Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: BOP Crisis, LPG Reforms
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- S. Venkitaramanan, former Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), passed away, leaving behind a legacy of significant contributions.
- His tenure is marked by crucial interventions during India’s economic crises and a commitment to open dialogue and innovative policies.
Navigating the Balance of Payments Crisis
- Economic Turbulence in 1990: India faced a severe balance of payments crisis due to reduced remittances and increased oil prices.
- Critical Measures: Under Venkitaramanan’s leadership, the RBI took bold steps, including pledging gold reserves, to avert a default on international payments.
- Impact of Gold Pledging: This move, though criticized domestically, was crucial in maintaining India’s international credibility and financial stability.
Role in Economic Reforms
- Import Compression Strategy: Venkitaramanan initiated a program of import compression, significantly reducing the current account deficit.
- Foundation for Future Reforms: These measures laid the groundwork for the economic reforms introduced by the Narasimha Rao government and Dr. Manmohan Singh.
Challenges and Controversies
- The Harshad Mehta Scam: Venkitaramanan’s tenure was marred by the securities scandal involving Harshad Mehta, overshadowing his earlier achievements.
- Public Perception: Despite his significant contributions, the public memory often overlooks his role in steering India through economic turmoil.
Remarkable Openness and Inclusivity
- Engagement with Diverse Opinions: Venkitaramanan was known for his openness to different viewpoints, engaging with economists and critics alike.
- Innovative Approach to Policy Making: His willingness to consider varied perspectives contributed to more inclusive and effective economic policies.
Legacy in the RBI and Beyond
- Establishment of the Development Research Group: Venkitaramanan’s vision led to the creation of this group, aiming to foster interaction between the RBI and independent economists.
- Influence on Current Economic Policies: His belief in relying on India’s intellectual resources continues to influence the RBI’s approach, though challenges like inflation management persist.
Conclusion
- Enduring Impact: S. Venkitaramanan’s tenure as RBI Governor was marked by courageous decisions and a commitment to intellectual openness.
- Remembering His Contributions: While his term had its challenges, his role in safeguarding India’s economy and fostering a culture of dialogue and research within the RBI remains a significant part of his legacy.
- Inspiration for Future Leaders: His approach to economic policy and management continues to serve as an inspiration for current and future leaders in the field.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Electoral Bond Scheme
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- The government has announced a fresh tranche of electoral bond sales for a 10-day period starting through the authorised branches of State Bank of India across the country.
About the Electoral Bond Scheme
| Definition |
Banking instruments for political party donations with donor anonymity. |
| Launch |
2017-18 Union Budget |
| Purchase Method |
Available to Indian citizens and Indian-incorporated companies from select State Bank of India branches. Can be bought digitally or via cheque. |
| Donation Process |
Purchasers can donate these bonds to eligible political parties of their choice. |
| Denominations |
Available in multiples of ₹1,000, ₹10,000, ₹10 lakh, and ₹1 crore. |
| KYC Requirements |
Purchasers must fulfill existing KYC norms and pay from a bank account. |
| Lifespan of Bonds |
Bonds have a 15-day life to prevent them from becoming a parallel currency. |
| Identity Disclosure |
Donors contributing less than ₹20,000 need not provide identity details like PAN. |
| Redemption |
Electoral Bonds can be encashed only by eligible political parties through an Authorized Bank. |
| Eligibility of Parties |
Only parties meeting specific criteria, including securing at least 1% of votes in the last General Election, can receive Electoral Bonds. |
| Restrictions Lifted |
Foreign and Indian companies can now donate without disclosing contributions as per the Companies Act. |
| Objective |
To enhance transparency in political funding and ensure funds collected by political parties are accounted or clean money. |
Also read:
Challenging the Electoral Bond Scheme
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Psychoanalysis
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- The Delhi Police’s use of psychoanalysis for assessing motives in the Parliament breach incident highlights its contemporary relevance.
Origins of Psychoanalysis
- Development by Freud: Sigmund Freud, a Viennese psychiatrist, developed psychoanalysis as a modern Western system of psychotherapy.
- Evolution over Time: Initially a treatment for unexplained symptoms, psychoanalysis has evolved, influenced by various scientific disciplines.
- Goal of Psychoanalysis: It aims to enhance self-awareness by uncovering unconscious wishes and defenses.
Concept of the Unconscious
- Freud’s Central Theory: The unconscious contains memories and impulses inaccessible to conscious awareness due to their threatening nature.
- Mechanisms of Repression: Repression plays a key role in psychoanalysis, involving the unconscious forgetting of painful ideas to protect the psyche.
- Id, Ego, and Superego: Freud’s model of the psyche includes the instinct-driven id, the rational ego, and the normative superego.
Fantasies, Defenses, and Resistance in Psychoanalysis
- Role of Fantasies: Fantasies, according to Freud, fulfill psychic needs and provide imaginary wish fulfillment.
- Defense Mechanisms: Intrapsychic processes like projection, reaction formation, and rationalization help avoid emotional pain.
- Concept of Resistance: Freud observed resistance in clients reluctant to engage in therapy, leading to the practice of free association.
Transference and Countertransference
- Transference Dynamics: Clients often project past relational templates onto the therapist, offering insights into their behavior.
- Countertransference Issues: Therapists’ unresolved conflicts can affect their feelings towards clients, necessitating self-analysis.
Psychoanalysis as a Therapeutic Tool
- Dream Interpretation: Freud viewed dreams as forms of wish fulfillment, central to psychoanalytic therapy.
- Making the Unconscious Conscious: The goal is to bring unconscious drives into awareness to understand self-defeating behaviors.
- Therapeutic Relationship: The therapist-client relationship can provide new relational experiences, challenging maladaptive models.
Contemporary Psychoanalytic Practice
- Shift to Shorter Sessions: Modern psychoanalysis often involves fewer sessions per week, adapting to practical and individual needs.
- Long-Term vs. Short-Term Therapy: While some issues require long-term treatment, contemporary practice accommodates shorter, more focused consultations.
Conclusion
- Enduring Relevance: Despite its evolution, psychoanalysis remains a vital tool for understanding human behavior and mental health.
- Adaptation and Integration: Modern psychoanalytic practice has adapted to contemporary needs while retaining core principles.
- Broader Applications: Beyond therapy, psychoanalysis offers insights into various aspects of human behavior, as evidenced by its use in legal and investigative contexts.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kharsawan Massacre
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- On January 1, 1948, the town of Kharsawan in present-day Jharkhand witnessed a massacre reminiscent of what happened in Jallianwala Bagh in 1919.
- Police opened fire at a crowd gathered for a protest and the weekly haat (market), killing hundreds, or by some accounts, thousands of Adivasis.
Kharsawan Massacre: A Background
- Since the creation of the Bihar and Orissa Province in 1912, Adivasis in the region sought a separate state, reflecting their unique culture and grievances.
- This demand gained momentum over the years, with the Simon Commission acknowledging the distinct nature of the region in 1930.
- In 1938, the Adivasi Mahasabha was established to further this cause, led by prominent leader Jaipal Singh Munda.
Kharsawan’s Merger Controversy
- Merger with Orissa: In 1947, Kharsawan, a princely state with a significant Odia-speaking population, decided to join Orissa during India’s princely states’ integration.
- Adivasi Opposition: However, most Adivasis opposed this merger, desiring a separate state instead.
The Massacre
- Protest Gathering: On January 1, 1948, a large gathering was organized in Kharsawan to protest the merger, coinciding with the weekly market day. Over 50,000 people, including those from distant villages, assembled, many to see Jaipal Munda, who was expected but did not arrive.
- Police Open Fire: The large crowd and tense atmosphere led the Orissa military police to open fire, resulting in a massacre. The exact number of casualties remains unclear, with estimates ranging from a few dozen to several thousand.
- Aftermath: The bodies were disposed of in a well and the jungle, and many injured were left untreated. The incident remains a dark and unresolved chapter in Indian history.
Legacy
- Uncertain Death Toll: Official records state 35 deaths, but other sources, like P.K. Deo’s “Memoir of a Bygone Era,” suggest numbers as high as 2,000.
- Lack of Accountability: No definitive report or accountability for the massacre has been established.
- Memorial and Remembrance: A memorial in Kharsawan serves as a reminder of this tragedy, with political leaders often visiting to pay respects.
Conclusion
- The Kharsawan massacre is a poignant reminder of the complexities and tragedies during India’s transition to independence, particularly for marginalized communities like the Adivasis.
- It underscores the unresolved issues of tribal rights and recognition in India’s history.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Earthquakes in Japan
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- On January 1, 2024, a 7.5-magnitude earthquake hit Ishikawa prefecture in Japan, triggering tsunami waves over a meter high.
Japan’s Geographical Vulnerability
- Japan’s geographical vulnerability, particularly concerning plate tectonics, is a critical aspect of its environmental and disaster management challenges.
- The country’s location at the convergence of several major tectonic plates makes it highly susceptible to seismic activities.
Here’s a detailed look at how plate tectonics contribute to Japan’s geographical vulnerability:
[1] Convergent Plate Boundaries:
- Pacific Ring of Fire: Japan is located on the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area with a high level of seismic activity due to the presence of numerous tectonic plate boundaries.
- Plates Involved: The primary tectonic plates interacting near Japan are the Pacific Plate, the Philippine Sea Plate, the Eurasian Plate, and the North American Plate.
- Subduction Zones: The Pacific and Philippine Sea plates are subducting beneath the Eurasian and North American plates. This subduction process is a significant source of seismic activity, including powerful earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
[2] Earthquake Activity:
- Frequent Earthquakes: The movement of these plates results in frequent earthquakes. Japan experiences thousands of tremors annually, ranging from minor to catastrophic.
- Major Earthquakes: Historical events like the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and the 1995 Great Hanshin Earthquake demonstrate the potential for massive destruction and loss of life due to Japan’s tectonic setting.
[3] Tsunami Risk:
- Generation of Tsunamis: Earthquakes occurring under the sea or along the coast can displace large volumes of water, leading to tsunamis. The 2011 tsunami, triggered by a massive undersea earthquake, caused widespread devastation and the Fukushima nuclear disaster.
- Coastal Impact: Japan’s extensive coastline makes it particularly vulnerable to tsunamis, which can arrive within minutes of an undersea earthquake, leaving little time for evacuation.
[4] Volcanic Activity:
- Volcanic Eruptions: The subduction of the Pacific and Philippine Sea plates not only causes earthquakes but also contributes to significant volcanic activity. Magma generated by the melting of the subducted plate rises to the surface, leading to volcanic eruptions.
- Active Volcanoes: Japan has over 100 active volcanoes, a direct result of its tectonic setting. Eruptions pose risks to nearby populations and can disrupt air travel and local economies.
[5] Geological Complexity:
- Intersecting Faults: The interaction of multiple tectonic plates creates a complex network of faults, increasing the unpredictability and variability of seismic events.
- Diverse Seismic Phenomena: This complexity leads to a range of seismic phenomena, including deep-focus earthquakes, which occur at greater depths and can affect broader areas.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs)
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- The Financial Intelligence Unit India (FIU IND) issued notices to offshore virtual digital asset service providers (VDA SPs) for non-compliance with the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA).
- A request was made to the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology to block URLs of these entities.
About Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs)
- Digital Value: Virtual Digital Assets are digital forms of value like cryptocurrencies and tokens. They are secured using cryptography and blockchain technology.
- Intangible and Digital: These assets exist only in digital form and can be used for transactions, investments, or as a store of value.
- Decentralized: They usually operate independently of central authorities, which makes them attractive but also prone to risks like money laundering. This has led to calls for regulation and oversight.
Premise of Non-Compliance with PMLA
- Regulatory Changes in 2023: VDA SPs were brought under anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing regulations in March 2023.
- Mandatory Compliance: These regulations required VDA SPs to register, verify client identities, and maintain records of financial transactions.
- Non-Registration Issue: Non-compliant entities continued to serve Indian users without registration, evading the AML and CFT framework.
Purpose of PMLA Compliance
- Monitoring Financial Transactions: The PMLA aims to track financial transactions to prevent money laundering and terror financing.
- Selective Compliance Advocacy: Legal experts suggest that FIU IND should enforce compliance only on entities fitting the March 2023 notification parameters.
- KYC Benefits: Adherence to KYC mandates is seen as beneficial for VDA SPs, addressing concerns about anonymity and unlawful use of crypto assets.
Global Efforts and Indian Enforcement
- India’s Global Advocacy: India’s enforcement aligns with its global efforts for cryptocurrency regulation, including proposed frameworks by the IMF and the Financial Stability Board.
- G-20 Influence: India’s role in the G-20 has been pivotal in advocating for global cryptocurrency regulation.
International Regulatory Landscapes
- Dubai’s VARA Model: Dubai’s Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) provides a comprehensive licensing framework, emphasizing consumer protection and AML-CFT compliance.
- EU’s MiCA Regulation: The Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) in the EU focuses on transparency, disclosure, and supervision, requiring service providers to be authorized.
- U.S. Regulatory Framework: The U.S. lacks a comprehensive nationwide framework but covers digital assets under existing regulations like the Bank Secrecy Act.
Considerations in Regulating Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs)
- Policy Options by BIS: The Bureau for International Settlements (BIS) outlines three policy options: outright ban, containment, and regulation.
- Challenges of an Outright Ban: An outright ban may be unenforceable due to the pseudo-anonymous nature of crypto markets.
- Containment Strategy: Containment involves controlling flows between crypto and traditional financial systems but may not address inherent vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory Motivations: The motivation to regulate varies, with the need to ensure regulatory benefits outweigh costs.
- Focus Areas for Emerging Markets: Emerging market economies (EMEs) need to define regulatory authority, scope of regulation, and fill data gaps to understand technology interconnections.
Conclusion
- Balancing Act: Regulating virtual digital assets presents a complex balancing act between innovation, consumer protection, and financial stability.
- Global Coordination: The varied approaches across jurisdictions highlight the need for global coordination and harmonization in VDA regulations.
- India’s Proactive Stance: India’s recent actions reflect a proactive stance in aligning with global standards while addressing local concerns.
- Future Challenges: As the virtual asset landscape evolves, regulators worldwide will continue to face challenges in adapting their frameworks to ensure effective oversight without stifling innovation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: POLIX’s beryllium disc
Mains level: detection of lower-energy X-rays

Central idea
Key Highlights:
- ISRO successfully launched XPoSat, an X-ray Polarimeter Satellite, on New Year’s Day in 2024.
- The indigenous instrument, POLIX, built at Raman Research Institute, is a crucial step for Indian astronomers.
- POLIX aims to study X-ray polarization, providing insights into celestial magnetic fields.
Key Challenges:
- Collecting X-rays from space is challenging due to their high energy, making traditional focusing methods impossible.
- Earth’s atmosphere absorbs most X-rays, complicating the study of cosmic X-rays.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- XPoSat: X-ray Polarimeter Satellite.
- POLIX: Indian X-ray Polarimeter.
- Pulsars: Exotic stars emitting X-rays with strong magnetic fields.
- IXPE: NASA’s X-ray Polarimeter Explorer.
- XSPECT: Instrument on XPoSat for studying timing and spectral properties.
Key Quotes:
- “The instrument, totally indigenous in design and fabrication, will herald yet another milestone for Indian astronomers.”
- “Measuring the polarisation of X-rays would enable astronomers to gauge the directions of magnetic fields in celestial objects.”
Key Statements:
- POLIX, a cubical cylinder with a beryllium disc, detects X-rays and works on the principle of polarization after scattering.
- XPoSat, complementing NASA’s IXPE, will provide valuable information about pulsars and black holes.
Key Examples and References:
- Pulsars, city-sized stars with immense mass, often shine in X-rays and have powerful magnetic fields.
- POLIX’s beryllium disc allows the probing of lower energy X-rays compared to NASA’s instrument.
Key Facts and Data:
- POLIX measures roughly half a meter and weighs nearly 200 kilograms.
- XPoSat focuses on studying the timing and spectral properties of X-ray-emitting objects.
Critical Analysis:
- POLIX’s unique design using beryllium enhances the detection of lower-energy X-rays, providing a significant advantage.
- The launch of XPoSat signifies a major advancement in Indian X-ray astronomy, offering a valuable complement to NASA’s efforts.
Way Forward:
- Anticipation surrounds XPoSat’s data collection, expected to deepen our understanding of pulsars and black holes.
- Ongoing collaboration and advancements in X-ray astronomy will likely lead to further discoveries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Non-Nuclear Aggression Agreement
Mains level: Pakistan's prospected economic default and collapse

Central Idea
- India and Pakistan has exchanged a list of their nuclear installations that cannot be attacked in case of an escalation in hostilities.
Non-Nuclear Aggression Agreement
- The Non-nuclear aggression agreement is a bilateral and nuclear weapons control treaty between India and Pakistan, on the reduction (or limitation) of nuclear arms.
- Both pledged not to attack or assist foreign powers to attack on each others nuclear installations and facilities.
- The treaty was drafted in 1988, and signed by PM Rajiv Gandhi and his counterpart Benazir Bhutto on 21 December 1988; it entered into force on January 1991.
- The treaty barred its signatories from carrying out a surprise attack (or to assist foreign powers to attack) on each other’s nuclear installations and facilities.
- Starting in January 1992, India and Pakistan have annually exchanged lists of their respective military and civilian nuclear-related facilities.
Need for the treaty
- In 1986-87, the massive exercise, ‘Brasstacks’ was carried out by the Indian Army, raising fears of an Indian attack on Pakistan’s nuclear facilities.
- Since then, the Foreign ministries of both countries have been negotiating to reach an understanding towards the control of nuclear weapons.
Significance of the agreement
- The treaty barred its signatories from carrying out a surprise attack (or to assist foreign powers to attack) on each other’s nuclear installations and facilities.
- The treaty provides a confidence-building security measure environment.
Other: Sharing of Prisoners information
- Both nations simultaneously share the list of prisoners in each other’s custody.
- These lists are exchanged under the provisions of the Agreement on Consular Access signed in May 2008.
- Under this pact, the two countries should exchange comprehensive lists on January 1 and July 1 every year (i.e. twice a year).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation
Mains level: revisiting the pension computation methodology
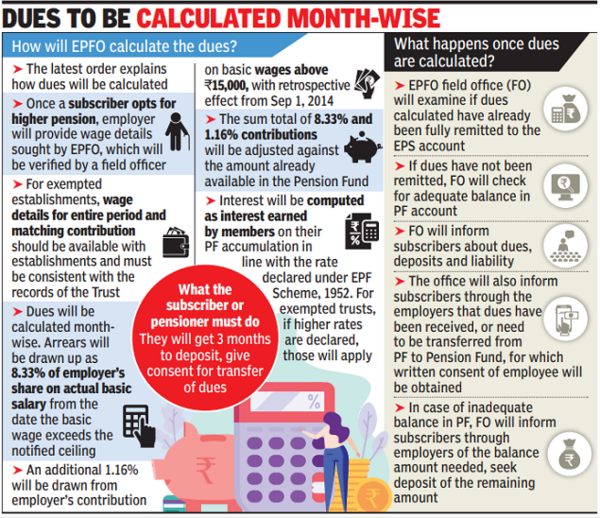
Central idea
The EPFO’s recent clarification on the 2022 Supreme Court verdict regarding higher PF pension has sparked concerns among pensioners due to ambiguity in pension computation methods. Challenges include discrepancies for pre-2014 and post-2014 retirees, with a demand for increased minimum monthly pension.
Key Highlights:
- The EPFO’s clarification on the 2022 Supreme Court verdict on higher PF pension has raised concerns among pensioners and PF members.
- The Court approved higher pension payments with certain conditions, including amendments to the pensionable salary cap and contribution rules.
- The clarification introduces ambiguity by tying pension computation to the “date of commencement of pension.”
Key Challenges:
- Pre-2014 retirees choosing pension post-amendments receive lower pensions due to the calculation based on the average pay of 60 months.
- Post-2014 retirees face ambiguity and discrepancies in the revised pension amounts, seeking clarity through a worksheet.
- Lack of incorporation of interest rate component in pension calculations.
- Long-standing demand to increase the minimum monthly pension beyond ₹1,000, with calls for linking it to the cost of living index.
Key Terms:
- EPFO: Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation
- EPS: Employees’ Pension Scheme
- Pensionable salary cap: ₹15,000/month
- Amendments (2014): Raised pensionable salary cap, altered contribution rules, and changed computation basis.
- Date of commencement of pension: Controversial factor in pension calculation.
Key Quotes:
- “There is also a demand for incorporating the component of interest rate… the pension amount would at least see a rise of ₹2,300 per month.” – MP M. Shanmugam
- “The government’s contributions should increase… to achieve a durable social security system for contributors to the economy.”
Key Statements:
- The clarification’s reliance on the “date of commencement of pension” has created confusion and dissatisfaction among pensioners.
- Ambiguity in post-2014 retirees’ pension calculations prompts the need for a clearer worksheet.
Way Forward:
- Address concerns by revisiting the pension computation methodology.
- Consider increasing the minimum monthly pension, as demanded by various stakeholders.
- Enhance government contributions to ensure a robust social security system.
- Provide clear guidelines and a comprehensive worksheet for post-2014 retirees to understand and verify their pension calculations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: COVID-19 subvariants
Mains level: Continuous tracking of virus variants is challenging due to the unpredictable nature of genetic changes.

Central idea
Dr. Chandrakant Lahariya discusses the emergence of the JN.1 sub-variant of SARS-CoV-2, highlighting its classification as a Variant of Interest (VoI). He emphasizes the need for ongoing genomic sequencing and data tracking while reassuring that, as of now, there’s no evidence of increased severity or immune escape. The central idea is to approach COVID-19 like any respiratory illness, maintaining standard preventive measures and avoiding unnecessary concerns.
Key Highlights:
- Dr. Chandrakant Lahariya, a medical doctor with extensive WHO experience, addresses the emergence of the JN.1 sub-variant of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2.
- Over 1,000 subvariants have been reported since the novel coronavirus outbreak in 2019.
- The designation of JN.1 as a Variant of Interest (VoI) prompts increased genomic sequencing for monitoring.
Key Challenges:
- Continuous tracking of virus variants is challenging due to the unpredictable nature of genetic changes.
- Distinguishing between inconsequential and significant genetic alterations requires careful assessment by international agencies and experts.
Key Terms:
- SARS-CoV-2: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2.
- VoI: Variant of Interest.
- VoC: Variant of Concern.
- Hybrid Immunity: Combined immunity from natural infection and vaccination.
Key Phrases:
- “Silent wave”: JN.1 circulated without causing a significant increase in reported or clinical cases.
- “Genetic material changes”: Variants and subvariants result from alterations in the virus’s genetic structure.
Key Quotes:
- “Designating a variant as VoI does not automatically mean there is a reason to worry.”
- “JN.1 is not a new virus but a sub-variant of BA.2.86, itself a subvariant of Omicron.”
- “There is no scientific evidence to support having a fourth shot of COVID-19 vaccines.”
Key Statements:
- WHO declared the end of the COVID-19 pandemic in May 2023 but emphasized the need for ongoing virus and variant tracking.
- JN.1, as a VoI, requires heightened genomic sequencing and data tracking but doesn’t indicate an immediate cause for concern.
Key Examples and References:
- JN.1 is a subvariant of BA.2.86, part of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2.
- Waste-water surveillance in some Indian cities suggested JN.1 circulated widely without a significant increase in reported cases.
Key Facts:
- Since 2019, more than 1,000 subvariants and recombinant sub-lineages of SARS-CoV-2 have been reported.
- Immunologically, current evidence supports continued protection from COVID-19 vaccines against subvariants.
Key Data:
- Average daily deaths due to respiratory diseases and tuberculosis in India are 50 to 60 times higher than COVID-19 deaths.
Critical Analysis:
- Dr. Lahariya emphasizes the need for nuanced government responses, responsible citizen behavior, and clear science communication.
- The spike in COVID-19 cases may be due to increased testing, and deaths attributed to COVID-19 might be incidental in already sick individuals.
Way Forward:
- Handle SARS-CoV-2 like any other respiratory illness, focusing on standard public health measures.
- Individual and community levels should maintain routine activities, and school closure should not be considered in response to a COVID-19 case surge.
- Continuous surveillance, waste-water monitoring, and improved health facility services are essential for effective response.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now








