Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Farakka Barrage
Why in the News?
It was nearly 50 years ago, that India had completed the construction of the Farakka Barrage.
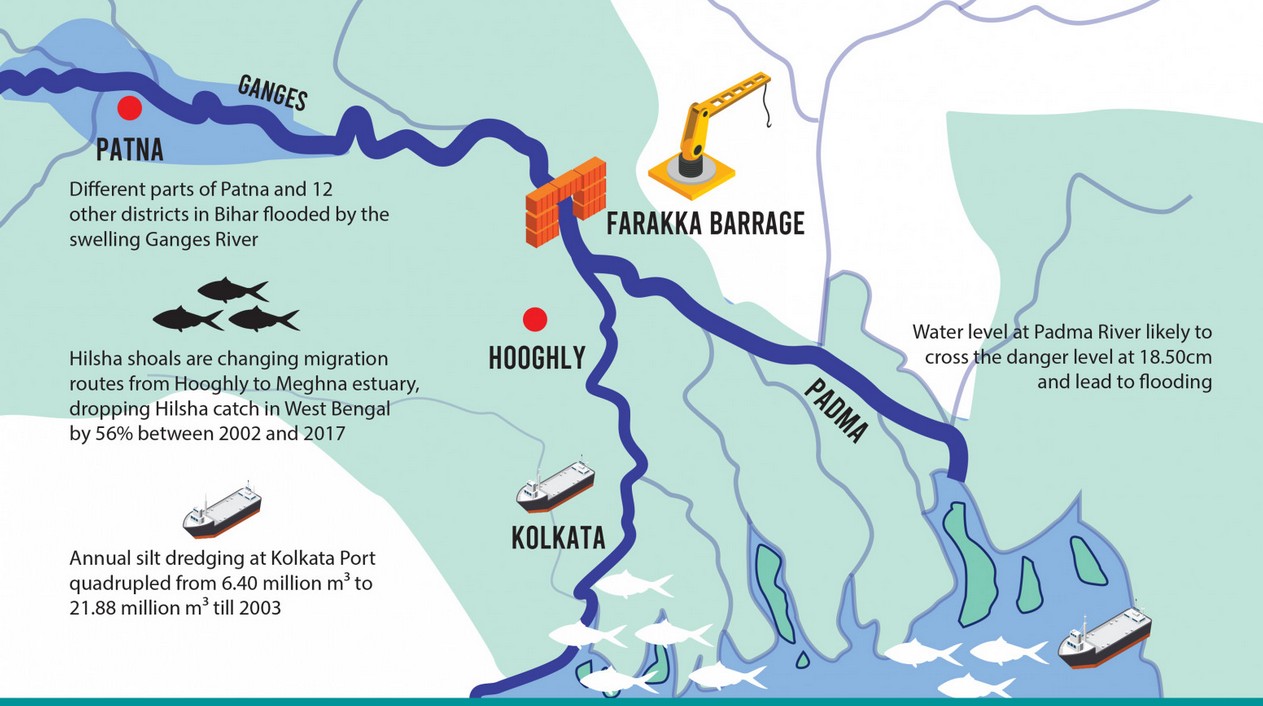
About Farakka Barrage
- The Farakka Barrage is located on the Ganges River in Murshidabad District, West Bengal, India, about 18 km from the Bangladesh border.
- The barrage measures 2,304 meters (7,559 feet) in length.
- Its construction began in 1962 and was completed in 1970 at a cost of 1 billion dollars. It became operational on April 21, 1975.
- The Feeder Canal is approximately 42 km long, connecting the barrage to the Hooghly River.
- Purpose:
- It diverts water to the Hooghly River to maintain the navigability of Kolkata Port and to flush out sediment from the river.
- It diverts 1,800 cubic meters per second of water from the Ganges.
- Construction Details:
- Built by Hindustan Construction Company, it consists of 109 gates, with 108 over the river and one over low-lying land as a precaution.
- Supports the Farakka Super Thermal Power Station.
- The 1996 Ganges Water Sharing Treaty ensured fair water distribution:
- 70,000 cusecs or less: 50% to both India and Bangladesh.
- 70,000 – 75,000 cusecs: India gets 35,000 cusecs, Bangladesh the balance.
- 75,000 cusecs or more: India receives 40,000 cusecs, Bangladesh gets the remainder.
Significance in India-Bangladesh Water Sharing:
- The Farakka Barrage is crucial for irrigation in West Bengal, supporting agriculture during the dry season.
- Bangladesh, particularly Mongla and Khulna, depends on the Ganges for water.
- The diverted water has led to water scarcity, impacting agriculture, fisheries, and livelihoods in Bangladesh, causing diplomatic tensions.
- This treaty ensures equitable distribution and guarantees a minimum flow for Bangladesh.
- Issues:
-
- Water diversion has led to salinization and soil degradation in Bangladesh, affecting agriculture and freshwater supplies.
- Biodiversity loss and damage to the Sundarbans mangrove forests have been significant environmental impacts.
| [UPSC 1997] The canal-carrying capacity of Farakka is:
(a) 40,000 cusecs (b) 60,000 cusecs (c) 80,000 cusecs (d) 100,000 cusecs |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
