Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Antarctic
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
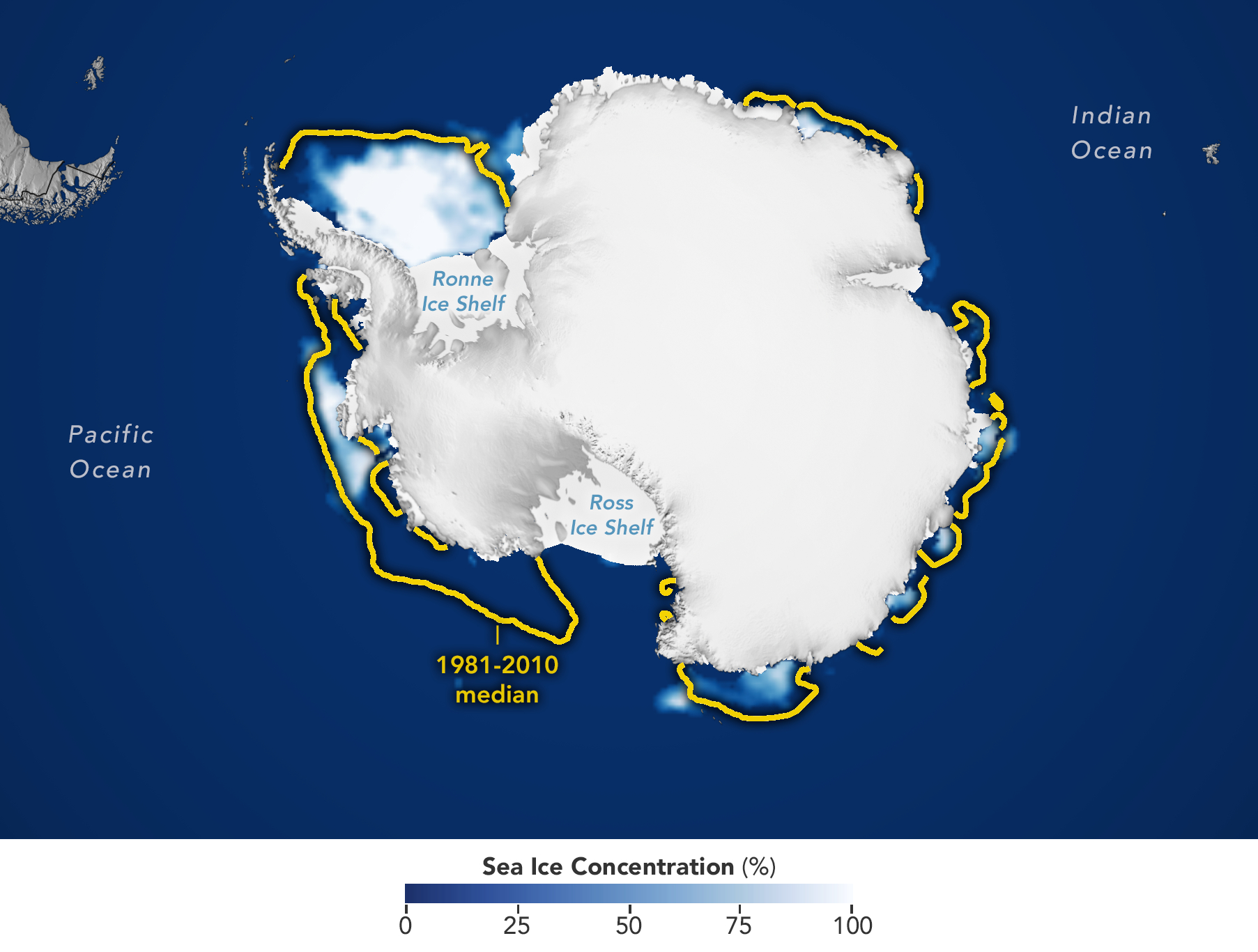
- Sea ice in Antarctica reached its smallest area on record in February for the second consecutive year, continuing a decade-long decline.
Ice cover decline: Key data
(1) Square km decline
- The European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) provided the figures, highlighting the significant decrease in Antarctic sea ice.
- On February 16, the ocean surface covered by ice around Antarctica shrank to 2.09 million square kilometers (800,000 square miles), the lowest level since satellite records began.
(2) Warming trends
- Both the North and South poles have experienced significant warming, with temperatures rising by approximately 3 degrees Celsius compared to late 19th-century levels, three times the global average.
- Arctic sea ice has been diminishing by about 3 percent per year since the late 1970s, while sea ice in Antarctica has remained relatively constant with large annual variations.
(3) Regional variances and vulnerabilities
- Recent ice cover reduction during the southern hemisphere summer has been most pronounced in West Antarctica, which is more vulnerable to the impacts of global warming compared to East Antarctica.
- Antarctica witnessed its first recorded heatwave in 2020, with temperatures 9.2 degrees Celsius above the mean maximum. Unusual temperature spikes have been observed in various parts of Antarctica.
- The Arctic has also experienced significant declines in sea ice, with the record minimum sea ice extent occurring in 2012.
Impact of declining Ice Cover
- Global sea level rise: Melting ice in Antarctica contributes to rising sea levels worldwide.
- Disruption of ecosystems: Declining ice cover disrupts habitats and food sources for ice-dependent species.
- Increased warming: Less ice reflects sunlight, leading to more heat absorption and further ice melting.
- Changes in ocean circulation: Declining ice cover can disrupt currents and impact global climate patterns.
- Release of stored carbon: Melting ice releases trapped carbon, potentially affecting marine ecosystems and contributing to climate change.
- Amplification of global warming: Reduced ice cover creates a positive feedback loop, exacerbating climate change.
- Disruption of biodiversity and food chains: Changing ice conditions impact species relying on ice algae and affect the overall Southern Ocean ecosystem.
Future projections
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) predicted with high confidence that the Arctic Ocean would become practically ice-free in September at least once by mid-century.
- The decreasing trends in both Arctic and Antarctic sea ice highlight the urgent need to address climate change and its impact on the Polar Regions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
