From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Driest region in India
Mains level: Why do different regions of Maharashtra experience varied levels of water stress?
Why in the news?
After last year’s deficient monsoon, the Maharashtra government declared several parts of the state as drought-hit.
Why do different regions of Maharashtra experience varied levels of water stress?
- Geographical Differences: Coastal areas receive excessive rainfall leading to flooding. Marathwada lies in the rain-shadow region, receiving significantly less rainfall (600-800 mm) compared to the western side of the Western Ghats (2,000-4,000 mm).
- Topography and Soil: Marathwada has clayey black soil (regur) which retains moisture but has a low infiltration rate, leading to poor groundwater recharge. The region’s topography, with parallel tributaries and gently sloping hills, results in uneven water distribution, with valleys having perennial groundwater and upland areas facing acute water scarcity.
- Impact of Climate Change: Increasing drought severity and frequency in central Maharashtra due to climate change, worsening water stress in regions like Marathwada and North Karnataka.
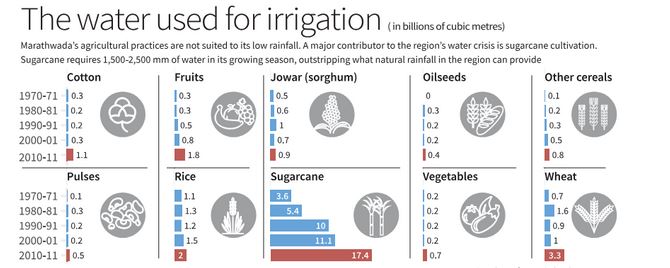
Why is sugarcane production not suited for regions with less rainfall?
- High Water Requirement: Sugarcane needs 1,500-2,500 mm of water during its growing season, which is much higher than the annual rainfall in low-rainfall areas like Marathwada.
- Irrigation Demands: Sugarcane requires almost daily irrigation, consuming 61% of the region’s irrigation water while occupying only 4% of the cropped area. This heavy water usage restricts the irrigation of other crops that are more suitable for the region’s climate, such as pulses and millet.
- Government Policies: Long-standing government support for sugarcane pricing and sales has encouraged its cultivation in unsuitable regions. The recent promotion of sugarcane-juice-based ethanol production exacerbates the issue, diverting water resources away from more sustainable agricultural practices.
What is meant by the rain-shadow effect?
- The rain-shadow effect occurs when moist winds from the Arabian Sea rise over the Western Ghats, causing heavy rainfall on the western side. By the time these winds descend on the eastern side (Western Maharashtra and Marathwada), they lose most of their moisture, resulting in significantly lower rainfall.
- Impact on Marathwada: Marathwada, located in the rain-shadow region, receives only 600-800 mm of annual rainfall, contributing to its dry climate and water scarcity issues.
Note: Marathwada and North Karnataka have emerged as the second driest regions in India after Rajasthan.
How can supply-side solutions help the situation?
- Watershed Management: Building water-conserving structures such as contour trenches, earthen bunds, and gully plugs to capture and store runoff. Designing silt-trapping mechanisms to prevent soil erosion and maintain water retention structures.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Implementing measures to capture rainwater runoff from agricultural fields to recharge groundwater and reduce dependency on external water sources.
- Utilizing Government Programs: Leveraging funds from the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) for watershed management projects and training farmers in water conservation techniques.
- Promoting Water-Efficient Practices: Encouraging the use of water-efficient irrigation methods, such as drip irrigation, to optimize water usage. Shifting to drought-resistant crops and high-value, low-water-using crops to reduce water demand and improve agricultural sustainability.
Conclusion: The state government has announced a massive Rs 59,000 crore package to transform the Marathwada region, with a focus on tackling the water crisis. This includes reviving stalled irrigation projects worth Rs 13,677 crore to make the region drought-free through water linking and diverting floodwaters to the Godavari basin
Mains PYQ:
Q Elaborate the impact of National Watershed Project in increasing agricultural production from waterstressed areas. (UPSC IAS/2019)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
