Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: World History: Pearl Harbor Attack and its aftermath
US President Mr Trump has said the COVID-19 pandemic is a worse “attack” on the U.S. than either Pearl Harbor or 9/11.
Practice Question :
Discuss how the world order changed post Pearl Harbour attack with context to the US hegemony in Asia-Pacific.
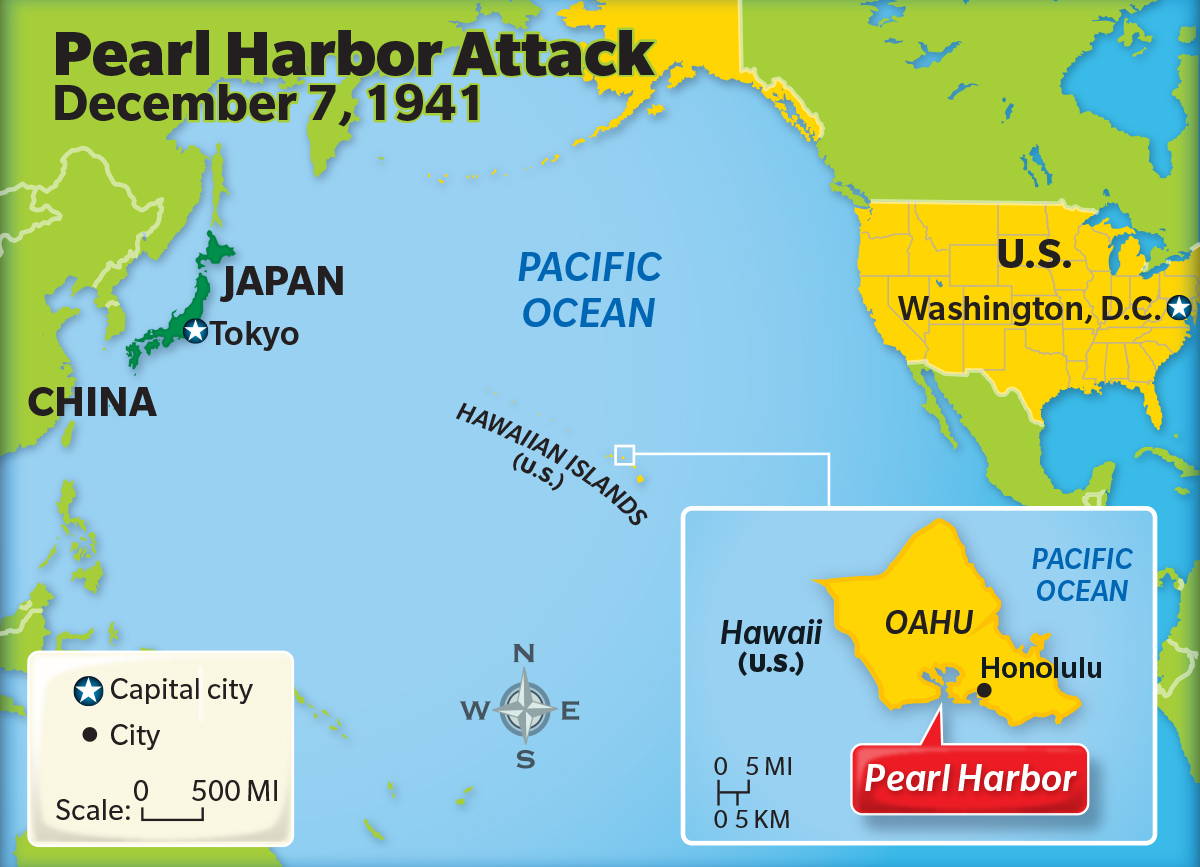
Attack on Pearl Harbor
- The December 7, 1941 attack on Pearl Harbour was among the most significant moments of the World War II.
- It signalled the official entry of the US into the hostilities, which eventually led to the dropping of nuclear bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
- Significantly, in December 2016, Shinzo Abe became the first sitting Japanese Prime Minister to visit Pearl Harbour.
What led up to the attack on Pearl Harbour?
- Before Japan attacked Pearl Harbour in 1941, relations between the US and Japan were already worsening.
- In 1910, Japan annexed Korea and, in 1937, it invaded China, sending alarm bells ringing in the US and other Western powers about Japan’s manifest expansionist agenda.
- Between December 1937 and January 1938, an episode which is referred to as the “Nanking Massacre” or the “Rape of Nanking”, occurred — Japanese soldiers killed and raped Chinese civilians and combatants.
- Japanese historians estimate that anywhere between tens of thousands and 200,000 Chinese were killed.
- The US was against Japan’s aggression in China, and imposed economic sanctions and trade embargoes after its invasion.
Immediate causes
- Japan was reliant on imports for oil and other natural resources — this was one of the reasons why it invaded China and later French Indo-China (present-day Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia).
- The intention was to take control of the major Chinese ports to have access to resources such as iron, rubber, tin, and most importantly, oil.
- In July 1941, the US ceased exporting oil to Japan.
- Negotiations between the two countries ended with the “Hull Note”, the final proposal delivered to Japan by the US. Essentially, the US wanted Japan to withdraw from China without any conditions.
- Ultimately, the negotiations did not lead to any concrete results, following which Japan set its task for Pearl Harbour in the last week of November 1941.
- Japan considered the attack to be a preventive measure against the US interfering with Japan’s plans to carry out military operations in some parts of Southeast Asia.
What happened at Pearl Harbour?
- About 7.55 am on December 7, 1941, about 180 aircraft of the Imperial Japanese Navy attacked the US Naval base at Pearl Harbour on the island of Oahu in Hawaii.
- The bombing killed over 2,300 Americans and destroyed the battleships USS Arizona and USS Oklahoma.
- Roughly 160 aircraft were destroyed, and 150 were damaged.
Impact on the US
- In the short term, the American naval presence in the Pacific was severely weakened.
- However, the Japanese had largely ignored the harbour’s infrastructure, and many of the damaged ships were repaired on-site and returned to duty.
- American opinion immediately shifted to favouring war with Japan, a course that would conclude with Japan’s unconditional surrender less than four years later.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
