Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: School of Happiness
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- Assam’s Bodoland Territorial Region (BTR) is set to launch the International School of Peace and Happiness, a pioneering institution dedicated to teaching lessons on humanity and societal happiness.
School of Happiness: A Backgrounder
- Bodoland Territorial Council’s Initiative: The Bodoland Territorial Council (BTC), which governs the BTR, has been planning this project for a year.
- Addressing Regional Conflicts: The BTR has experienced ethnic conflicts and extremism. The school aims to instill human values and co-existence in a region marked by diverse faiths, cultures, and ethnicities.
- BTC’s Vision: It emphasizes the need for formal schooling in peace-building and happiness to create peace ambassadors for conflict resolution.
Genesis of the School
- Pilot Project: The concept originated from the Bodoland Happiness Mission, a pilot project introduced a year ago.
- Training Peace Volunteers: Around 400 youth and community leaders were trained as peace and happiness volunteers at Bodoland Community Counselling Centres.
- Training Focus: The program included awareness of social issue-related laws, bias removal, self-awareness, counselling techniques, and stress management.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Veto Power
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- A recent UN resolution vote, where 153 countries voted in favor and 10 against, including the USA’s support for Israel, underscores the influence of a few nations in global decisions.
- This voting pattern brings into focus the veto powers within the UN Security Council (UNSC) and their persistence for over seven decades.
What is the Veto Power in the UNSC?
- Exclusive Membership: The UNSC comprises five permanent members (P5) – the USA, UK, France, Russia, and China – along with 10 non-permanent members.
- Power of Resolutions: Unlike the General Assembly, resolutions passed by the UNSC are legally binding.
- Veto Mechanism: Any P5 member can veto a resolution, blocking its adoption even with the required majority support.
Rationale behind Veto Power for Permanent Members
- Post-WWII Context: The P5, instrumental in forming the UN after World War II, were granted special rights, including veto power, as recognition of their role.
- Strategic Necessity: The veto was considered vital to ensure the participation of these major powers in global peacekeeping efforts.
Formation and Evolution of the UN and Veto Power
- Foundational Discussions: The structure of veto power was developed during key meetings like the Dumbarton Oaks and Yalta Conferences.
- FDR’s Influence: President Franklin D. Roosevelt envisioned the UN as a post-war peacekeeping body, with the ‘Four Policemen’ (USA, USSR, UK, and China) at its core.
- USA’s Diplomatic Efforts: The United States employed strategies, including intelligence, to secure veto power in the UN Charter.
Debate and Criticism of the Veto Power
- Global Dissatisfaction: The exclusive nature of veto power has been a point of contention for many countries.
- Resistance to Change: Attempts to expand the P5 or modify veto rights have been largely unsuccessful due to the vested interests of the permanent members.
- Acknowledging Changes: The increase in non-permanent UNSC members in 1965 was a nod to the changing international environment.
- Reforms agenda: Proposals include making all 15 seats temporary with five-year terms, encouraging open competition for seats, and imposing lobbying and term limits.
Conclusion
- Continued Discussions: The use of veto power in the UNSC remains a contentious issue, reflecting the complex nature of global politics.
- Adapting to Modern Times: As the world’s political landscape evolves, there may be growing pressure to reform the UNSC’s structure and veto mechanism to better align with the current global order.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CRISPR Technology
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- Revolutionary Development: The medical world is witnessing a significant breakthrough with the approval of CRISPR-based therapies for sickle-cell disease and β-thalassemia in the U.K. and the U.S.
- Global Impact: These advancements hold the potential to transform the lives of millions suffering from these inherited blood disorders.
CRISPR Technology: From Discovery to Application
- Origins of CRISPR: Discovered in archaea in 1993, CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) elements were later found to form an antiviral defense system in bacteria with Cas (CRISPR-associated) proteins.
- Nobel Prize-Winning Innovation: Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna’s work on CRISPR-Cas9 as a ‘molecular scissor’ earned them the 2020 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
- Eukaryotic Genome Editing: Subsequent research demonstrated CRISPR-Cas9’s ability to edit eukaryotic genomes, paving the way for various applications in genetic therapies and agriculture.
CRISPR in Medicine: Recent Approvals and Applications
- CRISPR-Based Treatment for Blood Disorders: The MHRA in the U.K. and the FDA in the U.S. approved ‘Casgevy’ for treating sickle-cell disease and transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia.
- Treatment Mechanism: Casgevy involves modifying a patient’s blood stem cells to correct the genetic defect causing sickling, then regrafting them to produce normal red blood cells.
- Historical Context: This approval marks a full circle from Linus Carl Pauling’s description of sickle-cell disease as a molecular disorder 74 years ago.
Emerging CRISPR Technologies and Approaches
- Base-Editing: This technique allows genome editing at the single nucleotide level.
- Prime Editing: A newer method that uses a search-and-replace strategy for precise genome modifications.
- Epigenetic Modifications: CRISPR systems are also being developed to target epigenetic effects.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- Safety and Accuracy Concerns: Issues like off-target events, where CRISPR-Cas9 edits unintended parts of the genome, pose significant challenges.
- Balancing Risks and Benefits: While the potential of these technologies is enormous, their risks must be weighed against both short- and long-term benefits.
- Ongoing Research and Surveillance: Continuous scrutiny is essential to uncover potential side effects that are currently unknown.
Conclusion
- Celebrating Advances: The approval of therapies like Casgevy heralds a new era for millions suffering from genetic diseases.
- Optimistic Outlook: The advancements in CRISPR technology signal a promising future in the field of genetic medicine and disease treatment.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Guru Teg Bahadur
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- PM paid homage to Guru Teg Bahadur, the ninth Sikh Guru, on his martyrdom day, highlighting his bravery, moral integrity, and teachings that foster unity and peace.
- His sacrifice, especially his defence of Kashmiri Pandits against Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb’s forced religious conversions in the 17th century, stands as a pivotal moment in Indian history.
Guru Teg Bahadur’s Life and Contributions
- Extensive Travels: Guru Teg Bahadur, born on April 1, 1621, was known for his extensive travels across India, akin to Guru Nanak Dev, the founder of Sikhism.
- Reviving Sikh Centers: His journeys were instrumental in revitalizing Sikh centers beyond Punjab, setting the stage for the formation of the Khalsa by his son, Guru Gobind Singh, in 1699.
- Poetic Legacy: A prolific poet, Guru Teg Bahadur’s hymns are an integral part of the Guru Granth Sahib, the central religious scripture of Sikhism.
- Founder of Anandpur Sahib: He founded Anandpur Sahib in 1665, a city of great religious and historical significance for Sikhs.
Execution by Aurangzeb
- Protection of Kashmiri Pandits: In 1675, Kashmiri Pandits approached Guru Teg Bahadur for protection against Aurangzeb’s religious persecution.
- Arrest and Martyrdom: Guru Teg Bahadur was arrested and later executed in Delhi on November 24, 1675, in Chandni Chowk, for refusing to convert to Islam and standing up for religious freedom.
- Memorials in Delhi: Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib marks the place of his execution, and Gurudwara Rakab Ganj Sahib commemorates the site where his body was cremated.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Consider the following Bhakti Saints:
- Dadu Dayal
- Guru Nanak
- Tyagaraja
Who among the above was/were preaching when the Lodi dynasty fell and Babur took over?
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 2
Post your answers here.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zero Trust Authentication (ZTA)
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- In response to rising cyberattacks, the Centre has established a secure e-mail system for 10,000 users across critical ministries and departments.
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC) has designed this system, incorporating Zero Trust Authentication (ZTA).
What is Zero Trust Authentication (ZTA)?
- ZTA is a security concept and framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.”
- This approach to cybersecurity is a significant shift from traditional security models that operated under the assumption that everything inside an organization’s network should be trusted.
- In contrast, Zero Trust assumes that trust is never granted implicitly but must be continually evaluated and authenticated, regardless of the user’s location or the network’s perimeter.
Key Principles of ZTA
- Least Privilege Access: Users are granted only the minimum level of access needed to perform their job functions. This limits the potential damage in case of a security breach.
- Strict User Verification: Every user, whether inside or outside the organization’s network, must be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated for security configuration and posture before being granted access to applications and data.
- Micro-segmentation: The network is divided into small zones to maintain separate access for separate parts of the network. If one segment is breached, the others remain secure.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): ZTA often requires multiple pieces of evidence to authenticate a user’s identity. This could include something the user knows (password), something the user has (security token), and something the user is (biometric verification).
- Continuous Monitoring and Validation: The system continuously monitors and validates that the traffic and data are secure and that the user’s behaviour aligns with the expected patterns.
Implementation of Zero Trust Authentication
- Technology: Implementation of Zero Trust requires technologies like identity and access management (IAM), data encryption, endpoint security, and network segmentation tools.
- Policy and Governance: Organizations need to establish comprehensive security policies that enforce Zero Trust principles, including how data is accessed and protected.
- User Education and Awareness: Training users on the importance of cybersecurity and the role they play in maintaining it is crucial.
Benefits of Zero Trust Authentication
- Enhanced Security Posture: By verifying every user and device, Zero Trust reduces the attack surface and mitigates the risk of internal threats.
- Data Protection: Sensitive data is better protected through stringent access controls and encryption.
- Compliance: Helps in meeting regulatory requirements by providing detailed logs and reports on user activities and data access.
- Adaptability: Zero Trust is adaptable to a variety of IT environments, including cloud and hybrid systems.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LEADS Report
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The govt has released the LEADS (Logistics Ease across Different States) 2023 report, assessing logistics performance across Indian States and Union Territories (UTs).
- The report includes 11 States and two UTs, encompassing coastal, landlocked, North Eastern States, and UTs.
About LEADS Report
- The LEADS index was launched in 2018 by the Commerce and Industry Ministry and Deloitte.
- It was inspired by the Logistics Performance Index (LPI) of World Bank, and has evolved over time.
- It ranks states on the score of their logistics services and efficiency that are indicative of economic growth.
- States are ranked based on quality and capacity of key infrastructure such as road, rail and warehousing as well as on operational ease of logistics.
Key Highlights of the 2023 Report
- ‘Achievers’ Category: States like Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Punjab, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Sikkim, Tripura, and UTs Chandigarh, Delhi are named as ‘Achievers’.
- Category Shifts: Maharashtra moved from ‘Achievers’ to ‘Fast Movers’, while Odisha shifted from ‘Achievers’ to ‘Aspirers’.
- ‘Fast Movers’: Kerala and Maharashtra among coastal States, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand among land-locked States, and Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland among North Eastern States are ‘Fast Movers’.
- ‘Aspirers’: Goa, Odisha, West Bengal, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and UTs like Daman & Diu/Dadra & Nagar Haveli, Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh are categorized as ‘Aspirers’.
Policy perspectives
- Digital Initiatives: Digital reforms like PM GatiShakti, Logistics Data Bank, ULIP, and GST are driving India’s improved global ranking.
- India’s Improved LPI Rank: India’s LPI rank improved by six places to 38th position in 2023, reflecting the positive impact of these efforts.
- Vision for Logistics Sector: India’s logistics sector is set to grow from a $3.5 trillion to $35 trillion economy by 2047.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Enceladus, Cassini, Saturn
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- A re-analysis of data from the Cassini mission has revealed a complex mix of molecules in the gaseous plumes of Saturn’s moon Enceladus.
About Cassini Mission
|
Details |
| Launch Date |
October 15, 1997 |
| Mission Agencies |
NASA, European Space Agency (ESA), Italian Space Agency (ASI) |
| Primary Focus |
Study of Saturn, its rings, moons, and magnetosphere |
| Key Objectives |
– Study Saturn’s atmosphere
– Investigate Saturn’s rings
– Detailed studies of Saturn’s moons
– Explore Saturn’s magnetosphere |
| Major Achievements |
– Successful landing of the Huygens probe on Titan
– Discovery of geysers on Enceladus
– Identification of new moons
– Detailed analysis of Saturn’s rings |
| Enceladus Discoveries |
– Detection of water-ice geysers erupting from the south pole
– Indications of a subsurface ocean
– Analysis of organic compounds in the plumes |
| Significant Milestones |
– Jupiter Flyby: December 2000
– Saturn Orbit Insertion: July 1, 2004
– Huygens Titan Landing: January 2005 |
| Mission Duration |
1997-2017 (including extended missions) |
Discovery of Plumes and Initial Analysis
- Cassini’s Initial Discovery: In 2005, the Cassini spacecraft discovered large plumes escaping from Enceladus’s southern hemisphere.
- Source of Plumes: These plumes are believed to originate from a subsurface ocean through fissures in the moon’s icy surface.
- Initial Molecular Findings: Earlier analyses identified water, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia, and molecular hydrogen in the plume samples.
Re-examination of Cassini Data
- Research Team: Led by Jonah Peter from the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California.
- Methodology: The team re-examined data using a statistical analysis technique, comparing it against a vast library of known mass spectra.
- Newly Identified Molecules: The analysis revealed the presence of hydrocarbons like hydrogen cyanide (HCN), acetylene (C2H2), propylene (C3H6), ethane (C2H6), along with methanol and molecular oxygen.
Significant Discovery of Nitrogen
- Definite Presence of Nitrogen: The study confirmed the presence of nitrogen in the form of HCN, resolving previous uncertainties due to overlapping signals in mass spectrometry data.
- Potential for Habitability: The diverse chemical reservoir under Enceladus’s surface suggests conditions that might be consistent with a habitable environment.
- Support for Microbial Life: The presence of these compounds, along with mineralogical catalysts and redox gradients, could potentially support microbial communities or complex organic synthesis.
- Caveat on Life Support: The ability of these compounds to support life depends on their concentration in Enceladus’s subsurface ocean.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: algorithmic auditing
Mains level: challenge of developing capabilities for AI regulation
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Forest Rights Act features
Mains level: deeper understanding of the FRA's intent

Central idea
The Forest Rights Act (FRA) aims to rectify historical injustices faced by forest communities, addressing issues through individual and community forest rights. Implementation challenges, political opportunism, and bureaucratic resistance hinder the FRA’s potential to democratize forest governance. Despite recognizing past injustices, the FRA’s full realization faces obstacles.
Key Highlights:
- The Forest Rights Act (FRA) and its Aim: The FRA, enacted in 2006, seeks to rectify historical injustices faced by forest-dwelling communities due to colonial forest policies.
- Acknowledgment of Injustices: It recognizes the disruption caused by the colonial takeover of forests, imposition of eminent domain, and subsequent injustices post-Independence.
- Addressing Issues through Recognition: The FRA tackles ‘encroachments,’ access, and control by recognizing individual and community forest rights, fostering decentralized forest governance.
Key Challenges:
- Implementation Hurdles: Challenges include political opportunism, forester resistance, bureaucratic apathy, and a distorted focus on individual rights.
- Concerns in Individual Rights Recognition: Shabby recognition of individual forest rights, especially in ‘forest villages,’ remains a concern.
- Obstacles in Community Rights Recognition: Slow and incomplete recognition of community rights to access and manage forests (CFRs) faces opposition from the forest bureaucracy.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Defining Concepts: Individual Forest Rights (IFRs), Community Forest Rights (CFRs), ‘Forest encroachments,’ Eminent domain, ‘Grow More Food’ campaign, Net Present Value fees, Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972, Forest (Conservation) Act 1980.
Key Quotes:
- Highlighting the Lag in Delivering Promises: “17 years after it was enacted, the FRA has barely begun to deliver on its promise of freeing forest-dwellers from historic injustices.”
- Opposition to CFRs: “The forest bureaucracy vehemently opposes CFRs as it stands to lose its zamindari (control).”
Key Statements:
- FRA’s Remarkable Aspects: The FRA stands out for acknowledging historical injustices and providing redress through the recognition of individual and community forest rights.
- Lacunas in Implementation: Implementation challenges include political misrepresentation, bureaucratic hindrance, and slow recognition of community rights.
Key Examples and References:
- State Recognition of CFRs: Maharashtra, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh are highlighted as states recognizing CFRs, with Maharashtra enabling their activation through de-nationalizing minor forest produce.
Key Facts and Data:
- Scale of Challenge: Estimates indicate that 70%-90% of the forests in central India should be under CFRs, emphasizing the magnitude of the challenge in implementing community rights.
Critical Analysis:
- Addressing Issues in Individual Rights Focus: The article critiques the distorted focus on individual rights, digital processes causing hardships, and the forest bureaucracy’s opposition to community rights.
- Importance of Understanding FRA’s Intent: Emphasizes the need for a deeper understanding of the FRA’s intent to address historical injustices and democratize forest governance.
Way Forward:
- Comprehensive Recognition: To realize the FRA’s potential, there is a need for comprehensive recognition of both individual and community forest rights.
- Appreciation of Intent: Political leaders, bureaucrats, and environmentalists must appreciate the spirit and intent of the FRA to ensure meaningful implementation and address historical injustices.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Delimitation Commission
Mains level: Role of delimitation in preserving political equality
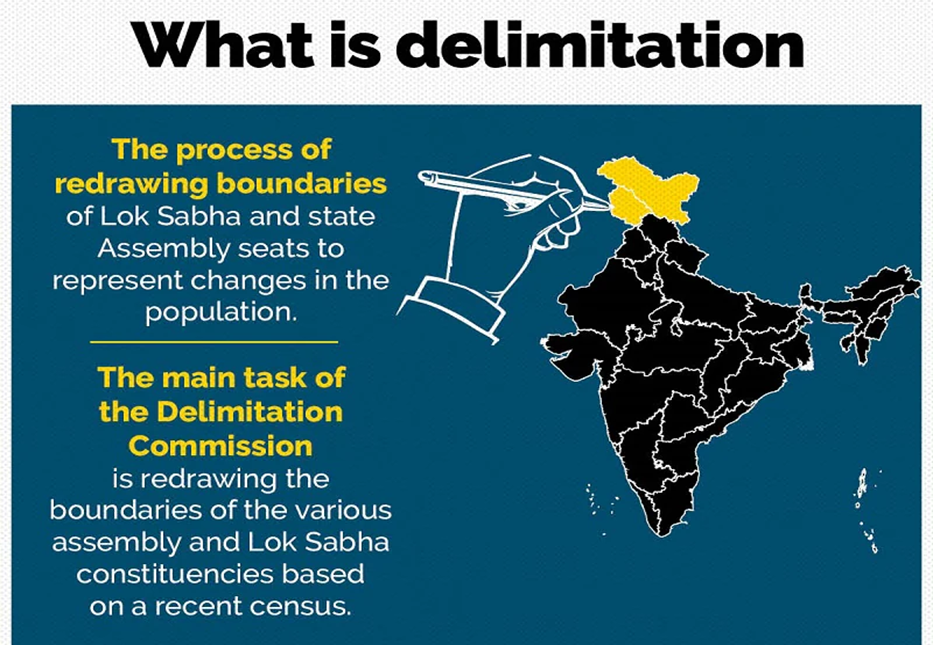
Central idea
Key Highlights:
- Political Equality in Liberal Democracies: In liberal democracies, political equality extends beyond the opportunity to participate; it includes ensuring that each citizen’s vote holds equal value.
- Types of Dilution: Quantitative dilution is observed when population deviations among constituencies result in unequal representation. Qualitative dilution, on the other hand, occurs through gerrymandering, impacting the chances of minority representation.
- Constitutional Safeguards: Articles 81, 170, 327, 330, 332 of the Constitution establish safeguards to guarantee political equality. They empower Parliament to enact laws related to delimitation and address concerns of both quantitative and qualitative dilution.
- Role of Delimitation Commissions: Delimitation commissions, formed periodically, play a crucial role in maintaining population-representation equality by adjusting constituency boundaries.
Key Challenges:
- Population Growth Disparities: Unequal population growth among states poses a challenge, leading to quantitative dilution where the weight of votes varies significantly.
- Impact of Gerrymandering: Gerrymandering can qualitatively dilute the value of votes, particularly affecting minority representation. Techniques like cracking, stacking, and packing can be employed to manipulate electoral boundaries.
- Issues with Freezing and Variation Allowance: The freezing of population figures and the allowance for a 10% variation have resulted in imbalances, allowing deviations from the ideal population-representation ratio.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Dilution Types: Understanding the distinctions between quantitative and qualitative dilution is essential for addressing challenges in the democratic process.
- Legal Framework: Key legal terms include gerrymandering, the Delimitation Commission, Two Member Constituencies (Abolition) Act, 1961, 42nd Amendment Act, 1976, and the Sachar Committee Report, which provide the foundation for delimitation processes.
Key Quotes:
- “The right to vote can be diluted quantitatively and qualitatively by redrawing constituency boundaries.” – Pamela S. Karlan This quote emphasizes the importance of maintaining the integrity of the voting process and avoiding dilution through boundary manipulations.
- “Delimitation of constituencies needs to be carried out regularly based on the decennial Census.” Regular delimitation, aligned with the decennial Census, is crucial for adapting to demographic changes and ensuring fair representation.
Key Statements:
- Population Growth Variations: Differences in population growth among states create a significant gap in the value of votes, impacting the democratic principle of equal representation.
- Issues with Freezing and Variation Allowance: The freezing of population figures and the allowance for variation contribute to imbalances in representation, requiring careful consideration in the delimitation process.
Key Examples and References:
- Impact of Delimitation on SC-Reserved Seats: Delimitation’s impact on Scheduled Caste (SC)-reserved seats, especially concerning the majority Muslim population, highlights the complexities of fair representation.
- Discrepancies in Muslim Representation: Discrepancies between the percentage of Muslim MPs in Parliament (4.42%) and their overall population (14.2%) underscore the qualitative dilution in the representation of minority communities.
Key Facts and Data:
- Population Growth Between 1971 and 2011: Disparities in population growth across states, with some experiencing over 125% growth, contribute to the quantitative dilution of votes.
- Representation Disparity: The average representation disparity, where an MP in some states represents significantly more people than in others, reflects the challenges in achieving equal representation.
Critical Analysis:
- Threats to Democracy: Both quantitative and qualitative dilution pose significant threats to the democratic process, undermining the principle of equal political representation.
- Challenges with Freezing and Variation Allowance: The freezing of population figures and the allowance for variation may result in continued imbalances, demanding a critical evaluation of the current delimitation framework.
- Impact on Minority Representation: The qualitative dilution of votes has a notable impact on minority representation, requiring a nuanced approach in delimitation to address these disparities.
Way Forward:
- Urgent Delimitation: Urgent delimitation is necessary to rectify population-representation deviations and uphold the principles of equal representation in a timely manner.
- Comprehensive Delimitation: Future delimitation processes must consider both quantitative and qualitative aspects, ensuring a comprehensive approach to achieve fair representation.
- Protecting State Interests: Special attention is required to protect the interests of states with slower population growth, balancing the need for representation across regions.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular monitoring and adjustments in delimitation processes are essential for maintaining a robust and inclusive democratic system. Continuous adaptation to demographic changes will help address evolving challenges in representation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






