From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Heatwaves, heat domes ,el nino , ocean warming etc and their interactions and impacts
Mains level: Rising Heatwaves across the globe, factors, impacts and mitigating strategies
What’s the news?
- The average daily global temperature on Thursday was recorded at 17.12 degrees Celsius, encompassing measurements over land, ocean, ice sheets, and mountainous snow regions.
Central idea
- In a concerning announcement, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) declared June as the hottest month ever recorded on Earth since temperature tracking began 174 years ago. The heatwave has persisted into July, with 18 out of the first 20 days witnessing unprecedented average daily global temperatures.
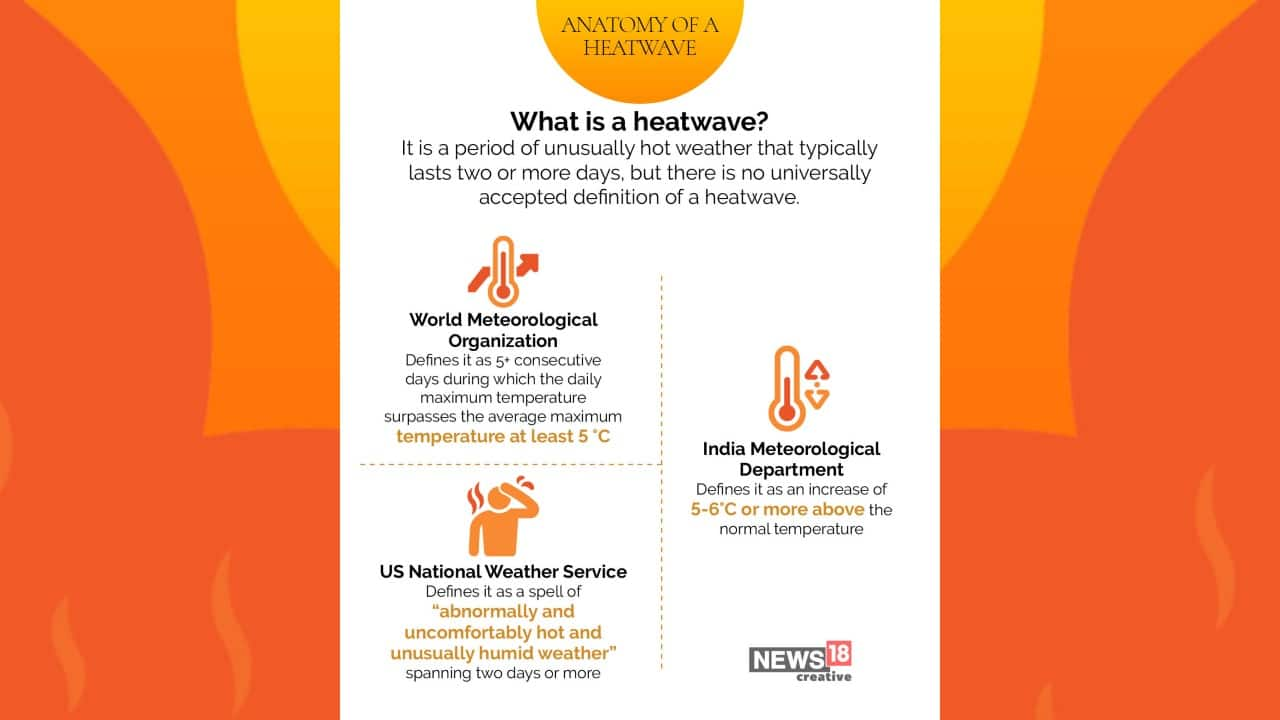
What is Heat-wave?
- A heatwave is a prolonged period of abnormally hot weather.
- Heatwaves usually last for several days or weeks and can occur in both dry and humid
- Characterized by temperatures that are significantly higher than the average for a particular region during that time of year.
What are heat domes?
- A heat dome occurs when an area of high-pressure stays over a region for days and weeks. It traps warm air, just like a lid on a pot, for an extended period.
- The longer that air remains trapped, the more the sun works to heat the air, producing warmer conditions with every passing day.
- Heat domes, if they last for a long period, may cause deadly heat waves.
What are Anticyclones?
- An anticyclone, also known as a high-pressure system, is essentially an area of high pressure in which the air goes downwards towards the Earth’s surface.
- As the air sinks, its molecules get compressed, which increases the pressure, making it warmer. This causes dry and hot weather.
- The winds remain calm and gentle during an anticyclone, and there is almost no formation of clouds because here the air sinks rather than rises.
Factors behind this scorching trend?
- Climate change: The primary driver behind the escalating heatwaves and rising global temperatures is human-induced climate change.
- The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial processes, and other human activities release greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat and lead to the greenhouse effect, resulting in the warming of the Earth’s surface.
- El Nino events, characterized by abnormal warming of surface waters in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, can elevate temperatures worldwide and exacerbate heatwaves.
- Heat domes and anticyclones are weather phenomena that can intensify and extend heatwaves.
- Warmer oceans release more heat into the atmosphere, fueling extreme weather events like heatwaves.
- Urban areas with concrete and asphalt surfaces can create heat islands that retain and amplify heat, leading to higher temperatures within cities compared to surrounding rural areas.
- Climate change can trigger feedback loops that amplify its effects. For example, melting ice in the Arctic reduces the Earth’s reflective surface, leading to increased absorption of sunlight and further warming.
*NOTE: Although heat domes and anticyclones don’t occur due to climate change, they have become more intense and longer as a result of soaring global temperatures.
Impact of Heatwaves
1.Human Health Impacts:
- Heat-related Illnesses: Heatwaves can cause heat-related illnesses such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. The elderly, young children, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are more vulnerable.
- Dehydration: High temperatures and excessive sweating can lead to dehydration, especially if individuals do not consume enough fluids.
2.Impact on Agriculture:
- Crop Failure: Prolonged heatwaves can cause damage to crops and reduce agricultural yields due to drought conditions and water shortages.
- Livestock Stress: High temperatures can lead to heat stress in livestock, affecting their productivity and overall health.
3.Environmental Impact:
- Drought: Heatwaves can contribute to drought conditions by increasing evaporation and reducing water availability, leading to water scarcity and affecting ecosystems.
- Wildfires: Hot and dry conditions during heatwaves can increase the risk of wildfires, leading to extensive damage to forests and wildlife habitats.
- Water Quality: Heatwaves can lead to higher water temperatures, which may negatively impact aquatic ecosystems and decrease water quality.
4.Energy Demand and Infrastructure Stress:
- Increased Energy Consumption: Heatwaves result in higher energy demand due to the use of air conditioning and cooling systems, putting strain on the power grid.
- Power Outages: The increased demand for electricity during heatwaves can lead to power outages if the electrical infrastructure becomes overloaded.
5.Social and Economic Impact:
- Disruption of Daily Activities: Heatwaves can disrupt daily life, making it uncomfortable to work, travel, or engage in outdoor activities.
- Economic Losses: Heatwaves can result in productivity losses, increased healthcare costs, and damage to infrastructure, leading to economic impacts on communities and businesses.
Worse affected countries
- United States: North America, particularly the United States, has experienced prolonged heatwaves covering a large swath of the country. States like California, Florida, New Mexico, and Arizona have been experiencing extreme temperatures. Temperature remained around 43.3 degree Celsius.
- Europe: Countries in Europe, such as Italy and Greece, have been gripped by two consecutive heatwaves. Italy’s island of Sardinia saw temperatures reaching 47.7 degrees Celsius, and Greece experienced temperatures exceeding 40 degrees Celsius, leading to wildfires and affecting historical sites.
- Spain: Spain witnessed a temperature of 45.4 degrees Celsius in the town of Figueres, the highest temperature recorded in the country since 1928. It led to dry spells and wildfires.
- Asia: China, Iraq and Saudi Arabia remain some of the worst affected countries. A remote township in China saw temperatures touching 52 degree Celsius
- Algeria: North Africa’s Algeria has reported record-breaking temperatures, with some experts suggesting temperatures exceeding 50 degrees Celsius in certain areas.
- Tunisia: Tunisia has also been impacted by severe heatwaves, with temperatures reaching up to 49 degrees Celsius in some regions.
Mains Marks enhancer: Best Practices in India
- Andhra Pradesh:
- Setting up Heat Action Plans: Cities like Vijayawada have implemented Heat Action Plans that include public awareness campaigns, heat helplines, and designated cooling centers to provide relief to vulnerable populations.
- Telangana:
- Early Warning Systems: The Telangana State Development Planning Society issues heatwave alerts and early warnings to district authorities and the public, allowing them to take precautionary measures.
- Rajasthan:
- Urban Heat Island Mitigation: Cities like Jaipur have implemented measures to reduce the urban heat island effect by promoting green spaces, reflective surfaces, and better urban planning.
- Gujarat:
- Cool Roofs: The Gujarat government has encouraged the use of cool roofs in buildings to reflect sunlight and reduce indoor temperatures during heatwaves.
- Tamil Nadu:
- Heatwave Awareness Programs: The Tamil Nadu government conducts awareness programs through schools, colleges, and community organizations to educate people about heatwave safety and preparedness.
Way forward: Urgent actions needed
- The international community must strengthen and implement the commitments made under climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement.
- Countries should set more ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Provide support to developing nations to enhance climate resilience and adaptation.
- Prioritize the transition to renewable energy sources and invest in clean technologies.
- Develop robust adaptation strategies such as involves establishing heat emergency response plans, cooling centers, and public awareness campaigns.
- Cities should adopt green urban planning practices, incorporating green spaces, green roofs, and sustainable building designs to mitigate the urban heat island effect and promote natural cooling.
- Promote sustainable land management practices, including reforestation and afforestation
- Enhance early warning systems to detect and respond to extreme heat events promptly.
Conclusion
- The alarming surge in global temperatures, culminating in devastating heatwaves across continents, is a potent reminder of the urgency to combat climate change. As nations grapple with the immediate impacts of heatwaves, it is imperative to take collective action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigate the effects of climate change, and safeguard the planet for future generations. The time to act is now; the consequences of inaction are too dire to ignore.
Also read:
Heatwaves in India: Increasing Frequency Needs Range of Measures to Mitigate
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024