Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: DPDP Bill
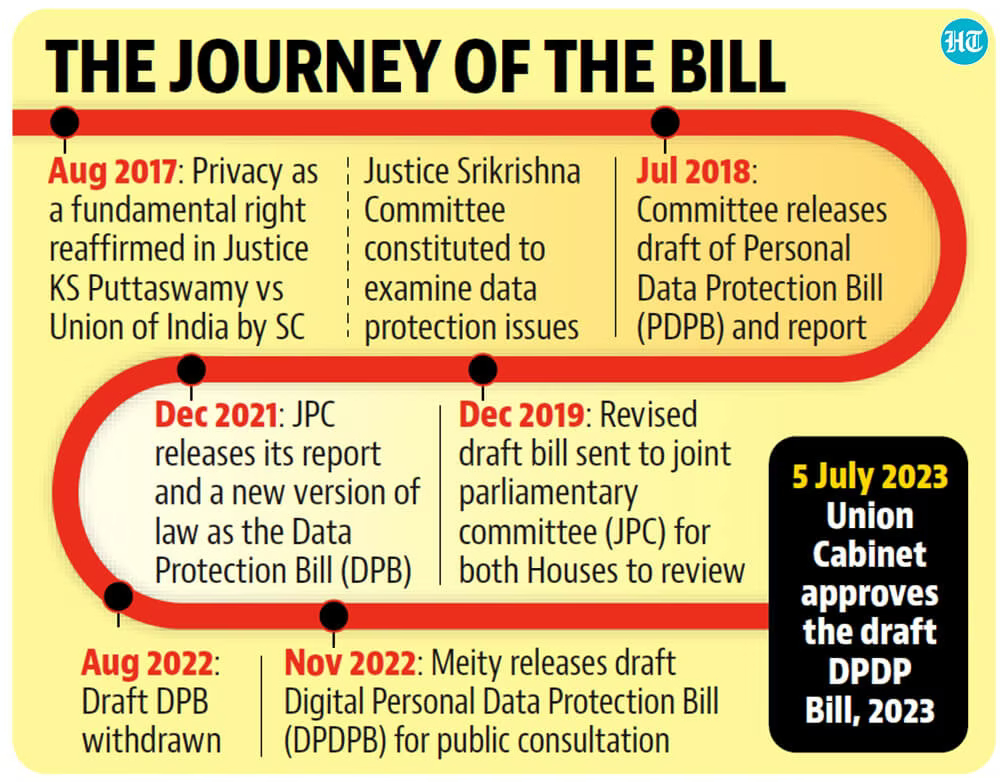
Central Idea
- The Union Cabinet has granted clearance for the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Bill, which is set to be introduced in the upcoming Monsoon Session of Parliament.
- This legislation aims to regulate the management of personal data of Indian residents, emphasizing explicit consent for data collection and usage.
DPDP, Bill: Key Features and Concerns
(A) Data Protection Norms and Consent
- Data Protection Law: The DPDP Bill establishes norms for the management of personal data and mandates explicit consent from individuals whose data is collected and used.
- Limited Transparency: More than 20,000 comments were received during the public consultation on the draft Bill, but these comments have not been made publicly available.
- Minimal Changes: The final Bill, to be presented in Parliament, reportedly shows little deviation from the initial draft circulated for public consultation.
(B) Data Protection Board and Grievance Redressal
- Role of the Data Protection Board: The DPDP Bill enables individuals to lodge complaints with the Data Protection Board of India, consisting of government-appointed technical experts, in case of unauthorized data usage.
- Investigation of Breaches: The Board will initiate an investigation into reported breaches of personal data.
(C) Provisions and Penalties
- EU Influence: The DPDP Bill draws inspiration from the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation, outlining practices for entities collecting personal data, storage, processing, and the rights of data subjects.
- Voluntary Undertaking: Entities can admit a breach and pay a penalty as a mitigation measure to avoid court litigation.
- Penalties and Fines: Penalties for breaches can reach up to ₹250 crore, with a possibility of upward revision to ₹500 crore. Individual offenses may attract fines starting from ₹10,000.
- Data Protection Board’s Role: The Board will levy fines and penalties for breaches, with a maximum penalty of ₹500 crore for data breaches.
(D) Exemptions and Concerns
- Exemptions for Courts and Law Enforcement: The Bill exempts courts and law enforcement agencies from certain requirements when processing personal data for the prevention, detection, investigation, or prosecution of offenses.
- Concerns over RTI Amendment: An amendment in the DPDP Bill raises concerns among Right to Information activists, as it may restrict the sharing of “personal information” by government departments, potentially impeding transparency and accountability.
Potential Changes in the Final Draft
- Cross-Border Data Flows: The approach to cross-border data transfers may shift from a ‘whitelisting’ approach to a ‘blacklisting’ mechanism.
- Stricter Deemed Consent: The provision on “deemed consent” for private entities could be reworded to be more stringent, while government departments may assume consent for processing personal data in the interest of national security and public interest.
International Comparisons

- Global Data Protection Laws: A significant number of countries have enacted data protection and privacy legislation, with the GDPR serving as a template for many jurisdictions.
- EU, US, and China Models: The EU focuses on comprehensive data protection, the US emphasizes privacy as “liberty protection,” and China has introduced new laws on data privacy and security.
Why discuss this yet again?
- Previous Withdrawal: An earlier version of the data protection Bill was withdrawn from Parliament in 2021 due to pushback from various stakeholders.
- International Relevance: The DPDP Bill’s implementation is crucial for India’s trade negotiations, particularly with regions like the European Union, which has comprehensive privacy laws under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Conclusion
- The Bill marks a significant step toward safeguarding personal data in India.
- The legislation introduces stricter norms for data collection and usage, emphasizing explicit consent and establishing penalties for breaches.
- However, concerns have been raised regarding the limited transparency of the consultation process and potential exemptions that may impact transparency and accountability.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
