Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Activated Carbon, Supercapacitors
Why in the News?
Researchers at Government College for Women, Thiruvananthapuram, have developed a way to make activated carbon from coconut husks, which are a common leftover from farming in Kerala. This activated carbon is well-suited for making supercapacitors.
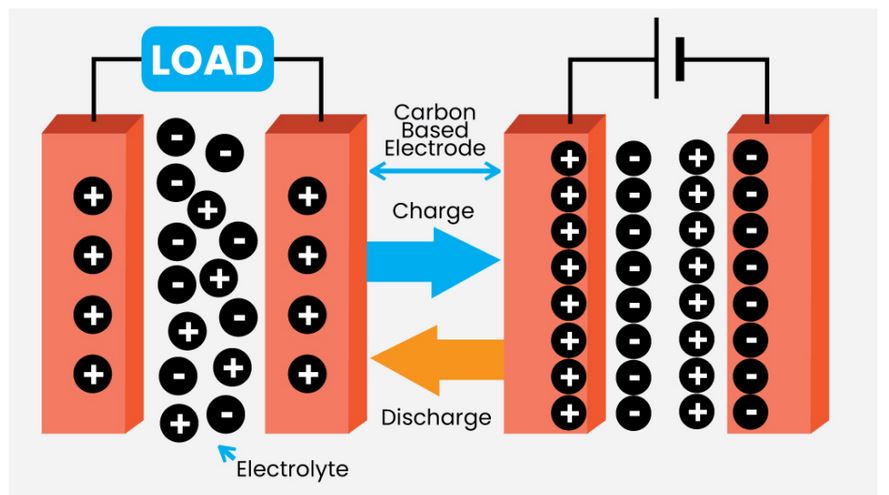
Back2Basics: Supercapacitors
Key Characteristics:
Structure and Components:
|
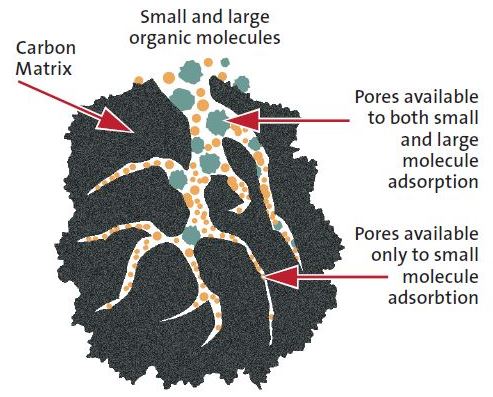
What is Activated Carbon?
- Activated Carbon, also known as activated charcoal, is a highly porous form of carbon.
- It is processed to have small, low-volume pores with increased surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.
- It is widely used for purification, decontamination, and as a filtration medium.
- Key Characteristics:
- High Surface Area: Due to its extensive network of pores, activated carbon has a very high surface area, typically ranging from 500 to 1500 m²/g.
- Porosity: The structure includes micropores, mesopores, and macropores, allowing it to adsorb a variety of molecules.
How is it produced?
- Activated carbon is produced from carbonaceous source materials such as coconut shells, peat, wood, coir, lignite, coal, and petroleum pitch.
- The production involves two main steps:
- Carbonization: The raw material is subjected to high temperatures (600-900°C) in an inert atmosphere (usually nitrogen or argon) to remove volatile components.
- Activation/Oxidation: The carbonized material is treated with oxidizing agents (such as steam or carbon dioxide) at high temperatures (800-1000°C) to develop a porous structure.
Types:
- Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC): Finely ground carbon particles primarily used in liquid phase applications.
- Granular Activated Carbon (GAC): Larger particles used in both liquid and gas phase applications, such as water and air filtration.
- Extruded Activated Carbon (EAC): Cylindrical pellets used mainly for gas phase applications due to their low pressure drop and high mechanical strength.
- Impregnated Activated Carbon: Activated carbon treated with chemicals to enhance its adsorption capacity for specific contaminants.
Applications:
- Water Treatment: Removes contaminants like chlorine, odors, and organic compounds from drinking water.
- Air Purification: Adsorbs volatile organic compounds (VOCs), odors, and airborne pollutants.
- Medical Uses: Used in poisoning cases to absorb toxins in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Industrial Processes: Utilized in the recovery of solvents, purification of gases, and in gold purification.
- Food and Beverage: Helps in decolorization and purification processes in sugar, wine, and juice production.
About Coconut Husk-Derived Activated Carbon
- Coconut husk-derived activated carbon is a sustainable and efficient green solution for high-performance supercapacitors.
- This material is readily available, low-cost, and eco-friendly.
- It was produced by Microwave-Assisted Method designed at the Centralised Common Instrumentation Facility (CCIF) at the college.
Importance of Supercapacitors
- Energy Storage: Supercapacitors have significantly higher capacitance and energy storage capacity compared to conventional capacitors.
- Search for Ideal Material: Finding the ideal supercapacitor electrode material has been a significant challenge in sustainable energy storage solutions.
Research Findings:
- Efficiency: Prototype supercapacitors made from coconut husk-derived activated carbon are four times more efficient than existing supercapacitors.
- Cost-Effective and Efficient: Activated carbon produced using this technology is inexpensive and exhibits exceptional supercapacitor capability.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024