Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: China’s Lunar Exploration Program, Chandrayaan 4
Why in the News?
- On June 25, Chang’e-6 became the world’s first spacecraft to bring back samples from the far side of the Moon.
- Chang’e-6 successfully returned with samples from the lunar far side, making China the first country to achieve this feat.
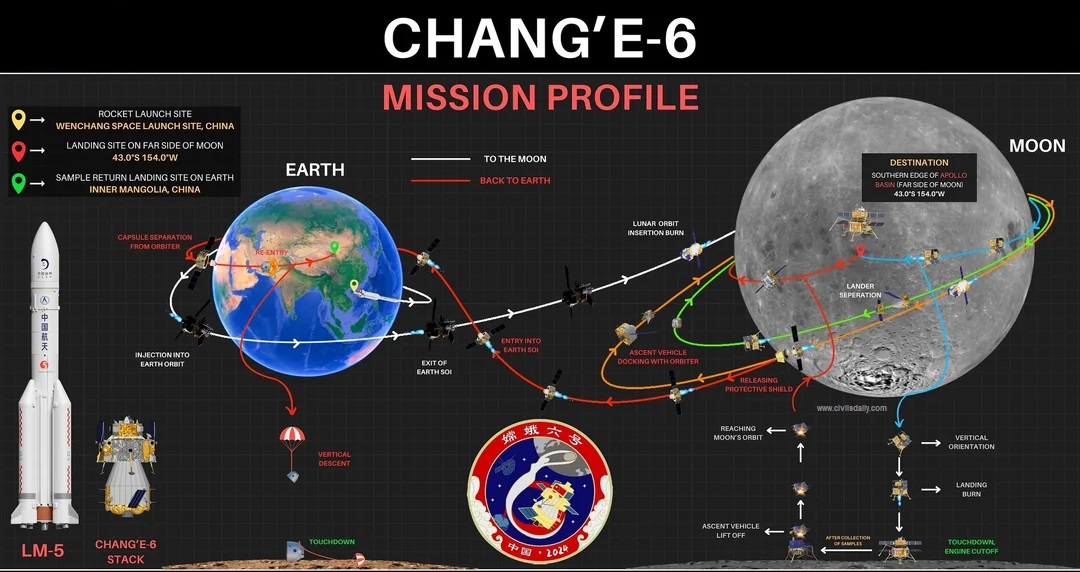
About Chang’e-6 Mission
|
Components of Chang’e-6
- Lander: Equipped with drills and scoops for sample collection.
- Ascender: Transported samples from the lunar surface to lunar orbit.
- Orbiter: Carried the samples from lunar orbit back to Earth.
- Returner: Brought the samples safely back to Earth.
Collaboration and Payloads
The mission carried instruments from international partners, including:
- French DORN: Studied lunar dust and volatiles.
- Italian INRRI: Measured distances using a retroreflector.
- Swedish NILS: Detected negative ions on the lunar surface.
- Pakistani ICUBE-Q CubeSat: Imaged the lunar surface and obtained magnetic field data.
Scientific Goals
- Sample Analysis: Scientists aim to learn more about the Moon’s internal structure and the differences between its near and far sides.
China’s Lunar Exploration Program
- Chang’e-6 follows previous missions under China’s Lunar Exploration Program, marking the next step in incremental technological advancements.
- Phases of Exploration: The program has four phases:
- First Phase: Reaching lunar orbit, completed by Chang’e 1 (2007) and Chang’e 2 (2010).
- Second Phase: Landing and roving, achieved by Chang’e 3 (2013) and Chang’e 4 (2019).
- Third Phase: Sample collection and return, accomplished by Chang’e 5 (2020) and Chang’e 6 (2024).
- Fourth Phase: Developing a robotic research station near the Moon’s South Pole, aiming for crewed lunar landings in the 2030s.
Previous Lunar Sample Missions
- Apollo 11 Mission (1969): The US mission brought 22 kg of lunar material, including 50 rocks.
- Luna 16 Mission (1970): Soviet robotic mission brought lunar samples to Earth.
- Chang’e-5 Mission (2020): Predecessor to Chang’e-6, returned 2 kg of lunar soil from the near side.
Significance of Sample Return Missions
- Laboratory Analysis: Allows the use of sophisticated instruments to study the chemical, isotopic, mineralogical, structural, and physical properties of samples.
- Long-term Preservation: Samples can be preserved and re-examined by future generations with advanced technology.
- Technological Feat: Recovering samples from the far side is a significant technological achievement.
- Step Towards Human Exploration: Success of Chang’e-6 is seen as a step towards China’s goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by 2030.
- Launch Pad for Deep Space: The Moon could serve as a base for future deep space missions and extraterrestrial exploration.
Outcome: New Lunar Race
- Global Participation: India, China, Japan, the US, and Russia launched lunar missions in 2023.
- Future Missions: Over 100 Moon missions by governments and private companies are expected by 2030.
- Long-term Goals: Unlike the 20th-century space race, today’s missions aim to establish a long-term presence and use lunar resources.
India’s Chandrayaan-4 Mission
|
PYQ:[2016] Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

