Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aditya L1 Mission
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved a significant milestone by placing the Aditya-L1 spacecraft in a halo orbit around the Lagrangian point (L1).
- Launched on September 2, 2023, Aditya-L1 reached the L1 point on January 6, after a 127-day journey covering 1.5 million km.
What is a Halo Orbit?
- Halo orbits are three-dimensional, periodic orbits around Lagrange points in a two-body system like Earth-Sun or Earth-Moon.
- It is commonly linked with L1, L2, and L3 Lagrange points, where the gravitational forces of two large bodies and centrifugal force balance each other.
- It provides a stable line of sight to Earth and the Sun, beneficial for continuous communication and solar power.
- Unlike typical two-dimensional orbits, halo orbits form a 3D loop, resembling a halo around Lagrange points.
- These orbits, especially around L1 and L2 points, require periodic adjustments for a spacecraft to maintain its trajectory.
- It offers energy-efficient positions in space due to balanced gravitational forces, requiring minimal propulsion for orbit maintenance.
- James Webb Space Telescope utilizes a halo orbit around the Earth-Sun L2 point for a stable observation position.
Aditya-L1’s Mission Objectives and Operations
- Orbit Characteristics: Aditya-L1 is in a periodic halo orbit around L1, approximately 1.5 million km from Earth, with an orbital period of about 177.86 days.
- Mission Life and Goals: With a mission life of five years, Aditya-L1 aims to study the sun’s photosphere, chromosphere, and corona, along with in-situ studies of particles and fields at L1.
- Continuous Solar Observation: The satellite’s position allows for uninterrupted solar observation, crucial for understanding solar activities and space weather dynamics.
Understanding Lagrange Points and L1
- Lagrange Points Explained: Lagrange Points are positions in space where a small object can maintain its position relative to two larger bodies due to the gravitational balance.
- L1 Point Advantage: The L1 point, located about 1.5 million km from Earth, offers continuous solar viewing without occultation or eclipse, providing a strategic advantage for solar observation.
Aditya-L1’s Journey Timeline
- Launch and Initial Orbits: Following its launch, ISTRAC conducted four earth-bound maneuvers to position Aditya-L1 in progressively higher orbits.
- Trans-Lagrangian1 Insertion: The spacecraft underwent a crucial manoeuvre on September 19, marking the start of its 110-day journey to L1.
Why Study the Sun?
- Understanding Solar Dynamics: Studying the sun is crucial for comprehending its energy production, temperature variations, and radiation emissions.
- Monitoring Solar Activities: Continuous monitoring of solar flares and coronal mass ejections is vital for predicting space weather and mitigating its impact on space-reliant technologies.
Conclusion
- Unprecedented Solar Study: Aditya-L1’s unique position and advanced instruments enable an unparalleled study of the sun, contributing significantly to our understanding of solar phenomena.
- ISRO’s Achievement: This successful mission underscores ISRO’s expertise in navigating complex space missions and reinforces India’s position as a leading player in space exploration and research.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Alternate Investment Funds (AIFs)
Mains level: NA
Introduction
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has implemented its decisions, introducing significant changes to the regulations governing Alternate Investment Funds (AIFs).
- These include extending the mandatory custodian appointment to smaller AIFs and requiring the dematerialization of AIF investments.
About Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs)
|
Details |
| Definition |
AIFs are privately pooled investment vehicles established in India, collecting funds from sophisticated investors for investing. |
| Regulation |
Governed by the SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012. |
| Formation |
Can be formed as a company, Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), trust, etc. |
| Investor Profile |
Aimed at high rollers, including domestic and foreign investors in India. Generally favored by institutions and high net worth individuals due to high investment amounts. |
| Categories of AIFs |
Category I: Invests in start-ups, early-stage ventures, SMEs, etc. Includes venture capital funds, angel funds, etc.
Category II: Includes funds not in Category I/III, like real estate funds, debt funds, etc. No leverage or borrowing except for operational requirements.
Category III: Employs complex trading strategies, may use leverage. Includes hedge funds, PIPE Funds, etc. |
| Fund Structure |
Category I and II AIFs must be close-ended and have a minimum tenure of three years.
Category III AIFs can be open-ended or close-ended. |
Extended Custodian Appointment Requirements
- Previous Norms: Earlier, the mandatory custodian appointment was required for Category III AIFs and Category I and II AIFs with a corpus exceeding ₹500 crore.
- New Extension: As of January 5, this requirement has been extended to all AIFs, regardless of their corpus size.
Mandatory Dematerialization of Investments
- Amendment to AIF Regulations: SEBI has amended its 2012 AIF Regulations to mandate that AIFs hold securities of their investments only in dematerialized form, with certain exceptions.
- Exceptions: These include investments in instruments not eligible for dematerialization and those held by a liquidation scheme of AIF not available in dematerialized form.
- Future Provisions: SEBI has also reserved the right to specify other investments or schemes that may be exempt from this dematerialization requirement.
New Conditions for Custodian Appointment
- Restrictions on Associates: AIFs can appoint a Custodian who is an Associate of a Manager or a Sponsor of an alternate fund only under specific conditions.
- Net Worth and Independence Requirements: These conditions include the Sponsor or Manager having a minimum net worth of ₹20,000 crore and ensuring the Custodian’s independence from the Sponsor or Manager.
Closing Regulatory Gaps
- Addressing Past Breaches: The latest changes aim to close various regulatory gaps that previously allowed breaches in the spirit of the law and the use of investment vehicles to escape regulatory oversight.
- RBI’s Complementary Measures: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has also tightened norms for banks and NBFCs investing in AIFs to prevent potential ever-greening and other regulatory circumventions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0
Mains level: Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0

Central Idea:
The article delves into the repercussions of excessive jail provisions in Indian laws, particularly those affecting employers, advocating for the Jan Vishwas Bill Version 2.0 as a viable solution. The focus is on transitioning from a retail approach to a wholesale strategy for filtering out unnecessary criminal provisions, aiming to curb corruption, foster good job creation, and alleviate the judicial system’s burden.
Key Highlights:
- Jan Vishwas Bill 1.0 successfully eliminated 113 jail provisions across 23 laws, alleviating corruption demands on employers.
- Labor laws, notably the Factories Act, contain a significant number of imprisonment clauses, impeding high-productivity enterprises.
- The article suggests transitioning from a retail to a wholesale filtering approach for decriminalization, involving a government committee to identify criteria justifying jail provisions.
- Decriminalization is shown to ease the judicial system’s load, exemplified by the Ministry of Company Affairs’ actions outside the Jan Vishwas Bill.
- Excessive regulatory cholesterol, resulting from numerous compliances and filings, obstructs the growth of productive and compliant employers.
Key Challenges:
- Resistance to change from institutions defending the status quo.
- Balancing the need for compliance without stifling entrepreneurship.
- The complexity of labor laws and other regulations, making it challenging to identify and eliminate unnecessary jail provisions.
Key Terms:
- Jan Vishwas Bill: Legislation aimed at reducing corruption demands on employers by eliminating unnecessary jail provisions.
- Regulatory cholesterol: Excessive regulatory burden hindering productivity and compliance.
- Decriminalization: The process of removing criminal penalties from certain offenses.
Key Phrases:
- “Retail to wholesale filtering”: Shifting the strategy from individual ministries volunteering for change to a positive list approach for decriminalization.
- “Regulatory arbitrage”: Corruption resulting from the subjective interpretation and enforcement of laws.
- “Civil service reform”: Advocating for changes in the civil service to address the root cause of regulatory issues.
Key Quotes:
- “Show me the person, and I’ll show you the crime.” – Lavrentiy Beria, highlighting the selective use of imprisonment clauses for corruption.
- “The most sustainable reform for keeping regulatory cholesterol low is civil service reform.” – Emphasizing the need for changes in the civil service to address regulatory issues.
Key Statements:
- “The most sustainable reform for keeping regulatory cholesterol low is civil service reform.”
- “Excessive regulatory cholesterol currently hurts productive and compliant employers.”
Key Examples and References:
- Mention of the Jan Vishwas Bill Version 1.0 and its success in eliminating 113 jail provisions.
- Reference to the Ministry of Company Affairs’ decriminalization efforts outside the Jan Vishwas Bill.
Key Facts and Data:
- Over 25,000 employer jail provisions, with 5,000 arising from central legislation.
- The Ministry of Company Affairs decriminalized over four dozen violations, leading to increased orders issued by the Registrar of Companies.
Critical Analysis:
The article emphasizes the need for a comprehensive strategy to address the issue of excessive jail provisions in Indian laws. It identifies labor laws and other regulations as major contributors to the problem and suggests that a wholesale approach to decriminalization, guided by a government committee, would be more effective. The author contends that reducing regulatory cholesterol is crucial for fostering a conducive environment for job creation and economic growth.
Way Forward:
- Implement Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 with a focus on wholesale filtering for decriminalization.
- Establish a government committee with cognitive diversity to identify criteria justifying jail provisions for employers.
- Encourage collaboration between central ministries to remove unnecessary jail provisions that do not meet the committee’s criteria.
- Emphasize the importance of civil service reform for long-term sustainability in reducing regulatory cholesterol.
- Monitor and assess the impact of the Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 on corruption, job creation, and the judicial system to ensure effectiveness.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Alternative dispute resolution
Mains level: disability rights

Central Idea:
Structured negotiation is an effective and collaborative approach for resolving disputes, particularly in disability rights cases. It emphasizes a win-win situation where defaulting service providers avoid the drawbacks of litigation, and complainants achieve barrier-free access to services.
Key Highlights:
- Success in addressing issues like inaccessible ATMs, point of sale devices, and websites.
- Convincing major companies like Walmart, CVS, and Caremark to create accessible prescription bottles.
- Driving institutional reform for more accessible voting machines and websites.
- Win-win situation: Service providers avoid litigation costs, complainants gain accessible services.
- Relies on a strong body of disabled-friendly legal precedents for success.
Key Challenges:
- Red tape and bureaucracy in Indian civil courts dissuading traditional dispute resolution methods.
- PayTM incident highlights the challenge of real-time accessibility and constant vigilance.
- Success depends on the willingness of service providers to prioritize the needs of persons with disabilities.
Key Terms:
- Structured negotiation
- Disability rights, Litigation
- Accessibility
- Compliance
- Win-win situation
- PayTM
- Alternative dispute resolution
Key Phrases:
- “Win-win situation”
- “Barrier-free participation in the marketplace”
- “Constant vigilance and user inputs”
- “Level of priority from service providers”
- “Enormous buying capacity of persons with disabilities”
Key Quotes:
- “Optimism is the faith that leads to achievement.” – Helen Keller
Key Statements:
- Structured negotiation offers a pathway for businesses to ensure accessibility without litigation.
- Red tape in Indian civil courts poses a challenge to traditional dispute resolution.
Key Examples and References:
- Walmart, CVS, and Caremark creating accessible prescription bottles.
- CCPD directing PayTM to make its mobile applications accessible.
Key Facts:
- Success in addressing issues related to ATMs, point of sale devices, and websites.
- PayTM incident revealing challenges in real-time accessibility.
Critical Analysis:
Structured negotiation’s success relies on creating a strong foundation of disabled-friendly legal precedents. The challenges of bureaucracy and the need for constant vigilance in real-time accessibility highlight the potential limitations. The willingness of service providers to prioritize persons with disabilities is crucial for the model’s effectiveness.
Way Forward:
Businesses in India should prioritize the needs of disabled users and consider structured negotiation as a powerful step. The enormous buying capacity of persons with disabilities should be recognized, urging businesses to embrace accessibility for both legal compliance and economic benefits.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA)
Mains level: Implement stringent safety reporting and accountability measures in the Indian aviation industry.

Central Idea:
The article discusses the recent aviation accident at Tokyo’s Haneda airport involving a Japan Airlines (JAL) Airbus A350 and a Japanese Coast Guard Bombardier Dash 8. It highlights the disciplined evacuation and professionalism displayed by JAL’s crew, contrasting it with incidents where passengers’ lack of discipline during emergencies led to safety concerns. The author also points out flaws in training and safety reporting within the Indian aviation industry, focusing on a recent hard landing incident involving an Air India Airbus.
Key Highlights:
- The Tokyo aviation accident as an example of Murphy’s law.
- Disciplined evacuation by JAL crew saved lives.
- Comparison with incidents of passenger indiscipline during emergencies.
- Flaws in reporting and handling safety incidents in Indian aviation.
- The importance of crew training and adherence to safety procedures.
Key Challenges:
- Lack of discipline among passengers during emergencies.
- Flaws in training and safety reporting within the Indian aviation industry.
- History of covering up serious incidents and accidents in Air India.
- Need for proactive action and accountability in the face of safety concerns.

Key Terms:
- Notice to airmen (NOTAM)
- Aviation Safety Adviser
- Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA)
- Simulator proficiency check
- Emergency evacuation procedures
- Hard landing
- Aircraft type conversion
Key Phrases:
- “If there is a possibility of several things going wrong, the one that will cause the most damage will be the one to go wrong.”
- “High professional standards in JAL’s training of its crew.”
- “A disturbing fact is the failure of the Air India management to act proactively.”
- “The hard landing accident at Dubai should serve as a wake-up call for the airline.”
Key Quotes:
- “The world witnessed the highest quality of discipline and crew training.”
- “Many questions will be raised, and we will not have any reasonable answers.”
- “Merely stating that safety is paramount when so many incidents are being swept under the carpet will not improve the reputation of the airline.”
Key Statements:
- The disciplined evacuation from the JAL aircraft showcased the importance of crew training and adherence to safety procedures.
- Flaws in training and safety reporting in the Indian aviation industry, especially in incidents like the hard landing at Dubai, raise concerns about passenger safety.
Key Examples and References:
- Tokyo aviation accident involving JAL Airbus A350 and Coast Guard Dash 8.
- Air France flight AF 358 overshooting runway incident.
- Emirates flight EK 521 crash incident with passenger indiscipline.
- Air India’s history of covering up incidents, including the recent hard landing at Dubai.
- Indian Airlines Airbus crash in Bangalore in 1990 and TAM Airlines Airbus crash in Sao Paulo in 2007.
Key Facts:
- All 379 passengers on the JAL plane in the Tokyo incident escaped, with five fatalities on the smaller aircraft.
- Aircraft manufacturers must demonstrate complete evacuation within 90 seconds in maximum density configuration.
- The hard landing by an Air India Airbus in Dubai involved a 3.5g impact, posing serious risks.
Critical Analysis:
The article critically examines the disciplined response of JAL’s crew in contrast to incidents of passenger indiscipline during emergencies. It sheds light on the flaws in training and safety reporting within the Indian aviation industry, emphasizing the need for accountability and proactive measures. The historical context of accidents caused by confusion in flying different aircraft types is highlighted, urging the industry to focus on standards and crew proficiency.
Way Forward:
- Implement stringent safety reporting and accountability measures in the Indian aviation industry.
- Emphasize crew training and adherence to safety procedures, learning from incidents like the Tokyo aviation accident.
- Ensure transparency in reporting and addressing safety concerns to improve the reputation of airlines.
- Evaluate crew selection criteria for new aircraft types, prioritizing proficiency and experience over seniority.
- Collaborate with international aviation standards to enhance overall safety in the industry.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Regional languages assertiveness

Introduction
- Activists protested against non-Kannada signboards in Bengaluru, leading to vandalism across the city.
Kannada Signboards Issue
- Demand for Kannada Signboards: The issue dates back to the early 2000s when Bengaluru emerged as a global IT hub. The then Chief Minister S.M. Krishna issued a circular in 2002 for Kannada signboards, which lacked legal backing.
- Legal Challenges: Attempts to mandate Kannada signboards faced legal hurdles, with the High Court staying and striking down related rules in 2009 and 2014.
Recent Developments: Legislation and Protests
- Kannada Language Comprehensive Development Act, 2022: The Act, passed by the State Legislature in 2022, mandates that 60% of signboards be in Kannada.
- KRV’s Campaign: KRV campaigned for the implementation of this norm, leading to the protest and subsequent vandalism.
- State Government’s Ordinance: The government plans to promulgate an ordinance to clarify the 60:40 rule for signboards and set a compliance deadline of February 28.
Impact on Commercial Establishments
- Anxiety among Businesses: The new rule has caused concern among retailers, with fears of increased vigilante actions and financial burdens due to signboard changes.
- Opposition from Retailers: The Retailers Association of India and other business groups have opposed the mandate, citing its impact on Bengaluru’s cosmopolitan nature and brand image.
Political Dynamics
- Election Context: The issue has gained political significance ahead of the parliamentary polls, with both the Congress and BJP staking positions on the language issue.
- Kannada as a Political Plank: Despite political consensus on promoting Kannada, the language has not been a successful political issue in the state.
Concerns over Bengaluru’s Image
- Brand Bengaluru at Risk: The vandalism and language controversy could potentially harm Bengaluru’s reputation as a global investment destination.
- Calls for Government Action: Industry leaders and civic activists have urged the government to take measures to restore confidence and preserve the city’s inclusive culture.
Conclusion
- Need for Sensible Policy: The government faces the challenge of promoting Kannada while maintaining Bengaluru’s cosmopolitan and investor-friendly image.
- Addressing Vandalism: Strong action against vandalism and a balanced approach to language policy are essential to prevent further damage to Bengaluru’s brand and social harmony.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Can be used as case study

Introduction
- Prof. Akeel Bilgrami, a distinguished professor from Columbia University, delivered a lecture at Madras Christian College in Tambaram.
- His talk, titled ‘Gandhi in his time and ours: Reflections on Secularism and Multiculturalism’, explored the nuances of secularism in India and Europe.
Prof Bilgrami on Secularism
He emphasized on three commitments primarily on which Secularism is based:
- Freedom of Religion: The first commitment emphasizes the freedom of religious belief and practice.
- Constitutional Principles: The second commitment involves principles unrelated to religion, such as equality and freedom of speech, enshrined in the constitution.
- Meta-Commitment: The third commitment dictates that in case of a clash between the first two, the constitutional principles must take precedence.
Gandhi’s Perspective on Secularism
- European Context: Gandhi viewed secularism as a doctrine to address the damage caused by religious majoritarianism in Europe.
- Irrelevance to India: He believed that the issues secularism aimed to address in Europe were not present in India, making it irrelevant in the Indian context.
- Nationalism and Anti-Imperialism: For Gandhi, nationalism was synonymous with anti-imperialism and inherently inclusive, contrasting with European forms of nationalism.
Distinguishing Secularisation from Secularism
- Secularisation: Prof. Bilgrami described secularisation as a social process involving the loss of religious belief and changes in religious practices.
- Secularism: In contrast, secularism is a political doctrine advocating for the separation of religion from politics.
Rejecting the Notion of ‘Indian’ Secularism
- Misconception: Prof. Bilgrami dismissed the popular notion that ‘Indian’ secularism is about the acceptance of all religions.
- Pluralism vs. Secularism: He clarified that the acceptance of all religions is more accurately described as pluralism, not secularism.
Conclusion
- Deeper Understanding: Prof. Bilgrami’s lecture provided a deeper understanding of secularism and its application in different contexts.
- Relevance to Contemporary India: His insights are particularly relevant in contemporary India, where secularism and multiculturalism continue to be subjects of intense debate and discussion.
- Future Discourse: The lecture sets the stage for further discourse on how secularism should be interpreted and implemented in India’s diverse and multi-religious society.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Deep Tech
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Indian government is set to approve a new ‘deep tech’ policy. Following public comments on the draft released in July 2023, the final version of the policy is ready for Cabinet approval.
Understanding ‘Deep Tech’
- Definition and Scope: ‘Deep tech’ refers to startups that develop intellectual property based on new scientific breakthroughs, aiming for significant impact. Ex. AI, ML, Blockchain, Quantum Computing etc.
- Startup India Data: As per Startup India, there are 10,298 startups in various sub-sectors of deep tech as of May 2023.
- Exclusion Criteria: Businesses based on easily replicable ideas do not qualify as deep tech startups.
Draft National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP) 2023
- Policy Goals: The NDTSP aims to address challenges in funding, talent acquisition, and scaling R&D operations for deep tech startups.
- Strategic Approach: The policy is designed to promote innovation, economic growth, and societal development in the deep tech sector.
India’s Deep Tech Ecosystem
- Global Ranking: India ranks third globally in the startup ecosystem, with over 3000 deep tech businesses.
- Sectoral Expansion: These firms are expanding into areas like agriculture, life sciences, chemistry, aerospace, and green energy.
Policy Foundations and Prospects
- Public Consultation: The draft policy was open for public feedback until September 15, after consultations with stakeholders in the deep tech ecosystem.
- Key Pillars: The policy focuses on securing India’s economic future, progressing towards a knowledge-driven economy, bolstering national capability, and encouraging ethical innovation.
Policy Elements and Recommendations
- Funding and Innovation: The policy proposes financial support through grants, loans, and venture capital, along with regulatory simplifications and academia-industry collaboration.
- Talent Development: Emphasis on STEM education, training opportunities, and attracting international talent.
- Infrastructure and Technology Access: Establishment of deep tech incubation centers, testing facilities, and shared infrastructure resources.
- Public Procurement and Market Opportunities: Encouraging government agencies to adopt deep tech solutions and facilitating international market access.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Establishing a uniform IP framework and implementing cybersecurity measures.
Conclusion
- Transformative Potential: The NDTSP is poised to guide India’s deep tech landscape, fostering technological innovation and economic growth.
- Measuring Success: The policy’s effectiveness will be gauged by its impact on startups, innovation depth, and societal transformation.
- Democratizing Deep Tech: The strategy aims to make deep tech benefits accessible across society, leveraging research-driven breakthroughs for national advancement.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Paleolithic Age
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Floods Uncover Historical Artifacts: The recent floods in Mulugu district, Telangana, have led to the discovery of Paleolithic quartzite tools, shedding new light on the region’s ancient human habitation.
- Discovery by Amateur Historians: The tools were found in a dried-up stream bed by a team led by Sriramoju Haragopal, an amateur historian.
About Paleolithic Age
|
Details |
| Timeframe |
Approximately 2.6 million years ago to about 10,000 BCE. |
| Characteristics |
Marked by the use of stone tools by early humans. Tools were mainly hand axes, cleavers, and choppers. |
| Major Sites |
- Bhimbetka in Madhya Pradesh
- Soan Valley in Punjab
- Sites in Rajasthan, Karnataka, and Maharashtra
- Narmada Valley in Central India
- Attirampakkam in Tamil Nadu
- Hunsgi in Karnataka
- Kurnool in Andhra Pradesh
- Didwana in Rajasthan
- Belan Valley in Uttar Pradesh
|
| Lifestyle |
Nomadic hunter-gatherers; relied on hunting animals and gathering plants for food. |
| Cultural Developments |
Development of basic stone tools and control of fire. |
| Art and Symbolism |
Evidence of early art found in Bhimbetka rock shelters, with paintings and engravings. |
| Climate and Environment |
Varied climatic conditions over millennia; included ice ages and warmer periods. |
| Human Species |
Mainly Homo erectus and Homo sapiens. |
Details of the Discovery
- Location of Find: The hand axes were discovered between Gurrevula and Bhupatipuram villages in Mulugu district.
- Specific Find: Researchers found a significant stone axe measuring 15.5 cm in length, 11 cm in width, and 5.5 cm in thickness.
Context and Comparison
- Global Significance: Similar hand axes have been discovered worldwide, indicating a common tool type used by early humans for various purposes.
- Historical Context in India: The first discovery of a Paleolithic site in India was in 1863 at Attirampakkam near Madras (now Chennai), with bifacial hand-axes dating back to about 15 lakh years, known as the Madras Hand-Axe Industry or Madrasian Culture.
Historical Significance
- Paleolithic Era Tools: According to paleontologists, the stone axe dates back to the Lower Paleolithic period, approximately 30 lakh years ago.
- Tool Identification: The tools were identified based on their chipping style, material, and size, typical of Paleolithic hunter-gatherers who used heavy quartzite for large tools.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully tested a 100 W class Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell based Power System (FCPS) in space.
- The FCPS was part of the POEM3 orbital platform, launched onboard PSLV-C58 on January 1, 2024.
About FCPS Experiment
- Primary Goal: The experiment aimed to assess the operation of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel cells in space and gather data for future mission designs.
- Power Generation: During the test, 180 W power was generated using Hydrogen and Oxygen gases, providing valuable data on the performance of the power system.
About Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells
|
Details |
| Basic Principle |
Converts chemical energy from hydrogen into electrical energy, producing water and heat as byproducts. |
| Key Components |
Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA)
Platinum-based catalyst
Gas Diffusion Layers (GDLs)
Bipolar Plates |
| Operation |
Hydrogen Oxidation: At the anode, hydrogen molecules (H2) are split into protons (H+) and electrons (e-).
Proton Conduction: The PEM allows only protons to pass through to the cathode, blocking electrons.
Electron Flow: Electrons travel through an external circuit to the cathode, creating an electric current.
Oxygen Reduction: At the cathode, oxygen molecules (O2) from the air combine with the protons and electrons to form water (H2O).
Heat Production: The reaction generates heat, which can be used for heating purposes in some applications. |
| Types of Membranes |
Perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) membranes (common)
Hydrocarbon-based membranes (alternative) |
| Advantages |
High power density
Low operating temperatures (60-80°C)
Zero emissions with pure hydrogen |
Applications in Space and Society
- Multipurpose Space Use: Fuel cells are particularly suitable for human space missions, providing essential power, water, and heat from a single system.
- Societal Benefits: They have significant potential for societal applications, including as replacements for conventional vehicle engines and in standby power systems.
- Advantages over Batteries: Fuel cells offer range and refuelling times comparable to conventional engines and are expected to enable emission-free transportation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Prithvi Vigyan Scheme
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Union Cabinet, led by Prime Minister, has sanctioned the “Prithvi Vigyan (Prithvi)” scheme, a significant project of the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- With a budget of Rs 4,797 crore, the scheme is planned for the period from 2021 to 2026.
About Prithvi Vigyan Scheme
- Consolidation of Programs: The Prithvi scheme unifies five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS),
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART),
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER),
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE),
- Research, Education, Training and Outreach (REACHOUT).
- Aim: This integration is designed to enhance our understanding of Earth’s systems and apply scientific knowledge for societal, environmental, and economic benefits.
Objectives and Focus Areas
- Comprehensive Observations: The scheme emphasizes long-term monitoring across the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth to track Earth System’s vital signs and changes.
- Development of Predictive Models: It focuses on creating models for weather, ocean, and climate hazards and advancing climate change science.
- Exploration Initiatives: Exploration of Polar Regions and high seas is a key aspect, aiming to discover new phenomena and resources.
- Technological Advancements: The scheme also stresses the development of technology for the sustainable exploitation of oceanic resources for societal applications.
Role of the Ministry of Earth Sciences
- Provision of Critical Services: The Ministry is responsible for delivering crucial services related to weather, climate, ocean and coastal states, hydrology, seismology, and natural hazards.
- Support in Disaster Management: These services are essential for issuing forecasts and warnings for natural disasters, thereby aiding in disaster preparedness and risk mitigation.
Holistic Approach to Earth System Sciences
- Broad Scope of Study: Earth System Sciences involve studying the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere, and their complex interactions.
- Integrated Research Efforts: The Prithvi scheme aims to address these components comprehensively, enhancing understanding and providing reliable services for India.
Impact and Future Prospects
- Addressing Major Challenges: The scheme’s integrated research and development efforts will tackle significant challenges in various fields like weather, climate, oceanography, cryospheric studies, and seismology.
- Harnessing Resources Sustainably: It explores sustainable methods to utilize both living and non-living resources, contributing to national development and environmental conservation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Jan Vishwas Bill 2023
Mains level: The impact of voice votes, the Anti-Defection Law, and the dismissal of division calls on legislative transparency and accountability
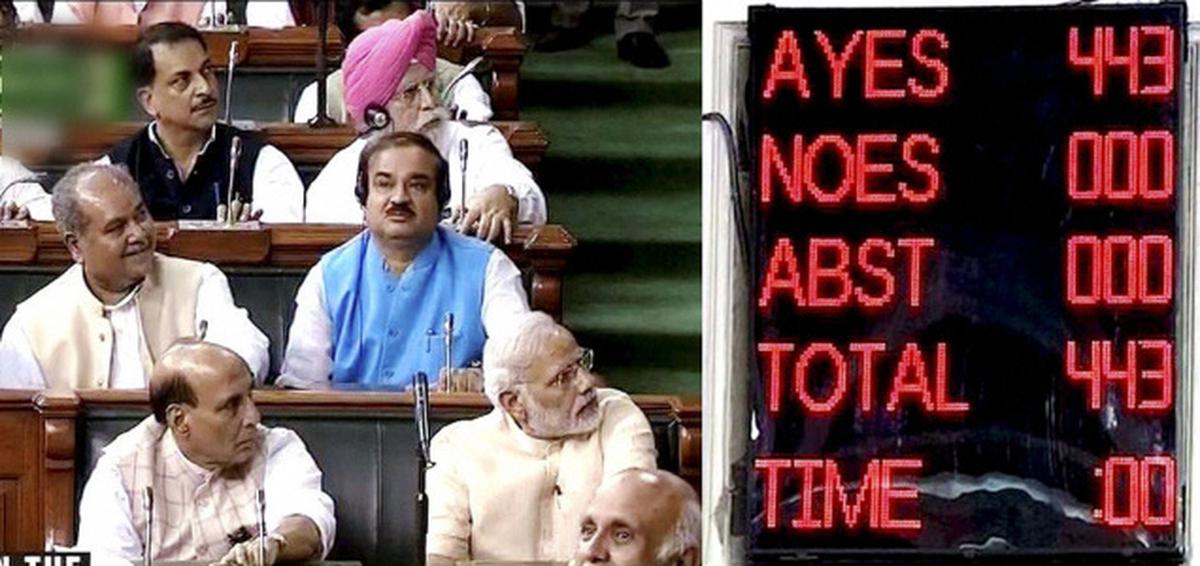
Central Idea:
The article discusses the absence of voting records during the recent Parliament session, highlighting the significance of recorded votes in representing legislators’ stances and fostering transparency in the legislative process. It also explores the impact of the Anti-Defection Law on MPs’ dissent and the increasing use of voice votes, leading to a lack of accountability.
Key Highlights:
- 19 bills were passed in the recent Parliament session, but voting records were not made available.
- The use of voice votes, lacking individual records, is a preferred method for passing legislative motions.
- The Anti-Defection Law has limited MPs’ ability to dissent, reducing the significance of debates and votes.
- The scarcity of voting records hampers Opposition parties in communicating their positions to the electorate.
Key Challenges:
- Lack of transparency due to the absence of voting records.
- The impact of the Anti-Defection Law on MPs’ freedom to dissent.
- Dismissal of division calls during crucial legislative moments.
Key Terms:
- Voice vote
- Anti-Defection Law
- Division call
- Legislative transparency
- Accountability
- Dissent
Key Phrases:
- “A shadow of opacity has fallen over our legislative processes.”
- “The scarcity of voting records can be a symptom of a deeper problem.”
- “The impact of the Anti-Defection Law on MPs’ dissent is a matter of concern.”
Key Quotes:
- “Transparency defines the measure to which our parliamentarians’ political decisions are traceable, which begets accountability.”
- “The right to a division, meant to be readily available, has become shrouded in subjective judgement.”
Key Examples and References:
- The passage of the Jan Vishwas Bill 2023 and the farm bills through voice votes.
- Asaduddin Owaisi’s dissent on various bills, illustrating the importance of voting records.
- Dismissal of division calls during the passage of the Weapons of Mass Destruction Bill and the Electricity Amendment Bill.
Key Facts:
- In Modi I, 40 divisions were raised for 180 bills, while in Modi II, only 20 divisions were allowed for 209 bills.
- Only 15.4% of bills in the BJP’s 10-year tenure have voting records.
Critical Analysis:
The article critically examines the impact of voice votes, the Anti-Defection Law, and the dismissal of division calls on legislative transparency and accountability. It emphasizes the need for voting records to ensure a clear representation of MPs’ stances.
Way Forward:
- Reevaluate the impact of the Anti-Defection Law on MPs’ dissent.
- Ensure the availability of voting records to enhance legislative transparency.
- Address the dismissal of division calls to uphold the right to record votes.
- Promote a more accountable and transparent legislative process through recorded votes.
In essence, the article advocates for the restoration of transparency in the legislative process through the provision of voting records and a reconsideration of the Anti-Defection Law’s impact on MPs’ dissent.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Corbett Tiger Reserve (CTR)
Mains level: Complexity of human-wildlife conflicts

Central Idea:
The article highlights the success of Corbett Tiger Reserve (CTR) in India in managing and conserving its tiger population, emphasizing the importance of a balanced approach involving wildlife protection, community engagement, and ecological sustainability.
Key Highlights:
- CTR, spanning 1288.31 sq.km, has shown significant progress in tiger conservation, recording the highest density of wild tigers globally, from 231 to 260 in four years.
- The richly-forested, highly-biodiverse landscape attracts various enthusiasts and researchers.
- The article acknowledges the unsung heroes among the forest staff and local communities who contribute to the reserve’s ecosystem.
- Grassland and water management practices, strategic wildlife corridors, and addressing human-wildlife conflicts are vital aspects of CTR’s holistic approach.
Key Challenges:
- Human-wildlife conflicts, particularly with tigers and elephants, pose a formidable challenge.
- Ensuring the safety and security of the forest staff, who face risks while patrolling the reserve.
- Balancing the economic dependence of local communities on tiger-related tourism with the risks posed by wild animals.
Key Terms:
- Tiger Conservation Plan
- Core and buffer zones
- Biodiversity
- Grassland management
- Wildlife corridors
- Human-wildlife conflict
- Eco Development Committees (EDCs)
Key Phrases:
- “An unforgettable sight: the dread and danger lurking in the treacherous gaze of a stalking tiger.”
- “A delicate balance of forest flora and fauna is crucial for a healthy forest ecology.”
- “The rising incidence of human-elephant and tiger-human conflict poses a formidable challenge.”
- “Living with Tigers initiative aims at creating awareness and behavioral changes among local communities.”
Key Quotes:
- “A glimpse of the peerless king of the jungle in all his majesty is truly captivating.”
- “The only way ahead is by enjoining forest conservation upon all local stakeholders.”
- “The revival of the tiger since 1973 has meant a cultural renaissance and revival of our conservation ethics and values.”
Key Examples and References:
- The success of the beehive-fencing project to guard crops against wild elephants.
- The “Living with Tigers” initiative promoting awareness and behavioral changes among school children and villagers.
- The economic dependence of Ramnagar district on tiger-related tourism.
Key Facts:
- CTR covers 1288.31 sq.km and recorded 260 tigers in 2022.
- 27 different kinds of grasslands are present at CTR.
- The beehive-fencing project resulted in the creation of “Corbee Honey,” managed by local Eco Development Committees.
Critical Analysis:
The article acknowledges the complexity of human-wildlife conflicts as “wicked problems,” requiring unique solutions. It emphasizes the need for a collaborative, engaging, and socio-culturally-sensitive approach in addressing conservation challenges.
Way Forward:
- Continue efforts to balance economic benefits of tiger-related tourism with wildlife conservation.
- Scale up successful initiatives like the beehive-fencing project and “Living with Tigers” awareness program.
- Strengthen community engagement for long-term conservation efforts.
- Promote sustainable practices for wildlife protection, grassland management, and water conservation.
In essence, the article underscores the success of CTR in tiger conservation and the imperative of a comprehensive approach involving ecological sustainability, community engagement, and innovative solutions to address ongoing challenges.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: DigiYatra
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- Travellers at Indian airports have raised privacy concerns over the Digi Yatra initiative, which involves collecting facial biometrics without explicit consent.
About DigiYatra
- DigiYatra offers paperless airport entry using facial recognition technology.
- It aims for paperless, contactless airport checkpoints, identifying travelers by facial features linked to boarding passes.
- This system automates passenger entry at various points like airport entry, security checks, and boarding using facial recognition.
- Passengers no longer need to present ID cards and boarding passes.
- The DigiYatra Foundation, a joint venture with stakeholders including the Airports Authority of India and major Indian airports, is implementing the project.
- The Airports Authority of India holds a 26% stake, while five major airports equally share the remaining 74%.
How to Use DigiYatra?
- Passengers register on the DigiYatra app with Aadhaar validation and a self-captured image.
- Next, they scan their boarding pass, sharing credentials with airport authorities.
- At the airport e-gate, passengers scan their boarding pass; the facial recognition system validates their identity and travel documents.
- After validation, passengers can enter through the e-gate.
- Normal security clearance and boarding procedures still apply.
Need for DigiYatra
- Facial recognition technology streamlines flying and reduces airport congestion.
- This technology, already in use at airports like Dubai, Singapore, Atlanta, and Narita (Japan), enhances efficiency.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
- Data Usage and Deletion: Passenger data will be used only for defined purposes and deleted 24 hours after flight departure.
- Compliance and Concerns: The FRT system will adhere to India’s data privacy and protection practices. However, concerns have been raised about the adequacy of the Personal Data Protection Bill (PDPB), 2019, which falls short of the standards set by the Justice Srikrishna Committee and does not fully align with the Justice K.S. Puttaswamy vs Union of India judgment on the right of privacy.
Concerns Over Biometric Scanning at Airports
- Privacy and Consent: Issues of data storage, access, and the option to opt-out raise privacy concerns among passengers.
- Biometric Data Misuse: Without clear regulations, there’s a risk of personal data being accessed or misused by unauthorized entities.
Issues with Biometric Scanning Technologies
- Inherent Bias: Research indicates that FRT and AI can be biased, with higher misidentification rates for non-white individuals.
- Algorithmic Discrimination: Studies have shown that machine learning algorithms can discriminate based on race and gender.
Conclusion
- Advancements in Air Travel: The implementation of FRT in Indian airports marks a significant technological advancement in air travel.
- Addressing Privacy Concerns: Ensuring robust data privacy measures and addressing inherent biases in technology are crucial for the successful and ethical implementation of FRT systems.
- Future of Air Travel Security: As FRT becomes more prevalent, continuous evaluation and improvement of these systems will be essential to safeguard passenger privacy and enhance travel efficiency.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2022:
Consider the following (2022)
- Aarogya Setu
- CoWIN
- Digi Locker
- DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Post your answers here.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Na
Mains level: critical examination of the challenges in the current education system

Central Idea:
The article discusses the challenges and inadequacies in the current examination systems of educational institutions in India. It emphasizes the need for transparency, oversight, and credibility in assessments to ensure that degrees and certificates truly reflect students’ learning achievements.
Key Highlights:
- Credibility of the examination system is crucial for maintaining educational standards.
- Decentralized systems in India with numerous universities and boards face challenges in maintaining transparency and standardization.
- The article criticizes the focus on memory-based testing, inflation of marks, and a lack of emphasis on higher-order thinking skills.
- Employers often rely on their own assessments rather than institutional certifications.
- The article suggests the use of technology, external audits, and adherence to minimum standards to improve assessment processes.
Key Challenges:
- Lack of transparency and oversight in examination processes.
- Inconsistency and inadequacies in syllabi and teaching methods.
- Confidentiality leading to malpractices and scandals in examinations.
- The need for balancing autonomy with proper oversight in educational institutions.
- Negligence, fraud, and quality issues in assessment processes.
Key Terms:
- Decentralized system
- Transparency
- Oversight
- Standardization
- Higher-order thinking
- Autonomy
- External audit
- Credibility
- Minimum standards
- Technology in assessment
Key Phrases:
- “Credibility of assessment and standard of education can be ensured only through transparency in teaching and assessment.”
- “Inconsistency of the examination system is cause for concern.”
- “Confidentiality is also a cause for scandals in examinations.”
- “Transparency and proper oversight take lead roles in the examination systems.”
Key Quotes:
- “A credible examination system is one of the key ways to improve the standard of education.”
- “The employability of a graduate depends on higher order learning, while examination boards do not certify students on those skills.”
- “The higher education regulator truly believes in decentralization through autonomous institutions without oversight.”
Key Examples and References:
- Instances of question papers with language errors, conceptualization issues, and irrelevant questions.
- Employers disregarding institutional certifications in favor of their own assessments.
- The coaching market for competitive examinations and skilling due to a lack of faith in institutional certifications.
Key Facts:
- India has over 1,100 universities, 50,000 affiliated colleges, and 60 school boards.
- Total enrollment in higher education is 40.15 million students.
- Employers conduct rigorous assessments of candidates’ academic achievements and suitability for employment.
Critical Analysis:
The article provides a critical examination of the challenges in the current education system, emphasizing the need for transparency, oversight, and credibility. It highlights the disconnect between institutional certifications and actual learning outcomes, calling for a shift towards higher-order thinking skills.
Way Forward:
- Emphasize transparency in teaching and assessment processes.
- Implement external audits of assessment systems to ensure reliability and consistency.
- Balance autonomy with proper oversight in educational institutions.
- Use technology to standardize question paper setting and evaluation processes.
- Codify and address issues of negligence, fraud, and academic inadequacies in assessments.
- Release audit reports regularly to assess examination boards in terms of transparency, reliability, and consistency.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Supreme Court Legal Services Committee
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Justice BR Gavai has been appointed as the Chairman of the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee (SCLSC), succeeding Justice Sanjiv Khanna.
Understanding the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee
- Constitution and Purpose: The SCLSC, established under Section 3A of the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, aims to provide free legal services to weaker sections of society in cases under the Supreme Court’s jurisdiction.
- Composition: Chaired by a sitting Supreme Court judge, the committee includes members with prescribed experience and qualifications, all nominated by the Chief Justice of India (CJI).
Composition and Functioning of the SCLSC
- Current Members: As of now, the SCLSC comprises Chairperson BR Gavai and nine other members appointed by the CJI.
- Staffing and Administration: The Committee can appoint officers and employees as per the Centre’s guidelines, in consultation with the CJI.
Need for Legal Services in India
- Constitutional Basis: The Indian Constitution, particularly Article 39A, emphasizes the state’s role in ensuring legal justice is accessible to all citizens, regardless of economic or other disabilities.
- Historical Development: The concept of legal aid in India evolved over decades, with significant progress marked by the establishment of a national committee under Justice PN Bhagwati in 1980.
Legal Services Authorities Act and Its Provisions
- Statutory Framework: The 1987 Act provides a legal basis for offering free and competent legal services to eligible groups, including women, children, SC/ST, EWS categories, and others.
- Establishment of NALSA: Formed in 1995, the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) oversees legal aid programs and formulates policies for legal services.
- Nationwide Network: The Act envisions a network across India for legal aid, with State Legal Services Authorities (SLSAs) and District Legal Services Authorities (DLSAs) implementing these services at state and district levels, respectively.
Role of State and District Legal Services Authorities
- State-Level Implementation: Each SLSA, led by the Chief Justice of the respective High Court, executes NALSA’s policies and provides free legal services.
- District and Taluk Committees: DLSAs and Taluk Legal Services Committees, chaired by district and senior civil judges respectively, conduct legal awareness programs and provide various legal services.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zosurabalpin
Mains level: Read the attached story
Introduction
- New Antibiotic Class: Researchers have identified zosurabalpin, a new class of antibiotics showing potential against the drug-resistant bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii.
- Effective against CRAB: Zosurabalpin has been found effective against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB)-induced pneumonia and sepsis in mouse models.
About Zosurabalpin
- Development Process: The antibiotic originated from a tethered macrocyclic peptide (MCP) selectively targeting A. baumannii and was optimized for efficacy and tolerability.
- Novel Mode of Action: Zosurabalpin operates through a previously unknown mechanism, inhibiting the transport of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in bacteria.
- Inhibition of LPS Transport: By blocking a protein complex essential for LPS transport to the bacterial surface, zosurabalpin disrupts the outer membrane structure of Gram-negative bacteria, leading to bacterial death.
Effectiveness and Clinical Trials
- Laboratory and Animal Studies: Zosurabalpin demonstrated effectiveness against over 100 CRAB clinical samples in the lab and significantly reduced bacterial levels in mice with CRAB-induced pneumonia and sepsis.
- Phase I Clinical Trials: The antibiotic has undergone evaluation in two phase I clinical trials, marking the initial steps towards potential human use.
Implications and Future Prospects
- Addressing Antibiotic Resistance: The discovery of zosurabalpin offers hope in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a growing global health concern.
- Potential Clinical Application: If further trials are successful, zosurabalpin could become a vital tool in treating infections caused by drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.
- Continued Research: Ongoing and future studies will be crucial to fully understand the antibiotic’s safety, efficacy, and potential resistance mechanisms.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: KLI-SOFC Project
Mains level: NA

Introduction
- The Prime Minister has inaugurated Kochi-Lakshadweep islands submarine optical fiber connection (KLI-SOFC) project.
About KLI-SOFC Project
- The KLI-SOFC project extends submarine cable connectivity from Kochi to eleven Lakshadweep Islands, including Kavaratti, Agatti, and Minicoy.
- The project aims to provide high-speed wireline broadband connectivity through FTTH and 5G/4G Mobile networks to the Lakshadweep Islands population.
- Funded by the Universal Services Obligation Fund (USOF), Department of Telecommunication.
- The total link distance of the project is 1,868 kms.
- Implementing agencies include BSNL as the Project Executing Agency and M/s NEC Corporation India Pvt Ltd for contract work.
Benefits of the Project
- Contributes to ‘Digital India’ and ‘National Broadband Mission’, enabling e-governance projects in Lakshadweep.
- Boosts E-Governance, Tourism, Education, Health, Commerce, and Industries, potentially improving living standards and accelerating social and economic development.
- The bandwidth created will be available to all Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) to enhance telecom services in the Lakshadweep Islands.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Buxa Tiger Reserve
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Camera traps in the Buxa National Park, West Bengal captured images of a tiger, reigniting hopes among forest officials and experts.
- The last sighting before December 2021 was 23 years ago, indicating the tiger’s absence from the reserve for decades.
Buxa Tiger Reserve: Geography and Ecology
|
Details |
| Location |
Alipurduar district, West Bengal, India. Near the Bhutan border. |
| Establishment |
Created in 1983 as a tiger reserve; declared a national park in January 1992. |
| Area |
Total area of approx. 760 sq km (core area: 390 sq km, buffer zone: 370 sq km). |
| Ecological Significance |
Part of the Eastern Himalayan subregion, known for its unique biodiversity. |
| Geographical Connectivity |
Shares a northern boundary with Bhutan. Connected with Bhutanese forests, Kochugaon forests, Manas Tiger Reserve, and Jaldapara National Park. |
Reasons for the Tiger’s Return
- Habitat Improvement: Efforts to reduce human interference, expand grasslands, and increase the prey base have created a more suitable habitat for tigers.
- Conservation Measures: The introduction of chital (spotted deer) as prey and the creation of watering holes have been part of these efforts.
Conservation Initiatives and Future Plans
- Tiger Augmentation Project: Launched in 2018, this project involves the state forest department, Wildlife Institute of India, and the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Village Relocation: Plans to relocate villages from the core area aim to reduce human presence and further improve the habitat.
- Expert Insights: Scientists note the importance of habitat connectivity between Bhutan and Buxa and the reduction of human disturbances as key factors in attracting tigers back to Buxa.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Old Pension Scheme , NPS
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Maharashtra Cabinet has approved a proposal allowing certain state government employees to opt for the old pension scheme (OPS).
- The option is extended to employees who joined the service after November 1, 2005, based on recruitment advertisements issued before that date.
Transition in Pension Schemes
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS): The OPS guaranteed a pension of half the last basic salary plus dearness allowance after a minimum of 10 years of service, without employee contributions. It also provided family pension and Death cum Retirement Gratuity (DCRG).
- New Pension Scheme (NPS): Introduced to address the growing pension bill, the NPS is a market-linked, participatory scheme requiring contributions from both employees and employers.
Background and Implementation of NPS
- OASIS Project: Initiated in 1999, it led to the recommendation of the NPS by the Atal Bihari Vajpayee government in 2003.
- Scheme Details: Employees contribute 10% of their basic salary, matched up to 14% by the employer. The funds are invested in PFRDA-regulated pension funds with market-linked returns.
- Account Management: NPS provides a Permanent Retirement Account Number (PRAN) for lifelong account management.
- State Adoption: All states except West Bengal have implemented the NPS. Some opposition-ruled states announced plans to revert to the OPS.
Rationale Behind NPS Adoption
- Pension Debt Sustainability: The OPS was a fiscal burden without accumulated funds, whereas the NPS relies on accumulated funds.
- Addressing Ageing Population: With increasing life expectancy, the OPS became unsustainable.
- Preventing Early Retirements: The NPS encourages longer service due to its long-term investment fund ideology.
- Investment and Flexibility: NPS offers flexible investment options and the freedom to switch investment options and fund managers.
Criticism of NPS
- Market Risks: The exposure of retirement funds to market uncertainties raises concerns about old age security.
- Pension Amount Concerns: There is no minimum pension guarantee, and pensions under NPS do not adjust for inflation.
- Accountability Issues: Questions remain about the security of the invested corpus and accountability in market failures.
Conclusion
- State Governments’ Challenge: Reverting to OPS requires careful consideration of financial implications on future generations.
- Review and Strengthening of NPS: Measures such as introducing inflation-indexed annuities, assuring minimum returns, and ensuring timely registration and contributions can strengthen the NPS.
- Balanced Approach: A nuanced approach is needed to balance fiscal sustainability with providing adequate social security to retirees.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now


















