bills based on perceived procedural violations.
- This landmark decision ensures the preservation of democratic principles and the effective functioning of State Legislatures.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now